NN-extrapolate
HOW NEURAL NETWORKS EXTRAPOLATE: FROM FEEDFORWARD TO GRAPH NEURAL NETWORKS
ICLR 2021
这篇文章主要从理论和实验角度研究了MLP和GNN的外推(extrapolate)性能。
We study how neural networks trained by gradient descent extrapolate, i.e., what they learn outside the support of the training distribution. Previous works report mixed empirical results when extrapolating with neural networks: while feedforward neural networks, a.k.a. multilayer perceptrons (MLPs), do not extrapolate well in certain simple tasks, Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) – structured networks with MLP modules – have shown some success in more complex tasks. Working towards a theoretical explanation, we identify conditions under which MLPs and GNNs extrapolate well. First, we quantify the observation that ReLU MLPs quickly converge to linear functions along any direction from the origin, which implies that ReLU MLPs do not extrapolate most nonlinear functions. But, they can provably learn a linear target function when the training distribution is sufficiently “diverse”. Second, in connection to analyzing the successes and limitations of GNNs, these results suggest a hypothesis for which we provide theoretical and empirical evidence: the success of GNNs in extrapolating algorithmic tasks to new data (e.g., larger graphs or edge weights) relies on encoding task-specific non-linearities in the architecture or features. Our theoretical analysis builds on a connection of over-parameterized networks to the neural tangent kernel. Empirically, our theory holds across different training settings.
Introduction
什么是模型的外推性能?
We say a neural network extrapolates well if it learns a task outside the training distribution.
作者的两点贡献:
- 分析并证明了MLP外推的结果以及什么情况下MLP外推效果好
- 解释了为什么GNN能够在一些算法任务上(比如动态规划DP)外推效果好,并且提出了合适的改进方法
一些相关的关键工作。
- 有研究者证明了ReLU MLP最后学习到的是分段线性函数,例如《Complexity of linear regions in deep networks》
- 有研究者在更大的graph上测试GNN的外推性能,发现在找最短路径等任务上外推性能好,但是没有使用理论分析
HOW FEEDFORWARD NEURAL NETWORKS EXTRAPOLATE
外推效果的定义,通过定义外推loss:
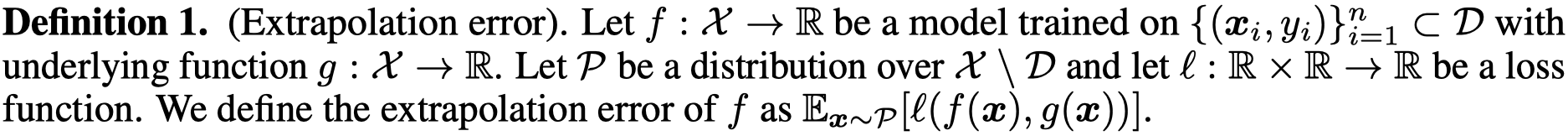
一个ReLU MLP是如何外推的:

ReLU MLP不会顺着灰色的期望进行外推,而是很快就外推成为一个线性function。看一看下面的定理(MLP是使用NTK来训练的):
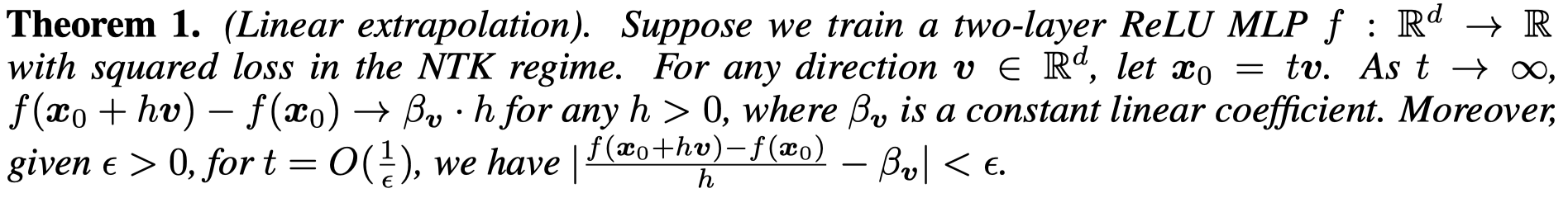
怎么样让ReLU MLP能够外推结果好?
