LLM-ICL-survey-pku
A Survey on In-context Learning
arXiv 2023.05,北大。ICL首个survey。
With the increasing ability of large language models (LLMs), in-context learning (ICL) has become a new paradigm for natural language processing (NLP), where LLMs make predictions only based on contexts augmented with a few examples. It has been a new trend to explore ICL to evaluate and extrapolate the ability of LLMs. In this paper, we aim to survey and summarize the progress and challenges of ICL. We first present a formal definition of ICL and clarify its correlation to related studies. Then, we organize and discuss advanced techniques, including training strategies, demonstration designing strategies, as well as related analysis. Finally, we discuss the challenges of ICL and provide potential directions for further research. We hope that our work can encourage more research on uncovering how ICL works and improving ICL.
1. Introduction
这篇survey中对于in-context learning的定义和在GPT-3中给出的正式定义有所区别。这篇survey认为ICL必须要有demonstrations,但是GPT-3的原始定义则不是:
Recent work [GPT-2] attempts to do this via what we call “in-context learning”, using the text input of a pretrained language model as a form of task specification: the model is conditioned on a natural language instruction and/or a few demonstrations of the task and is then expected to complete further instances of the task simply by predicting what comes next.
下面图是作者划分的一个分类:
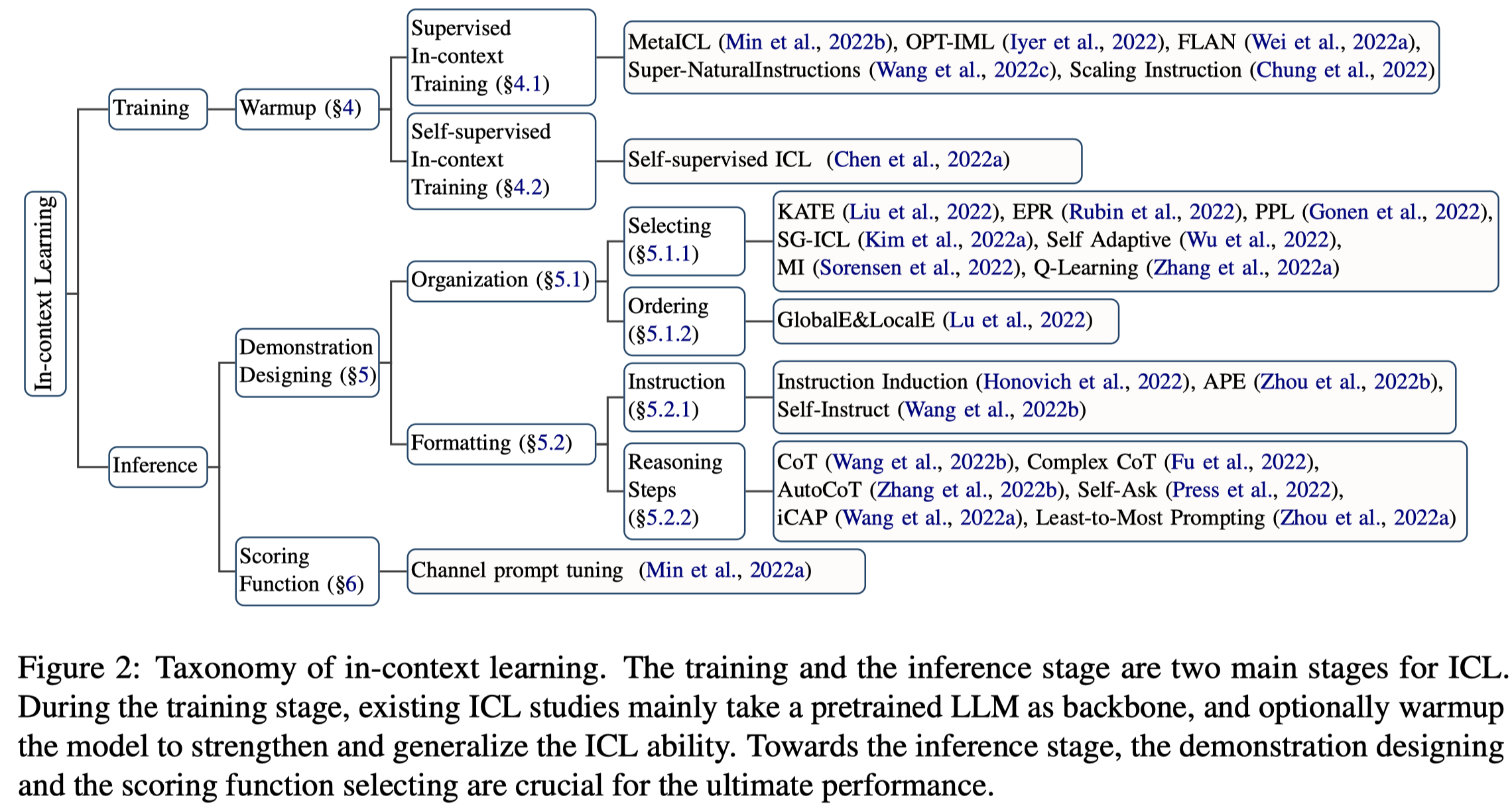
ICL最吸引人的点就在于在inference的时候,完全无需训练,并且在某些task下已经达到了SOTA的结果 (当然在很多任务下还有差距)。作者指出了三个ICL优势点:
- since the demonstration is written in natural language, it provides an interpretable interface to communicate with LLMs
- in-context learning is similar to the decision process of human beings by learning from analogy
- compared with supervised training, ICL is a training-free learning framework.
2. Model Warmup
在LLM的预训练任务是语言建模,这和ICL的任务形式是有gap的。因此很多研究讨论通过在pre-training和ICL之间加入一个额外的训练过程以进一步提升ICL的效果。作者称为warmup training。
比如MetaICL就是在一系列加入了demonstrations的ICL的训练数据中进行Supervised In-context Training。
另一个能够提升ICL的训练方法是instruction tuning。
Compared to MetaICL, which constructs several demonstration examples for each task, instruction tuning mainly considers an explanation of the task and is more easier to scale up.
instruction tuning对于构造训练数据的要求更小,更容易构造一系列不同task的训练数据。
加入一个额外的训练过程已经在很多研究中发现效果提升很明显,并且发现一直增加相应的训练数据不会带来持续的性能提升,可能数据的分布、task的覆盖范围和差异性这些因素是更关键的。
3. Demonstration Designing
3.1 Demonstration Organization
Demonstration Organization指如何选择合适的examples和排序?
Demonstration Selection. 又可以分为无监督和有监督的方法。无监督的方法比如使用kNN这些方法,选择和当前测试的instance最相似的demonstrations;比如使用互信息,perplexity等;比如选择的时候还要考虑demonstrations的差异性;还有的直接使用LLM自己生成的demonstrations。
有监督的选择方法比如先无监督的检索,再用一个打分函数进行选择;比如可以使用强化学习不断更新检索的模型。
Demonstration Ordering. 已经有研究发现demonstrations的顺序对于结果有影响。比如可能LLM倾向于输出最靠近测试样例的demonstration一样的结果。如果有\(k\)个demonstrations,会有\(k!\)种排列组合。(个人认为这种情况属于LLM的一个不稳定、不鲁棒的缺陷。需要想办法去解决,而不是利用…)
3.2 Demonstration Formatting
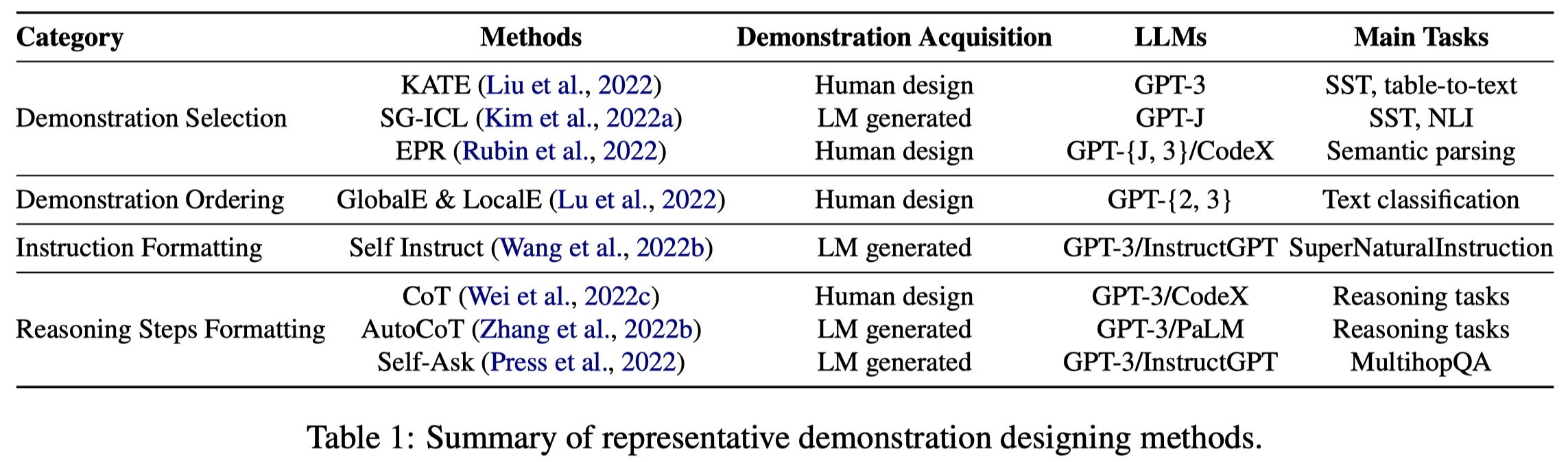
怎么样设计具体的输入模板。
Instruction Formatting. instruction需要准确的描述任务,依赖于人工设计。
- Instruction induction: From few examples to natural language task descriptions. 使用LLM自动从几个demonstrations中生成task instruction。
- Large language models are human-level prompt engineers. 提出自动生成和选择instruction。
Reasoning Steps Formatting. survey这里提到的是将CoT加入到ICL进一步提升LLM对于复杂task的推理能力。
4. Scoring Function
是指怎么样将LLM的输出转化为一个恰当的概率估计。
The scoring function decides how we can transform the predictions of a language model into an estimation of the likelihood of a specific answer.
