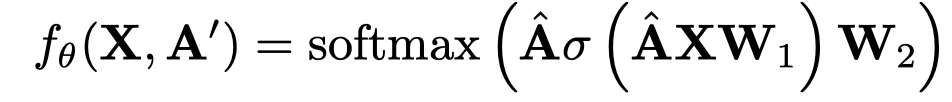HGSL
Heterogeneous Graph Structure Learning for Graph Neural Networks
AAAI 2021
作者声称是首个尝试为异质图神经网络寻找最优的图结构进行学习的方法,提出了HGSL(Heterogeneous Graph Structure Learning)。核心方法有两个,异质图结构学习和图神经网络。 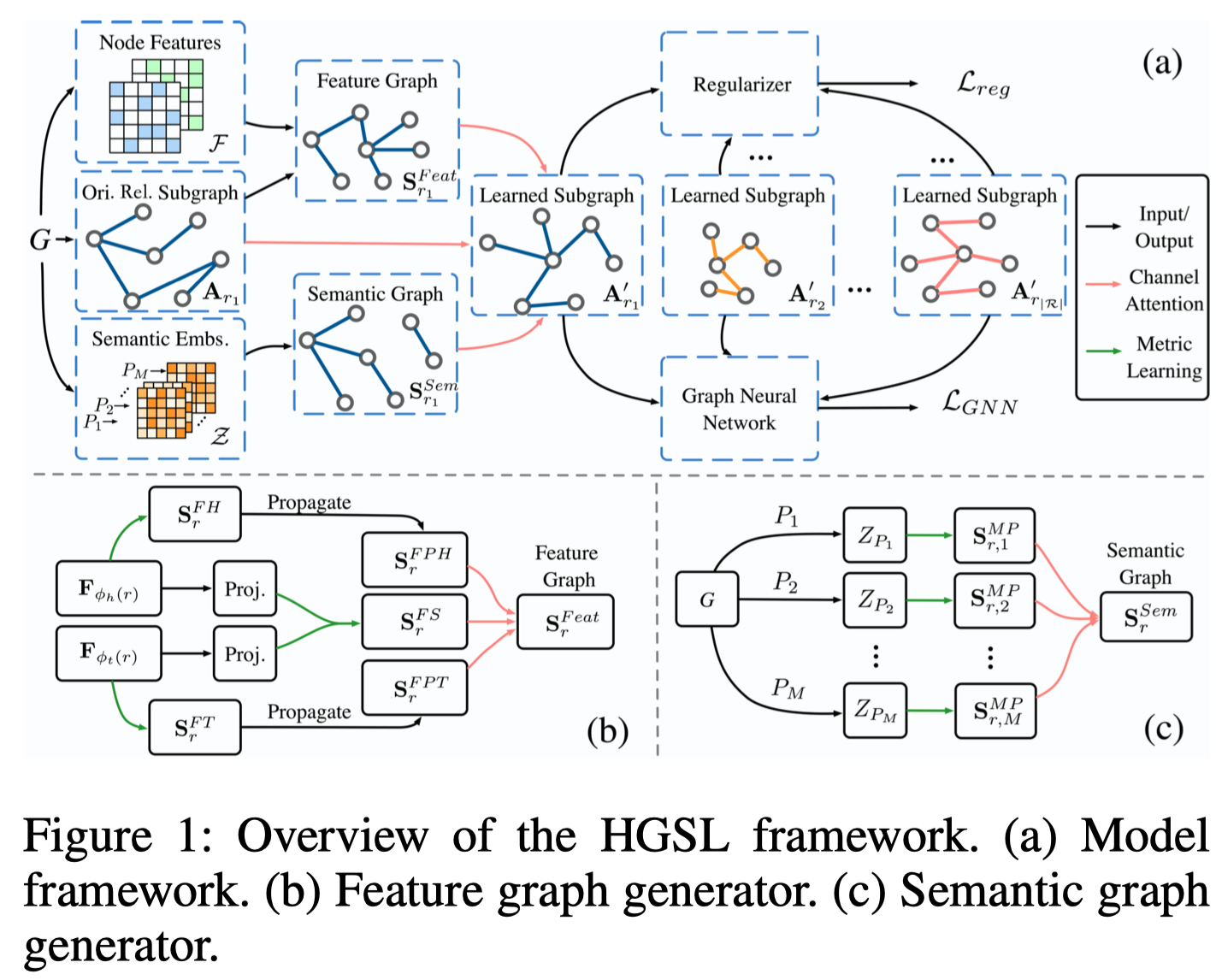
Introduction
motivation:目前的异质图神经网络基于一个假设,学习使用的graph是足够好的。但是实际上这个假设不一定总能够满足。两个方面的原因,(1)在建模graph的时候,使用到的信息难免会包含错误的信息,导致最终的graph是不够好的(2)另一个原因是异质图结构本身与下游任务是独立的,不一定是有利于下游任务的最优解。为了解决上面的问题,图结构学习graph structure learning (GSL)被提出来,但是这些方法主要是在考虑同质图,无法很好的考虑异质图中的异质性以及异质图中存在的复杂的交互。
method:提出HGSL,首先学习合适的graph structure,然后在这个graph structure上使用GCN进行学习。这种heterogeneous graph structure learning是核心创新点,包括三种graph的融合,feature similarity graph,feature propagation graph,和semantic graph。
Heterogeneous Graph Neural Networks (HGNNs) have drawn increasing attention in recent years and achieved outstanding performance in many tasks. The success of the existing HGNNs relies on one fundamental assumption, i.e., the original heterogeneous graph structure is reliable. However, this assumption is usually unrealistic, since the heterogeneous graph in reality is inevitably noisy or incomplete. Therefore, it is vital to learn the heterogeneous graph structure for HGNNs rather than rely only on the raw graph structure. In light of this, we make the first attempt towards learning an optimal heterogeneous graph structure for HGNNs and