OpenIE-LLM
Open Information Extraction 1
开放域信息抽取相关论文合集1
UniversalNER
UniversalNER: Targeted Distillation from Large Language Models for Open Named Entity Recognition. 2023-08,ICLR 2024,南加州大学,项目
Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable generalizability, such as understanding arbitrary entities and relations. Instruction tuning has proven effective for distilling LLMs into more cost-efficient models such as Alpaca and Vicuna. Yet such student models still trail the original LLMs by large margins in downstream applications. In this paper, we explore targeted distillation with mission-focused instruction tuning to train student models that can excel in a broad application class such as open information extraction. Using named entity recognition (NER) for case study, we show how ChatGPT can be distilled into much smaller UniversalNER models for open NER. For evaluation, we assemble the largest NER benchmark to date, comprising 43 datasets across 9 diverse domains such as biomedicine, programming, social media, law, finance. Without using any direct supervision, UniversalNER attains remarkable NER accuracy across tens of thousands of entity types, outperforming general instruction-tuned models such as Alpaca and Vicuna by over 30 absolute F1 points in average. With a tiny fraction of parameters, UniversalNER not only acquires ChatGPT’s capability in recognizing arbitrary entity types, but also outperforms its NER accuracy by 7-9 absolute F1 points in average. Remarkably, UniversalNER even outperforms by a large margin state-of-the-art multi-task instruction-tuned systems such as InstructUIE, which uses supervised NER examples. We also conduct thorough ablation studies to assess the impact of various components in our distillation approach. We will release the distillation recipe, data, and UniversalNER models to facilitate future research on targeted distillation.
