T-GAP
Learning to Walk across Time for Interpretable Temporal Knowledge Graph Completion
T-GAP KDD 2021
https://github.com/sharkmir1/T-GAP
Static knowledge graphs (KGs), despite their wide usage in relational reasoning and downstream tasks, fall short of realistic modeling of knowledge and facts that are only temporarily valid. Compared to static knowledge graphs, temporal knowledge graphs (TKGs) inherently reflect the transient nature of real-world knowledge. Naturally, automatic TKG completion has drawn much research interests for a more realistic modeling of relational reasoning. However, most of the existing models for TKG completion extend static KG embeddings that do not fully exploit TKG structure, thus lacking in 1) accounting for temporally relevant events already residing in the local neighborhood of a query, and 2) path-based inference that facilitates multi-hop reasoning and better interpretability. In this paper, we propose T-GAP, a novel model for TKG completion that maximally utilizes both temporal information and graph structure in its encoder and decoder. T-GAP encodes query-specific substructure of TKG by focusing on the temporal displacement between each event and the query timestamp, and performs path-based inference by propagating attention through the graph. Our empirical experiments demonstrate that T-GAP not only achieves superior performance against state-of-the-art baselines, but also competently generalizes to queries with unseen timestamps. Through extensive qualitative analyses, we also show that T-GAP enjoys transparent interpretability, and follows human intuition in its reasoning process.
Introduction
作者期望解决的问题:
目前对于TKG补全的方法大多是之前对于静态KG方法的拓展,而在静态KG上的邻居信息已经证明了是有效的,但是如何在TKG上利用邻居信息还没有充分探究。
作者的解决方案:
编码阶段:作者看重对于捕获的邻居边的timestamp和要查询的timestamp之间的时间位移进行探究
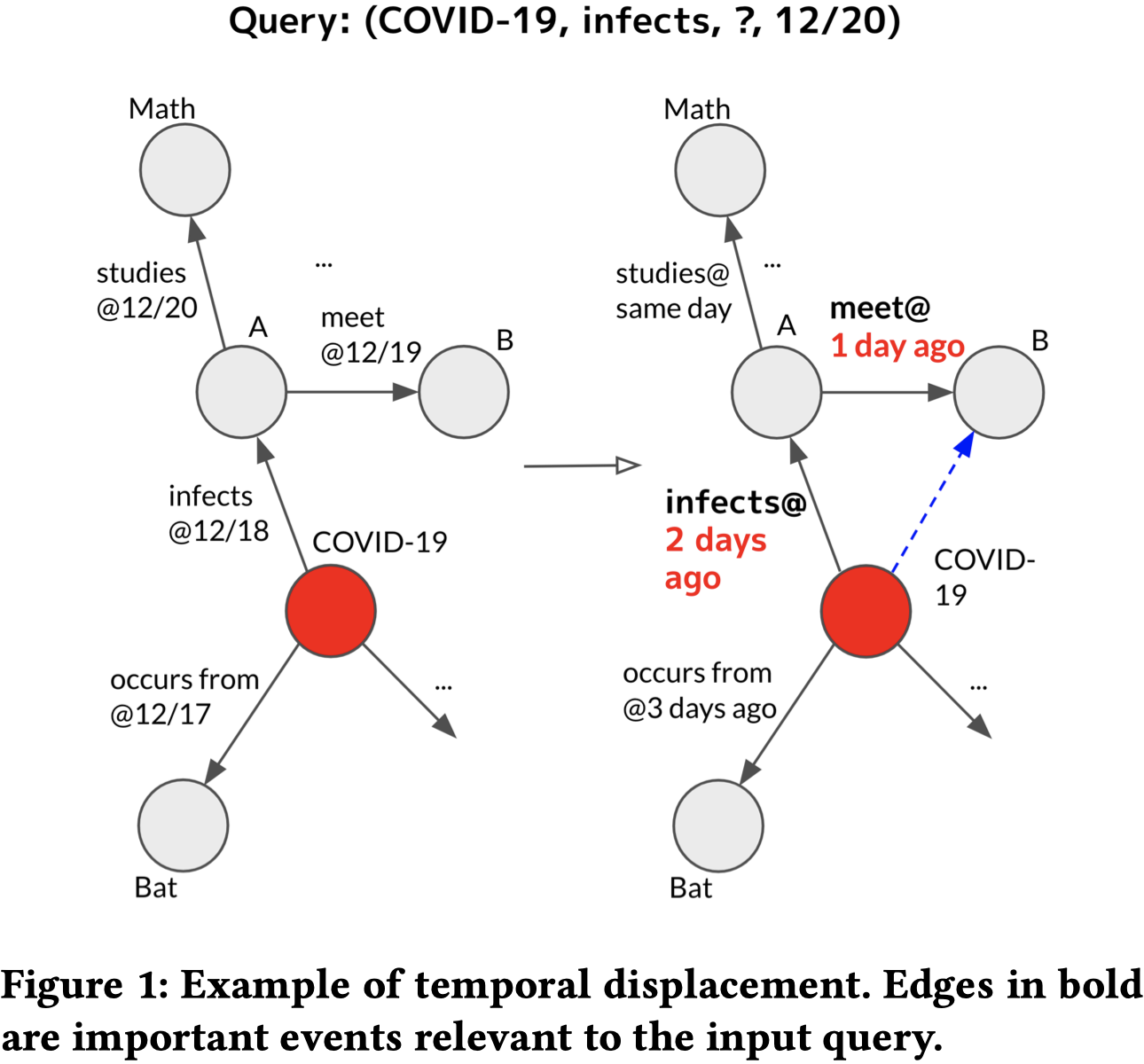
we focus on encoding the temporal displacement between the timestamps of the input query and each edge being encoded.
