MM-DA
Multimodal data augmentation
多模态数据增强调研。
Large model DA survey
A Survey on Data Augmentation in Large Model Era. arXiv 2024. 吉林大学
Large models, encompassing large language and diffusion models, have shown exceptional promise in approximating human-level intelligence, garnering significant interest from both academic and industrial spheres. However, the training of these large models necessitates vast quantities of high-quality data, and with continuous updates to these models, the existing reservoir of high-quality data may soon be depleted. This challenge has catalyzed a surge in research focused on data augmentation methods. Leveraging large models, these data augmentation techniques have outperformed traditional approaches. This paper offers an exhaustive review of large model-driven data augmentation methods, adopting a comprehensive perspective. We begin by establishing a classification of relevant studies into three main categories: image augmentation, text augmentation, and paired data augmentation. Following this, we delve into various data post-processing techniques pertinent to large model-based data augmentation. Our discussion then expands to encompass the array of applications for these data augmentation methods within natural language processing, computer vision, and audio signal processing. We proceed to evaluate the successes and limitations of large model-based data augmentation across different scenarios. Concluding our review, we highlight prospective challenges and avenues for future exploration in the field of data augmentation. Our objective is to furnish researchers with critical insights, ultimately contributing to generating sufficient and diverse data to train more sophisticated large models. We consistently maintain the related open-source materials at: https://github.com/MLGroup-JLU/LLM-data-aug-survey.
这篇survey作者认为大模型LM包括LLM和diffusion model。
作者认为使用大模型和传统方法的优缺点:

作者从增强的数据类型的角度划分:
- Image Augmentation:增强image
- Text prompt-driven approaches
- Visual prompt-driven approaches
- Subject-driven approaches:Subject-driven approaches aim at synthesizing diverse and personalized images based on user-provided images capturing a specific subject. 给定一个subject,来创建包含subject的新images
- Text Augmentation:增强文本
- Label-based approaches:In the label-based approach, models are employed to annotate text data, effectively enriching the text dataset with a larger volume of labeled instances. 数据标注
- Generated content-based approaches:In contentbased strategies guide models to synthesize new text data to expand the dataset with freshly generated textual material.
- Paired Data Augmentation:增强文本+image
作者认为的几个未来发展方向:
- Theoretical Understanding:一般的DA方法常常假设augmented data are label-preserving and do not alter the data distribution. 但是这种假设通常没有理论验证
- The Number of Augmented Data:关于DA方法的一个有趣常见现场是An intriguing aspect of data augmentation is that the enhancement in training data quantity does not invariably correlate with a linear improvement in performance. 随着增强数据的增加,模型性能的提升往往不能够持续提升。增强的数据量多少是合适的,并没有一个统一的结论。
- Multimodal Data Augmentation:以前的绝大多数方法是集中在生成单个模态数据
- Automatic Data Augmentation:如何自选选择合适的DA策略、选择合适的DA数据
- Robust and Consistent Data Augmentation:tailor general-domain large models with domain-specific data when addressing particular tasks, ensuring the augmented data’s relevance and accuracy. 比如说当LLM生成medical texts时,常常会生成领域无关的文本
- The Instruction Following Ability of Large Models:如何评估DA任务上,LLM的指令跟随能力
- The Evaluation of Augmented Data:如何设计直接评估增强的数据的质量的metric(能够评估diversity、faithfulness、the diversity of individual data points、the overall consistency of the dataset)、benchmark
- Beyond Augmentation: Training Large Models Using Augmented Data:如何生成能够训练大模型的增强数据
T-SciQ
T-SciQ: Teaching Multimodal Chain-of-Thought Reasoning via Mixed Large Language Model Signals for Science Question Answering. SMU. AAAI 2024. 代码.
Large Language Models (LLMs) have recently demonstrated exceptional performance in various Natural Language Processing (NLP) tasks. They have also shown the ability to perform chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning to solve complex problems. Recent studies have explored CoT reasoning in complex multimodal scenarios, such as the science question answering task, by fine-tuning multimodal models with high-quality human-annotated CoT rationales. However, collecting high-quality COT rationales is usually time-consuming and costly. Besides, the annotated rationales are hardly accurate due to the external essential information missed. To address these issues, we propose a novel method termed T-SciQ that aims at teaching science question answering with LLM signals. The T-SciQ approach generates high-quality CoT rationales as teaching signals and is advanced to train much smaller models to perform CoT reasoning in complex modalities. Additionally, we introduce a novel data mixing strategy to produce more effective teaching data samples for simple and complex science question answer problems. Extensive experimental results show that our T-SciQ method achieves a new state-of-the-art performance on the ScienceQA benchmark, with an accuracy of 96.18%. Moreover, our approach outperforms the most powerful fine-tuned baseline by 4.5%. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/T-SciQ/T-SciQ.
Issue: 之前的工作利用LLM在文本模型上进行CoT推理,没有考虑多模态场景。一个思路是把图像转换为文本模态,然后再进行推理。但是这会使得大量的image信息丢失,特别是在处理复杂image的情况下。最近的一个方法Multimodal-CoT能够同时处理图像和文本,但是需要人工标注CoT,这存在两个问题:
- First, the human annotation of CoT reasoning is time-consuming. 成本高
- Second, the annotated rationale may lack essential external information to derive the final answer due to the limited expertise of human annotators. 由于标注人员的经验,可能标注中缺少必要的额外信息

Solution:作者的思路是让LLM来生成CoT,然后蒸馏出小模型获得更好的效果。
作者的方法分为三步,第一步是基于zero-shot获取两个CoT标注,Question-Answer-CoT和Planning-based CoT。
下面是获取普通CoT的prompt:

下面是分阶段获取Planning-based CoT的prompt:



第二步是为不同的sample选择合适的CoT。因为简单的Question不需要分解,而复杂的question需要分解。The QA-PCoT dataset is effective for teaching problem-solving skills for complex problems, while simpler problems don’t require decomposition. In contrast, the QA-CoT dataset is suitable for teaching problem-solving skills for simple problems.
这一步作者的操作是基于validation set,对不同的skill的sample分别使用CoT和PCoT。然后对比生成的答案的正确率,选择更容易生成正确答案的CoT类型。
第三步是微调小模型来学会生成CoT以及推理答案。先是微调小模型生成rationales。然后使用rationales作为输入,生成预测的答案。
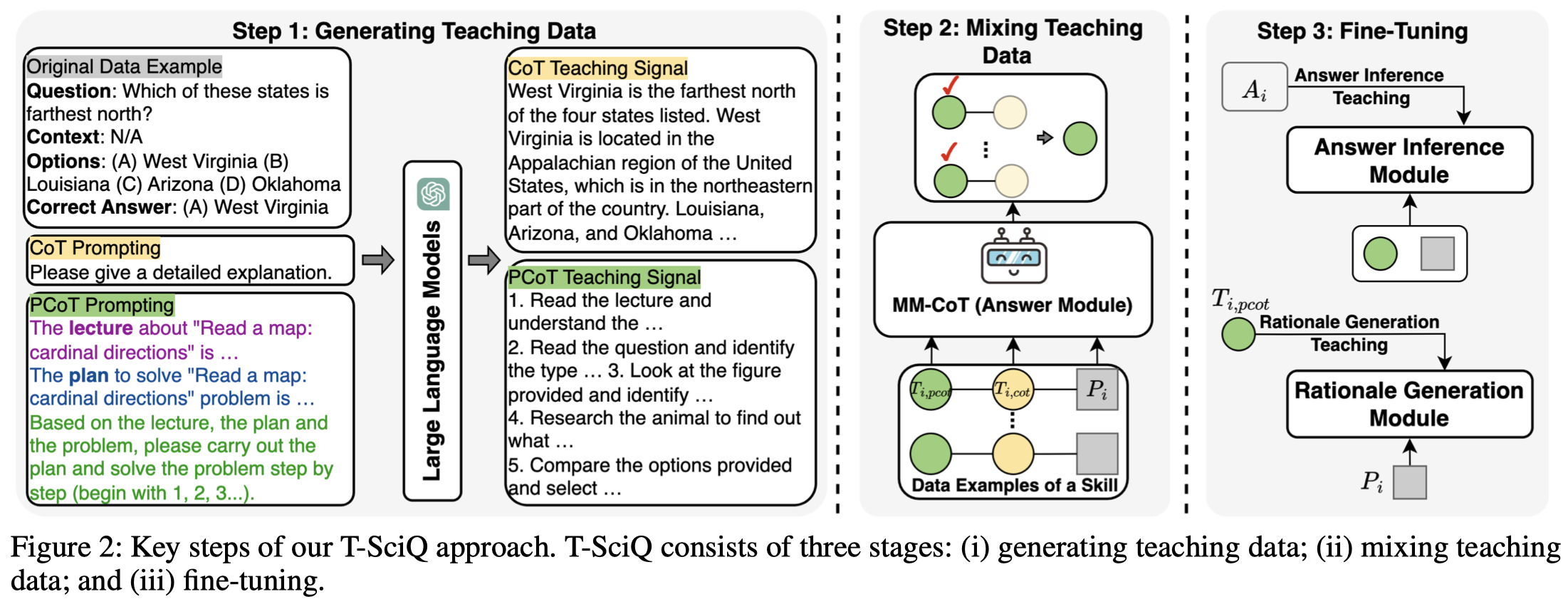
作者使用的LLM是text-davinci-003。
SelTDA
Q: How to Specialize Large Vision-Language Models to Data-Scarce VQA Tasks? A: Self-Train on Unlabeled Images!. Northeastern University. CVPR 2023. 代码.
Finetuning a large vision language model (VLM) on a target dataset after large scale pretraining is a dominant paradigm in visual question answering (VQA). Datasets for specialized tasks such as knowledge-based VQA or VQA in non natural-image domains are orders of magnitude smaller than those for general-purpose VQA. While collecting additional labels for specialized tasks or domains can be challenging, unlabeled images are often available. We introduce SelTDA (Self-Taught Data Augmentation), a strategy for finetuning large VLMs on small-scale VQA datasets. SelTDA uses the VLM and target dataset to build a teacher model that can generate question-answer pseudolabels directly conditioned on an image alone, allowing us to pseudolabel unlabeled images. SelTDA then finetunes the initial VLM on the original dataset augmented with freshly pseudolabeled images. We describe a series of experiments showing that our self-taught data augmentation increases robustness to adversarially searched questions, counterfactual examples and rephrasings, improves domain generalization, and results in greater retention of numerical reasoning skills. The proposed strategy requires no additional annotations or architectural modifications, and is compatible with any modern encoder-decoder multimodal transformer. Code available at https://github.com/codezakh/SelTDA.
Issue:VQA任务在面临特定领域的时候,第一个思路是迁移学习,但是这种做法可能加剧缺少一致性、shortcut learning等问题。另一种思路是要收集大量标注数据,但是成本太大。
VQA任务中,往往无标注的images是很容易获取的,如何利用这些无标注的图像来进行特定领域的VQA任务?一个可能的方法是生成针对这些unlabeled images的QA pairs,但是现有的方法往往依赖于images有某种标注,比如caption或者bounding box。
Solution:作者进行了一个motivation experiment发现,经过VQA任务微调的VLM可能会否认自己之前生成的答案,这说明VLM内部面临不同的任务时,会调用不同的knowledge。即针对图像生成描述text,和回答问题时,调用不同的knowledge。
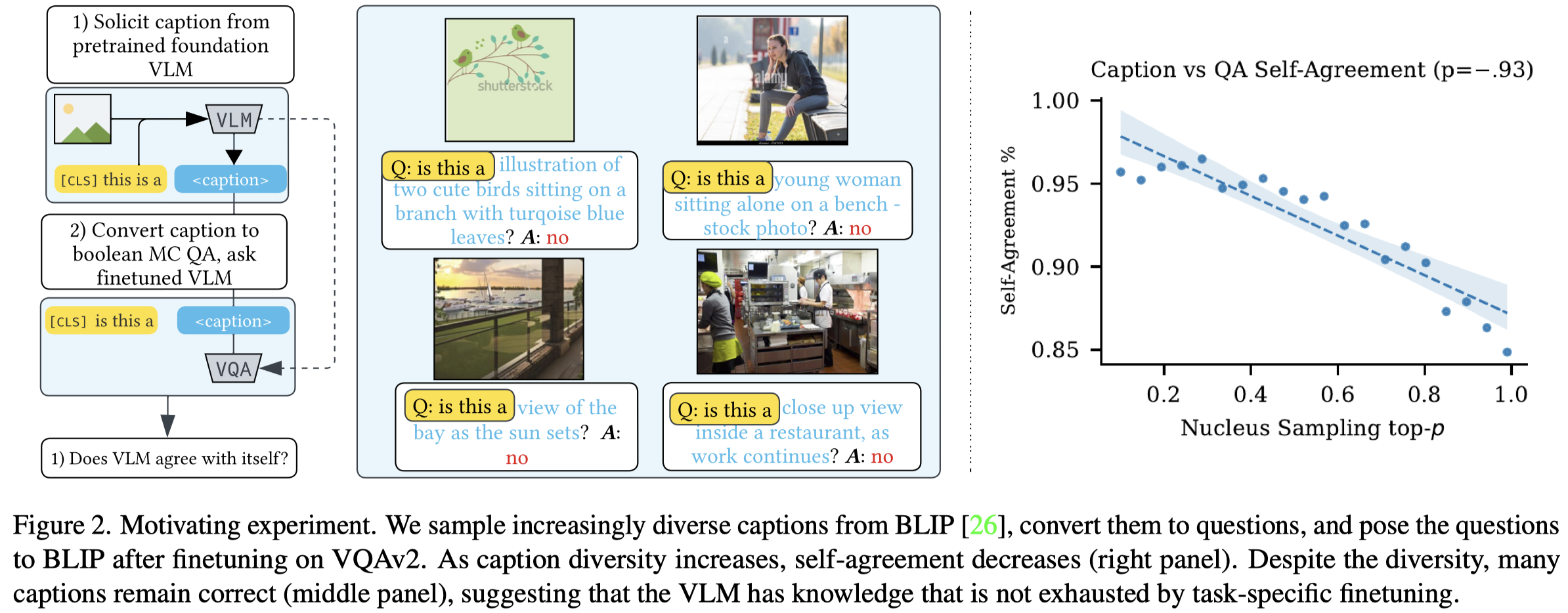
作者的方法是,先训练一个\(VQG_{IC}\),实现给定image,直接生成其对应的QA pairs。这个\(VQG_{IC}\)是在少量的特定任务VQA数据上进行微调的。
为什么可以直接利用少量的领域特定数据,来微调一个VQA生成高质量的QA pairs?作者认为是因为给定一个image,将其转化为text,已经在预训练阶段得到了很好的学习。此时的微调只是让其适应对应的任务输出样式。

生成的新数据和少量的特定任务VQA数据混合,然后再按照一般的VQA微调方法训练进行VQA任务的模型。
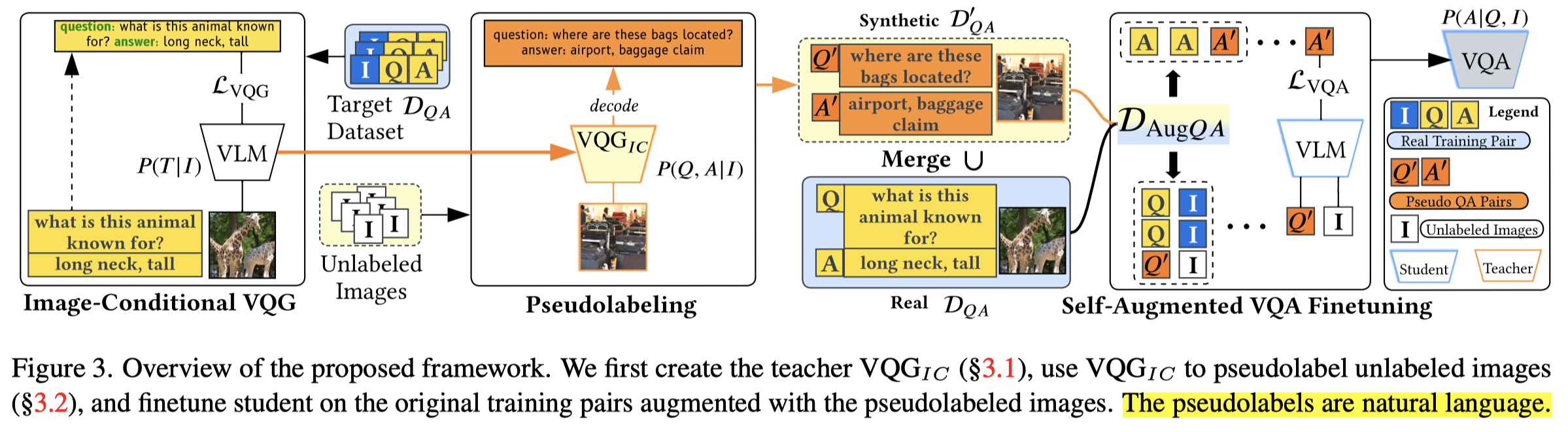
作者的foundation model是BLIP。
ALIA
Diversify Your Vision Datasets with Automatic Diffusion-Based Augmentation. UC Berkeley. NeurIPS 2023. 代码.