一篇和InstructIE和InstructUIE相似思想的工作,都是训练IE LLM。这篇论文同时结合了现有的NER数据集和利用ChatGPT从raw text中进行open NER标注后的新构造的数据集进行训练。foundation model是LLaMA 7B/13B,作者也提到了同时尝试了LLaMA2,没有很大区别。
Issue: 作者在论文强调的观点是,很多现有的instruction-tuning工作是利用了ChatGPT等更大size的LLM来构造指令,这可以看做是一种蒸馏技术。但是很多instruction-tuning工作是关注让student LLM学会在不同任务上遵循指令,这种做法是不可能超越teacher LLM如ChatGPT的。
Solution: 因此作者觉得应该让LLM更加关注某一类任务,作者选择了NER任务作为探究任务。作者的指令重点不在于为不同的task构造不同的描述,而是想办法能够描述清楚不同数据集、不同领域的NER label的含义。增加输入input的多样性,而不是增加instruction的多样性。
作者利用ChatGPT(gpt-3.5-turbo-0301)从Pile corpus中进行sentence-level open NER标注,不限制entity类型。只要是GPT认为是entity的mention都被导出。下面是进行标注的prompt:
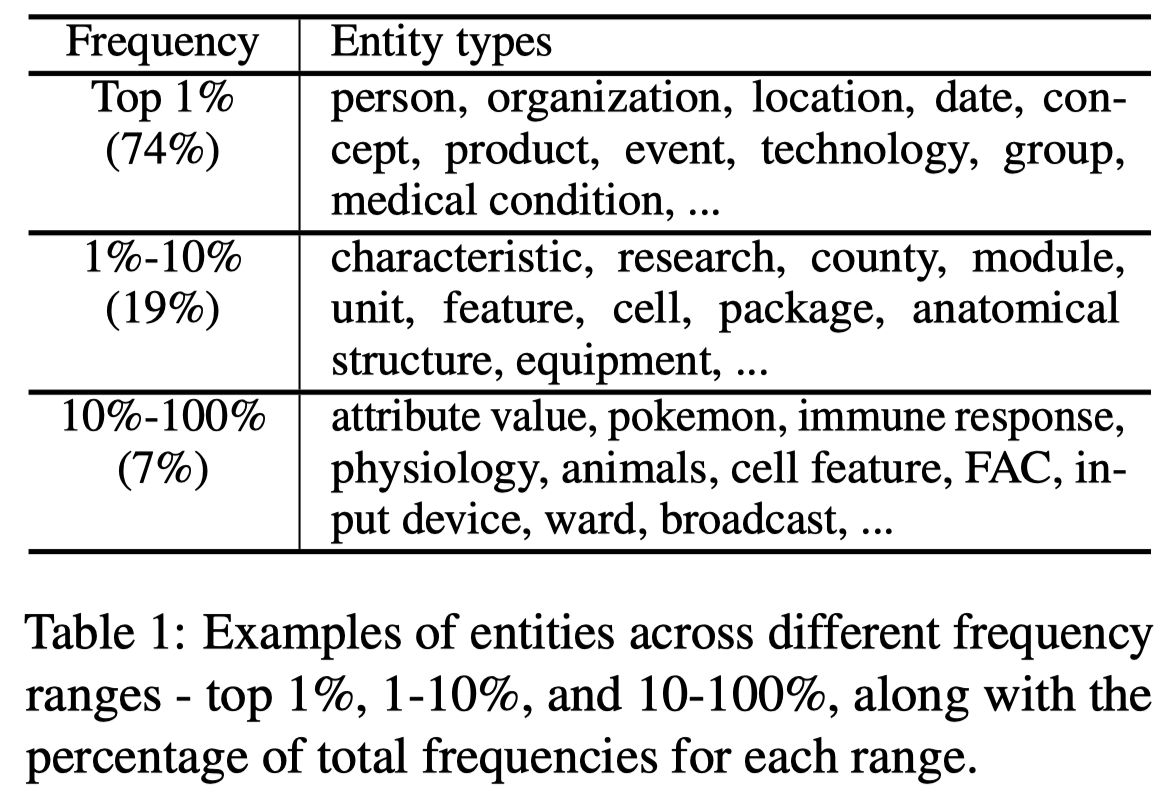
经过清洗后,作者获得了240,725实体,13,020实体类型,形成了Pile-type data。
 然后是如何构造instruction,以及如何训练。
然后是如何构造instruction,以及如何训练。
作者根据ChatGPT的标注,直接询问某一类entity在text中的mention,相当于ChatIE方法的第二步,迭代的提问具有对应label verbalization的名词,并不是一口气把所有的entity type都抽取出来。下面是instruction:

Negative sampling,作者发现需要让LLM学会回答什么entity type没有在text中出现能够极大的提高模型学习效果(实验中有20%以上的效果提升)。进行依据entity type frequency的采样,构造负样本。
除去了利用ChatGPT标注的新数据外,作者也提到如果利用现有的各类NER datasets做Supervised finetuning可以进一步提升模型效果。为了解决不同数据集之间label definitions的差异问题(如PERSON entity在ACL数据集中包括了she, he这些人称代词,而在multiNERD就没有包括人称代词),因此label需要和dataset相关联,作者额外的在prompt左侧加入dataset的name来进行辨别:

为了便于评估,作者收集了现有的43个NER数据集作为benchmark Universal NER benchmark,涉及9个domain,包括general, biomedical, clinical, STEM, programming, social media, law, finance, and transportation domains。作者对齐进行的改进有: - 作者人工把所有的label转化为了自然语言 - 考虑到类似于ELSE这样的entity type没有统一的标准和本体定义,作者没有把这样的entity包括进来 - 对于document-level的数据集,作者将其切分为了sentence-level的实例
 训练遵循和Vicuna一样的训练规划。 实验结果:
训练遵循和Vicuna一样的训练规划。 实验结果:
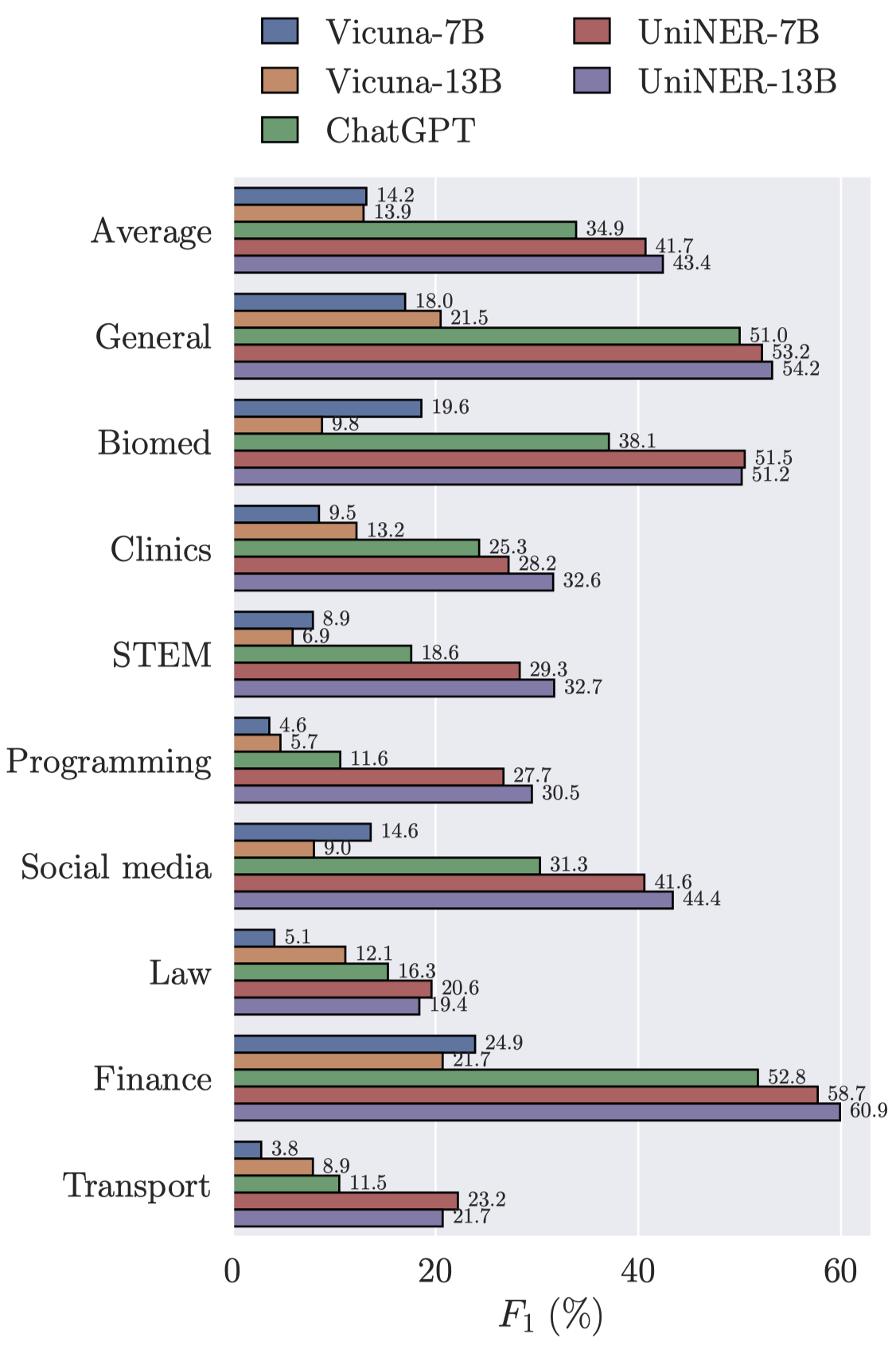
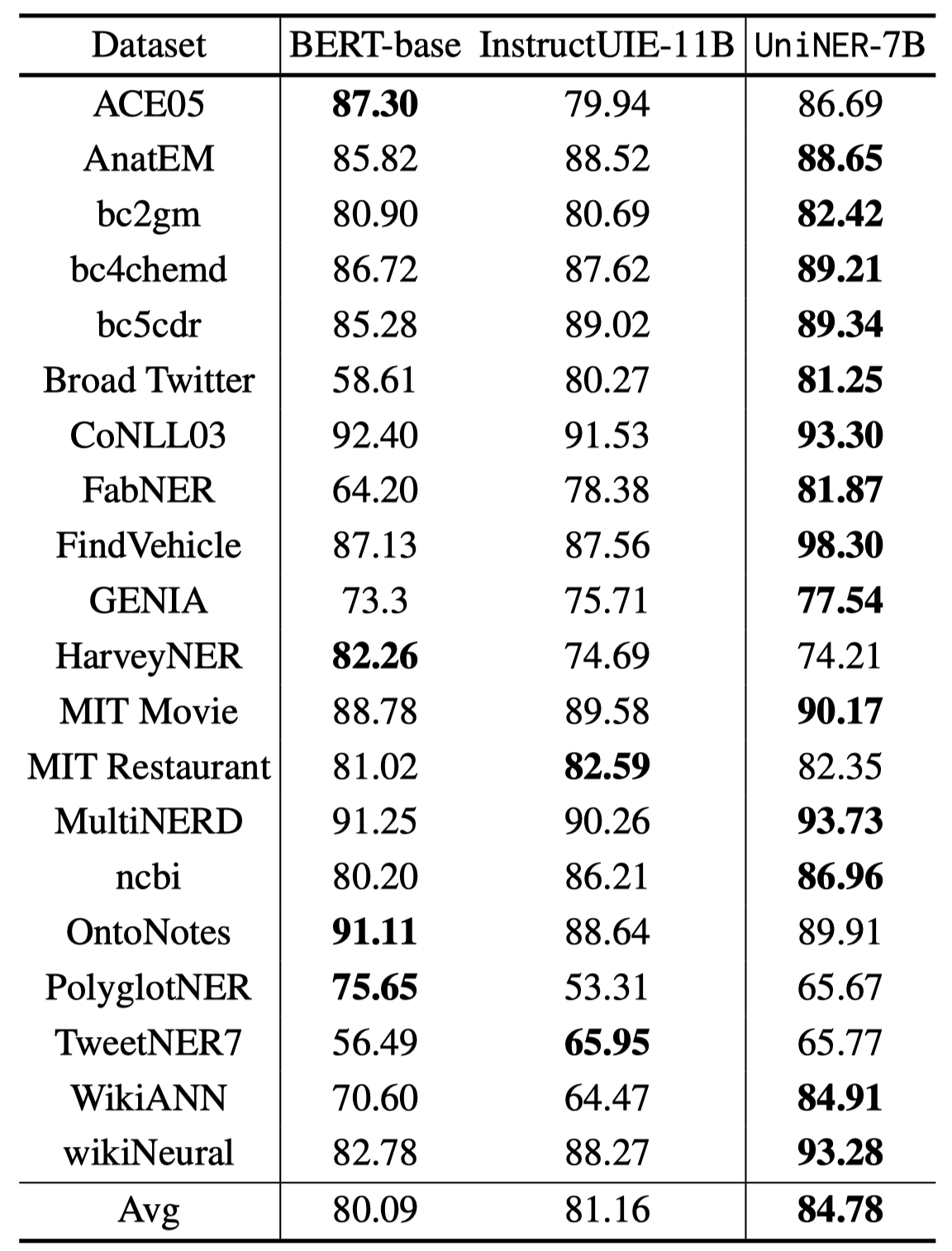 从实验结果可以看出来,从
从实验结果可以看出来,从7B到13B效果平均提升了2-3个点。 下面是对负采样的消融实验,可以看到让LLM学会回答自己不知道什么/什么东西不存在是很关键的: 
Pivoine
PIVOINE: Instruction Tuning for Open-world Entity Profiling. 南加州大学. EMNLP 2023 Findings. 代码.
