01-intro-graph
Introduction of graphs
Introduction
为什么network/graph很重要?
Networks are a general language for describing complex systems of interacting entities
当我们谈论network的时候,经常讨论两种图:
- Natural graph:对于现实事物的直接描述,例如社交网络、大脑神经元的链接网络等
- Information graph:经过处理之后,带有信息的图,例如链接知识的图等
实际上在某些情况下上面两种network的分界线是很模糊的。
很多事物都拥有图的结构,利用这些图的结构能够帮助我们更好的预测。
Why networks?
- Universal language for describing complex data
- Shared vocabulary between fields
- Data availability & computational challenges
Ways to analyze networks:
- Predict the type/color of a given node
- Node classification
- Predict whether two nodes are linked
- Link prediction
- Identify densely linked clusters of nodes
- Community detection
- Measure similarity of two nodes/networks
- Network similarity
Structure of Graphs
graph的component:
- Objects: nodes, edges \(N\)
- Interactions: links, edges \(E\)
- System: network, graph \(G(N, E)\)

We will try to make this distinction whenever it is appropriate, but in
most cases we will use the two terms interchangeably
graph的基本概念:
- 无向图
- 有向图
node degree:对于无向图来说就是一个节点连接的边,因此一个无向图的平均度就是\(2E/N\)。对于有向图来说度分为入度和出度,一个节点的in-degree就是有多少条箭头指向该节点;out-degree就是多少条边末端链接到该节点上。
几种特殊的graph:
- complete graph:对于无向图,一个complete graph指所有节点之间都存在边:\(E=E_{max}=\frac{N(N-1)}{2}\)
- Bipartite graph:a graph whose nodes can be divided into two disjoint sets \(U\) and \(V\) such that every link connects a node in \(U\) to one in \(V\); that is, \(U\) and \(V\) are independent sets
- Weighted graph:在邻接矩阵中的非0值不再只是1,而是其它衡量重要程度的实值,比如道路图
- Self-edge graph:边的起始点都是同一个节点,比如蛋白质图protein graph
- Multigraph:在节点和节点当中存在多条边,比如Communication graph、Collaboration graph
在数学上表示一个图可以使用adjacent matrix表示。
- 对于无向图,行和列求和相等,并且是对应节点的degree
- 对于有向图,行求和是out-degree,列求和是in-degree
对于这种表示方式,需要在脑海里保持的一种直觉观点是,邻接矩阵是非常稀疏的。矩阵的稠密度计算:\(E/N^2\)。
还可以使用edge list和adjacent list表示:
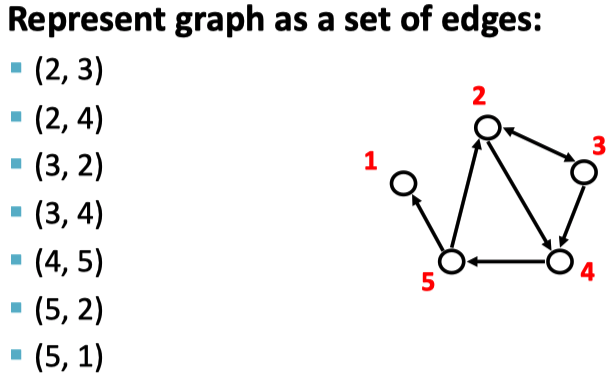

graph的连通性connectivity:
- 对于无向图,如果说一个graph是Connected graph,这意味着任意两个节点都可以通过某个路径连接起来
- 对于有向图,分为强连接性图和弱连接性图

在研究图的连通性当中,可能存在关键的边或者节点,如果把这些关键点或边删除整个图就不再连通。
- Bridge edge: If we erase the edge, the graph becomes disconnected
- Articulation node: If we erase the node, the graph becomes disconnected