LSTM-CRF
Neural Architectures for Named Entity Recognition
NAACL 2016,CMU
作者针对NER问题,提出了基于bi-LSTM和CRF(条件随机场)的模型以及transition-based的方法s-LSTM(该模型为详细阅读)。
State-of-the-art named entity recognition systems rely heavily on hand-crafted features and domain-specific knowledge in order to learn effectively from the small, supervised training corpora that are available. In this paper, we introduce two new neural architectures—one based on bidirectional LSTMs and conditional random fields, and the other that constructs and labels segments using a transition-based approach inspired by shift-reduce parsers. Our models rely on two sources of information about words: character-based word representations learned from the supervised corpus and unsupervised word representations learned from unannotated corpora. Our models obtain state-of-the-art performance in NER in four languages without resorting to any language-specific knowledge or resources such as gazetteers.
作者使用双向LSTM学习sentence的context信息。
输入层拼接了pretrained好的word embedding以及character-level的embedding。
输出层采用CRF,主要原因是合理NER的标注序列是满足某些内部约束的。也就是说不同token的tag之间不是完全独立的,某个token的tag的标注会对其它token的tag标注产生影响。
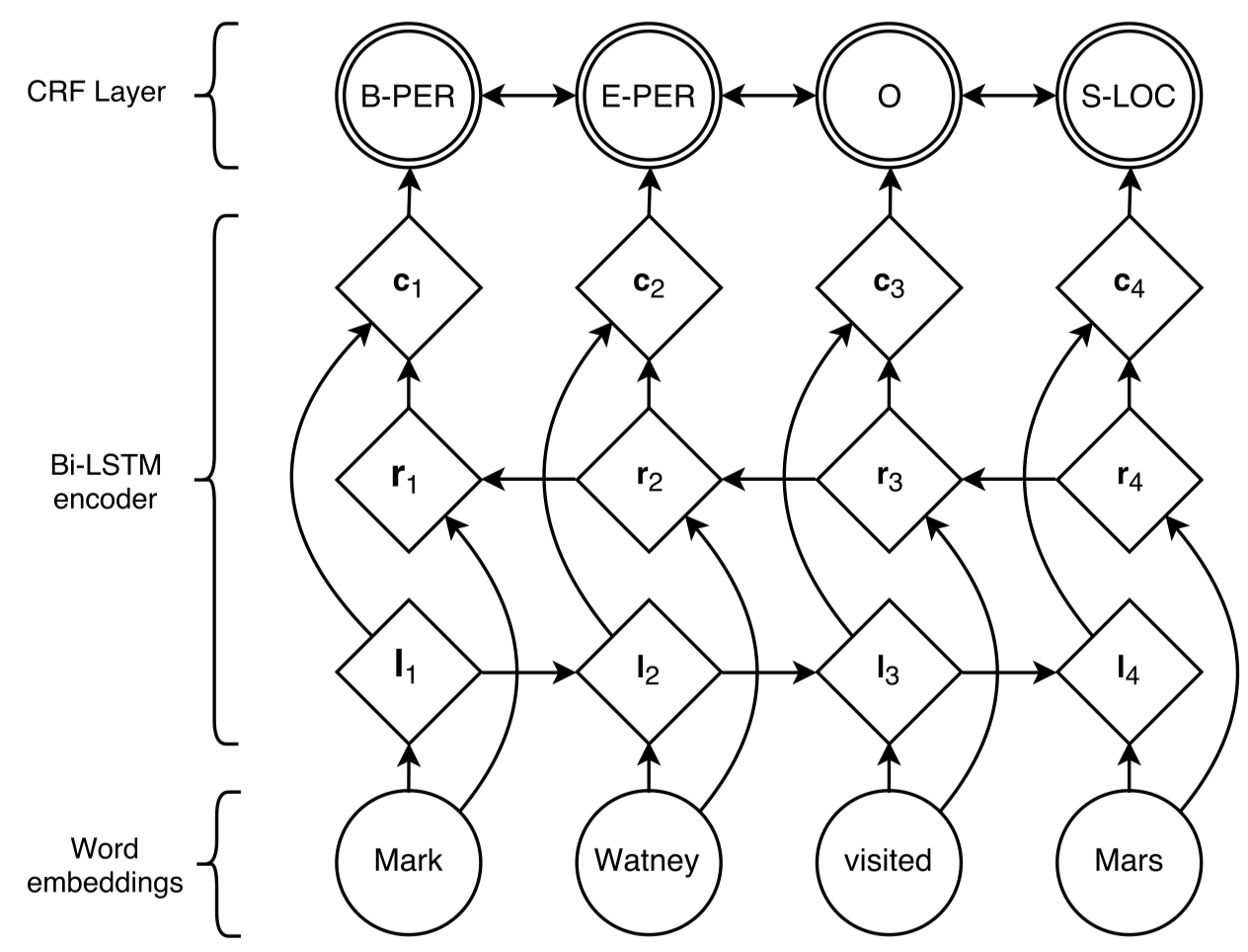
整体模型架构:
输入层word embedding的产生:
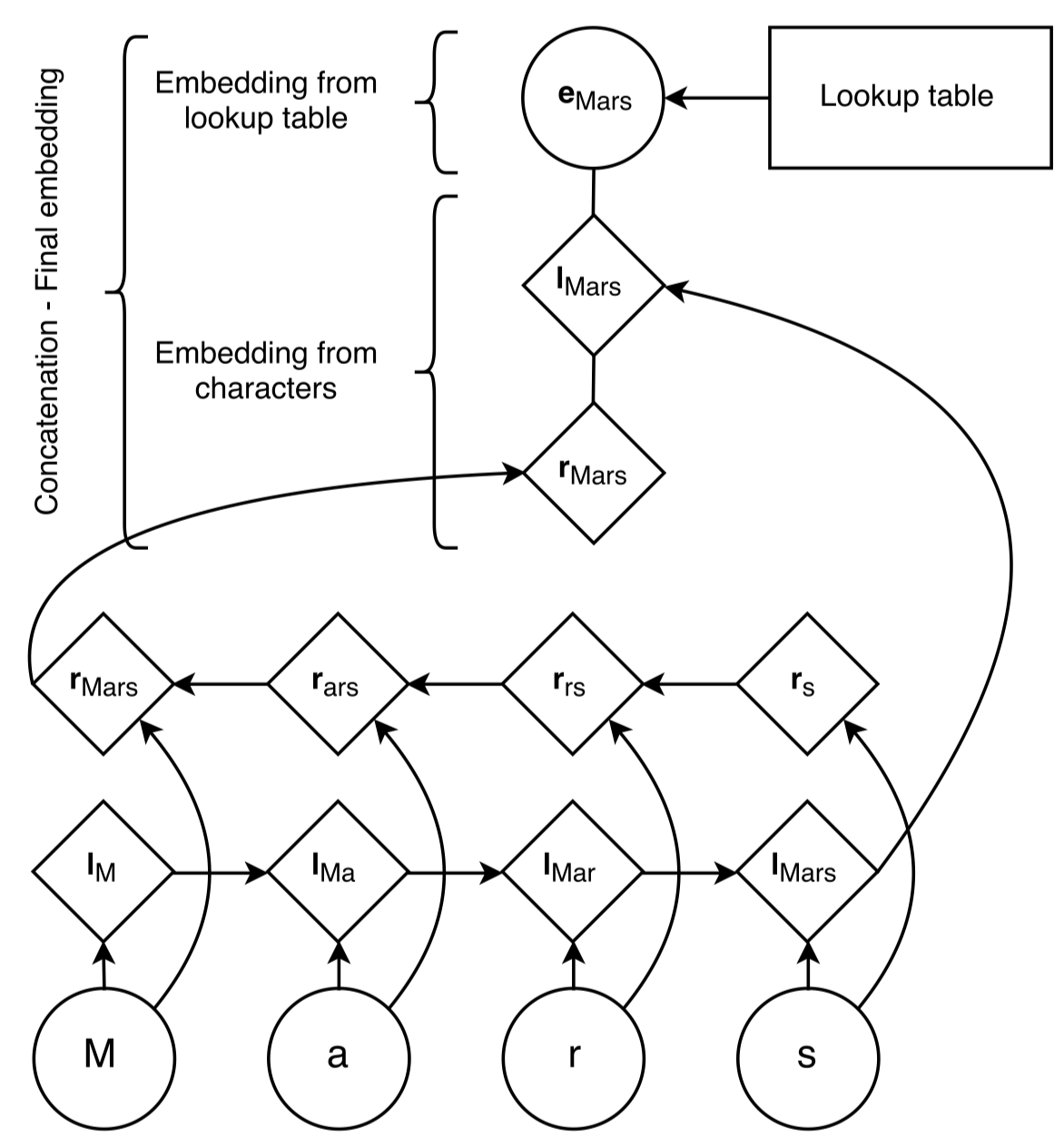
图中的\(e_{Mars}\)是来自于前人基于skip-n-gram,从语料无监督学习到的word embedding。用于捕获distributional evidence(比如常常是表示实体的单词倾向于出现在什么位置?)。
\(l_{Mars}\)和\(r_{Mars}\)是使用一个新的character bi-LSTM建模得到的character-level的word embedding。用于捕获语言可能具备的orthographic evidence,拼写层次的特征(比如常常成为一个name的单词通常长什么样子?)。
两个embedding拼接,再经过dropout,得到了最后输入到LSTM-CRF模型的final word embedding。
输出预测序列标签的时候,最简单的方法是使用LSTM输出的hidden state为每个token单独进行预测。但是在NER任务中,实际上在不同token输出的标签之间,存在内部的依赖,比如I-PER这个tag不可能紧跟着出现在B-LOC后面。因此,作者考虑使用Conditional Random Field对不同token的预测标签进行联合建模,而不是单独建模。
对于输入序列:
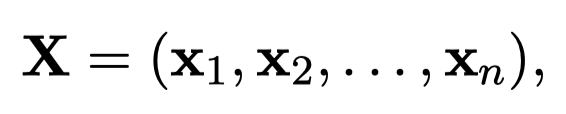
计划输出序列:

首先,会输出一个矩阵\(P\in R^{n\times k}\),\(n\)表示\(n\)个token,\(k\)表示一共有\(k\)个不同的tag。\(P_{ij}\)就表示第\(i\)个token成为第\(k\)个tag的概率。
为了建模不同token的tag之间的依赖,还定义了一个转移矩阵transition matrix \(A\in R^{k+2\times k+2}\)。\(k+1\)是因为新增了表示句子start和end的tag。\(A_{ij}\)表示从tag \(i\)转移到tag \(j\)的score。
因此,可以定义下面的输出NER序列score:
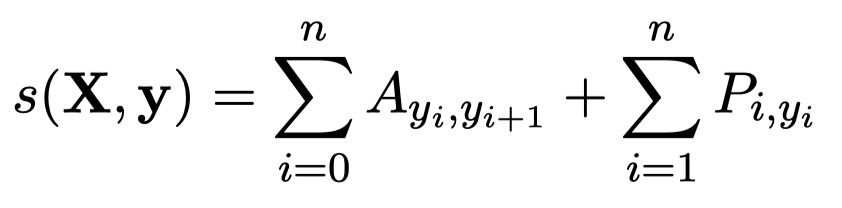

最大化概率目标:
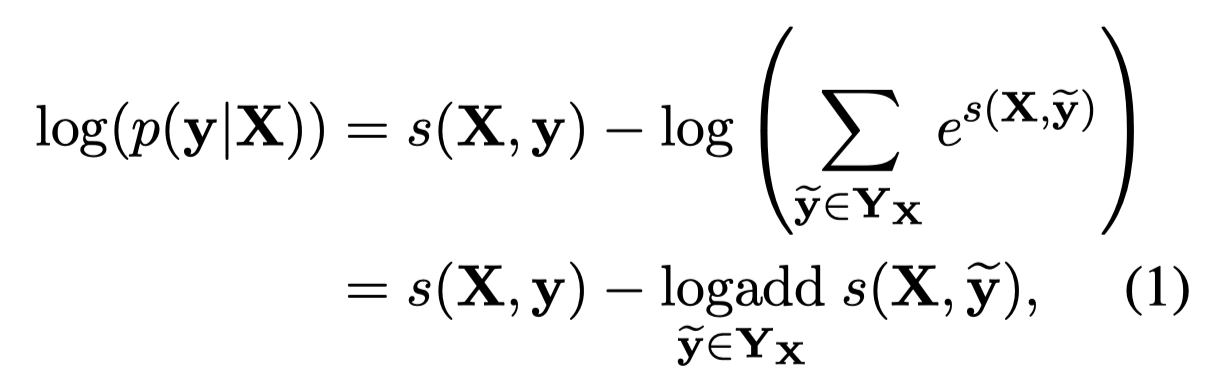
最后,选择最大score的\(y\)就是预测的NER序列。
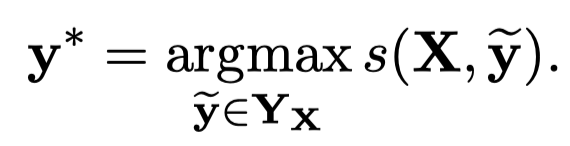
NER的输出标签,常用的IOB格式(Inside, Outside, Beginning),Beginning表示当前token是某个entity的开始,Inside表示当前token是某个entity的中间,Outside表示当前token不属于任何token。在这篇论文中,作者采用了IOB格式的拓展IOBES,除了I,O,B外还包括了singleton entities(S)和the end of named entities(E)。作者在实验中没有发现IOB和IOBES有太大差距。