Many fine-grained classification tasks, like rare animal identification, have limited training data and consequently classifiers trained on these datasets often fail to generalize to variations in the domain like changes in weather or location. As such, we explore how natural language descriptions of the domains seen in training data can be used with large vision models trained on diverse pretraining datasets to generate useful variations of the training data. We introduce ALIA (Automated Language-guided Image Augmentation), a method which utilizes large vision and language models to automatically generate natural language descriptions of a dataset’s domains and augment the training data via language-guided image editing. To maintain data integrity, a model trained on the original dataset filters out minimal image edits and those which corrupt class-relevant information. The resulting dataset is visually consistent with the original training data and offers significantly enhanced diversity. We show that ALIA is able to surpasses traditional data augmentation and text-to-image generated data on fine-grained classification tasks, including cases of domain generalization and contextual bias. Code is available at https://github.com/lisadunlap/ALIA.
Issue: 经过现有的预训练数据已经很庞大,但是一些特定的任务比如说珍惜鸟类的识别的相关数据仍然很少,这导致了其分类的效果很差。直接获取新数据成本大。为了解决这一问题,之前出现了language-guided data augmentation方法,利用user-supplied domain descriptions或者是descriptions generated from word-to-sentence models来生成新图像。
这种生成式的方法要么需要微调,代价比较大;要么生成的图像缺少在真实数据中的grounding。对于后一点,生成没有在原始数据中出现过的visual context的image对于特定任务可能是没有太大意义的。而直接利用扩散模型进行text-to-image的生成,很难直接特定领域图像相似的图像。
Solution:为了解决这一点,作者不是直接生成全新的图像,而是进行图像编辑,从而保留原始image中的任务相关信息。之前方法和作者的增强方法的对比:
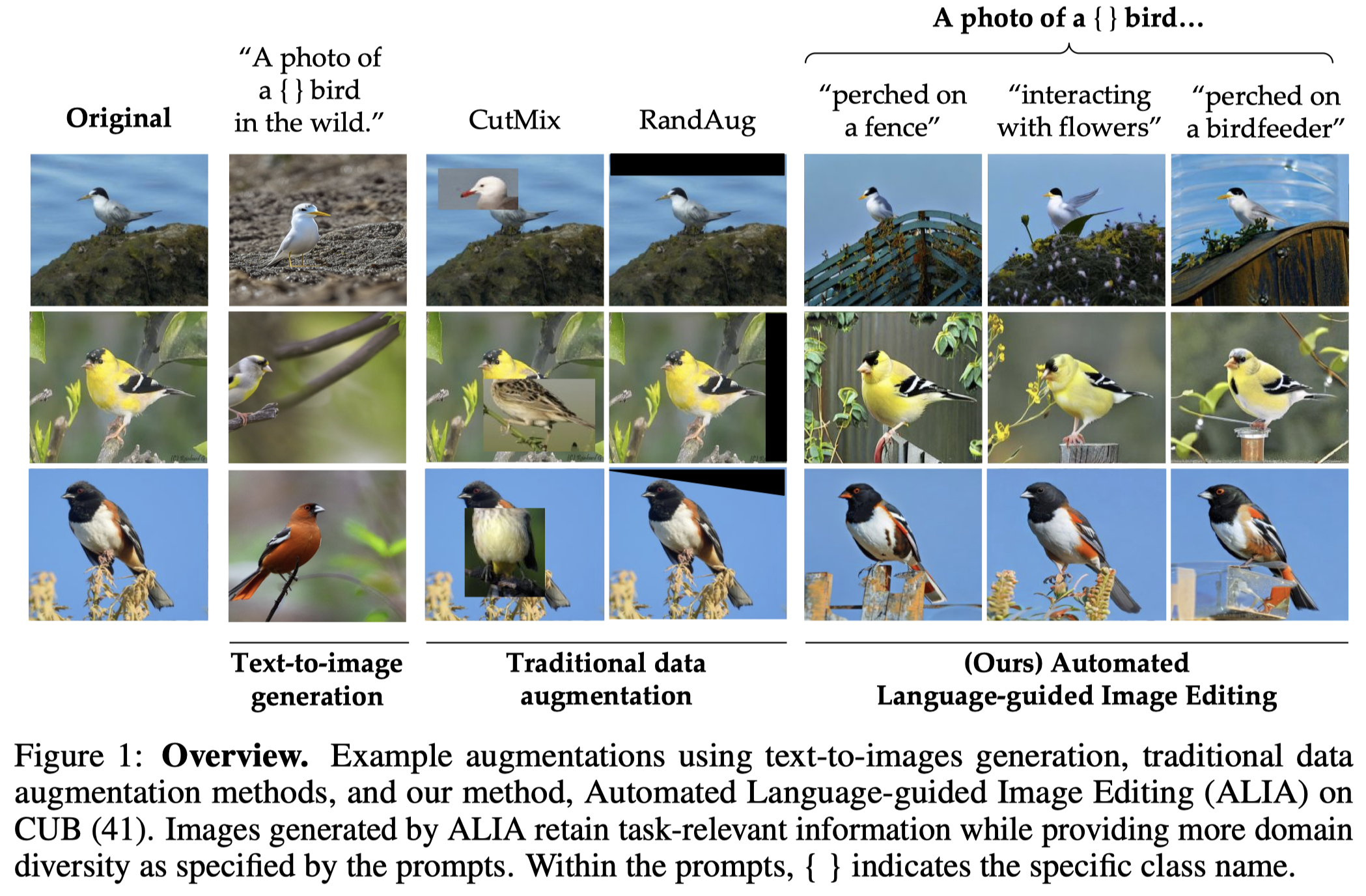
所谓的image的domain,不同于NLP中常提到的domain,是指image的各个关键因素:
We define domain to be any aspect of an image that is not intended to be used for classification (e.g. location, weather, time of day).
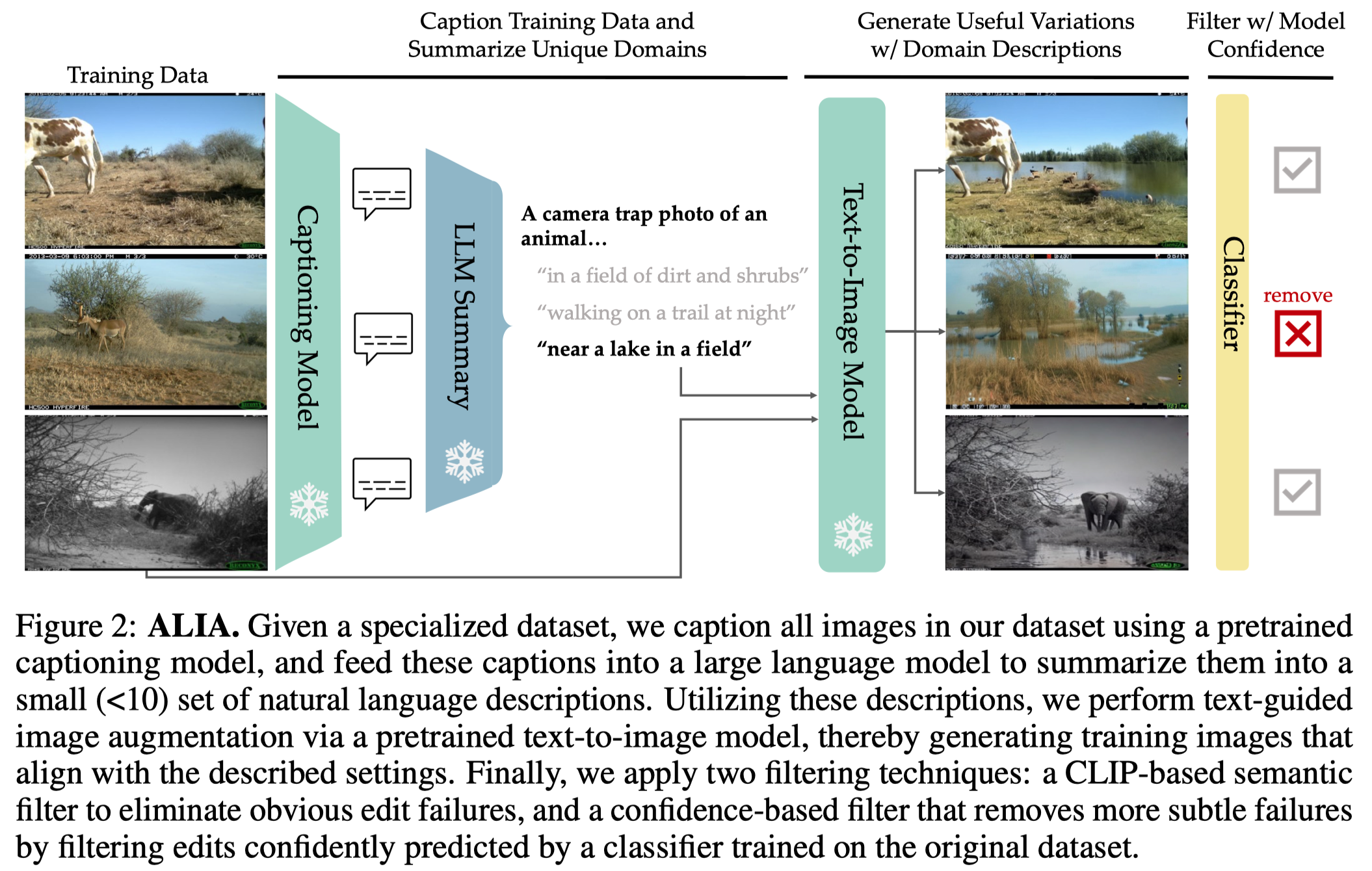
作者的方法第一步是先利用captioning model(BLIP)生成比较通用的caption,包括环境、鸟的动作等,不需要具体的任务相关的信息,比如鸟的种类等。
Note that these captions do not need to accurately describe the task-specific information, such as the species of the bird, as their purpose is to provide a broad overview of the context, such as the environment the bird is in or the actions of the bird.
随后利用这些captions,调用LLM(GPT-4)总结class-agnostic的image domains,下面是prompt:


第二步是利用前一步总结的图像描述作为编辑prompt,调用两种基于扩散模型的图像编辑方法:
- Image to Image with Text Guidance (30; 2; 22)
- Instruct Pix2Pix
第三步是对编辑图像进行过滤,两种过滤手段:
Semantic Filtering:利用CLIP,确保编辑后的图像仍然和原来的task相关:

Confidence-based Filtering:过滤掉和原来的图像没有太大差异,以及破坏了原来的class的编辑图像
- 如果在编辑后的image上,训练的model预测y和原来的y一致,那么认为编辑的图像包含了相近的信息,应该过滤掉; 如果在编辑后的image上,训练的model预测的y不一致,并且confidence非常高超过了阈值,则认为编辑的图像已经损坏了原来的类信息,应该过滤掉。
方法图:
GPT4Tools
GPT4Tools: Teaching Large Language Model to Use Tools via Self-instruction. 清华. NeurIPS 2023. 代码.
This paper aims to efficiently enable Large Language Models (LLMs) to use multimodal tools. Advanced proprietary LLMs, such as ChatGPT and GPT-4, have shown great potential for tool usage through sophisticated prompt engineering. Nevertheless, these models typically rely on prohibitive computational costs and publicly inaccessible data. To address these challenges, we propose the GPT4Tools based on self-instruct to enable open-source LLMs, such as LLaMA and OPT, to use tools. We generate an instruction-following dataset by prompting an advanced teacher with various multi-modal contexts. By using the Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) optimization, our approach facilitates the open-source LLMs to solve a range of visual problems, including visual comprehension and image generation. Moreover, we provide a benchmark to evaluate the ability of LLMs to use tools, which is performed in both zero-shot and fine-tuning ways. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our method on various language models, which not only significantly improves the accuracy of invoking seen tools but also enables the zero-shot capacity for unseen tools. The code and demo have been available at https://github.com/AILab-CVC/GPT4Tools.
Issue:商用的LLM可以学会使用工具来处理图像(比如Visual ChatGPT),但是开源LLM还未学会。特别是商用的LLM的训练数据通常不公开,并且有巨大的计算代价。
Solution:作者使用商用的LLM作为teacher,生成指令数据集,微调开源LLM,使得开源LLM也学会调用工具。
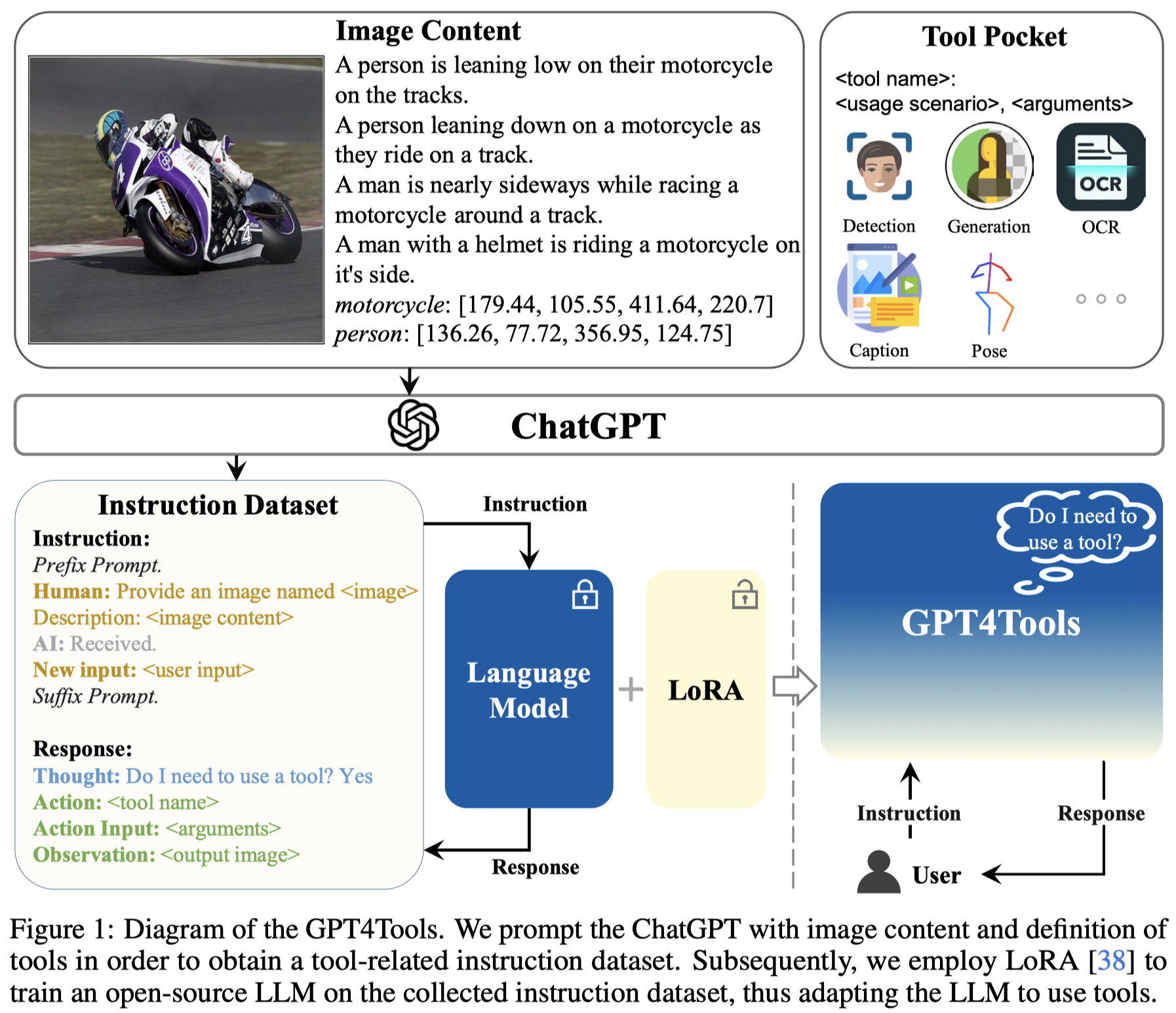
核心在于如何构造指令数据集。作者基于coco数据集(每个image有bounding box和对应的描述),调用GPT-3.5(gpt-3.5-turbo)来生成工具调用的指令。具体是使用了visual ChatGPT类似的prompt来构造对应的工具调用指令\(P_T\)(包括工具的定义、使用场景、传入参数等)。
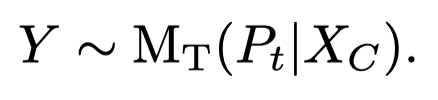
输出的\(Y\)是一系列instruction-output pairs: <instruction>, <tool name>, <arguments>
利用输出的\(Y\),作者构造三种不同的指令:
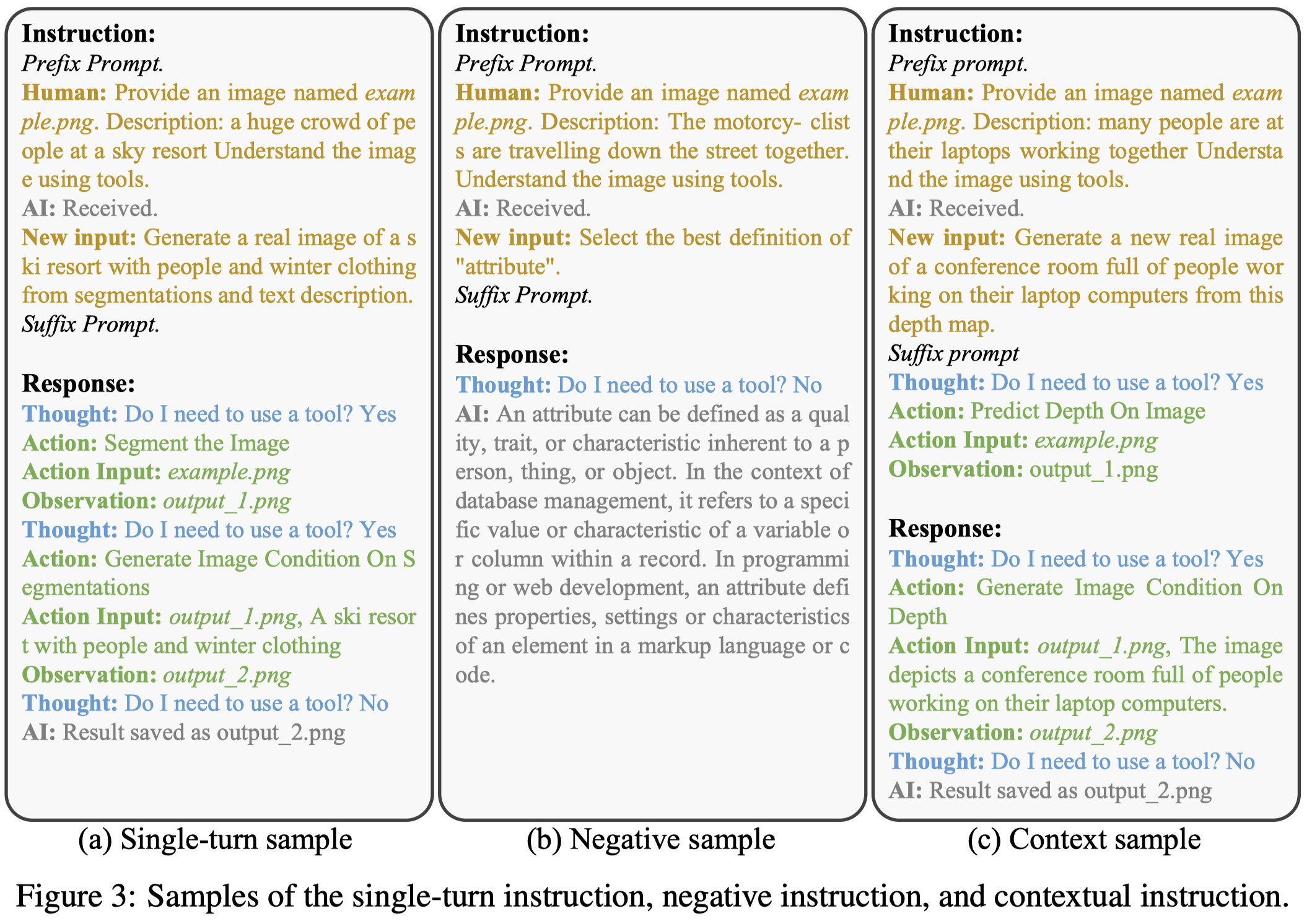
- Single-turn sample: LLM的输入prompt包括image内容的文本描述、用户的输入指令;LLM的输出包括:(1) Thought, meaning the model’s cognition when to use tools; (2) Action, signifying which tools the model will use or action the model will take; (3) Action Input, representing arguments of the selected tool; and (4) Observation, reflecting outcomes of the used tool.
