synthetic-data-llm-sub
Synthetic Data Generation with Large Language Models for Text Classification: Potential and Limitations
Purdue University, 作者评论接收至EMNLP 2023。
The collection and curation of high-quality training data is crucial for developing text classification models with superior performance, but it is often associated with significant costs and time investment. Researchers have recently explored using large language models (LLMs) to generate synthetic datasets as an alternative approach. However, the effectiveness of the LLM-generated synthetic data in supporting model training is inconsistent across different classification tasks. To better understand factors that moderate the effectiveness of the LLM-generated synthetic data, in this study, we look into how the performance of models trained on these synthetic data may vary with the subjectivity of classification. Our results indicate that subjectivity, at both the task level and instance level, is negatively associated with the performance of the model trained on synthetic data. We conclude by discussing the implications of our work on the potential and limitations of leveraging LLM for synthetic data generation.
Issue: 目前在不同的task里,对于使用LLM生成的data是否能够和真实人工标注的data相比,没有定论。
Solution: 作者认为出现这种现象的原因之一和具体text classification任务的主观程度subjectivity有关,实验发现主观性越强的分类任务,LLM生成数据的效果也会越差。
Methodolgy
作者采用了zero-shot和few-shot ICL两种设置。
对于zero-shot ICL prompt:
- “context prompt” relevant to the targeted domain of interest is used to set the context. 与具体task context相关的prompt
- the “data generation prompt”, is provided to the LLM, instructing the model to generate texts with a specific style, label (with respect to the classification task of interest), and word limit. 提供具体的label、生成字数限制等要求的prompt
- a “diversity prompt” to the LLM—“Can you provide something more diverse compared to the previously generated data?”—aiming to increase the diversity of the synthetic data generated. 生成具体的几个text data后,提示LLM生成更多不同的text data
对于few-shot ICL prompt:
- “context prompt”与前面zero-shot ICL一样
- 随机采样的几个demonstrations,其中说明了对应的label
- 还强制限制了不允许仅仅是修改原来的句子,而是期望生成更多的具体data,比如
You should imitate the example I have provided, but you cannot simply modify or rewrite the example I have given
下面是不同task用到的具体prompt:

更多具体task的prompt参考paper附录。
Evaluation I: Comparison Across Different Types of Tasks
一些实验设置:
10个不同task,AG’s news (Zhang et al., 2015), IMDB reviews (Maas et al., 2011), SMS spam (Almeida et al., 2011), Financial phrase bank (Malo et al., 2014), Reddit emotion (Demszky et al., 2020), Relation classification (Gao et al., 2019) FewRel 2.0, Tweet irony speech (Van Hee et al., 2018), Tweet emotions (Mohammad et al., 2018), Sarcasm news (Misra and Arora, 2023, Misra and Grover, 2021), and Humor speech (Annamoradnejad and Zoghi, 2020).
对于关系分类任务,只讨论了FewRel 2.0数据集中‘country’, ‘league’, ‘screenwriter’, and ‘tributary’的4种relation
主要基于
GPT-3.5-Turbo进行数据生成,但是在附录里提供了关于GPT2-large (774M)和Llama2 (7B)的对比实验对于每个label生成\(3000\)条数据用于实验,微调BERT和RoBERTa进行实验
具体task的主观程度,是通过众包人工打分得出的,每个worker会被要求判断随机的从两个task里找到的句子,哪个更加客观。具体的众包过程可以参考论文。在众包时,提示worker的对于任务客观性的定义:
the classification of a piece of text is based on clear, identifiable features in the text (e.g., keywords or phrases), and can be done without being affected by any personal interpretation of the text resulted from personal biases, emotions or beliefs.
分类结果可以根据text很清楚的判断出来,并且不会受到个人的偏好、情感、信仰等发生变化。
Evaluation Results
分别独立的在真实数据、生成数据上进行训练的实验结果:
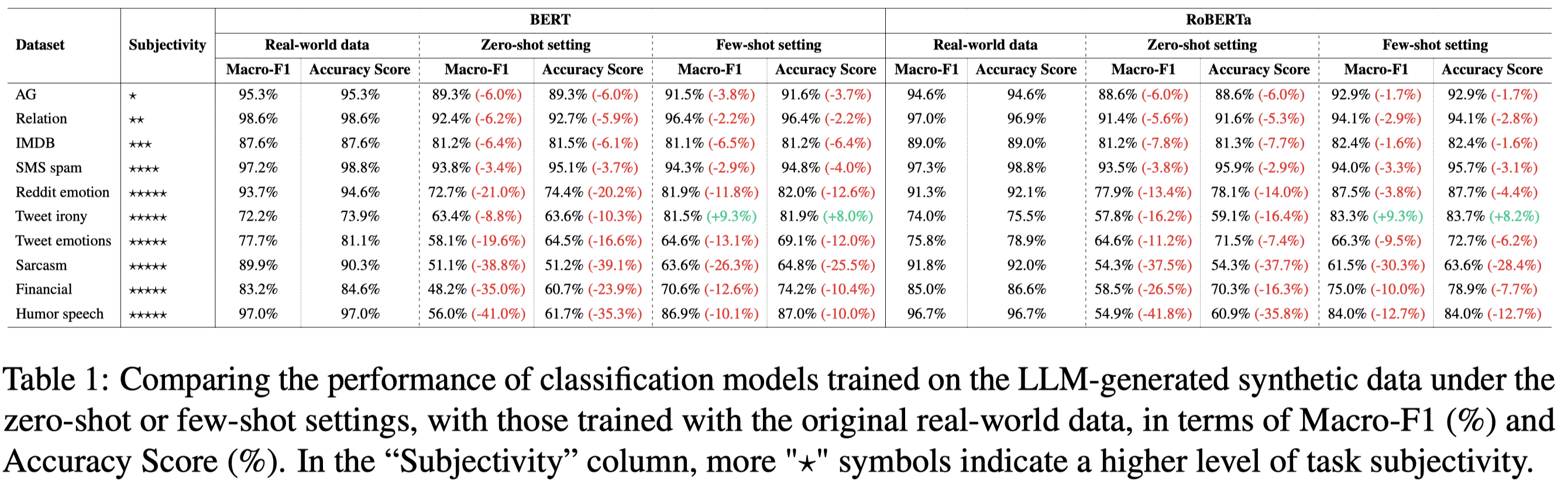
观察:
- 直接使用真实数据训练的效果最好
- few-shot ICL生成数据效果比zero-shot ICL效果好
- LLM在生成带有更多人类主观性的数据上,效果更差
为什么任务的主观程度会增大LLM生成数据的效果?作者提供了两个解释:
- highly subjective tasks often require a deep understanding of nuanced human emotions and contextual subtleties, as well as the ability to discern and accurately interpret different perspectives. 越主观,越要求对于人类情感等有非常微妙的理解
- it may be challenging for LLMs to generate synthetic data to recover such potentially biased “majority view,” especially if the LLMs are trained to maintain neutrality. 大多数的任务实例是利用众包标注的,也就是说在数据集里的gold label可能只反映了多个人的主要投票意见。对于LLM来说,要生成反映这种majority view的句子可能比较难。
使用一小部分真实数据进行训练,然后拿这一小部分真实数据作为demonstrations进行数据增强的实验结果:
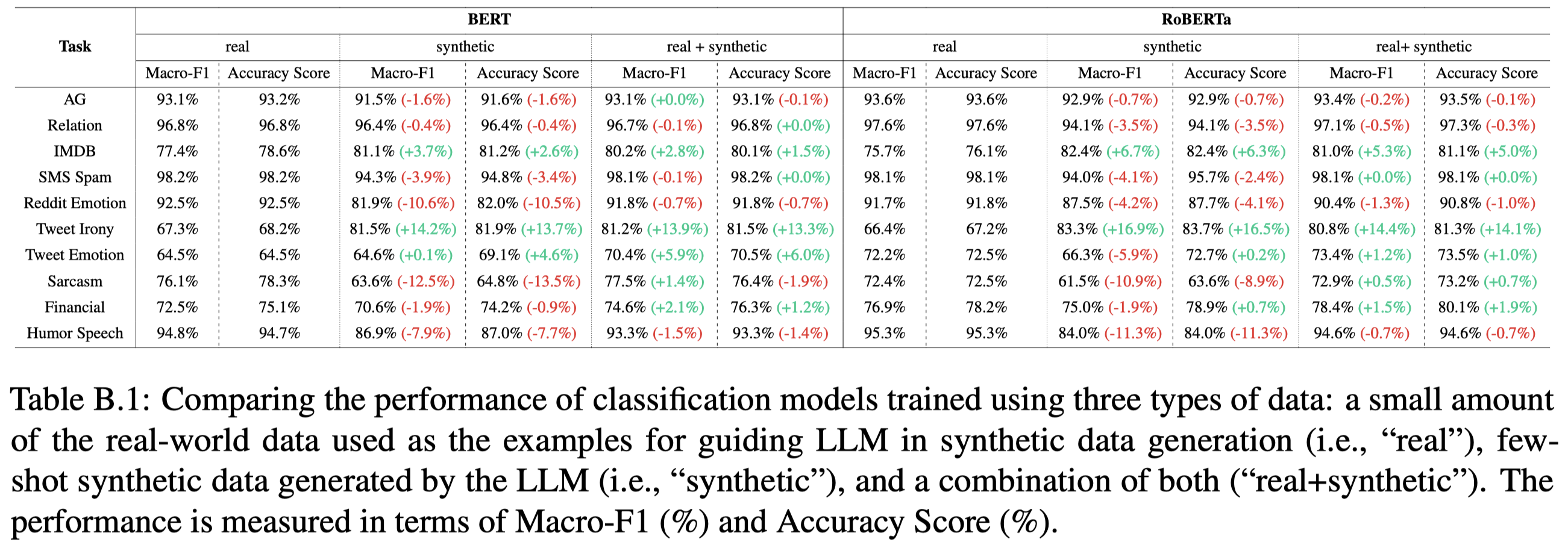
观察:
- 在关系抽取任务上,作者的这种比较简单的生成数据的方法,没有明显提升效果
不同LLM生成数据的对比:

Diversity and Similarity between the Synthetic Data and the Real Data
对于生成的数据,作者从多样性和原有数据的相似性两个角度进行了分析。
对于多样性,follow前人的工作[Directed diversity: Leveraging language embedding distances for collective creativity in crowd ideation. 2021],采用Remote Clique Score和Chamfer Distance Score两个metric计算多样性:
- Remote Clique Score (i.e., the average mean distance of a data instance to other instances)
- Chamfer Distance Score (i.e., the average minimum distance of a data instance to other instances)
实验结果:
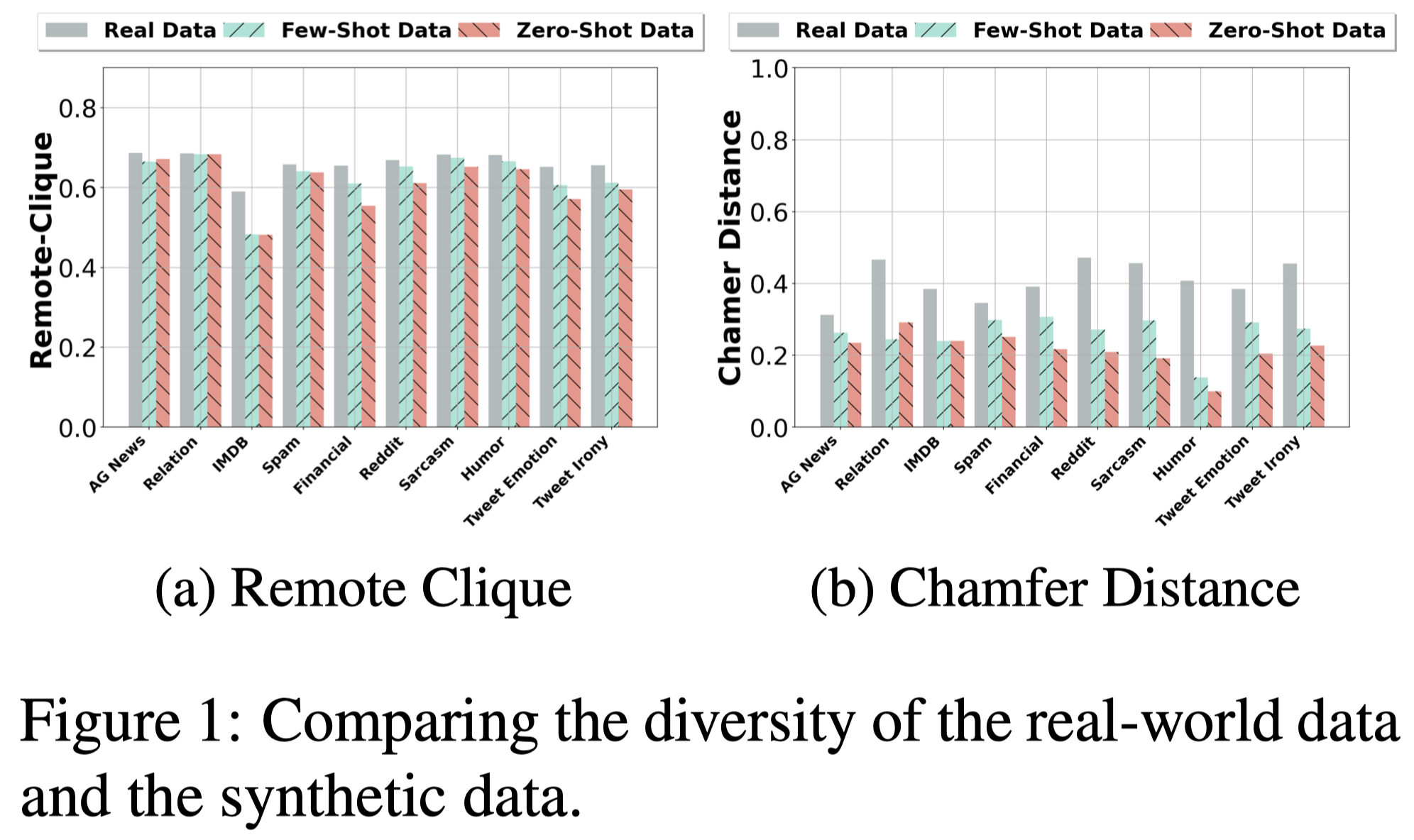
可以看到真实数据多样性更强;而few-shot ICL生成数据的多样性比zero-shot ICL生成数据的多样性更强。
相似度是衡量生成数据与真实数据的相似程度,具体来说,对于真实的text,利用Sentence Transformer(all MiniLM-L6-v2)转化为embedding,然后计算和各个生成数据embedding的余弦相似度,取前5个最大的相似度的值来计算平均相似性。实验结果:

可以看到,用few-shot ICL生成的数据比zero-shot ICL生成的数据,和原有真实数据更加一致。
Evaluation II: Comparison Across Different Task Instances
作者进一步探究了,利用LLM生成的data训练的模型,是否对于同一任务下,不同主观程度的instance也会有不同的表现?
instance的主观程度同样是利用众包人工标记,多个worker对于某种instance分类结果,判断越不一致,越认为instance的主观性越强。利用多个worker的投票分类结果,可以计算最多的投票分类在所有投票中的占比,作为主观程度的度量:
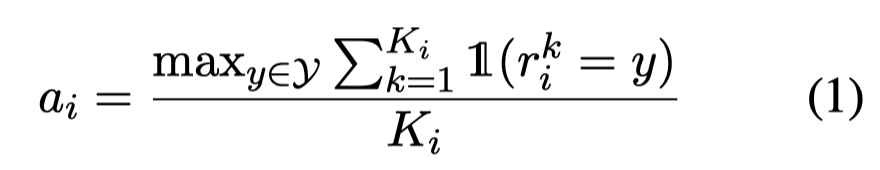
上面的度量论文里称作annotation agreement。下面是不同task的annotation agreement平均值:

作者在实验时,设定了阈值\(\gamma\),instance的annotation agreement \(\alpha_i\)超过一定阈值后,才会被评估。因此阈值gamma越大,代表着剩下的测试实例主观性越弱。实验结果:
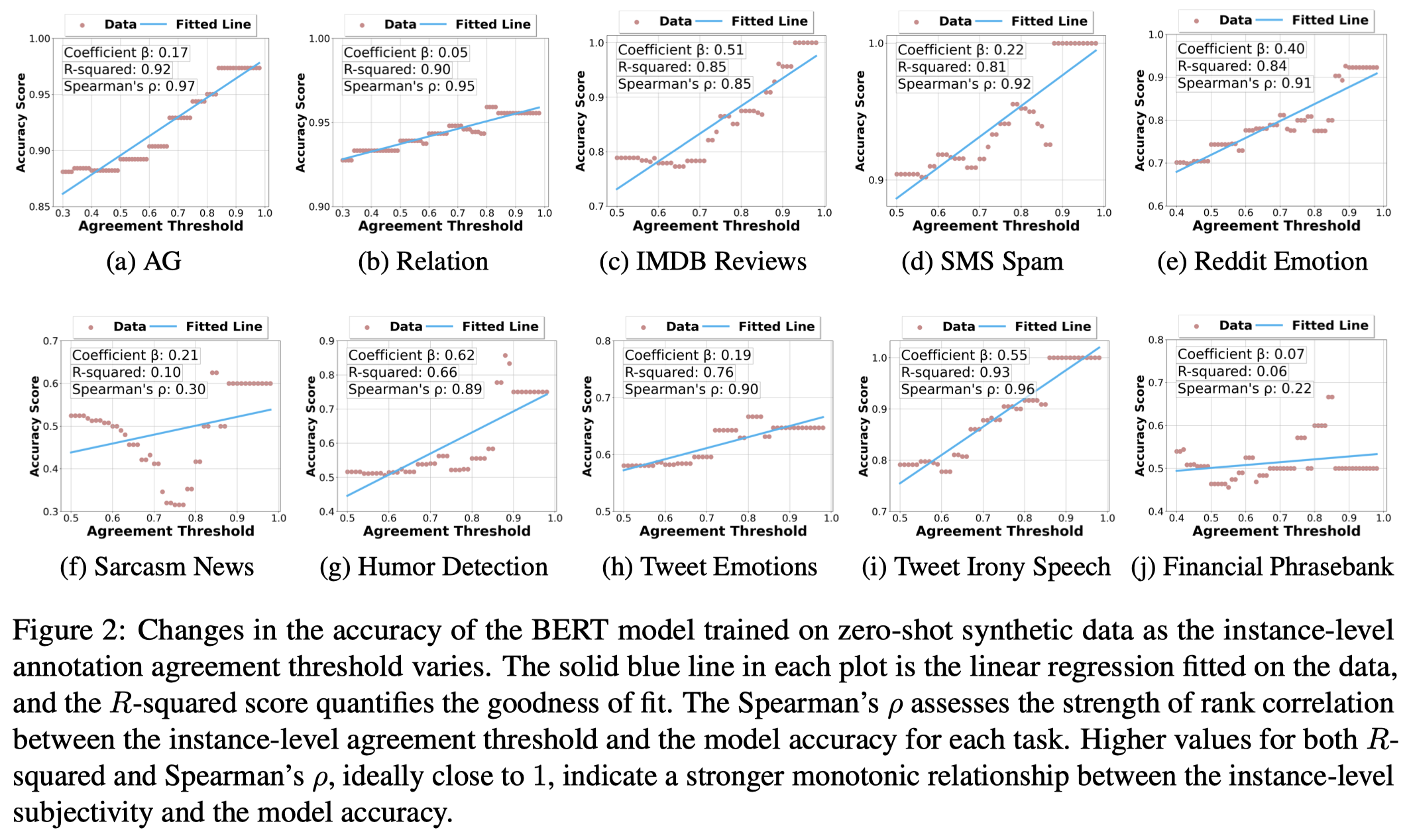
可以看到,instance的主观性越弱,训练好的model越有可能分类正确。
只在real data上训练的model,也会表现出类似的趋势,但是没有单纯在生成数据上训练的model表现出来的趋势强。这证明了,生成数据的加入,可能要考虑给model带来的bias的影响。