MEGA
Multimodal Relation Extraction with Efficient Graph Alignment
ACM MM 21,代码
作者提出了一种,通过识别图像的scene graph和textual graph,进行图对齐的多模态关系抽取方法MEGA。
Relation extraction (RE) is a fundamental process in constructing knowledge graphs. However, previous methods on relation extraction suffer sharp performance decline in short and noisy social media texts due to a lack of contexts. Fortunately, the related visual contents (objects and their relations) in social media posts can supplement the missing semantics and help to extract relations precisely. We introduce the multimodal relation extraction (MRE), a task that identifies textual relations with visual clues. To tackle this problem, we present a large-scale dataset which contains 15000+ sentences with 23 pre-defined relation categories. Considering that the visual relations among objects are corresponding to textual relations, we develop a dual graph alignment method to capture this correlation for better performance. Experimental results demonstrate that visual contents help to identify relations more precisely against the text-only baselines. Besides, our alignment method can find the correlations between vision and language, resulting in better performance. Our dataset and code are available at https://github.com/thecharm/Mega.
1 Introduction
problem:之前的关系抽取主要有两种,sequence-based和dependency-based方法。但是这些方法主要集中在文本信息的抽取,如果应用到social media posts这样文本信息比较少,缺乏上下文信息的时候,效果会很差。
motivation:作者发现,可以使用post中的image来补充缺失的上下文信息。作者认为,和多模态命名实体有所区别的是,MRE不仅要考虑捕获visual object和textual entity的联系,还要考虑visual object之间的visual relation和textual relation之间的联系。
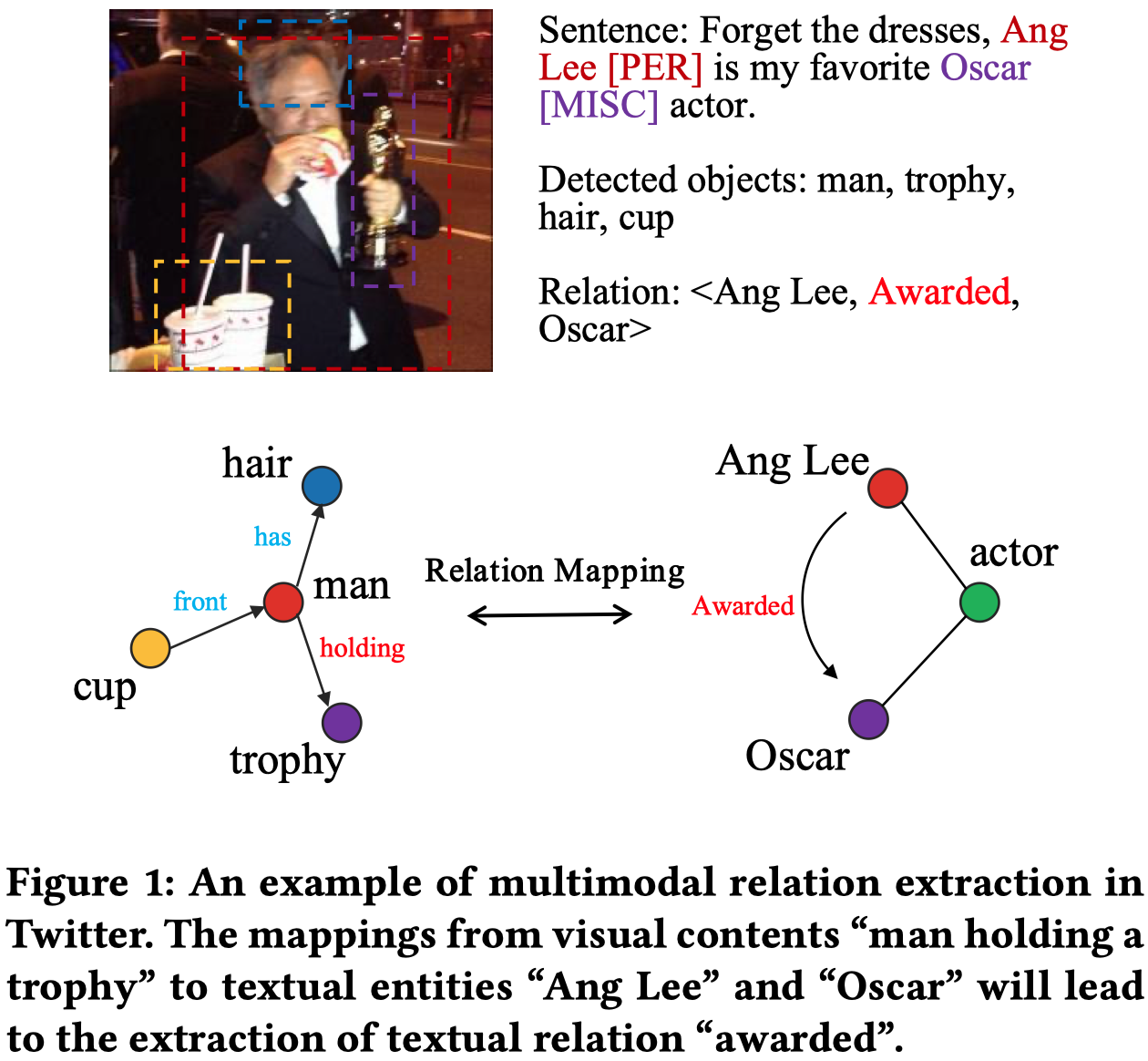
比如在上面的实例中,visual relation holding可以用来辅助推测textual relation awarded。
2 Method
总体结构:
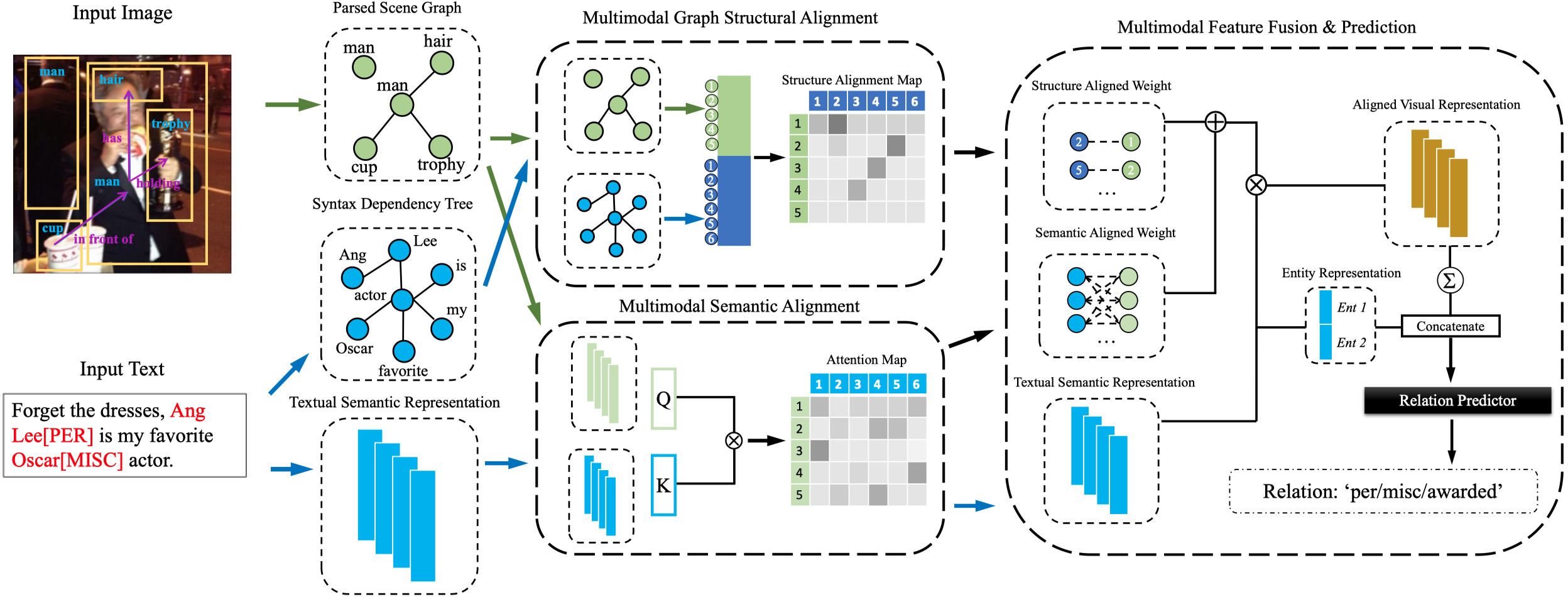
2.1 Semantic Feature Representation
首先是通过BERT和scene graph generation来获得文本和视觉的表征。
2.1.1 Textual Semantic Representation
对于输入的文本序列\(s_1\),添加token为下面的形式:
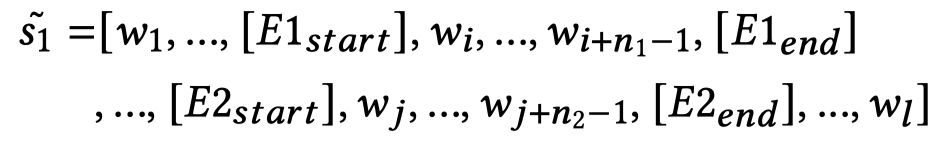
为了让所有的序列有固定长度\(l\),对于长度不足\(l\)的序列添加token \([PAD]\)。
随后,作者还设置了另一个序列\(s_2\)区分正常token和\([PAD]\) token,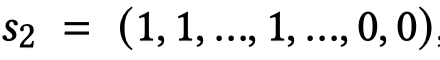 。
。