propose a novel framework HGSL, which jointly performs Heterogeneous Graph Structure Learning and GNN parameter learning for classification. Different from traditional homogeneous graph structure learning, considering the heterogeneity of different relations in heterogeneous graph, HGSL generates each relation subgraph separately. Specifically, in each generated relation subgraph, HGSL not only considers the feature similarity by generating feature similarity graph, but also considers the complex heterogeneous interactions in features and semantics by generating feature propagation graph and semantic graph. Then, these graphs are fused to a learned heterogeneous graph and optimized together with a GNN towards classification objective. Extensive experiments on real-world graphs demonstrate that the proposed framework significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art methods.
Method

Feature Graph Generator
基于node feature,通过计算相似度,学习node之间潜在的relationship。
对于边类型\(r\),首先,对于\(r\)下的所有edge的头/尾node \(i\),根据node的类型对node feature进行转换

之后,计算利用余弦相似性计算两个节点的相似性
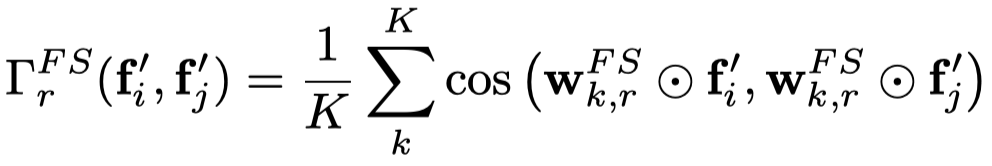
设计一个阈值,然后创建graph
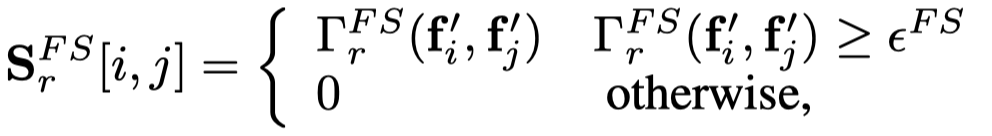
这个graph,是边类型\(r\)下的不同类型的头、尾实体的feature similarity graph \(\mathbf{S}^{FS}_r\)。
Feature Propagation Graph
不同的关系\(r\),不同的node feature之间是存在complex的交互interaction的。为了建模这种复杂的交互,HGSL让node features和topology structure产生交互,然后构造一个feature propagation graph。核心思想是具有相似特征的节点可能具有相似的邻居。
关系r的邻接矩阵是\(\mathbf{A}_r\),头node和尾node可能具有不同的type。
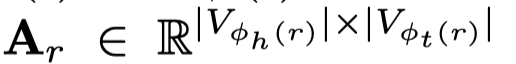
对于相同类型type的头结点\(i\)和\(j\),构造一个头结点的相似特征图
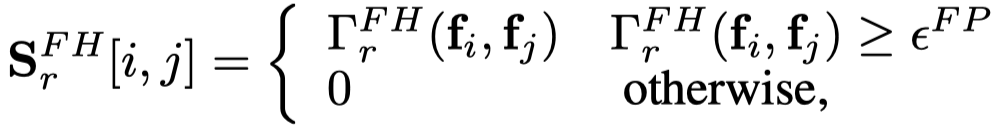
之后,这些相似头结点可以通过拓扑结构传播,最终实现效果是相似头结点可以往相似头结点传播消息,获得了head feature propagation graph。
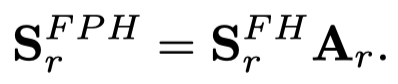
类似的,构造相似尾结点图,然后传播,获得了tail feature propagation graph。
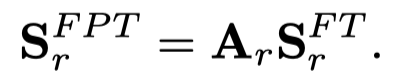
之后,通过获得单纯的特征图、头实体的特征-拓扑结构交互图、尾实体的特征-拓扑结构交互图,进行融合,使用一个channel attention layer,学习一个\(1\times 1\times 3\)的卷积核\(W^{Feat}_{\Psi,r}\)。
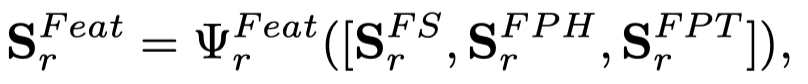

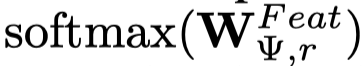
Semantic Graph Generator
接下来,是学习多阶拓扑结构信息的合适图。在异质图中,不同阶的邻居信息当然是差异非常大的。
The semantic graph is generated depending on the high-order topology structure in HIN, describing the multi-hop structural interactions between two nodes.
HGSL使用MP2Vec去进行学习,定义了\(M\)个元路径
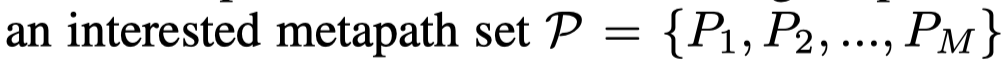
对于所有的node,学习到\(M\)个embedding集合,
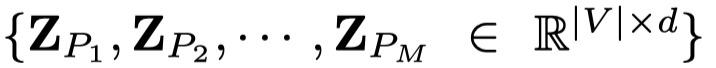
对于表示不同semantic的metapath信息,同样是构造一个相似图

使用channel attention layer融合semantic subgraph,
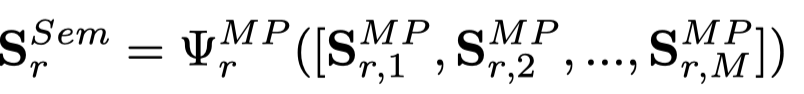
Overall generated graph
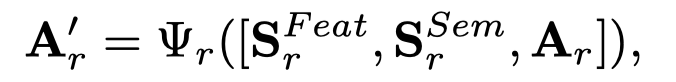
Optimization
前面为每个关系都学习了一个融合的graph \(\mathbf{A}_r\),接下来作者直接使用GCN进行学习,通过直接认为只要有两个相连的node就可以认为是1,构造了\(\mathbf{A}^\prime\),推测就是直接所有的\(\mathbf{A}_r\)相加。