modality-discriminator
Different Data, Different Modalities! Reinforced Data Splitting for Effective Multimodal Information Extraction from Social Media Posts
COLING 2022,代码。
作者认为,不是所有的social media post都需要多模态信息,可能有的post更适合单模态模型,如果加入多模态信息反而可能造成错误的后果。因此,作者基于强化学习,提出了一种可以把social post分为单模态集合和多模态集合的方法。
Recently, multimodal information extraction from social media posts has gained increasing attention in the natural language processing community. Despite their success, current approaches overestimate the significance of images. In this paper, we argue that different social media posts should consider different modalities for multimodal information extraction. Multimodal models cannot always outperform unimodal models. Some posts are more suitable for the multimodal model, while others are more suitable for the unimodal model. Therefore, we propose a general data splitting strategy to divide the social media posts into two sets so that these two sets can achieve better performance under the information extraction models of the corresponding modalities. Specifically, for an information extraction task, we first propose a data discriminator that divides social media posts into a multimodal and a unimodal set. Then we feed these sets into the corresponding models. Finally, we combine the results of these two models to obtain the final extraction results. Due to the lack of explicit knowledge, we use reinforcement learning to train the data discriminator. Experiments on two different multimodal information extraction tasks demonstrate the effectiveness of our method. The source code of this paper can be found in https://github.com/xubodhu/RDS.
1 Introduction
问题 :不是所有的social post都适合于多模态信息抽取方法。比如下图:

对于(a)和(c)来说,加入图像信息能够辅助信息抽取,比如我们可以知道[Kolo MISC]是一条狗,而不是一个人;从图像中两个人拉着手,可以判断出Meghan Markle和Prince Harry是夫妻而不是同事。
但是对于(b)和(d)来说,加入图像信息反而可能导致错误判断。在(b)里可能因为看到图像中有个人像,然后判断[Nasa ORG]是个人;在(d)里因为看到很多人类似的服装,错误判断出Angel和Jesennia Rodriguez是同事而不是夫妻。
方法:作者期望能够设计一种把不同social post分类为适用于单模态和适用于多模态的方法。由于不存在这样的数据集,因此作者提出了一种基于强化学习的data discriminator。
2 Method
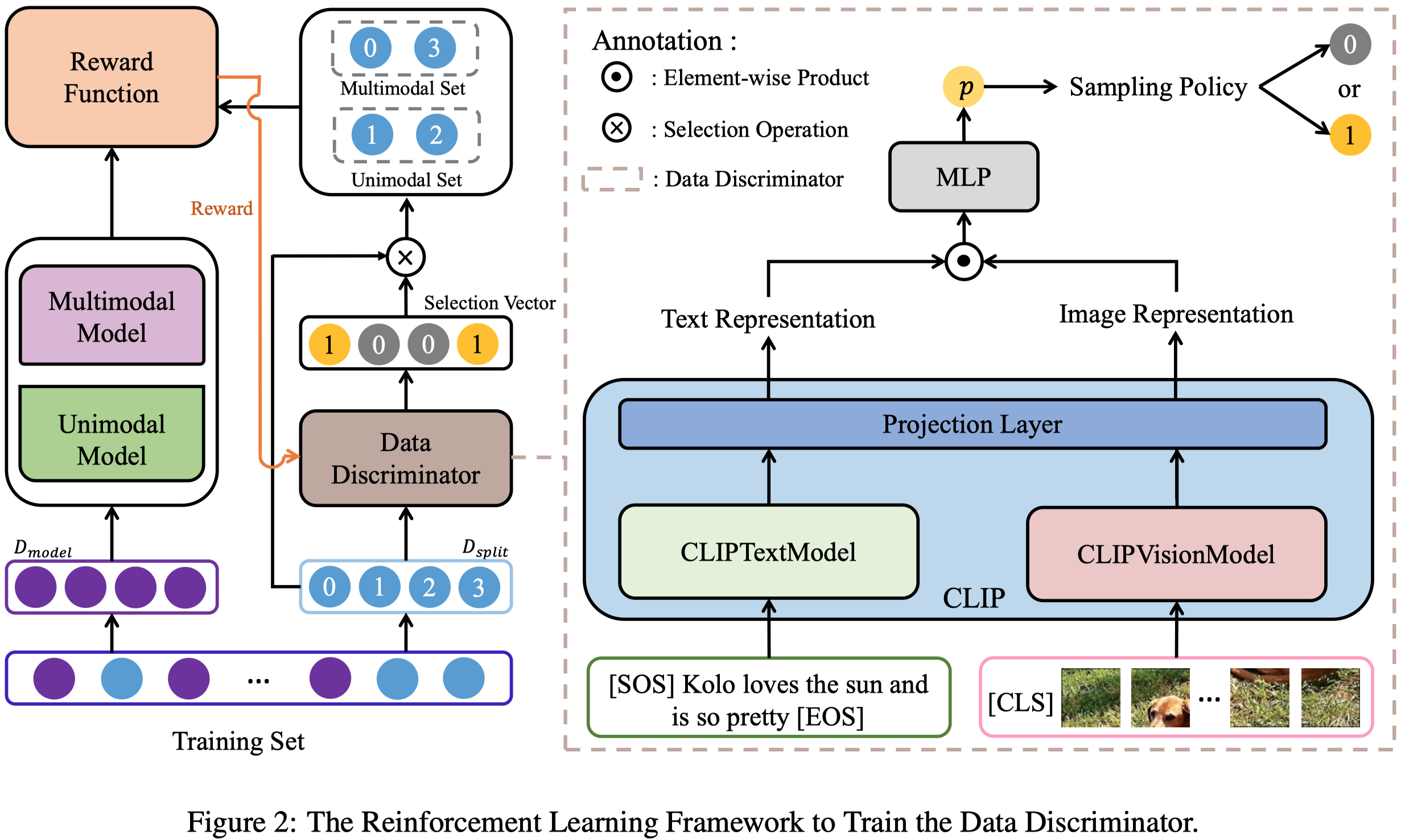
首先,作者会把训练集随机分为\(D_{model}\) (80%)和\(D_{split}\) (20%)。
\(D_{model}\)用来训练单模态和多模态模型,这两种模型可以是任意的方法,训练完毕之后,就freeze所有参数。
\(D_{split}\)是用来训练Data discriminator,Data discriminator会判断某个输入样本是否适用于多模态方法,根据Data discriminator的判断结果,检测单模态和多模态模型在判断的单模态集合和多模态集合上的表现效果。如果在划分的多模态集合中,多模态模型效果比单模态模型效果越好;在划分的单模态集合中,单模态模型效果比多模态模型效果越好,就证明这个Data discriminator的判断效果越准确。
2.1 Data Discriminator
作者基于\(CLIP_{32}\)进行实现,对CLIPTextModel和CLIPVisionModel的输出进行投影、element-wise相乘,最后经过MLP得到预测结果:
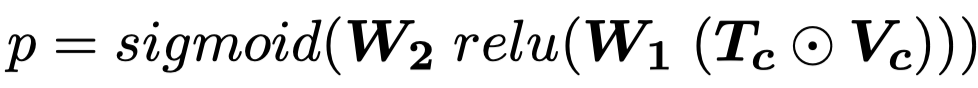
\(p\)越大,表示越适合于使用多模态方法进行信息抽取
在划分单模态集合和多模态集合的时候,在训练阶段,依据伯努利采样;在测试阶段,\(p\)大于\(0.5\)的被放入多模态集合,\(p\)小于\(0.5\)的被放入单模态集合。
2.2 Reward Function
如何判断划分结果的好坏?核心思想是让单模态模型在单模态集合上表现效果更好;让多模态模型在多模态集合上表现效果更好。

\(k\)代表适合于使用多模态数据的数据; \(l\)代表适合用于单模态数据的数据
计算reward:
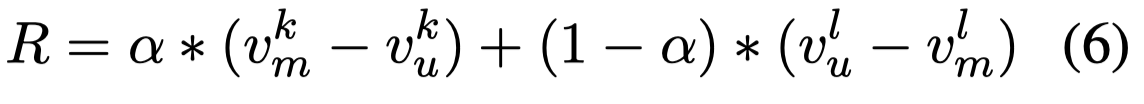
在得到了reward之后,data discriminator如何更新参数?