最后,fine-tune下pretrained好的BERT就得到了token的表征:

2.1.2 Visual Semantic Representation
使用前人的工作Unbiased Scene Graph Generation From Biased Training CVPR 2020来获得scene graph以及对应的表征:
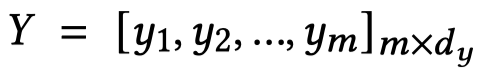
由于可能识别出很多不相关的visual object,因此作者设置一个阈值,只有大于这个阈值的,并且是前\(m\)个最大分类得分的object才会被使用。如果选择出来的数量小于\(m\),就添加0向量。
2.2 Structural Feature Representation
使用ELMo (Deep contextualized word representations. NAACL 2018)将input text解析为语法依赖树Syntax Dependency Tree。
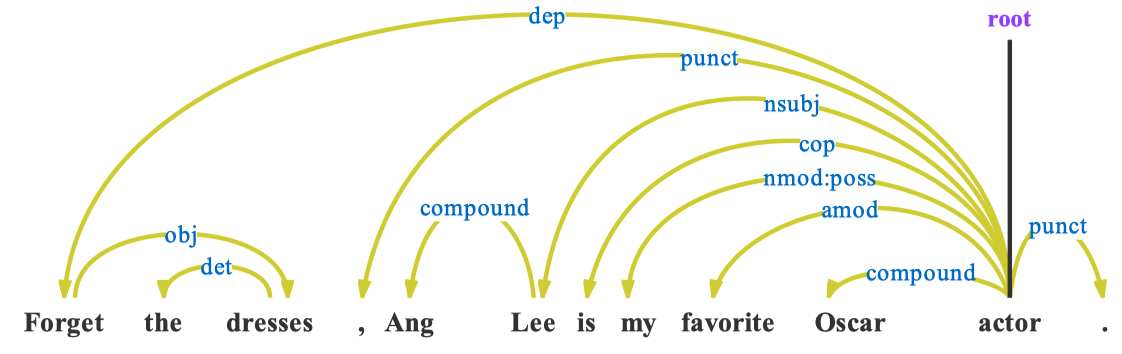
这样的语法依赖树就可以表示为一个文本图 \(G_1\):
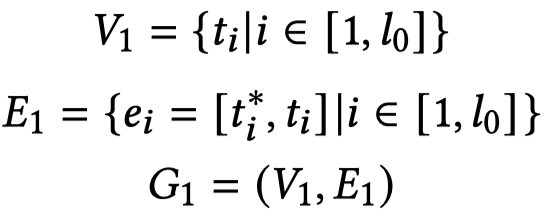
类似的,场景图也是一个graph \(G_2\):
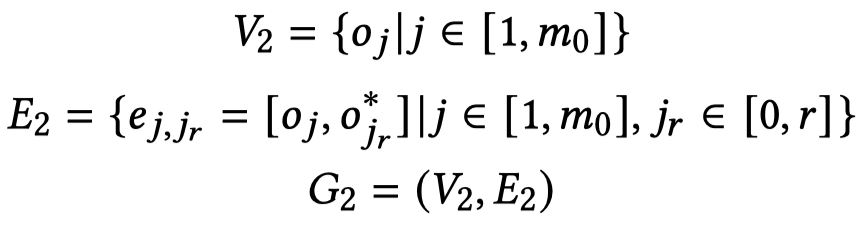
2.3 Multimodal Feature Alignment
2.3.1 Graph Structure Alignment
图结构的对齐,主要是有两步,一是通过分解节点标识node identity相似矩阵来获取node embedding;二是通过计算node embedding之间的相似度来对齐实体。
在学习node embedding时,作者follow了REGAL: Representation Learning-based Graph Alignment. CIKM 2018的工作。下面的具体原理没懂。
首先是统计两个graph下每个node的度分布:
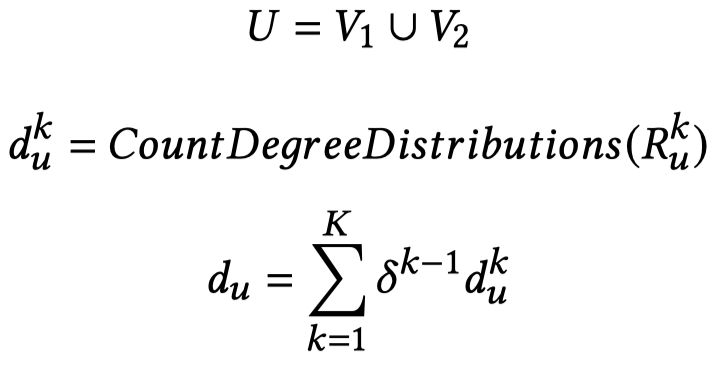
然后,利用这样的度分布可以评估两个node之间的节点相似度:
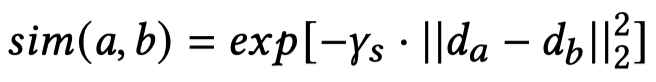
