NLP4P-Collection
NLP4P
和LLM-based programing相关的论文
NLP4P survey
A Survey on Natural Language Processing for Programming. 哈工大-北航. LREC-COLING 2024
Natural language processing for programming aims to use NLP techniques to assist programming. It is increasingly prevalent for its effectiveness in improving productivity. Distinct from natural language, a programming language is highly structured and functional. Constructing a structure-based representation and a functionality-oriented algorithm is at the heart of program understanding and generation. In this paper, we conduct a systematic review covering tasks, datasets, evaluation methods, techniques, and models from the perspective of the structure-based and functionality-oriented property, aiming to understand the role of the two properties in each component. Based on the analysis, we illustrate unexplored areas and suggest potential directions for future work.
Natural language processing for programming(NLP4P)值得研究的原因:
- 减小编程工作量,比如自动创建文档等
- 帮助非专业用户提升效率,自然语言更加抽象和贴近人类思考的逻辑
这篇survey,认为编程语言有两类特征:structure-based和functionality-oriented:
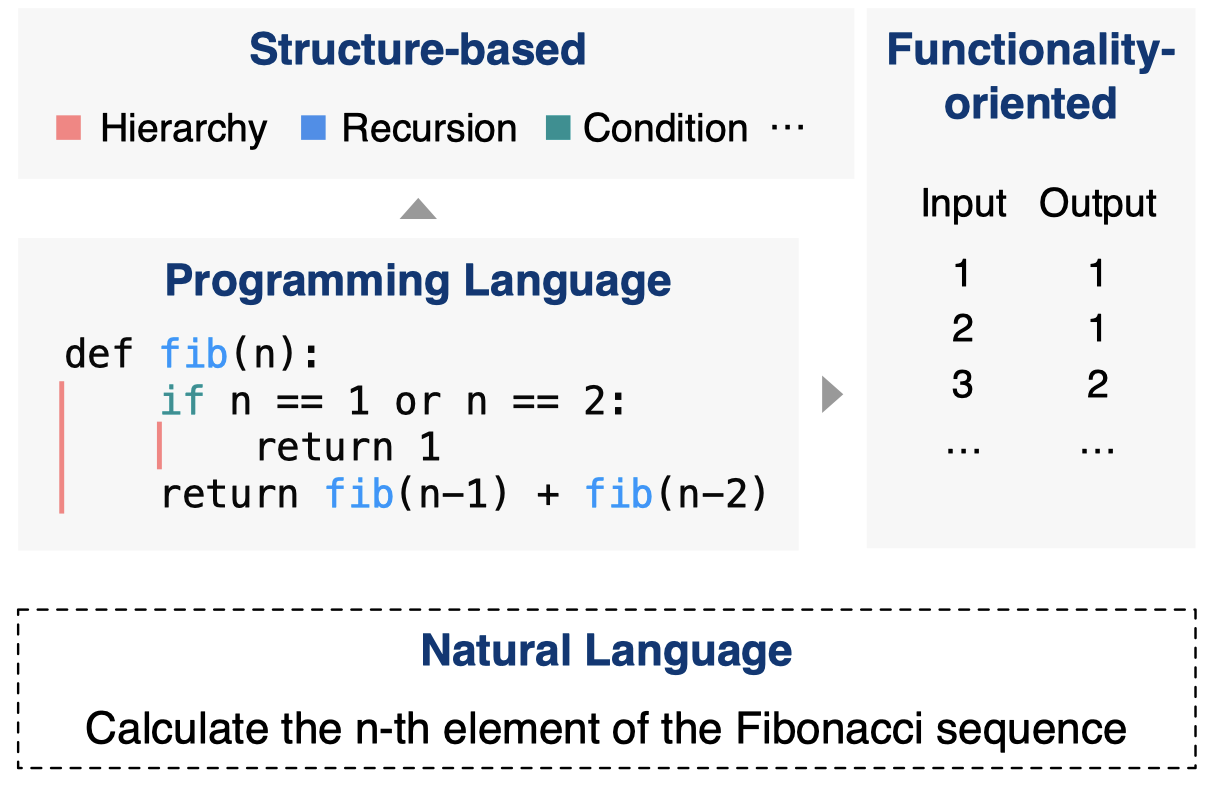
根据这两类属性,划分相关任务,前一类特征更加倾向于对代码的理解,后一类特征更加倾向代码的生成。
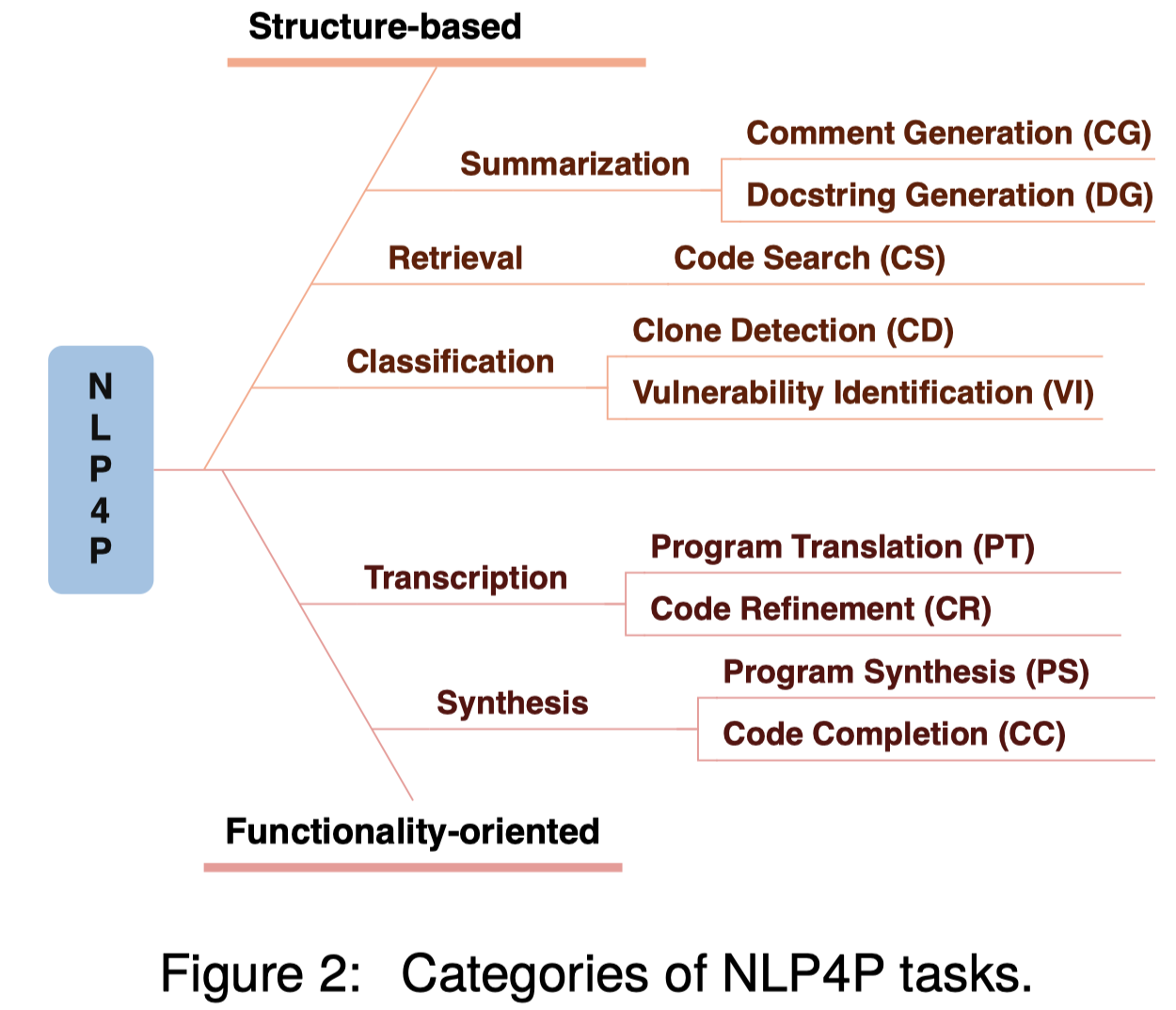
vulnerability identification是指漏洞识别。
program synthesis和code completion的区别不太大;synthesis更强调生成一个相对独立的输出,比如function;而completion就比较灵活,可以是小的token也可以是code snippets。现在这两个任务实质上没有本质区别。
program translation aims to convert between high-level PL, e.g., C++ and Java (Zhu et al., 2022).
Code refinement aims to convert a buggy program into correct one (Wang et al., 2021)
任务的评估方法,如果输出是NL自然语言,就使用n-gram、BLEU、ROUGE这种自动评估方法结合人工评估。
如果输出是PL编程语言,有两类评估方法:Reference based Evaluation和Test Case based Evaluation。Reference based Evaluation是结合了code特征的NL自动评估方法,比如CodeBLEU。
Test Case based Evaluation是评估生成程序的测试样例通过率。
- Test Case Average computes the average test case pass rate over all samples
- Strict Accuracy is a relatively rigorous metric. A program is regarded as accepted if and only if it passes all test cases, and the final Strict Accuracy is the ratio of accepted programs.由于可以生成多个程序,因此有指标:
p@K:对某一问题,生成K个program,其中存在某个program通过了所有的测试样例的概率n@K:对某一问题,生成K个program,然后提交n个program,能够通过测试的概率
GenLine
Discovering the Syntax and Strategies of Natural Language Programming with Generative Language Models. CHI 2024.
In this paper, we present a natural language code synthesis tool, GenLine, backed by 1) a large generative language model and 2) a set of task-specifc prompts that create or change code. To understand the user experience of natural language code synthesis with these new types of models, we conducted a user study in which participants applied GenLine to two programming tasks. Our results indicate that while natural language code synthesis can sometimes provide a magical experience, participants still faced challenges. In particular, participants felt that they needed to learn the model’s “syntax,” despite their input being natural language. Participants also struggled to form an accurate mental model of the types of requests the model can reliably translate and developed a set of strategies to debug model input. From these fndings, we discuss design implications for future natural language code synthesis tools built using large generative language models.
作者设计的GenLine工具
CoPrompt
CoPrompt: Supporting Prompt Sharing and Referring in Collaborative Natural Language Programming. CHI 2024.
Natural language (NL) programming has become more approachable due to the powerful code-generation capability of large language models (LLMs). This shift to using NL to program enhances collaborative programming by reducing communication barriers and context-switching among programmers from varying backgrounds. However, programmers may face challenges during prompt engineering in a collaborative setting as they need to actively keep aware of their collaborators’ progress and intents. In this paper, we aim to investigate ways to assist programmers’ prompt engineering in a collaborative context. We first conducted a formative study to understand the workflows and challenges of programmers when using NL for collaborative programming. Based on our findings, we implemented a prototype, CoPrompt, to support collaborative prompt engineering by providing referring, requesting, sharing, and linking mechanisms. Our user study indicates that CoPrompt assists programmers in comprehending collaborators’ prompts and building on their collaborators’ work, reducing repetitive updates and communication costs.
作者设计了CoPrompt原型来支持协同编程:

ANPL
ANPL: Towards Natural Programming with Interactive Decomposition. NeurIPS 2023. 中科院. 代码.
Though LLMs are capable of generating plausible programs, it’s challenging to interact with the LLMs further to revise the program, especially if the user’s specific requirements are different from the initial proposal. In this paper, we introduce ANPL, an interactive programming system that ensures users can always refine the generated code towards their specific programmatic intents via structured decompositions. Borrowing the paradigm of sketching from program synthesis, an ANPL program consists of a set of input-outputs that it must satisfy, a “sketch” — control/data flow expressed in precise code (e.g. Python), and “holes” — submodules to be implemented by the LLM specified with natural language. The user revises an ANPL program by either modifying the sketch, changing the language used to describe the holes, or providing additional input-outputs to a particular hole, turning it into a sub-ANPL program that can be solved recursively. This workflow allows the users to offload programming burdens to the LLM as much as possible while retaining the ability to pinpoint and resolve bugs locally, without exposing the rest of the program to the LLM. We deploy ANPL on the Abstraction and Reasoning Corpus (ARC), a set of unique tasks that are challenging for state-of-the-art AI systems, showing it outperforms baseline programming systems that (a) without the ability to decompose tasks interactively and (b) without the guarantee that the modules can be correctly composed together. Additional evaluations on APPS, HumanEval, and real-world programming tasks have validated that the ANPL framework is applicable to multiple programming domains. We release the ANPL solutions to the ARC tasks as a dataset, providing insights into how humans decompose novel tasks programmatically.