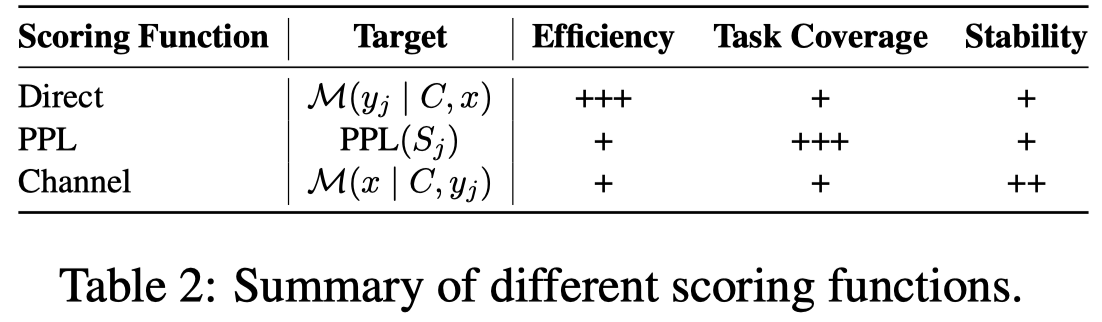
作者提及了三种方法:
- A direct estimation method (Direct) adopts the conditional probability of candidate answers that can be represented by tokens in the vocabulary of language models. 直接使用预测的答案在LLM中的条件概率,但是这要求预测的答案出现在模板的最后,作为要续写的token进行输出。
- Perplexity (PPL) is another commonly-used metric, which computes the sentence perplexity of the whole input sequence. 对模板没有要求
- Min et al. (2022a) proposed to utilize channel models (Channel) to compute the conditional probability in a reversed direction, i.e., estimating the likelihood of input query given the label. 反过来让模型decode加入了label之后的query。
5. Analysis
5.1 What Influences ICL Performance
有哪些因素会影响ICL的效果?

Pre-training Stage:
- Putting multiple corpora together may give rise to emergent ICL ability, pretraining on corpora related to the downstream tasks does not always improve the ICL performance.
- a pretrained model suddenly acquires some emergent ICL abilities when it achieves a large scale of pre-training steps or model parameters.
Inference Stage:
- Min et al. (2022c) investigated that the influence of demonstration samples comes from four aspects: the input-label pairing format, the label space, the input distribution, and the input-label mapping. They prove that all of the input-label pairing formats, the exposure of label space, and the input distribution contribute substantially to the ICL performance.
- Lu et al. (2022) indicated that the demonstration sample order is also an important factor.
5.2 Understanding Why ICL Works
ICL原理分析
- Distribution of Training Data. Chan et al. (2022) showed that the ICL ability is driven by data distributional properties. They found that the ICL ability emerges when the training data have examples appearing in clusters and have enough rare classes. 发现ICL能力的出现需要训练数据的分布多样性足够。
- Learning Mechanism.
- Garg et al. (2022) proved that Transformers could encode effective learning algorithms to learn unseen linear functions according to the demonstration samples. 认为Transformer能够从demonstration samples学习没有见过的linear functions。
- Dai et al. (2022) figured out a dual form between Transformer attention and gradient descent and further proposed to understand ICL as implicit fine tuning. 将ICL和梯度下降对齐,认为ICL是在进行一种隐式的梯度下降。
- Functional Modules. Olsson et al. (2022) found that there exist some induction heads in Transformers that copy previous patterns to complete the next token. 发现Transformer中可能有可以实现归纳功能的induction head。
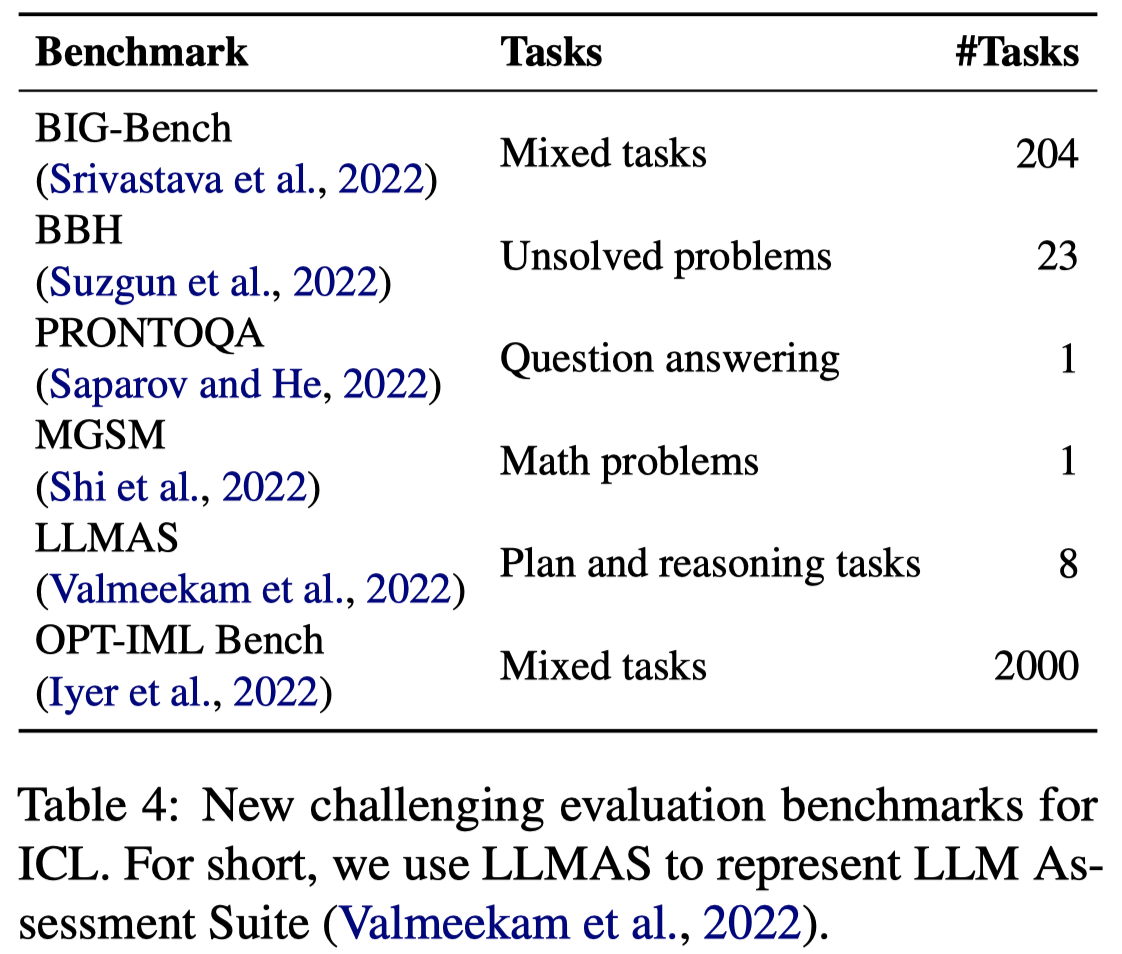
6. Evaluation and Resources
7. Challenges and Future Directions
一些新的挑战:
- New Pre-training Strategies. 比如instruction-tuning
- Distill the ICL Ability to Smaller Models. Transferring the ICL ability to smaller models could facilitate the model deployment greatly.
- Knowledge Augmentation and Updating
- Knowledge Augmentation. Retrieving correct knowledge and integrating the correct knowledge with the context in a lightweight manner is possibly promising for ICL.
- Knowledge Updating. Updating the wrong or out-of-date knowledge for ICL is worth further exploration.
- Robustness to Demonstration. Previous studies have shown that ICL performance is extremely unstable, from random guess to SOTA, and can be sensitive to many factors.
- ICL for Data Engineering. How to use ICL for data annotation remains an open question. For example, Ding et al. (2022) performed a comprehensive analysis and found that generation-based methods are more cost-effective in using GPT-3 than annotating unlabeled data via ICL.