HoLE
HoLE: Holographic Embeddings of Knowledge Graphs
AAAI 2016
这篇文章提出了holographic embeddings (HOLE),来学习KG的compositional vector space representations。
motivation:However, existing embedding models that can capture rich interactions in relational data are often limited in their scalability. Vice versa, models that can be computed efficiently are often considerably less expressive.
methods:直接从subject entity embedding和object entity embedding中,使用circular correlation获得新的embedding,称作holograph embedding,然后使用这个holograph embedding与relation embedding做点积,得到预测概率。
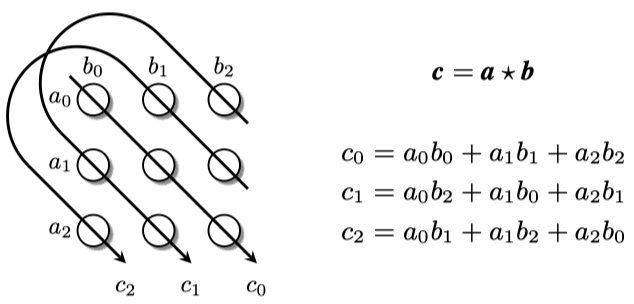
理解circular correlation:
它是一种捕获feature interaction的方法,首先我们来看以下几个不同的捕获特征交互的方法。
- Tensor Product
\[ [\mathbf{a}\ \otimes\ \mathbf{b}]_{ij} = \mathbf{a}_{i}\mathbf{b}_j \in \mathbb{R}^{d^2} \]
形成了一个矩阵。这样捕获的feature的特点是获得了所有的pairwise multiplicative interactions between the features of \(\mathbf{a}\) and \(\mathbf{b}\)。
从直观上来看,如果是来自\(\mathbf{a}\) 和\(\mathbf{b}\)的同时起作用时,这样的方法比较好。它能够用来捕获通用,共有的特征,例如a和b是自由人和自由党,liberal persons are typically members of liberal parties,这样的事实。
Intuitively, a feature in the tuple representation a ⊗ b is “on” (has a high absolute magnitude), if and only if the corresponding features of both entities are “on”
这样的方法在RESCAL和NTN,DistMult中都得到了使用。
缺点在于(1)计算量相对较大(2)无法捕获独立的特征
- Concatenation, Projection, and Non-Linearity
这是最常见的方法,对于向量输入\(\mathbf{a}\) 和\(\mathbf{b}\),先拼接,然后linear projection,最后经过一层non-linearity function。 \[ f(W[\mathbf{a};\mathbf{b}]) \] 这种方法捕获的特征是如果有特征至少在\(\mathbf{a}\) 和\(\mathbf{b}\)中起到作用。
Intuitively, a feature in the tuple representation W(a ⊕ b) is “on” if at least one of the corresponding features is “on”.
缺点是对于\(\mathbf{a}\) 和\(\mathbf{b}\)没有直接的交互。
- Circular Convolution
\[ [\mathbf{a}\ *\ \mathbf{b}]_{k} = \sum_{i=0}^{d-1} a_i b_{k-i\ mod\ d} \]
将\(\mathbf{b}\)反转,然后与\(\mathbf{a}\)进行卷积。
- Circular Correlation
\[ [\mathbf{a}\ \star\ \mathbf{b}]_{k} = \sum_{i=0}^{d-1} a_i b_{k+i\ mod\ d} \]
\(\mathbf{b}\)不需要反转,然后与\(\mathbf{a}\)进行卷积。
一个图示:
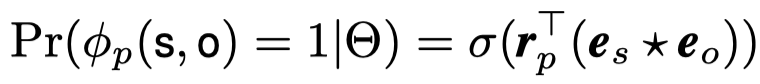
从这个图能够看出来,Circular Correlation可以看做是tensor dot的一种压缩方式,它的输出结果的每一维都是tensor dot结果的一部分。
它与Circular Convolution的区别:
- Non Commutative:对于Circular Convolution,\(\mathbf{a}\ *\ \mathbf{b} = \mathbf{b}\ *\ \mathbf{a}\),但是对于Circular Correlation,\(\mathbf{a}\ \star\ \mathbf{b} \not= \mathbf{b}\ \star\ \mathbf{a}\)。
- Similiarity Component:在计算Circular Correlation的0维输出的时候,实际是在计算\(\mathbf{a}\) 和\(\mathbf{b}\)的相似程度。
它与Circular Convolution的联系: \[ \mathbf{a}\ \star\ \mathbf{b} = \tilde{\mathbf{a}}\ *\ \mathbf{b} \] 其中,\(\tilde{\mathbf{a}}\)是\(\mathbf{a}\)的involution,\(\tilde{\mathbf{a}}_i=\mathbf{a}_{-i\ mod\ d}\)
为什么会想到使用Circular Correlation?
这个问题需要回归到题目 Holographic,作者受到基于Associative Memory的holographic models的启发。
在holographic reduced representations方法中,使用circular convolution来store \(\mathbf{a}\) 和\(\mathbf{b}\)的关联信息: \[ \mathbf{m} = \mathbf{a}\ *\ \mathbf{b} \] \(\mathbf{m}\)保存了memory,然后,使用circular correlation来retrieve和 \(\mathbf{a}\) 相关的信息: \[ \mathbf{b}^\prime = \mathbf{a}\ \star\ \mathbf{m} = \mathbf{a}\ \star\ (\mathbf{a}\ *\ \mathbf{b} )= \mathbf{b} * (\mathbf{a}\ \star\ \mathbf{a}) \] 使用\(\mathbf{b}^\prime\)可以与所有的候选\(\mathbf{b}\)求相似度。
因此,这个问题作者类比到了KGE,\(\mathbf{m}\)类比到\(\mathbf{e}_o\),\(\mathbf{a}\)类比到\(\mathbf{e}_s\),\(\mathbf{b}\)类比到\(\mathbf{r}_p\)。
对于HoLE,Circular Correlation就是用来retrieve stored in \(\mathbf{e}_o\),然后与所有的候选\(\mathbf{r}_p\)求相似度。