LLM-DA-survey
Data Augmentation using LLMs: Data Perspectives, Learning Paradigms and Challenges
南洋理工. ACL 2024 Findings
In the rapidly evolving field of large language models (LLMs), data augmentation (DA) has emerged as a pivotal technique for enhancing model performance by diversifying training examples without the need for additional data collection. This survey explores the transformative impact of LLMs on DA, particularly addressing the unique challenges and opportunities they present in the context of natural language processing (NLP) and beyond. From both data and learning perspectives, we examine various strategies that utilize LLMs for data augmentation, including a novel exploration of learning paradigms where LLM-generated data is used for diverse forms of further training. Additionally, this paper highlights the primary open challenges faced in this domain, ranging from controllable data augmentation to multimodal data augmentation. This survey highlights a paradigm shift introduced by LLMs in DA, and aims to serve as a comprehensive guide for researchers and practitioners.
数据是实现AGI的核心之一。
Data-centric approaches to Artificial Intelligence (AI) constitute a pivotal element in the advancement towards Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), centering on the construction of AI systems underpinned by high-quality data (Zha et al., 2023).
LLM的出现使得对于data的需求更加强烈,因为LLM的缩放定律与数据量相关。之前有研究预测到2026年可获取的高质量数据就不足了。因此,有必要关注如何能够构造更多的高质量数据。
作者论文中对于数据增强的定义:
Data augmentation fundamentally involves the adoption of innovative methods aimed at bolstering model efficacy through the broadening of training data diversity, all without necessitating further data collection efforts.
作者的论文从数据和学习范式两个角度进行了总结。
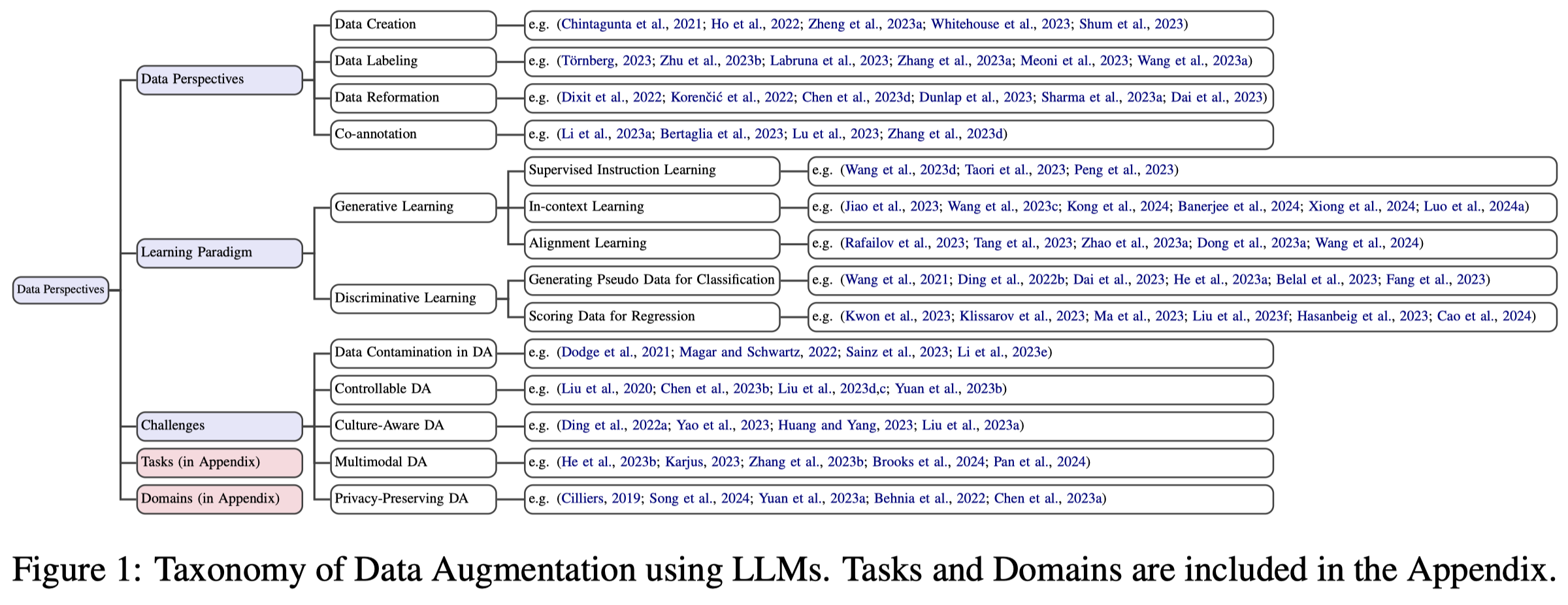
从数据的角度来看,数据增强包括了:
数据创建:Data Creation,
Data Creation focuses on leveraging the few-shot learning ability of LLMs to quickly create a large amount of synthetic data. It is most used in tasks with a large label space.
适用于annotations are usually difficult or expensive to collect的情况,以及label space非常巨大的情况。类似于创造CoT数据的都属于这一类型。
数据标注:Data Labeling,
Data Labeling seeks to utilize the general language comprehension abilities of LLMs to annotate unlabeled datasets.
它主要用于无标注数据可以很容易获得的场景,比如多语言、多模态的场景。It is primarily useful in tasks that have a large enough unlabeled data corpus, such as cross-lingual and multimodal tasks.
数据变形:Data Reformation,
Data Reformation techniques attempt to reformulate the existing data into more variations for more fine-grained augmentation.
对已有的数据进行变动,获取更多的数据版本,例如反事实生成、对图像的编辑等。
协同标注:Co-annotation,
Co-annotation refers to the collaborative annotation process between humans and LLMs.
人机协同地标注数据。
从学习范式的角度来看,作者简单的划分为了生成式和判别式:
Generative learning exploits LLMs to create instructional datasets and demonstration examples, enriching model training.
Discriminative learning, conversely, focuses on refining task-specific models through pseudolabeling and pseudo-scoring.
作者认为的将来挑战有:
- Data Contamination in Data Augmentation:数据污染有input contamination和input-and-label contamination
- Controllable Data Augmentation:生成data的质量,常常在target dimension之外难以保持。如果生成数据和真实数据之间差异过大,会出现模型塌陷现象
- Culture-Aware Multilingual Data Augmentation:对于多语言场景需要考虑当地文化
- Multimodal Data Augmentation:不仅仅是简单的生成多模态数据,还需要理解原来的长下文的和保持原来语义的完整性。此外,还需要考虑如何结合graph模态
- Privacy issues of Data Augmentation:生成的数据不能泄露隐私