- 让MLP拟合的目标函数是线性的
- 让训练集足够的diverse,这样训练好的模型能够学到足够多合适“方向”便于外推

其它激活函数MLP什么时候效果好?
- 当目标函数的分布和激活函数大致相似的时候
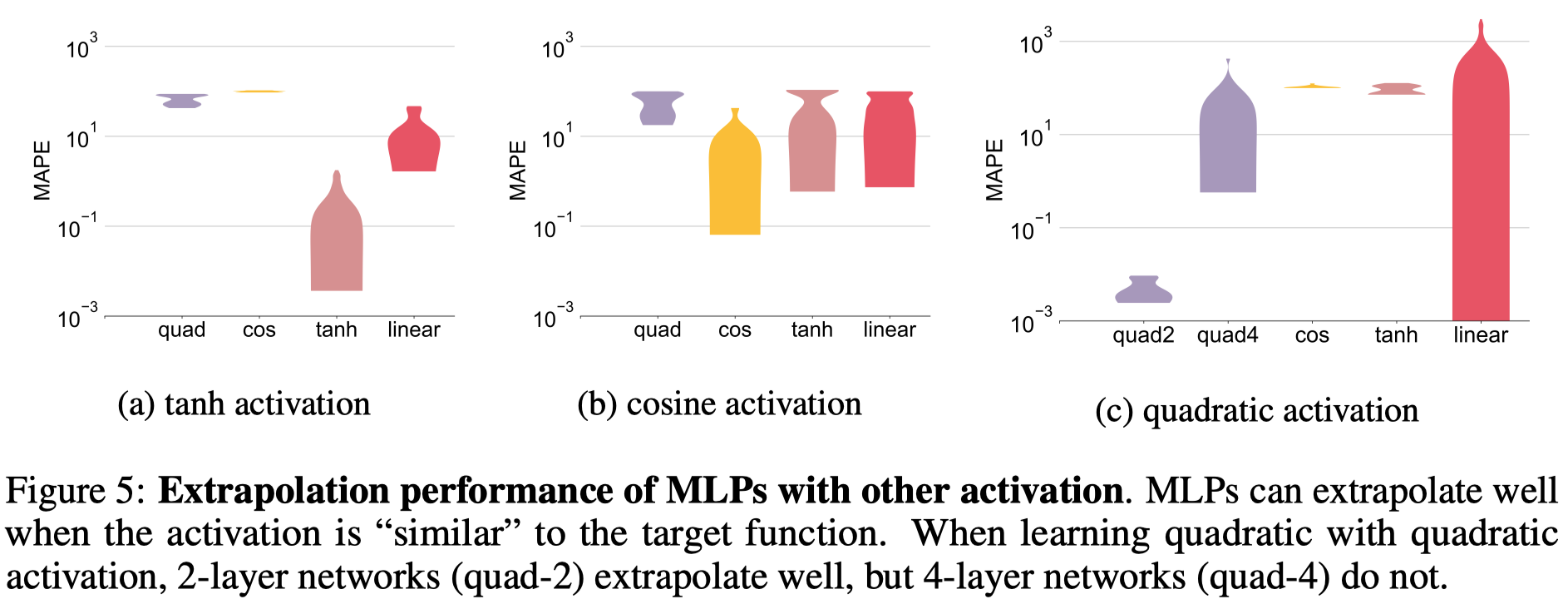
图中MAPE是指平均绝对误差比例,越小越好(原论文没提)。
HOW GRAPH NEURAL NETWORKS EXTRAPOLATE
GNN实际是在MLP拟合线性function的基础上,通过让模型本身就编码了task-specific的非线性,来获得好的外推性能。
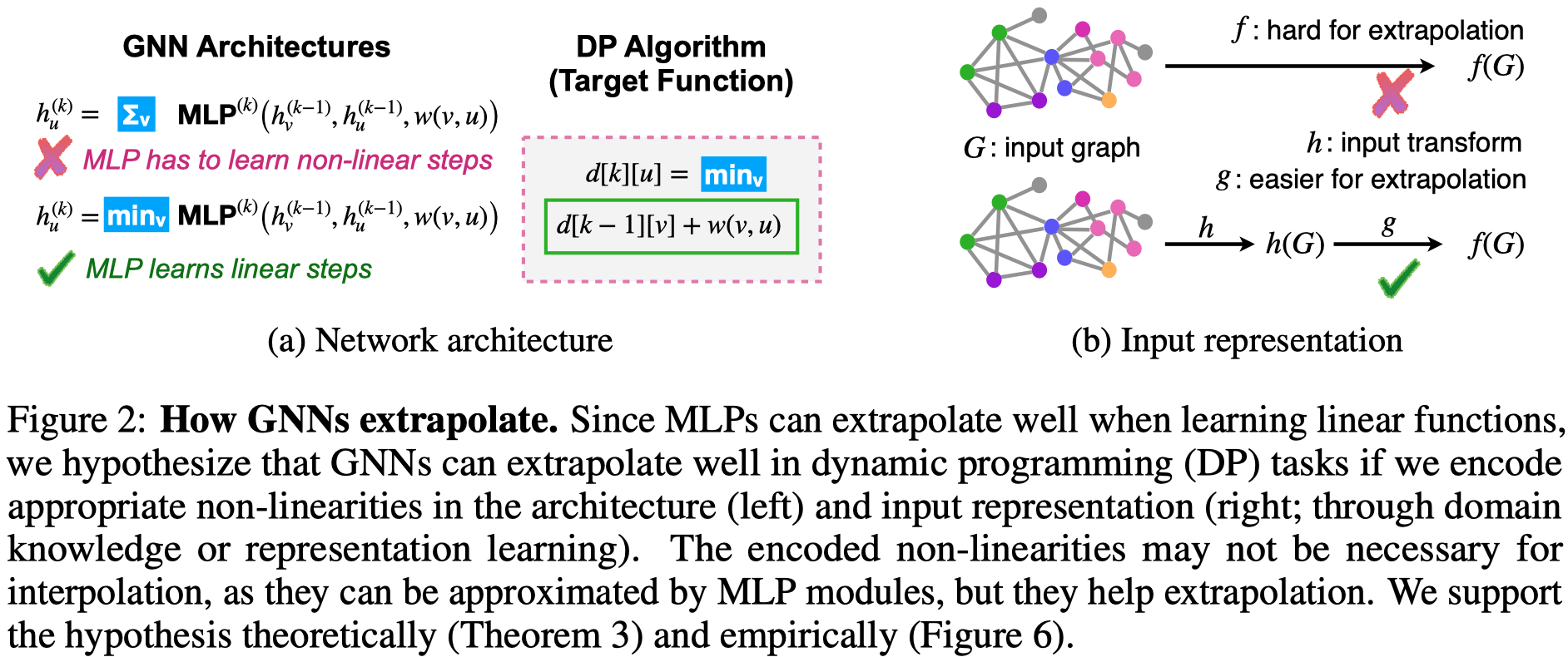
上面第一个图是使用GNN进行最短路径寻找的任务,如果使用sum的聚合方法,外推效果就差;如果是使用min的聚合方法,外推效果就比较好。这是因为此时的GNN实际上是在拟合BF最短路径算法:
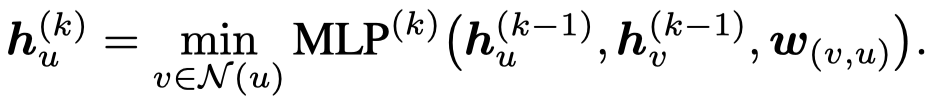
GNN拟合BF算法:
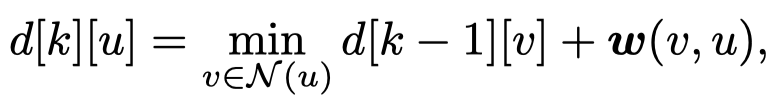
\(d[k][u]\)是指第\(k\)轮迭代,到节点\(u\)的最短路径。
此时GNN只是使用MLP来拟合一个线性函数\(d[k-1][v]+w(v,u)\),因此外推效果较好。
同样的道理,可以使用max聚合方法,让GNN在计算graph的最大度任务上,外推效果好。
可以拓展来看,很多可以使用DP算法解决的问题,由于DP算法和GNN的聚合思想很像,或许可以从算法的角度改进GNN,让GNN外推效果好:

作者还提出了另外一种让GNN能够外推效果好的方法,就是提前获得某些合适的非线性的表示,然后让GNN只需要使用MLP拟合线性部分即可,最后结合非线性的表示就可以逼近理想的函数。