Issue:使用LLM生成代码是很难一次性生成理想的code的,在软件开发过程中,代码不是第一次写好就行的,需要持续的改进/测试、debuging。如何让LLM更好的服务人进行后续的editing和debugging仍然需要研究。
Solution:人类往往有某个solution的通用解法,而更不擅长实现program的detail。因此作者提出对program进行分解,让用户使用PL定义sketch来描述data flow,然后分解的子任务holes用NL描述,交给LLM来实现;持续改进的时候,用户只需要改进每个hole对应的自然语言即可。
- A sketch is the control/data flow connecting different holes, specified with a programmatic language. Users constitute the sketch by assigning names to variables and using them as hole parameters in a data flow graph. 实质上是对任务的分解,有人来写
- A hole implements a function module with a natural language description, which will be fleshed out by LLMs during the compiling process. 具体子任务的实现,由LLM实现
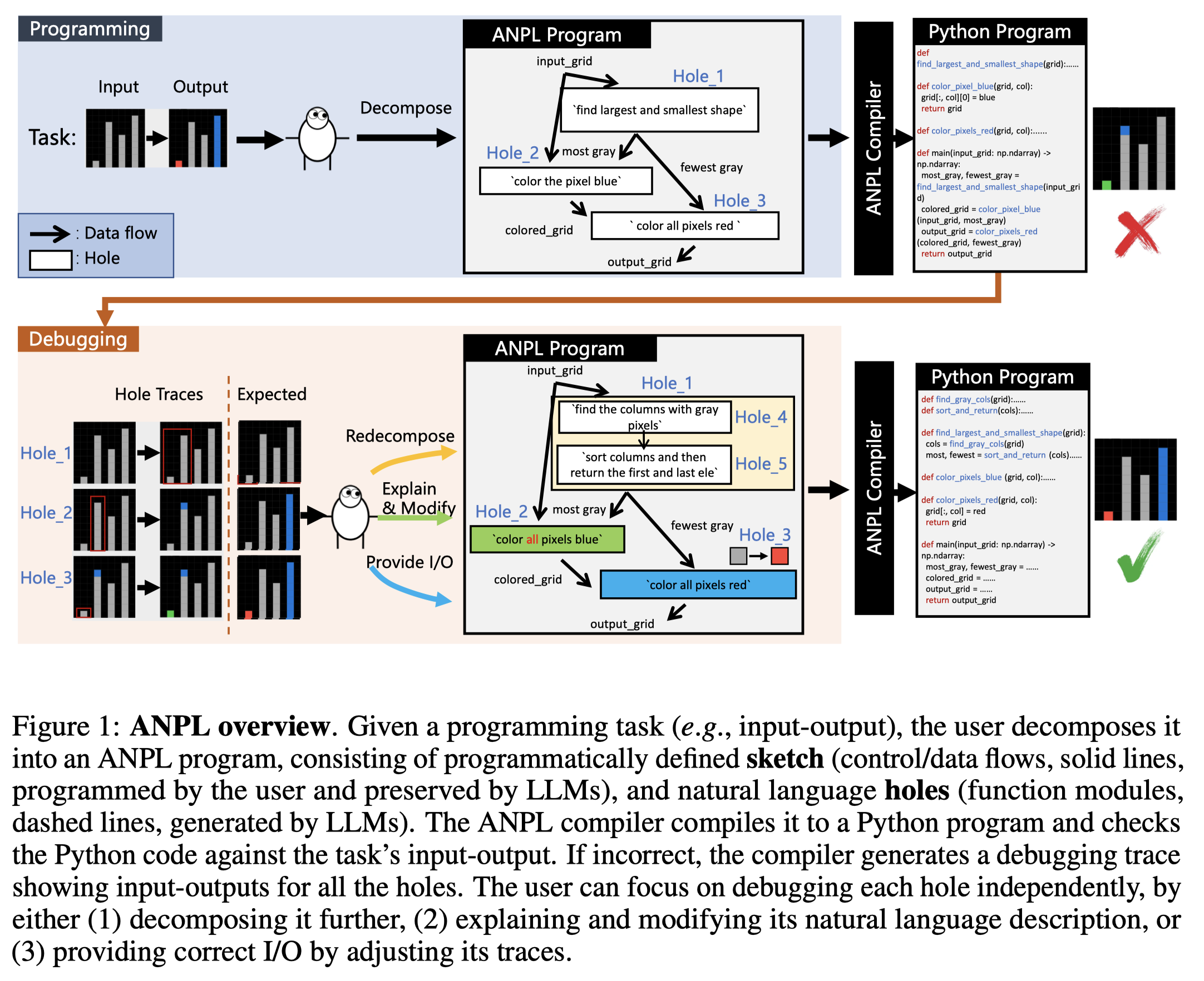
下面是一个例子:

上面自然语言描述的部分就是hole,需要LLM进行填充;下面是填充使用的prompt:

研究的语言是python,使用GPT-3.5。
Grounded Abstraction Map
“What It Wants Me To Say”: Bridging the Abstraction Gap Between End-User Programmers and Code-Generating Large Language Models. CHI 2023. Microsoft Research.
Code-generating large language models map natural language to code. However, only a small portion of the infinite space of naturalistic utterances is effective at guiding code generation. For non-expert end-user programmers, learning this is the challenge of abstraction matching. We examine this challenge in the specific context of data analysis in spreadsheets, in a system that maps the user’s natural language query to Python code using the Codex generator, executes the code, and shows the result. We propose grounded abstraction matching, which bridges the abstraction gap by translating the code back into a systematic and predictable naturalistic utterance. In a between-subjects, think-aloud study (n=24), we compare grounded abstraction matching to an ungrounded alternative based on previously established query framing principles. We find that the grounded approach improves end-users’ understanding of the scope and capabilities of the code-generating model, and the kind of language needed to use it effectively.
Issue: 使用自然语言的好处:
- Programming languages are an extremely powerful form of user interface. They also happen to be extremely difficult to learn, especially for non-expert end-user programmers who lack training in computing [48]. Natural language is already known to the user, and ostensibly requires little conscious investment of effort or learning.
- Natural language (NL) has been seen as an attractive mode of programming due to its (perceived) lower learning requirements.
作者认为使用自然语言,然后让LLM生成对应的code存在抽象匹配abstraction matching问题:
In this paper, we consider the specific problem of abstraction matching [95]: when the user has a well-formed intent, how do they select an utterance from the near infinite space of naturalistic utterances that they believe the system will reliably map to a satisfactory solution?
This involves “matching” the utterance to the right level of “abstraction”, by specifying the utterance at a level of granularity and detail that matches the set of actions the system can take, and selecting suitable words and grammar.
NL的表达空间是无限的,到底要表达到哪种抽象程度,使用何种语法或单词才能够让LLM生成预期的code。
以前的方法主要有showing example commands 使用示例, teaching users techniques such as breaking down their problem分解问题, operating with a restricted vocabulary and grammar [77]使用有限的词库和语法, and incorporating other interface elements (e.g., graphical menus) 或者加入更多的交互元素to help users formulate their query. 但是这些方法都存在问题:
examples are not necessarily reflective of user interests and do not help the user generalize to a wider range of utterances 样例不一定反映了user的interestes并且泛用性差, tutorials take time教导用户需要额外事件, and restricted grammar reduces user flexibility有限的词库或语法会限制灵活性.
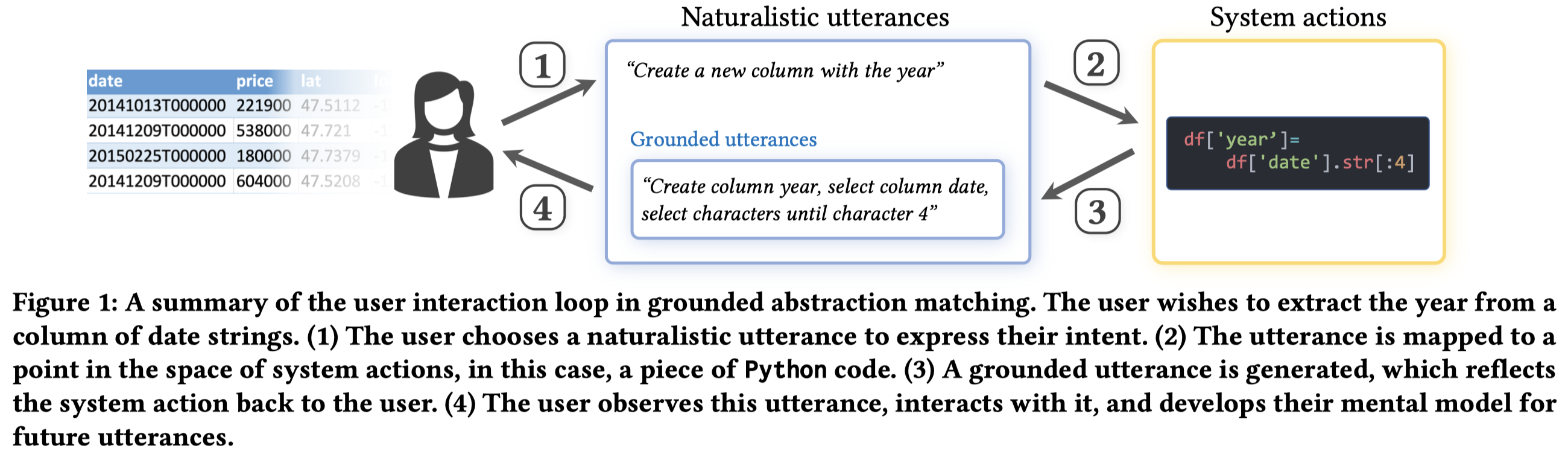
Solution:作者的方法是使用grounded abstraction matching
An interface supports grounded abstraction matching if the user’s naturalistic utterance is mapped to a system action, and then mapped back to a naturalistic utterance that is an editable example of how to consistently invoke the same action. This gives a grounded example of the level of abstraction at which the system expresses its solutions.
思想示意图:
系统架构图:
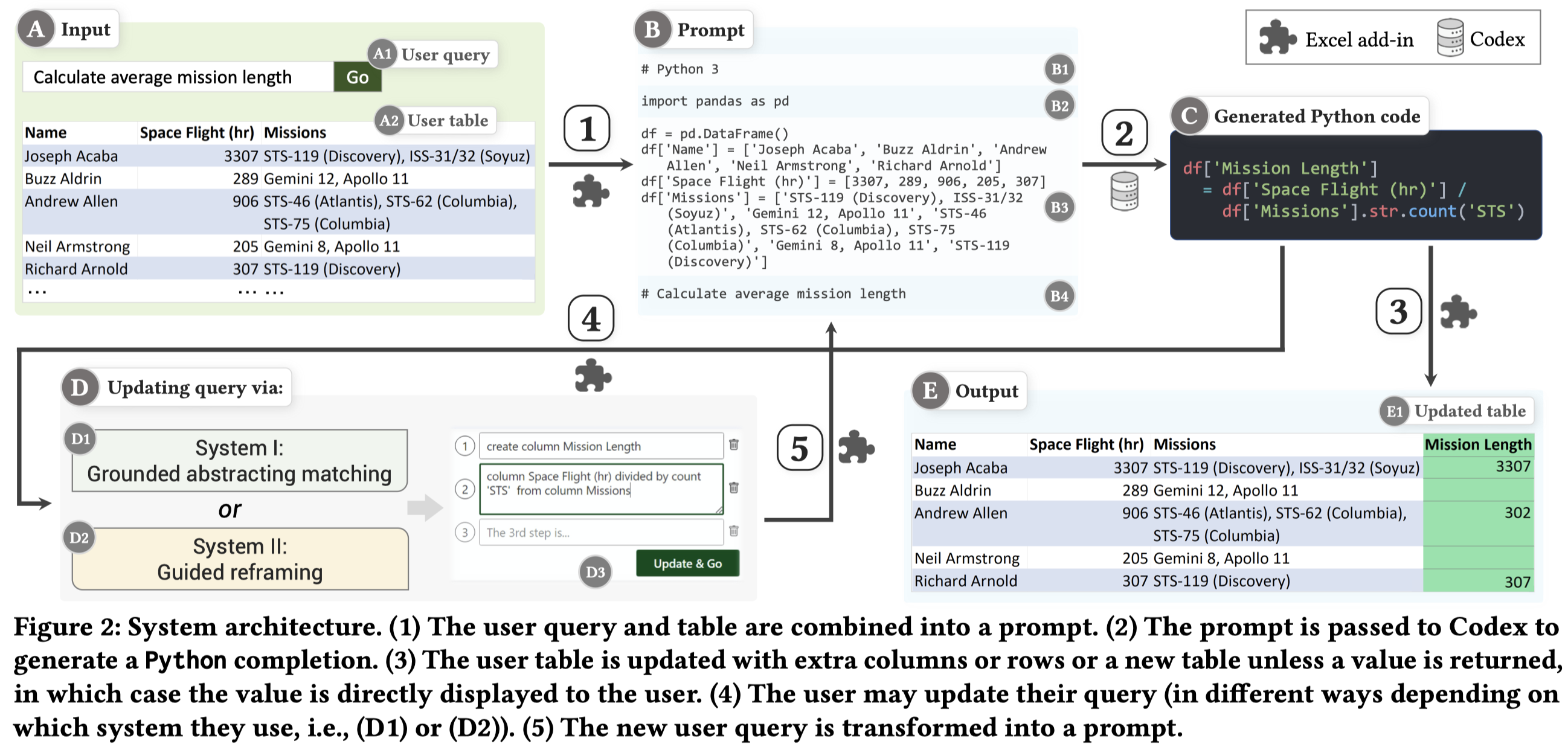
实验主要以对表格的操作进行探究,使用python、pandas的代码。
AssistV
Learning Task Decomposition to Assist Humans in Competitive Programming. ACL 2024. 清华
When using language models (LMs) to solve complex problems, humans might struggle to understand the LM-generated solutions and repair the flawed ones. To assist humans in repairing them, we propose to automatically decompose complex solutions into multiple simpler pieces that correspond to specific subtasks. We introduce a novel objective for learning task decomposition, termed assistive value (AssistV), which measures the feasibility and speed for humans to repair the decomposed solution. We collect a dataset of human repair experiences on different decomposed solutions. Utilizing the collected data as in-context examples, we then learn to critique, refine, and rank decomposed solutions to improve AssistV. We validate our method under competitive programming problems: under 177 hours of human study, our method enables non-experts to solve 33.3% more problems, speeds them up by 3.3x, and empowers them to match unassisted experts.
