LLM-know-what-they-dont-know
Do Large Language Models Know What They Don’t Know?
复旦大学,ACL 2023 Findings,代码。
Large language models (LLMs) have a wealth of knowledge that allows them to excel in various Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks. Current research focuses on enhancing their performance within their existing knowledge. Despite their vast knowledge, LLMs are still limited by the amount of information they can accommodate and comprehend. Therefore, the ability to understand their own limitations on the unknows, referred to as self-knowledge, is of paramount importance. This study aims to evaluate LLMs’ self-knowledge by assessing their ability to identify unanswerable or unknowable questions. We introduce an automated methodology to detect uncertainty in the responses of these models, providing a novel measure of their self-knowledge. We further introduce a unique dataset, SelfAware, consisting of unanswerable questions from five diverse categories and their answerable counterparts. Our extensive analysis, involving 20 LLMs including GPT-3, InstructGPT, and LLaMA, discovering an intrinsic capacity for self-knowledge within these models. Moreover, we demonstrate that in-context learning and instruction tuning can further enhance this self-knowledge. Despite this promising insight, our findings also highlight a considerable gap between the capabilities of these models and human proficiency in recognizing the limits of their knowledge.
这篇论文主要讨论了LLM是否知道一个question是否有准确的答案?或者说LLM是否knowing what you don’t know,作者把这种能力成为LLM的self-knowledge。
Introduction
LLM的参数里可能蕴含了很多的knowledge,但是LLM能够知道自己已知哪些知识,知道自己不知道哪些知识吗?
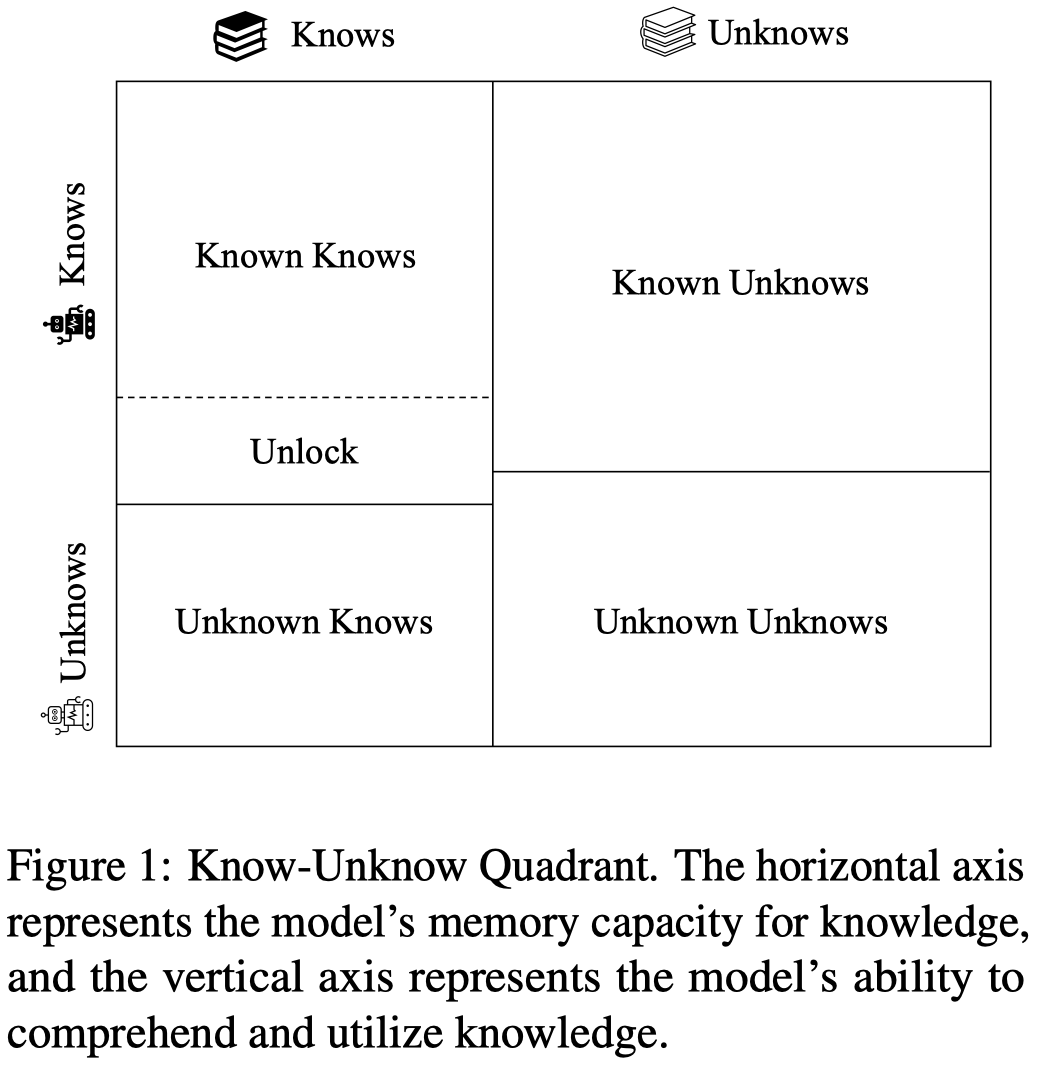
让LLM给出不确定的回答,让LLM承认自己不知道是很重要的。这种能力是能够提高LLM可信度的一种重要度量。
这篇工作作者主要讨论上面图中的”Known Unknows”和“Unknown Unknows“之间的比值,作者将这种判断问题是否有准确回答的判别能力来看做评估LLM的self-knowledge的手段。
Dataset
作者创建了一个新的数据集,SelfAware,包括1,032 unanswerable questions和2,337 questions that are classified as answerable。在这篇工作前是有其它类似数据集的,如KnowUnknowns。作者的SelfAware数据集包括了更多的问题数量和更多的问题类型:
- unanswerable questions:来源于online platforms like Quora and HowStuffWorks。经过人工标注后判断不可回答
- answerable questions:we opted for answerable questions drawn from three datasets: SQuAD (Rajpurkar et al., 2016), HotpotQA (Yang et al., 2018), and TriviaQA (Joshi et al., 2017).
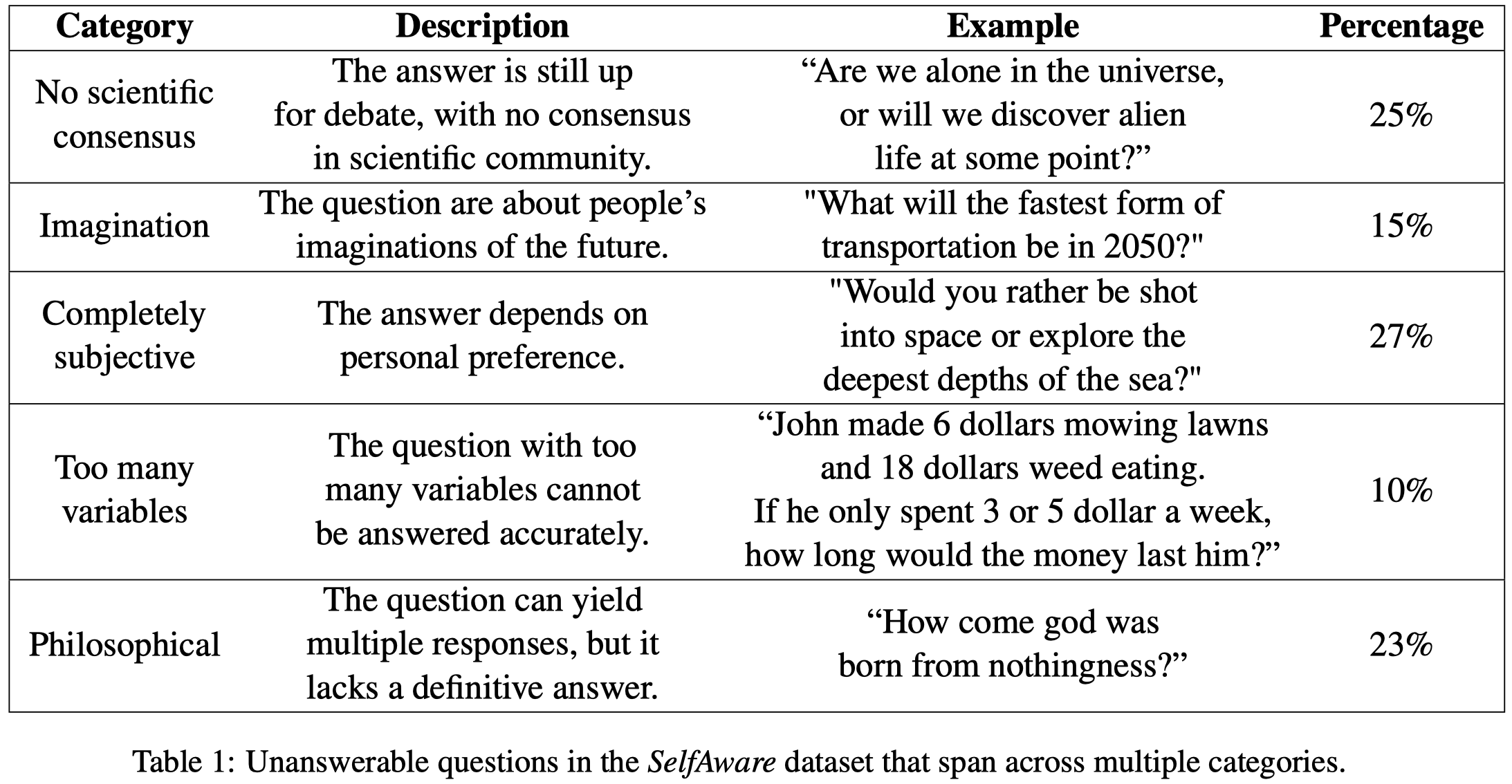
下面Table是作者随机从数据集中找了100个样例分析后得到的,不能够完全准确的描述数据集全体的情况:
Experiment
然后是如何判断LLM的回答是不知道呢?作者通过SimCSE方法计算LLM的回答和作者提前定义好的uncertain sentences的相似度,只要相似度大于一定阈值(实验中取\(0.75\)),就认为LLM的回答是不确定。下面是uncertain sentences的示例:

这些句子的创建就是随机选择100个样例让GPT回答;然后人工挑选出那些表达不清楚/不知道的句子。 (个人认为是否可以让LLM自己评估回答是不是不确定/不知道的?)
GPT-4的评估样例用了100个;其它LLM是用了整个SelfAware dataset。
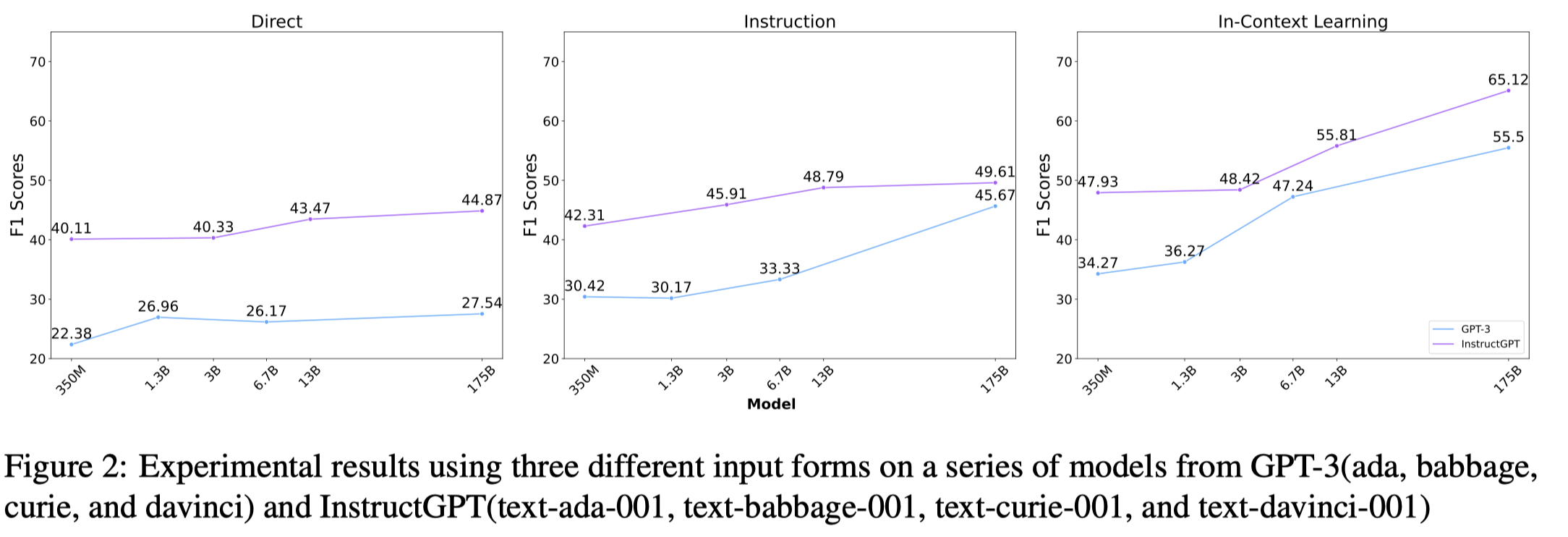
观察:
- model size越大,越知道自己不知道什么
- 上下文学习最能够激发LLM的潜力
下面是作者在使用中使用的三种输入形式:



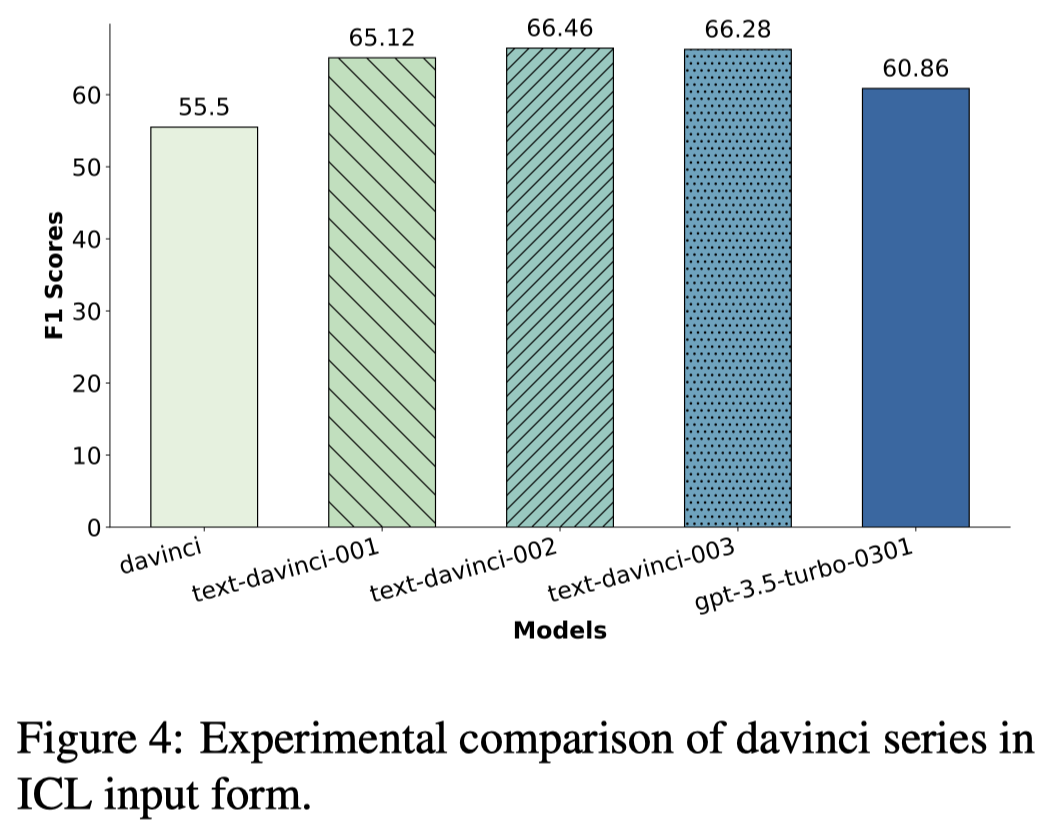
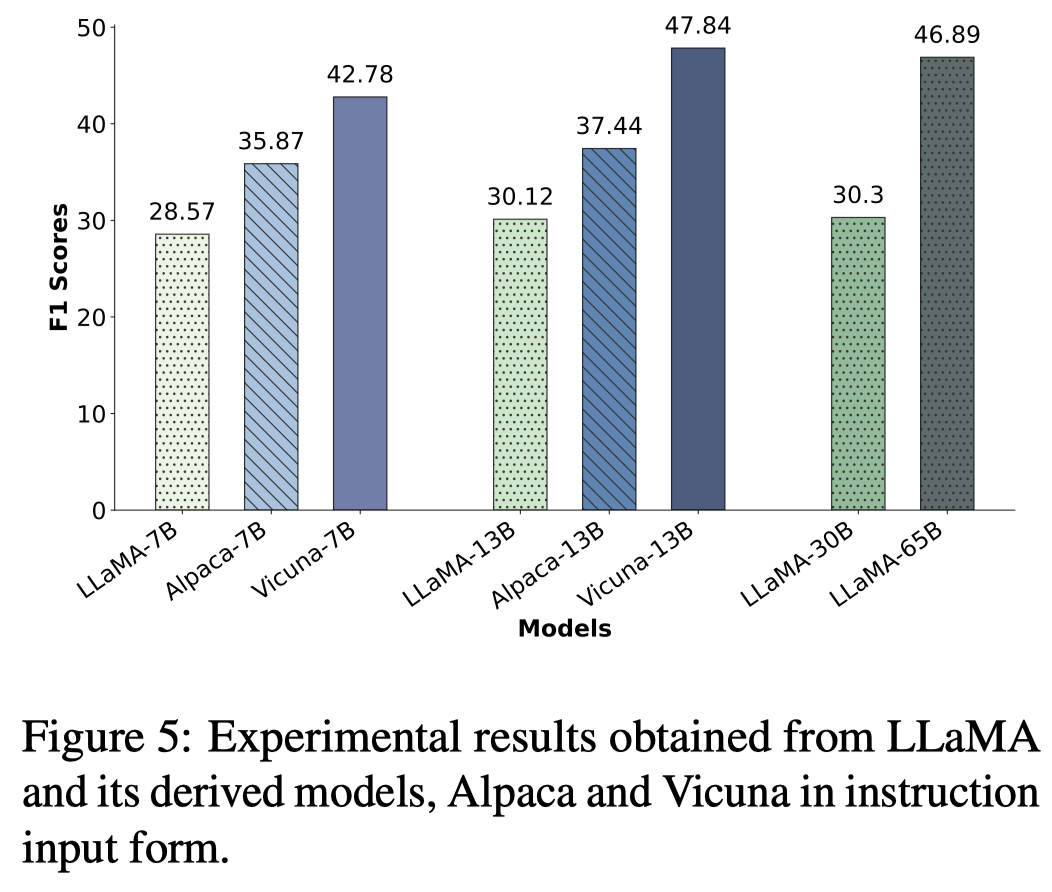
观察:
- 指令微调能够让模型更好的知道自己不知道;也就是回答不确定/不清楚
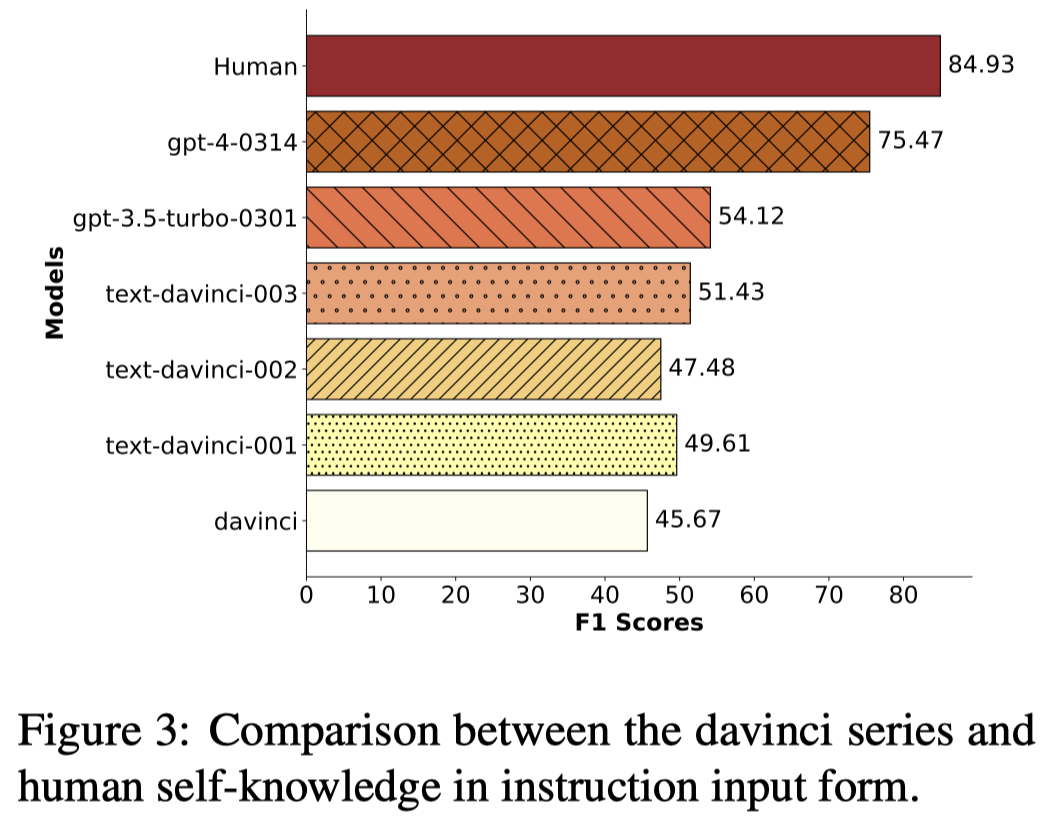
观察:
- 最好的GPT-4和人类仍有差距,但是结果仍然是非常promising的
下面是作者