比如下面的例子,要查询COVID-19在12月20日感染的人,明显重要的信息是COVID-19在两天前感染了A,然后在一天前A和B相遇。重要的是相对时间关系和时间的跨度,而不是具体的时间点。
解码阶段:作者提出了基于注意力value的路径传播方法
Method
整体上使用了GNN作为编码器,attention flow作为解码器。
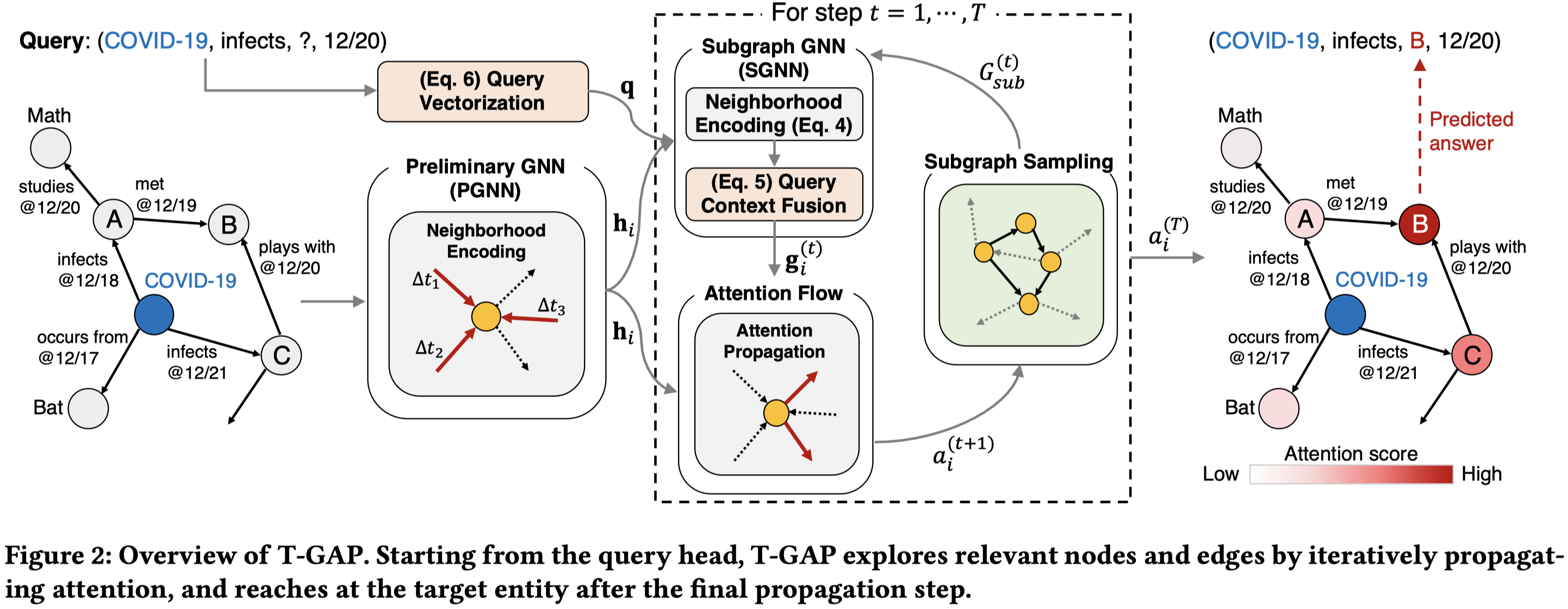
在编码器部分,就是在原始的graph上(论文中是称作preliminary graph)进行GNN操作。核心是通过不同相对时间关系的参数+时间位移的embedding来改造基于transformer-attention的GNN。
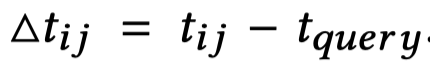