Issue:LMs might fail to provide reliable solutions for these problems, but it is also difficult for humans to evaluate and improve LMs’ solutions due to therequired significant time and expertise.
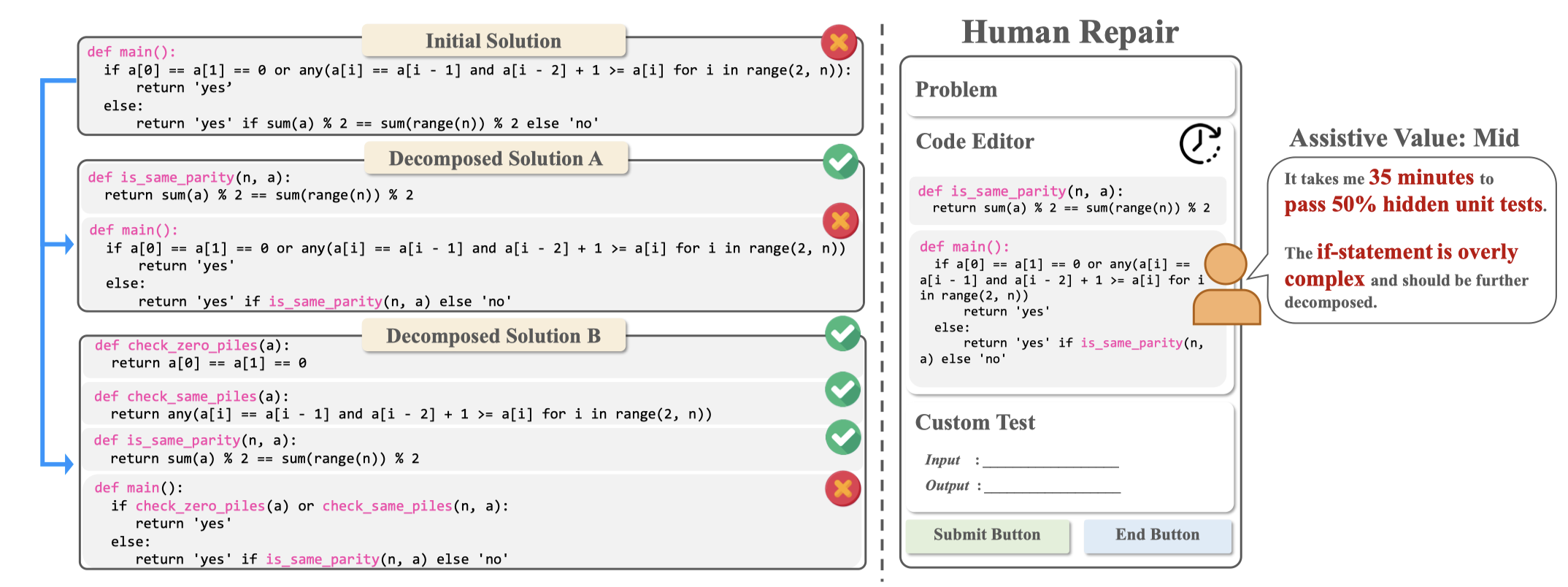
Solution: 通过将复杂的solution分解更加小的solution,让人快速理解和改进。但是如何分解是个难题。作者人工收集了一个关于分解的dataset,利用人工判断某个分解方案是否有用。作者提出了一个新的指标AssistV来评估任务分解帮助人类更快修复的质量:

作者的实验是通过雇佣了30个程序员(11 experts and 19 nonexperts)通过修复LM生成的solution来解决编程问题。
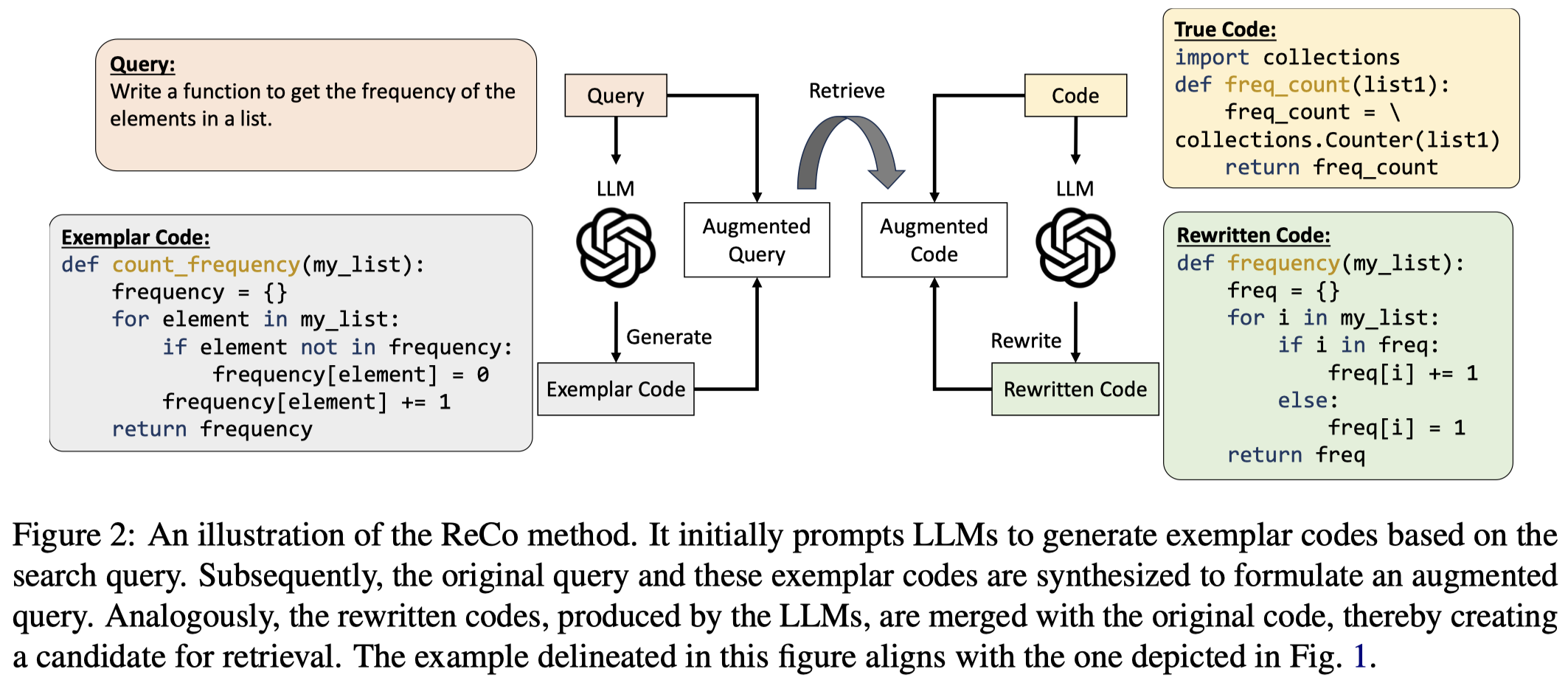
ReCo
Rewriting the Code: A Simple Method for Large Language Model Augmented Code Search. 南洋理工. 代码.
In code search, the Generation-Augmented Retrieval (GAR) framework, which generates exemplar code snippets to augment queries, has emerged as a promising strategy to address the principal challenge of modality misalignment between code snippets and natural language queries, particularly with the demonstrated code generation capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs). Nevertheless, our preliminary investigations indicate that the improvements conferred by such an LLM-augmented framework are somewhat constrained. This limitation could potentially be ascribed to the fact that the generated codes, albeit functionally accurate, frequently display a pronounced stylistic deviation from the ground truth code in the codebase. In this paper, we extend the foundational GAR framework and propose a simple yet effective method that additionally Rewrites the Code (ReCo) within the codebase for style normalization. Experimental results demonstrate that ReCo significantly boosts retrieval accuracy across sparse (up to 35.7%), zero-shot dense (up to 27.6%), and fine-tuned dense (up to 23.6%) retrieval settings in diverse search scenarios. To further elucidate the advantages of ReCo and stimulate research in code style normalization, we introduce Code Style Similarity, the first metric tailored to quantify stylistic similarities in code. Notably, our empirical findings reveal the inadequacy of existing metrics in capturing stylistic nuances. The source code and data are available at https://github.com/Alex-HaochenLi/ReCo.
Issue:对于query,LLM生成的exemplar code是正确的,但是和codebase中的true code在风格上存在差异。
Solution: 利用LLM改写code风格,改进检索性能
UniCode
UniCode: Scaling Code Large Language Model via Universal Code. ACL 2024. 代码. 北航
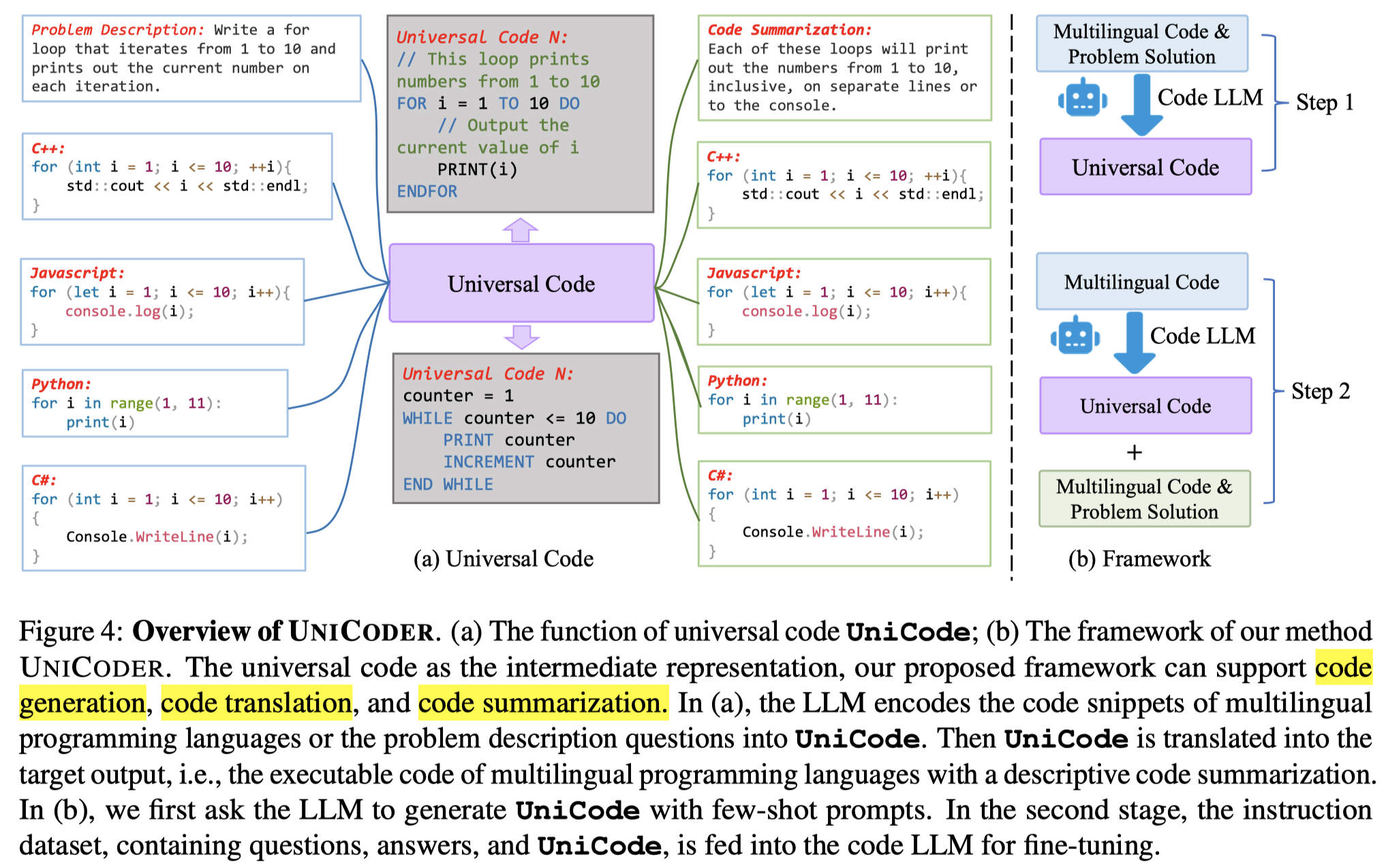
Intermediate reasoning or acting steps have successfully improved large language models (LLMs) for handling various downstream natural language processing (NLP) tasks. When applying LLMs for code generation, recent works mainly focus on directing the models to articulate intermediate natural-language reasoning steps, as in chain-of-thought (CoT) prompting, and then output code with the natural language or other structured intermediate steps. However, such output is not suitable for code translation or generation tasks since the standard CoT has different logical structures and forms of expression with the code. In this work, we introduce the universal code (UniCode) as the intermediate representation. It is a description of algorithm steps using a mix of conventions of programming languages, such as assignment operator, conditional operator, and loop. Hence, we collect an instruction dataset UniCode-Instruct to train our model UniCode on multi-task learning objectives. UniCode-Instruct comprises natural-language questions, code solutions, and the corresponding universal code. The alignment between the intermediate universal code representation and the final code solution significantly improves the quality of the generated code. The experimental results demonstrate that UniCode with the universal code significantly outperforms the previous prompting methods by a large margin, showcasing the effectiveness of the structural clues in pseudo-code.
利用某种通用的中间code表示能够减小不同PL之间的差异:
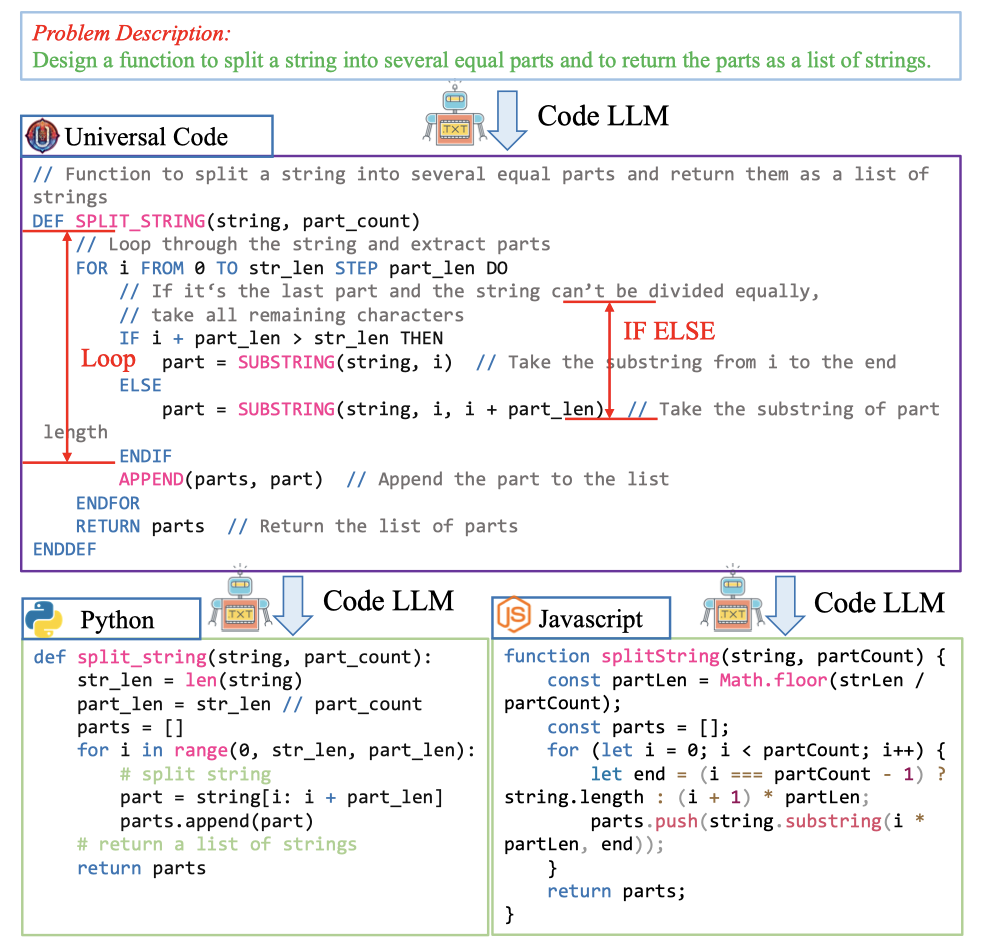
作者收集了140K的instruction-tuning数据集,来训练Code-Llama和DeepSeek-Coder-Base学会生成universal code。

VulLLM
Generalization-Enhanced Code Vulnerability Detection via Multi-Task Instruction Fine-Tuning. ACL 2024. 华中科技. 代码.
Code Pre-trained Models (CodePTMs) based vulnerability detection have achieved promising results over recent years. However, these models struggle to generalize as they typically learn superficial mapping from source code to labels instead of understanding the root causes of code vulnerabilities, resulting in poor performance in real-world scenarios beyond the training instances. To tackle this challenge, we introduce VulLLM, a novel framework that integrates multi-task learning with Large Language Models (LLMs) to effectively mine deep-seated vulnerability features. Specifically, we construct two auxiliary tasks beyond the vulnerability detection task. First, we utilize the vulnerability patches to construct a vulnerability localization task. Second, based on the vulnerability features extracted from patches, we leverage GPT-4 to construct a vulnerability interpretation task. VulLLM innovatively augments vulnerability classification by leveraging generative LLMs to understand complex vulnerability patterns, thus compelling the model to capture the root causes of vulnerabilities rather than overfitting to spurious features of a single task. The experiments conducted on six large datasets demonstrate that VulLLM surpasses seven state-of-the-art models in terms of effectiveness, generalization, and robustness.
Issue: 现有的利用Code Pre-trained Model进行漏洞检测的方法存在两个问题:
- existing approaches tend to capture superficial rather than in-depth vulnerability features when learning the mapping from source code to labels. 没有捕获深度features
- the learning paradigm via mapping from source code to labels struggles with the generalization ability when handling vulnerable code from multiple projects. 学习到的mappings不够泛用
Solution:LLM有很强的泛化能力,但是其也不能简单的直接在漏洞检测上表现出很好的效果。简单的直接微调同样会使得微调后的LLM出现上述两个问题。因此,作者引入了两个额外的训练任务:漏洞定位、漏洞Casue解释。这两个辅助任务强迫模型对于不同的输入,给定不同的输出,从而使model学会更加通用的解决方案和特征。
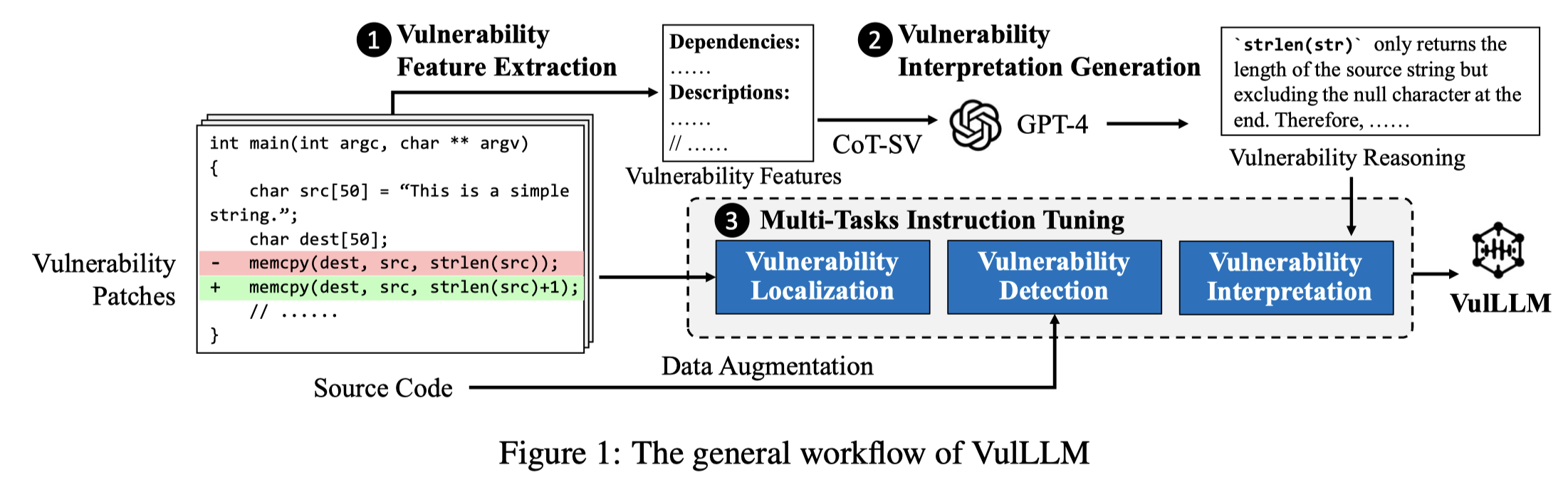
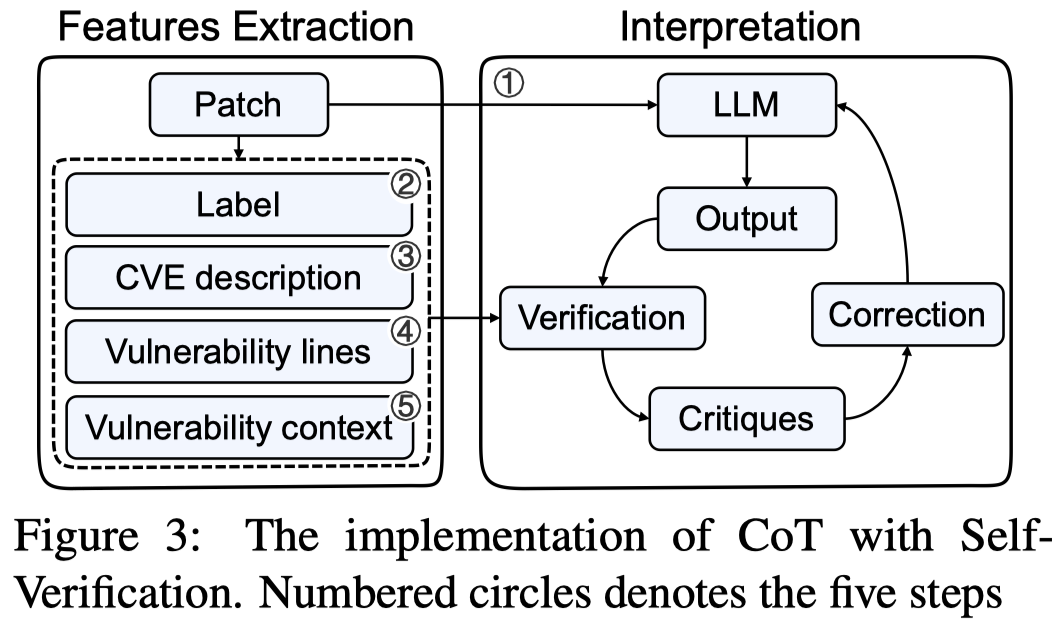
作者的指令数据构造利用最强大的GPT-4生成漏洞检测的解释和定位。
为了保证生成结果的正确性,引入了CoT-SV方法。细节参考论文。
作者在两块80G A800上微调Llama-2, CodeLlama, and StarCoder。都在20B参数以内。
Sense
Synthesizing Text-to-SQL Data from Weak and Strong LLMs. ACL 2024. 代码. 中科院
The capability gap between open-source and closed-source large language models (LLMs) remains challenging in text-to-SQL tasks. In this paper, we introduce a synthetic data approach that amalgamates strong data generated by larger, more potent models (strong models) with weak data produced by smaller, less wellaligned models (weak models). Our approach contributes to the improvement of domain generalization in text-to-SQL models and investigates the potential of weak data supervision through preference learning. Moreover, we utilize the synthetic data approach for instruction tuning on open-source LLMs, yielding S ENSE, a specialized text-to-SQL model. The effectiveness of S ENSE is substantiated by achieving state-of-the-art results on the SPIDER and BIRD benchmarks, thereby mitigating the performance disparity between open-source models and the methods derived from closed-source models.
Issue:目前闭源LLM比如GPT-4在text-to-SQL任务上已经取得了很好的效果。但是使用闭源LLM在开放性、隐私以及花费上都有问题the adoption of closedsource LLMs introduces concerns pertaining to issues of openness, privacy, and substantial costs.
Solution:作者期望通过微调开源LLM来使其能够达到闭源LLM的效果。
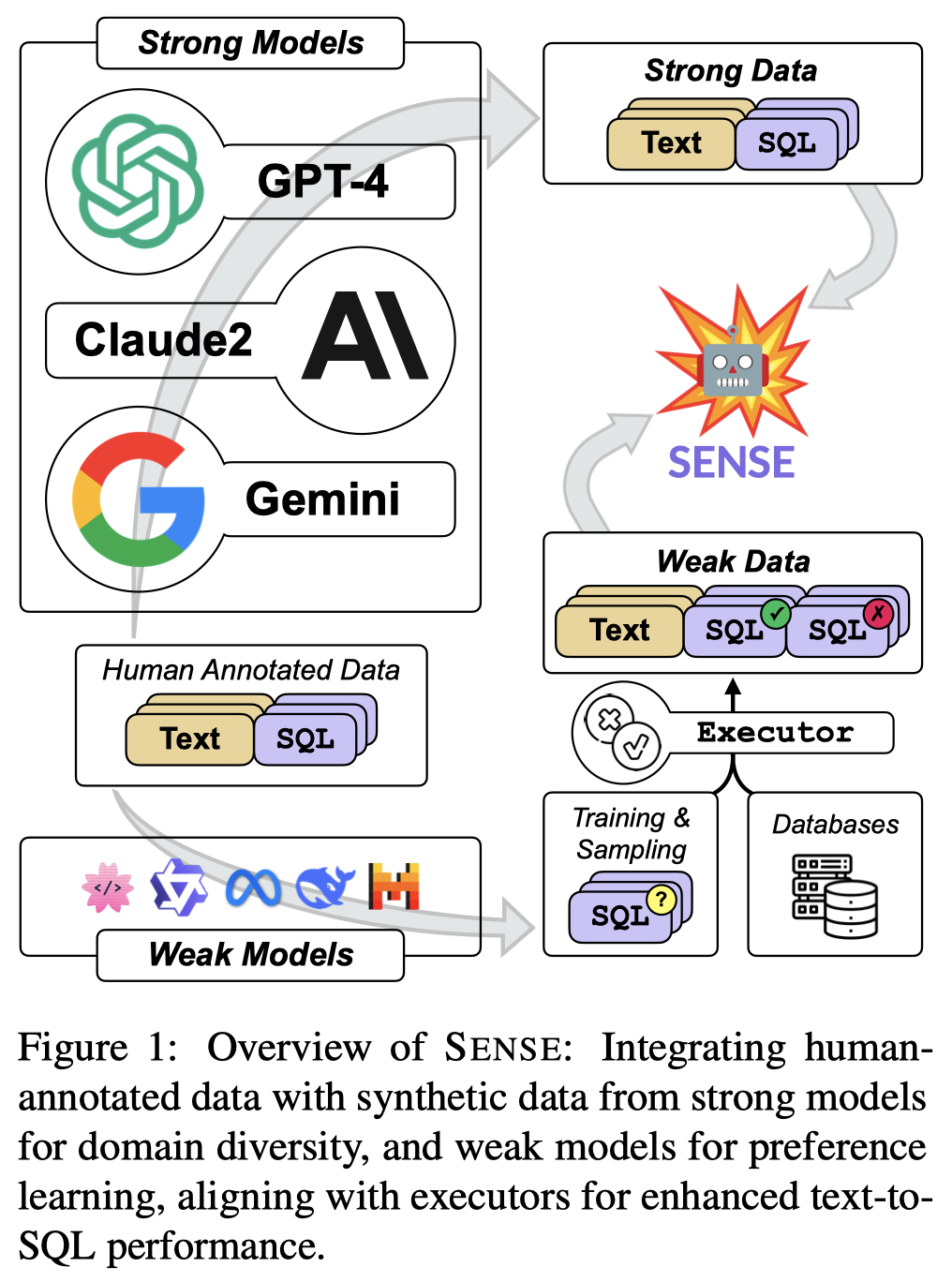
作者先是利用GPT-4来构造训练数据strong data,保证数据的多样性(不同领域、问题难度、排除重复的领域等操作)。在构造数据和已有人工数据上,监督微调开源LLM。
只使用strong data使得LLM反而不会分辨什么是错误的。GPT-4生成的结果往往是正确的。因此,作者利用效果比较差的开源LLM(DeepSeek-Coder-1.3B)来生成weak data。其中存在正确的和错误的数据。利用SQL执行器,判断生成的数据是positive还是negative,然后利用偏好学习DPO算法使得模型学会分辨正确和错误。
作者在CodeLLaMA-7B和CodeLLaMA13B上进行了微调,用到了8块 A100GPU。
TypeGen
Generative Type Inference for Python. 港中大. ASE 2023
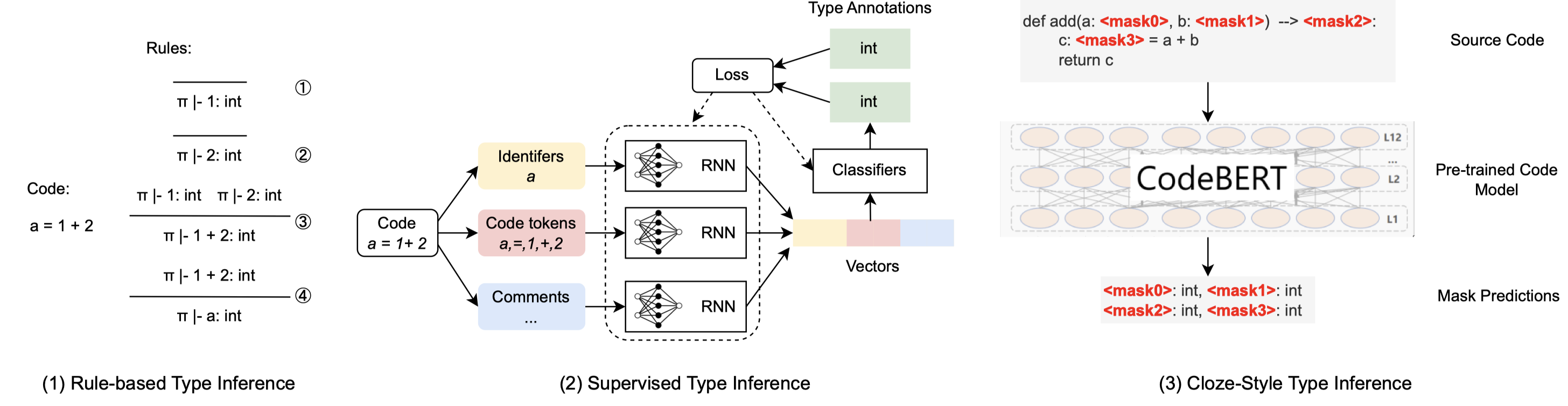
Python is a popular dynamic programming language, evidenced by its ranking as the second most commonly used language on GitHub. However, its dynamic type system can lead to potential type errors, leading researchers to explore automatic type inference approaches for Python programs. Existing type inference approaches can be generally grouped into three categories, i.e., rule-based, supervised, and cloze-style approaches. The rule-based type inference approaches can ensure the accuracy of predicted variable types, but they suffer from low coverage problems caused by dynamic features and external calls. Supervised type inference approaches, while feature-agnostic and able to mitigate the low coverage problem, require large, high-quality annotated datasets and are limited to pre-defined types. As zero-shot approaches, the cloze-style approaches reformulate the type inference problem into a fill-in-the-blank problem by leveraging the general knowledge in powerful pre-trained code models. However, their performance is limited since they ignore the domain knowledge from static typing rules which reflect the inference logic. What is more, their predictions are not interpretable, hindering developers’ understanding and verification of the results.
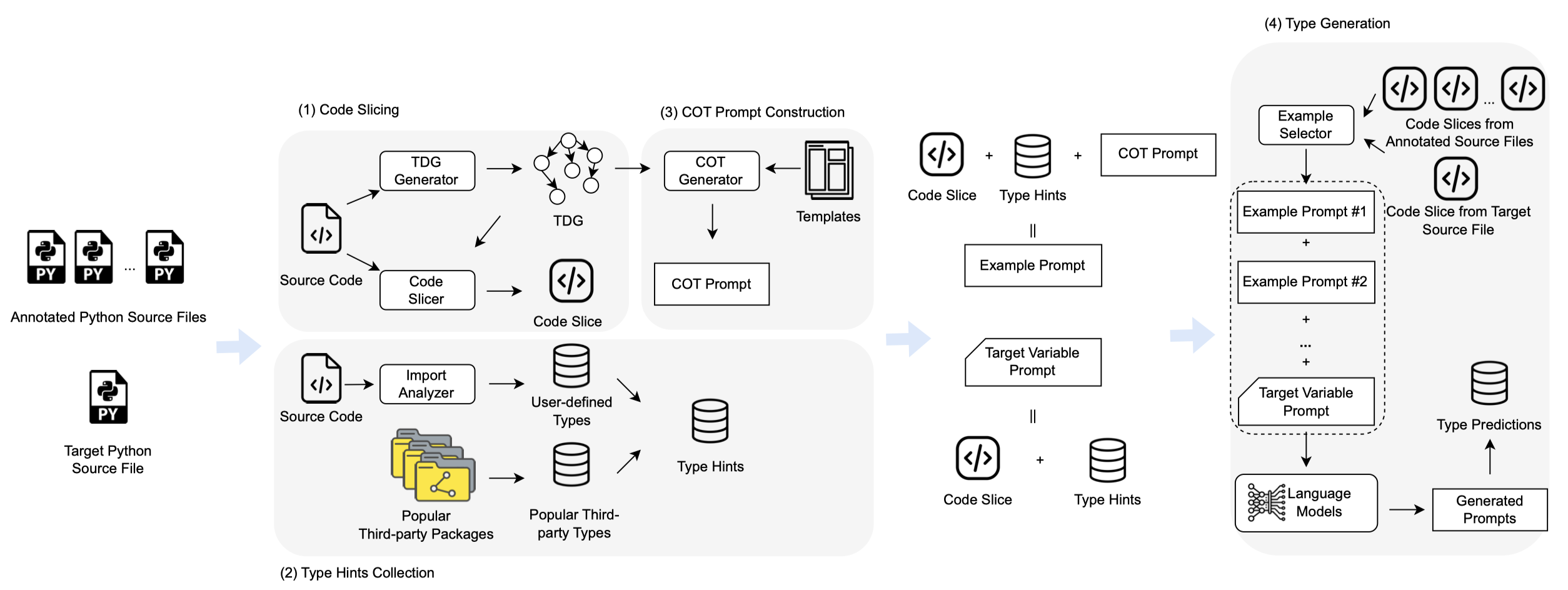
This paper introduces TypeGen, a few-shot generative type inference approach that incorporates static domain knowledge from static analysis. TypeGen creates chain-of-thought (COT) prompts by translating the type inference steps of static analysis into prompts based on the type dependency graphs (TDGs), enabling language models to learn from how static analysis infers types. By combining COT prompts with code slices and type hints, TypeGen constructs example prompts from human annotations. TypeGen only requires very few annotated examples to teach language models to generate similar COT prompts via in-context learning. Moreover, TypeGen enhances the interpretability of results through the use of the inputexplanation-output strategy, which generates both explanations and type predictions in COT prompts. Experiments show that TypeGen outperforms the best baseline Type4Py by 10.0% for argument type prediction and 22.5% in return value type prediction in terms of top-1 Exact Match by using only five examples. Furthermore, TypeGen achieves substantial improvements of 27% to 84% compared to the zero-shot performance of large language models with parameter sizes ranging from 1.3B to 175B in terms of top-1 Exact Match.
Issue: 作者认为以前的type prediction的方法存在的问题是:
- Lack of static domain knowledge
- Lack of interpretability
Solution: 作者的方法是利用Type Dependency Graphs来创建CoT prompt来辅助预测。
以前的几种type prediction方法:
作者输入的prompt:

方法:
Distilltion for Code Summarization
Distilled GPT for Source Code Summarization. ASE 2024 (期刊). University of Notre Dame
A code summary is a brief natural language description of source code. Summaries are usually only a single sentence long, and yet form the backbone of developer documentation. A short descriptions such as “changes all visible polygons to the color blue” can give a programmer a high-level idea of what code does without the effort of reading the code itself. Recently, products based on Large Language Models such as ChatGPT have demonstrated a strong ability to write these descriptions automatically. However, to use these tools, programmers must send their code to untrusted third parties for processing (e.g., via an API call). This loss of custody is not acceptable to many organizations. In this paper, we present an alternative: we train an open source model using sample output generated by GPT-3.5 in a process related to knowledge distillation. Our model is small enough (350m parameters) to be run on a single 16gb GPU, yet we show in our evaluation that it is large enough to mimic GPT-3.5 on this task.
Issue:利用闭源大模型进行code summarization存在的问题:
- 需要把code提供给第三方,这对于很多组织/公司是不实际的
- lack of reproducibility, potential data contamination from public test sets to private training data, and resultant loss of scientific rigor
Solution: 作者的做法就是利用GPT-3.5生成训练数据,然后蒸馏出更小的模型(jam和starcoder)。

作者评估的时候使用的指标:METEOR和USE。
DraCo
Dataflow-Guided Retrieval Augmentation for Repository-Level Code Completion. ACL 2024. 南大. 代码.
Recent years have witnessed the deployment of code language models (LMs) in various code intelligence tasks such as code completion. Yet, it is challenging for pre-trained LMs to generate correct completions in private repositories. Previous studies retrieve cross-file context based on import relations or text similarity, which is insufficiently relevant to completion targets. In this paper, we propose a dataflow-guided retrieval augmentation approach, called DraCo, for repository-level code completion. DraCo parses a private repository into code entities and establishes their relations through an extended dataflow analysis, forming a repo-specific context graph. Whenever triggering code completion, DraCo precisely retrieves relevant background knowledge from the repo-specific context graph and generates well-formed prompts to query code LMs. Furthermore, we construct a large Python dataset, ReccEval, with more diverse completion targets. Our experiments demonstrate the superior accuracy and applicable efficiency of DraCo, improving code exact match by 3.43% and identifier F1-score by 3.27% on average compared to the state-of-the-art approach.
Issue:以前的Repository-Level Code Completion方法没有能够检索到合适的相关信息:

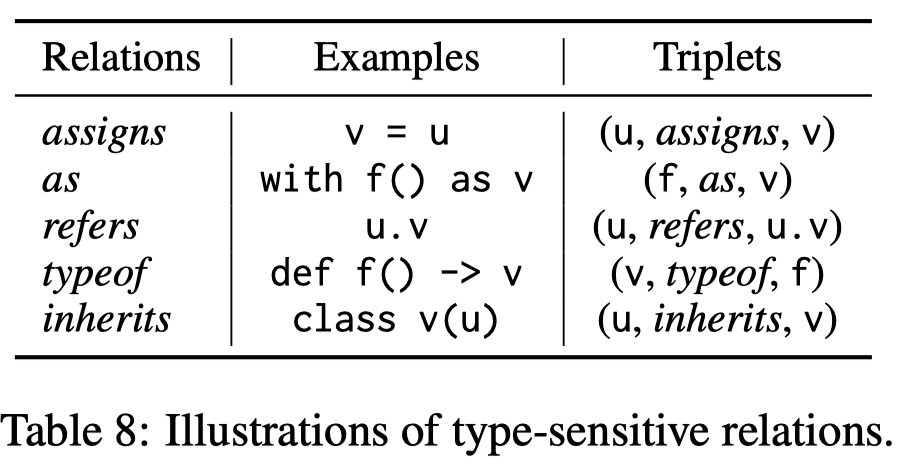
Solution:一个正常程序员会根据数据来源去检索对应的代码,因此作者为每个Repository都构造一个数据流图type-sensitive dependency relations,下面是作者定义的数据流图的relation,数据流图中的entity是code变量(包括标识符和属性)。

方法图:
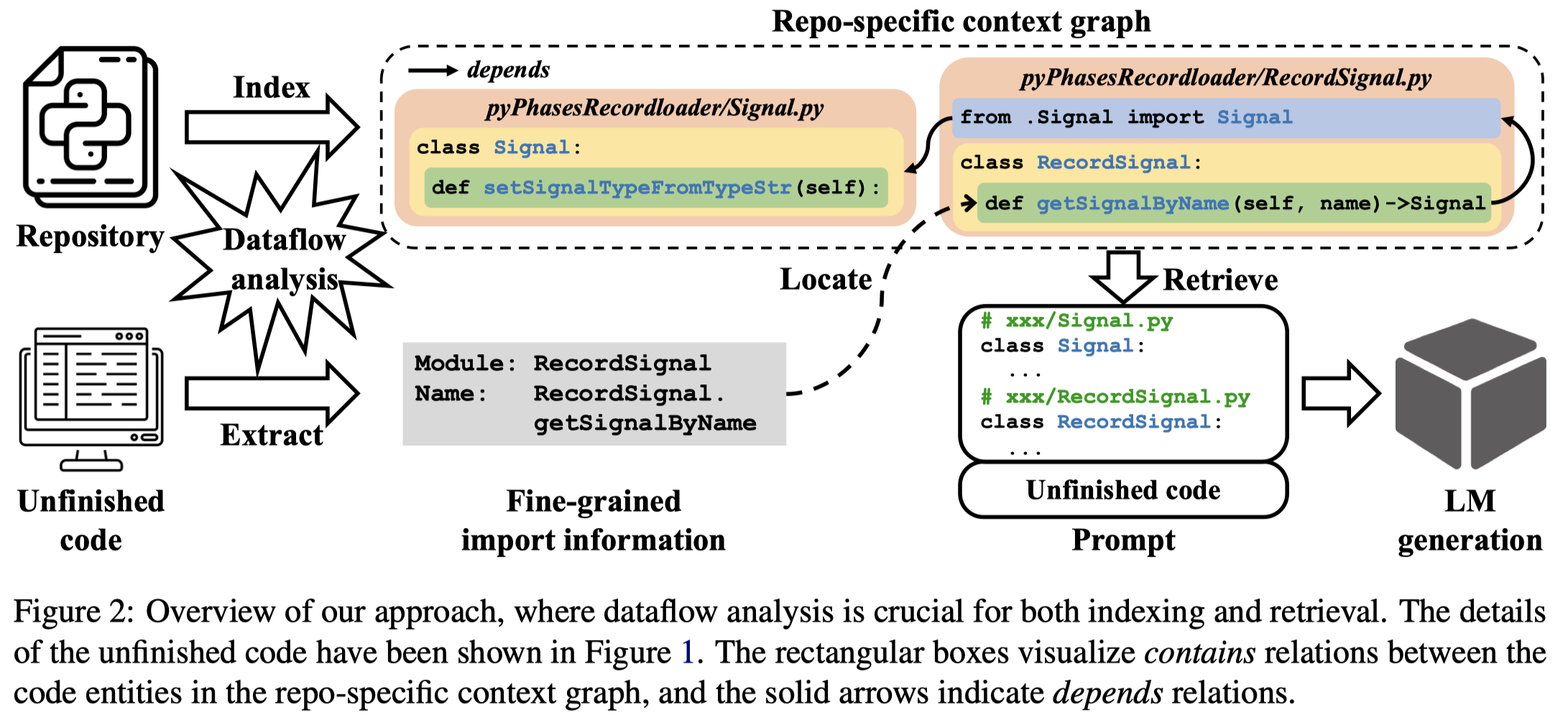
作者还自己构造了一个新的python评估数据集,ReccEval。代码补全的指标:

作者调用的LLM:
CodeAgent
CodeAgent: Enhancing Code Generation with Tool-Integrated Agent Systems for Real-World Repo-level Coding Challenges. 北大. ACL 2024
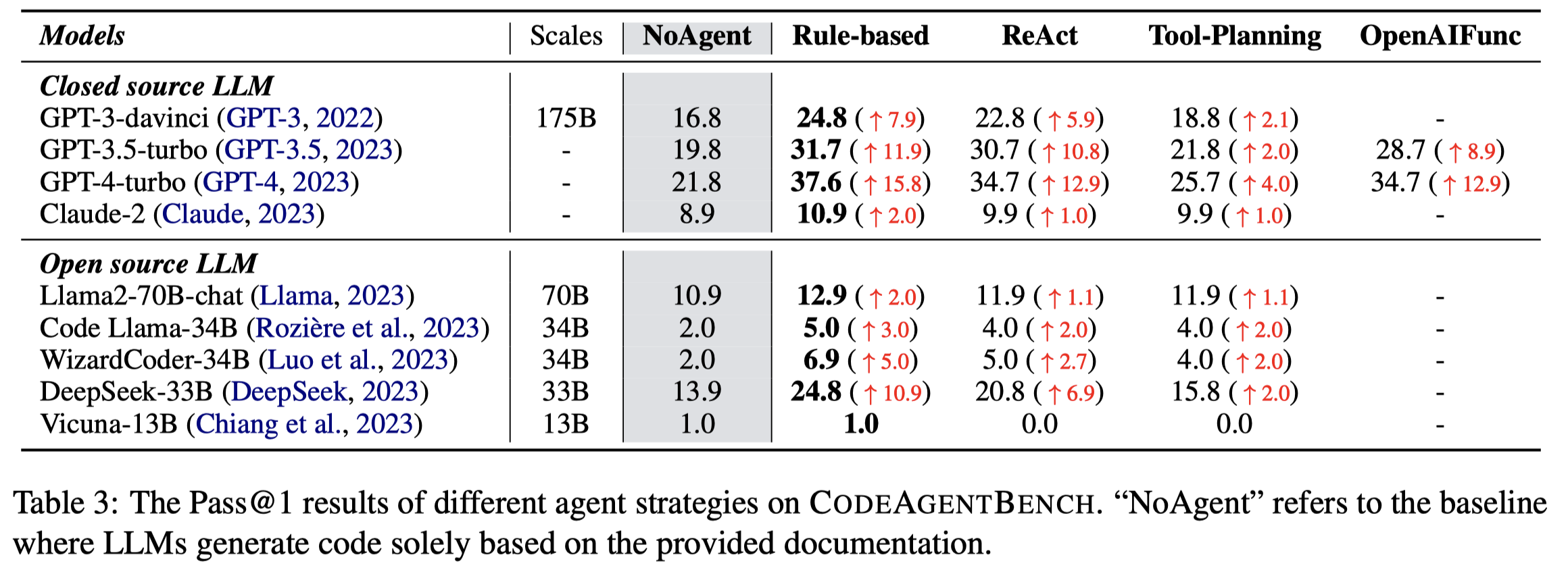
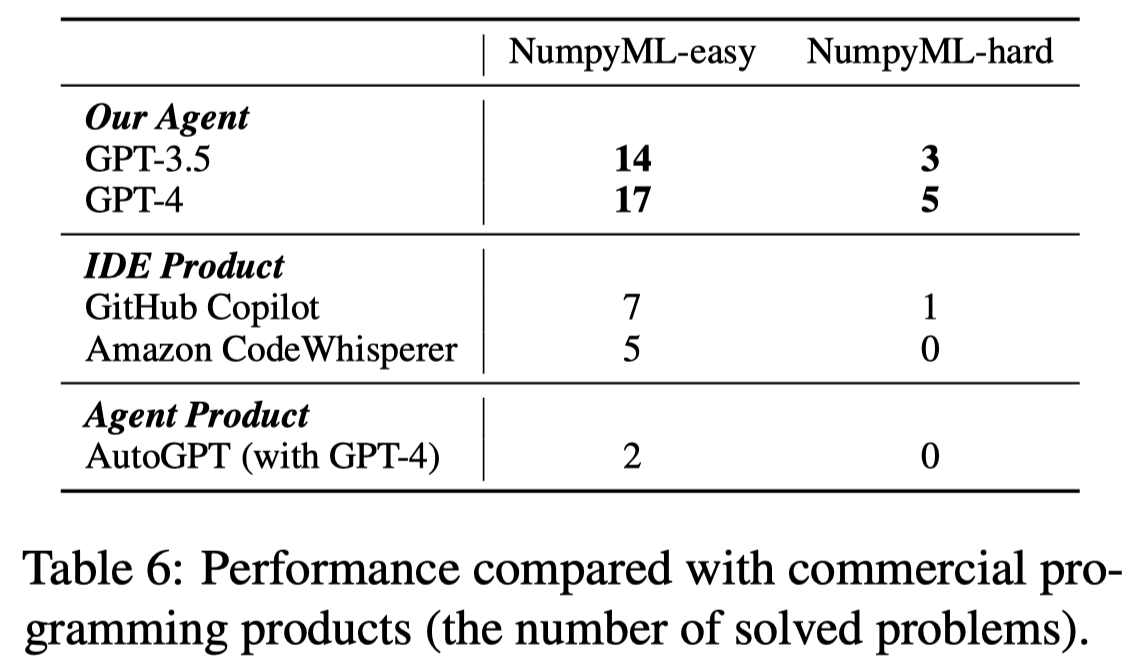
Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown promise in automated code generation but typically excel only in simpler tasks such as generating standalone code units. However, real-world software development often involves complex code repositories with complex dependencies and extensive documentation. To enable LLMs to handle these realworld repo-level code generation, we present CodeAgent a novel LLM-based agent framework that employs external tools for effective repo-level code generation. CodeAgent integrates five programming tools, enabling interaction with software artifacts for information retrieval, code implementation, and code testing. We implement four agent strategies to optimize these tools’ usage. To the best of our knowledge, CodeAgent is the first agent framework specifically for repolevel code generation. In order to measure the effectiveness of our method at the repository level, we design a repo-level benchmark CodeAgentBench. The performance on this benchmark shows a significant improvement brought by our method, with improvements in pass rate ranging from 2.0 to 15.8. Further tests on the HumanEval benchmark confirm CodeAgent’s adaptability and efficacy across various code generation tasks. Notably, CodeAgent outperforms commercial products like GitHub Copilot, showcasing superior accuracy and efficiency. These results demonstrate CodeAgent’s robust capabilities in code generation, highlighting its potential for real-world repo-level coding challenges.
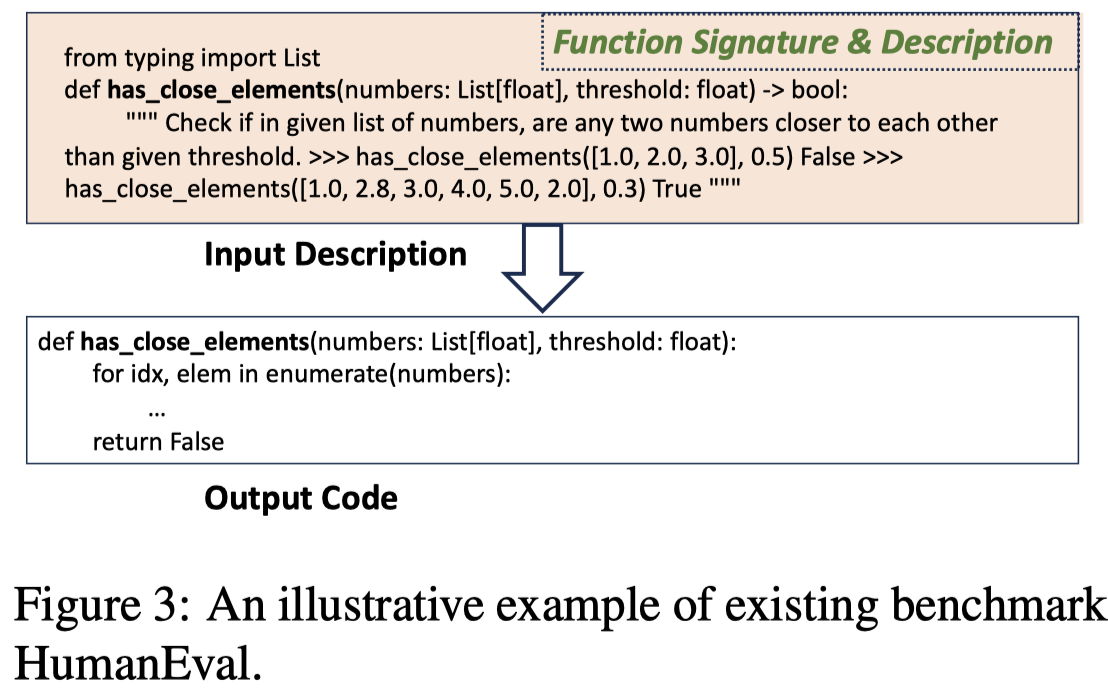
Issue: 之前很多的代码生成是statement-level或者functionlevel code generation层级的,比如下面的HumanEval benchmark的评估sample:
但是more than 70% functions in the open-source projects are non-standalone (Yu et al., 2023). 这些仓库级别的代码生成具有复杂的contextual dependencias,往往LLM难以处理。
Solution: 作者提出了首个针对repository-level code generation任务的LLM-based agent framework。
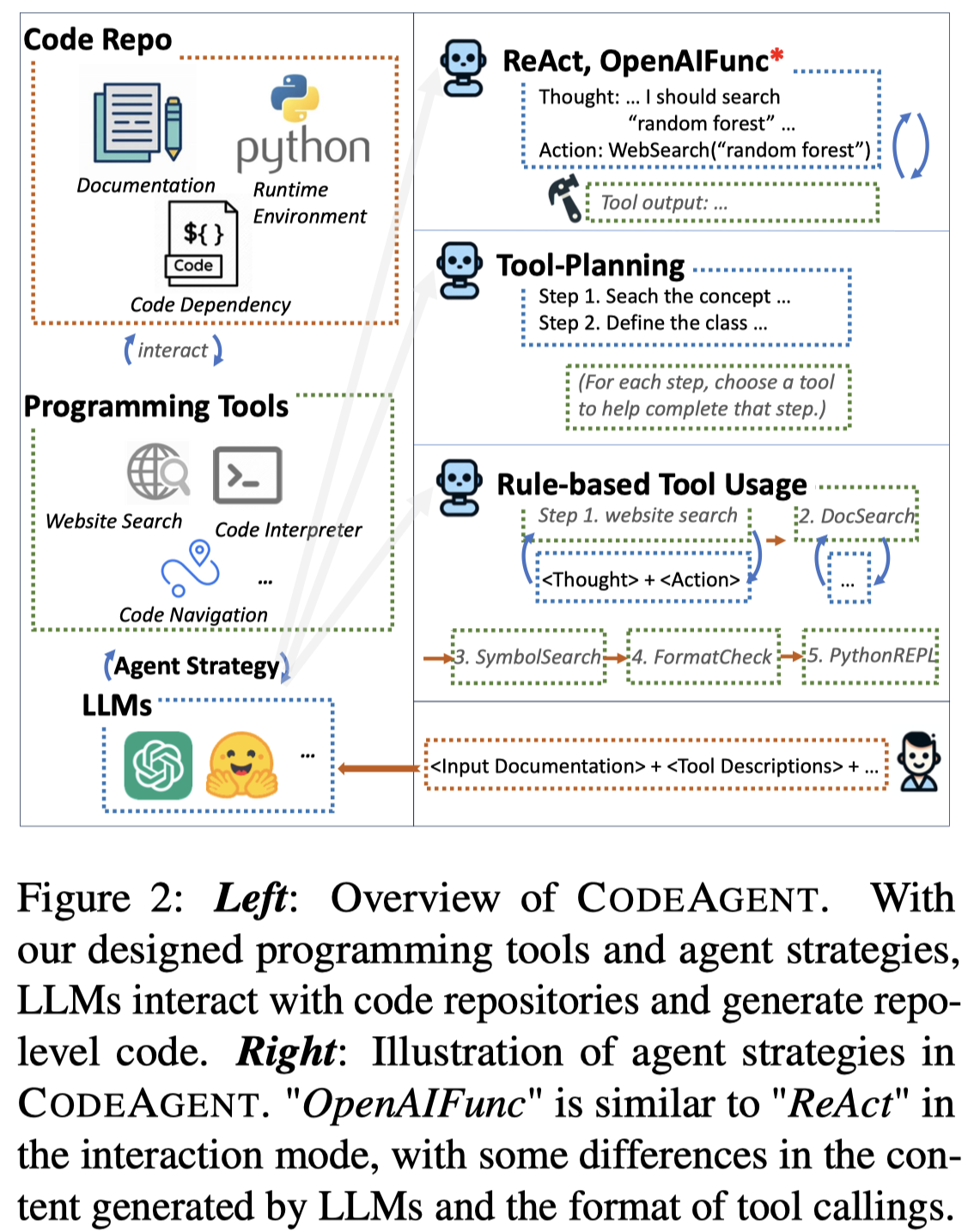
作者的生成任务的输入更加复杂,包括:documentation, code dependency, runtime environment。
作者的agent框架里集成了很多外部工具,比如进行web search的工具(DuckDuckGo)、调用相关代码相关文档的工具(BM25)、代码符号导航的工具(tree-sitter,能够返回代码定义的文件路径和相应代码实现)、测试工具(如Black进行格式检查、解释器进行编译错误检查)。
为了评估效果,构造了一个新的benchmark,选择在github上流行的5个task的python仓库:
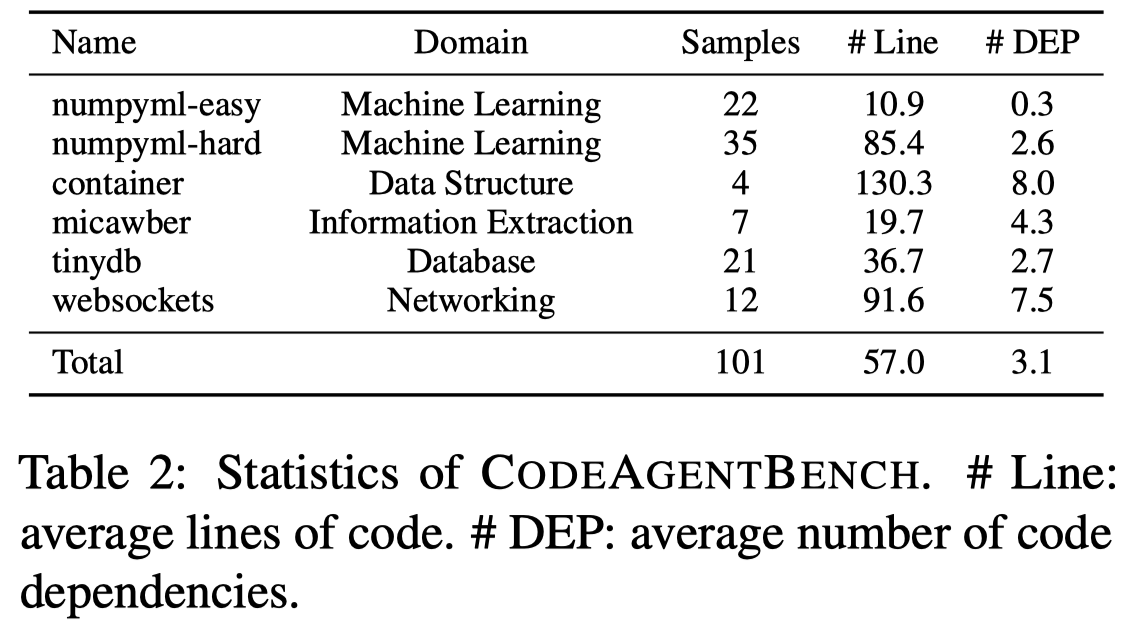
实验评估使用了一系列的LLM:
与现有商业代码补全工具的对比:
ICL Multi-Intent Comment Generation
Large Language Models are Few-Shot Summarizers: Multi-Intent Comment Generation via In-Context Learning. ICSE 2024. 国防科大. 代码.
Code comment generation aims at generating natural language descriptions for a code snippet to facilitate developers’ program comprehension activities. Despite being studied for a long time, a bottleneck for existing approaches is that given a code snippet, they can only generate one comment while developers usually need to know information from diverse perspectives such as what is the functionality of this code snippet and how to use it. To tackle this limitation, this study empirically investigates the feasibility of utilizing large language models (LLMs) to generate comments that can fulfill developers’ diverse intents. Our intuition is based on the facts that (1) the code and its pairwise comment are used during the pre-training process of LLMs to build the semantic connection between the natural language and programming language, and (2) comments in the real-world projects, which are collected for the pre-training, usually contain different developers’ intents. We thus postulate that the LLMs can already understand the code from different perspectives after the pre-training. Indeed, experiments on two large-scale datasets demonstrate the rationale of our insights: by adopting the in-context learning paradigm and giving adequate prompts to the LLM (e.g., providing it with ten or more examples), the LLM can significantly outperform a state-of-the-art supervised learning approach on generating comments with multiple intents. Results also show that customized strategies for constructing the prompts and post-processing strategies for reranking the results can both boost the LLM’s performances, which shed light on future research directions for using LLMs to achieve comment generation.
Issue:之前的comment generation方法忽略了comment的多意图,因为不同程序员可能是倾向于comment有不同的意图。
Solution:作者利用LLM的ICL学习能力来生成不同意图的comment,原因有两个:
- Firstly, LLMs designed for the code domain are typically pre-trained using code and its associated pairwise comments to establish semantic connections between programming language and natural language.
- Secondly, existing research has shown that code comments from real-world projects, which form the training corpus for LLMs, often contain multiple intents [47].
作者为不同的意图设计了不同的task instruction:
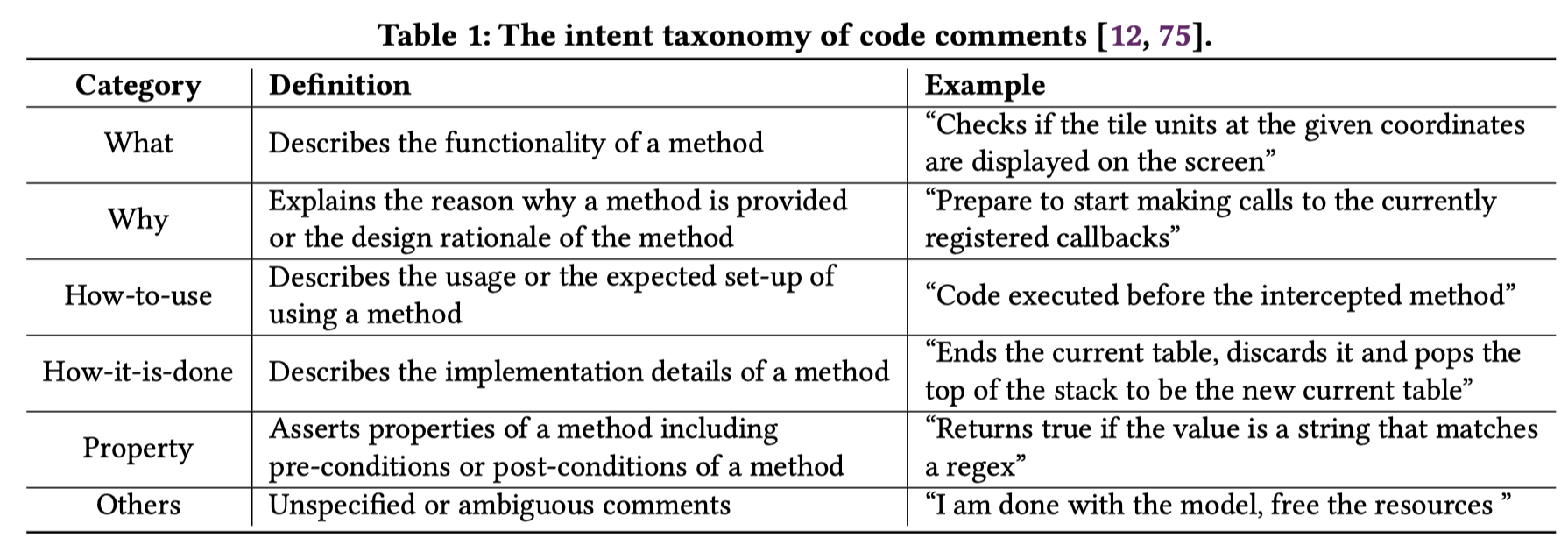
下面是what意图的prompt:
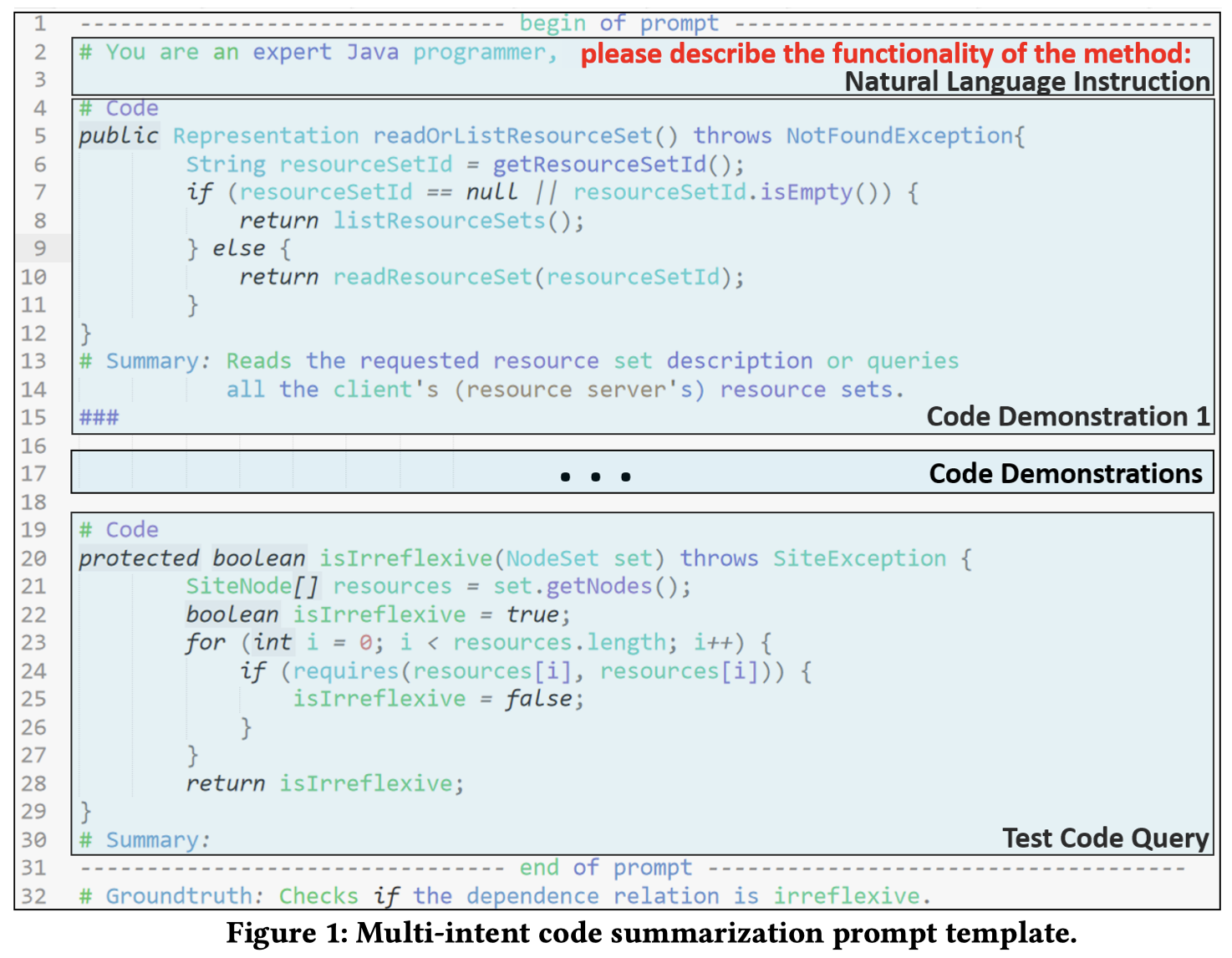
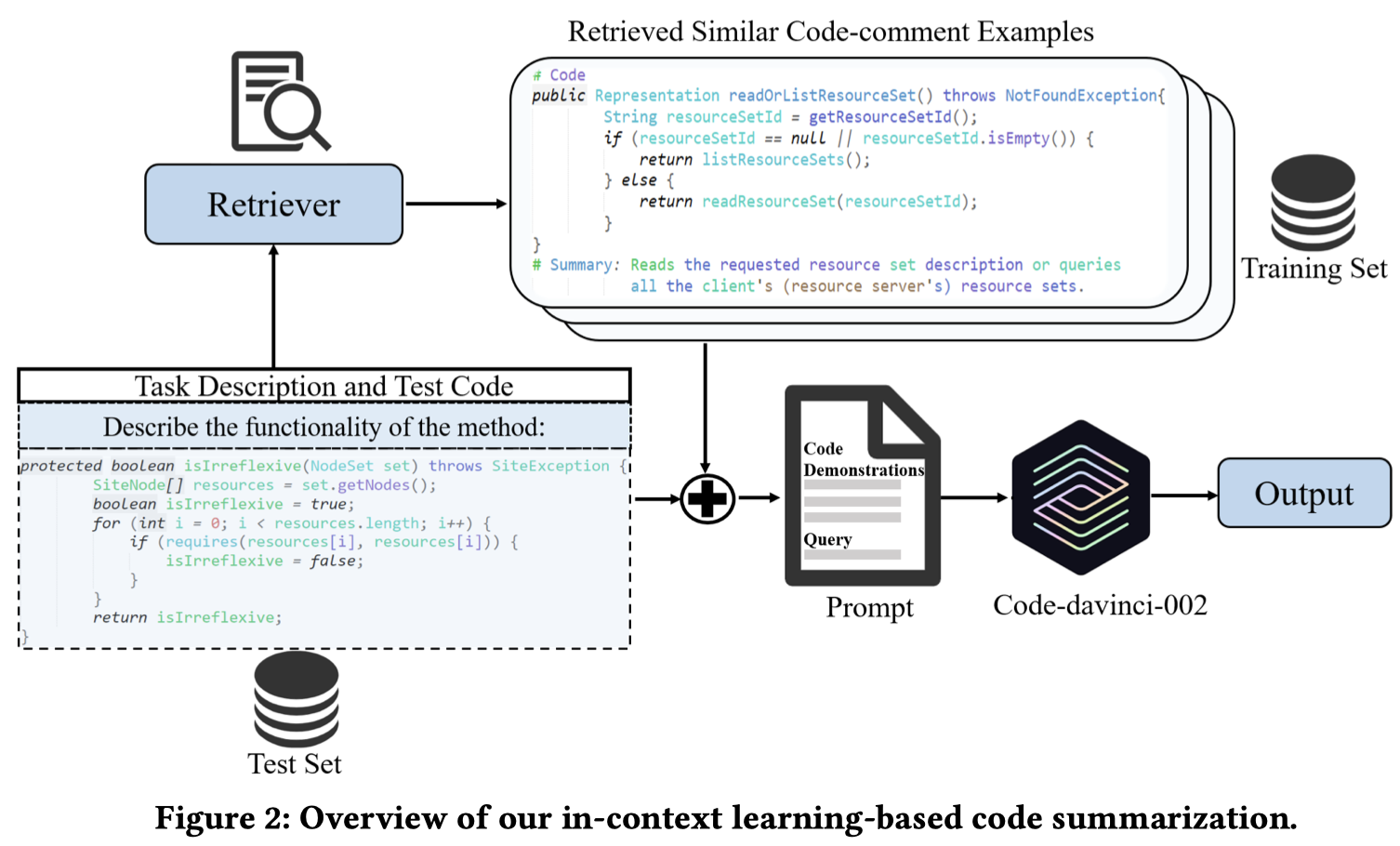
使用code-davinci-002进行实验。metric是BLEU, ROUGE-L和METEOR。