This work considers the problem of Open-world Entity Profiling, which is a sub-domain of Open-world Information Extraction (Open-world IE). Unlike the conventional closed-world IE, Open-world IE considers a more general situation where entities and relations could be beyond a predefined ontology. We seek to develop a large language model (LLM) that can perform Open-world Entity Profiling with instruction tuning to extract desirable entity profiles characterized by (possibly fine-grained) natural language instructions. In particular, we construct InstructOpenWiki, a substantial instruction-tuning dataset for Open-world Entity Profiling enriched with a comprehensive corpus, extensive annotations, and diverse instructions. We finetune pretrained BLOOM models on InstructOpenWiki and obtain Pivoine, an LLM for Open-world Entity Profiling with strong instruction-following capabilities. Our experiments demonstrate that Pivoine significantly outperforms traditional methods and ChatGPT-based baselines, displaying impressive generalization capabilities on both unseen instructions and out-of-ontology cases. Consequently, Pivoine emerges as a promising solution to tackle the open-world challenge in entity profiling.
Issue:得益于大模型的泛化能力,其能够更好的解决开放域的问题。但是之前的研究发现,在zero-shot场景下,直接用LLM难以直接解决IE任务。因此,作者认为有必要加强LLM对于IE任务相关的指令跟随的能力。
Solution:作者的方法,就是在开源LLM BLOOM 1B/7B的基础上,构造一个包括了各种能够导出entity相关信息(即Open-world Entity Profiling任务)的instruction的数据集,然后全监督微调,获得一个专用的LLM。
作者的提出的使用LLM的方法:

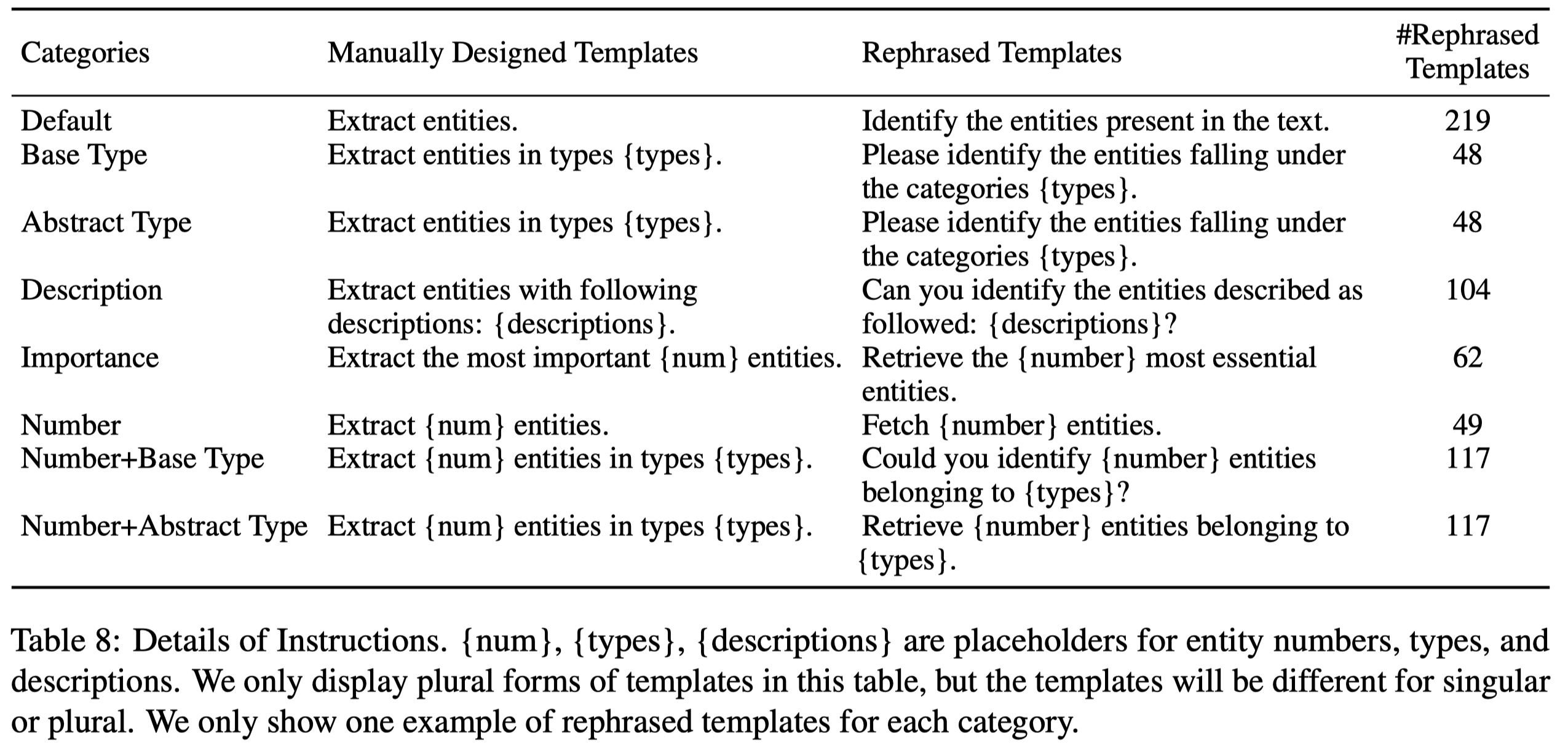
注意以下的几个要点: 1. 作者的instruction一共有6大类: - Default:让LLM抽取出所有的实体和关系 - Base Type:对应Wikidata中的属性 P31 (instance of) - Abstract Type:对应Wikidata中的属性 P279 (subclass of),base type的parent - Description:phrases or sentences describing entities’ properties - Importance:对应Wikidata中的entity的优先级属性(priorities) - Number:数量 - Number+Base Type:特殊的instruction,只会作为评估 - Number+Abstract Type:特殊的instruction,只会作为评估