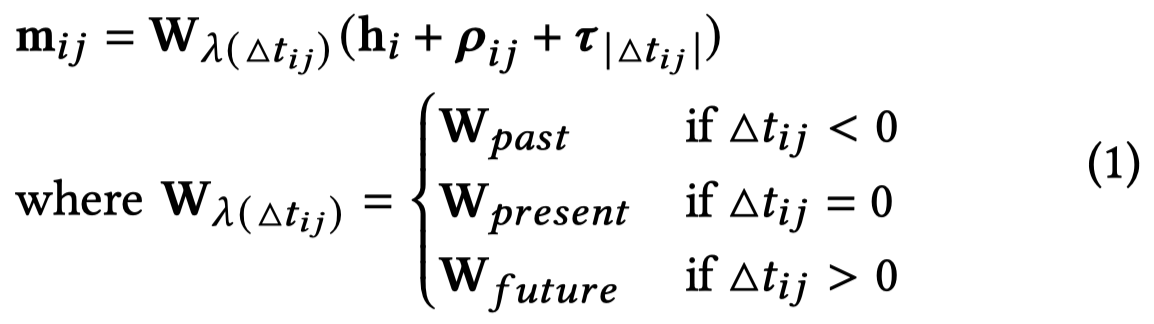
其中的,\(h_i\)表示头实体embedding,初始值为随机初始化;\(\rho_{ij}\)表示的是关系向量;\(\tau_{|\triangle t_{ij}|}\)表示相对时间位移大小的向量。随后基于多头注意力进行聚合:
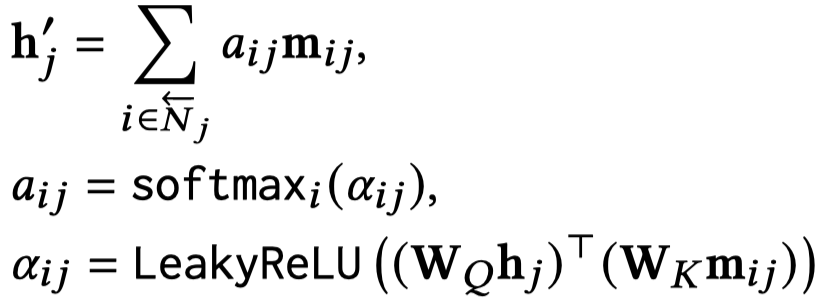
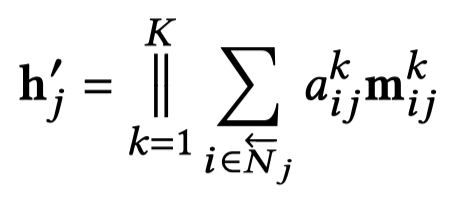
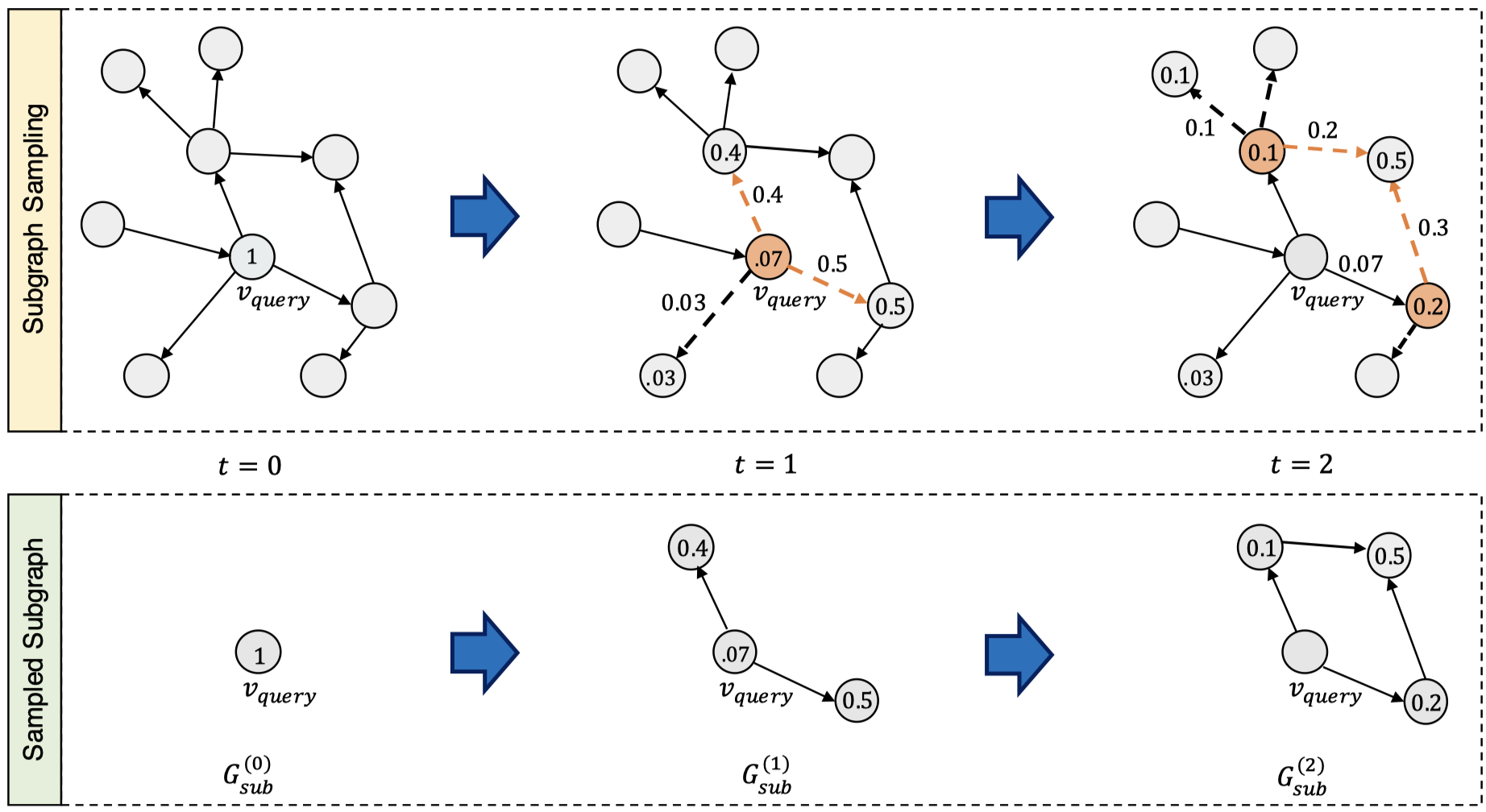
在编码器部分,是执行最多\(T\)次的解码过程,首先是采样得到新的子图;其次是利用这样的子图进行和编码器相同过程但是不同参数的GNN操作;最后进行attention flow,便于下一步的采样子图。
