ENTDA
Entity-to-Text based Data Augmentation for various Named Entity Recognition Tasks
ENTDA,ACL 2023 Findings,清华与阿里达摩
Data augmentation techniques have been used to alleviate the problem of scarce labeled data in various NER tasks (flat, nested, and discontinuous NER tasks). Existing augmentation techniques either manipulate the words in the original text that break the semantic coherence of the text, or exploit generative models that ignore preserving entities in the original text, which impedes the use of augmentation techniques on nested and discontinuous NER tasks. In this work, we propose a novel Entity-toText based data augmentation technique named ENTDA to add, delete, replace or swap entities in the entity list of the original texts, and adopt these augmented entity lists to generate semantically coherent and entity preserving texts for various NER tasks. Furthermore, we introduce a diversity beam search to increase the diversity during the text generation process. Experiments on thirteen NER datasets across three tasks (flat, nested, and discontinuous NER tasks) and two settings (full data and low resource settings) show that ENTDA could bring more performance improvements compared to the baseline augmentation techniques.
基于entity list生成对应的新data
1. Introduction
数据增强data augment的定义:
Data augmentation techniques (Shorten and Khoshgoftaar, 2019) expand the training set by generating synthetic data to improve the generalization and scalability of deep neural networks, and are widely used in NLP (Feng et al., 2021; Li et al., 2022a).
数据增强就是通过人造数据扩充训练集,从而导致能够提升模型的泛化性和可缩放性
在NER任务上的数据增强方法存在的问题:
- Rule Based Techniques:可能会破坏新句子的连贯性,甚至引入语法错误。However, it still inevitably introduces incoherent replacement and results in syntax-incorrect texts.