instruction prompt通过ChatGPT改写,获得了更多不同的expression:
输出是
JSON格式,原因在于json是常用的web传输数据的格式因此一个在code上训练过的LLM应该对json比较熟悉。
作者构造的数据集InstructOpenWiki是通过Wikipedia和Wikidata进行对齐得到的,具体的构造方法参见论文,其中的relation是利用distant supervision构造的。其中划分的验证集,是通过选择不相交的时间段内出现的新的entity,确保能够出现Unseen Ontologies,同时作者用GPT-4生成和人工编写了3个新的instruction,确保出现Unseen Instructions。
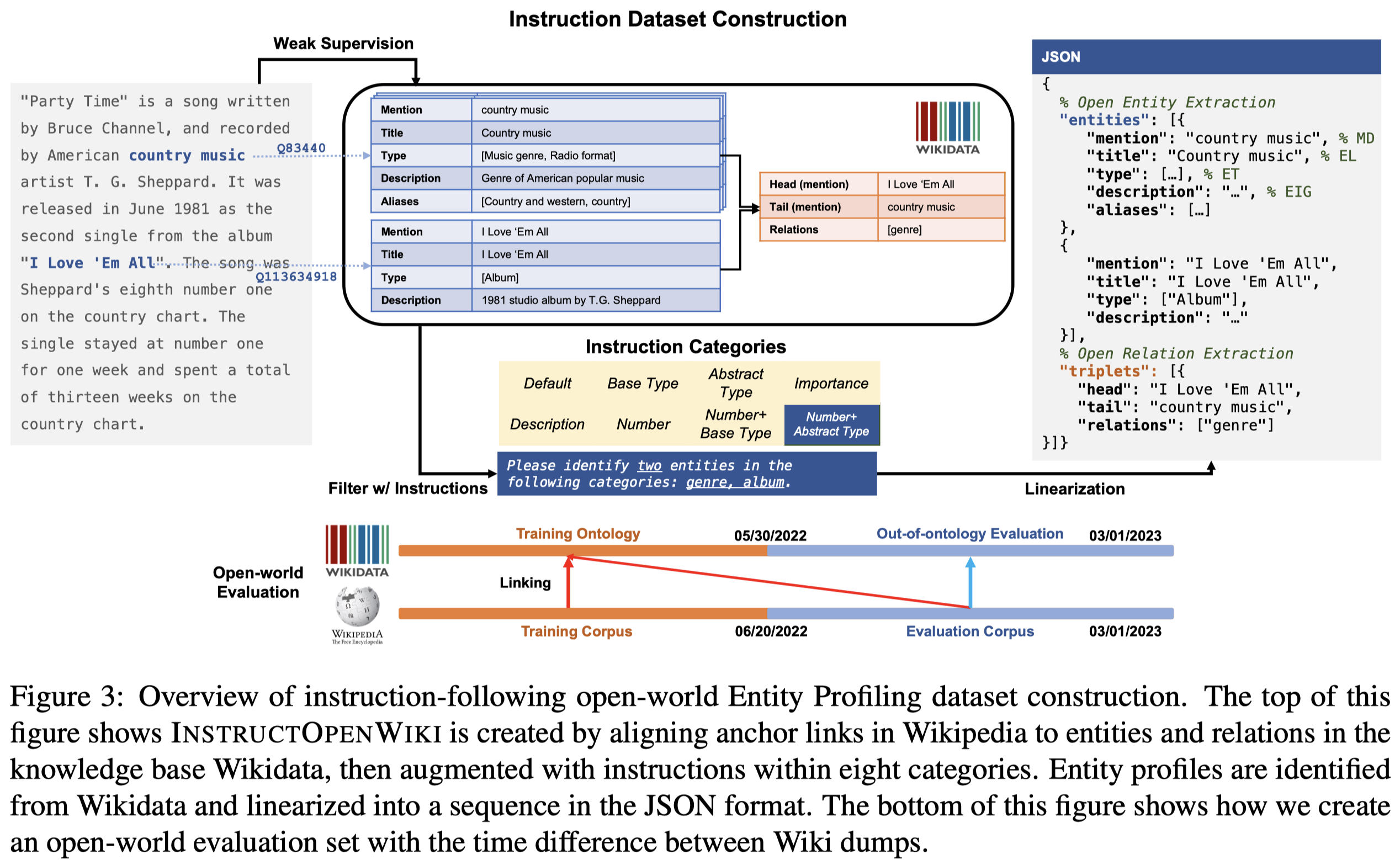
最后总体的实验结果:
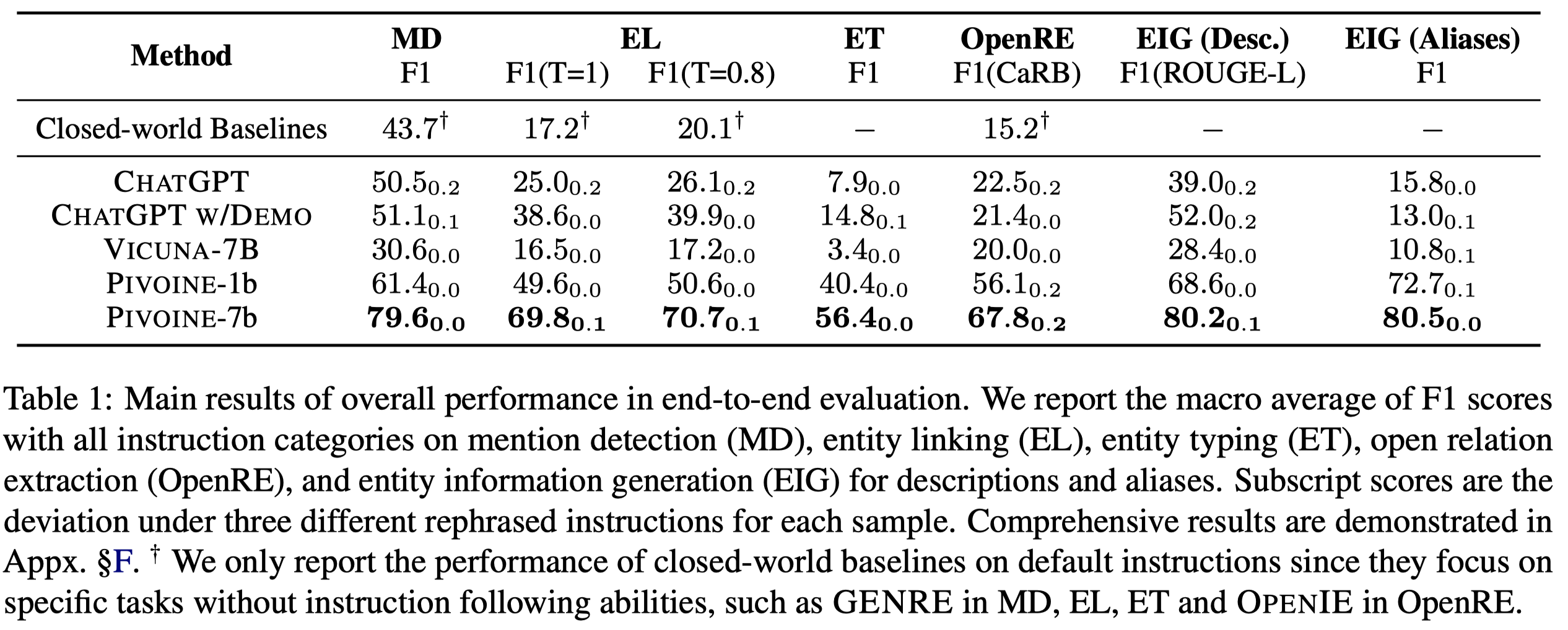
值得注意的是,作者的巨大训练成本,BLOOM 1B全监督微调64 NVIDIA V100 GPU for 92 hours;而BLOOM 7B全监督微调256 NVIDIA V100 GPU for 54 hours。
ROBUST
Preserving Knowledge Invariance: Rethinking Robustness Evaluation of Open Information Extraction. 清华. EMNLP 2023. 代码.
The robustness to distribution changes ensures that NLP models can be successfully applied in the realistic world, especially for information extraction tasks. However, most prior evaluation benchmarks have been devoted to validating pairwise matching correctness, ignoring the crucial validation of robustness. In this paper, we present the first benchmark that simulates the evaluation of open information extraction models in the real world, where the syntactic and expressive distributions under the same knowledge meaning may drift variously. We design and annotate a large-scale testbed in which each example is a knowledge-invariant clique that consists of sentences with structured knowledge of the same meaning but with different syntactic and expressive forms. By further elaborating the robustness metric, a model is judged to be robust if its performance is consistently accurate on the overall cliques. We perform experiments on typical models published in the last decade as well as a representative large language model, and the results show that the existing successful models exhibit a frustrating degradation, with a maximum drop of 23.43 F 1 score. Our resources and code are available at https://github.com/qijimrc/ROBUST.
