Deeper-insights-gcn
Deeper Insights into Graph Convolutional Networks for Semi-Supervised Learning
AAAI 2018,引用量578。
作者对GCN的机制进行了探讨,认为GCN是Laplacian smoothing的一种特殊形式。并且形式化证明了当GCN堆叠到很多层时,所有节点的表示会趋向于同一表示。发现GCN在带有label的data较少的情况下,表现出的性能差,为了解决这一问题,提出了一种联合训练co-traning的方法,主要是使用随机游走和GCN两种方法,寻找不同label下的most confident vertices,然后使用这些most confident vertices继续训练。
Many interesting problems in machine learning are being revisited with new deep learning tools. For graph-based semisupervised learning, a recent important development is graph convolutional networks (GCNs), which nicely integrate local vertex features and graph topology in the convolutional layers. Although the GCN model compares favorably with other state-of-the-art methods, its mechanisms are not clear and it still requires considerable amount of labeled data for validation and model selection.
In this paper, we develop deeper insights into the GCN model and address its fundamental limits. First, we show that the graph convolution of the GCN model is actually a special form of Laplacian smoothing, which is the key reason why GCNs work, but it also brings potential concerns of oversmoothing with many convolutional layers. Second, to overcome the limits of the GCN model with shallow architectures, we propose both co-training and self-training approaches to train GCNs. Our approaches significantly improve GCNs in learning with very few labels, and exempt them from requiring additional labels for validation. Extensive experiments on benchmarks have verified our theory and proposals.
作者认为的GCN的优点:
- 图卷积-即拉普拉斯平滑操作,让不同class的特征能够在图上传播
- MLP是一个强大的feature extractor
缺点:
- 图卷积是一个localized filter,当labeled data较少的时候,性能较差
- 使用neural network要求具备较多的训练数据以及使用额外的验证集进行模型选择
作者证明graph convolution是laplacian smoothing的过程:
laplacian smoothing在1995年就被提出来,A signal processing approach to fair surface design.
定义为:
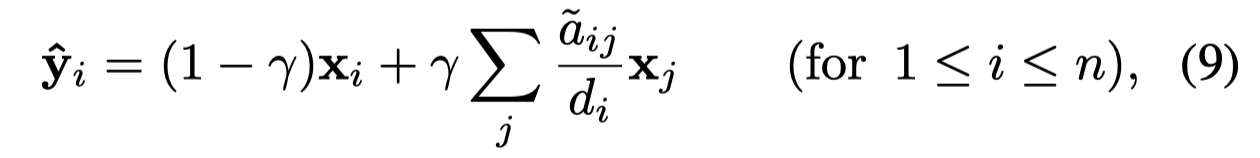
其中的\(\gamma\)是参数,控制当前vertex和邻居vertex的特征的weight。\(\mathbf{x}_j\)是邻居vertex。
将上面的形式写为矩阵形式: \[ \begin{align} Y &= (1-\gamma)X + \gamma \tilde{A} \tilde{D}^{-1} X \\ &= X - \gamma (X - \tilde{A} \tilde{D}^{-1} X ) \\ &= X - \gamma \tilde{D}^{-1} (\tilde{D} - \tilde{A}) X \\ &= X - \gamma \tilde{D}^{-1} \tilde{L} X \end{align} \] 对上面的式子进行简化,令 \(\gamma = 1\),替换\(\tilde{D}^{-1} \tilde{L}\)为\(\tilde{D}^{-1/2} \tilde{L} \tilde{D}^{-1/2}\)
得到下面的式子: \[ \begin{align} Y &= X - \tilde{D}^{-1/2} \tilde{L} \tilde{D}^{-1/2} X \\ &= (I - \tilde{D}^{-1/2} \tilde{L} \tilde{D}^{-1/2} ) X \\ &= (I - \tilde{D}^{-1/2} (\tilde{D} - \tilde{A}) \tilde{D}^{-1/2} ) X \\ &= \tilde{D}^{-1/2} \tilde{A} \tilde{D}^{-1/2} X \end{align} \] 最后得到了GCN。
这一操作背后的原理是属于同一类的vertex倾向于在一个cluster中,smoothing操作让它们具有了相近的表示,这使得之后的classification更加容易。
The Laplacian smoothing computes the new features of a vertex as the weighted average of itself and its neighbors’. Since vertices in the same cluster tend to be densely connected, the smoothing makes their features similar, which makes the subsequent classification task much easier.
另外,为了让GCN能够在data更受限制的情况下进行学习,作者结合ParWalks这种随机游走的方法,寻找各个class下most confident vertices——the nearest neighbors to the labeled vertices of each class。