CrossE
Interaction Embeddings for Prediction and Explanation in Knowledge Graphs
2019-3-12日发表
设计了一种有效的,浅层的KGE方法CrossE,能够让entity embedding和relation embedding进行更多的交互。
Abstract
在知识图谱embedding的现有技术当中,Crossover interactions信息没有被利用过,本文提出的CrossE就是利用这种信息,并且进行了link prediction和prediction explanation的实验。
1. INTRODUCTION
几个出名的知识图谱Yago,WordNet,Freebase都是以\((h, r, t)\)表示的三元组。
Knowledge graph embedding (KGE) learns distributed representations [11] for entities and relations, called entity embeddings and relation embeddings.
三种知识图谱embedding类型,
- tensor factorization based RESCAL ,
- translation-based TransE ,
- neural tensor network NTN
但是这些模型都没有使用过Crossover interactions。
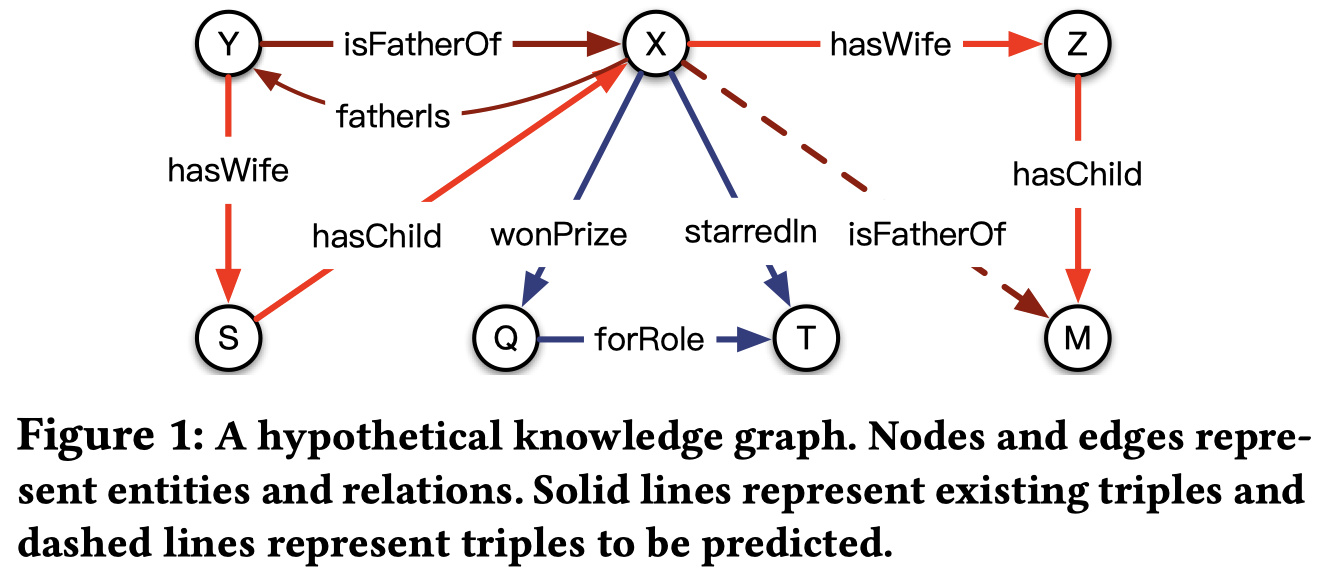
Crossover interactions包括interaction from relations to entities和interactions from entities to relations.
例如在上图中预测(X, isFatherOf, ? )
那么,与关系isFatherOf有关的实体只有Y,S这些与X是家庭关系的实体,与Q,T实体无关,这就叫做interaction from relations to entities,根据关系选择实体
同时,关系isFatherOf有两条途径,但头结点实体是X,所以只能选择X作为头结点的关系,这叫做interactions from entities to relations.
