MLP-Mixer
MLP-Mixer: An all-MLP Architecture for Vision
2021-5-4
谷歌大脑团队的新作MLP-Mixer,使用纯MLP进行CV任务,没有超越目前业界SOTA,但是效果很不错。最关键的是只使用了MLP,便于部署。同时要注意,该模型训练使用了TPU3.0,外加众多training skills,model size也很大,不是个人可以玩儿转的。
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are the go-to model for computer vision. Recently, attention-based networks, such as the Vision Transformer, have also become popular. In this paper we show that while convolutions and attention are both sufficient for good performance, neither of them are necessary. We present MLP-Mixer, an architecture based exclusively on multi-layer perceptrons (MLPs). MLP-Mixer contains two types of layers: one with MLPs applied independently to image patches (i.e. “mixing” the per-location features), and one with MLPs applied across patches (i.e. “mixing” spatial information). When trained on large datasets, or with modern regularization schemes, MLP-Mixer attains competitive scores on image classification benchmarks, with pre-training and inference cost comparable to state-of-the-art models. We hope that these results spark further research beyond the realms of well established CNNs and Transformers.1
1 Introduction
CNN是CV领域目前de-facto标准,近期的transformers-like的模型Vision Transformers (ViT),也得到了SOTA的结果。
2 Mixer Architecture
本文提出了MLP-Mixer,完全使用MLP的架构。看一下整体结构:
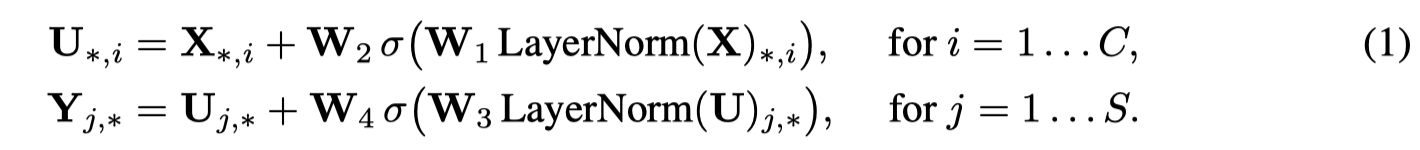
接收的输入固定size的,将输入划分为一系列的patch,然后所有的patch经过一个投影层,进入核心的Mixer层。
对于Mixer层,由两个不同的MLP组成,加上layer norm和GELU
token-mixing:不同patch的相同维度,应该如何产生输出
The token-mixing MLPs allow communication between different spatial locations (tokens); they operate on each channel independently and take individual columns of the table as inputs.
channel-mising:相同patch不同channel,应该如何产生输出
The channel-mixing MLPs allow communication between different channels; they operate on each token independently and take individual rows of the table as inputs.