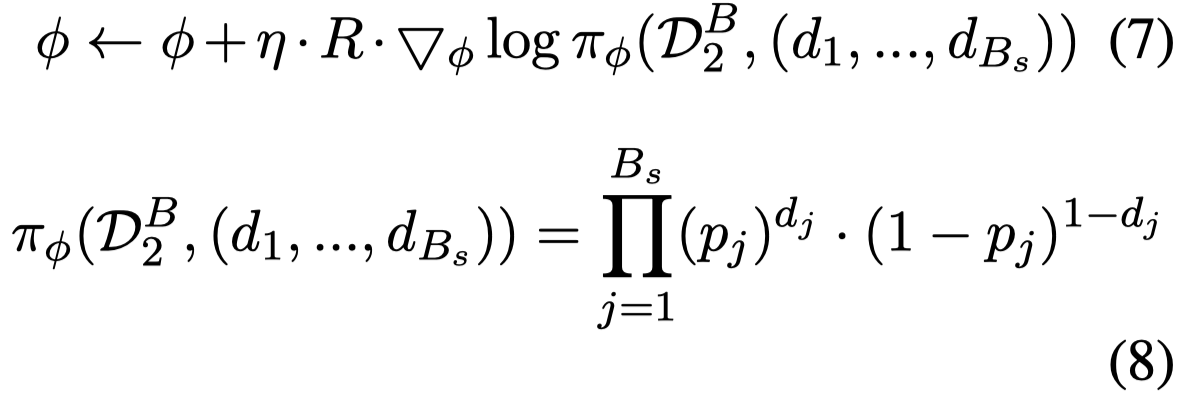
2.3 Training Algorithm

3 Experiment
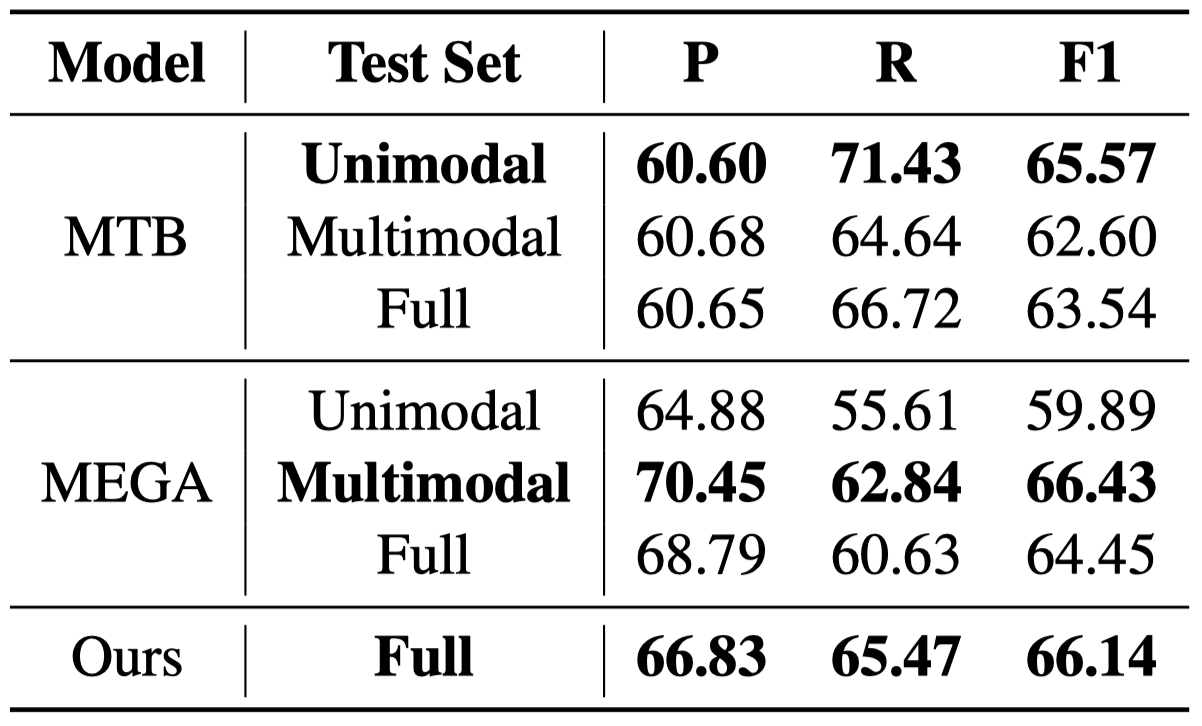
对于MRE,作者使用MTB作为单模态模型,MEGA作为多模态模型,最终MRE结果:
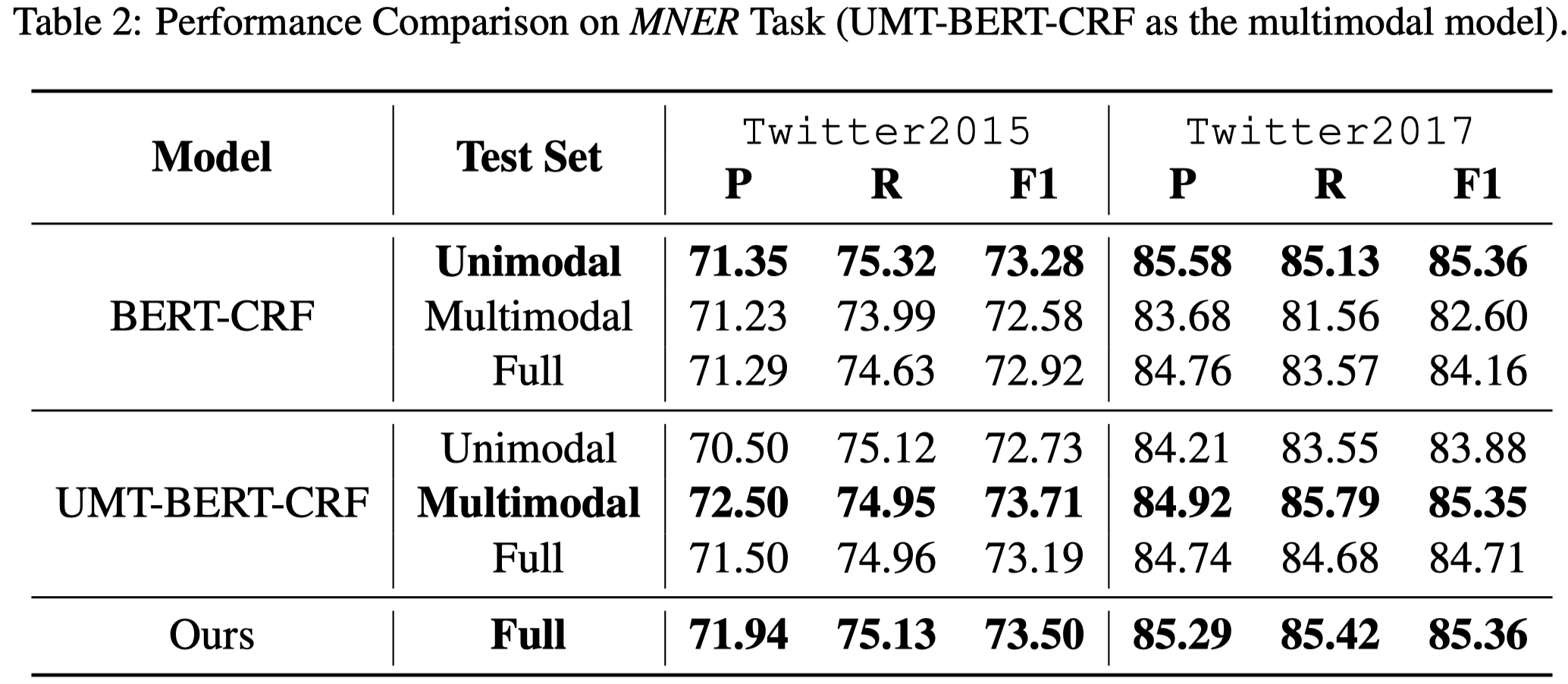
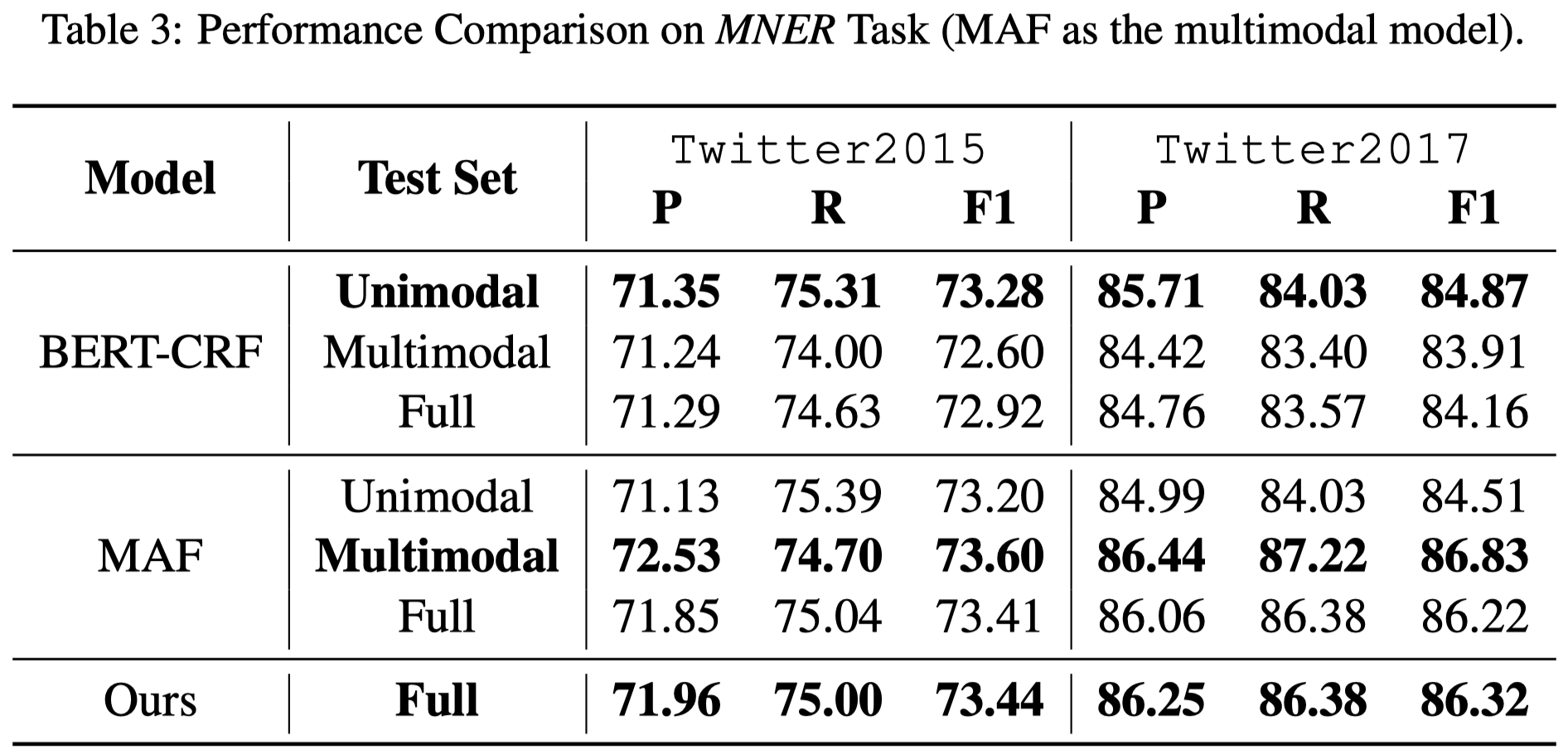
对于MNER,作者使用BERT-CRF作为单模态模型,UMT-BERT-CRF和MAF作为多模态模型,最终MNER结果:
案例研究,作者挑选了两个在Twitter-2017中,两个拥有最低分类得分的post:

可以看到,在这两个实例中,text本身就有足够的信息,不需要引入图像的信息。
两个拥有最高分类得分的post:

对于(c)如果没有图像,很容易把Harry Potter和the Philosopher’s Stone分开,然后把Harry Potter判断为是一个人名;对于(d)如果没有图像,很容易把R.Shemiste认为是人名,但实际上它是品牌名。
两个得分在中间的post:

可以看到,图像信息既没有带来更丰富的信息;也没有带来噪音。这两张图片里重复了一遍文本内容,实际上这一类的图像还挺常见的,使用单模态模型和多模态模型对这一类post的判断效果可能都差不多。