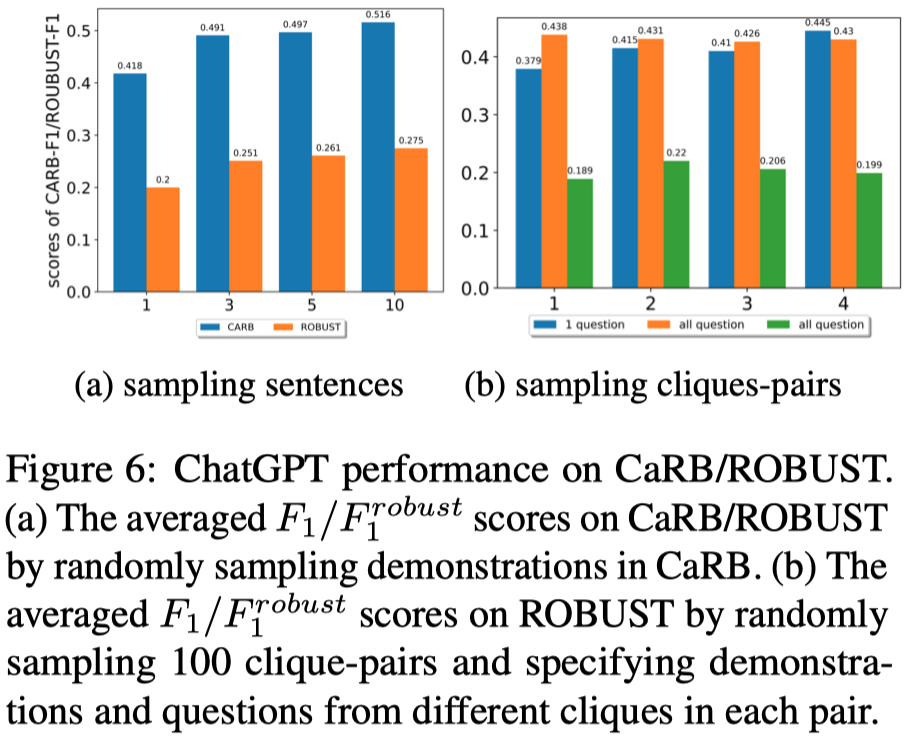
一个新的评估OpenIE模型效果鲁棒性的benchmark,作者评测了用ChatGPT的效果。下面是使用的prompt:

试验结果:
DualOIE
Exploiting Duality in Open Information Extraction with Predicate Prompt. WSDM 2024. 复旦
Open information extraction (OpenIE) aims to extract the schemafree triplets in the form of (subject, predicate, object) from a given sentence. Compared with general information extraction (IE), OpenIE poses more challenges for the IE models, especially when multiple complicated triplets exist in a sentence. To extract these complicated triplets more effectively, in this paper we propose a novel generative OpenIE model, namely DualOIE, which achieves a dual task at the same time as extracting some triplets from the sentence, i.e., converting the triplets into the sentence. Such dual task encourages the model to correctly recognize the structure of the given sentence and thus is helpful to extract all potential triplets from the sentence. Specifically, DualOIE extracts the triplets in two steps: 1) first extracting a sequence of all potential predicates, 2) then using the predicate sequence as a prompt to induce the generation of triplets. Our experiments on two benchmarks and our dataset constructed from Meituan demonstrate that DualOIE achieves the best performance among the state-of-the-art baselines. Furthermore, the online A/B test on Meituan platform shows that 0.93% improvement of QV-CTR and 0.56% improvement of UV-CTR have been obtained when the triplets extracted by DualOIE were leveraged in Meituan’s search system.
重点不是如何使用LLM去解决OpenIE问题作者使用ChatGPT进行OpenIE作为baseline,主要是使用了带有CoT解释的demonstrations:

在CaRB数据集上的结果:
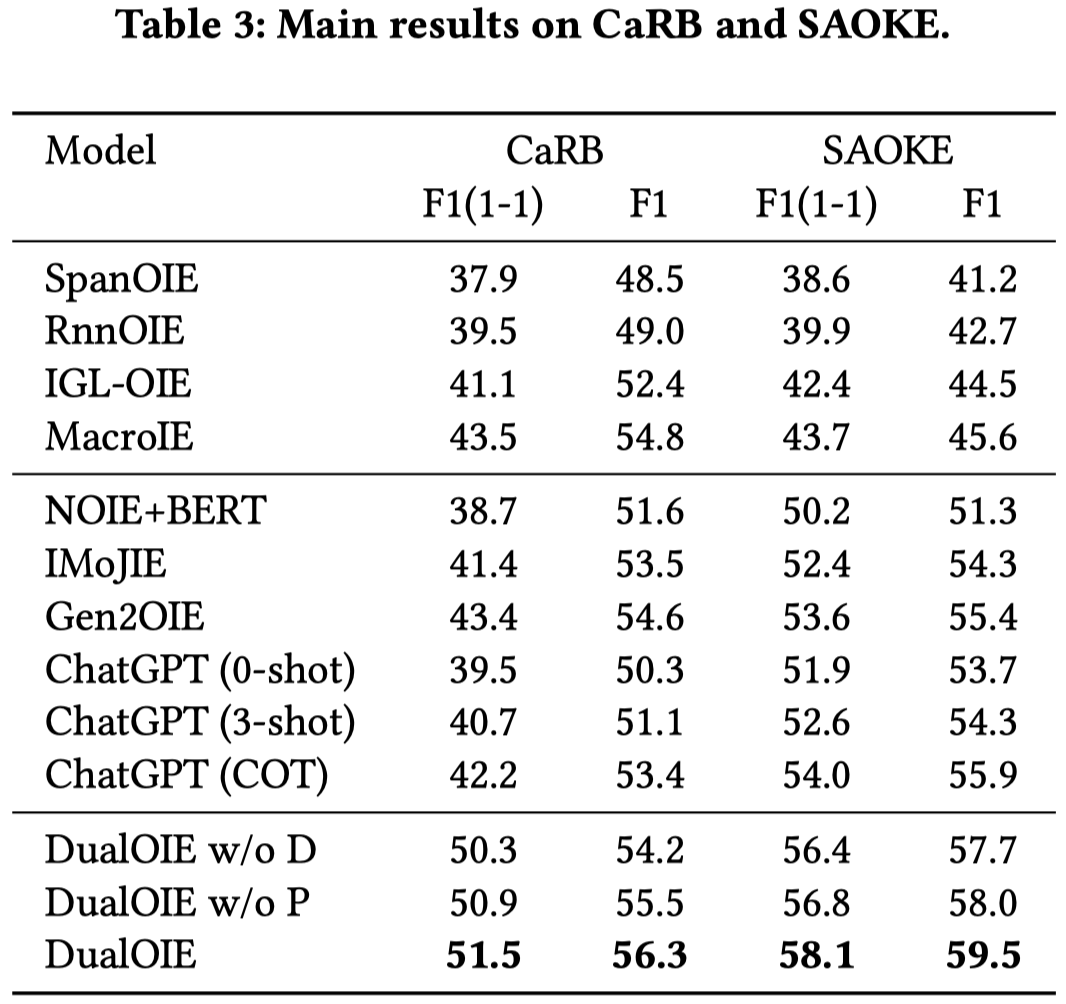
效果已经非常好了。
D-SD
Mastering the Task of Open Information Extraction with Large Language Models and Consistent Reasoning Environment. 清华. arXiv.
Open Information Extraction (OIE) aims to extract objective structured knowledge from natural texts, which has attracted growing attention to build dedicated models with human experience. As the large language models (LLMs) have exhibited remarkable in-context learning capabilities, a question arises as to whether the task of OIE can be effectively tackled with this paradigm? In this paper, we explore solving the OIE problem by constructing an appropriate reasoning environment for LLMs. Specifically, we first propose a method to effectively estimate the discrepancy of syntactic distribution between a LLM and test samples, which can serve as correlation evidence for preparing positive demonstrations. Upon the evidence, we introduce a simple yet effective mechanism to establish the reasoning environment for LLMs on specific tasks. Without bells and whistles, experimental results on the standard CaRB benchmark demonstrate that our 6-shot approach outperforms state-of-the-art supervised method, achieving an 55.3 F1 score. Further experiments on TACRED and ACE05 show that our method can naturally generalize to other information extraction tasks, resulting in improvements of 5.7 and 6.8 F1 scores, respectively.
Issue: 能够让LLM较好的执行OpenIE需要找到合适的demonstrations来提供任务相关的information。作者发现,ChatGPT习惯输出的text和实际的real text之间存在syntactic discrepancy,并且这种差异和GPT预测性能有关:
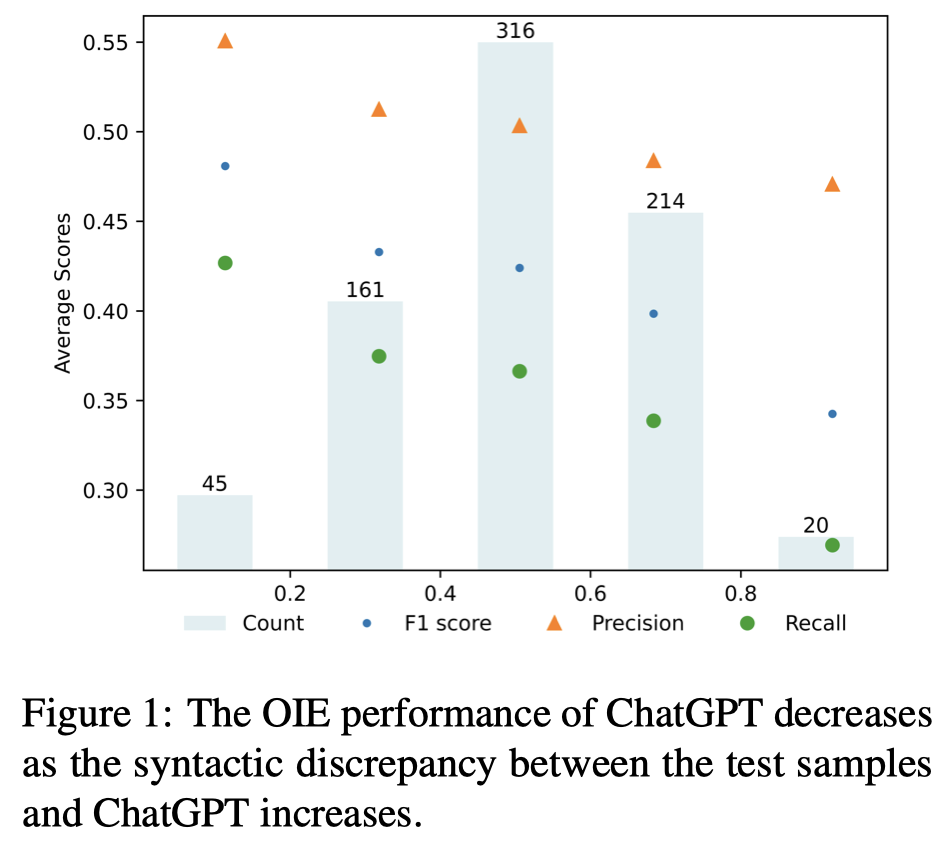
Solution:作者提出在选择demonstrations应该更倾向于选择和query的discrepancy较小的示例。
作者评估ChatGPT和test samples之间的discrepancy的方法是,首先选择\(k\)个测试样例\(S=\{ (x_i,y_i) \}^k\),对于每个测试样例\(x_i\),先人工改写,获得\(m\)个相同语义不同expression的source clique集合: \[ \{ C_i | C_i = (x_i^0,x_i^1,\dots,x_i^m,y_i) \} \] 随后,对于source clique集合中的每个人工改写的表达,利用LLM继续改写,获得target clique集合: \[ \{ C_i^\prime | C_i^\prime = (x_i^{\prime0},x_i^{\prime1},\dots,x_i^{\prime m},y_i) \} \] 下面是改写用的prompt:

最后,作者利用ROBUST benchmark中同样使用的Hierarchically Weighted Syntactic (HWS) distance来衡量每一个source clique中的sentence和target clique中每一个sentence的syntactic discrepancy(除了不和自身经过LLM改写后的sentence比较):
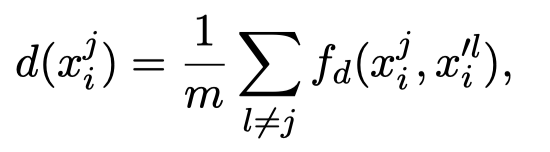
公式中的\(f_d(\cdot)\)就是计算HWS函数。下面是HWS指标计算说明(在Syntactically Robust Training on Partially-Observed Data for Open Information Extraction. EMNLP 2022 Findings中提出):

根据作者发现的discrepancy差异和performance之间的联系,作者使用了一种简单的选择示例的方法,对于query,计算和所有示例的HWS距离,然后归一化,再使用其逆值作为被选中的概率。这样能够倾向于选择差异最小的demonstrations。同时,考虑到如果总是只选择差异最小的样例,不一定能能够带来最多的效果提升。
作者利用gpt-3.5-turbo在CaRB上的效果:
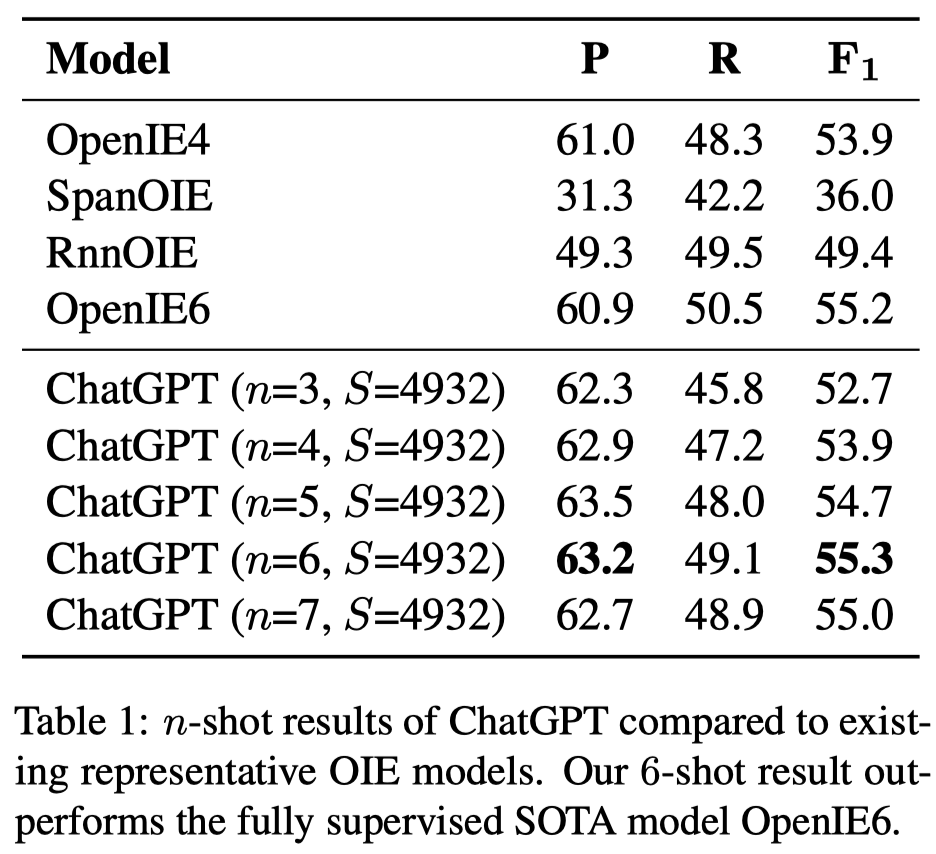
达到了和OpenIE6一样的效果。
另外,作者还尝试了在close-world RE上的效果,不过评估不够全面和鲁棒,在仅仅评测了500个测试样例,和使用20000个候选示例集的情况下,还没有超越之前的有监督小模型:

Uncertainty Demonstration
Improving Open Information Extraction with Large Language Models: A Study on Demonstration Uncertainty. Emory University, arXiv 2024. 代码.
Open Information Extraction (OIE) task aims at extracting structured facts from unstructured text, typically in the form of (subject, relation, object) triples. Despite the potential of large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT as a general task solver, they lag behind state-of-the-art (supervised) methods in OIE tasks due to two key issues. First, LLMs struggle to distinguish irrelevant context from relevant relations and generate structured output due to the restrictions on fine-tuning the model. Second, LLMs generates responses autoregressively based on probability, which makes the predicted relations lack confidence. In this paper, we assess the capabilities of LLMs in improving the OIE task. Particularly, we propose various in-context learning strategies to enhance LLM’s instructionfollowing ability and a demonstration uncertainty quantification module to enhance the confidence of the generated relations. Our experiments on three OIE benchmark datasets show that our approach holds its own against established supervised methods, both quantitatively and qualitatively. The code and data can be found at: https://github.com/lingchen0331/demonstration_uncertainty.
作者采用了多轮对话的形式进行OIE
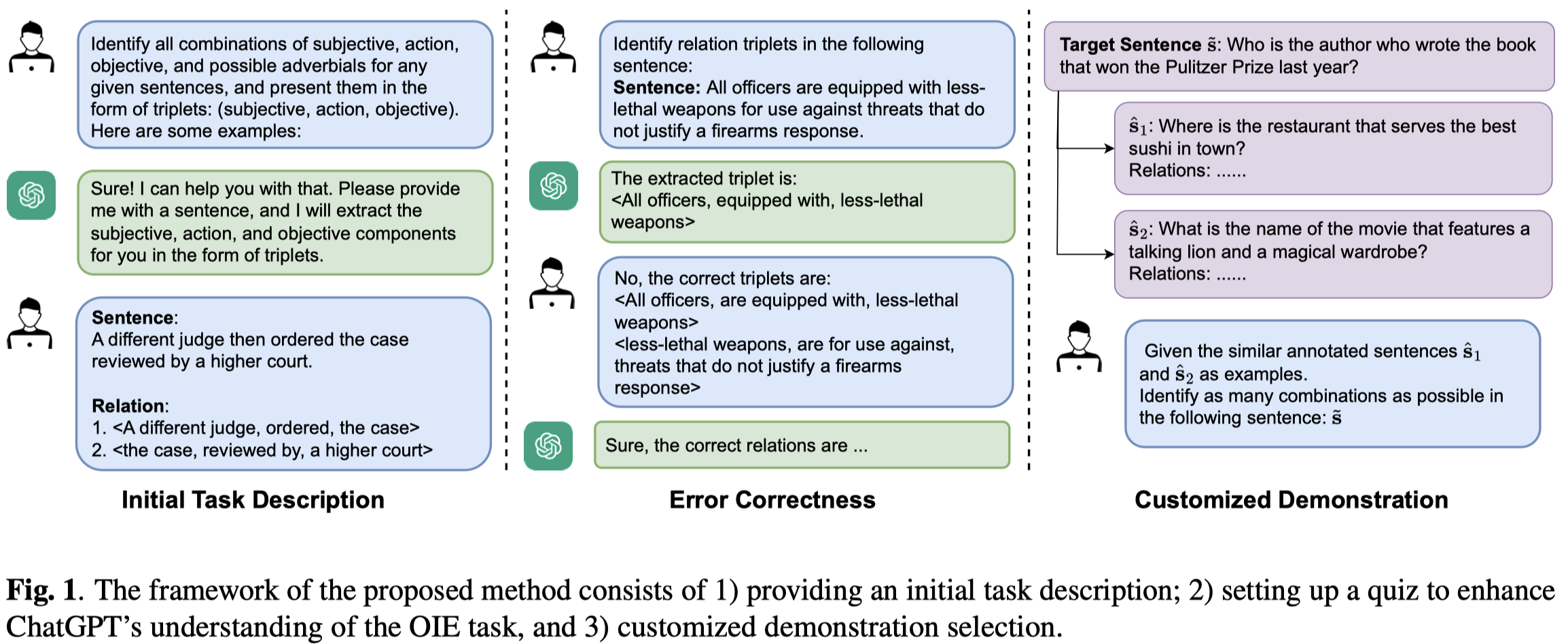
主要创新点在于如何找demonstrations,作者提出可以计算样例的不确定性,论文里讲的比较模糊,个人理解是迭代地检查每个样例作为上下文示例时,出现的结果在所有样例作为上下文时结果中出现次数的占比?然后过滤掉不确定性大的demonstrations。
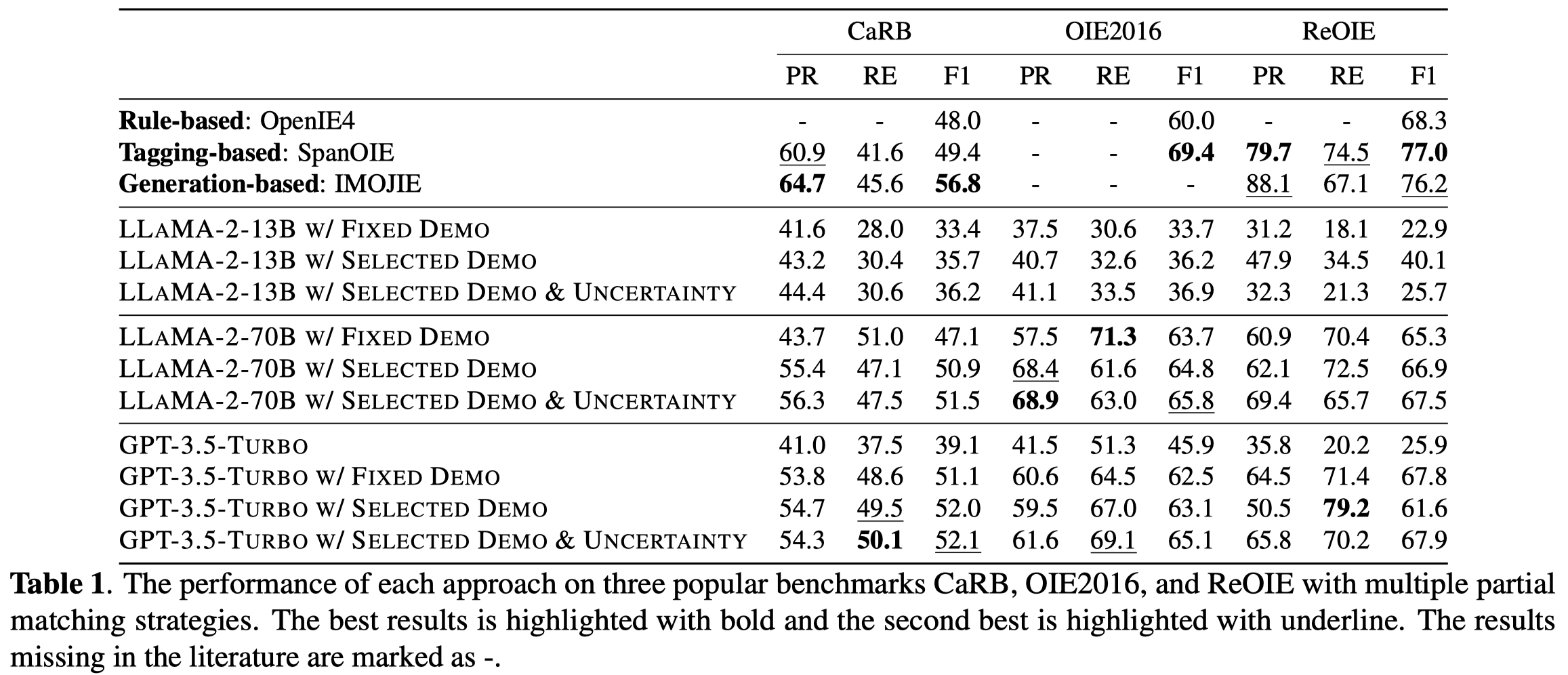
实验结果: