MMIE-collection1
MRE and MNER
多模态信息抽取相关论文总结
MNRE
MNRE: A Challenge Multimodal Dataset for Neural Relation Extraction with Visual Evidence in Social Media Posts
ICME 2021,作者创建了首个用于multimodal relation extraction的数据集MNRE,地址,Post not found: mmml/MNRE [详细博客]。
数据来源于Twitter posts,关注点是文本中的上下文信息不够充分时,通过post中的image,来补充上下文信息。
Extracting relations in social media posts is challenging when sentences lack of contexts. However, images related to these sentences can supplement such missing contexts and help to identify relations precisely. To this end, we present a multimodal neural relation extraction dataset (MNRE), consisting of 10000+ sentences on 31 relations derived from Twitter and annotated by crowdworkers. The subject and object entities are recognized by a pretrained NER tool and then filtered by crowdworkers. All the relations are identified manually. One sentence is tagged with one related image. We develop a multimodal relation extraction baseline model and the experimental results show that introducing multimodal information improves relation extraction performance in social media texts. Still, our detailed analysis points out the difficulties of aligning relations in texts and images, which can be addressed for future research. All details and resources about the dataset and baselines are released on https://github.com/thecharm/MNRE.
relation extraction(RE)是预测一个句子中两个命名实体之间的关系relation。
challenges:之前大多数的RE模型关注的是文本信息很充分的场景下的关系抽取,比如newswire domain。但是,一旦文本很短,并且缺少必要的上下文信息的时候,RE模型效果会出现严重的下降。即便是使用了pretrained modal来进行关系抽取,效果也很糟糕。
solution: 作者认为,对于在推特post这样很可能文本中缺乏足够充分的上下文信息的场景,可以使用image的visual information来补充上下文信息。
比如在下面的图中,如果只有文本,那么可能会判断出来JFK和Obama和Harvard的关系是residence;但是如果能够识别图像中的信息,比如校园、学位帽等,可以判断出来JFK和Obama和Harvard的关系应该是graduated_at。
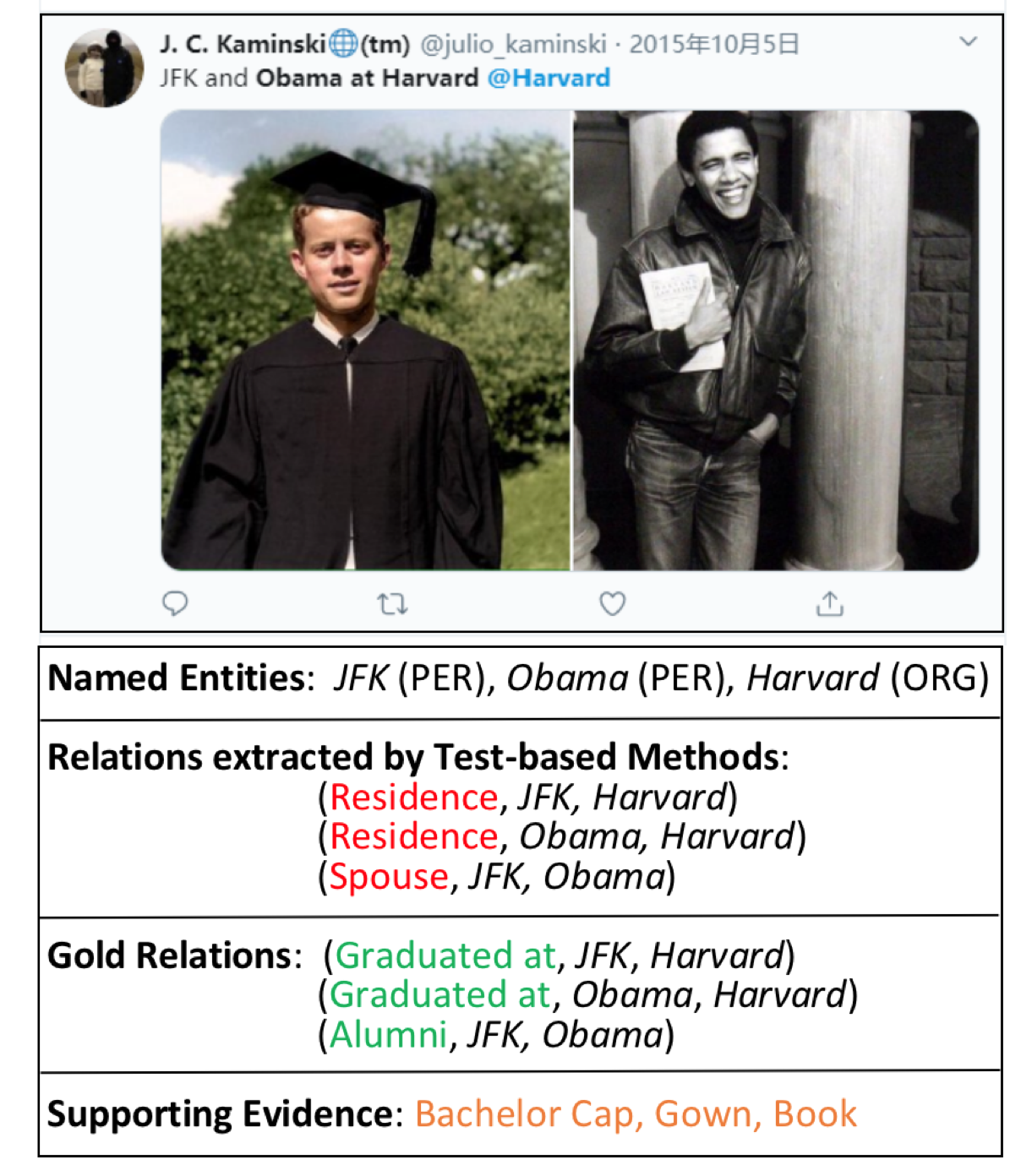
但是目前并没有这样满足文本+图像的数据集存在,因此作者就希望能够解决这一点,主要贡献如下:
- 创建了在社交媒体posts上的数据集Multimodal dataset for Neural Relation Extraction(MNRE)
- 在MNRE数据集基础上,构建了几个不同的baseline方法
数据来源有三个:
- Twitter 2015:有8357个候选实例(指一个完整的post和对应image、named entities和relations)
- Twitter 2017:有4819个候选实例
- Crawled Twitter data:爬取了Twitter 2019年1月到2月的post和对应图片,不限制具体的领域;如果一个post有多张图片,就随机选择一张。最终获取了20000候选实例
作者在后续更新了数据集,得到了MNRE-2:
2021.6.22 We provide MNRE-2, a refined version which merges several ambigious categories with much more support samples. The original version has been moved to Version-1
MNRE-2的统计: 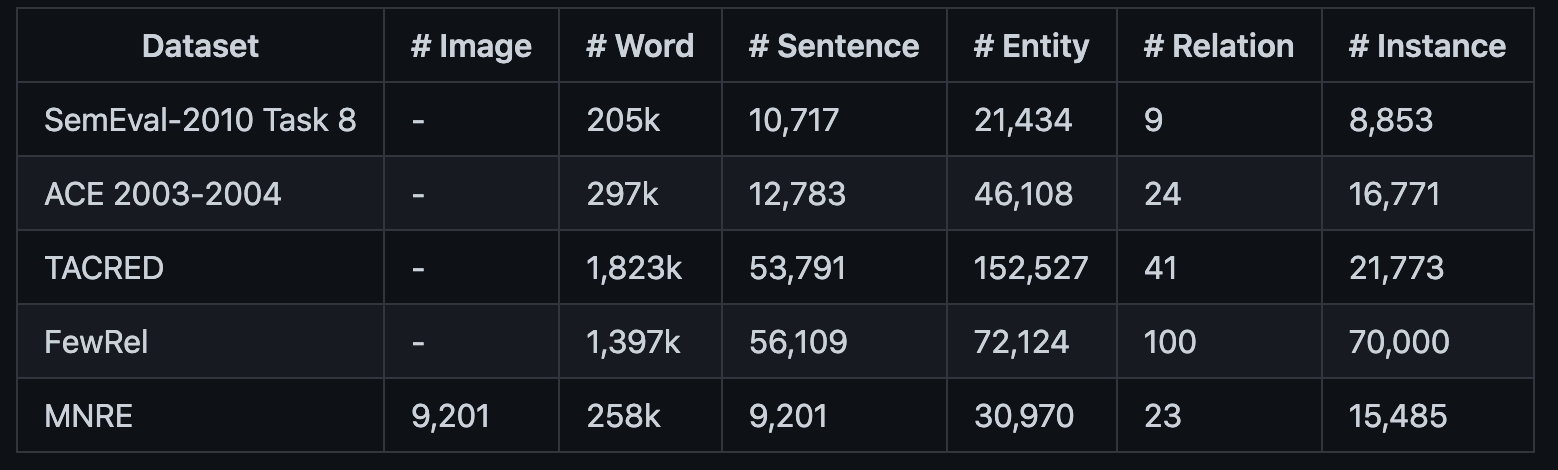
下图是不同关系类型的统计:
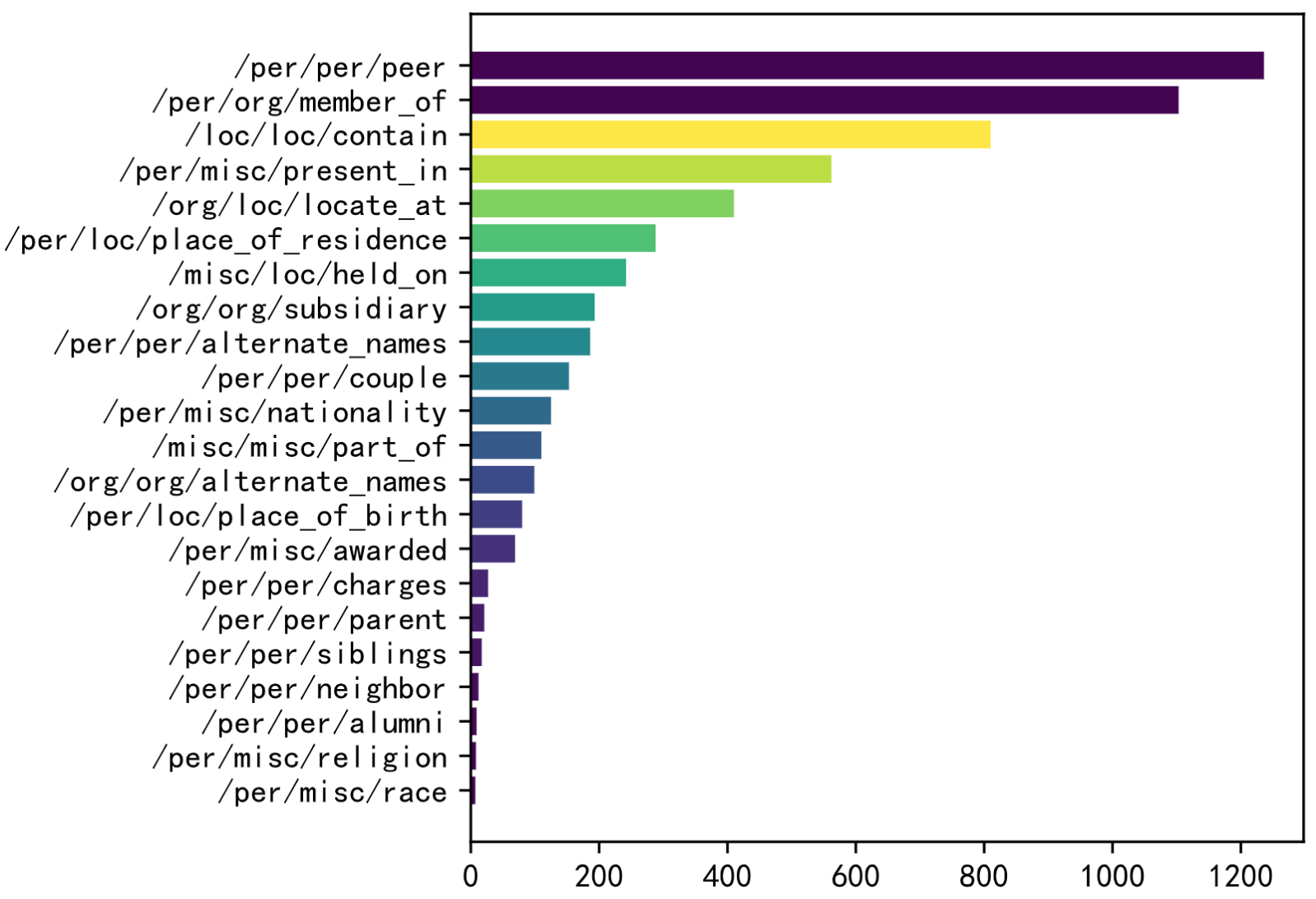
经过检查发现,实际的训练集还包括了关系None。上面的统计图没有展现出None关系的分布。
作者的MNRE-2数据集从32变为了23种关系,发现大部分的关系还是和人相关的。MNRE-2训练集有12247、验证集1624和测试集1614实例。
查看下具体的数据集内容,在一个训练实例中,包括
token:['The', 'latest', 'Arkham', 'Horror', 'LCG', 'deluxe', 'expansion', 'the', 'Circle', 'Undone', 'has', 'been', 'released', ':']h:{'name': 'Circle Undone', 'pos': [8, 10]}t:{'name': 'Arkham Horror LCG', 'pos': [2, 5]},这个Arkham Horror LCG应该是一种卡牌游戏img_id:'twitter_19_31_16_6.jpg',所有的图片下载完后是1.2GB,下图是对应的图片
relation:/misc/misc/part_of

上图是数据集中的实例。可以看到,需要同时结合视觉和文本信息,才能够做出准确的关系预测。
HVPNet
Good Visual Guidance Makes A Better Extractor: Hierarchical Visual Prefix for Multimodal Entity and Relation Extraction. NAACL 2022
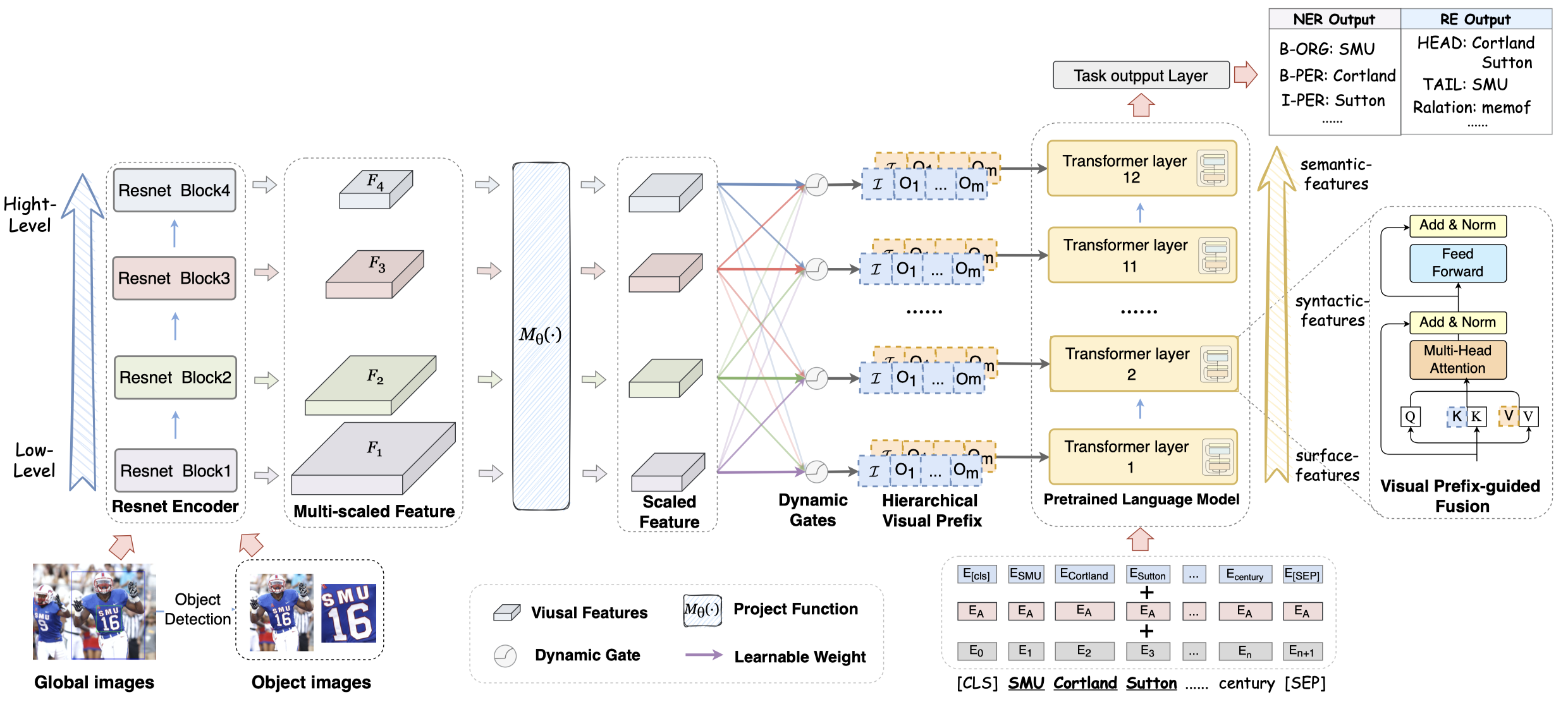
[详细博客]从图像中提取object-level的层级信息,用于补充文本信息。
利用ResNet作为图像encoder导出层级视觉表征,不同的层级信息,通过计算一个gate weight聚合到不同Bert层。输入到不同层的视觉表征,作为Bert的key和value,加入到文本表征学习过程中。
最后的relation预测是通过让[CLS] token embedding输入到MLP-softmax中。
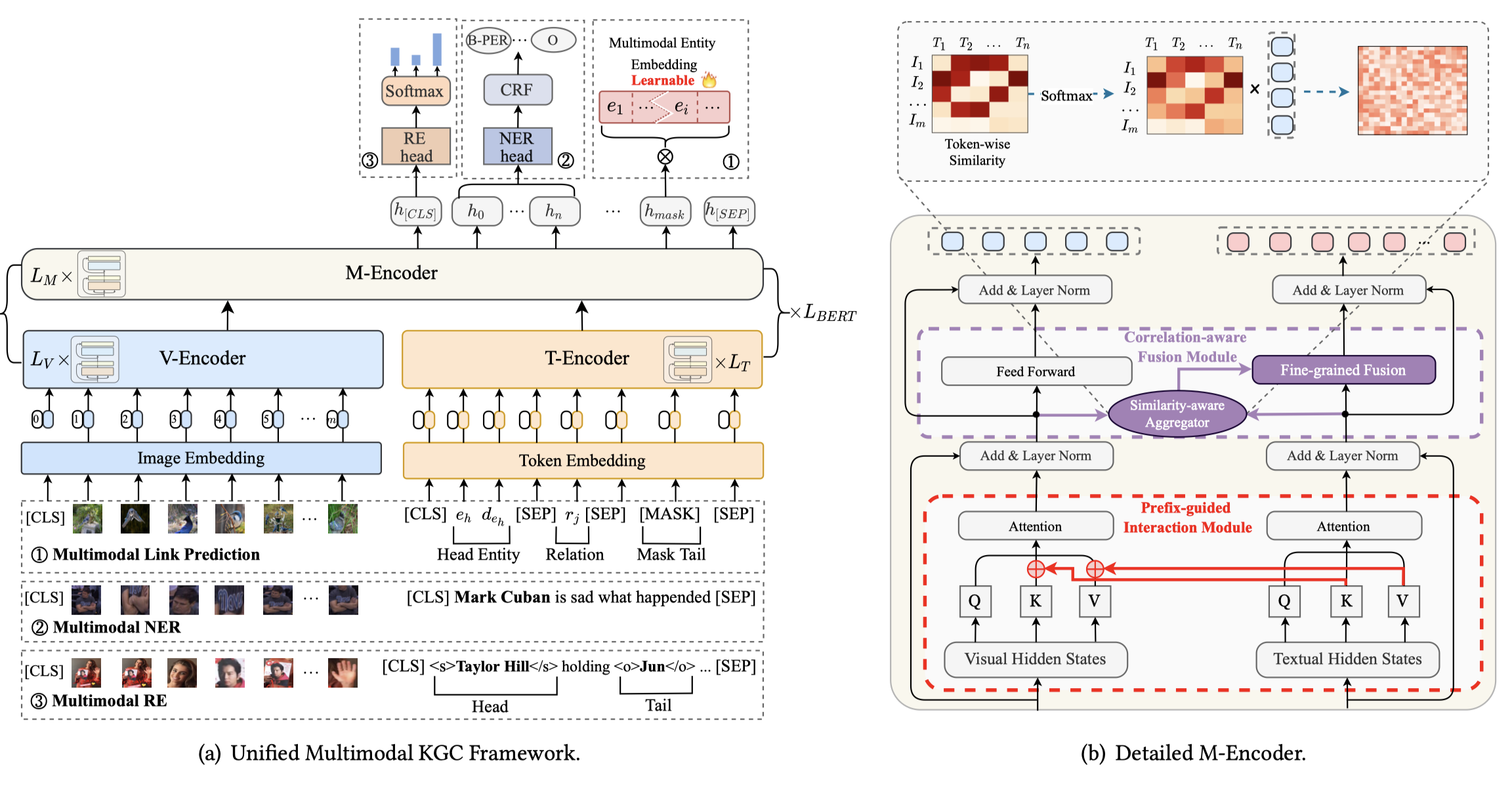
MKGformer
Hybrid Transformer with Multi-level Fusion for Multimodal Knowledge Graph Completion. SIGIR 2022
[详细博客]文本侧作为key和value输入到视觉侧;
视觉侧在FFN层,通过计算一个token-patch的相似度矩阵,让视觉侧信息进入到文本侧。
论文中声明的是让[CLS] token embedding作为MLP-Softmax输入,但是在代码中却是让[s]和[t] token作为MLP-softmax输入。
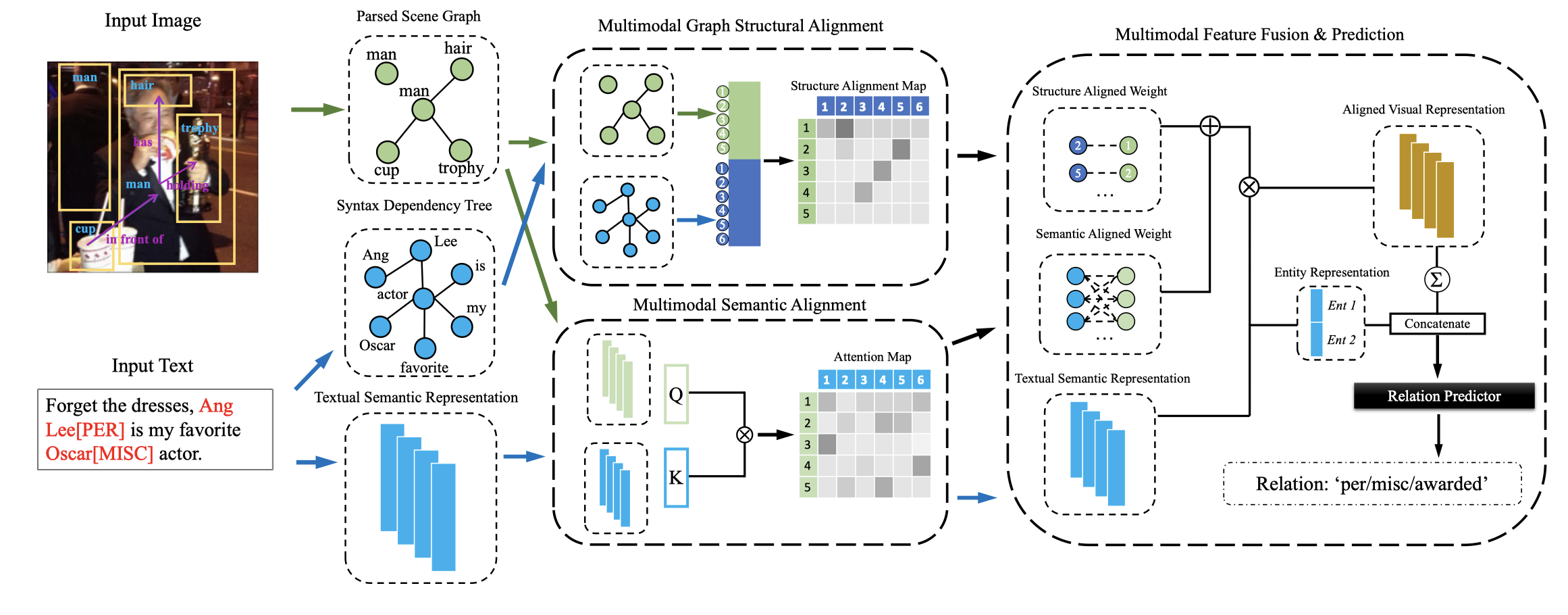
MEGA
Multimodal Relation Extraction with Efficient Graph Alignment. ACM MM 2021
[详细博客]通过image graph和textual graph上node对齐得到的结构上的attention weight;
通过image query和textual key计算得到的attention weight;
两个weight相加,将文本表征,融合到图像表征做query的学习过程中;最后把所有视觉表征相加,得到了总的图像表征。
图像表征拼接到文本表征上,进行最后的关系分类。
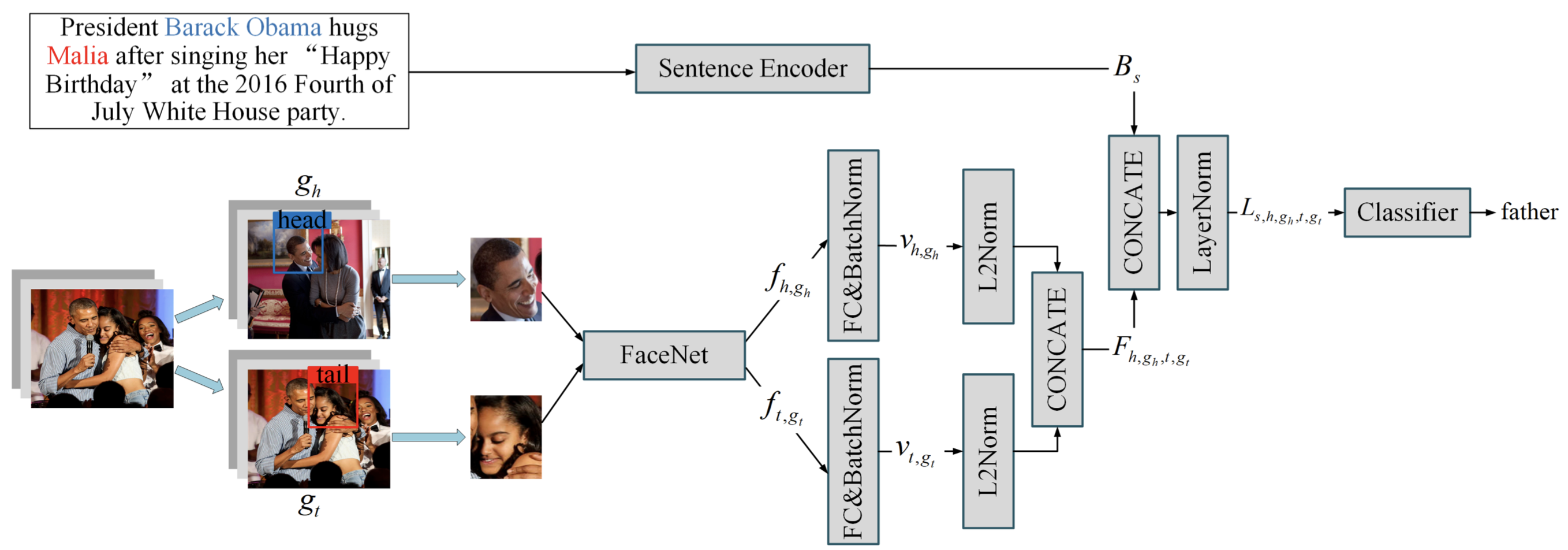
FL-MSRE
FL-MSRE: A Few-Shot Learning based Approach to Multimodal Social Relation Extraction. AAAI 2021
[详细博客]这里作者构造的数据集主要是包含了脸部图像,不太适用于MNRE数据集。
facial image表征和textual表征拼接后就作为了模态融合模块。
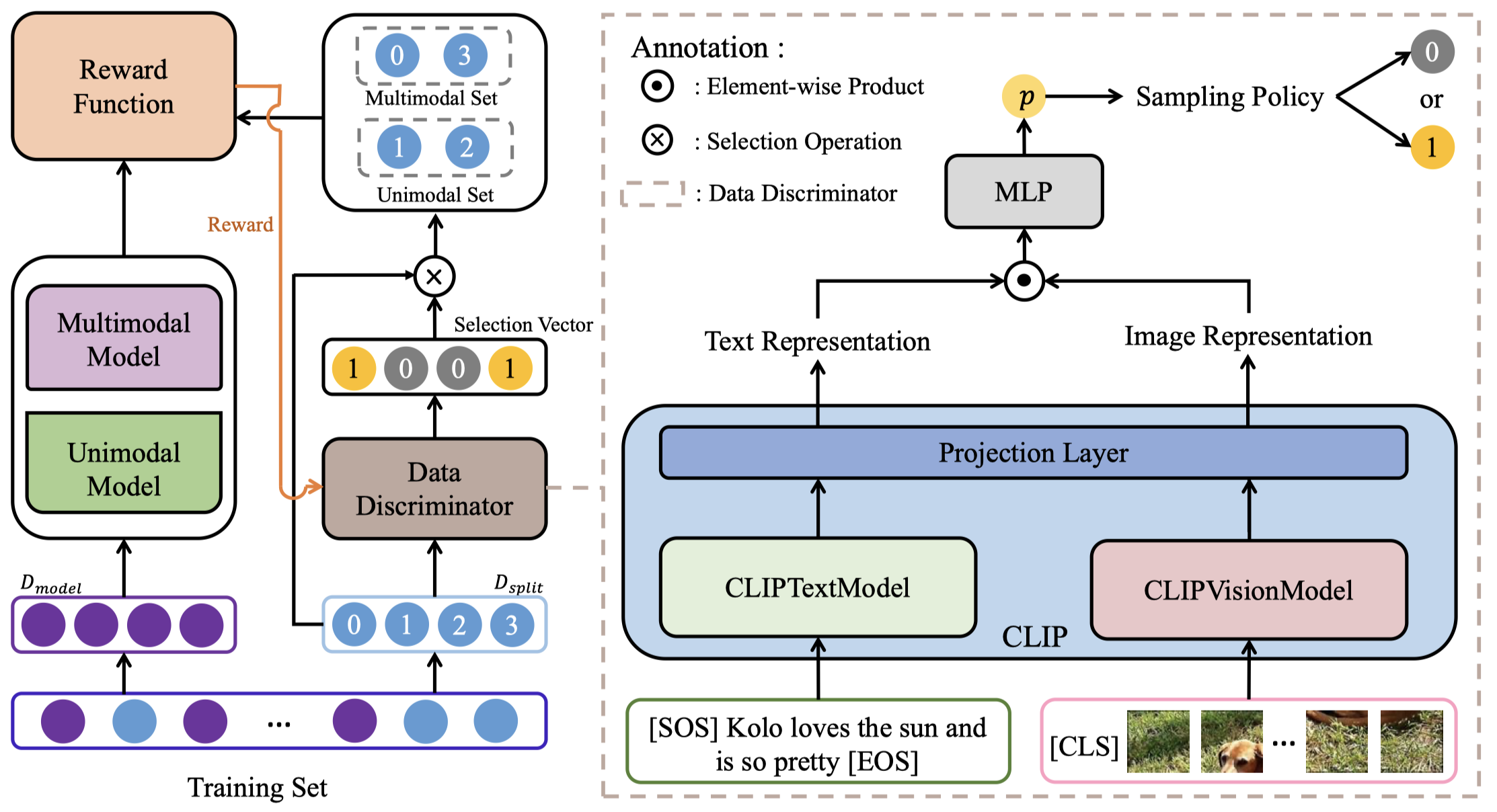
Modality-discriminator
Different Data, Different Modalities! Reinforced Data Splitting for Effective Multimodal Information Extraction from Social Media Posts. COLING 2022
[详细博客]重点不在于模态的融合。
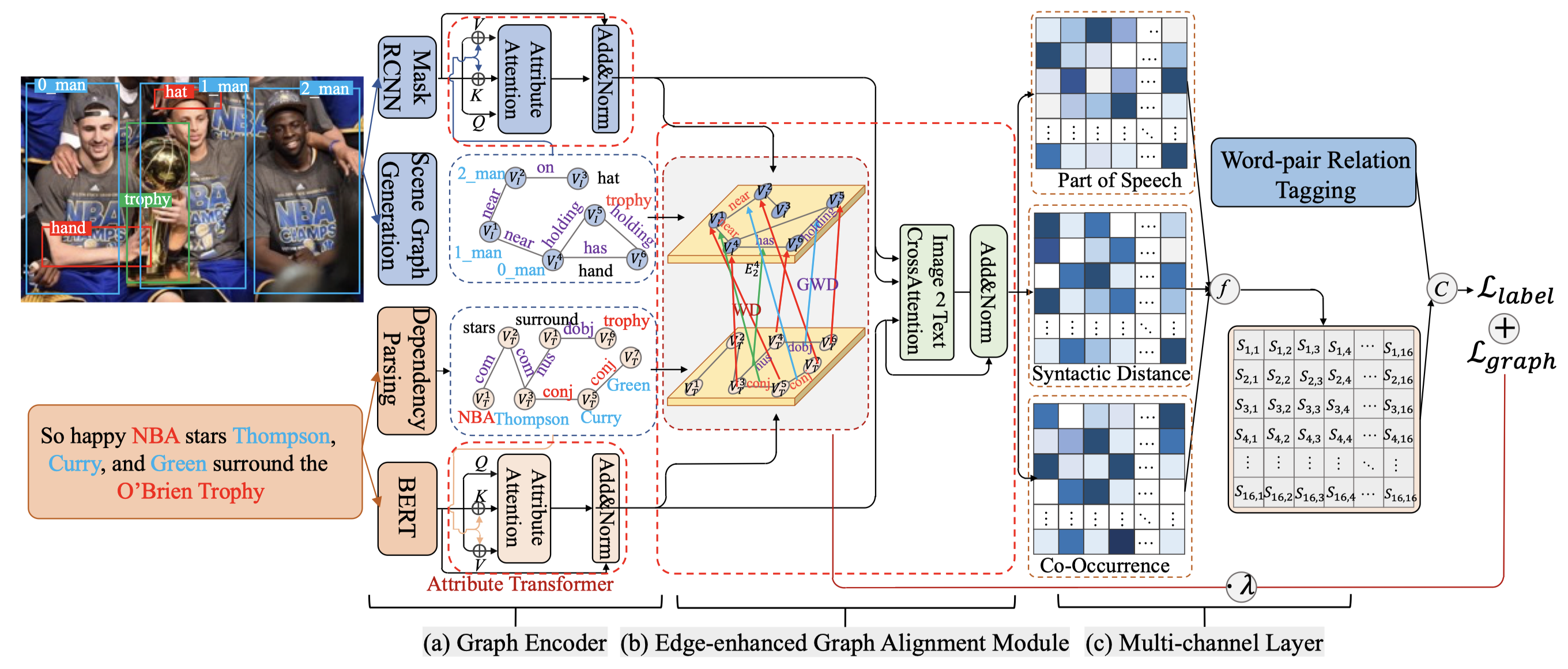
EEGA
Joint Multimodal Entity-Relation Extraction Based on Edge-enhanced Graph Alignment Network and Word-pair Relation Tagging. AAAI 2023
[详细博客]比起MEGA,还强调了边的对齐。
使用RCNN导出视觉特征。在Image2Text模块中,文本表征做query,视觉表征做key和value。然后文本表中输入到add&norm层。
RpBERT
RpBERT: A Text-image Relation Propagation-based BERT Model for Multimodal NER. AAAI 2021
这里提到的relation,是指image和text是否相关。
作者在这里使用的RpBERT是将ResNet的输出和token embedding拼接到一起作为BERT的输入:
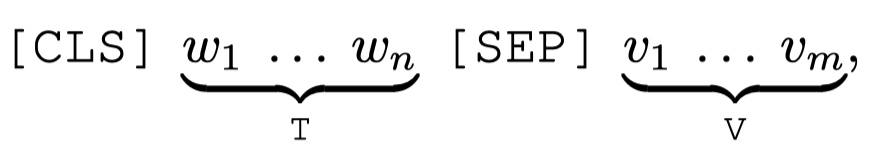
MAF
MAF: A General Matching and Alignment Framework for Multimodal Named Entity Recognition. WSDM 2022
[详细博客]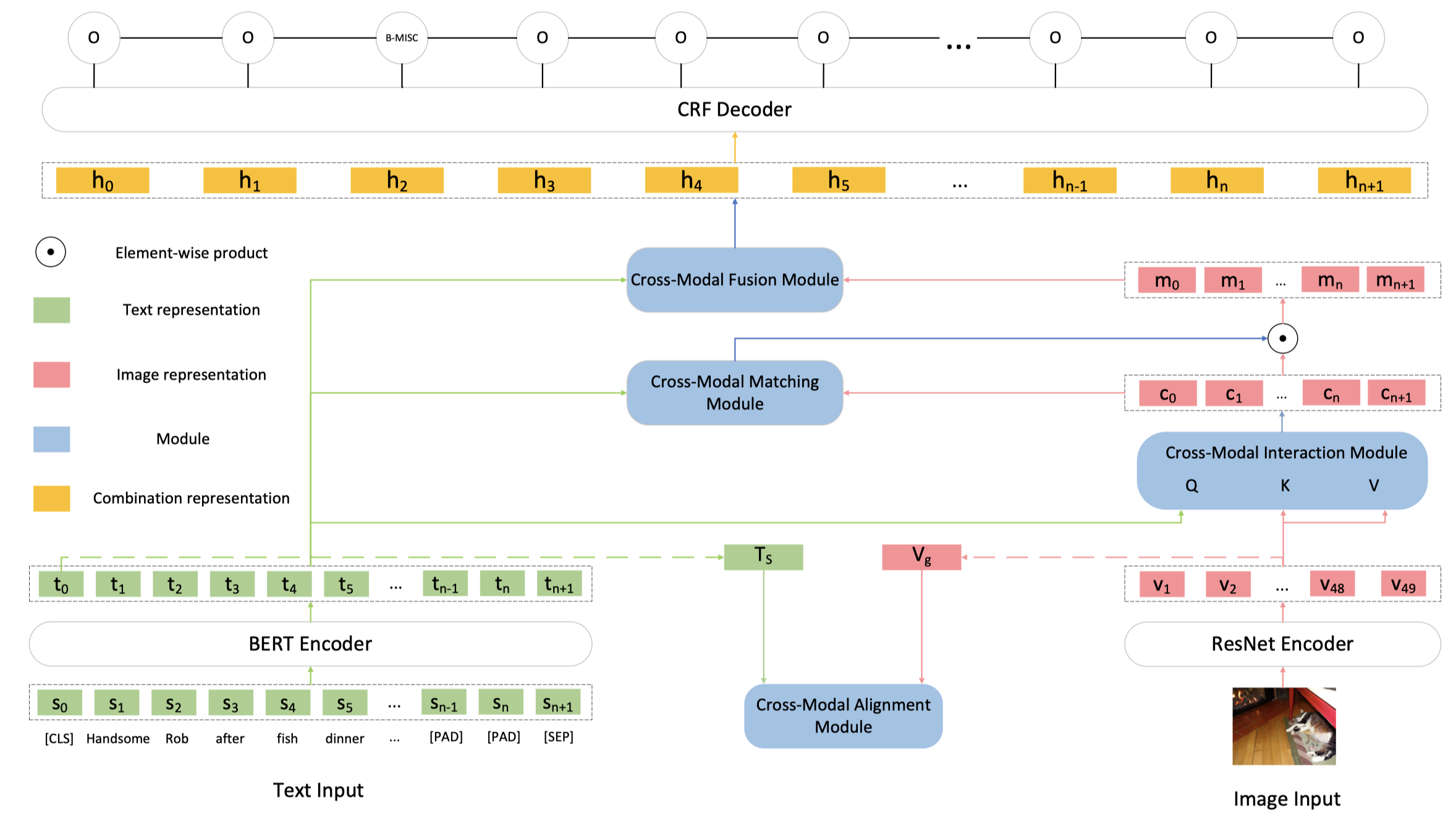
不是在BERT的每一层分别进行视觉信息的融合,而是在不同的模态独立的encoder的输出上进行对齐和融合。
对齐是为了让表征更加一致,作者通过替换post对应的image,利用对比学习,计算文本和图像是否匹配。
最后进行融合的时候,通过给每个token,计算一个gate weight来获得最后的token对应的视觉表征,与文本表征拼接后,输入到CRF层。
MRC-MNER
Query Prior Matters: A MRC Framework for Multimodal Named Entity Recognition. ACM MM 2022
单位:京东
问题:目前的MNER方法,大多是通过基于attention实现image-sentence的隐式语义对齐,这种方法很难解释和评估实体类型与image region之间的显式关联。
方法:作者把MNER看做是MRC任务(machine reading comprehension)。把最后要预测关系类型转化为query sentence:
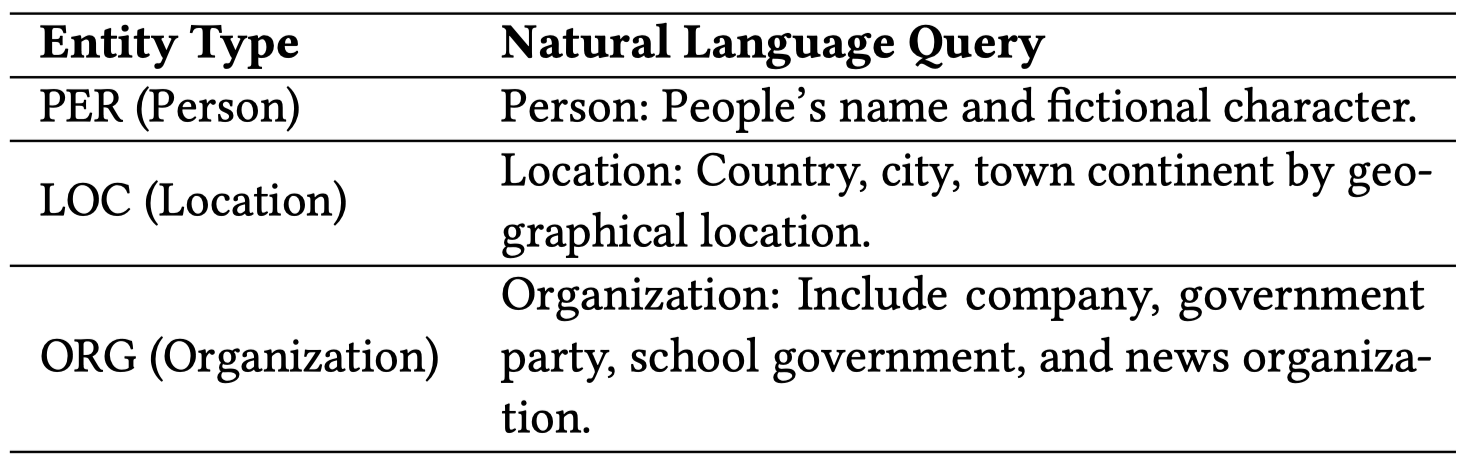
然后使用预训练好的BERT导出文本表征。对于视觉表征,作者首先需要导出一张图片上的regions,作者通过预训练好一个visual grounding模型,然后为了让这个visual grounding模型也能够适用于MNER领域,作者构造了一个语料库,用于微调训练好的visual grounding模型。使用ResNet导出图像表征。
对于多任务学习:作者除了entity span prediction,还引入了另外两个task辅助NER。region weights estimation和existence detection。region weights estimation是用于评估各个region embedding的重要性;Existence Detection用于预测句子中是否存在某个特定entity type的entity。
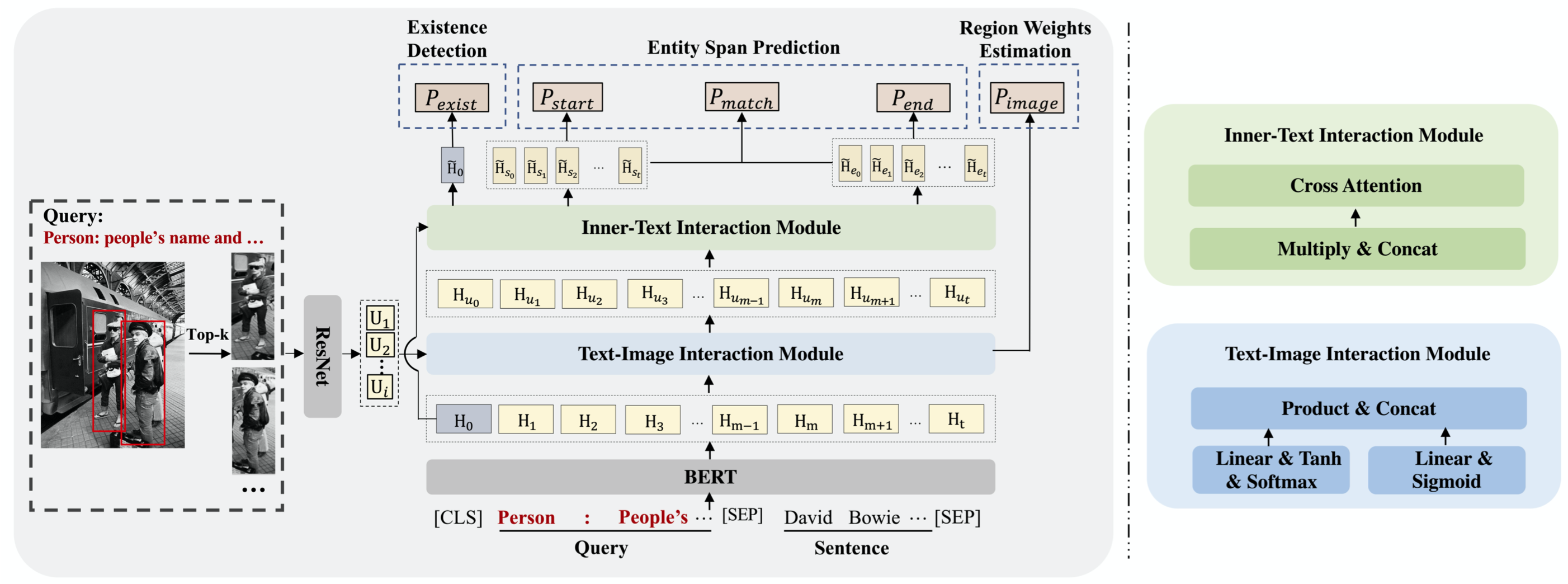
UMT
Improving Multimodal Named Entity Recognition via Entity Span Detection with Unified Multimodal Transformer. ACL 20
作者提出除了要学习word-aware的visual representation外,也要学习image-aware word representation,提出了UMT。为了避免过于强调视觉信息,可能导致会过于强调图像表示的实体,而忽略对其它实体的预测。作者额外训练了一个基于纯文本的模块,让这个模块进行textual entity span detection任务。这个任务实际上和MNER任务是一致的,因此通过设计一个conversion matrix,在优化MNER任务的同时,也优化textual entity span detection任务。
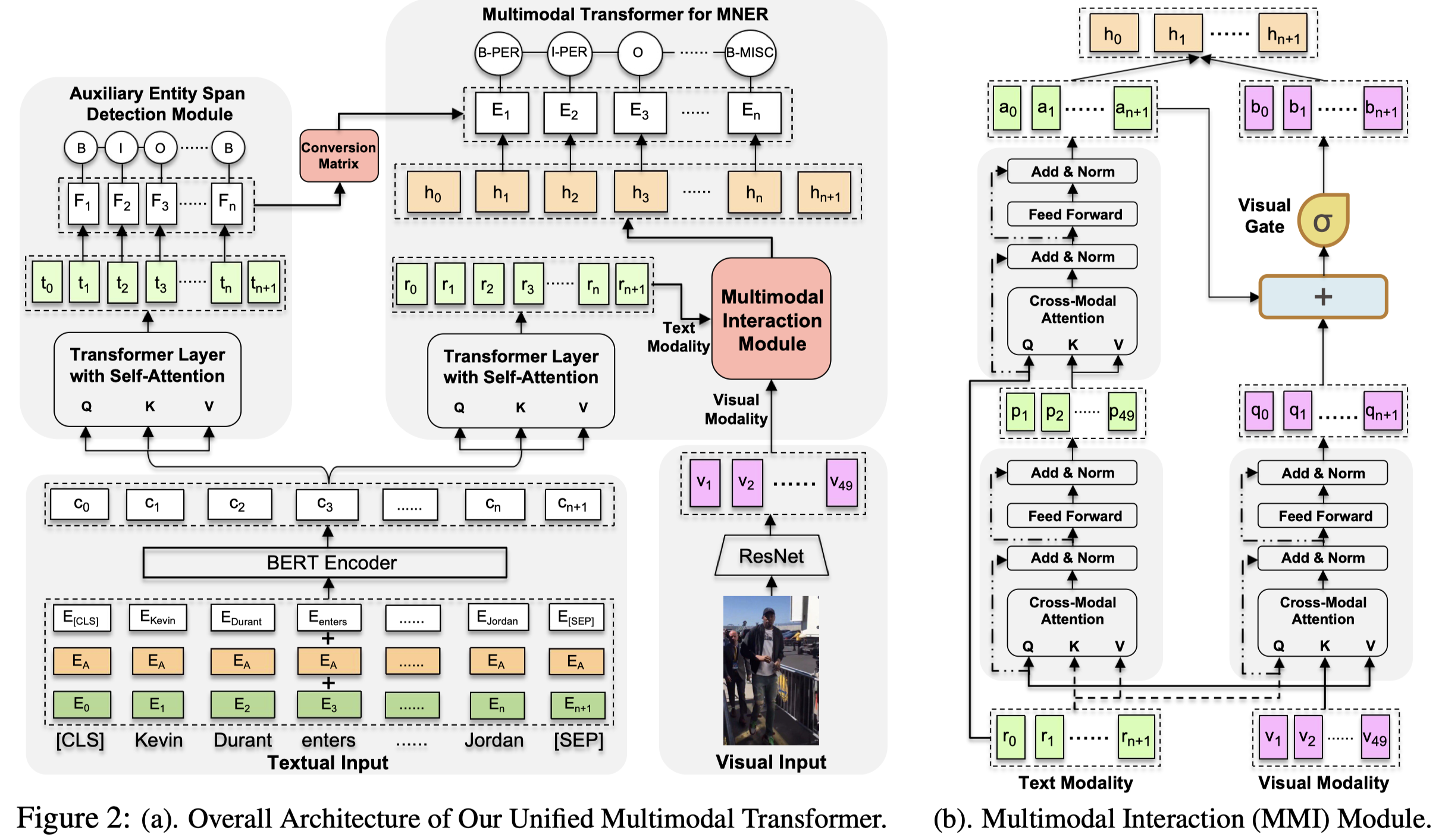
MMI模块是模态交互的核心,首先获得image-aware word representation(左侧)和word-aware image representation(右侧)。
将左侧的image-aware word representation再融合到原来的word representation中;然后与word-aware image representation一起经过visual gate,过滤掉不需要视觉信息的token对应的视觉表征(比如the/of/well这些word就不需要视觉信息)。
最后两侧的表征拼接,得到最后的多模态表征。
MoRe
Named Entity and Relation Extraction with Multi-Modal Retrieval
作者通过text和image检索在Wikipedia上相关的text信息来辅助多模态信息抽取。
上海科技与阿里达摩,EMNLP 2022,代码,[详细博客]。
Multi-modal named entity recognition (NER) and relation extraction (RE) aim to leverage relevant image information to improve the performance of NER and RE. Most existing efforts largely focused on directly extracting potentially useful information from images (such as pixel-level features, identified objects, and associated captions). However, such extraction processes may not be knowledge aware, resulting in information that may not be highly relevant. In this paper, we propose a novel Multi-modal Retrieval based framework (MoRe). MoRe contains a text retrieval module and an imagebased retrieval module, which retrieve related knowledge of the input text and image in the knowledge corpus respectively. Next, the retrieval results are sent to the textual and visual models respectively for predictions. Finally, a Mixture of Experts (MoE) module combines the predictions from the two models to make the final decision. Our experiments show that both our textual model and visual model can achieve state-of-the-art performance on four multi-modal NER datasets and one multimodal RE dataset. With MoE, the model performance can be further improved and our analysis demonstrates the benefits of integrating both textual and visual cues for such tasks.
作者的方法图:
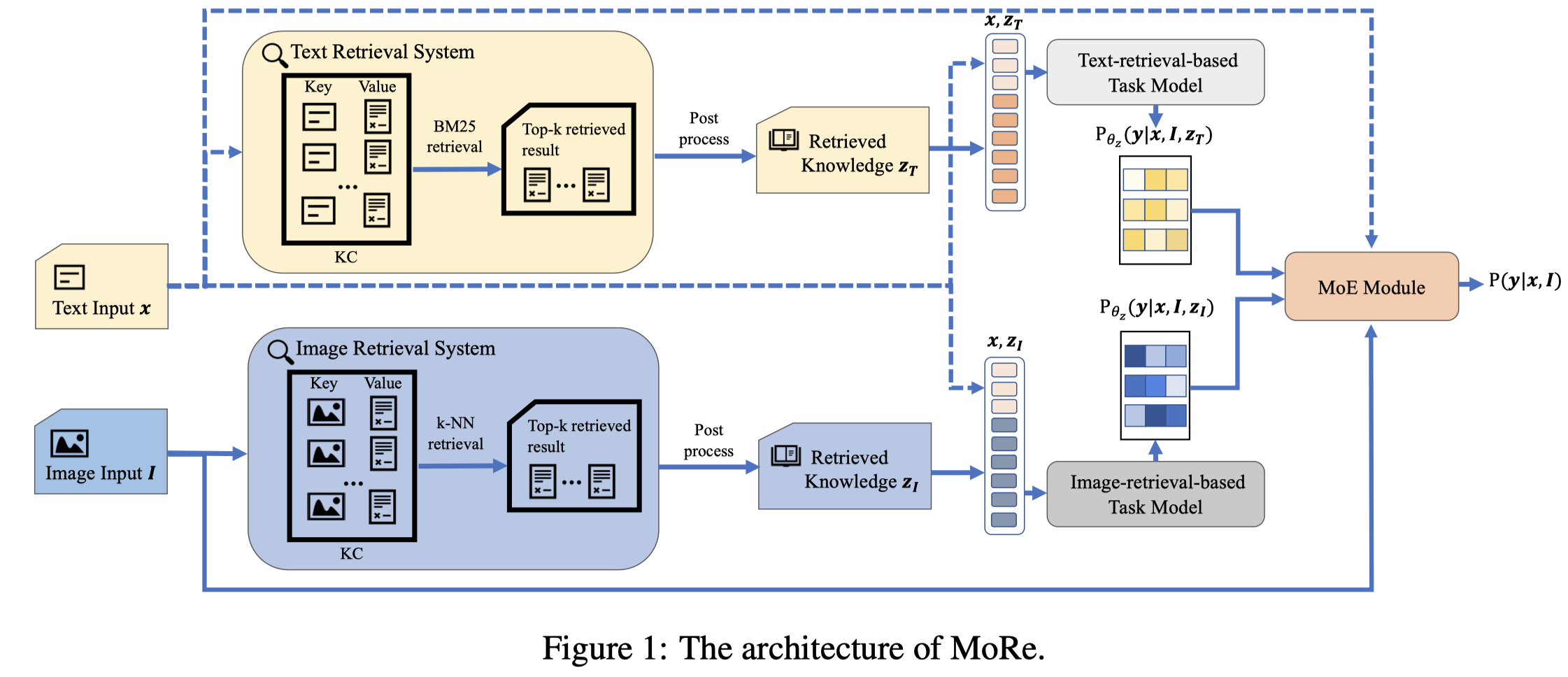
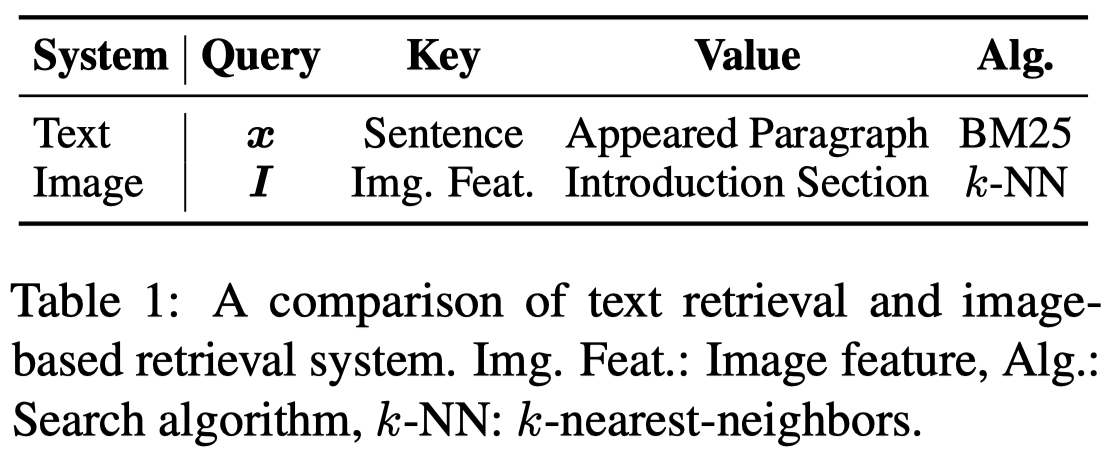
作者从English Wikipedia dump中分别以text和image作为关键进行检索:
具体来说:
- Textual Retrieval System:待抽取text作为query,使用ElasticSearch,基于BM25算法检索Wikipedia中语义相似的句子(key),然后把包含句子的paragraph返回(value)作为检索结果。
- Image-base Retrieval System:使用ViTB/32 in CLIP将待抽取image和Wikipedia article中的images都编码为vector,然后基于k-NN算法,使用Faiss进行高效搜索。把检索到的article的introduction section返回未做检索结果。
分别检索到top-K(实验中\(K=10\))的结果之后,检索到的结果与原有的待抽取text拼接,分别经过独立的task model输出对于实体或者关系的预测结果。NER任务使用CRF decoder,RE任务使用简单的线性softmax。task model在实验中是XLM-RoBERTa large。
对于两个prediction distributions,作者使用MoE进行混合:
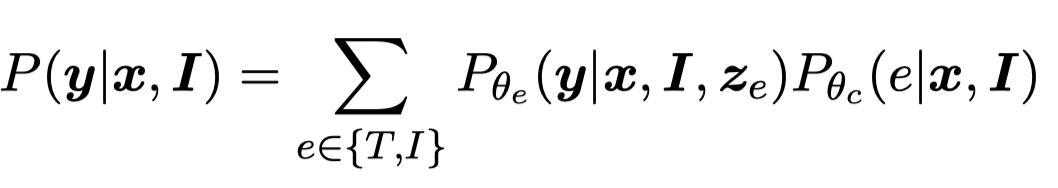
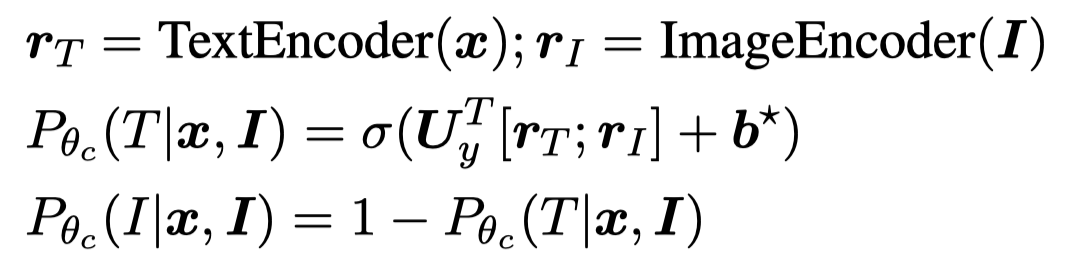
这里的MoE是计算两个prediction distributions的对应权重,然后进行混合。对于NER任务,由于CRF将NER看做是序列标注预测,对应可能的序列集合范围很大。因此作者使用了自己之前在CLNER工作中的方法,将序列标注预测转变为认为不同位置的NER label是互相独立的:
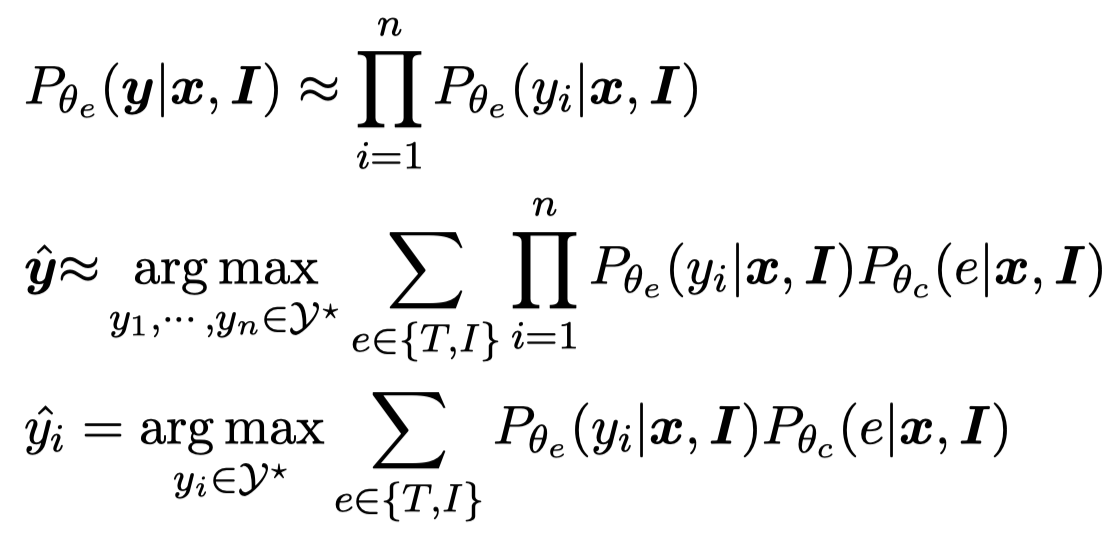
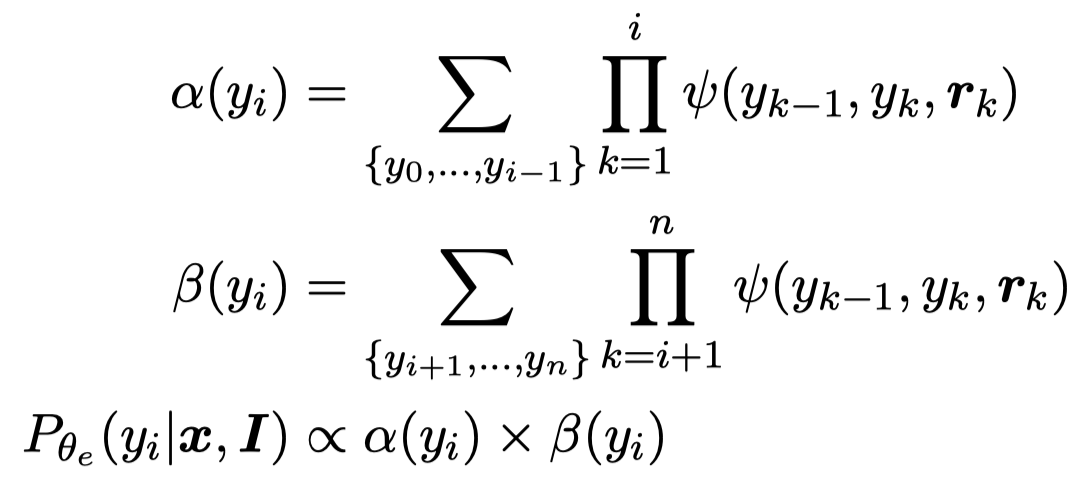
这样最后预测就是让每一个位置上的token的NER label概率最大,而不是让所有token的NER label组合序列的概率最大。
主要实验结果:
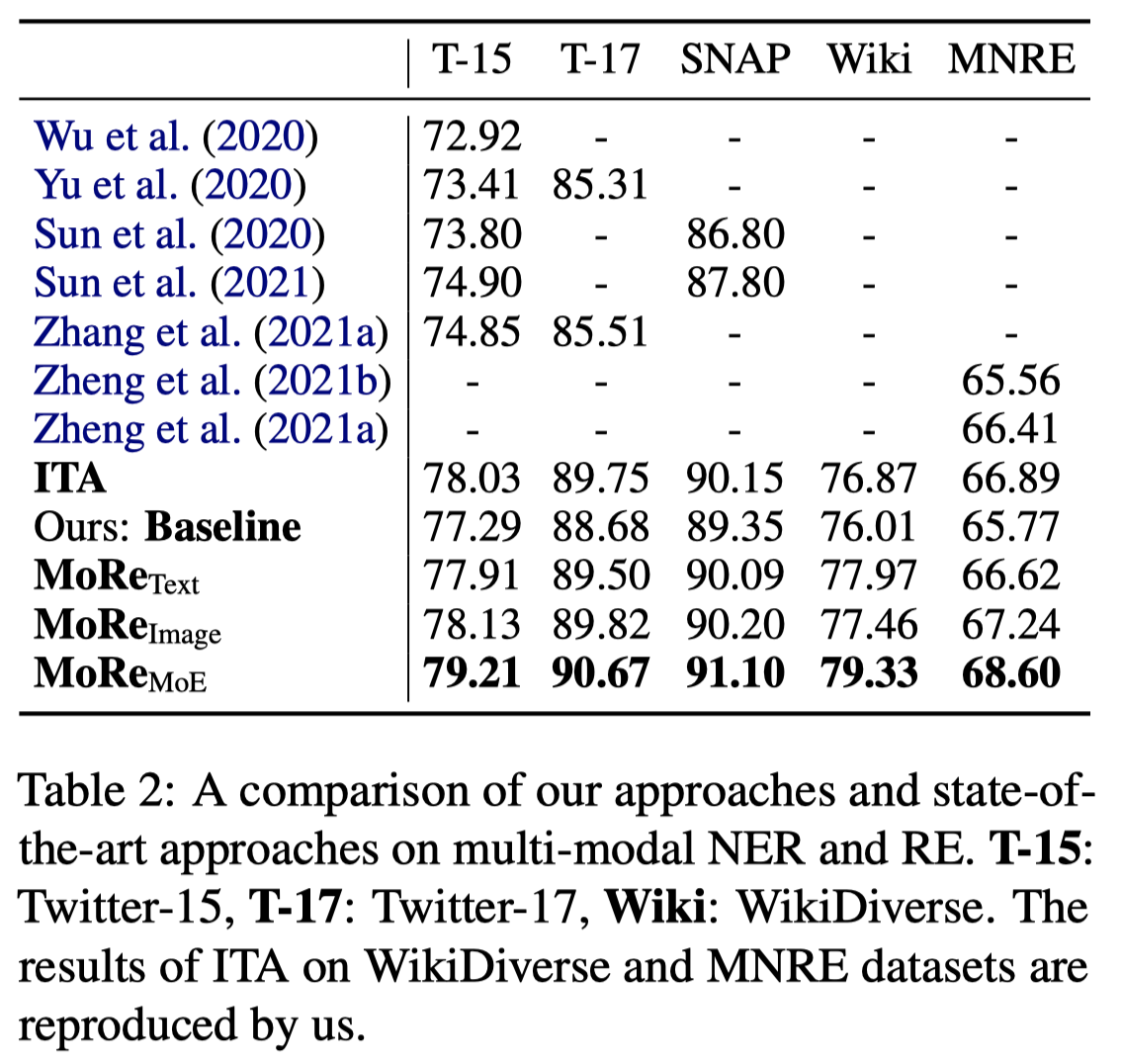
可以看到,如果仅仅是只使用text或image检索,大概带来了1%的提升。通过使用MoE将效果提升到了2%。但是总的效果来看还比不上目前直接使用multimodal representation进行prediction的方法,特别是在MNRE数据集上。
作者MNER任务除了使用最常用的Twitter2015和Twitter2017数据集外,还将WikiDiverse这个multimodal entity linking数据集中对于实体的标注导出来进行预测,这样除了可以对social media domain进行评估外,还可以对News domain进行评估。
The WikiDiverse dataset is a very recent multi-modal entity linking dataset constructed by Wang et al. (2022d) based on Wikinews. The dataset has annotations of entity spans and entity labels. We convert the multi-modal entity linking dataset into a multi-modal NER dataset to further show the effectiveness of MoRe on the news domain.
PromptMNER
PromptMNER: Prompt-Based Entity-Related Visual Clue Extraction and Integration for Multimodal Named Entity Recognition
复旦大学计算机科学学院,上海数据科学重点实验室,DASFAA 2022
作者提出了一种利用prompt来更好的导出实体相关的视觉特征的方法。
Multimodal named entity recognition (MNER) is an emerging task that incorporates visual and textual inputs to detect named entities and predicts their corresponding entity types. However, existing MNER methods often fail to capture certain entity-related but textloosely-related visual clues from the image, which may introduce taskirrelevant noises or even errors. To address this problem, we propose to utilize entity-related prompts for extracting proper visual clues with a pre-trained vision-language model. To better integrate different modalities and address the popular semantic gap problem, we further propose a modality-aware attention mechanism for better cross-modal fusion. Experimental results on two benchmarks show that our MNER approach outperforms the state-of-the-art MNER approaches with a large margin.
作者主要是提出了在图像中,对于MNER任务来说,更加重要的是entity-related的视觉特征,而单纯的text-related的视觉特征是和entity以外的文本关联,可能包括了更多的噪音。
为了解决这一问题,作者设计了entity-related prompts,通过利用pretrained vision-language model来判断不同prompt和图像之间的匹配程度,进而选择合适的prompt来作为entity-related的视觉特征。
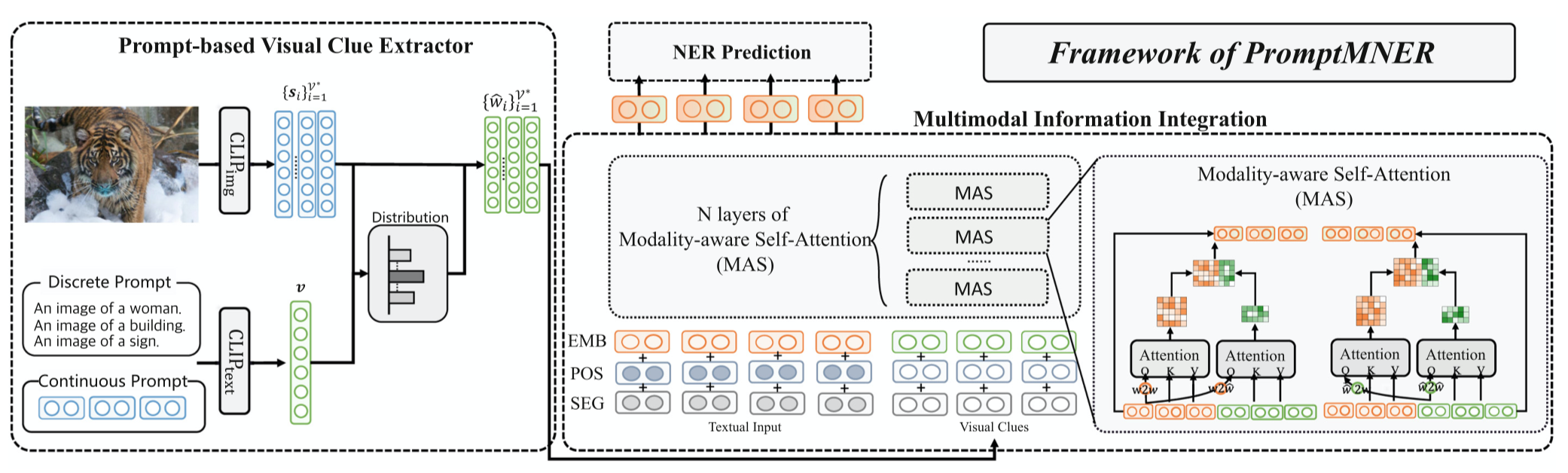
作者定义的prompt形式是\(P_i = \mbox{an image of }[w_i]\),\(w_i\)可以是discrete的word/phrase,也可以是continuous的embedding。
discrete的\(w_i\)来源如下:
- NER的所有实体标签,如person, location, organization
- 从Related Words中和实体标签相关的词,如person的关联词有people, someone, individual, worker, child
- 专家定义的实体标签,如person的人工定义的词有player, pants, hat, suit, group of people, team
因为想要找到所有合适的word描述图像内容是不实际的,因此作者也是用了continuous prompts作为补充,也就是定义没有现实意义的embedding直接作为\(w_i\)。作者发现定义100个continuous prompt达到了最好的效果。
为了确定哪个prompt是最好的描述了图像信息,作者使用CLIP对图像和prompt分别进行编码,然后计算匹配度:

\(<s_i,v>\)是表示余弦相似度。\(s_i\)是\(i\)-th prompt的embedding,\(v\)是图像信息。计算出来的匹配程度与prompt embedding相乘作为找到的视觉特征:
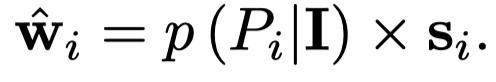
聚合的时候使用了跨模态注意力,这里看图即可,不再赘述。
最后使用基于span的NER分类器:
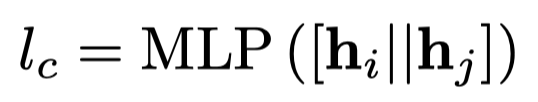
\(i,j\)表示的token \(i\)到token \(j\)的序列,把序列的头尾token embedding拿出来进行分类,\(\{\mbox{person, location, organization, misc, not entity}\}\)。
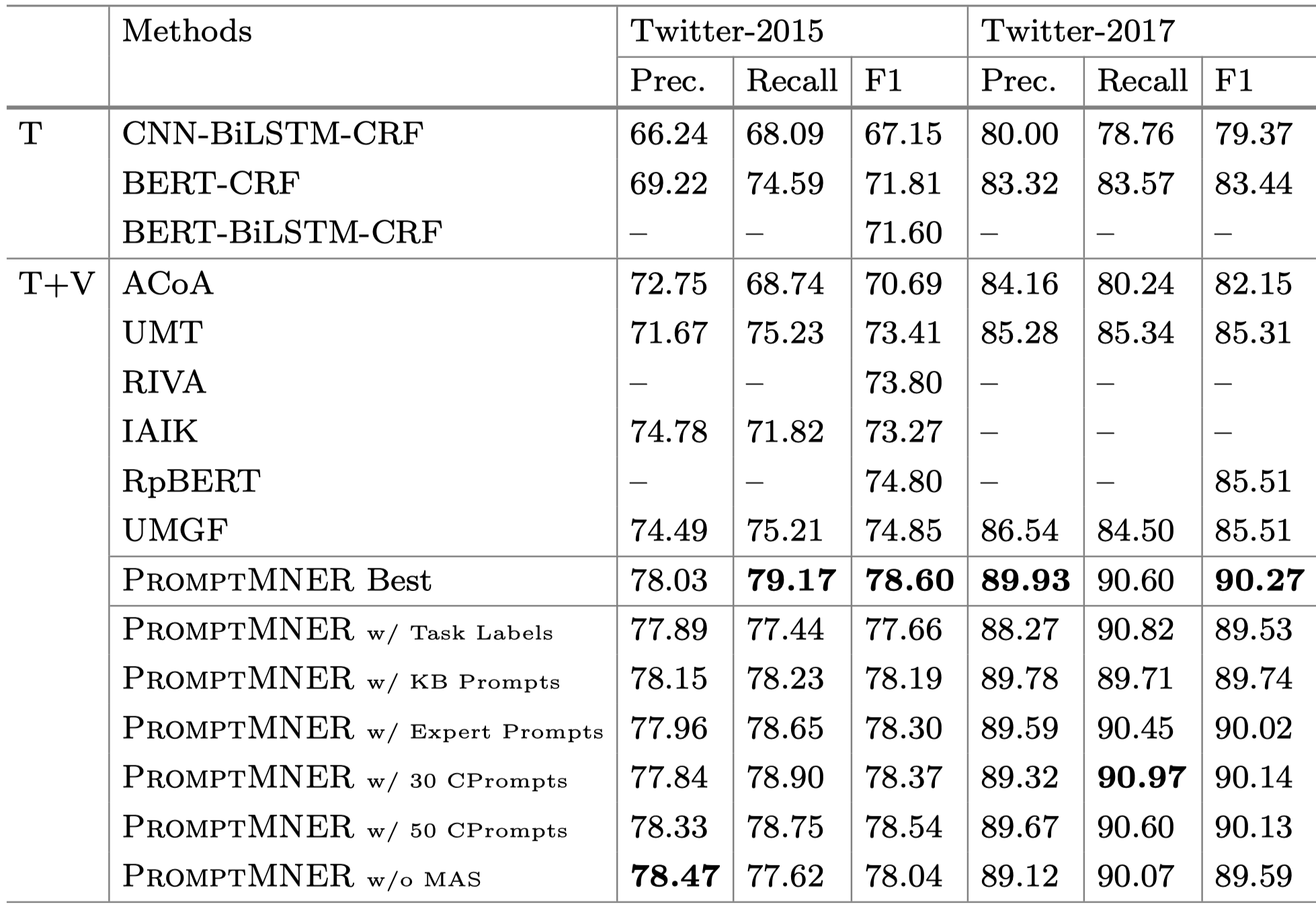
效果上来看还是可以的。
VisualPT-MoE
A Unified Visual Prompt Tuning Framework with Mixture-of-Experts for Multimodal Information Extraction.
东华大学,DASFAA 2023,代码。
Recently, multimodal information extraction has gained increasing attention in social media understanding, as it helps to accomplish the task of information extraction by adding images as auxiliary information to solve the ambiguity problem caused by insufficient semantic information in short texts. Despite their success, current methods do not take full advantage of the information provided by the diverse representations of images. To address this problem, we propose a novel unified visual prompt tuning framework with Mixture-of-Experts to fuse different types of image representations for multimodal information extraction. Extensive experiments conducted on two different multimodal information extraction tasks demonstrate the effectiveness of our method. The source code can be found at https://github.com/xubodhu/VisualPTMoE.
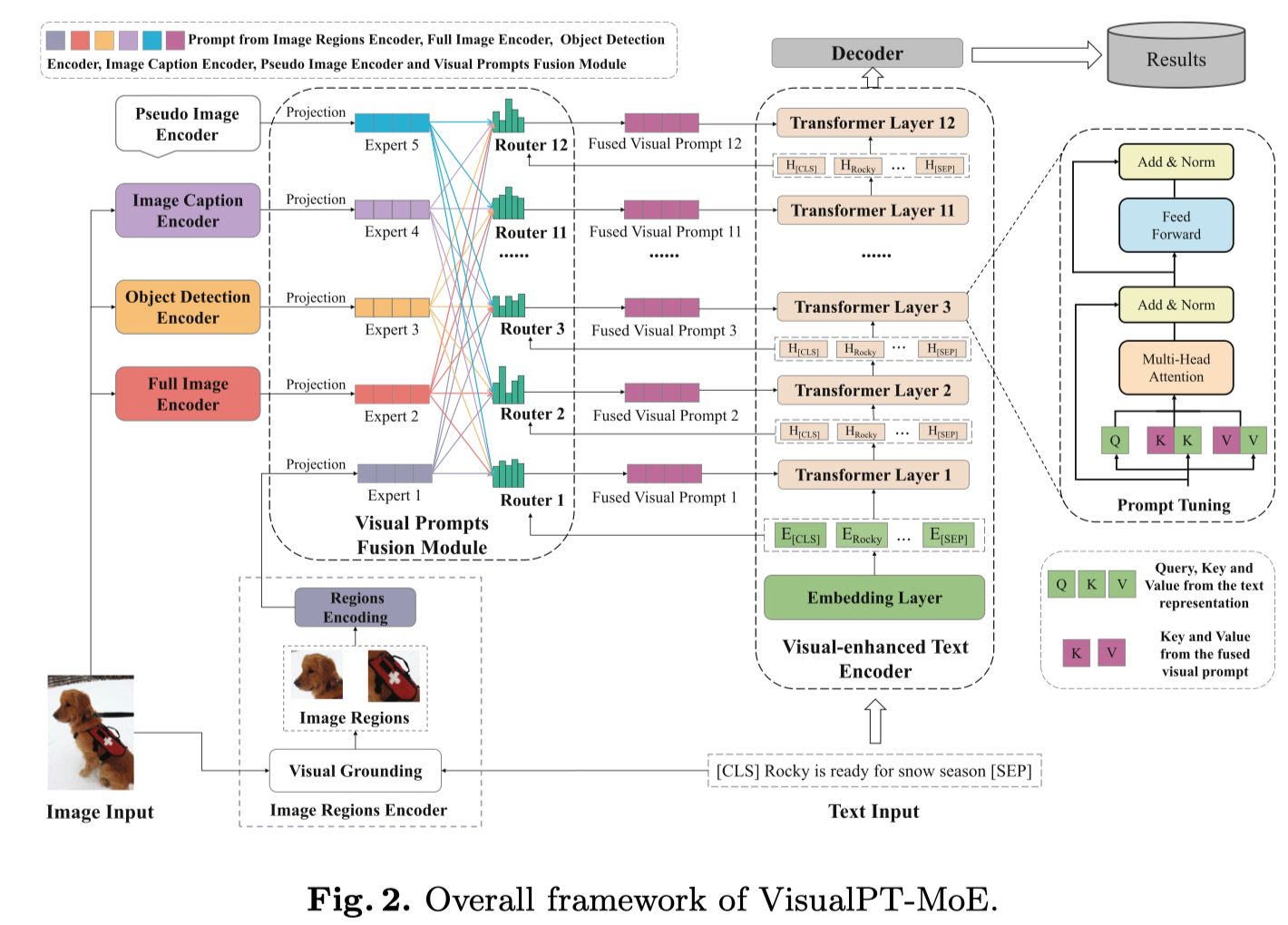
作者的方法图:
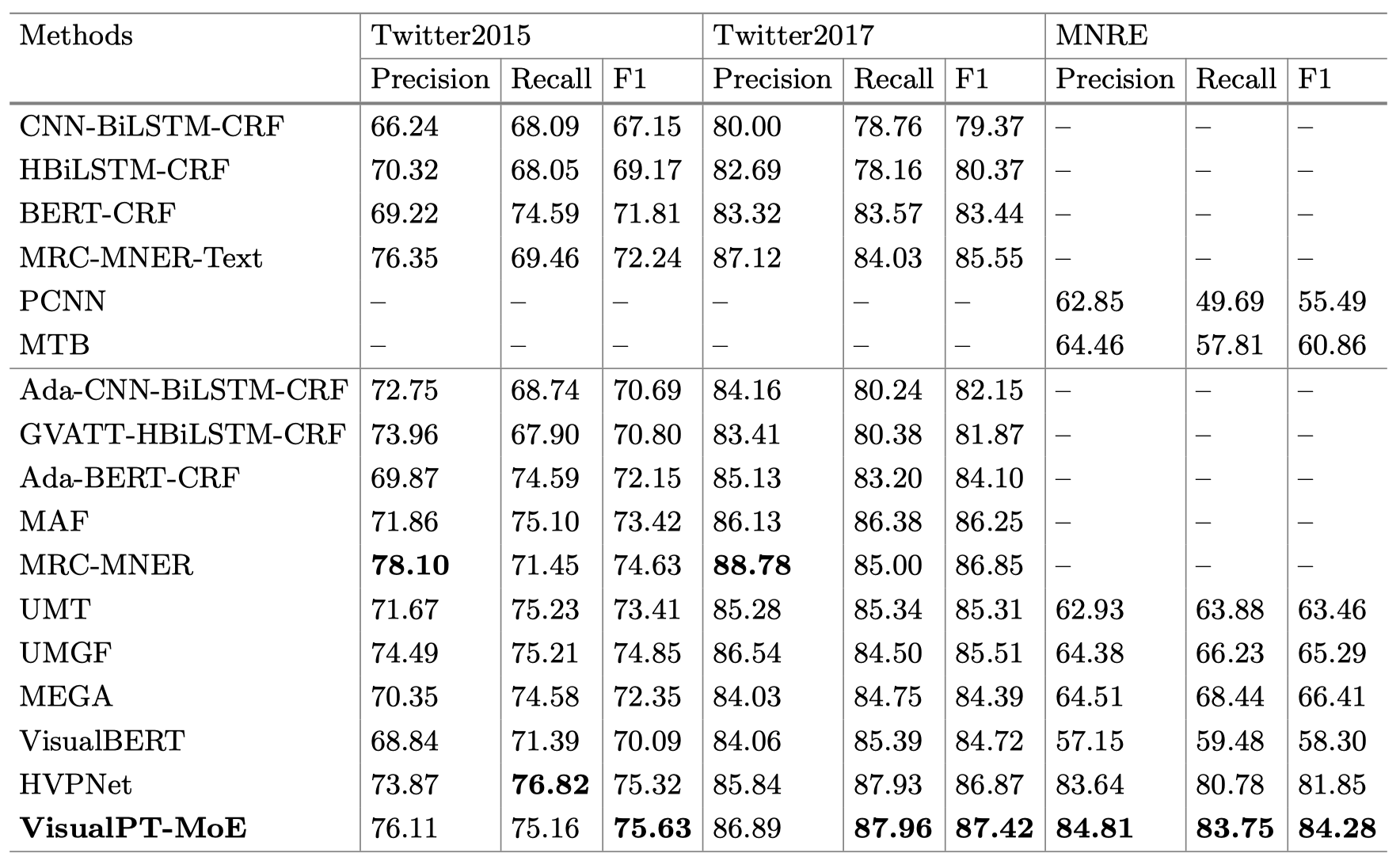
实验结果:
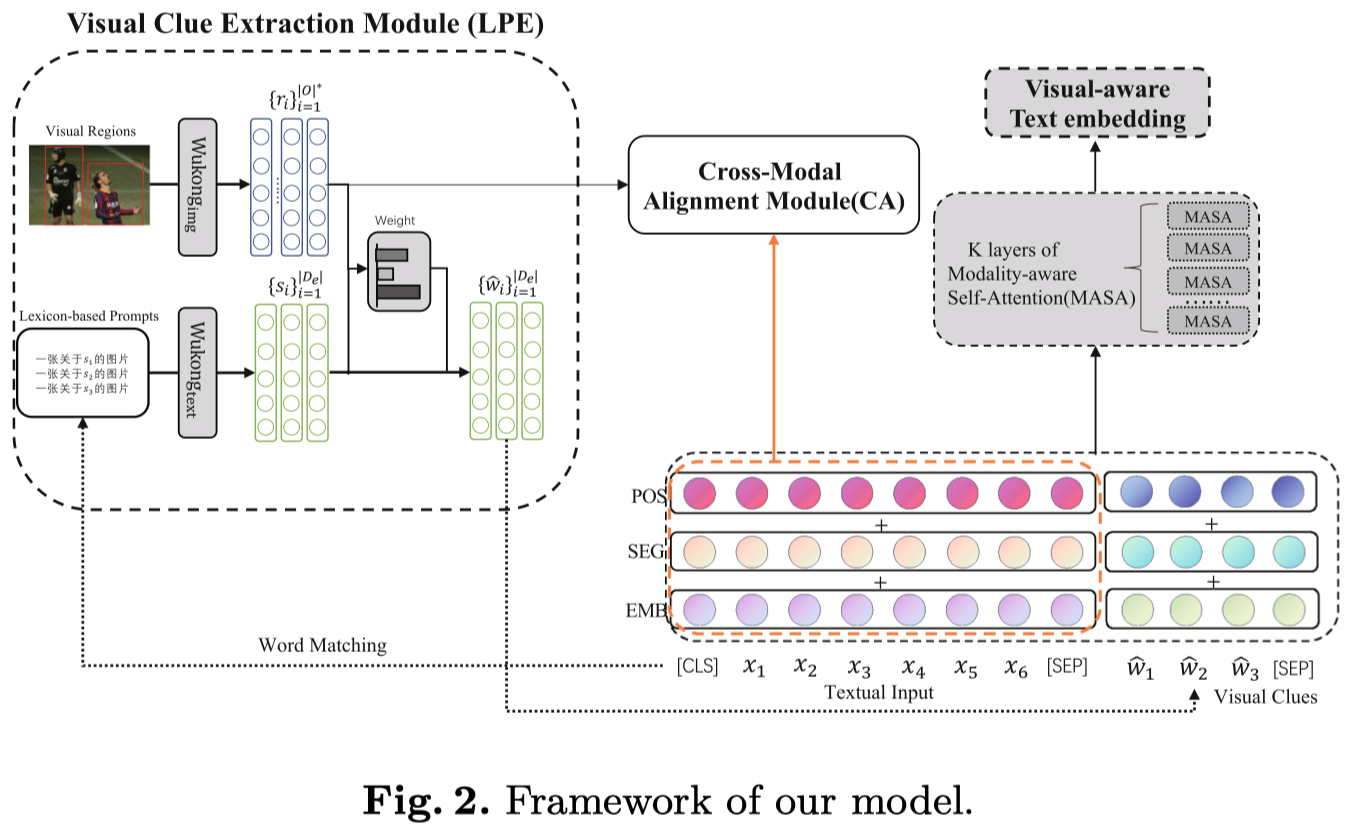
Wukong-CMNER
Wukong-CMNER: A Large-Scale Chinese Multimodal NER Dataset with Images Modality
人大,DASFAA 2023
So far, Multimodal Named Entity Recognition (MNER) has been performed almost exclusively on English corpora. Chinese phrases are not naturally segmented, making Chinese NER more challenging; nonetheless, Chinese MNER needs to be paid more attention. Thus, we first construct Wukong-CMNER, a multimodal NER dataset for the Chinese corpus that includes images and text. There are 55,423 annotated image-text pairs in our corpus. Based on this dataset, we propose a lexicon-based prompting visual clue extraction (LPE) module to capture certain entity-related visual clues from the image. We further introduce a novel cross-modal alignment (CA) module to make the representations of the two modalities more consistent through contrastive learning. Through extensive experiments, we observe that: (1) Discernible performance boosts as we move from unimodal to multimodal, verifying the necessity of integrating visual clues into Chinese NER. (2) Cross-modal alignment module further improves the performance of the model. (3) Our two modules decouple from the subsequent predicting process, which enables a plug-and-play framework to enhance Chinese NER models for Chinese MNER task. LPE and CA achieve state-of-the-art (SOTA) results on Wukong-CMNER when combined with W2NER [11], demonstrating its effectiveness.
作者创建了首个中文MNER数据集:

作者也提出了一个方法:
CoT-MIE
Chain-of-Thought Prompt Distillation for Multimodal Named Entity Recognition and Multimodal Relation Extraction
阿里Ant group,2023-08 arXiv
Multimodal Named Entity Recognition (MNER) and Multimodal Relation Extraction (MRE) necessitate the fundamental reasoning capacity for intricate linguistic and multimodal comprehension. In this study, we explore distilling the reasoning ability of large language models (LLMs) into a more compact student model by generating a chain of thought (CoT) – a sequence of intermediate reasoning steps. Specifically, we commence by exemplifying the elicitation of such reasoning ability from LLMs through CoT prompts covering multi-grain (noun, sentence, multimodality) and data-augmentation (style, entity, image) dimensions. Subsequently, we present a novel conditional prompt distillation method to assimilate the commonsense reasoning ability from LLMs, thereby enhancing the utility of the student model in addressing text-only inputs without the requisite addition of image and CoT knowledge. Extensive experiments reveal that our approach attains state-of-the-art accuracy and manifests a plethora of advantages concerning interpretability, data efficiency, and cross-domain generalization on MNER and MRE datasets.
作者声称是希望能够将LLM的推理能力交给小模型,但是个人阅读下来感觉小模型也没有学会推理能力。并且这里一直在强调CoT,事实上这篇论文个人更愿意看做是一种数据增强/知识检索的方法,毕竟LLM本身没有针对信息抽取给出中间的推理步骤。
作者的做法出发点是:
之前的基于检索的模型,难以保证检索到的结果和查询的句子是匹配的,比如下图:

大模型的推理成本比较高,但是它的推理能力比较好。希望能够用个小模型学会大模型的推理能力,并且有较低的推理成本。
作者的方法:
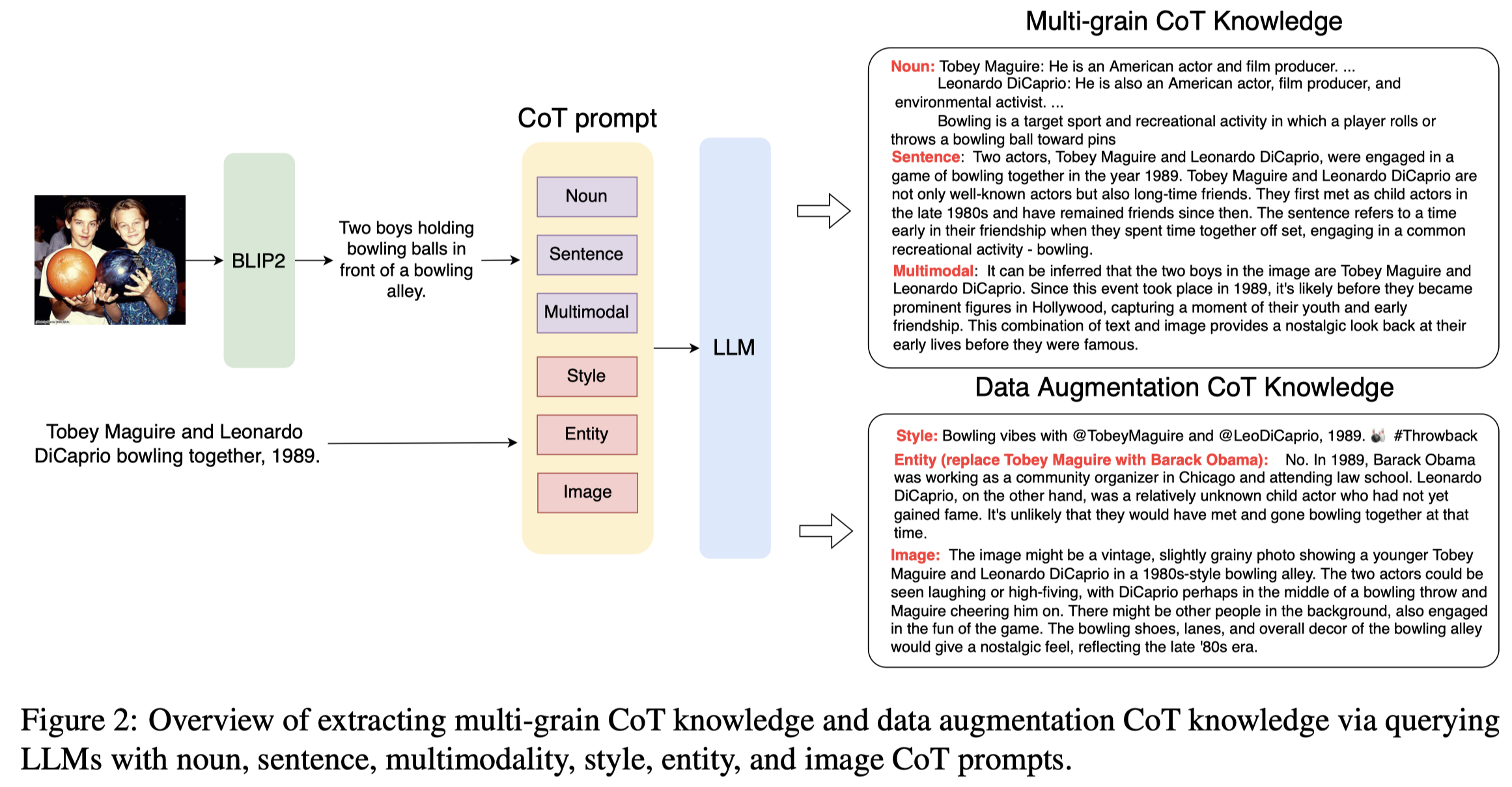
首先,作者用BLIP2把多模态信息抽取中的图片转化为文本caption。
然后利用LLM生成下面几种额外的知识:
- Noun:对于句子中的potential entities, slang, and terminology等名词进行查询,对应的prompt是:
Help me explain the meaning of special words for understanding. + x - Sentence:对于整个句子进行理解,It can explain the sentiment, cause, and subject of users. 对应的prompt是
Explain the sentence to me with necessary background. + x - Multimodality:让LLM解释潜在的image和text之间的关系,这一步可以用来去噪、潜在的对齐visual object和textual entity,对应的prompt是:
What is the relation between the text and the attached image? + x + I
作者还利用LLM进行了数据增强:
- Style:利用LLM转换输入句子的风格,让文本的描述保持一致的风格,对应的prompt是
Transform the sentence in Twitter style without changing the meaning. + x - Entity:用同类型的entity替换候选的entity,然后用LLM判断替换后的伪样本是否成立,判断的prompt是
Whether the sentence is possible in fact, answer yes or no. + x - Image:让LLM猜测能够和文本描述对应的image长什么样子,对应的prompt是
What is a possible image with the text in a tweet? + x
数据增强后的样本被看做是新的样本。
然后问题的关键是怎么样能够让小模型学会LLM的推理,作者声称提出了Conditional Prompt Distillation的方法。具体做法是首先作者把原始的text \(x\)、图像的caption \(I\)以及LLM生成的知识\(c\)拼接到一起,经过text encoder获得输出分布\(H_k\);然后,作者定义了可学习的soft prompt来作为conditional prompt聚合text:
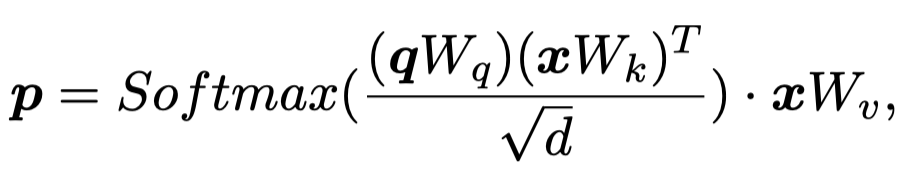
这里生成的\(p\)和原始的text \(x\)拼接在一起,经过text encoder获得输出分布\(H_t\);最后,作者期望这两种分布是相近的:
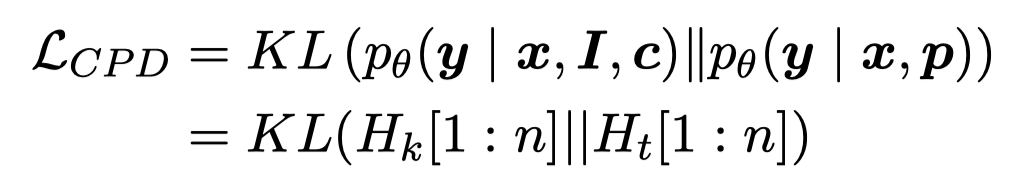
个人对于这个公式有点疑惑,这里的分布到底是信息抽取的classification distribution还是token distribution?
更疑惑的是,最后预测结果仍然是加入了LLM生成知识\(c\)的结果:
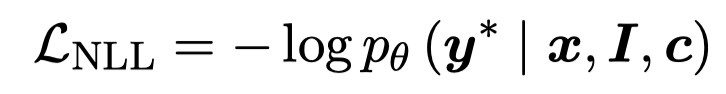
难道是在测试阶段仅仅用小模型,不需要LLM提前处理?
实验结果:
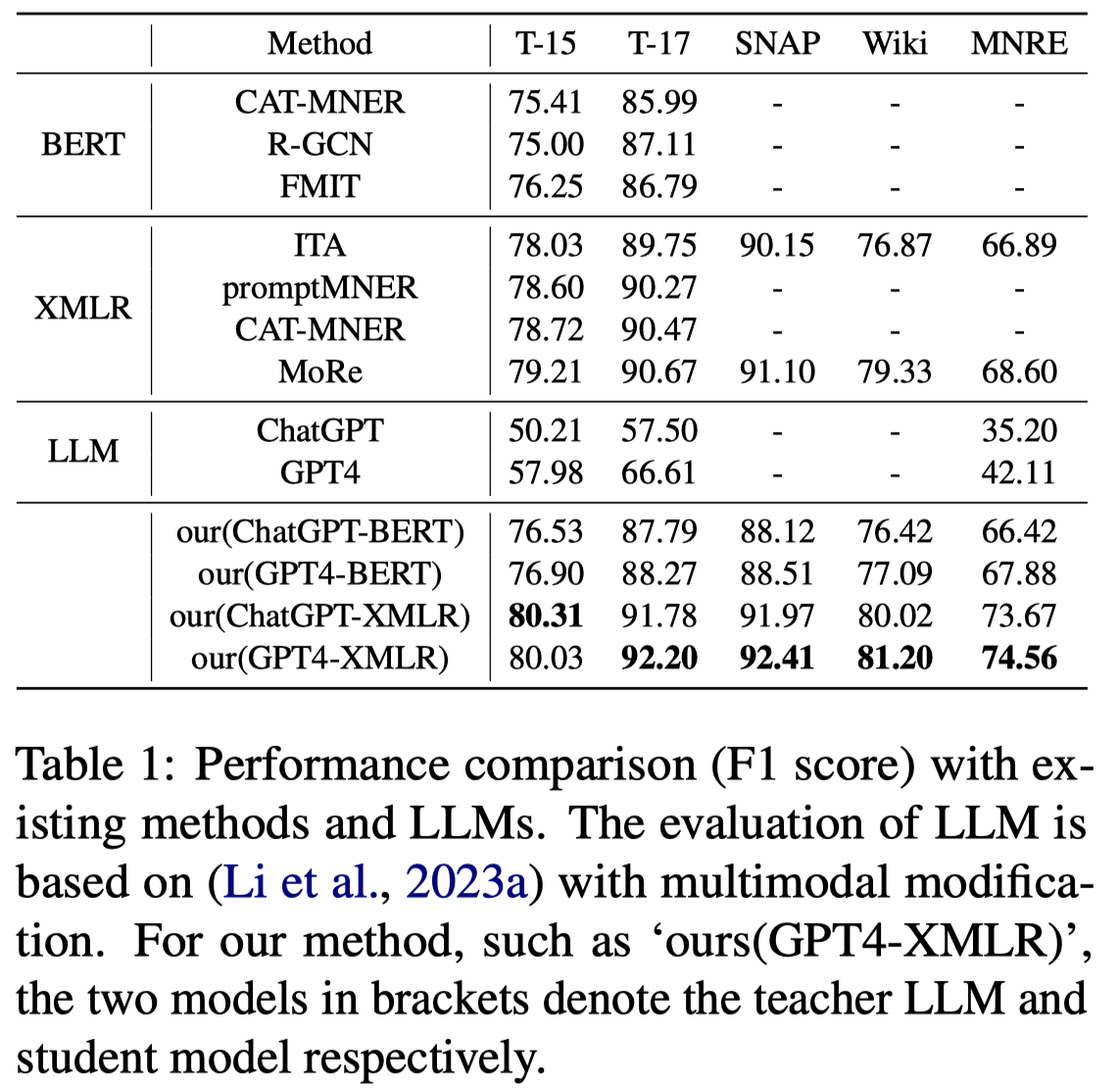
和目前的SOTA相比,MNRE数据集上还有10%的差距;而Twitter15和17数据集可以认为是达到了SOTA。
另外从消融的结果来看,对于名词的解释,可能作用相对比较大:
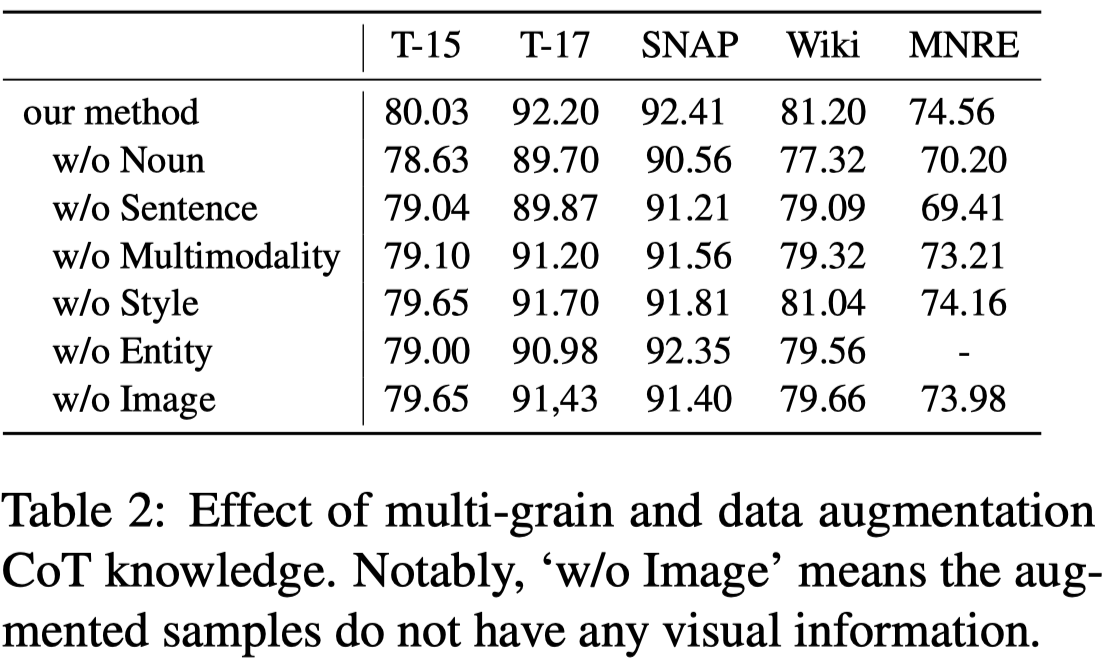
论文的case study可以看下,感觉这些LLM生成的knowledge还是比较有意义的,问题在于没有CoT..也不确定小模型是否学习到了推理能力:

PGIM
Prompt ChatGPT In MNER: Improved multimodal named entity recognition method based on auxiliary refining knowledge from ChatGPT
天津大学,2023-05,arXiv
Multimodal Named Entity Recognition (MNER) on social media aims to enhance textual entity prediction by incorporating image-based clues. Existing research in this domain has primarily focused on maximizing the utilization of potentially relevant information in images or incorporating external knowledge from explicit knowledge bases (KBs). However, these methods either neglect the necessity of providing the model with relevant external knowledge, or the retrieved external knowledge suffers from high redundancy. To address these problems, we propose a conceptually simple two-stage framework called Prompt ChatGPT In MNER (PGIM) in this paper. We leverage ChatGPT as an implicit knowledge engine to acquire auxiliary refined knowledge, thereby bolstering the model’s performance in MNER tasks. Specifically, we first utilize a Multimodal Similar Example Awareness module to select suitable examples from a small number of manually annotated samples. These examples are then integrated into a formatted prompt template tailored to the MNER task, guiding ChatGPT to generate auxiliary refined knowledge. Finally, the acquired knowledge is integrated with the raw text and inputted into the downstream model for further processing. Extensive experiments show that our PGIM significantly outperforms all existing state-of-the-art methods on two classic MNER datasets.
作者是期望利用LLM来解决:
一般的text+image的多模态小模型,可能需要外部的知识来进行识别
而基于外部knowledge的信息抽取方法检索到的外部知识可能相关性程较低,或者是冗余
作者同样把LLM看做是一个可以提供high-quality auxiliary knowledge的base。
方法:
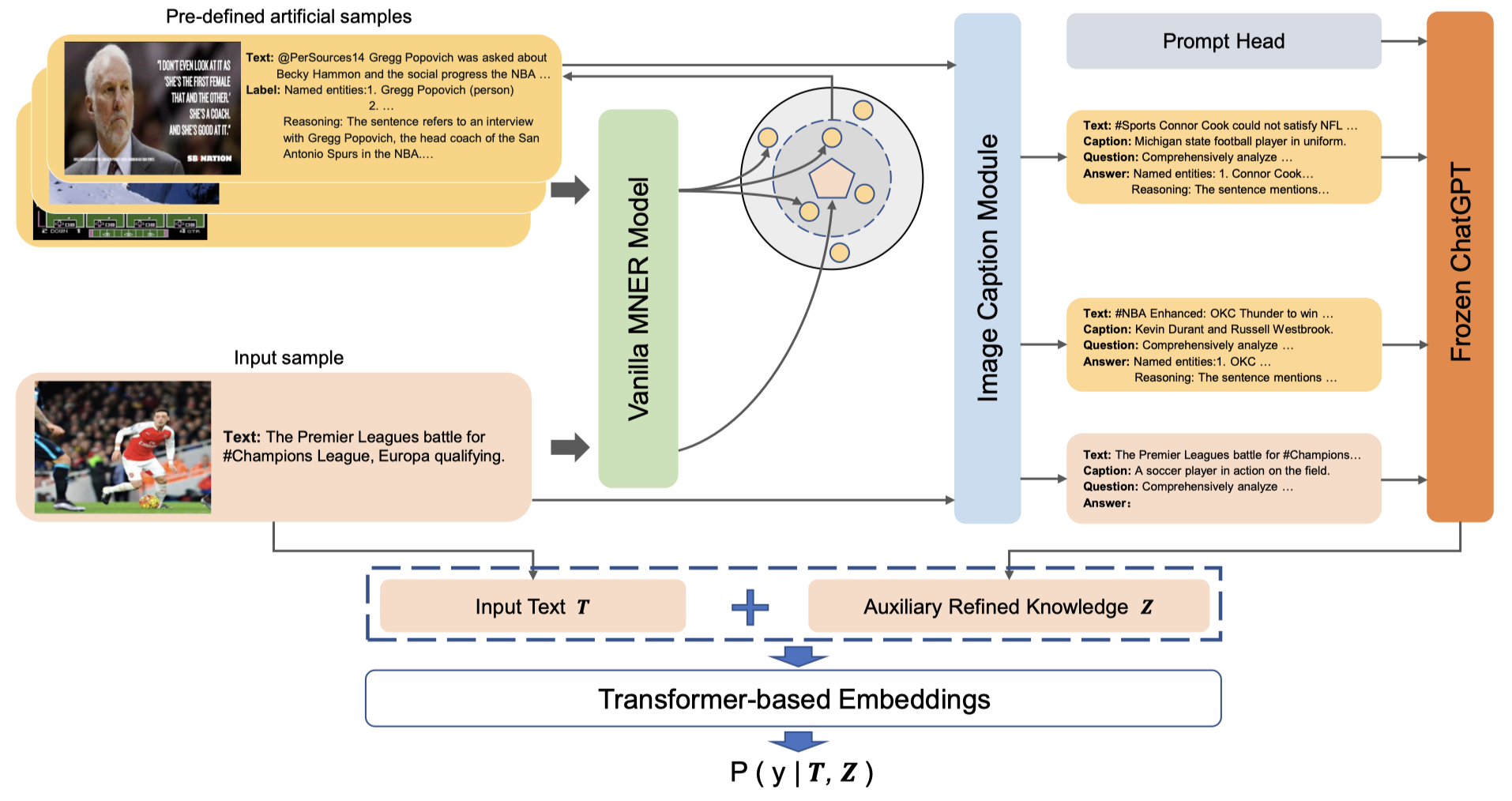
首先,作者在这里使用LLM导出的外部knowledge包括了LLM抽取出的实体,以及推理的原因。
那么怎么样让LLM能够生成这样的knowledge呢?
作者随机从数据集中选择了一小部分样例,然后人工写了推理原因,这一小部分样例会作为待抽取的句子的上下文来获取LLM的knowledge。
作者使用cosine相似度,从这小部分人工标注的样例中选择合适的样例作为上下文(实现中选择\(5\)个样例做上下文):
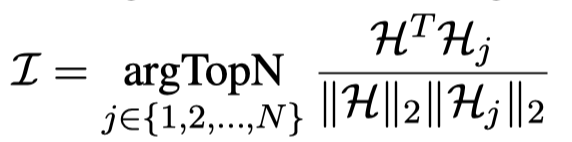
公式里的\(H\)代表着multimodal representations,作者使用UMT方法导出multimodal representations来计算样例相似度。(但不清楚这里的\(H\)具体是指序列中哪个embedding?)
拿到上下文之后,作者用来查询的prompt:
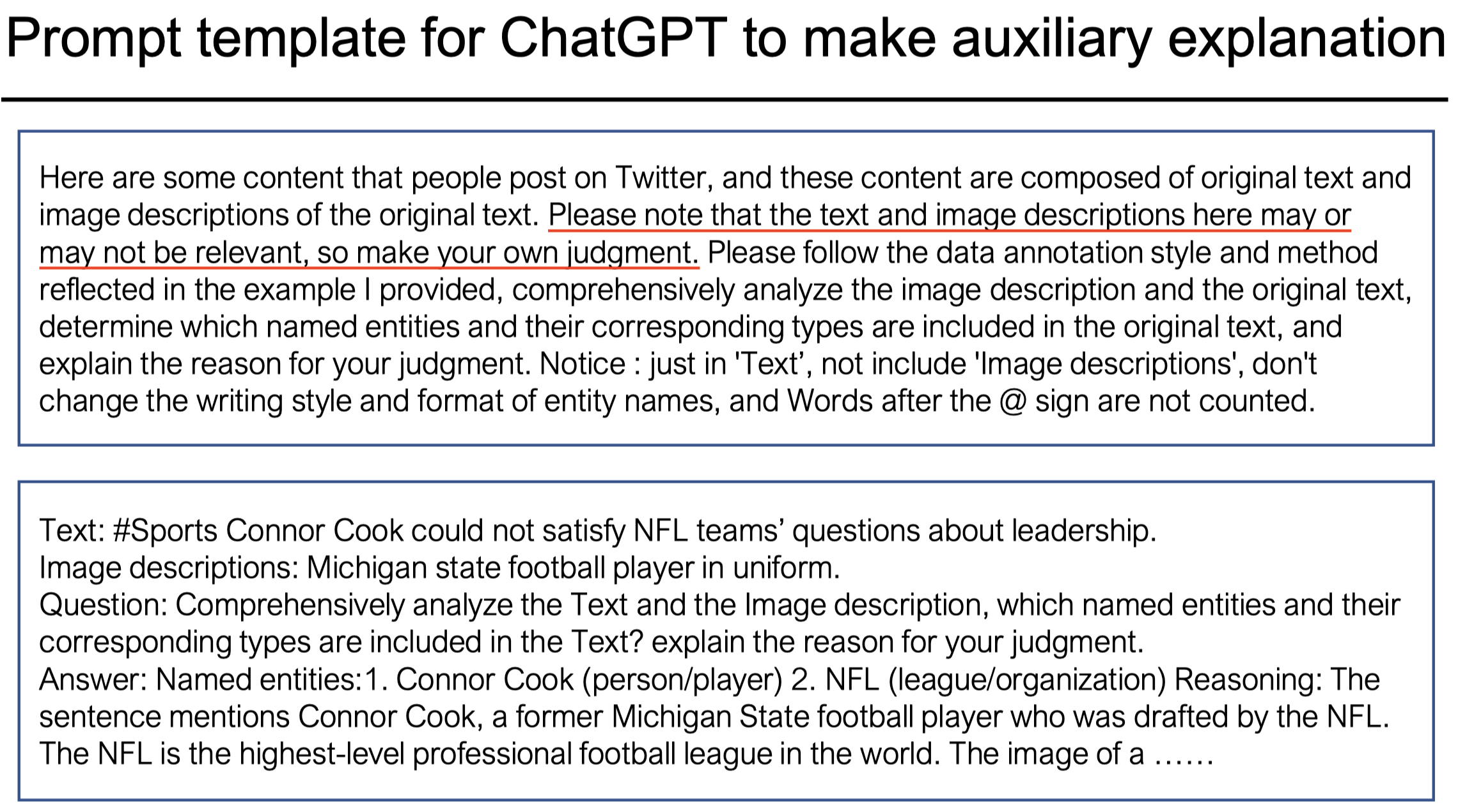
注意一下,只是使用了纯文本的ChatGPT,因此作者是使用BLIP2把image转化为text caption去查询的。并且在prompt里,作者提示LLM可以选择是否采用来自image的信息。
在拿到了LLM输出的auxiliary knowledge \(z\)之后,与原有的text拼接,经过一个Transformer encoder(实验中是XLM-RoBERTa-large),最后过CRF获取实体的BIO预测标注。
实验结果:
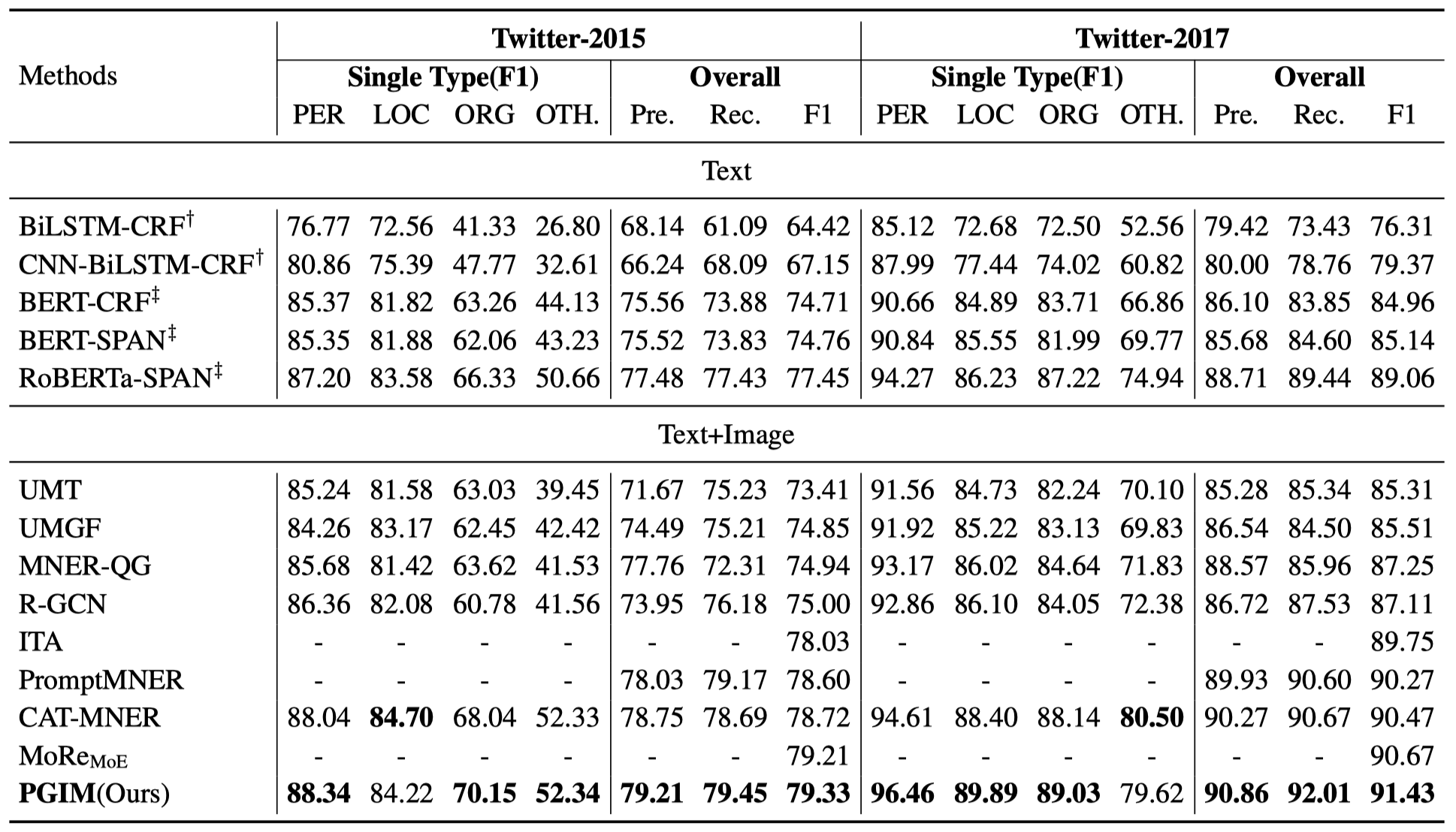
Twitter2015数据集相比较MoRe方法提升不太明显。(image在这两个Twitter数据集上到底有多大作用,个人现在很怀疑,并且标注也不够好,有很多的噪音…)
case study:
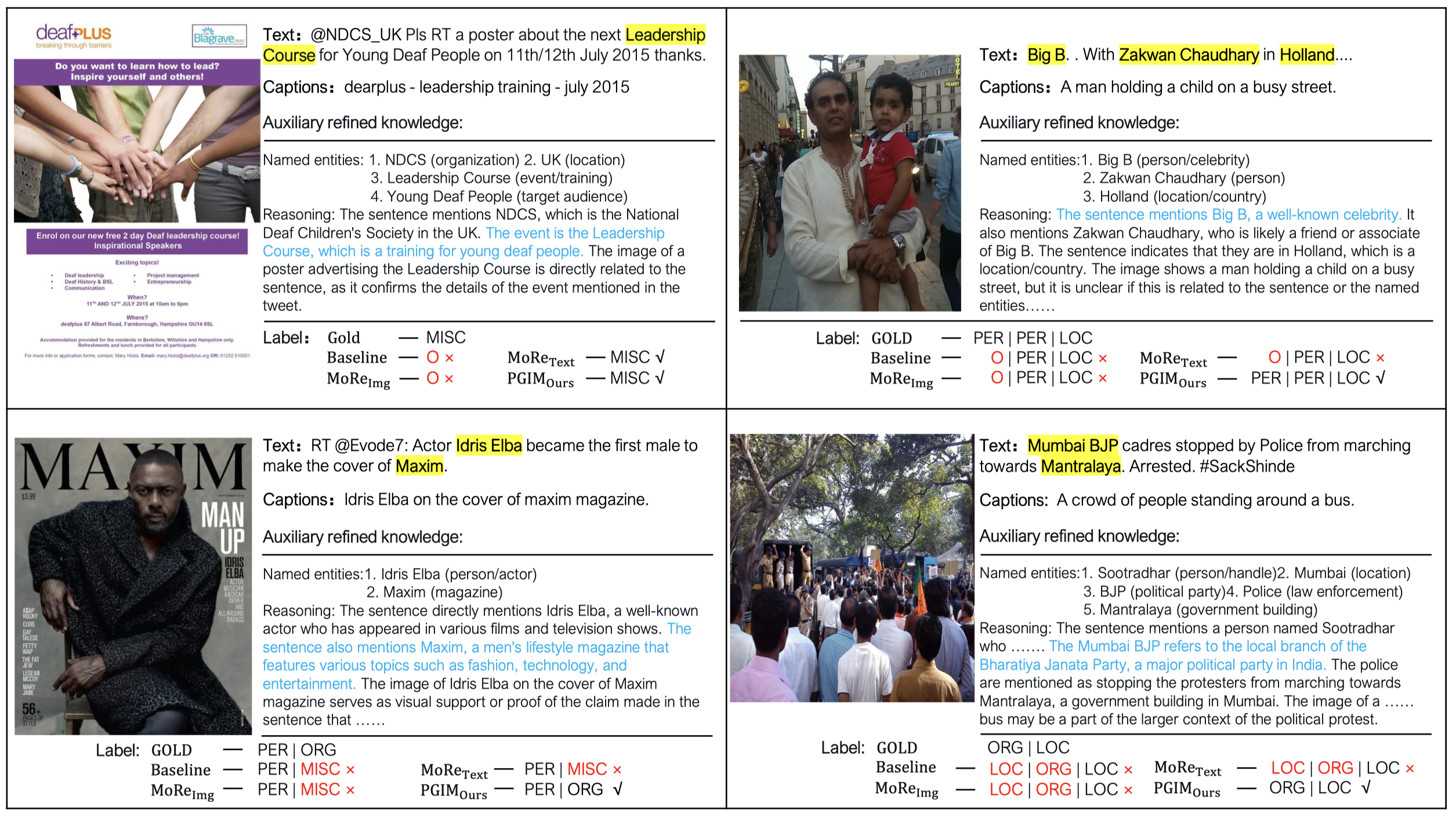
能够看出来,作者倾向于在LLM的输出推理过程中,直接对span进行解释,因此蓝色的句子里会很明显的线索来知道最后识别实体。