子图采样是一个非参数化的过程,核心思想是采样当前采样得到的子图中,最大attention value的node,然后在这些比较重要的node出发,采样它们引出的比较重要的边,加入到子图中去。


在采样得到的子图上,进行GNN操作,聚合邻居信息。主要过程和编码器部分一致。最后融合query相关的embedding:
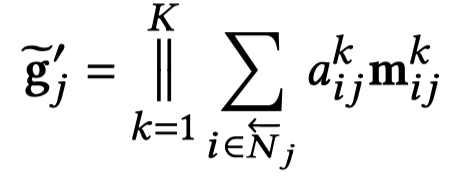
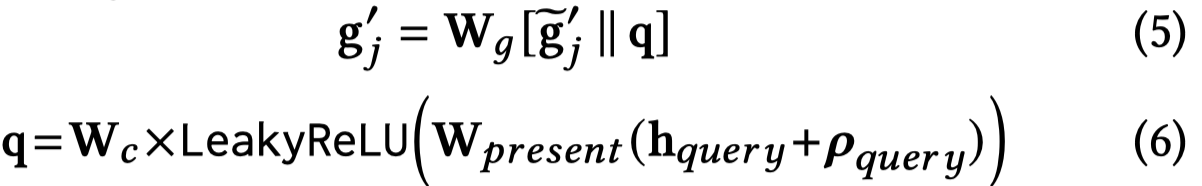
最后,进行attention flow,核心思想是给定中心节点attention value \(1\),然后让这个value通过GNN聚合得到的信息,在graph上不断传播,自动计算各个路径的重要程度。公式里的第一个score用来计算已经在当前采样得到的子图中的node的重要程度,第二个score会更加偏好采样得到还没在当前采样子图图中的node。
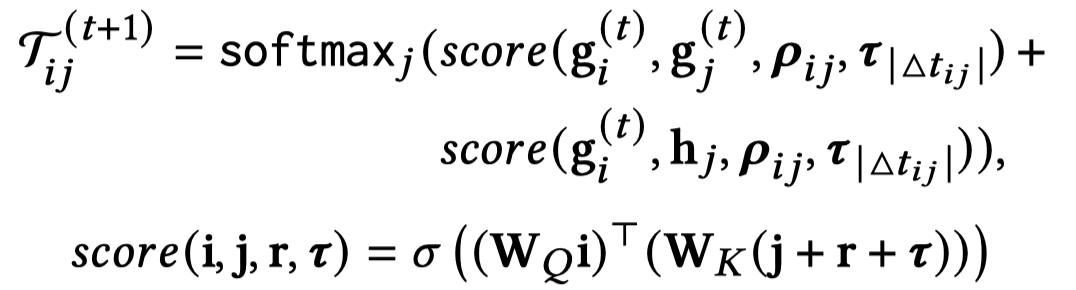

总的采样过程实例如下:
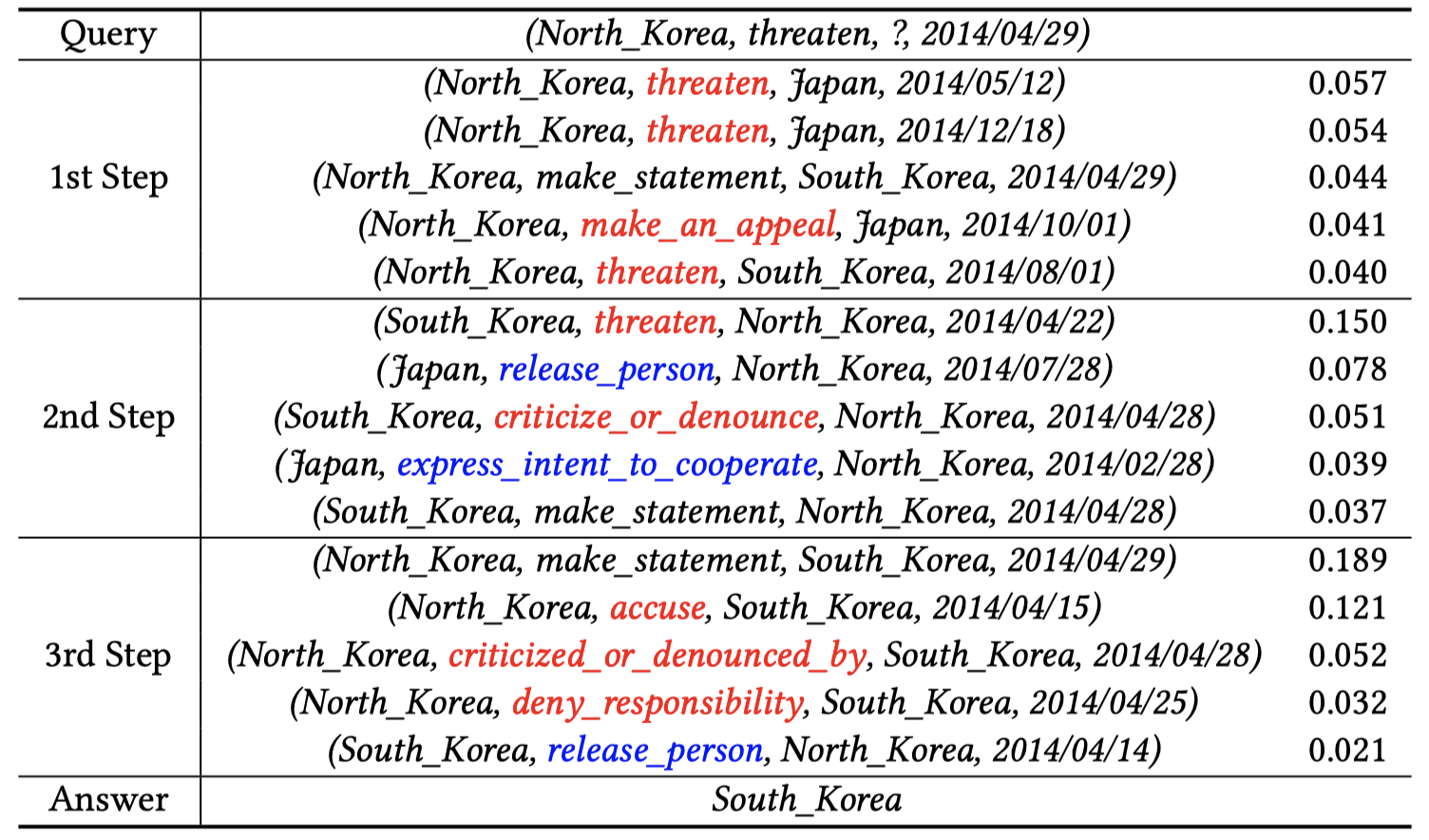
通过上面的过程,T-GAP可以让注意力不断通过路径在graph上流动,最后得到attention value最大的node,就可以看做是要预测的目标。训练使用的loss:

EXPERIMENT
T-GAP的实验包括下述三方面:
- 时序KG补全的性能
- 对于未见过的时间戳的泛化性
- 可解释性/与人类直观认识的关联
实验的数据集包括:ICEWS14, ICEWS05-15和Wikidata11k。这三个数据集是较为通用的数据集,被之前的研究者建议使用(Learning Sequence Encoders for Temporal Knowledge Graph Completion)
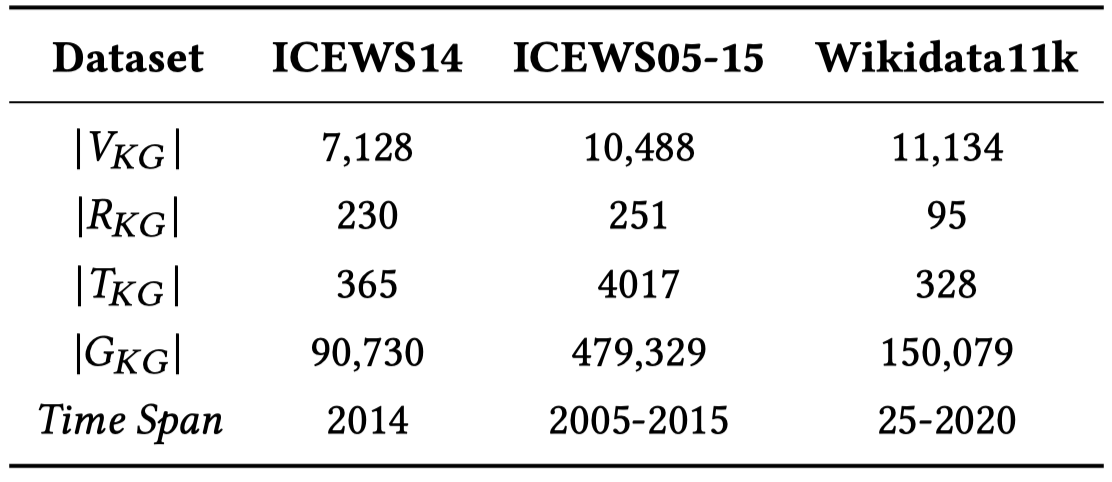
ICEWS14包括2014年发生的社会政治事件;ICEWS05-15包括A.D. 25到2020发生的事件;
Wikidata11k是Wikidata的子集,在其中所有的fact加入了时空标识符occurSince和occurUntil。随着Learning Sequence Encoders for Temporal Knowledge Graph Completion的做法,作者把原来的时空标识符和关系合并起来,作为新的relation,比如(A, loves, B, since, 2020)变为(A, loves-since, B, 2020)。
Benchmark Performance
总体性能:
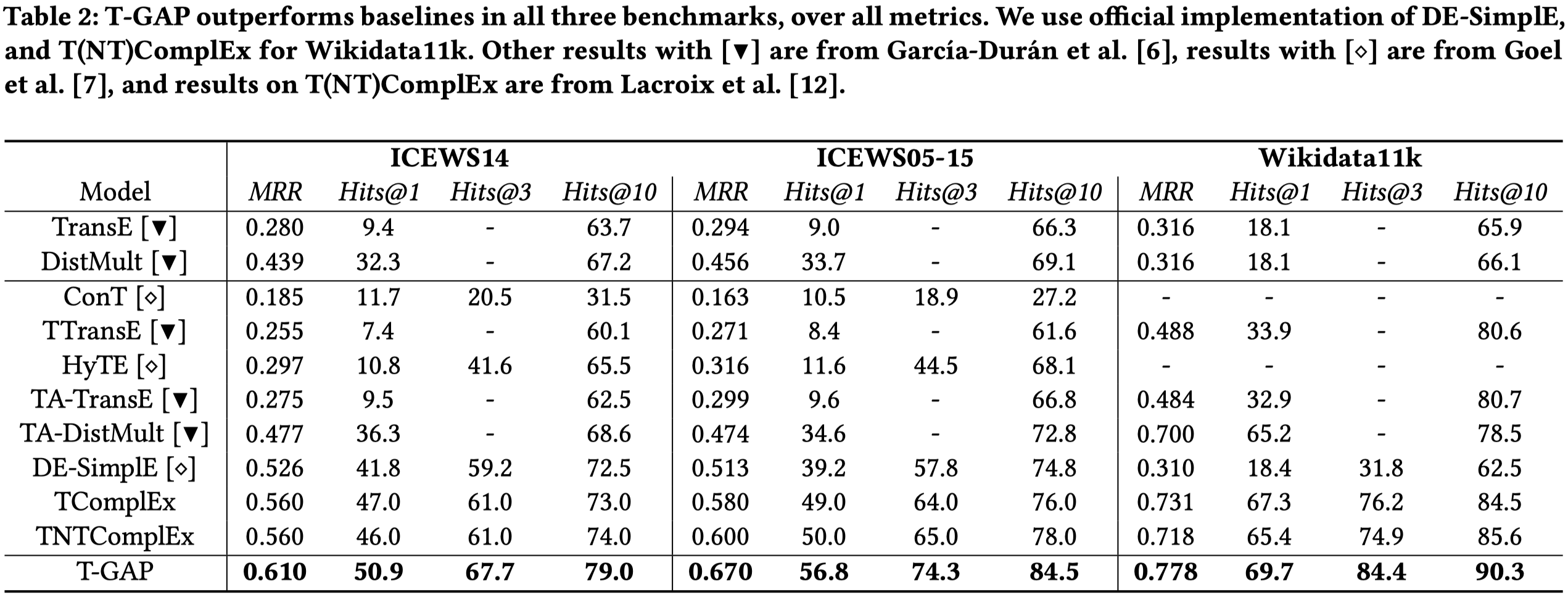
相对提升了10%,很明显的提升
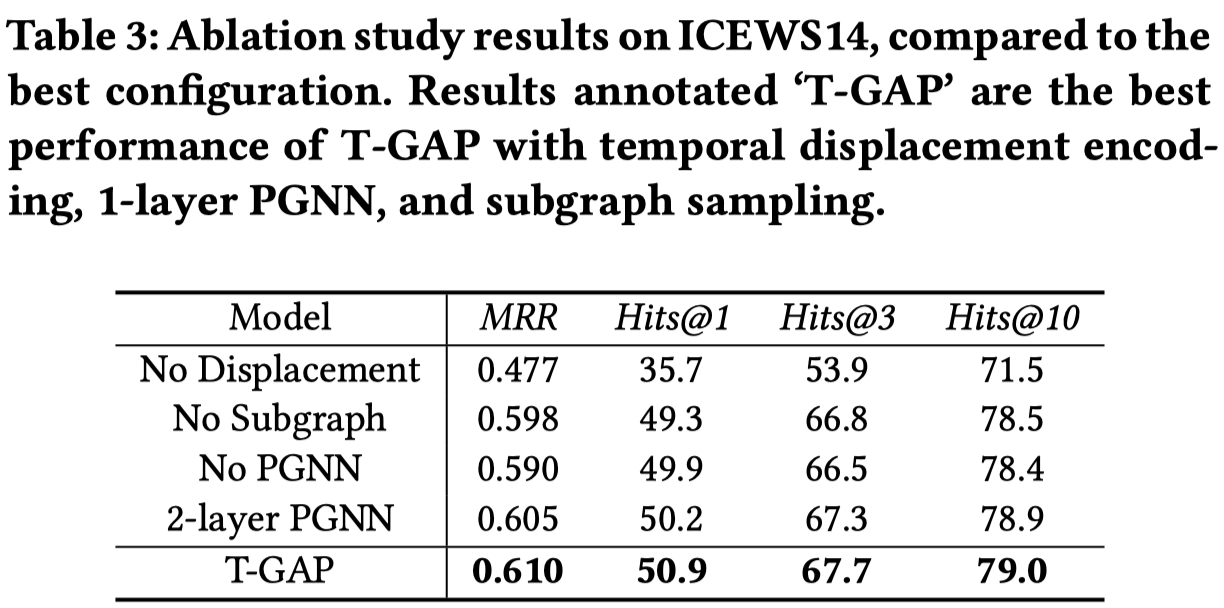
消融实验:
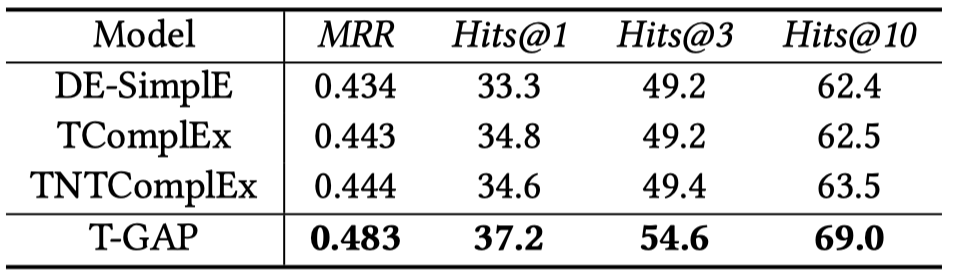
Temporal Generalization
沿着前人的做法(Diachronic embedding for temporal knowledge graph