写成公式:
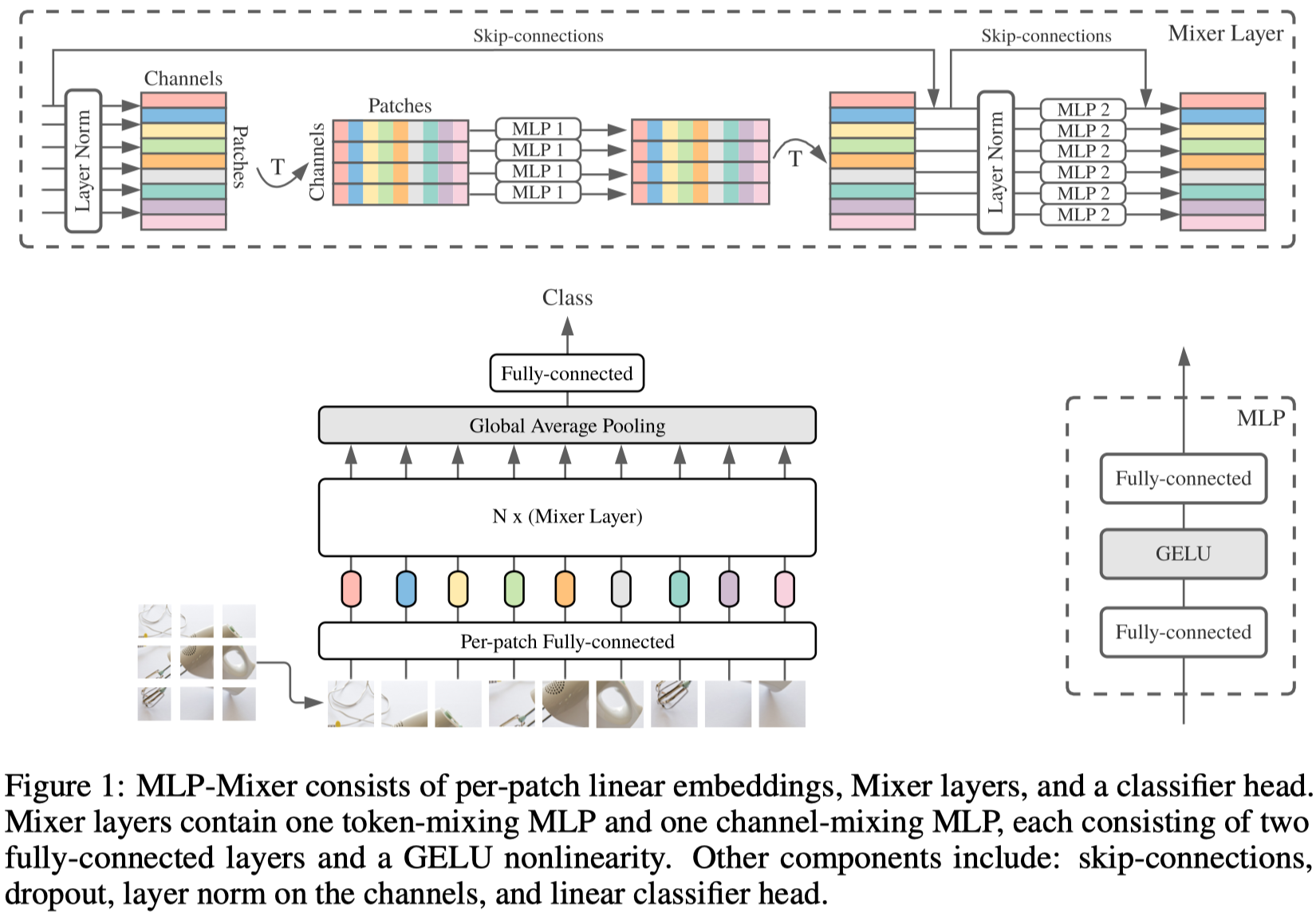
两个MLP的操作区别就是对于输入简单的转置操作。
另外,MLP-Mixer保持MLP的输出dim都是固定的。
- channel-mixing MLPs对于不同patch的处理是一样的,这提供了位置不变性,it provides positional invariance, a prominent feature of convolutions.
- token-mixing MLPs是跨patch,对于所有的channel使用相同的kernel,这点是和很多CNN模型有区别的。它带来的一个好处是不会随着channel的增加而增加参数量。另外,token-mixing MLPs是对输入patch的位置有感知的。一个patch的位置发生变化,对于channel-mixing来说,没有区别。但是对于token-mixing来说,patch位置变动在参数不变的情况下,会导致输出会发生变化,最终参数也会更新。所以它隐式的可以学习位置的表示。
3 Experiments
没有细看,很多细节都不了解,看不懂。
总结一下:
- 至少8层起步的MLP,也就是至少16层全连接;另外,MLP的size都是很大的,256size起步
- 使用了非常多的训练技巧!!
- 使用了谷歌的TPU 3.0,1小时8$
- 先预训练,再fine-tuning,但没看过CV paper,不理解为什么这么做