TokenButler
TokenButler
TokenButler: Token Importance is Predictable. arXiv 2025. 代码. 康奈尔大学
Large Language Models (LLMs) rely on the KeyValue (KV) Cache to store token history, enabling efficient decoding of tokens. As the KV-Cache grows, it becomes a major memory and computation bottleneck, however, there is an opportunity to alleviate this bottleneck, especially because prior research has shown that only a small subset of tokens contribute meaningfully to each decoding step. A key challenge in finding these critical tokens is that they are dynamic, and heavily input query-dependent. Existing methods either risk quality by evicting tokens permanently, or retain the full KV-Cache but rely on retrieving chunks (pages) of tokens at generation, failing at dense, context-rich tasks. Additionally, many existing KV-Cache sparsity methods rely on inaccurate proxies for token importance. To address these limitations, we introduce TokenButler, a highgranularity, query-aware predictor that learns to identify these critical tokens. By training a lightweight predictor with less than 1.2% parameter overhead, TokenButler prioritizes tokens based on their contextual, predicted importance. This improves perplexity & downstream accuracy by over 8% relative to SoTA methods for estimating token importance. We evaluate TokenButler on a novel synthetic small-context co-referential retrieval task, demonstrating near-oracle accuracy. Code, models and benchmarks: [Code]
Issue:随着LLM能够接收越来越长的context,需要保留的KV cache越来越多。会增加对内存和带宽的压力。而之前的研究表明,只有少部分token对于decoding是重要的。也就是可以不保留所有的K和V。这就是token pruning。
现有的token pruning策略大致有:
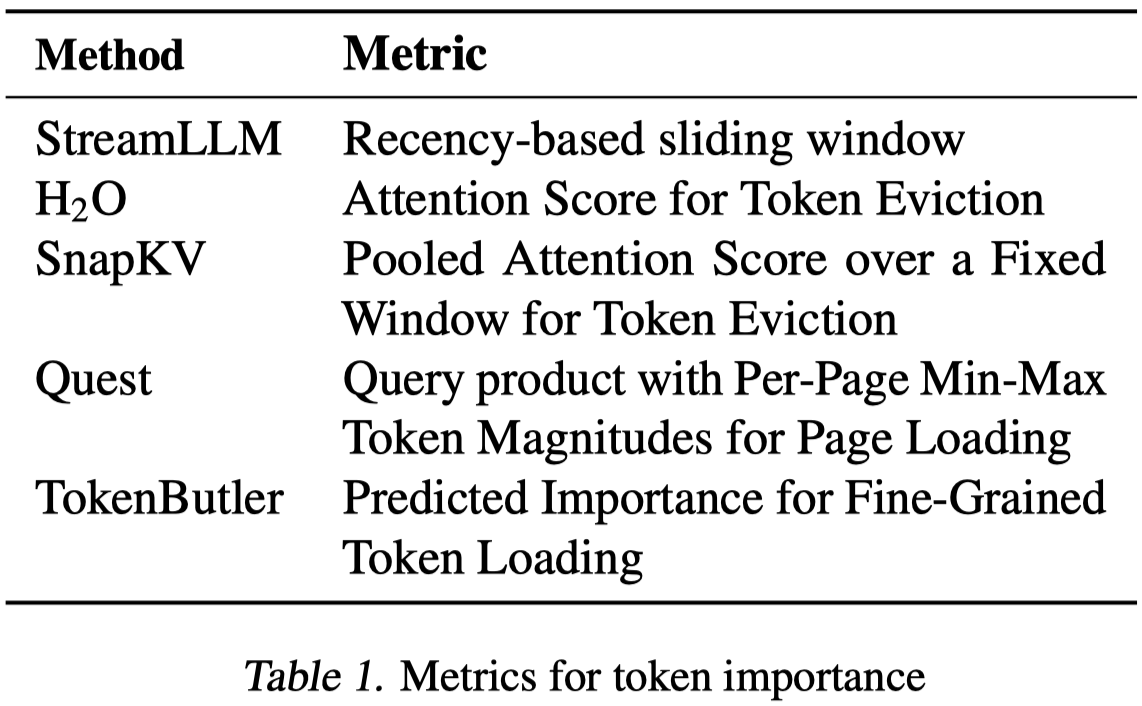
- Purely static strategies limiting KV-Cache to a fixed budget with fixed rules on removing tokens, naturally reducing bandwidth and storage (StreamingLLM (Xiao et al.), and Sliding Window Attention (Luong, 2015)) 静态的策略会丢失重要token
- Adaptive strategies that permanently sacrifice less important past-tokens effectively fixing the memory and bandwidth footprint (H2O, SnapKV (Zhang et al., 2023b; Li et al., 2024)) 自适应策略会在decoding前永久丢失一些可能被后面继续使用共指的token
- Adaptive dynamic strategies that preserve the entire KV-Cache but access only a subset of the Key-Value entries (the more important past-tokens), incurring higher memory (storage) cost, but reducing memory bandwidth (accesses to memory) during the decode stage (generation) 动态自适应的方法是最合理的,保留所有的K和V,但是只访问有用的K和V。动态是指每个decoding step都会访问重要的K和V。
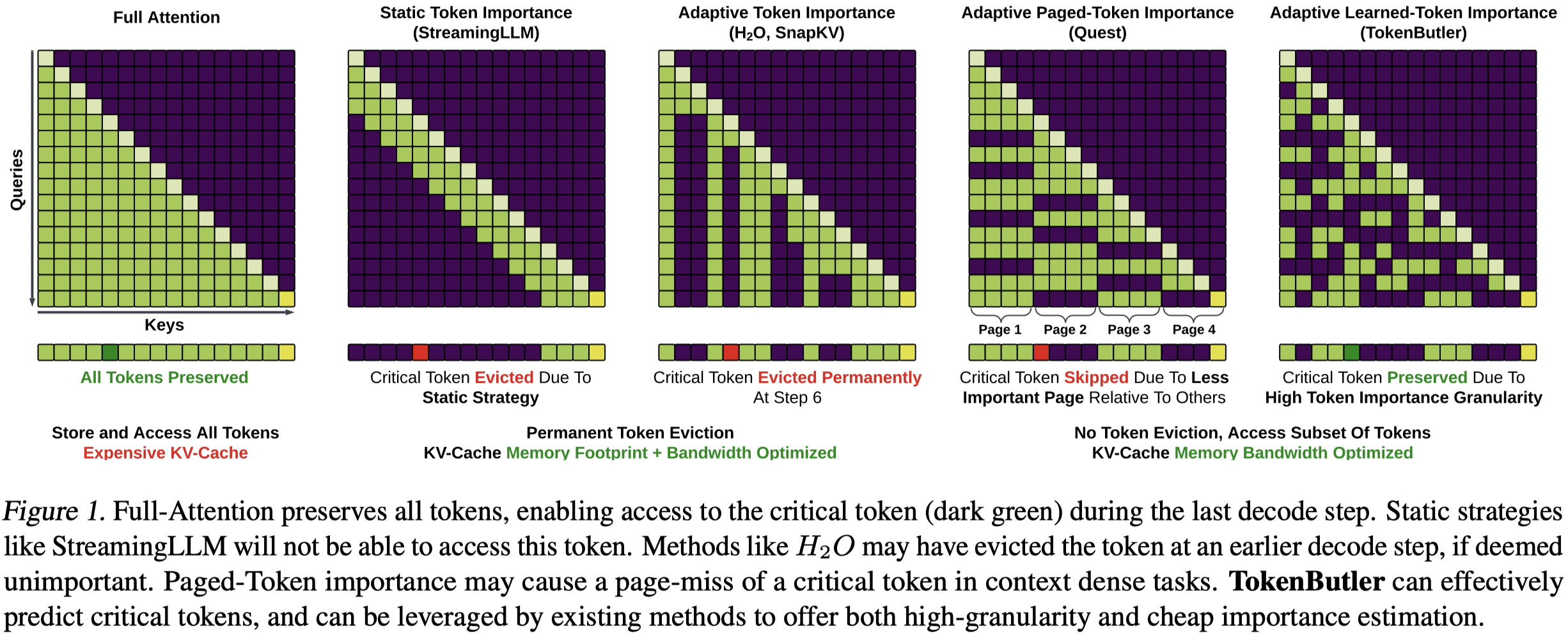
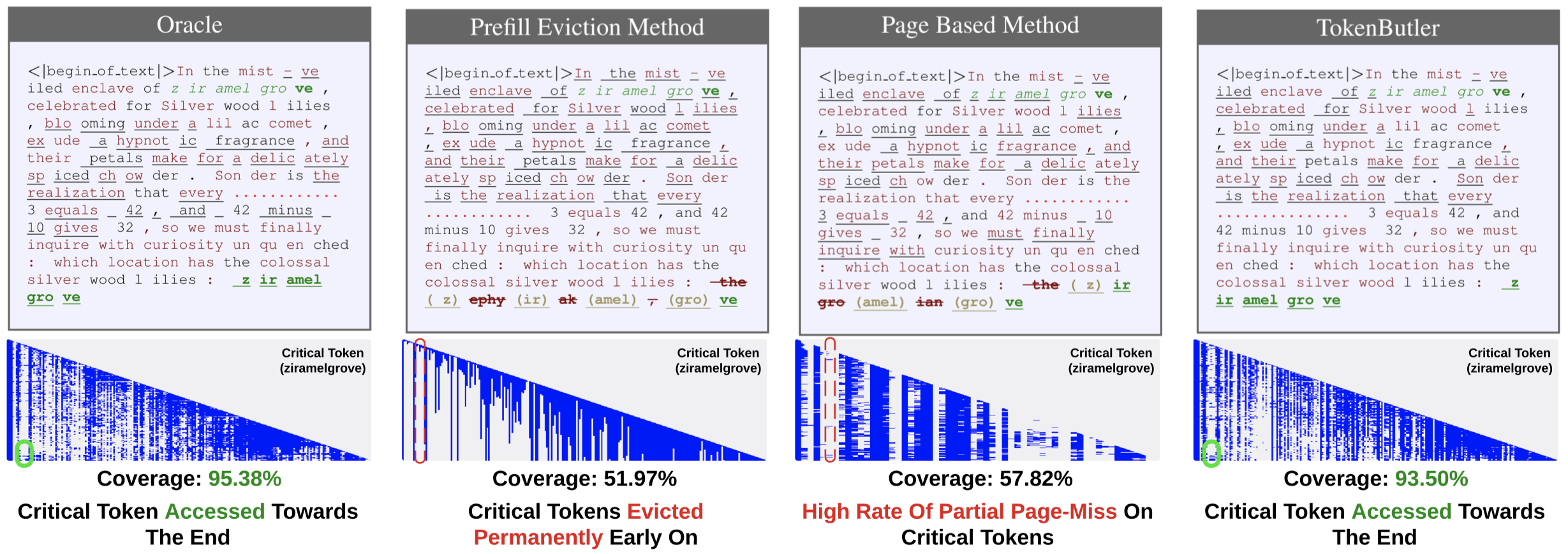
问题在于,当前的token重要性指标,无法直接用于token稀疏化。例如attention weight是一个很适宜用来预测token重要性的指标,但是动态策略意味着每次只能够根据token importance选择一部分token,无法获取全部的attention weight来作为后面预测token重要性的依据。
Solution: 无法计算获得全部的attention weight,那就预测。
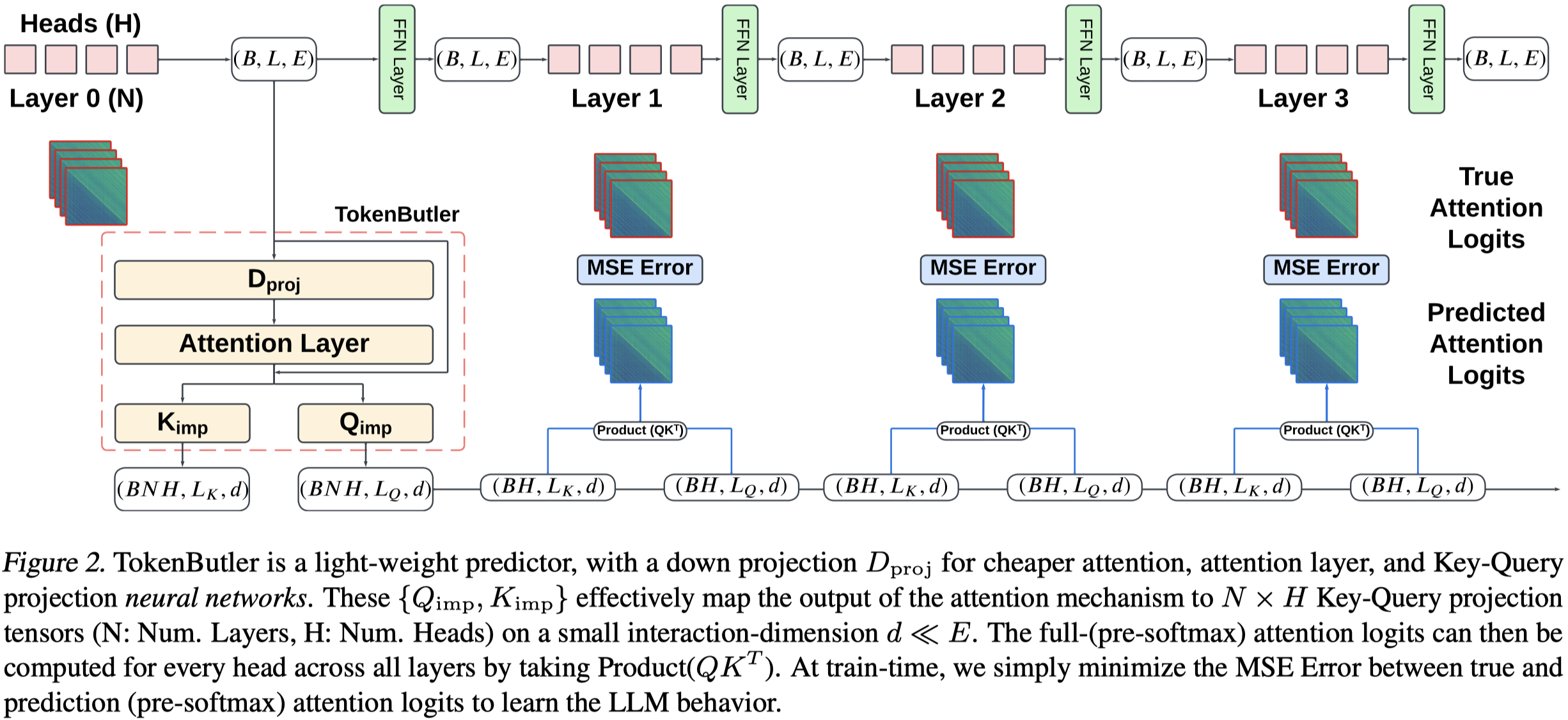
获取第一层的所有head的embedding \(I\),作者首先进行一个dimensionality-reduction projection,然后进过一个self-attention block捕获token的context,最后再up-projects将减小的embedding维度还原,与最原始的\(I\)相加,得到最后的\(I^\prime\)。
\(I^\prime\)分别经过两个投影网络获得估计的各个layer各个head的K和V embedding。投影网络是two linear layers with a SiLU activation in between。

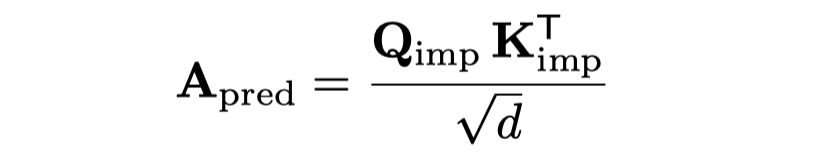
预测的注意力logit,和真实的logit,用均方误差计算loss。
为了高效训练,避免大量的梯度计算,作者使用了flash attention。
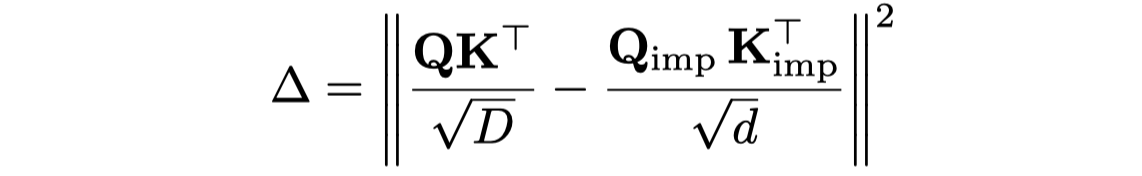
作者的预测效果大概是,有75%的准确率预测top 50% tokens。