MAF
MAF: A General Matching and Alignment Framework for Multimodal Named Entity Recognition
WSDM 2022,代码,复旦大学。
作者通过判断post的text和image的匹配程度,计算进入文本表征中的图像信息,并且期望能够通过保持text和image不同模态表征的一致性。
In this paper, we study multimodal named entity recognition in social media posts. Existing works mainly focus on using a crossmodal attention mechanism to combine text representation with image representation. However, they still suffer from two weaknesses: (1) the current methods are based on a strong assumption that each text and its accompanying image are matched, and the image can be used to help identify named entities in the text. However, this assumption is not always true in real scenarios, and the strong assumption may reduce the recognition effect of the MNER model; (2) the current methods fail to construct a consistent representation to bridge the semantic gap between two modalities, which prevents the model from establishing a good connection between the text and image. To address these issues, we propose a general matching and alignment framework (MAF) for multimodal named entity recognition in social media posts. Specifically, to solve the first issue, we propose a novel cross-modal matching (CM) module to calculate the similarity score between text and image, and use the score to determine the proportion of visual information that should be retained. To solve the second issue, we propose a novel cross-modal alignment (CA) module to make the representations of the two modalities more consistent.We conduct extensive experiments, ablation studies, and case studies to demonstrate the effectiveness and efficiency of our method.The source code of this paper can be found in https://github.com/xubodhu/MAF.
1. Introduction
问题:
- 很多目前的MNER方法建立在认为post的text和image是匹配的假设上,因此总是会同时使用text和image的信息进行NER。但是并不是所有的text和image都是匹配的。

- 现有的方法忽略了学习text和image两个模态表征的一致性,因此两个模态的表征之间存在语义差异(semantic gap)
方案:
- 提出了一个跨模态匹配模块(cross-modal matching,CM)来计算text和image的相似度得分
- 提出了一个跨模态对齐模块(cross-modal alignment,CA)使得两个模态的表征更加一致
2. Method
总体结构:
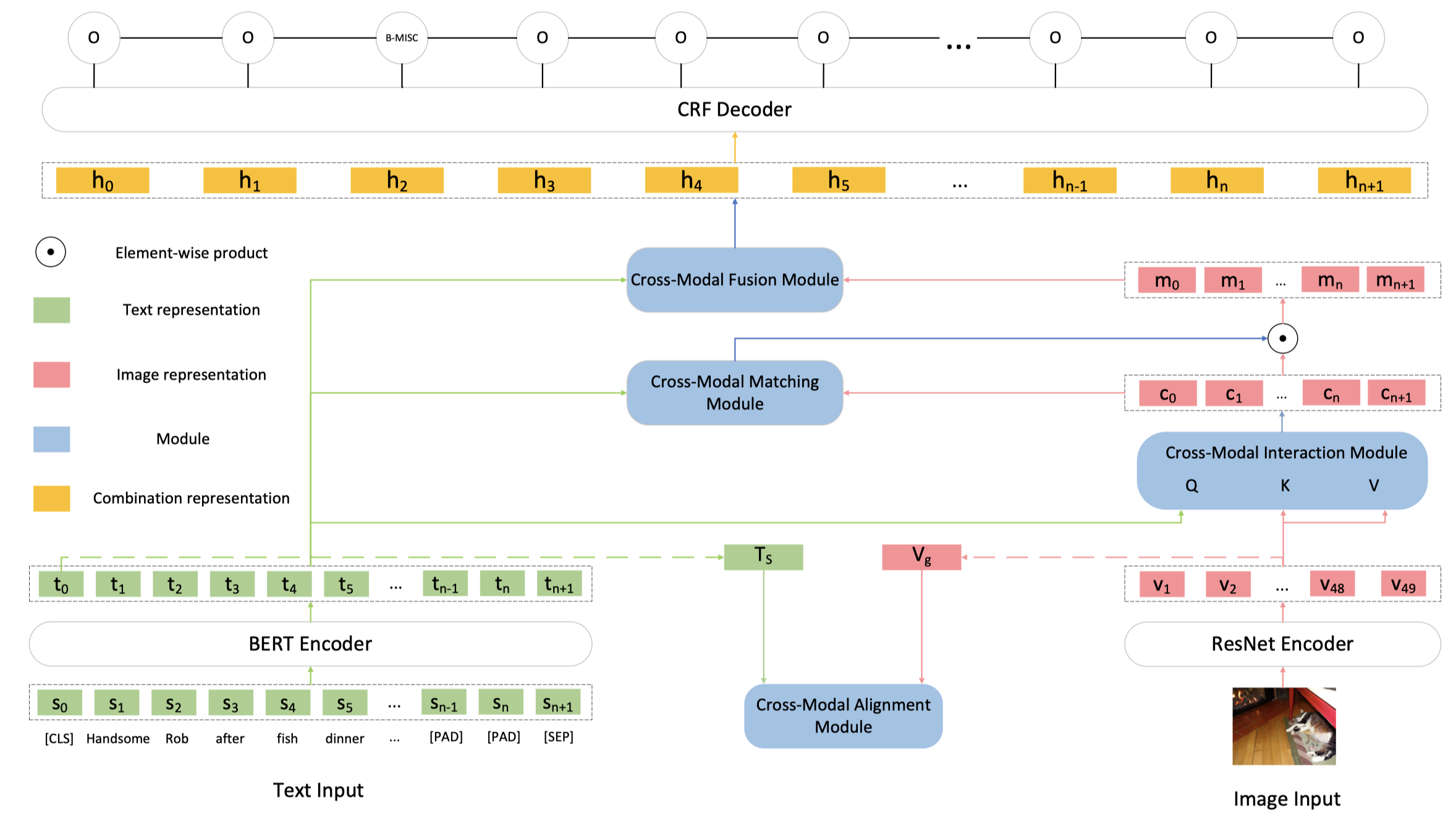
两个模态的encoder:
- text encoder:pretrained BERT-base。输入是最大长度128的token序列,在开头加入[CLS] token,在空白处加入[PAD] token。输出是768维向量。总的Transformer block有12层。
- image encoder:pretrained 152层ResNet。输入是224x224的resized image,输出是\(2048\times 7\times 7\)的代表49个region的张量。每个region向量通过独立的投影矩阵,转化为768维向量。
2.1 Cross-Modal Alignment Module (CA)
使用[CLS]的embedding作为文本序列的总表示\(T_s\);使用\(7\times 7\)的均值池化操作获得图像的总表示\(T_g\)。
两个表示通过独立的MLP来投影到具有相同维度大小的空间中,获得\(T_c\)和\(V_c\)。
然后使用这两个表征来尝试让两个模态空间下的向量表示具有更多的一致性。
基于对比学习学习text和image的匹配距离,在一个batch中,把image或者text换为其它post对应的image或者text作为负样本,把原来的样例作为正样本。
首先,计算正样本的Image embedding和所有样本的Text embeddings的距离,对比损失为:
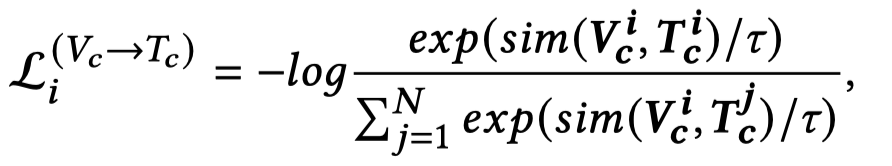
其中,计算相似度的函数是余弦相似度。
然后,计算正样本的Text embedding和所有样本的Image embeddings的距离,对比损失为:
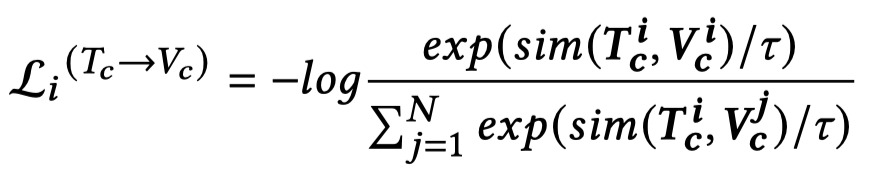
两个loss加载一起,就是CA模块的text-image匹配loss:
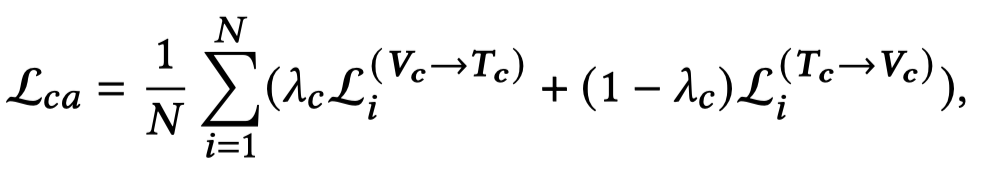
2.2 Cross-Modal Interaction Module
基于co-attention,text作为query,image作为key和value,学习text-aware的图像表征:
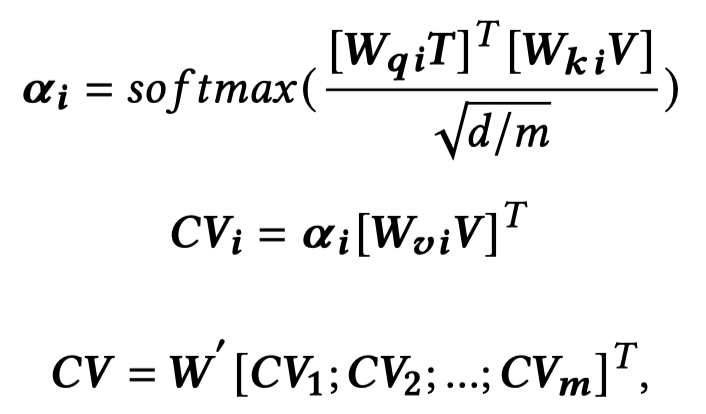
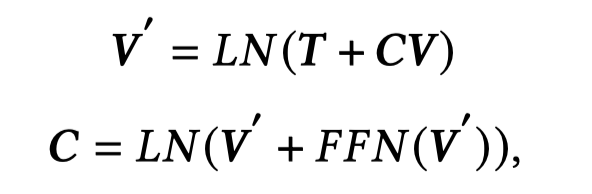
2.3 Cross-Modal Matching Module (CM)
作者设计了个CM模块,用来计算前一步学习到的text-aware的图像表征应该有多少被保留。
同样是基于text-image匹配任务,但是并不是基于对比学习,不使用对比学习,而是二分类问题,预测是否matching。
训练样本的构造也不同,不再是基于每个正样本都分别构造负样本,而是直接在一个batch中,选择2k个样本,前k个样本的image和后k个样本的image进行互换,构造出负样本;剩下的batch中的样本作为正样本。
预测是否匹配,直接把text和image图像展开,然后拼接输入到MLP
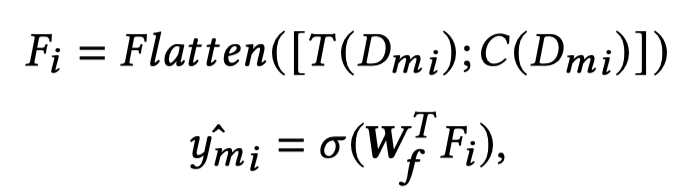
训练的loss就是BCE:
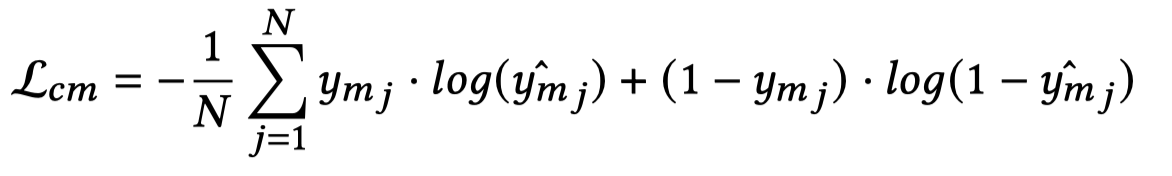
然后,根据这个分类器,可以判断在整个图像层次下,有多少信息应该保留:
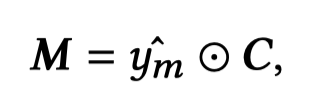
2.4 Cross-Modal Fusion Module
一个基于gate的模块被作者用来决定,在token level上有多少图像信息应该保留:
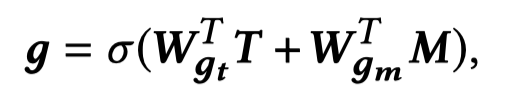
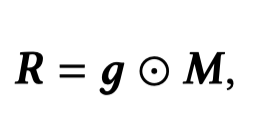
其中,\(g\in \mathbb{R}^{d\times (n+2)}\)是token level的权重。
最后,经过层层过滤的图像信息,与文本表征进行拼接,就得到了最后的表征\(H\)。
整个模型训练的loss,\(\alpha=\beta=0.2\):
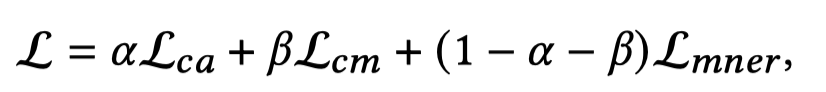
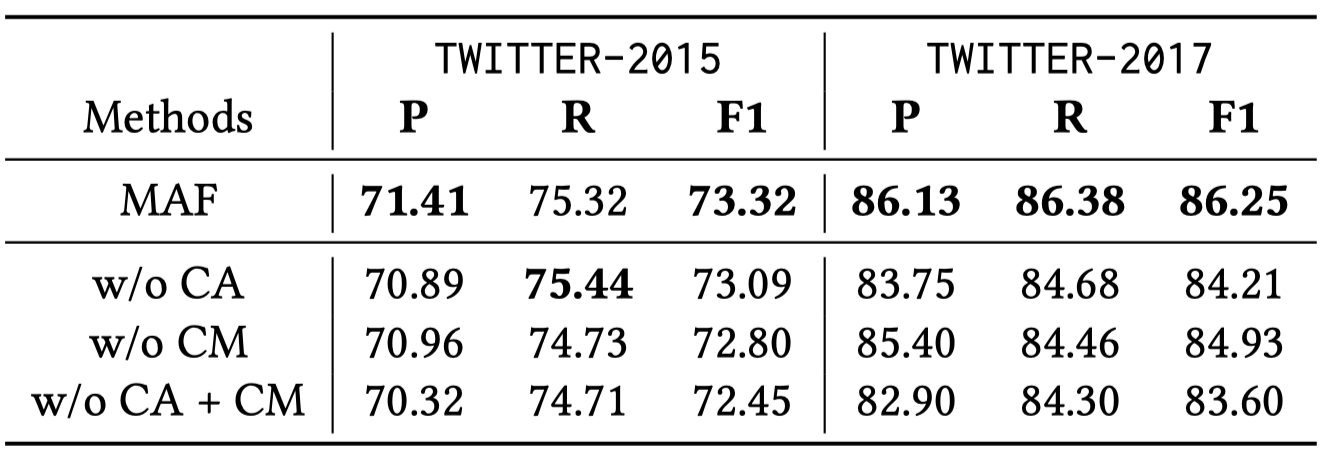
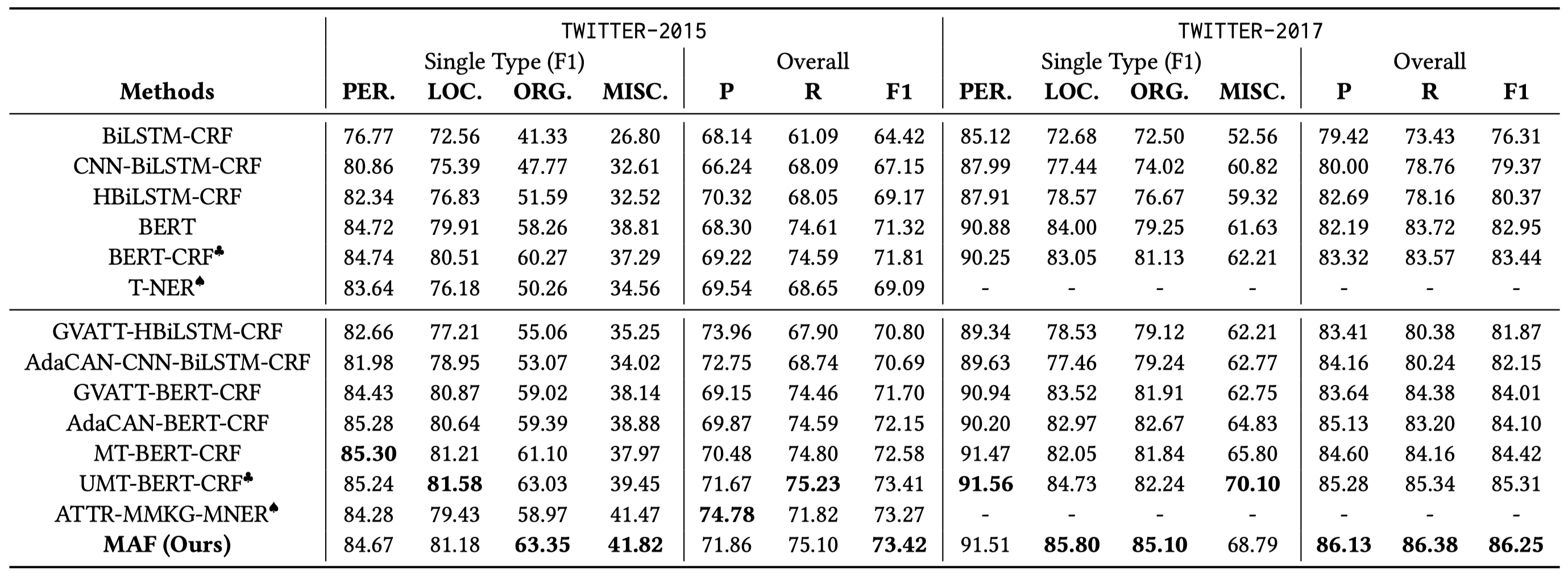
3. Experiment
整体性能并不是非常突出:
消融实验: