Increasing-Diver-Acc-Data-Gen-LLM
Increasing Diversity While Maintaining Accuracy: Text Data Generation with Large Language Models and Human Interventions
密歇根大学与Microsoft,ACL 2023
Large language models (LLMs) can be used to generate text data for training and evaluating other models. However, creating high-quality datasets with LLMs can be challenging. In this work, we explore human-AI partnerships to facilitate high diversity and accuracy in LLM-based text data generation. We first examine two approaches to diversify text generation: 1) logit suppression, which minimizes the generation of languages that have already been frequently generated, and 2) temperature sampling, which flattens the token sampling probability. We found that diversification approaches can increase data diversity but often at the cost of data accuracy (i.e., text and labels being appropriate for the target domain). To address this issue, we examined two human interventions, 1) label replacement (LR), correcting misaligned labels, and 2) out-of-scope filtering (OOSF), removing instances that are out of the user’s domain of interest or to which no considered label applies. With oracle studies, we found that LR increases the absolute accuracy of models trained with diversified datasets by 14.4%. Moreover, we found that some models trained with data generated with LR interventions outperformed LLM-based few-shot classification. In contrast, OOSF was not effective in increasing model accuracy, implying the need for future work in human-in-the-loop text data generation.
利用LLM生成训练数据,考虑生成数据的多样性与准确性。
1. Introduction
训练深度模型总是需要训练数据,而训练数据的获得一直是老大难问题。LLM的出现为这一个问题提供了新的解决思路,让LLM根据用户的去求直接生成domain text data。
虽然LLM通过ICL可以直接执行各类NLP任务,但是我们可能仍然需要小模型的几点理由:
- some might not have enough resources (e.g., GPUs) or budget (e.g., credit for GPT-3) to run expensive models. 资源
- Others might be concerned about privacy or security issues when they use LLMs from external APIs (e.g., OpenAI API). 隐私与安全
- Moreover, if we share generated datasets within the community, we can also benefit those who do not have access to LLMs. 生成的data可以帮助无法直接访问LLM的研究者
- Lastly, we can also use generated datasets to test models. 生成的数据集可以用来测试SLM
这篇文章就旨在讨论利用人机协作的方法创建高质量数据集,Ideal classification datasets need to have the following characteristics:
- Scoped: fall in the model builder’s domain of interest while classifiable with labels of interest,
- Label accurate: accompany accurate labels
- Diverse: cover cases the model would encounter during test time.
2. Diversified Text Data Generation
2.1 Method
第一大部分,作者主要讨论了2种在解码阶段增加多样性的方法:
Logit Suppression:decreases the probability of high-frequency tokens。之前生成的tokens,根据频率,降低它在下一次采样中的概率。这里叫做logit的原因应该是,作者通过调用OpenAI的logit bias API来实现这一点。
High Temperature:增大temperature \(T\),更大的temperature意味着最终的概率分布更加平滑flat:
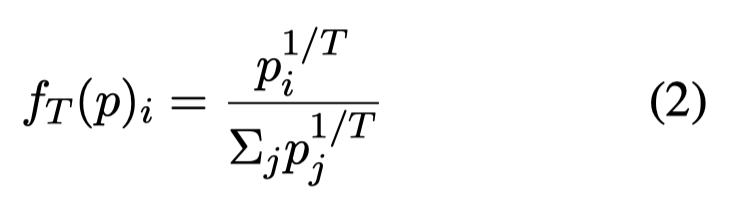
示意图:
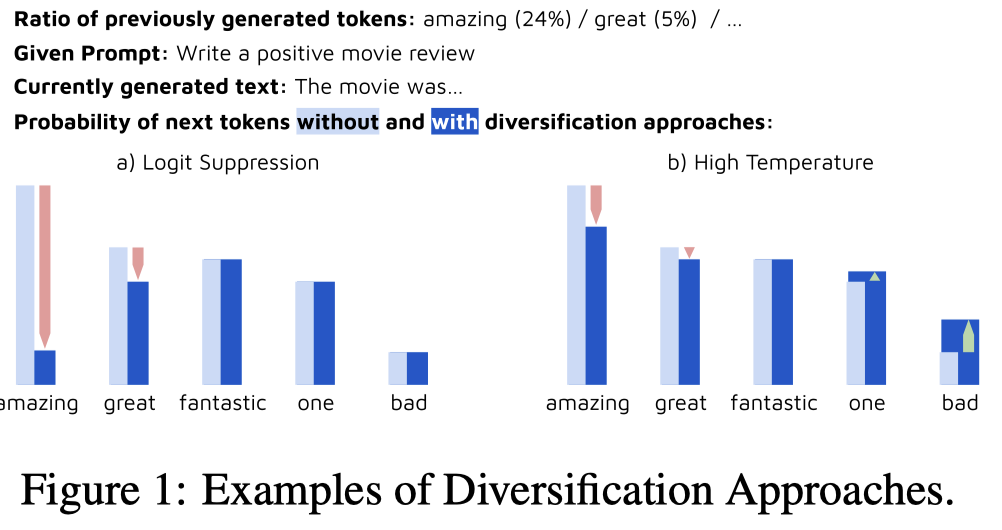
作者调用GPT生成数据的时候,考虑的是短文本分类任务,构造的prompt主要考虑text type和label:

下面是各个task用到的text type和label:

text type应该是用来控制输出符合task特点的文本。
2.2 Experiments
一些实验设置:
- 作者一共用了8个短文本分类数据集
- 调用
text-davinci-002,每次调用生成20个新data - 微调用的model是
BERT-base+Linear classifier - 原始的training data用来训练oracle model (很重要,后续在计算指标和提高质量的时候被用到);生成的新data用来训练各个实验model,保持两者样本数量一样;用原始的test set进行测试
- 作者实验了一个额外的example seeding设置,也就是初始第一次迭代,有没有个样例池。样例池中的样例被按照每个label对应1个样例的设置被随机选择,作为prompt上下文。如果一开始没有一个上下文样例池,作者第一次迭代就是使用zero-shot ICL的形式,在第二次迭代才开始从样例池中随机采样
实验指标:
- Diversity: We also measured the diversity of the dataset using Remote-Clique metric (Rhys Cox et al., 2021), which is the average mean pairwise distances.
- Label Accuracy: We also evaluated label accuracy, which is the accuracy of the alignment between the generated texts and the specified labels. 使用oracle model作为评估工具
- Model Accuracy: 微调的BERT在测试集上的准确率
- Similarity: We also measured the similarity of the generated dataset to the oracle dataset with the average mean pairwise distances between the two.
8个短文本分类数据集平均结果(原paper附录中有详细的结果):

观察:
- 一开始使用一个上下文样例池有助于提高生成数据多样性和最终的SLM性能;
- 增加多样性,可能会降低accuracy;两种解码策略都会降低accuracy,但是High temperature降低的稍微轻一点;
- 一味的增加生成数据的多样性,不一定能够对fine-tuned的SLM性能有提升作用,甚至会降低模型效果;
- To evaluate how diversity, label accuracy, and similarity impact model accuracy, we performed a linear regression analysis. The analysis showed that label accuracy, diversity, and similarity are positively correlated with model accuracy, with significance (coef=\(.4797\) and \(p<0.001\) for label accuracy, coef=\(.2260\) and \(p<0.001\) for diversity, and coef=\(0.1980\) and \(p<0.005\) for similarity). 生成数据的三种因素和最终fine-tuned之后的model有很强的相关系数;
3. Human Interventions to Fix Inaccurate Text Generation
3.1 Method
上面的实验揭露了单纯增加生成数据多样性不行,作者进一步考虑引入人类智能来缓解这一问题。简单的说,就是利用人去标注了小规模的分类器,用这个分类器去重新标注或过滤生成的数据。
作者考虑两种简单的方法:
- label replacement (LR):switching the misaligned label to the correct one. 修正label
- 作者考虑训练一个proxy model来重新标注生成的text
- 作者考虑了两种方法,一种是直接用oracle model来重新标注所有生成的text;一种是少量的采样,用oracle model标注,然后训练支持向量分类器来判断label正确与否
- out-of-scope data filtering (OOSF):removes instances that are outside the domain of interest and do not match any labels. 移除不符合task的生成数据
- 人工判断采样一小部分数据,然后判断句子是否outside the task,标注数据。用这个标注数据来训练一个支持向量分类器。最终用这个支持向量分类器去过滤掉不符合要求的句子
3.2 Experiments
第一种标签替换LR的策略:
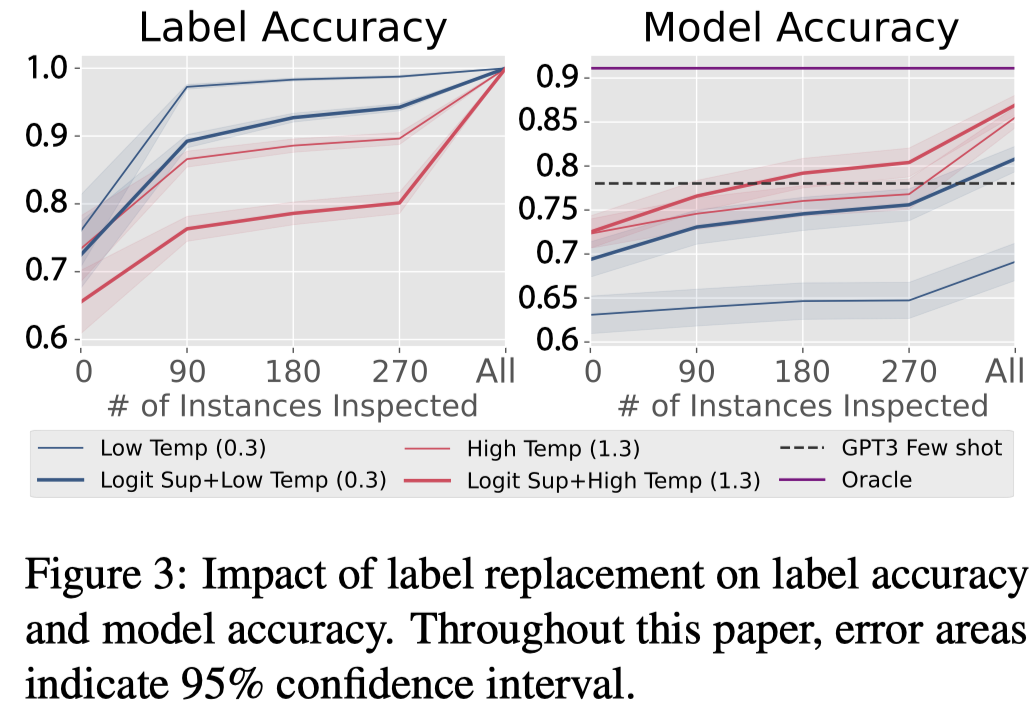
能够极大的提高最终的训练出来model的效果。由于只是修改label,因此不会影响多样性指标。
第二种OOSF过滤策略:
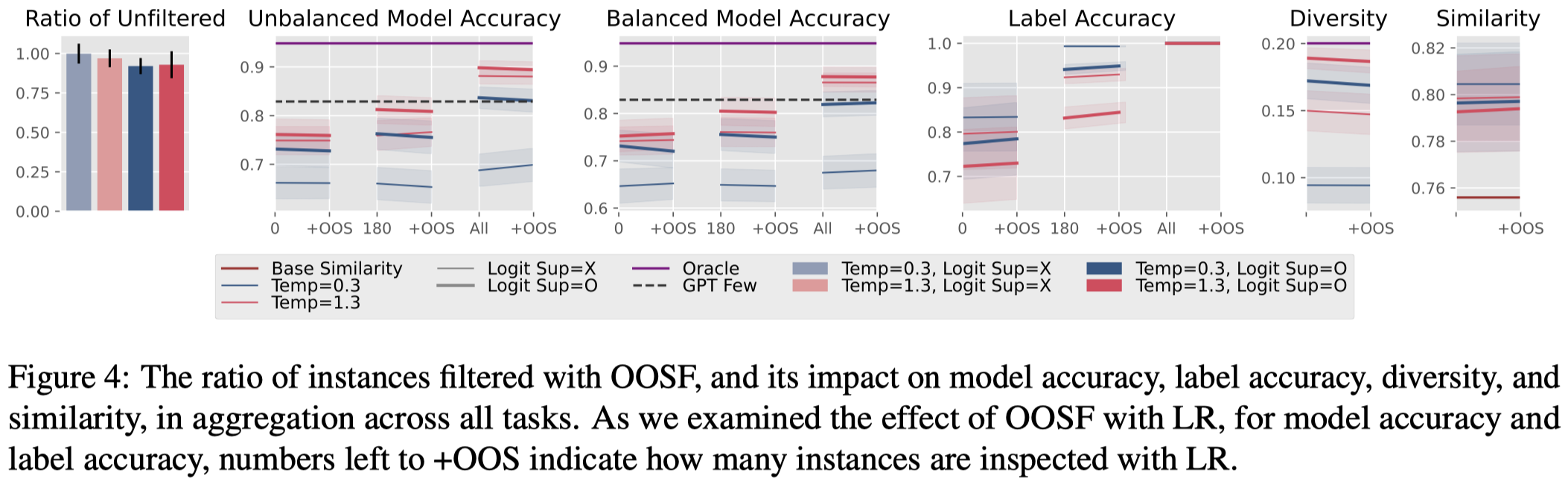
作者是在LR方法的基础上,继续加上OOSF(图中的+OOS)。实验发现OOSF不能够总是带来一致的效果提升,并且由于会移除生成数据,还会同时影响多样性指标。