因此提出了CrossE:
- generate interaction embeddings \(h_I\) for head entity \(h\)
- generate interaction embeddings \(r_I\) for relation \(r\)
- combine interaction embeddings \(h_I\) and \(r_I\) together
- compare the similarity of combined embedding with tail entity embedding\(t\)
2. Related work
不考虑利用了额外信息进行embedding的模型,剩下的模型从entity是否表示为统一的形式划分,
KGEs with general embeddings:
Existing embedding methods with general embeddings all represent entities as low-dimensional vectors and relations as operations that combine the representation of head entity and tail entity.
典型模型包括:TransE, RESCAL,DistMult,ComplEx
这些模型都没有考虑在不同情况下embedding应该是不同的,没有考虑crossover interaction
KGEs with multiple embeddings:
Some KGEs learn multiple embeddings for entities or relations under various considerations.
比如:Structured Embedding (SE)(每个关系有两个矩阵),ORC(每个entity有head embedding和tail embedding),TransH,TransR等
这些模型,relation的embedding是general的,只考虑了relation->entity的interaction
3. CrossE: MODEL DESCRIPTION
CrossE最大的创新就在于考虑了新的embedding内容,同时没有增加过多的参数。
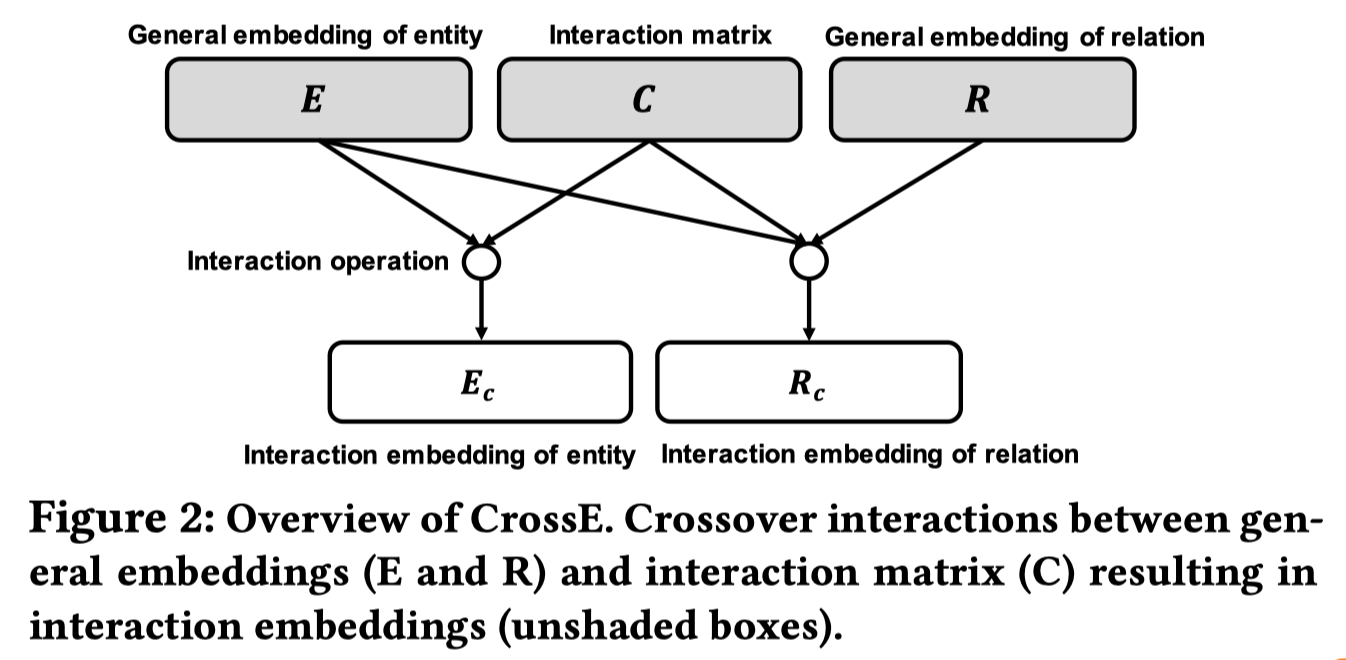
初始定义:
- \(E \in R^{n_e \times d}, R \in R^{n_r \times d}, C \in R^{n_r \times d}\)分别表示所有实体,关系和interaction matrix
- \(x_h, x_r, x_t\)分别表示(h, r, t)的one-hot形式
对于一个三元组(h, r, t)进行预测的顺序如下:
3.1 获取general embedding
\[ h=x_h^T E,\ r=x_r^T R,\ t=x_t^T E \]
3.2 Interaction Embedding for Entities.
对于头结点h, \[ h_I = c_r \circ h \\ c_r = x_r^TC \] 其中的\(\circ\)是Hadamard product, an element-wise operator
3.3 Interaction Embedding for Relations
对于关系r,模型来自头结点的信息, \[ r_I = h_I \circ r \]
3.4 Combination Operator
将前面的两个基于interaction的embedding联合起来, \[ q_{hr}=tanh(h_I+r_I+b) \]
3.5 Similarity Operator
计算最终的相似度, \[ f(h, r, t)=\sigma(q_{hr}t^T)=\sigma(tanh(c_r\circ h+c_r\circ h \circ r+b )t^T) \] 最终的loss function使用交叉熵。
4 EXPLANATIONS FOR PREDICTIONS
在知识图谱的explanation:
在知识图谱中对于(h, r, t)可以成立的explanation是指从h->t的路径
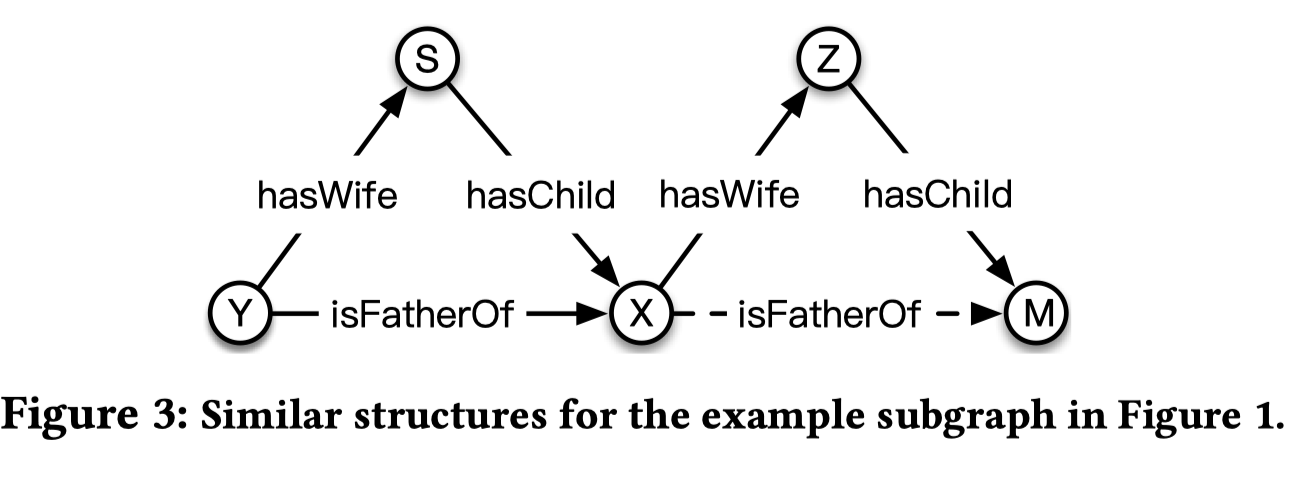
对于一个explanation,应该有对应的一个或多个support,在这篇论文当中,explanation的support就是现存的知识图谱中相似结构,如下图所示。
寻找explanation的步骤:
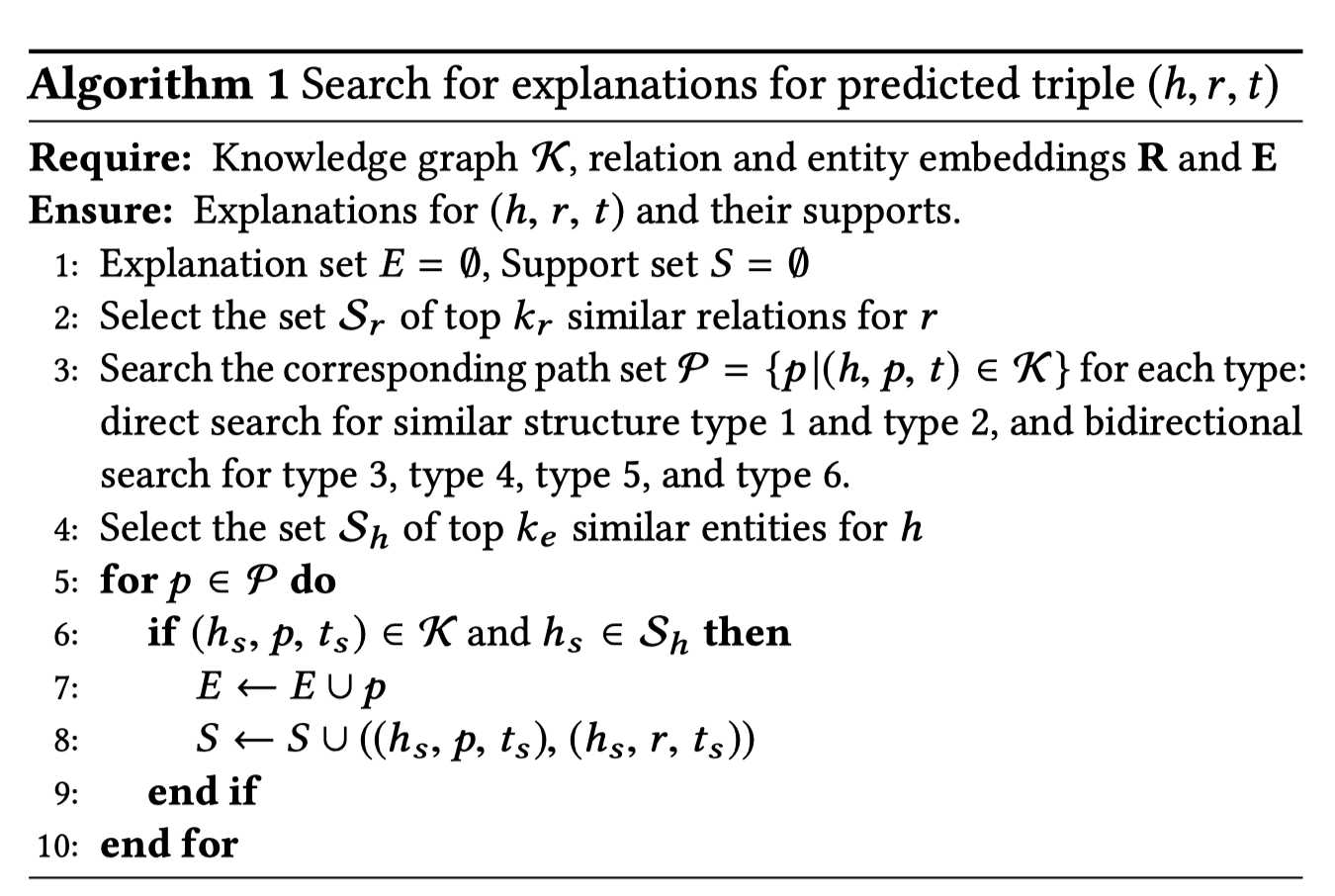
详细的请参考论文
5 EXPERIMENTAL EVALUATION
略