然后,随机选择\(p\)个node作为"landmark" node,计算它们和所有node之间的相似度,可以得到相似度矩阵\(C\in \mathbb{R}^{n\times p}\)。从矩阵\(C\)中,可以选出\(p\times p\)的landmark-to-landmark矩阵\(W_p\)。
。。。
最后 ,得到了node embedding:
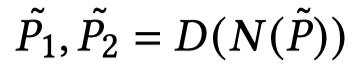
使用node embedding计算node之间的相似度,对于每个node,选择和它相似度最大的node作为对齐的node:
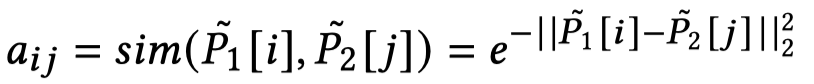
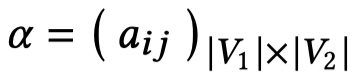
最后的矩阵\(\alpha\)的第\(i\)行\(j\)列表示第\(i\)个word和第\(j\)个object的结构的相似度。这本文当中,作者只保留了最相关的object(也就是每一行相似度最大的值保留下来),其它的都置为0。
2.3.2 Semantic Features Alignment
假设得到的文本表征是\(X\),视觉表征是\(Y\),通过自注意力来进行计算:
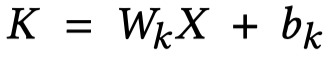
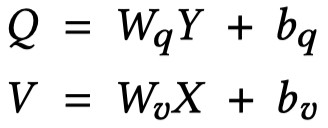
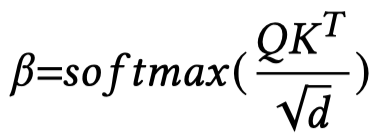
最后,同时使用structural和semantic对齐的结果:
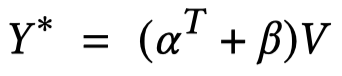
2.4 Entities Representation Concatenation
聚合所有object的视觉表征:
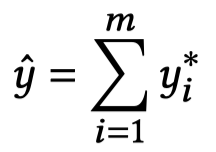
获得实体的文本表征:
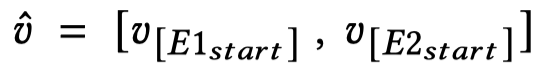
输出关系预测结果:
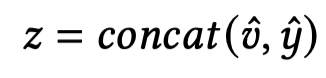
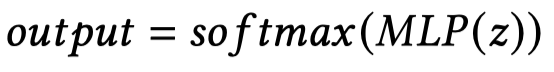
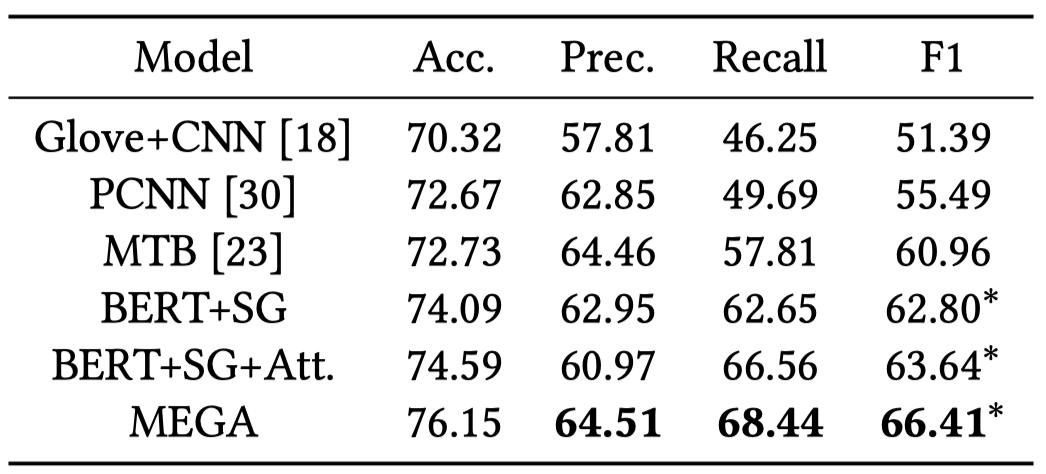
3 Experimental Results
MRE实验结果: