HVPNeT
Good Visual Guidance Makes A Better Extractor: Hierarchical Visual Prefix for Multimodal Entity and Relation Extraction
Findings of NAACL 2022,代码。
作者认为目前的MNER和MRE方法无法很好的处理图像和文本内容不匹配的问题,因此提出了一种从图像中提取object-level的层级信息,用于补充文本信息的多模态信息抽取方法HVPNeT (Hierarchical Visual Prefix fusion NeTwork)。
Multimodal named entity recognition and relation extraction (MNER and MRE) is a fundamental and crucial branch in information extraction. However, existing approaches for MNER and MRE usually suffer from error sensitivity when irrelevant object images incorporated in texts. To deal with these issues, we propose a novel Hierarchical Visual Prefix fusion NeTwork (HVPNeT) for visual-enhanced entity and relation extraction, aiming to achieve more effective and robust performance. Specifically, we regard visual representation as pluggable visual prefix to guide the textual representation for error insensitive forecasting decision. We further propose a dynamic gated aggregation strategy to achieve hierarchical multiscaled visual features as visual prefix for fusion. Extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our method, and achieve state-of-the-art performance 1 .
1 Introduction
问题:作者认为一开始的MNER和MRE工作倾向于把整个图像的特征考虑到文本表征中;后来的工作倾向于把object-level的图像特征考虑到文本表征中;最近,RpBERT虽然能够判断整个图像和文本内容是否相关,但是不能做到判断visual object和文本是否相关。但考虑到实际情况,一个图像中可能包含了比较相关的object,也可能包含了不太相关的object。
因此有必要更好的学习视觉表征,同时降低模型对不相关的visual object的错误敏感性。
方法:作者首先识别出图像中存在的多个visual object,然后利用CNN导出visual object的层级/金字塔型视觉特征;作者把这种层级的视觉特征看做是对于文本表征的视觉前缀visual prefix;visual prefix输入到BERT的每一层,用来提供文本表征所需的视觉信息。
2 Method
整体结构:
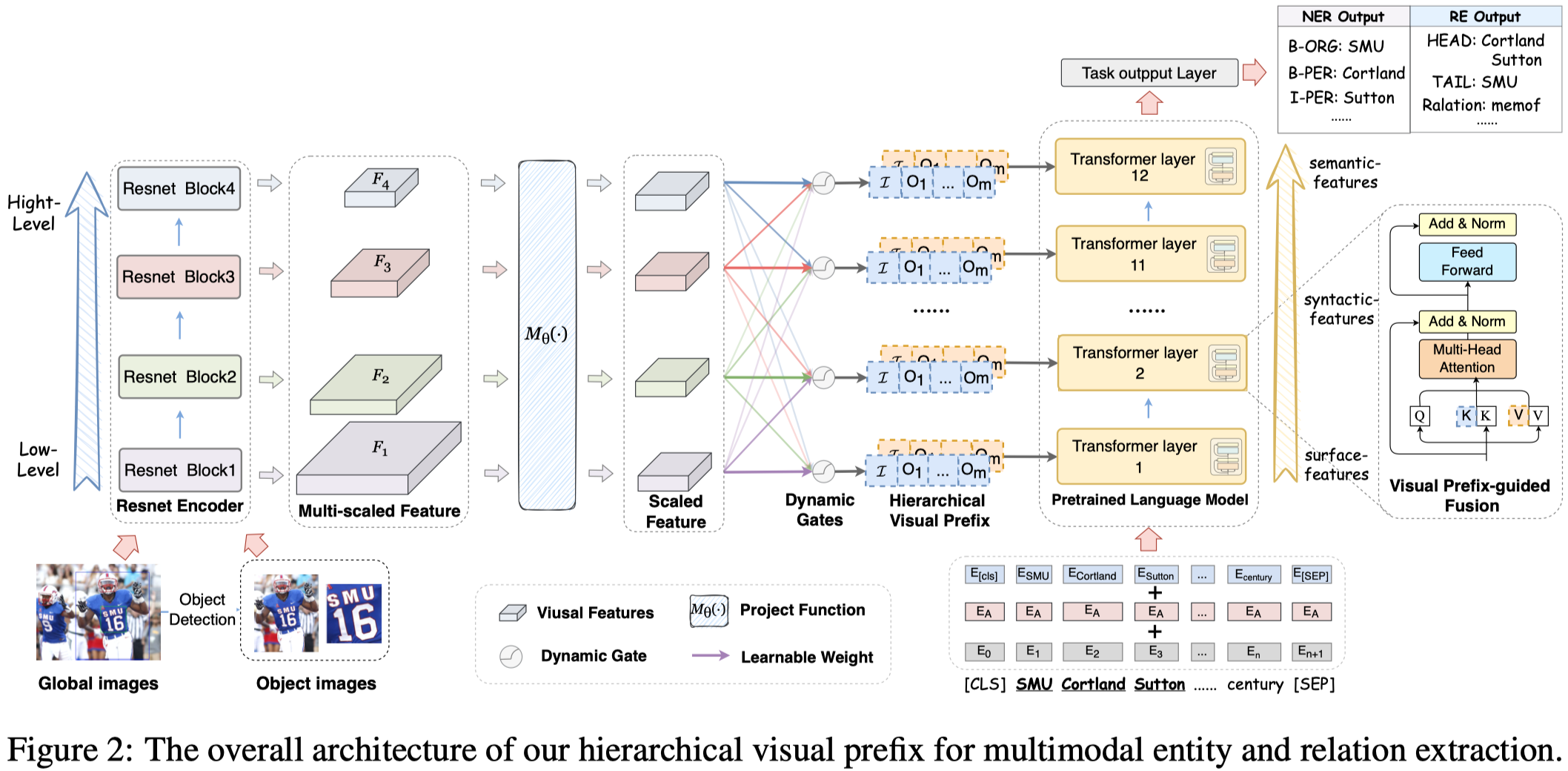
2.1 Collection of Pyramidal Visual Feature
作者首先利用visual grounding tool (A fast and accurate one-stage approach to visual grounding. ICCV 2019) 来标注出图像的前\(m\)个视觉对象(在实现中\(m=3\))。
然后把整个图像\(I\)和不同的视觉对象\(O=\{ o_1,o_2,\dots,o_m \}\) resale为\(224\times244\)的图像。
对于每个图像,作者利用Resnet-50的不同block,导出\(c\)层的视觉特征:
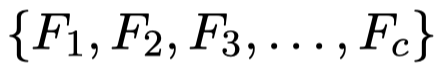
然后把这些不同size的特征,利用1维卷积和池化操作重新映射为具有相同size合适大小:
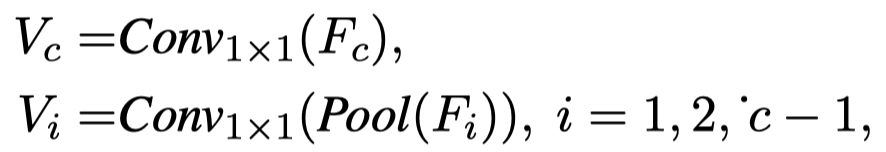
2.2 Dynamic Gated Aggregation
由于不同的Transformer层可能会需要不同的视觉特征,因此对于第\(l\)层的Transformer,对于单个图像导出的层级视觉信息\(V_i\),作者首先通过一个全局平均池化操作把3维张量进行压缩,然后求和,最后计算attention weight:
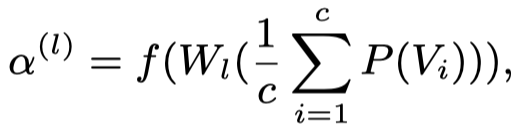
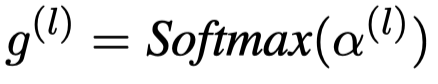
随后,聚合不同层的视觉特征:
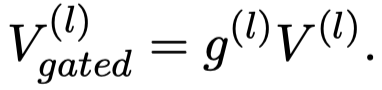
每个图像都进行了gated aggregation之后,把所有图像的聚合结果拼接到一起,作为最后要输入到第\(l\)层Transformer的视觉特征:
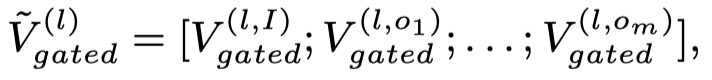
2.3 Visual Prefix-guided Fusion
接下来的问题是,如何把视觉特征加入到文本表征中去。
首先是,基于BERT-base结构,对于输入文本序列
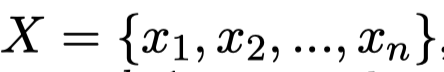
先产生query、key和value:
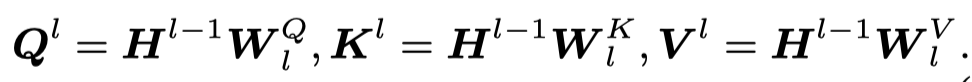
然后根据视觉特征,产生key和value作为visual prefix:
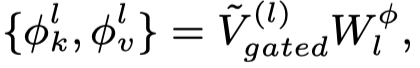
最后,进行聚合:
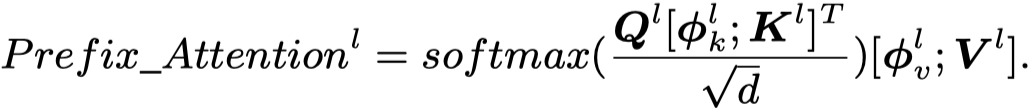
作者这种做法,是follow了Simvlm: Simple visual language model pretraining with weak supervision.的工作。
2.4 Classifier
对于MNER,采用常用的CRF层:
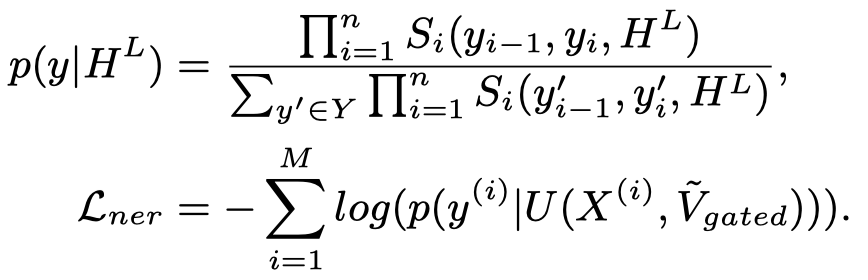
对于MRE,通过提前加入的\([CLS]\) token进行分类:
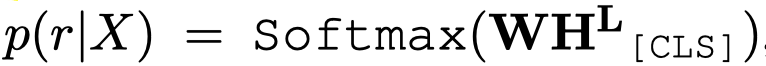
3 Experimental Results
总体实验结果:
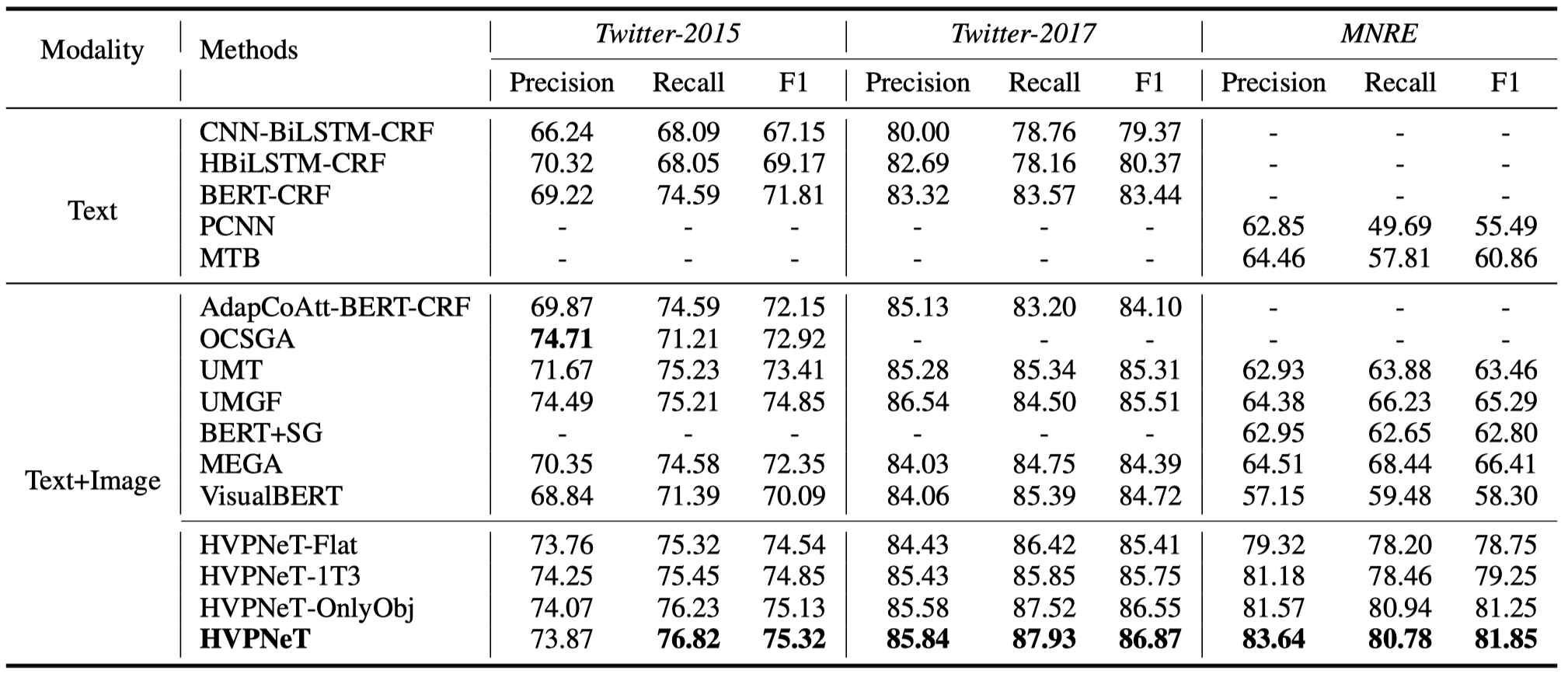
- HVPNeT-Flat:直接使用ResNet的最后输出结果,而不是使用层级的视觉特征(个人感觉从结果来看,不同层级的视觉特征对MRE的影响更大)
- HVPNeT-1T3:由于ResNet有4个block,BERT有12层,所以作者尝试了把1个block对应到3个BERT层,而不是直接把所有的block都输入到每一个BERT层
- HVPNeT-OnlyObj:只使用object-level的特征,不使用image-level的特征。(可以看到,即使不使用image-level的信息,差距也不是很大,说明主要起作用的还是object level的信息)