- Generative Techniques:之前的方法使用entity tagging的思路实现NER任务,没有保留原始entity,因此难以增强nested与discontinuous NER任务。
2. Method
作者提出的方法:
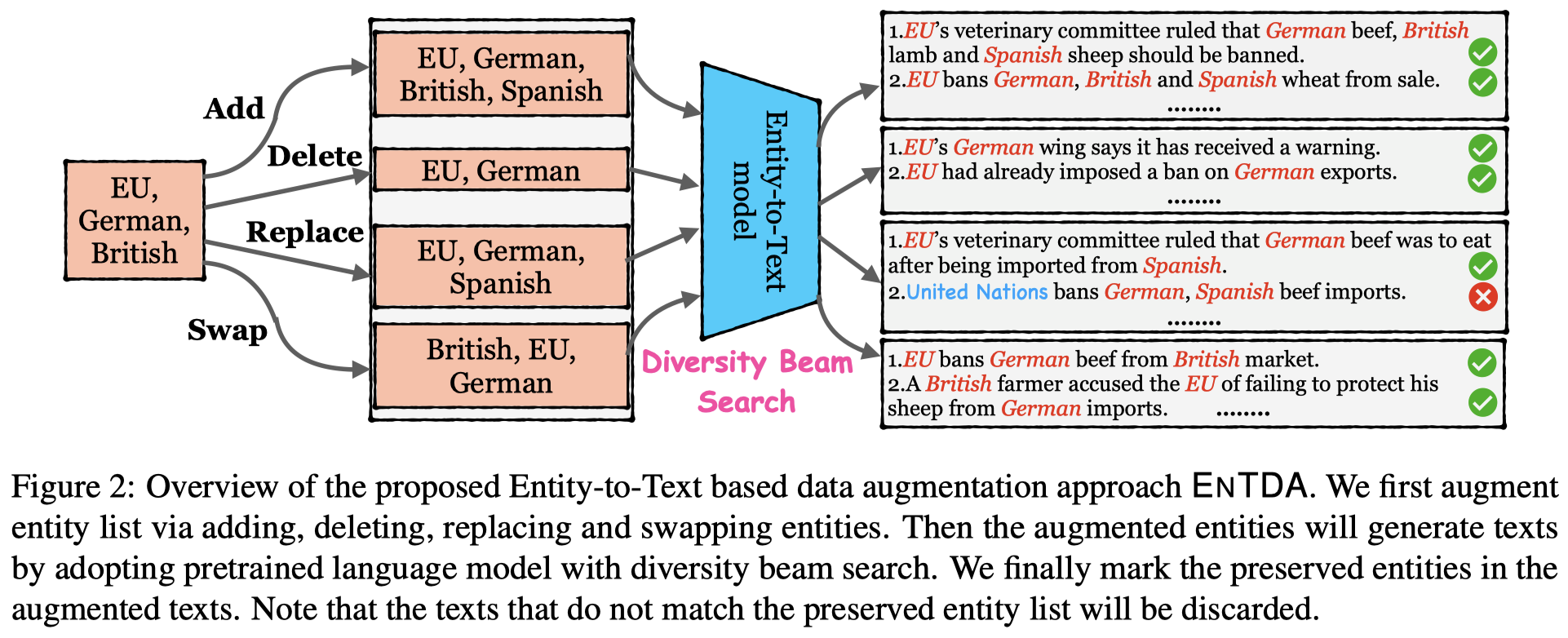
作者的生成data思路是根据entity list,让language model来直接生成相应的句子。作者期望能够生成各种不同类型NER的任务的数据。
作者的输入是entity list,\(E = [e_1, e_2, \dots, e_m, \dots, e_l]\),其中\(e_m= [s_{m1}, d_{m1}, ..., s_{mj}, d_{mj}, t_m]\),\(s\)和\(d\)表示entity某个span的开始位置和结束位置。最后的\(t\)表示实体类型。
首先是Entity List Augmentation,采用下面4中方法修改entity list:

然后,让language model基于entity list生成对应的句子。为了提升生成句子的多样性diversity,作者提出了一种diversity beam search decoding策略:
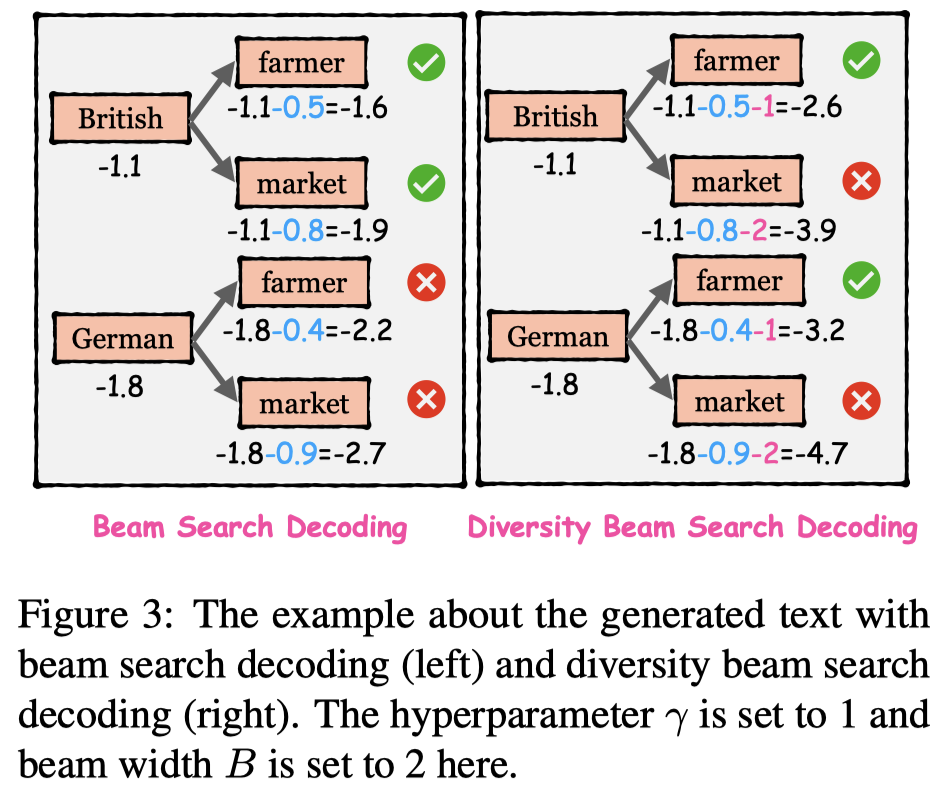
传统的beam search decoding策略:
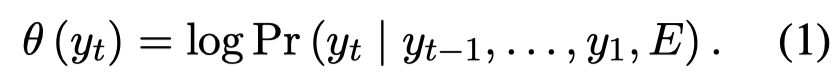
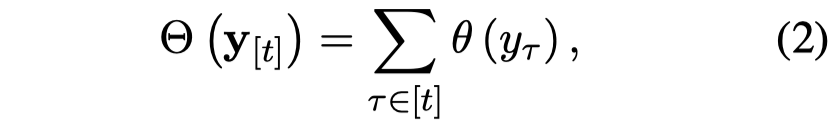
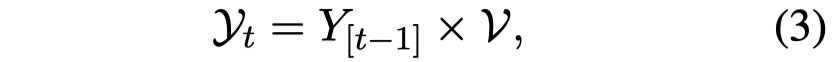
保留beam width \(B\)个候选项。
作者惩罚rank排在后面的候选项,让model更加选择倾向于由不同的previous tokens生成的候选项,这样就增大了产生前面由不一样的token产生的新token概率:
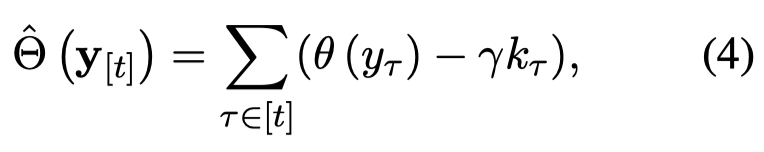
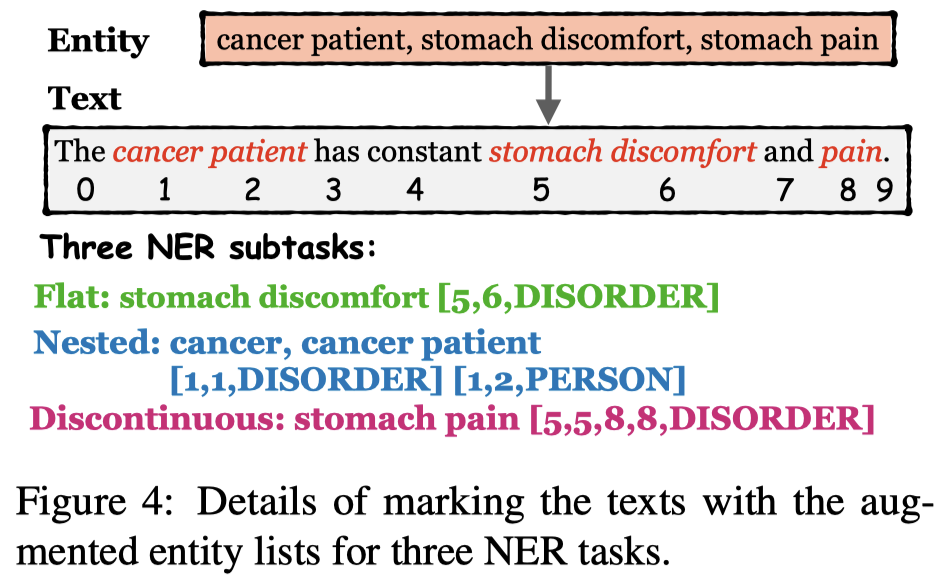
然后,作者检查生成的句子,排除掉所有没有包含准确的entity list的sentence。最后,作者将数据转变为下面的样子:
3. Experiments
一些具体的实现细节:
- we fine-tune the T5-Base (Raffel et al., 2020) with the initial parameters on the Entity-to-Text data of the training set. 在原来的dataset上,微调T5,让T5初步学会根据entity list来生成sentence
- \(\gamma = 10\),\(B = 3\)
- ENTDA and all baselines augment the training set by 3x for a fair comparison. 也就是说如果训练集有100个samples,生成新300个samples,把这300个新的samples加入到原来的training set中
3.1 Full Data Results
在3种NER任务下,使用全部的训练数据进行实验:
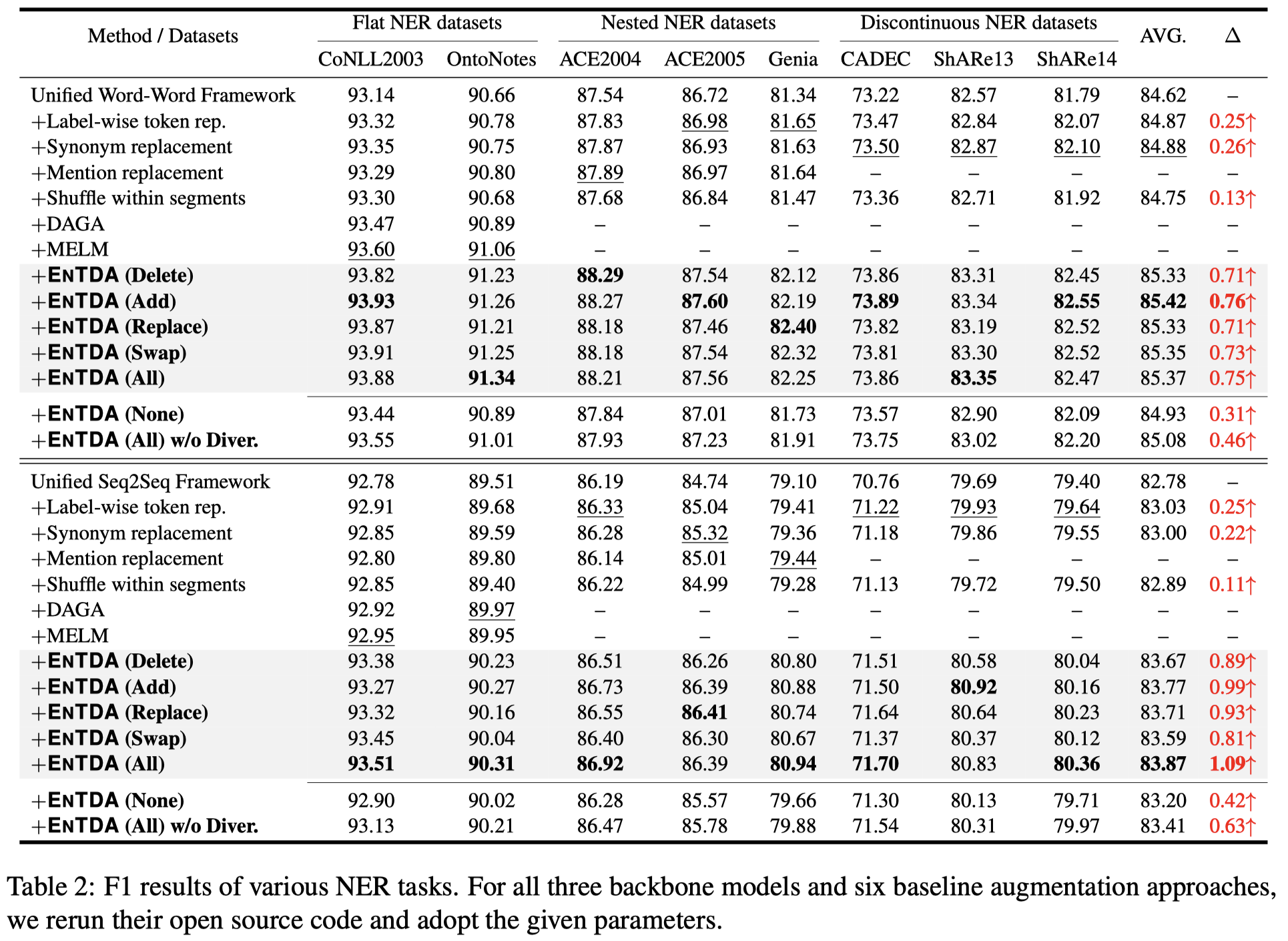
此时,作者的方法效果有提升;但是提升幅度不是很大
3.2 Low Resource NER
低资源NER,we randomly choose 10% training data from CoNLL2003/ACE2005/CADEC
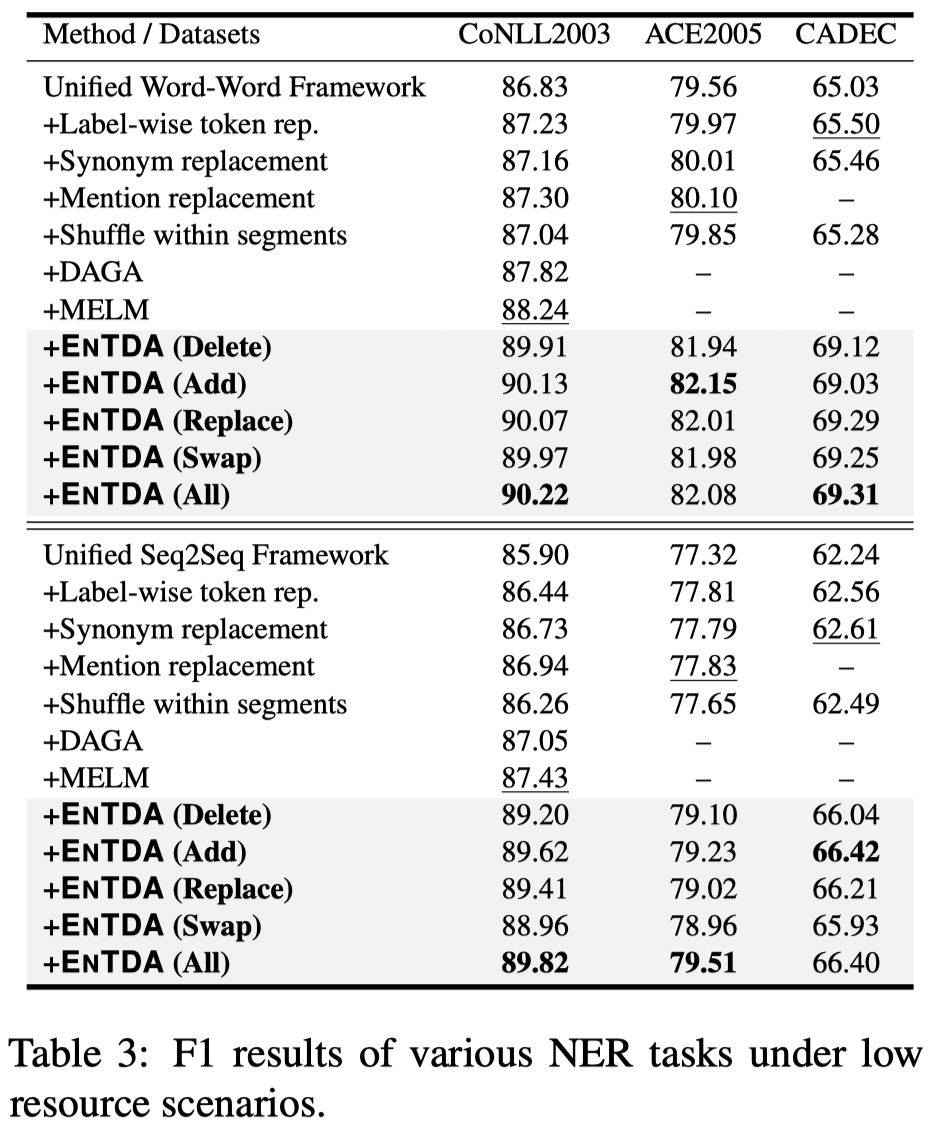
低资源的情况下,效果提升明显,有\(2\)%的提升幅度。
在真实的低资源NER数据集CrossNER的表现:
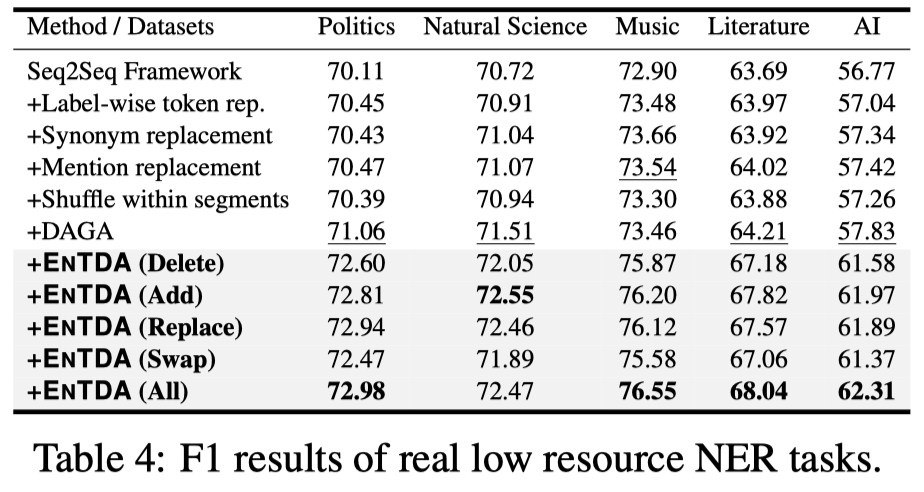
同样提升比较明显。
3.3 Various Augmentation Multiples
如果不断增大新数据的倍数multiples:
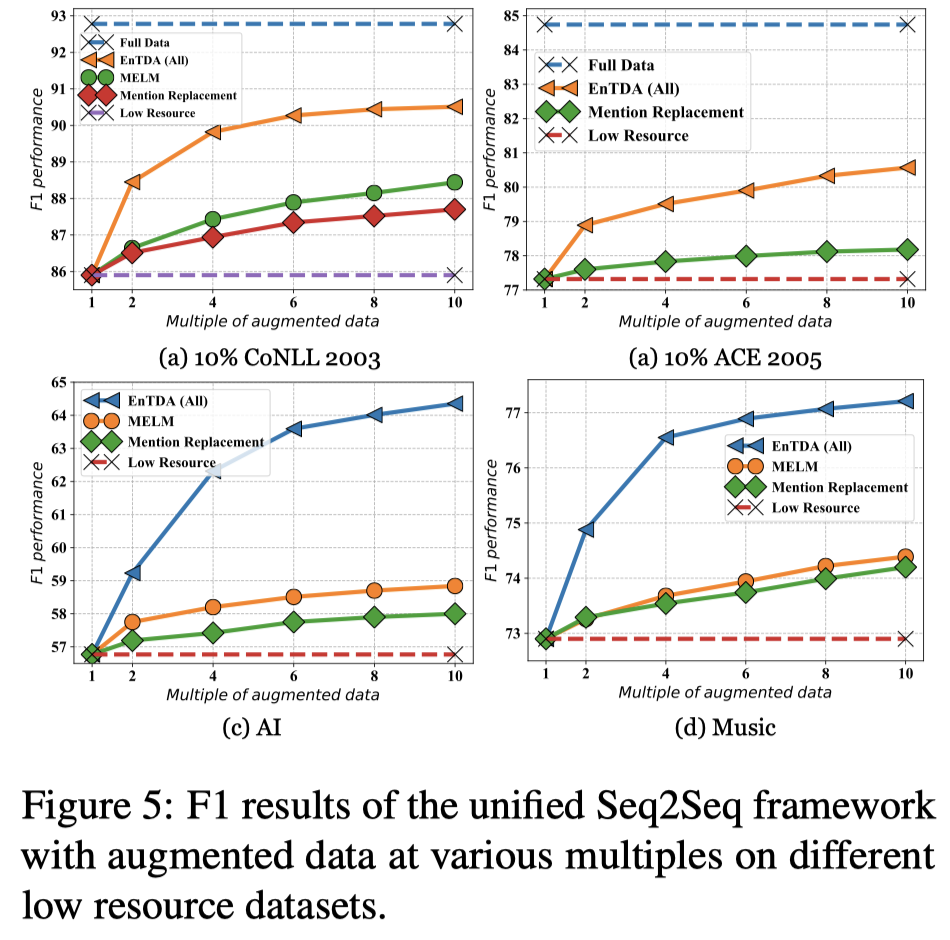
(上面这两个figure为什么没有MELM方法的比较呢?)
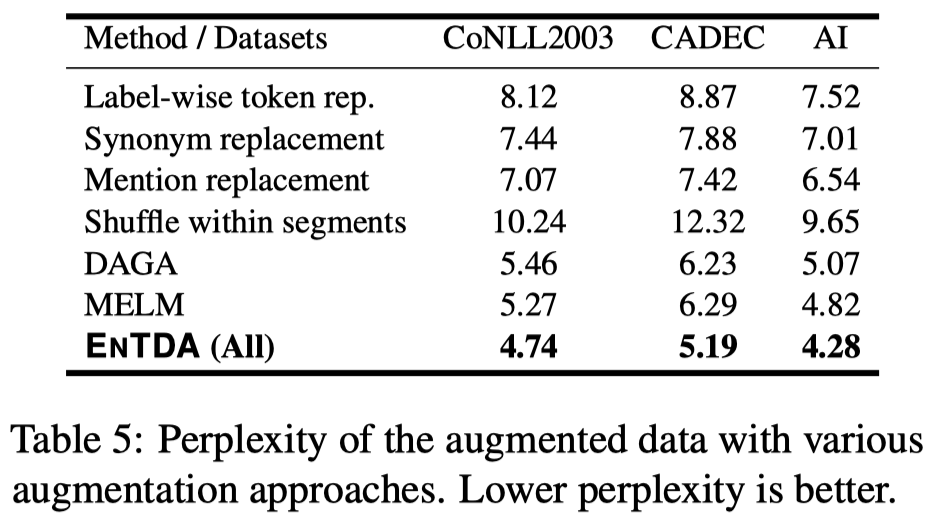
3.4 Semantic Coherence and Diversity Analysis
作者使用GPT-2来计算生成句子的perplexity,作为评估语义连贯性的指标:
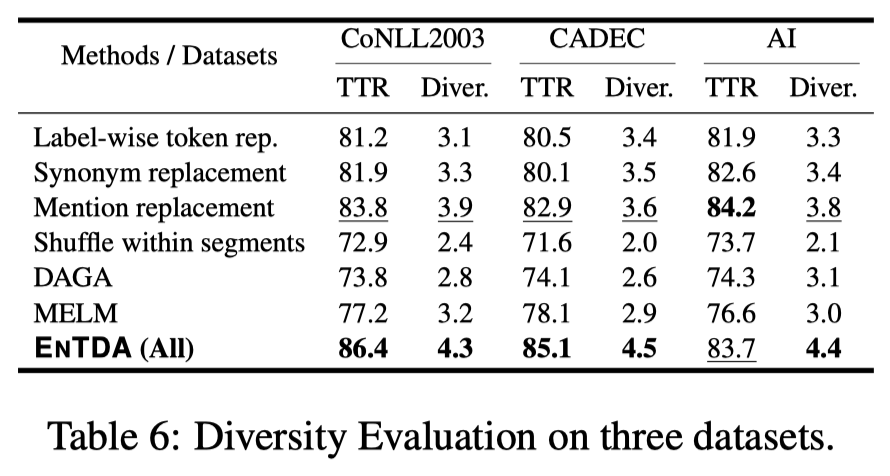
作者使用Type-Token Ratio (TTR) (Tweedie and Baayen, 1998)作为自动计算的指标评估多样性;同时雇佣了5个人类标注者,对生成的200个句子的多样性进行打分(\(1\)~\(5\)),作为人工指标:
3.5 Case Study