completion),把ICEWS14训练集中每个月的第5、15和25天发生的fact拿出来作为验证集和测试集,来验证对于queries with unseen timestamps的泛化性能。
结果:
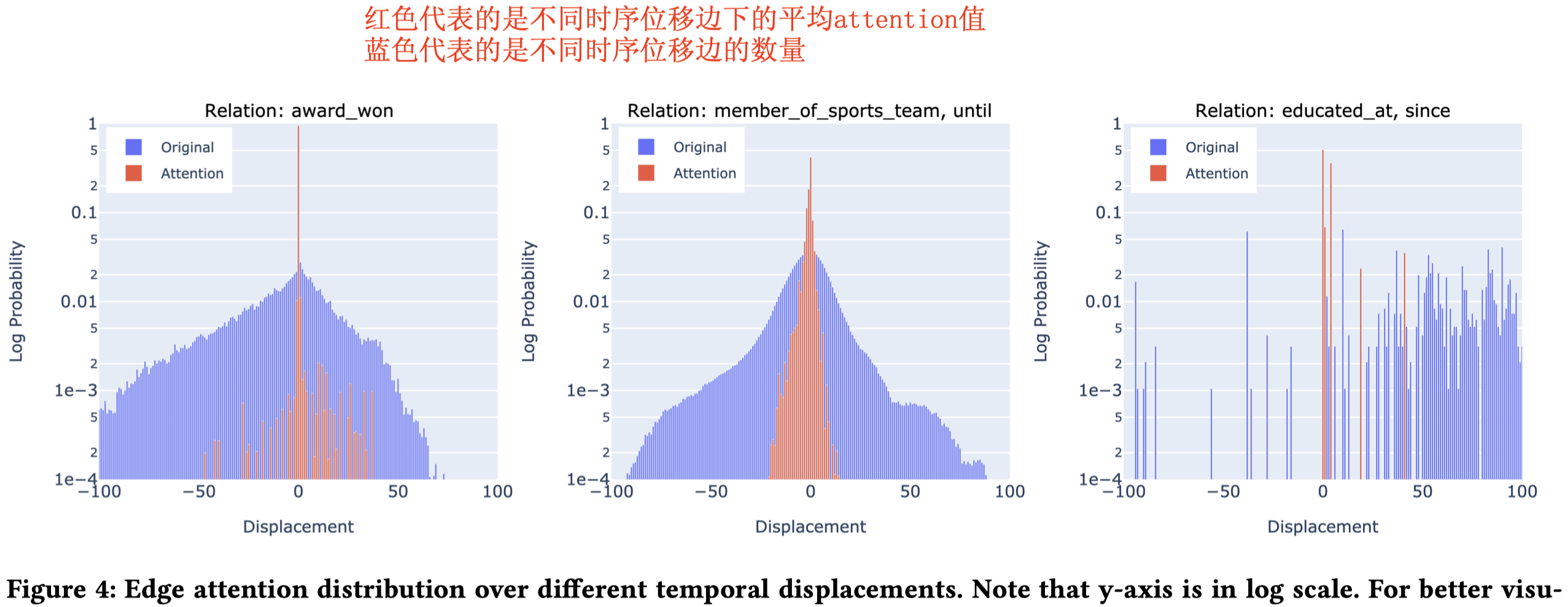
Interpretability
T-GAP的可解释性从两方面进行,(1)不同relation和时序位移的联系(2)attention flow推理过程的case study。
(1)Relation Type and Temporal Displacement
作者通过不同relation下,T-GAP学习到的attention的分布来分析relation和时序位移之间的联系。
(2)Reasoning Process