- Negative samples:创造negative sample,避免创造的指令全部都是要调用工具tool(Yes),而导致过拟合。用户的输入指令来源于对话数据,不需要调用工具
- Context samples:多个actions隔开,一部分actions作为输入的一部分。让LLM学会利用context进行思考
指令微调的时候利用LoRA。
作者还定义了一系列和工具调用有关的metric便于评估,具体参考论文。微调了LLaMA [13], Vicuna [12], and OPT [14]。让它们学会使用31种工具。
TMMDA
TMMDA: A New Token Mixup Multimodal Data Augmentation for Multimodal Sentiment Analysis. WWW 2023. 哈工大(深圳). 代码.
Existing methods for Multimodal Sentiment Analysis (MSA) mainly focus on integrating multimodal data efectively on limited multimodal data. Learning more informative multimodal representation often relies on large-scale labeled datasets, which are difcult and unrealistic to obtain. To learn informative multimodal representation on limited labeled datasets as more as possible, we proposed TMMDA for MSA, a new Token Mixup Multimodal Data Augmentation, which frst generates new virtual modalities from the mixed token-level representation of raw modalities, and then enhances the representation of raw modalities by utilizing the representation of the generated virtual modalities. To preserve semantics during virtual modality generation, we propose a novel cross-modal token mixup strategy based on the generative adversarial network. Extensive experiments on two benchmark datasets, i.e., CMU-MOSI and CMU-MOSEI, verify the superiority of our model compared with several state-of-the-art baselines. The code is available at https://github.com/xiaobaicaihhh/TMMDA.
Issue:作者要解决的是多模态情感分析,需要处理三种模态数据:
Multimodal Sentiment A ysis (MSA) employs high-dimensional inputs from modalities as diverse as language, vision, and acoustic to predict sentiment polarity of video clip.
之前的大多数方法是研究如何融合不同模态的信息,而忽略了少量训练数据的影响。
Solution:作者利用mixup方法混合不同模态序列获得新的混合序列,然后输入GAN网络来生成virtual modality,virtual modality被GAN中的判别器不断靠近原始的模态序列。随后,原始的模态数据基于跨模态注意力和virtual modality融合,最后用于预测。
方法图:

一开始的输入包括图像,文本和音频三种模态序列特征,是在训练集中提供的。经过分别的单模态编码器处理得到多模态序列输入,注意里面的序列长度是一样的,在数据集中提前进行了word-level forced alignment [23]:
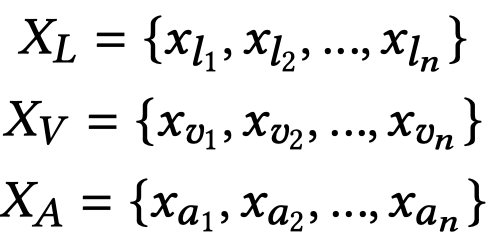
之后,进行mixup混合。简单来说,就是固定了两个概率超参,随机的从另外的模态序列中选择token embedding进行混合:
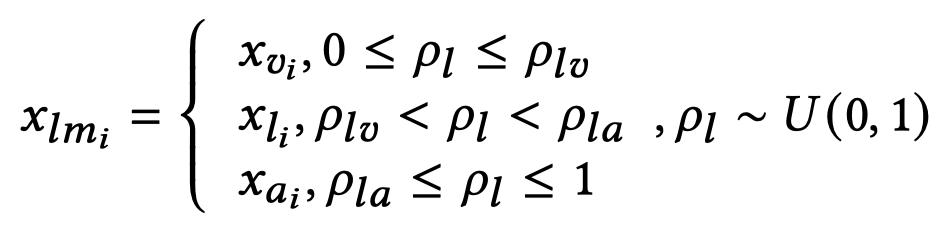
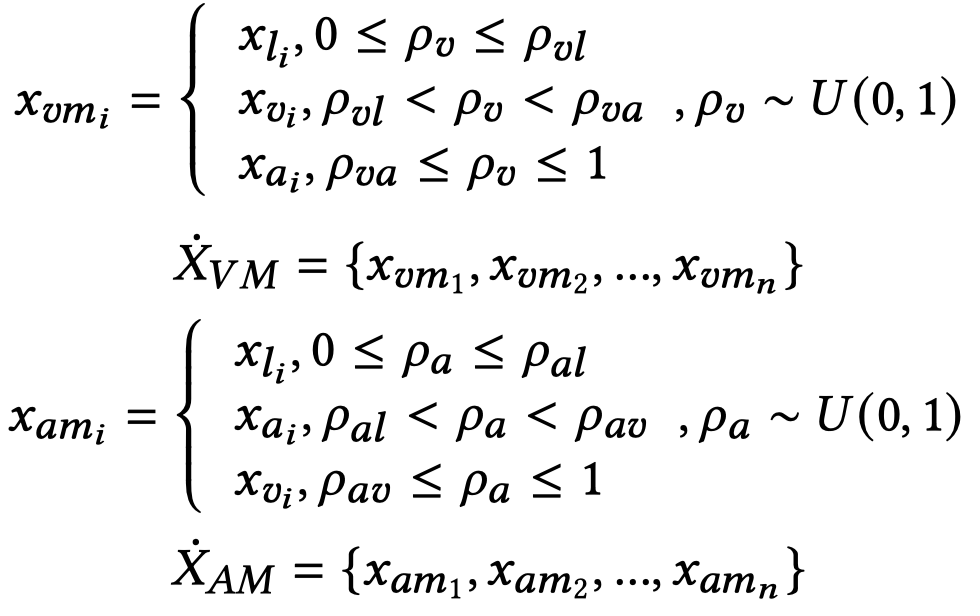
随后,混合序列被放入GAN中进行优化,GAN的生成器添加一个高斯噪音到输入上,然后输出virtual modalities。判别器用来判断是属于原始模态还是还是生成的virtual modalities。这里GAN的生成器和判别器都是全连接层结构。作者还额外增加了一个JSD loss,期望输出的virtual modalities靠近原始模态。
个人感觉这篇论文更像是一种新的模态融合策略,而不是一般的数据增强流程,因为并没有真正的新样本输出。
Cut Switch
Adaptive Multimodal Fusion for Facial Action Units Recognition. ACM MM 2020. State University of New York at Binghamton
Multimodal facial action units (AU) recognition aims to build models that are capable of processing, correlating, and integrating information from multiple modalities ( i.e., 2D images from a visual sensor, 3D geometry from 3D imaging, and thermal images from an infrared sensor). Although the multimodel data can provide rich information, there are two challenges that have to be addressed when learning from multimodal data: 1) the model must capture the complex cross-modal interactions in order to utilize the additional and mutual information effectively; 2) the model must be robust enough in the circumstance of unexpected data corruptions during testing, in case of a certain modality missing or being noisy. In this paper, we propose a novel Adaptive Multimodal Fusion method (AMF) for AU detection, which learns to select the most relevant feature representations from different modalities by a re-sampling procedure conditioned on a feature scoring module. The feature scoring module is designed to allow for evaluating the quality of features learned from multiple modalities. As a result, AMF is able to adaptively select more discriminative features, thus increasing the robustness to missing or corrupted modalities. In addition, to alleviate the over-fitting problem and make the model generalize better on the testing data, a cut-switch multimodal data augmentation method is designed, by which a random block is cut and switched across multiple modalities. We have conducted a thorough investigation on two public multimodal AU datasets, BP4D and BP4D+, and the results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method. Ablation studies on various circumstances also show that our method remains robust to missing or noisy modalities during tests.
Facial action unit (AU) detection has been an essential task for human emotion analysis. 使用单图像模态,轻微的肌肉移动不够充分的描述细微的改变。因此最近的方法开始使用多个模态,比如2D visual, 3D depth and thermal modalities。肌肉的移动会反映到3D图上。微循环或者血流这些特征也很重要,会反映到热力图上。
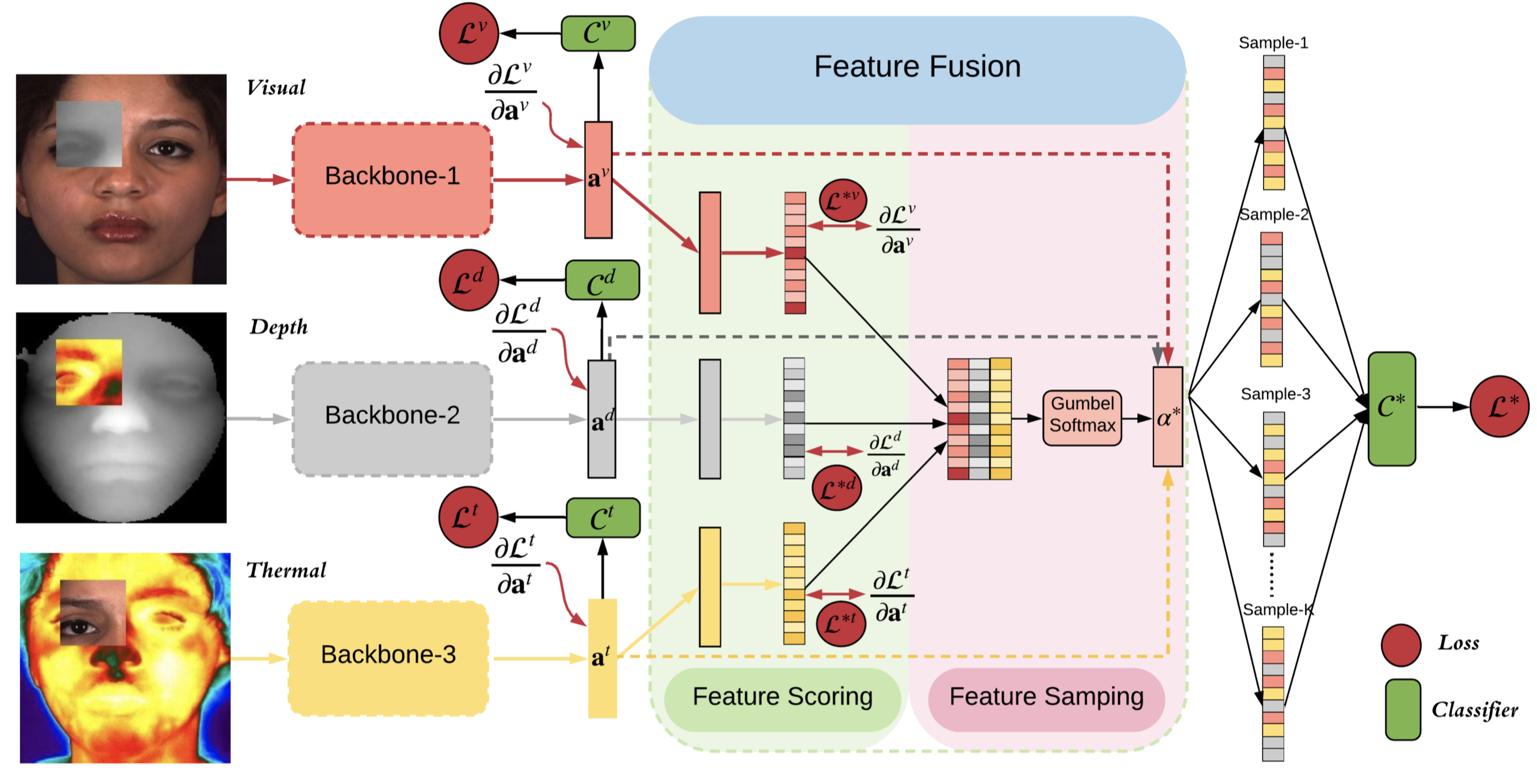
由于数据比较少,frame的变化依赖于少数的subject,variations比较低,容易过拟合。
利用数据增强作为正则,可以缓解过拟合,提高泛化能力。之前的Cutout方法会丢失信息;而Mixup、CutMix方法更适合单个label的场景。
作者声称自己是首个multimodal DA技术。通过随机采样的box,得到三种模态的patches,然后模态之间随机互换。这样不会造成信息丢失,也能够用于多标签任务。
MixGen
MixGen: A New Multi-Modal Data Augmentation. WACVW 2023. 中科院
Data augmentation is a necessity to enhance data efficiency in deep learning. For vision-language pre-training, data is only augmented either for images or for text in previous works. In this paper, we present MixGen: a joint data augmentation for vision-language representation learning to further improve data efficiency. It generates new imagetext pairs with semantic relationships preserved by interpolating images and concatenating text. It’s simple, and can be plug-and-played into existing pipelines. We evaluate MixGen on four architectures, including CLIP, ViLT, ALBEF and TCL, across five downstream vision-language tasks to show its versatility and effectiveness. For example, adding MixGen in ALBEF pre-training leads to absolute performance improvements on downstream tasks: imagetext retrieval (+6.2% on COCO fine-tuned and +5.3% on Flicker30K zero-shot), visual grounding (+0.9% on RefCOCO+), visual reasoning (+0.9% on NLVR 2 ), visual question answering (+0.3% on VQA2.0), and visual entailment (+0.4% on SNLI-VE).
Issue: 预训练VLM需要很多训练数据,但是这些数据通常是不公开的。数据增强可以用来扩充现有数据。传统的单模态数据增强无法直接应用与text-image对,可能会破坏text-image之间的匹配语义。
Solution:作者的方法很简单,对图像进行像素层面的线性相加,对文本直接拼接(尽可能保留原有的信息)。
We can see that most objects and scene layout remain in the blended image, while the text information is fully preserved.
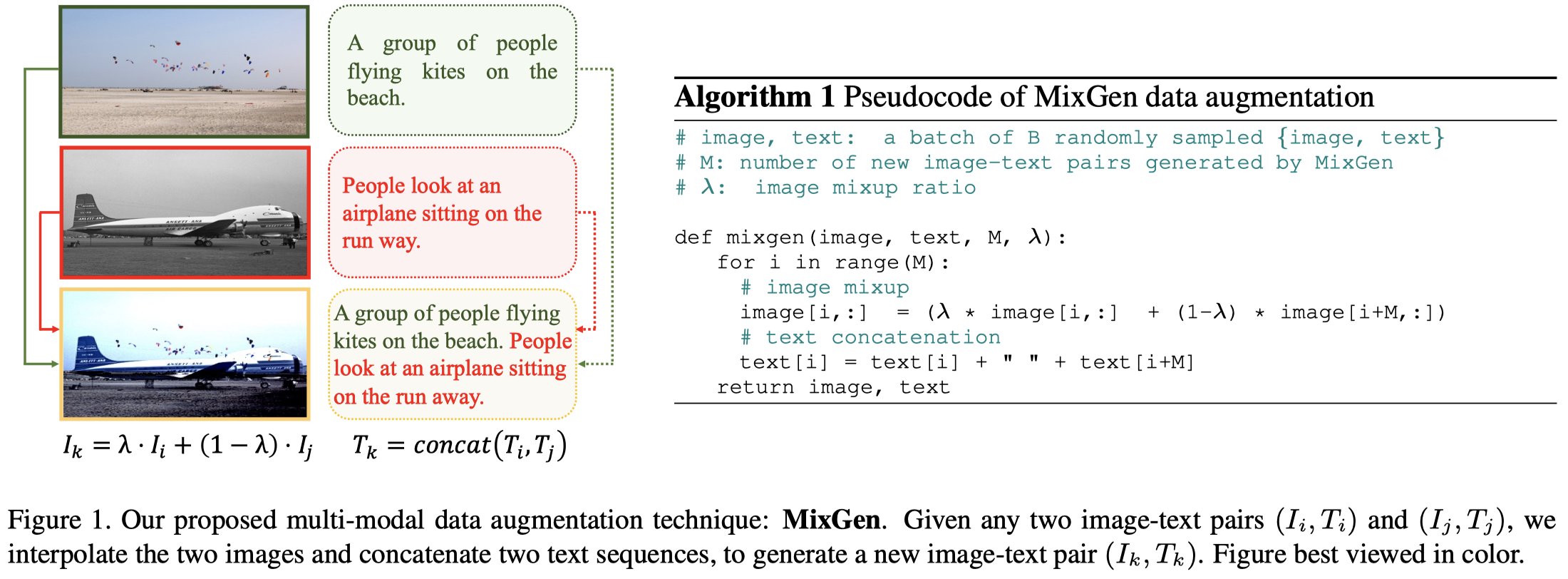
上面的方法\(\lambda\)是固定超参。作者在实验中也尝试了根据特定分布采样的\(\lambda\)。同时还试了在embedding层面进行混合,发现还是直接在输入层次上进行相加比较合适。
Culture Mixup
Cultural Concept Adaptation on Multimodal Reasoning. 浙大. EMNLP 2023. 代码.
Developing cultural adaptation methods is important, which can improve the model performance on the low-resource ones and provide more equitable opportunities for everyone to benefit from advanced technology. Past methods primarily focused on multilingual and multimodal capabilities, and the improvement of multicultural competence is still an unexplored problem. This is largely due to the difficulty of data scarcity and expensive annotation. In this paper, we navigate this uncharted territory by leveraging high-resource cultures to facilitate comprehension of low-resource ones. We first introduce an annotation-free method for cultural-concept adaptation and construct a concept mapping set. To facilitate the model’s comprehension of cultural-concept mappings, we propose a new multimodal data augmentation called CultureMixup. This approach employs a three-tier code-switching strategy on textual sentences. Additionally, it uses a cultural concept-based mixup method for the images. This combination effectively generates new data instances across culture, phrase, word, and image levels. For visually grounded reasoning across languages and cultures, experimental results on five languages show that our method consistently improves performance for four existing multilingual and multimodal models on both zero-shot and few-shot settings.
Issue:之前的方法更多是强调多模态/多语言的方法,对于多文化的探究常常被忽略。而现有的多文化研究更多是关注评估,而不是增强。这主要是因为低资源语言和其中的概念常常是数据稀疏的,并且关联不同文化之间的概念成本高。
Solution:作者首先是提出了利用现有语义网络Conceptnet (Speer et al., 2017) and Wordnet (Miller, 1995),基于上位词->同义词->下位词迭代关联低资源concept和高资源concept,构建cultural adaptation graph的方法:
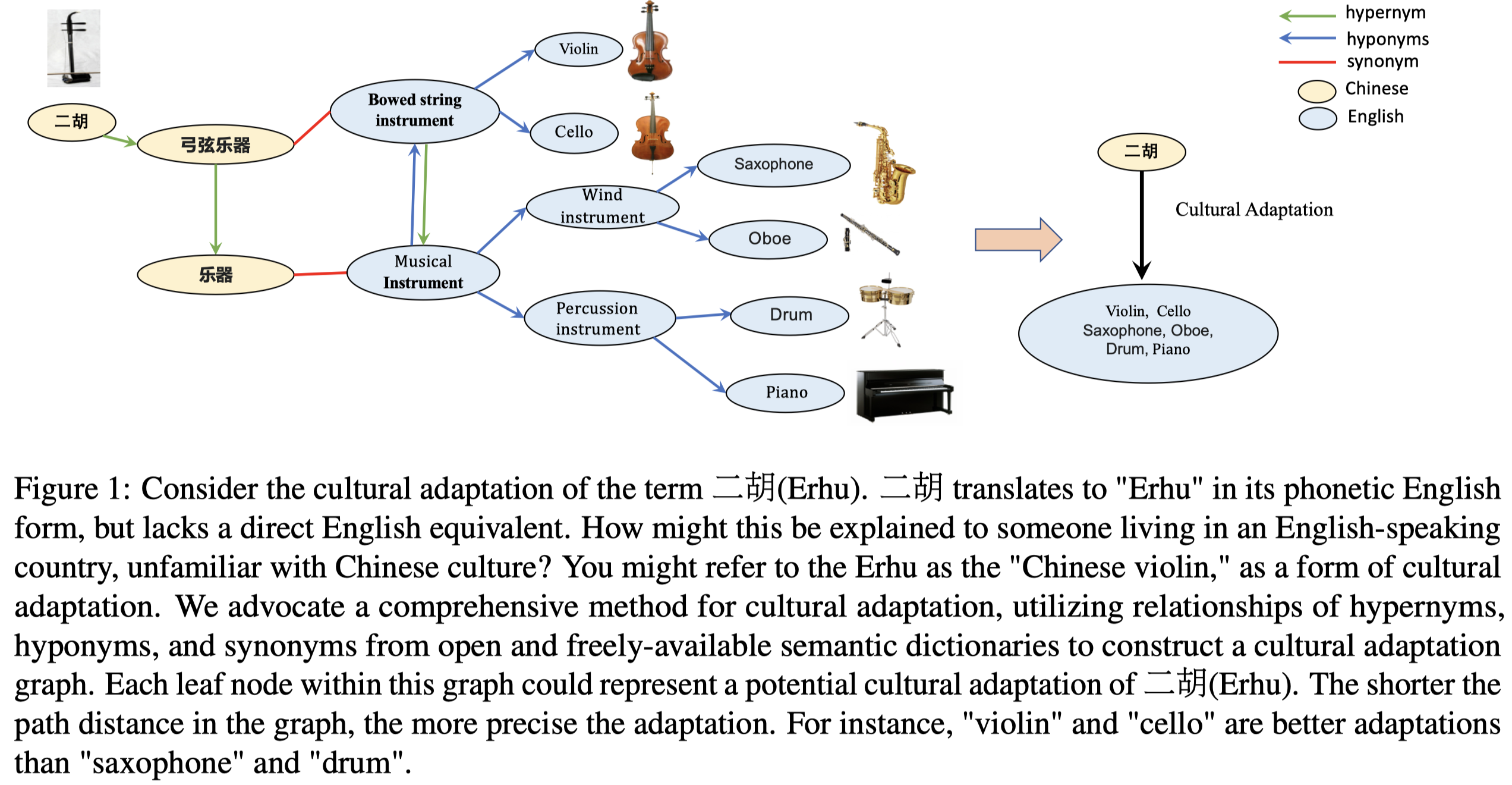
叶子节点就是概念,叶子节点之间的距离可以看做是概念之间的差异。需要注意的是,构建这个graph是无需人工的,但是初始的低资源的concept集合是需要人工确定的。关联到concept,作者从网络上找到有对应的image。
为了增强低资源文本语言的数据,作者分别从text和image进行增强。
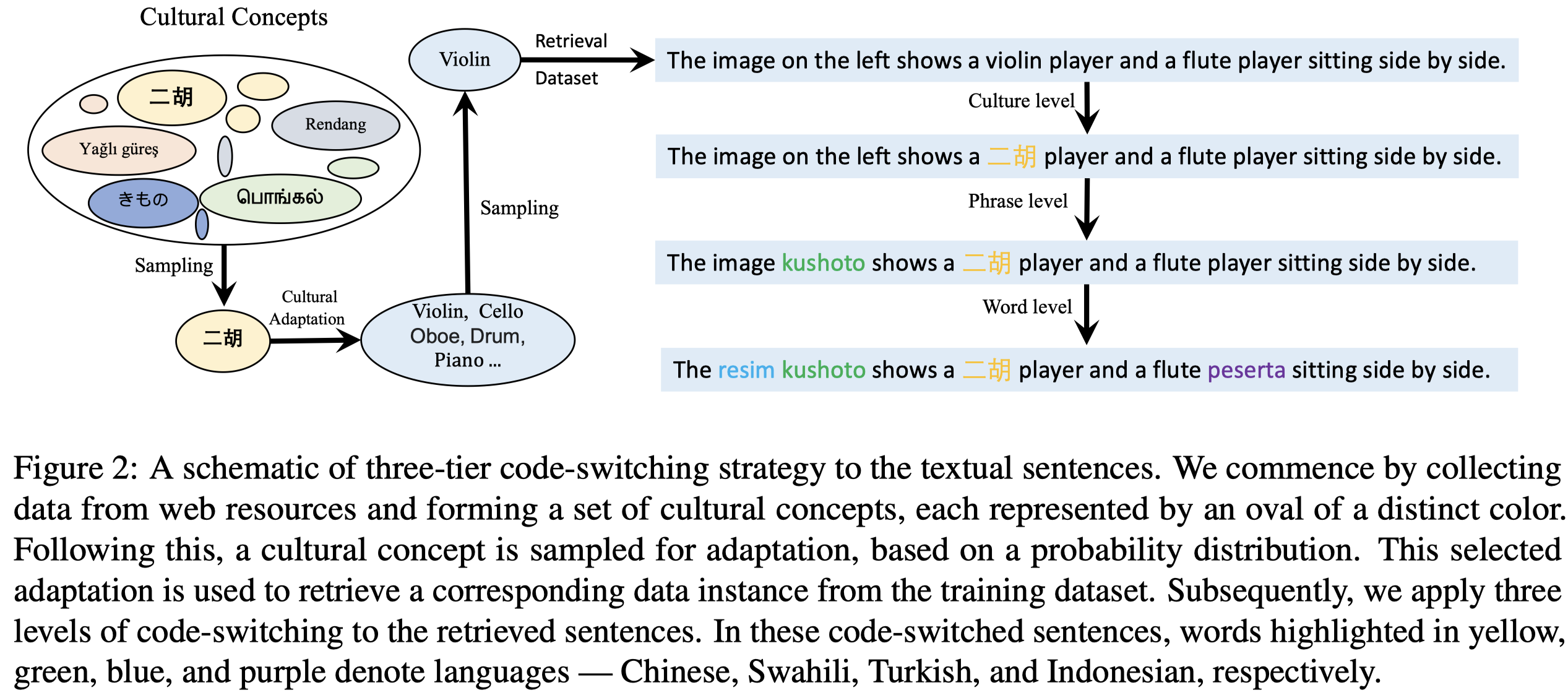
对于文本,分别从语言、常见短语、word进行code-switch:
Code-switching is a widespread phenomenon in multilingual communities, characterized by switching words and morphemes from two or more languages in speech or writing. The switched elements usually bear semantic similarity to the originals.
对于image,作者先进行object detection,然后把低资源concept的bounding box区域贴到高资源concept的bounding box上。
PromptMix
PromptMix: Text-to-image diffusion models enhance the performance of lightweight networks. IJCNN 2023. 代码.
Many deep learning tasks require annotations that are too time consuming for human operators, resulting in small dataset sizes. This is especially true for dense regression problems such as crowd counting which requires the location of every person in the image to be annotated. Techniques such as data augmentation and synthetic data generation based on simulations can help in such cases. In this paper, we introduce PromptMix, a method for artificially boosting the size of existing datasets, that can be used to improve the performance of lightweight networks. First, synthetic images are generated in an end-to-end data-driven manner, where text prompts are extracted from existing datasets via an image captioning deep network, and subsequently introduced to text-to-image diffusion models. The generated images are then annotated using one or more highperforming deep networks, and mixed with the real dataset for training the lightweight network. By extensive experiments on five datasets and two tasks, we show that PromptMix can significantly increase the performance of lightweight networks by up to 26%.
这篇论文的目的是利用扩散模型生成更多的images,然后利用能够有比较好效果的heavyweight network进行标注,进而训练lightweight network。lightweight network和heavyweight network都能够执行目标task,只不过架构不同。
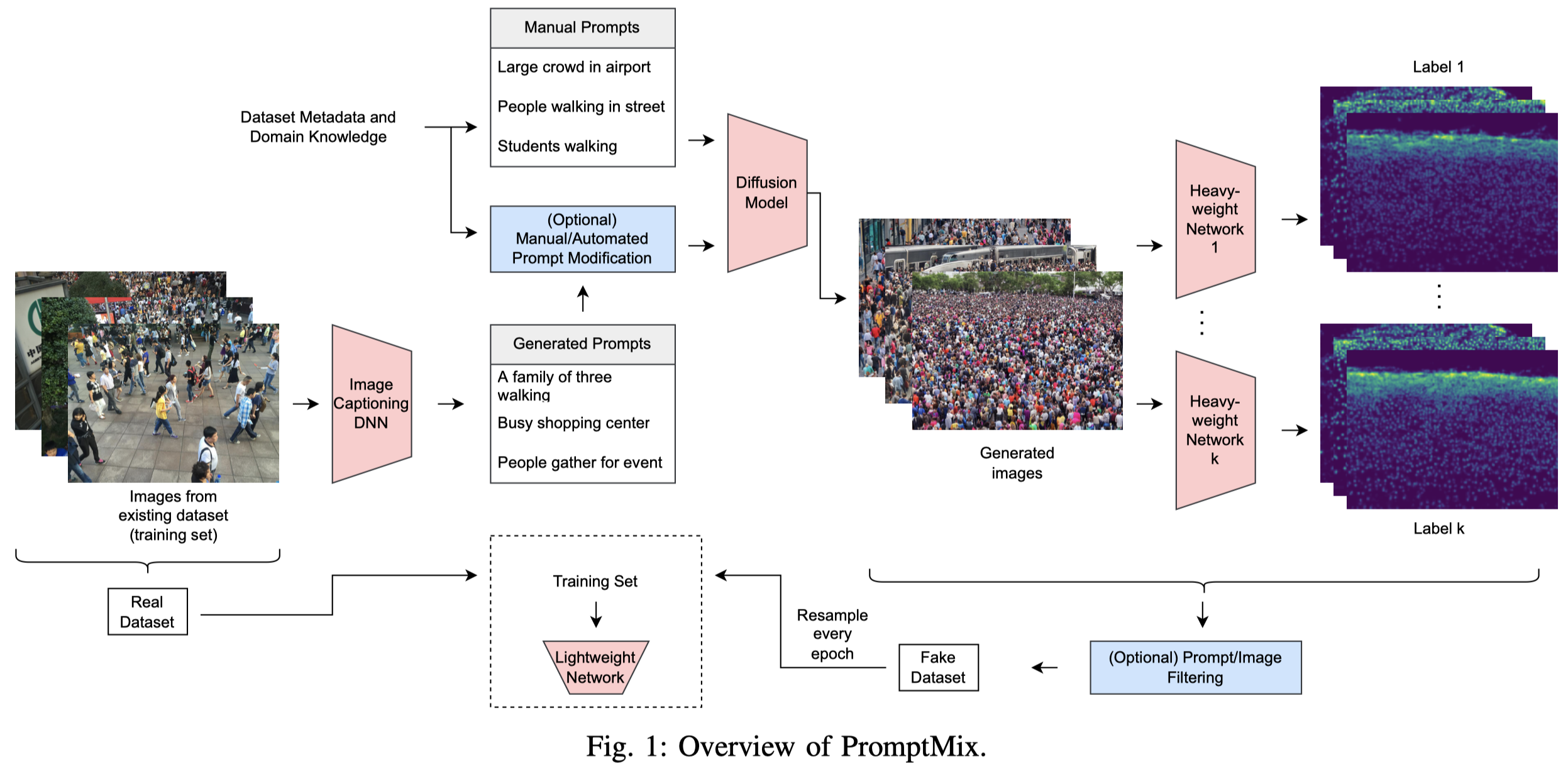
从真实image出发,利用caption model获得caption,然后对caption进行修改,可以是人工修改,也可以是基于可以获得的metadata进行修改,随后利用stable diffusion生成image。生成的image会利用heavyweight network去进行标注(实验时只使用了一个heavyweight network)。每轮迭代随机的选择一部分image进行训练。
作者的评估任务是Crowd Counting(统计图片中有几个人)和Monocular Depth Estimation。
LeMDA
Learning Multimodal Data Augmentation in Feature Space. ICLR 2023. Rice University
The ability to jointly learn from multiple modalities, such as text, audio, and visual data, is a defining feature of intelligent systems. While there have been promising advances in designing neural networks to harness multimodal data, the enormous success of data augmentation currently remains limited to single-modality tasks like image classification. Indeed, it is particularly difficult to augment each modality while preserving the overall semantic structure of the data; for example, a caption may no longer be a good description of an image after standard augmentations have been applied, such as translation. Moreover, it is challenging to specify reasonable transformations that are not tailored to a particular modality. In this paper, we introduce LeMDA, Learning Multimodal Data Augmentation, an easy-to-use method that automatically learns to jointly augment multimodal data in feature space, with no constraints on the identities of the modalities or the relationship between modalities. We show that LeMDA can (1) profoundly improve the performance of multimodal deep learning architectures, (2) apply to combinations of modalities that have not been previously considered, and (3) achieve state-of-the-art results on a wide range of applications comprised of image, text, and tabular data.
Issue:对于多模态DA最直接的方法就是针对不同模态分别应用以前的单模型增强方法,但是这会破坏数据完整性。
设计多模态DA的两个挑战:
- First, multimodal deep learning takes input from a diverse set of modalities. Augmentation transformations can be obvious for some modalities such as vision and language, but not others, such as sensory data which are often numeric or categorical. DA方法很难适用全部模态,比如text和image的增强是很直观的,但是对于分类地/数值类型的模态就不太直观
- Second, multimodal deep learning includes a diverse set of tasks with different cross-modal relationships. Some datasets have redundant or totally correlated modalities while others have complementary modalities. There is no reasonable assumption that would generally preserve labels when augmenting modalities in isolation. 不同模态之间有不同的关系,有的是互补,有的是冗余,有的是紧耦合
Solution:作者期望设计一种更通用的增强方法,在隐式表征空间上进行增强。
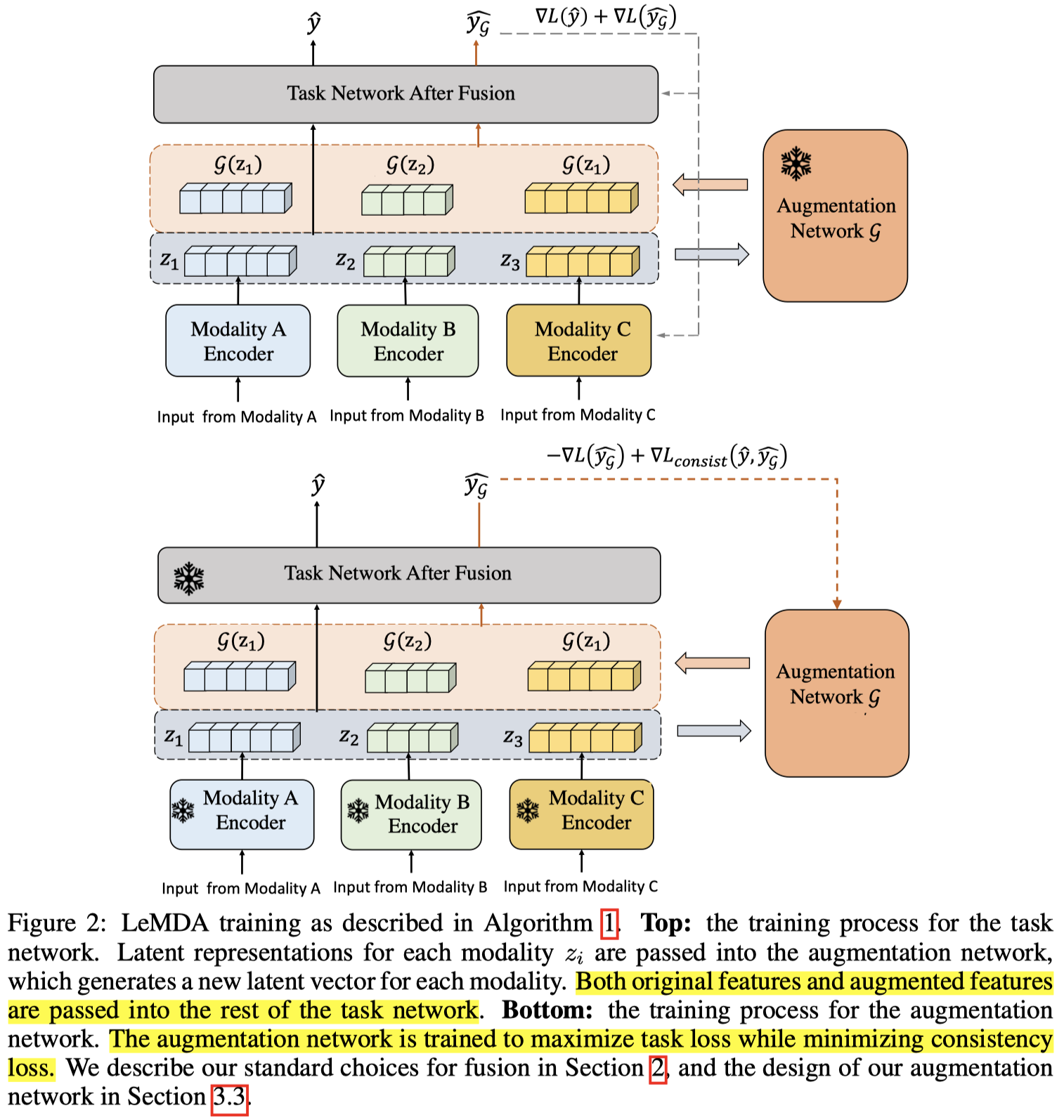
核心创新点是作者设计了一个增强网络\(\mathcal{G}\)。增强网络会接收单模态的embedding,然后分别生成增强的latent vectors \(\mathcal{G}(\{ z_i \})\)。增强的embedding和原来的embedding都会输入到下游任务task network来计算task loss。
具体增强网络是选择两种不同的VAE,MLP-VAE和Attention-VAE。
而为了训练增强网络\(\mathcal{G}\),作者采用了对抗训练的思路,并且加入一致性损失(只在有高预测confidence的samples上)。一方面让在增强embedding上的task loss增大,来使得task network更加关注增强的embedding进行参数更新。一方面加入了一致性损失(基于KL散度),给定原始embedding和增强的embedding,期望有相近的输出。
一致性损失的作用示例如下图:
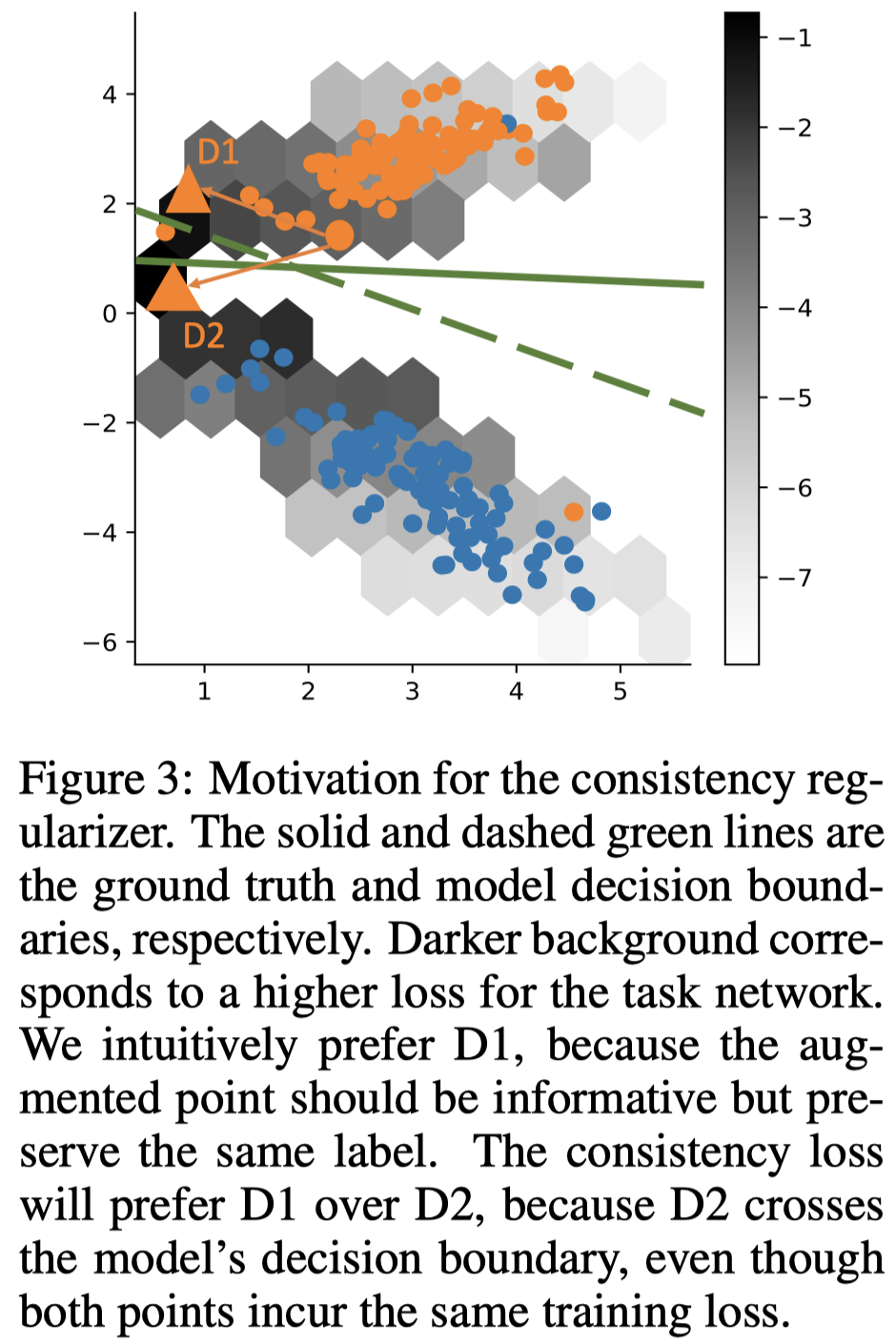
都是朝着task network训练loss更大的方向,但是同时又希望尽可能保持正确的分类结果。task loss变大意味着让增强数据朝着靠近决策边界的方向靠拢。如果采用在embedding之间的L2正则作为一致性损失,由于D1和D2到上一个起点的距离是一样的,无法保证label是一致的。
BiAug
Towards reporting bias in visual-language datasets: bimodal augmentation by decoupling object-attribute association. arXiv 2023. 东京大学
Reporting bias arises when people assume that some knowledge is universally understood and hence, do not necessitate explicit elaboration. In this paper, we focus on the wide existence of reporting bias in vision–language datasets, embodied as the object-attribute association, which can subsequentially degrade models trained on them. To mitigate this bias, we propose a bimodal augmentation (BiAug) approach through object–attribute decoupling to flexibly synthesize vision–language examples with a rich array of object–attribute pairing and construct cross-modal hard negatives. BiAug consists of three phases: (1) We employ large language models (LLMs) in conjunction with a object detector to detect and filter valid objects; (2) On the caption side, the LLM generates a detailed description for each object with each of the four preset attributes, and produces a corresponding hard negative counterpart; (3) On the image side, an inpainting model is used to modify the original object based on descriptions with different attributes. By doing so, the object-attribute association is decoupled. The synthesized examples explicitly complement omitted objects and attributes to learn, and the hard negative pairs steer the model to distinguish various attributes for an identical object. Our experiments demonstrated that BiAug excels not only in object-attribute understanding but also in improving the performance of zero-shot retrieval tasks on general benchmarks, such as MSCOCO and Flickr30K. BiAug refines the way of collecting text-image datasets. Mitigating the reporting bias helps models achieve a deeper understanding of vision–language phenomena, expanding beyond mere frequent patterns to encompass the richness and diversity of real-world scenarios.
Issue:作者认为现有的VL数据集由于是人工标注的,存在一个reporting bias:
Reporting bias denotes the inclination of individuals to under-report the information they have accessed (Gordon & Van Durme, 2013). This bias often arises when people assume that certain information, typically commonsense knowledge, is universally understood and, therefore, does not necessitate explicit elaboration, leading to the omission of some foundational details.
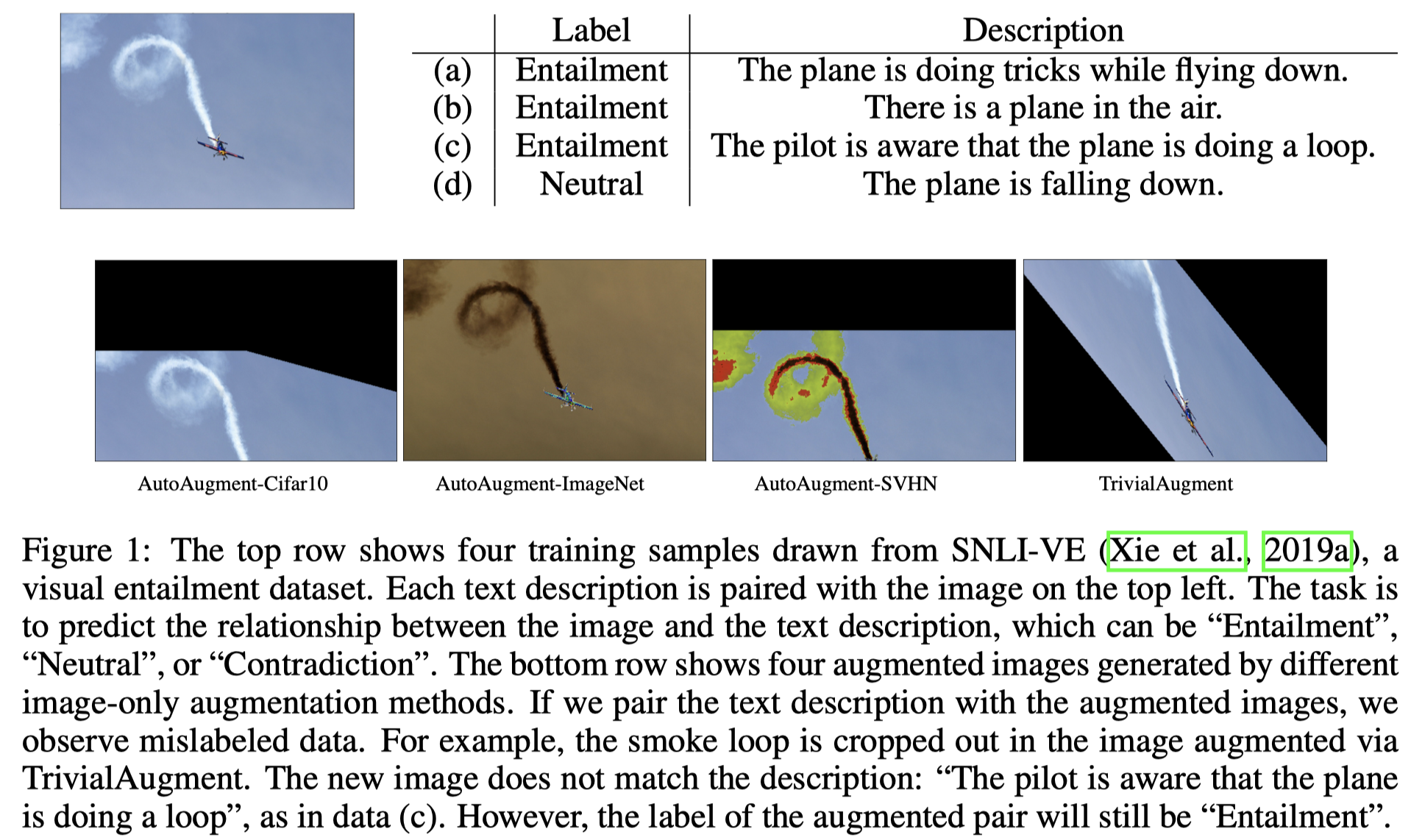
不报告已经见过/访问过的信息。常发生在特定信息比如常识,人们通常常识已经被理解了,而不需要详细解释。比如下图的三文鱼是一整条还是切片的,都有相同的caption。
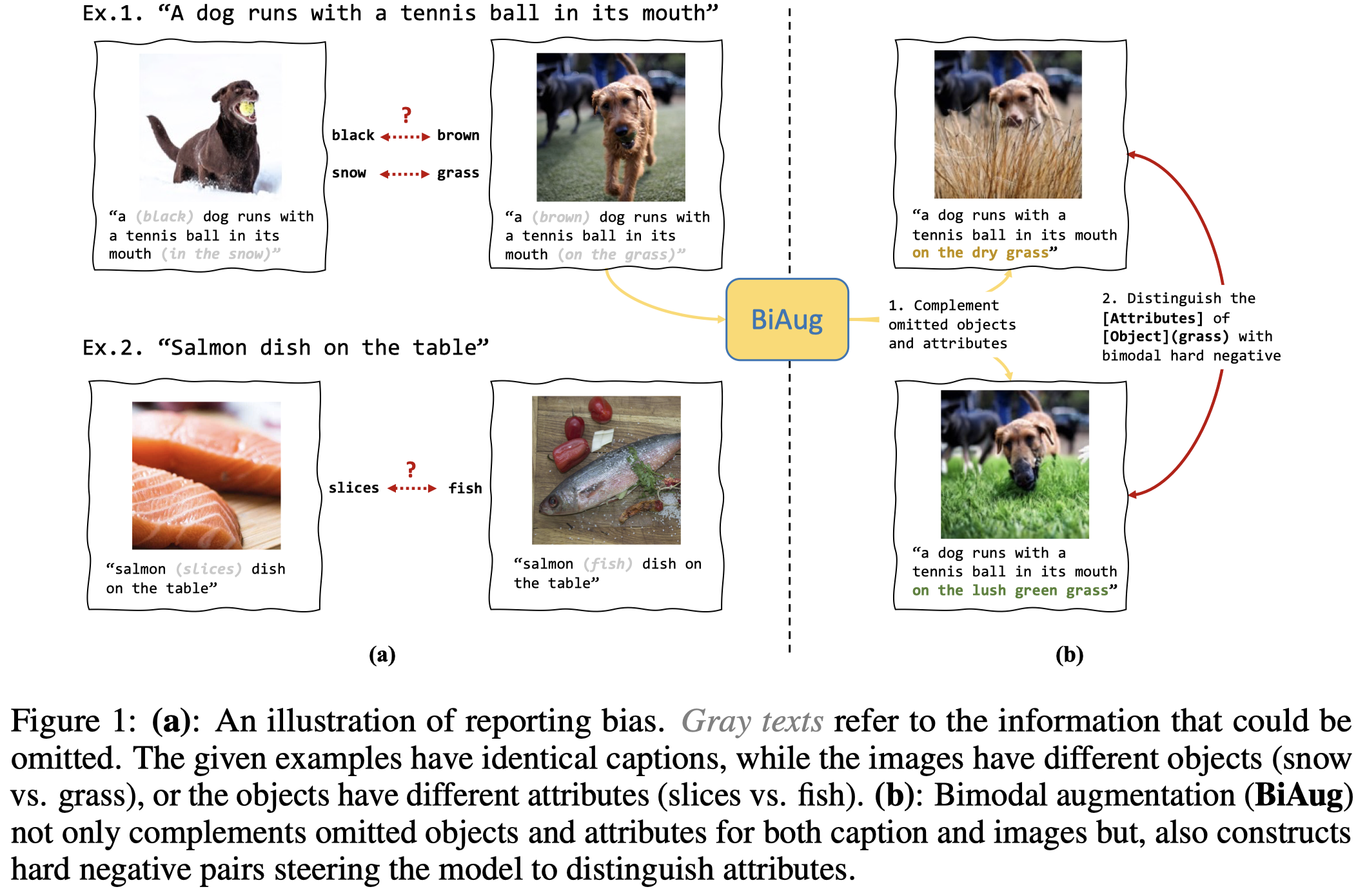
这种bias导致两个后果:
- (1): Biased captions, which might be perceived as lacking objects or attributes, can be associated with multiple images that are dissimilar. Such imprecise pairings can compromise the training quality of VL models because they do not naturally have the capability to grasp commonsense knowledge to discern the difference. 不相似的image的caption可能相似,由于缺少必要的objects/attributes。
- (2): Reporting bias skews the VL model towards frequently occurring patterns. For instance, with reporting bias, a search for ‘a flag’ might predominantly yield images of a USA flag, ignoring the broader spectrum of flags. This bias hinders the model’s efficacy in distinguishing nuanced object–attribute combinations. 使得训练出来的VLM总是倾向于频繁模式。
作者的方法:
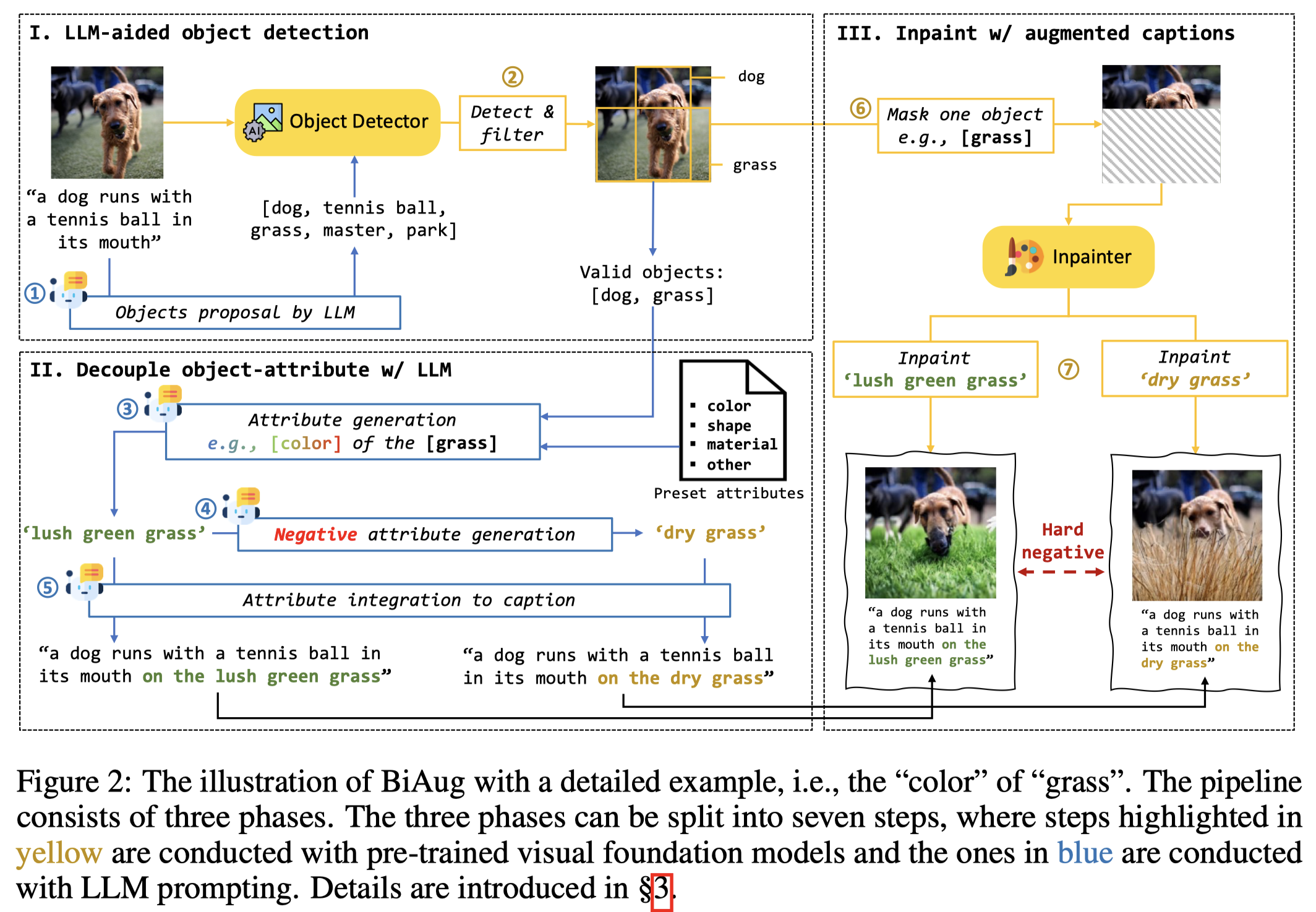
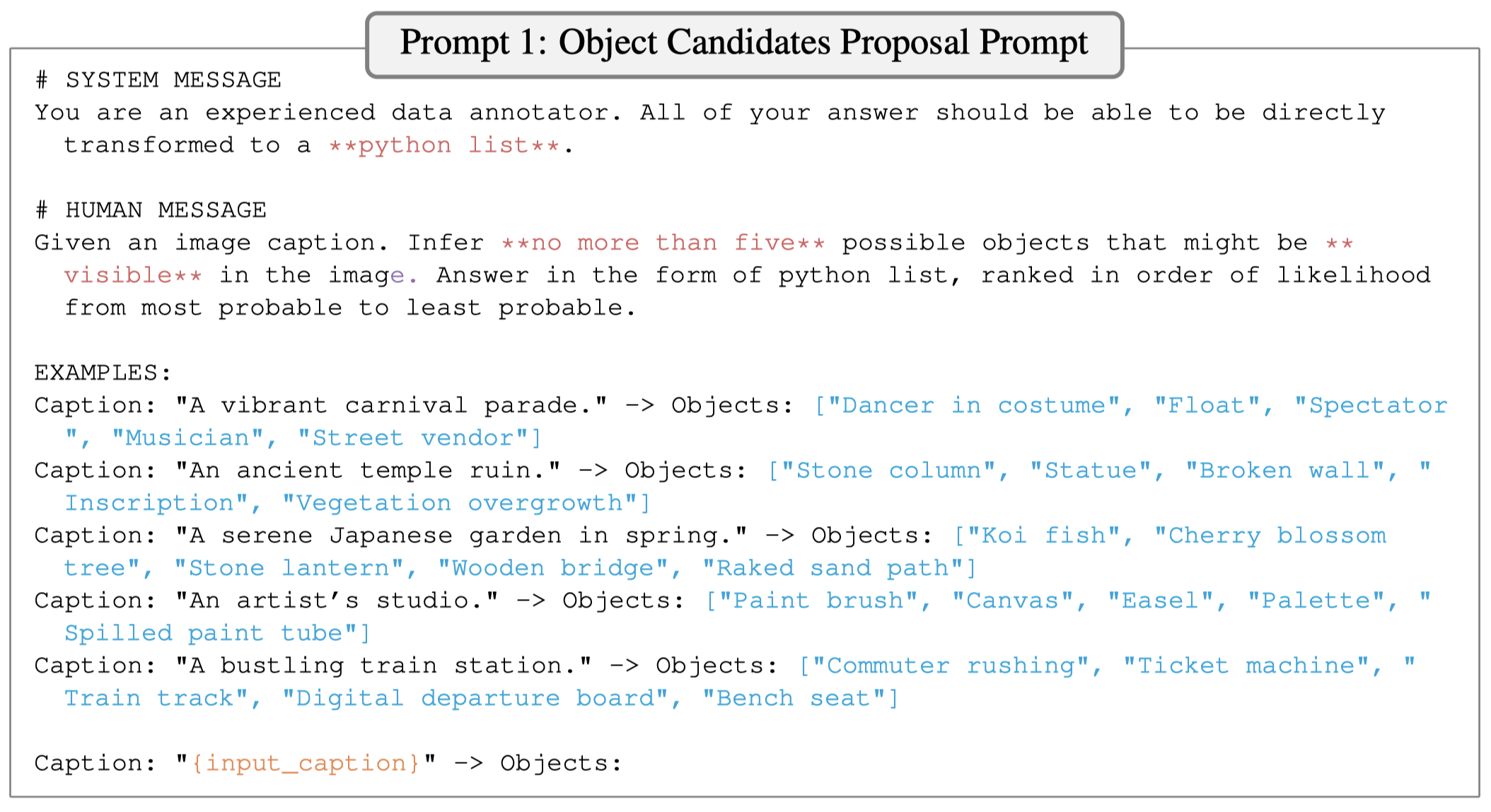
先调用gpt-3.5-turbo分析图像caption中可能在image上存在的object candidates(注意,由于使用了LLM,会输出并没有在caption中实际提及的object)。然后调用GroundingDino作为object detector来检测在image上是否存在对应的object。下面是使用的prompt:
第三步是对于某个object,让LLM生成4种不同的可能的属性值(color, shape, material, and other)。然后在让LLM对不同的属性值,生成相反的negative value,来后续构造hard negative sample。
之后mask探测到的object对应的bounding box。基于Stable-diffusion-inpainting来根据生成的新的加入了属性描述的caption修复图片,得到新的text-image pairs。
XmDA
Cross-modality Data Augmentation for End-to-End Sign Language Translation. EMNLP 2023 Findings. 港科大. 代码.
End-to-end sign language translation (SLT) aims to directly convert sign language videos into spoken language texts without intermediate representations. It has been challenging due to the data scarcity of labeled data and the modality gap between sign videos and texts. To tackle these challenges, we propose a novel Cross-modality Data Augmentation (XmDA) framework to transfer the powerful gloss-to-text translation capabilities to end-to-end sign language translation (i.e., video-totext). Specifically, XmDA consists of two key components: cross-modality mix-up and crossmodality knowledge distillation. The former one explicitly encourages the alignment between sign video features and gloss embeddings to bridge the modality gap. The latter one utilizes the generation knowledge from gloss-to-text teacher models to guide the spoken language text generation. Experimental results on two widely used SLT datasets, i.e., PHOENIX-2014T and CSL-Daily, demonstrate that the proposed XmDA framework significantly and consistently outperforms the baseline models. Extensive analyses confirm our claim that XmDA enhances end-to-end sign language translation by reducing the representation distance between sign videos and glosses, as well as improving the translation of low-frequency words and long sentences. Codes have been released at https://github.com/ Atrewin/SignXmDA.
作者的任务是手语视频翻译。
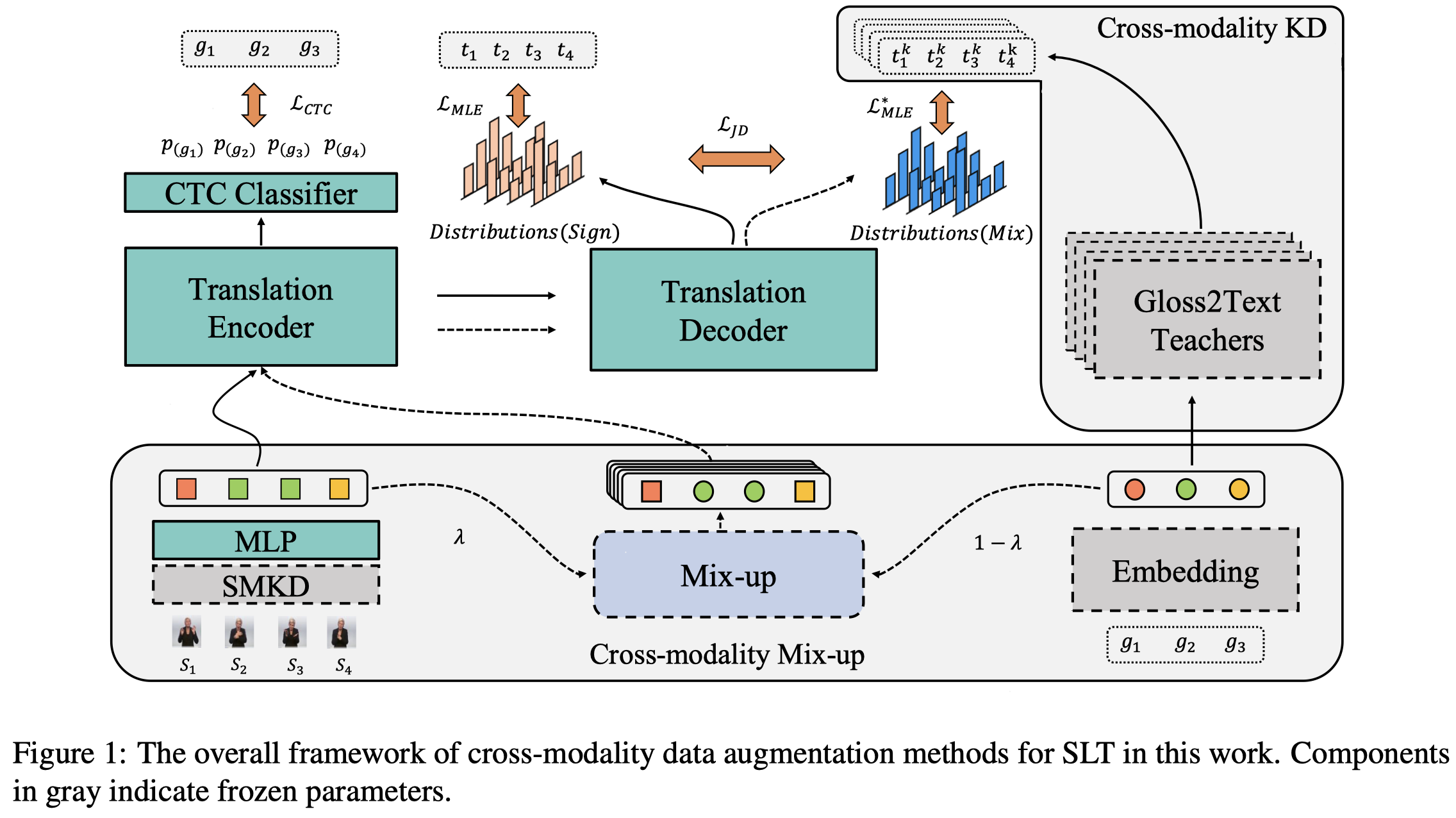
核心创新点是两个,一个是Cross-modality Mix-up来减小模态gap,混合的是利用之前的model SMKD导出的visual embeddings,以及gloss embeddings(没有理解loss在手语翻译任务中的意义)。
另一个是利用gloss-to-text进行数据增强。作者在已有的数据集上训练了K个gloss2text model,然后进行生成,可以获得多个不同的reference text用于训练。
SLUMA
Self-Adaptive Fine-grained Multi-modal Data Augmentation for Semi-supervised Muti-modal Coreference Resolution. ACM MM 2024. 武大
Coreference resolution, an essential task in natural language processing, is particularly challenging in multi-modal scenarios where data comes in various forms and modalities. Despite advancements, limitations due to scarce labeled data and underleveraged unlabeled data persist. We address these issues with a self-adaptive fine-grained multi-modal data augmentation framework for semisupervised MCR, focusing on enriching training data from labeled datasets and tapping into the untapped potential of unlabeled data. Regarding the former issue, we first leverage text coreference resolution datasets and diffusion models, to perform fine-grained textto-image generation with aligned text entities and image bounding boxes. We then introduce a self-adaptive selection strategy, meticulously curating the augmented data to enhance the diversity and volume of the training set without compromising its quality. For the latter issue, we design a self-adaptive threshold strategy that dynamically adjusts the confidence threshold based on the model’s learning status and performance, enabling effective utilization of valuable information from unlabeled data. Additionally, we incorporate a distance smoothing term, which smooths distances between positive and negative samples, enhancing discriminative power of the model’s feature representations and addressing noise and uncertainty in the unlabeled data. Our experiments on the widely-used CIN dataset show that our framework significantly outperforms state-of-the-art baselines by at least 9.57% on MUC F1 score and 4.92% on CoNLL F1 score. Remarkably, against weakly-supervised baselines, our framework achieves a staggering 22.24% enhancement in MUC F1 score. These results, underpinned by in-depth analyses, underscore the effectiveness and potential of our approach for advancing MCR tasks.
Issue:多模态共指消解需要判断文本中的mention是否指向同一实体,还要划出其在图像image上对应的bounding box。之前的多模态共指消解MCR方法更多是关注模型优化和特征学习,忽略了:
- Scarcity of labeled data
- Under-exploitation of unlabeled data:利用unlabeled data常常是基于model confidence进行过滤,这种固定的做法的缺陷:(1) Loss of useful information (2) Limitation on the quantity of training data (3) Ignoring the model’s learning status
之前的DA方法是纯文本的。
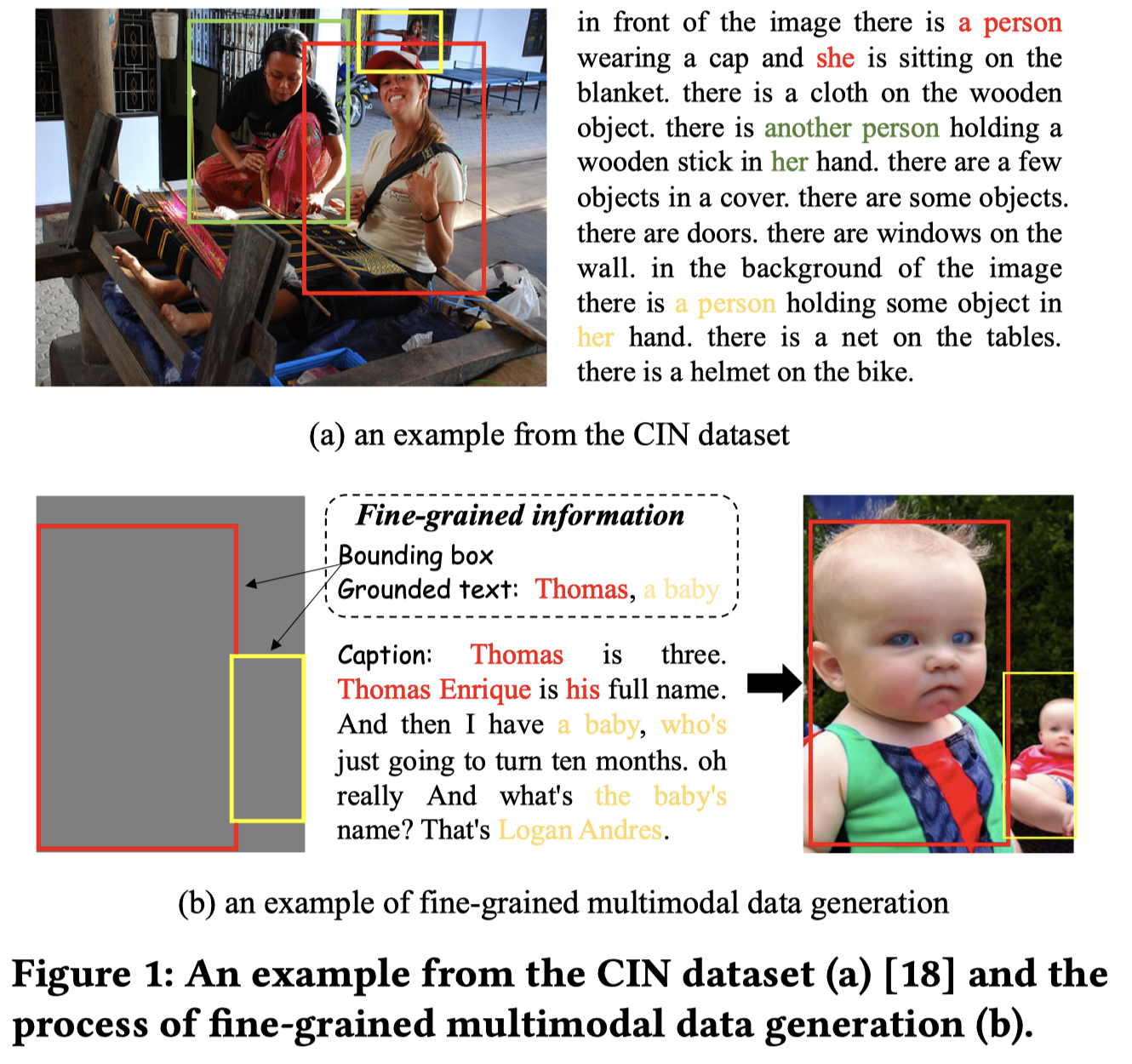
Solution:作者基于文生图,依据有标注文本数据来生成新的图片;为了利用无标注数据,提出self-adaptive threshold的方法。
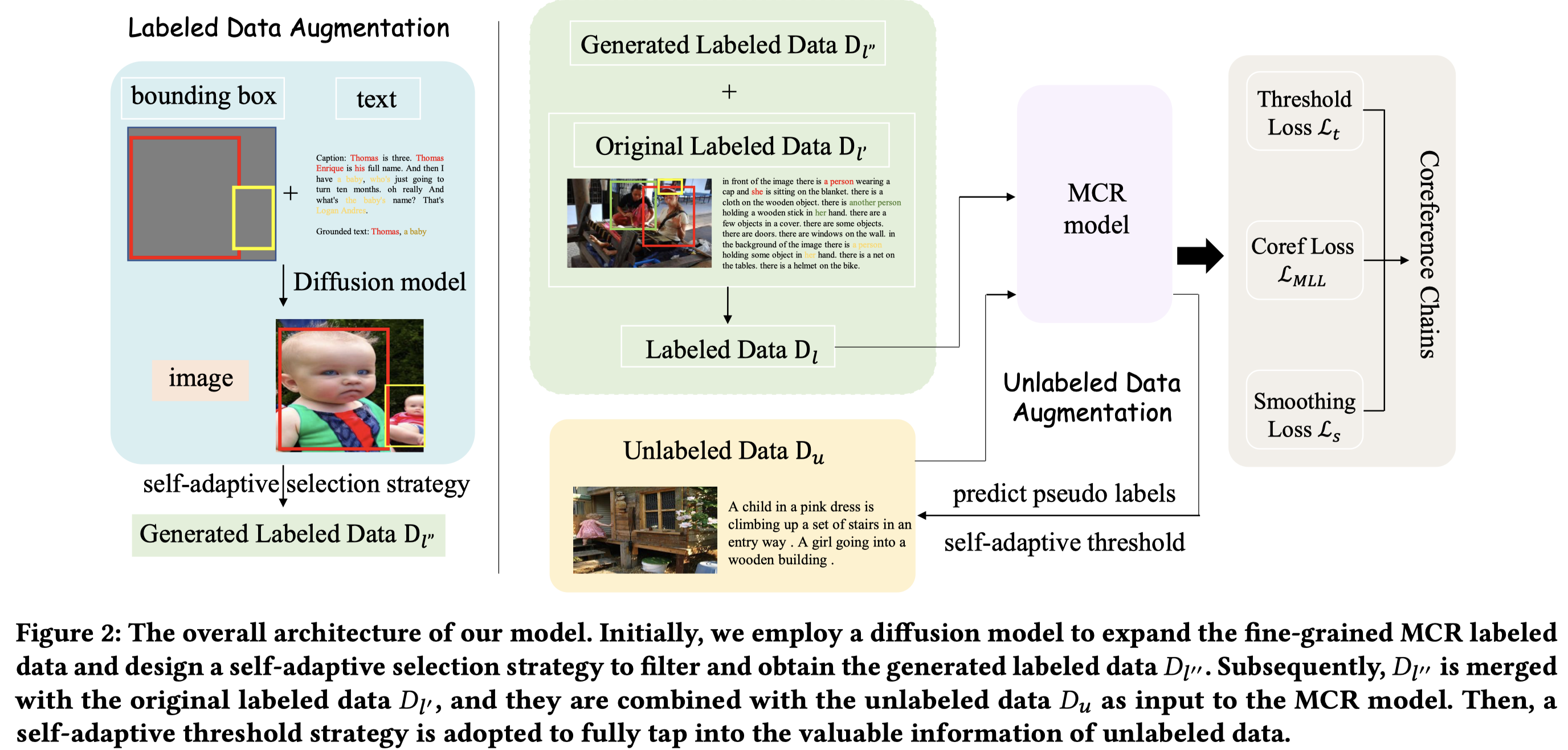
作者从纯文本的CR数据集,English OntoNotes 5.0获取文本,然后随机的构造bounding box,利用之前的方法GLIGEN [27]基于扩散模型生成新的image。
由于生成的image存在不确定性,作者使用一种自适应的数据选择策略,基于CLIPScore评估image和caption的匹配度。
一开始使用全部的训练样例确保多样性。随着训练过程,模型的性能逐渐增大,逐渐过滤掉生成的低score的数据。作者利用Exponential Moving Average (EMA)评估task model的学习状态:

当EMA值比较大的时候,task model效果比较好,过滤掉更多的生成数据以保证质量;当EMA比较小的时候,task model效果比较差,保留更多的生成数据用于训练。
利用训练的task model可以为unlabeled data进行标注,为了减小伪标注的noise,作者使用了self-adaptive threshold和distance smoothing两种技术。
self-adaptive threshold和上面过滤生成数据的思路一致,利用EMA(不同超参 \(\alpha\))评估model性能:
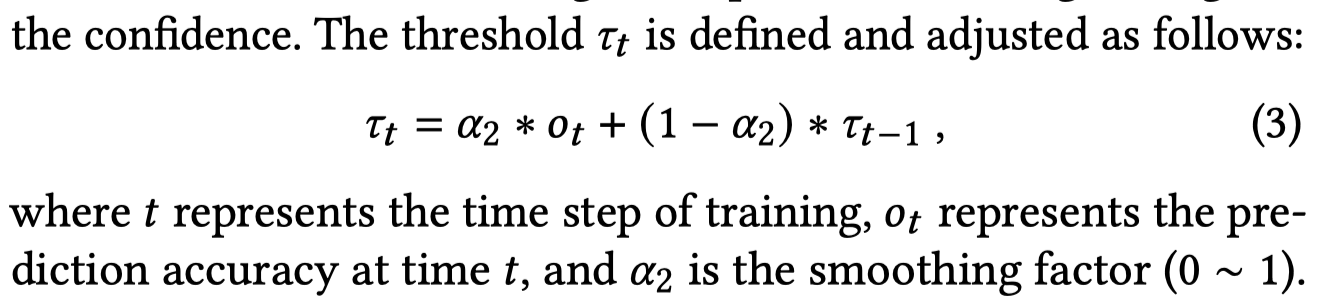
初期训练由于效果不太好,得到的阈值比较小,就会使用更多的无标注数据加速收敛;后期效果比较好,阈值比较大,就会过滤掉更多的无标注数据。利用无标注数据的训练loss是crossentropy loss with a confidence threshold:

Distance Smoothing是指作者在loss中,引入了正样本和负样本之间的差异大小的平滑系数。假设一个mention是\(m_i\),计算其和其它mention之间的余弦相似度,如果超过固定阈值(和前面的阈值应该不是一个),就认为是共指,属于positive mention;如果没有超过,就是negative mention。记positive mention是\(m_j\),记negative mention是\(m_k\)。分别计算正负样本对的特征欧式距离,然后评估差异大小作的平滑版本:
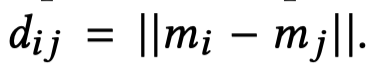
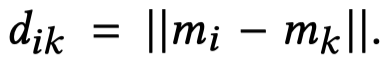
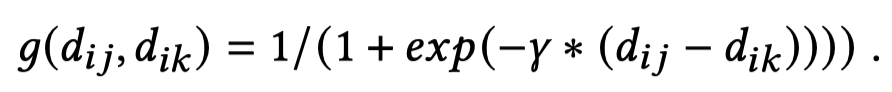
平滑系数把正负样本之间的差异平滑到0-1,起到了减小不同样本对之间差异大小的平滑作用。随后计算的loss:
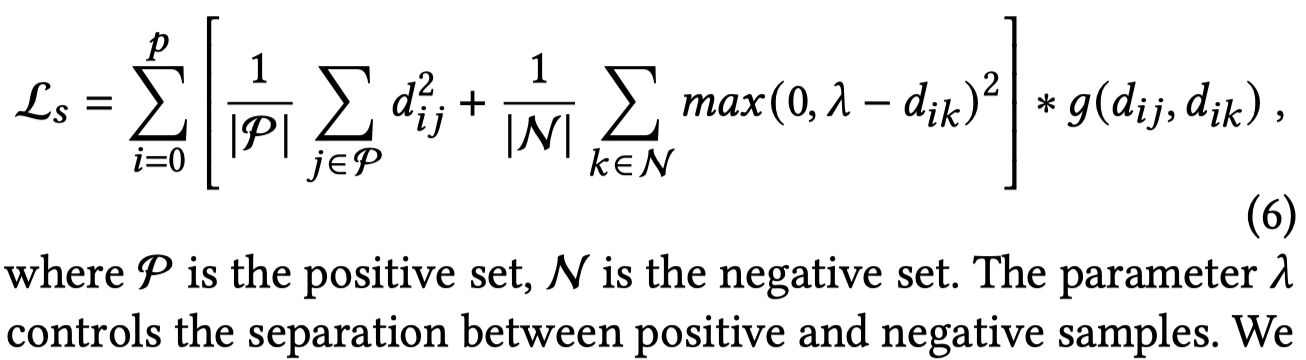
上述损失loss期望减小正样本之间的差异,增大正样本和负样本之间的差异。\(\lambda\)是正负样本对之间的差异距离。使得负样本的差异\(d_{ik}\)倾向于大于\(\lambda\),而\(d_{ij}\)倾向于变为0。
作者的MCR模型如图,使用BERT和RCNN作为编码器,然后单模态使用两个VAE,最后利用PoE的思想两个高斯分布相乘,得到多模态的高斯分布。
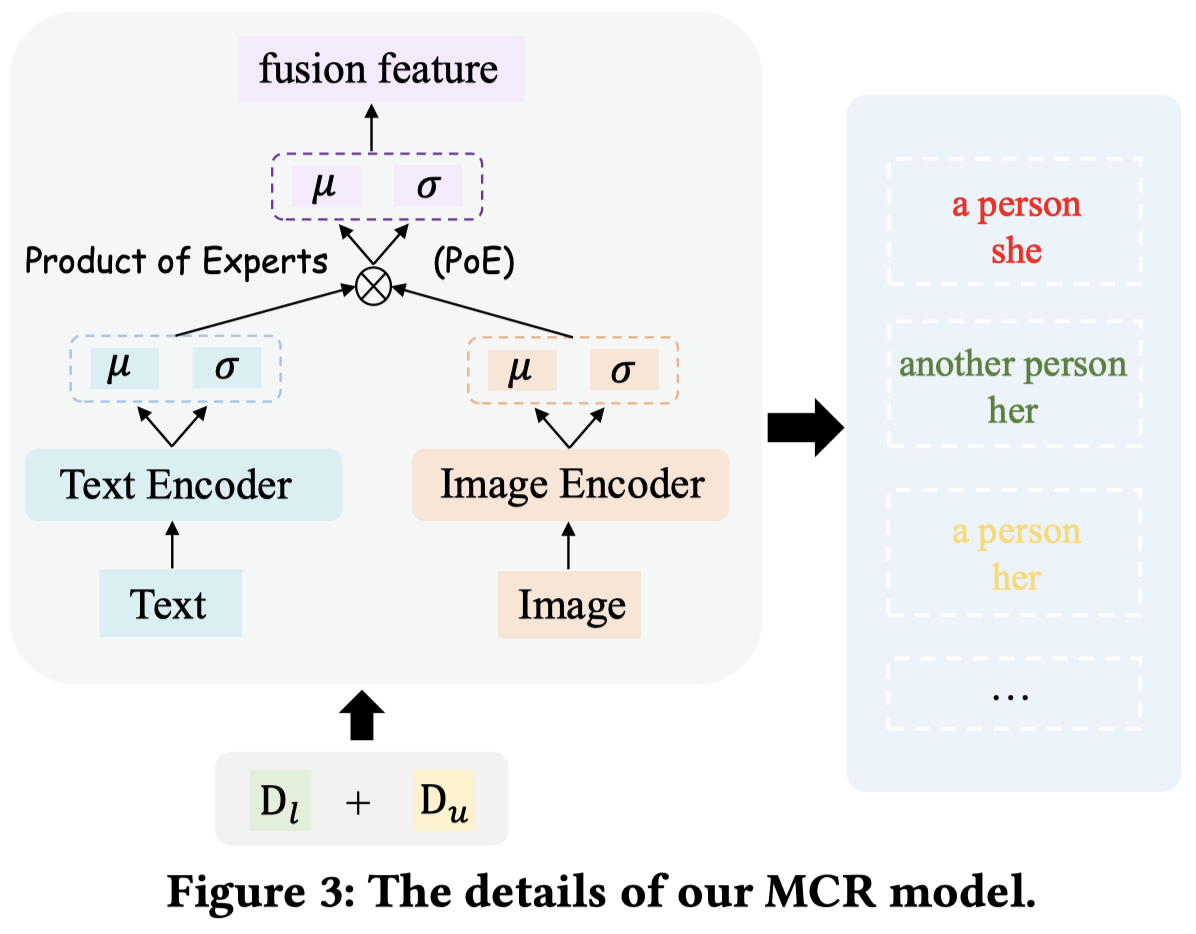
GMDA
Generative Multimodal Data Augmentation for Low-Resource Multimodal Named Entity Recognition. ACM MM 2024
As an important task in multimodal information extraction, Multimodal Named Entity Recognition (MNER) has recently attracted considerable attention. One key challenge of MNER lies in the lack of sufficient fine-grained annotated data, especially in low-resource scenarios. Although data augmentation is a widely used technique to tackle the above issue, it is challenging to simultaneously generate synthetic text-image pairs and their corresponding high-quality entity annotations. In this work, we propose a novel Generative Multimodal Data Augmentation (GMDA) framework for MNER, which contains two stages: Multimodal Text Generation and Multimodal Image Generation. Specifically, we first transform each annotated sentence into a linearized labeled sequence, and then train a Label-aware Multimodal Large Language Model (LMLLM) to generate the labeled sequence based on a label-aware prompt and its associated image. After using the trained LMLLM to generate synthetic labeled sentences, we further employ a Stable Diffusion model to generate the synthetic images that are semantically related to these sentences. Experimental results on three benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed GMDA framework, which consistently boosts the performance of several competitive methods for two subtasks of MNER in both full-supervision and low-resource settings.
Issue:MNER任务和GMNER任务都需要人工标注,特别是GMNER还需要标注visual objects的bounding box。获取人工标注在实际中成本大。DA可以缓解这一问题,但是之前的DA方法主要是考虑纯text的NER任务,没有考虑多模态场景下的DA挑战:
- First, it is necessary to generate both text and images, and each text-image pair should be semantically related.
- Second, each generated text-image pair is required to have the textual and visual entity annotations.

Solution:作者先是微调了一个MLLM(InstructBlip)来实现给定图像和entity list,生成带有实体标注的text;然后基于扩散模型(stable diffusion 1.5),生成符合text的image。
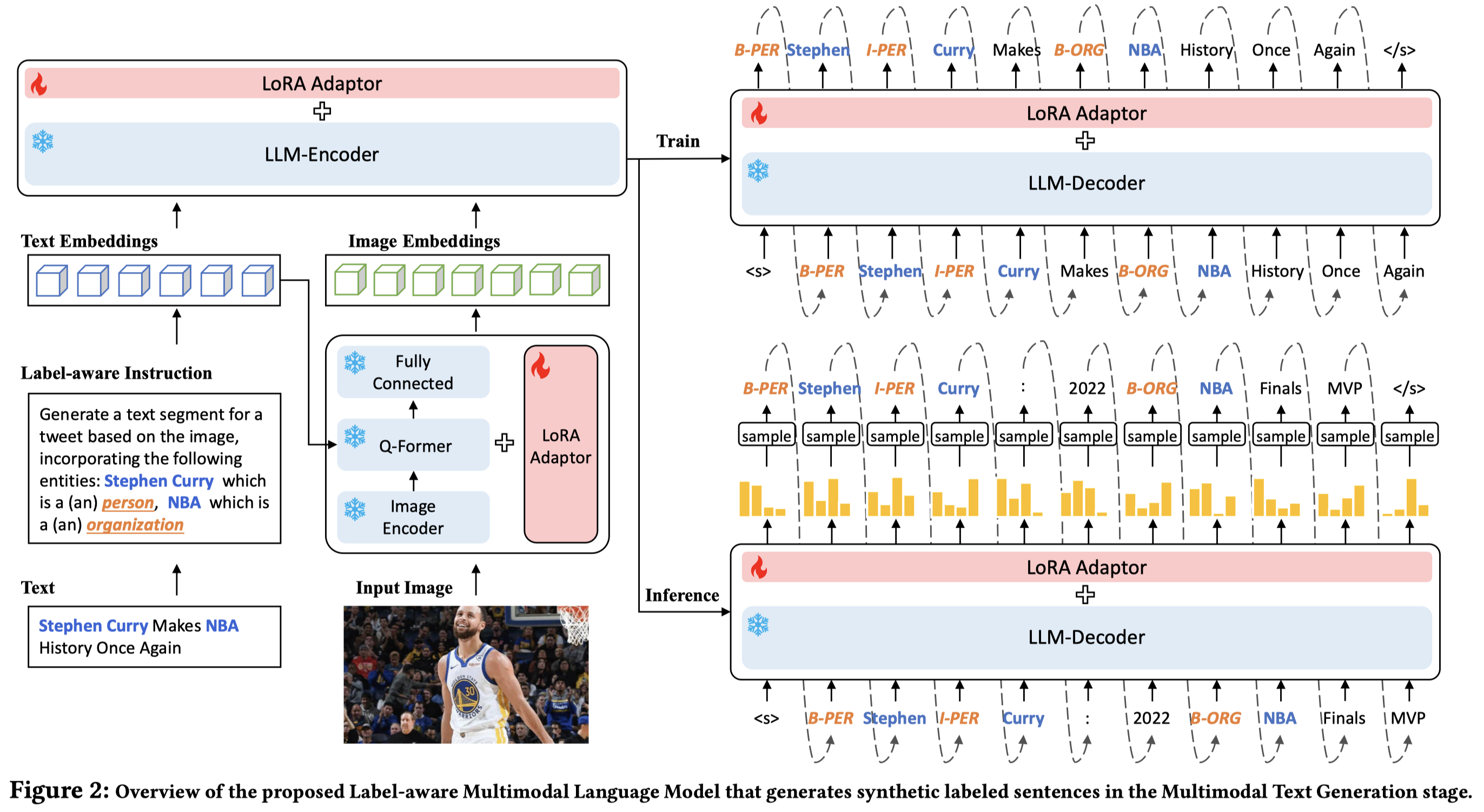
从现有的sample出发,利用其中的entity list构造instruction。作者使用LoRA微调了InstructBlip的image encoder(ViT-g/14)、LLM encoder(Flant-t5-XL 3B)。训练目标就是带有label的text。
训练完毕之后,为了获取更多样的text。作者同样是给定image和entity list,先进行top-k采样,再进行top-p采样,获取到多个的输出token序列集合。调用扩散模型生成image:
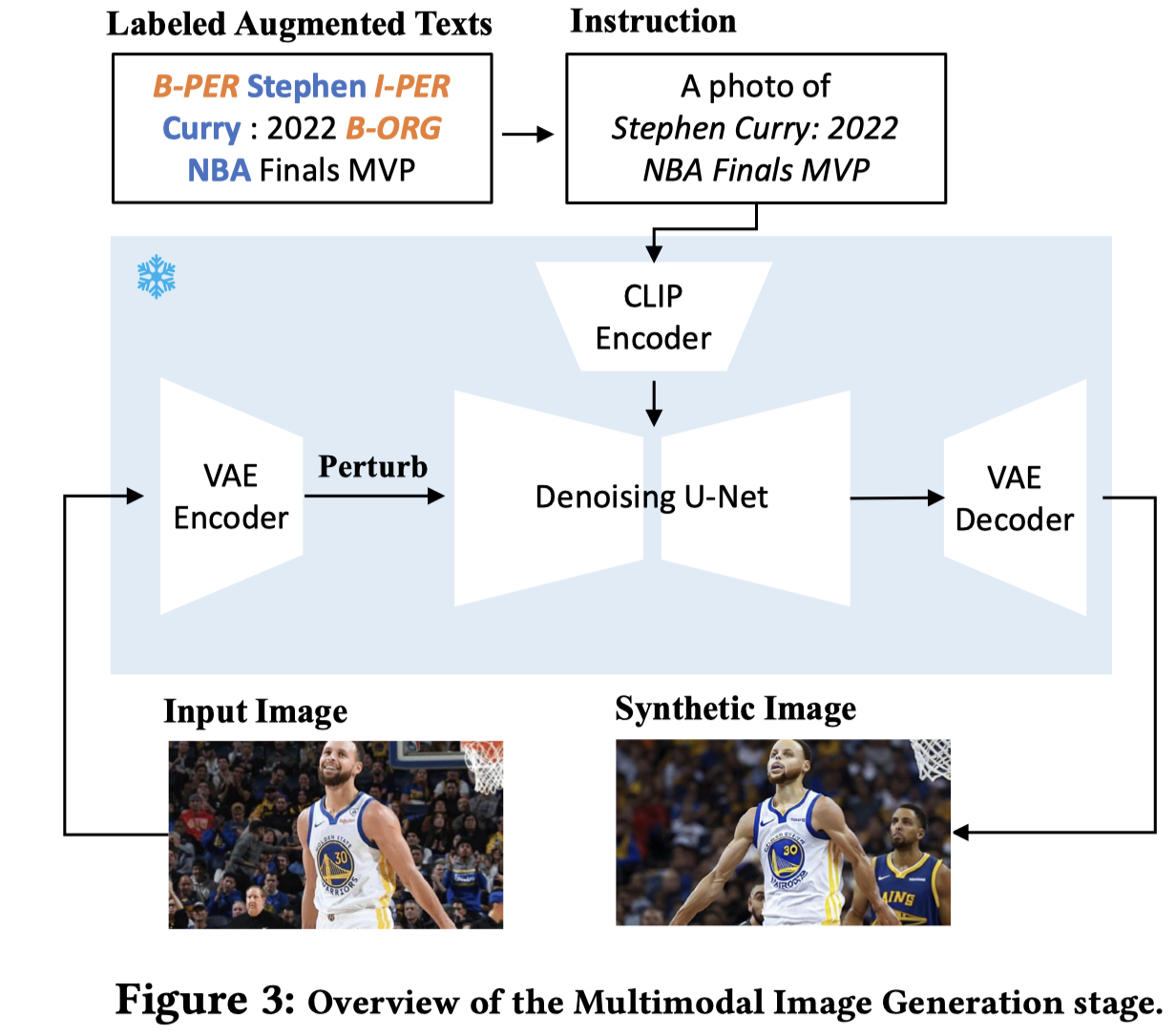
需要特别注意的一点是,扩散模型生成的是没有bounding box的。作者的做法很简单,作者发现通常生成的image和原始的image是非常相似的,因此作者直接使用原来image的bounding box作为生成image的bounding box。
生成的数据同样需要过滤。作者采用了很简单的方法,过滤掉特别端的text(words少于5个)、在真实数据集上训练对应的MNER model,然后预测生成的数据标注是否一致(这种做法不会损坏泛化性吗?如果可以正确预测,是否有很大的必要加入到训练集)、过滤掉重复的text。
作者的实验在3090上微调。对于GMNER任务,由于要进行visual object prediction,统计maximum IoU score是否超过0.5,如果超过了就预测正确。特别注意不是所有的entity都会有对应的bounding box。
在低资源情况下的对比:
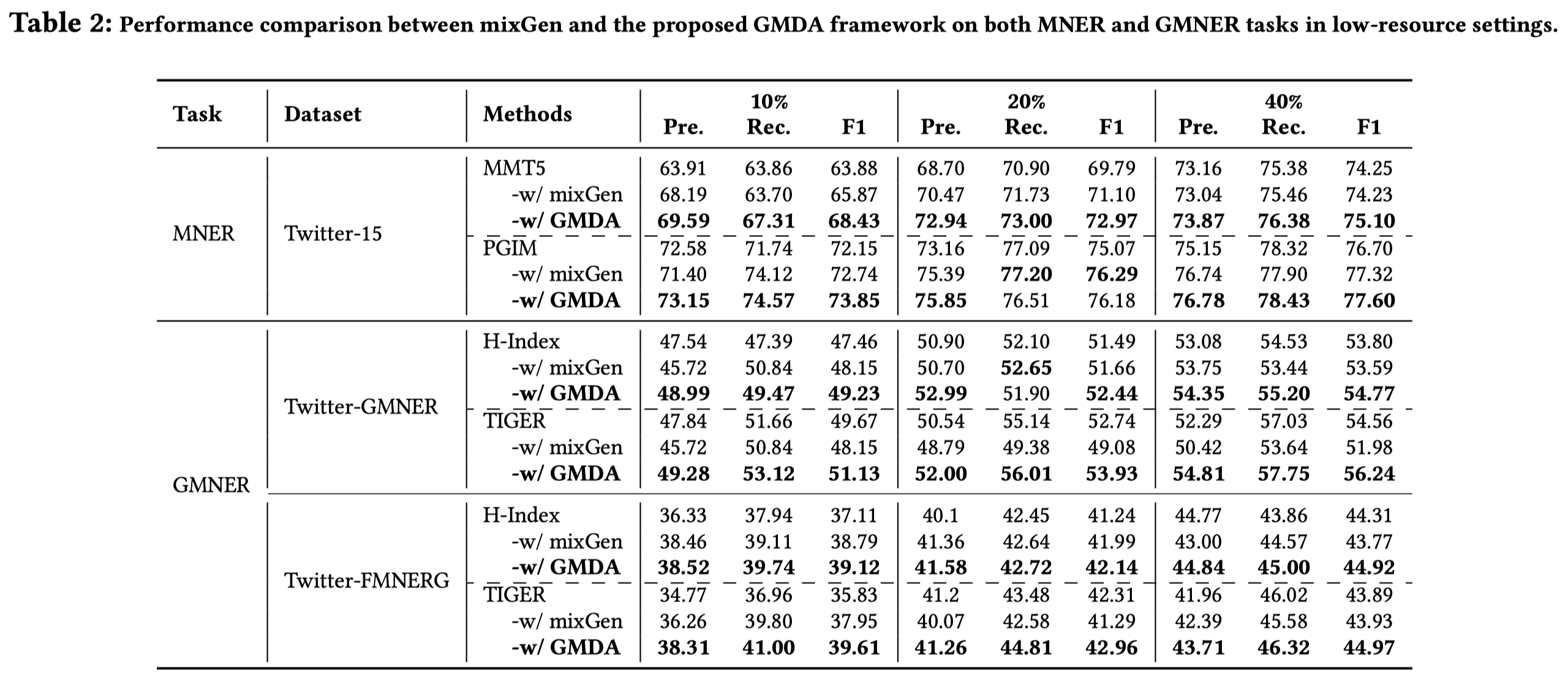
主要适合MM DA baseline mixGen进行了比较。
生成的case:
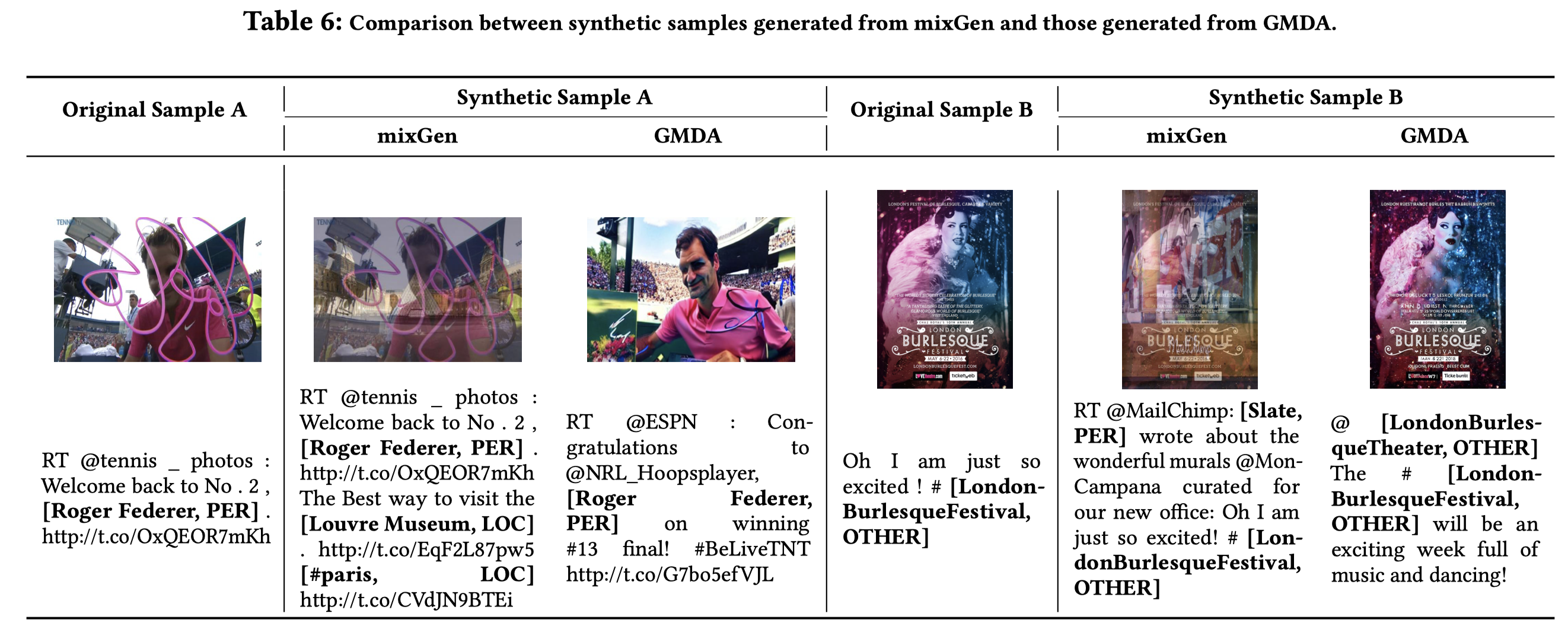
Data and MLLM survey
The Synergy between Data and Multi-Modal Large Language Models: A Survey from Co-Development Perspective. Alibaba group. arXiv 2024-08. 代码.
The rapid development of large language models (LLMs) has been witnessed in recent years. Based on the powerful LLMs, multi-modal LLMs (MLLMs) extend the modality from text to a broader spectrum of domains, attracting widespread attention due to the broader range of application scenarios. As LLMs and MLLMs rely on vast amounts of model parameters and data to achieve emergent capabilities, the importance of data is receiving increasingly widespread attention and recognition. Tracing and analyzing recent data-oriented works for MLLMs, we find that the development of models and data is not two separate paths but rather interconnected. On the one hand, vaster and higher-quality data contribute to better performance of MLLMs; on the other hand, MLLMs can facilitate the development of data. The co-development of multi-modal data and MLLMs requires a clear view of 1) at which development stages of MLLMs specific data-centric approaches can be employed to enhance certain MLLM capabilities, and 2) how MLLMs, utilizing those capabilities, can contribute to multi-modal data in specific roles. To promote the data-model co-development for MLLM community, we systematically review existing works related to MLLMs from the data-model co-development perspective. A regularly maintained project associated with this survey is accessible at https://github.com/modelscope/data-juicer/blob/main/docs/awesome_llm_data.md.
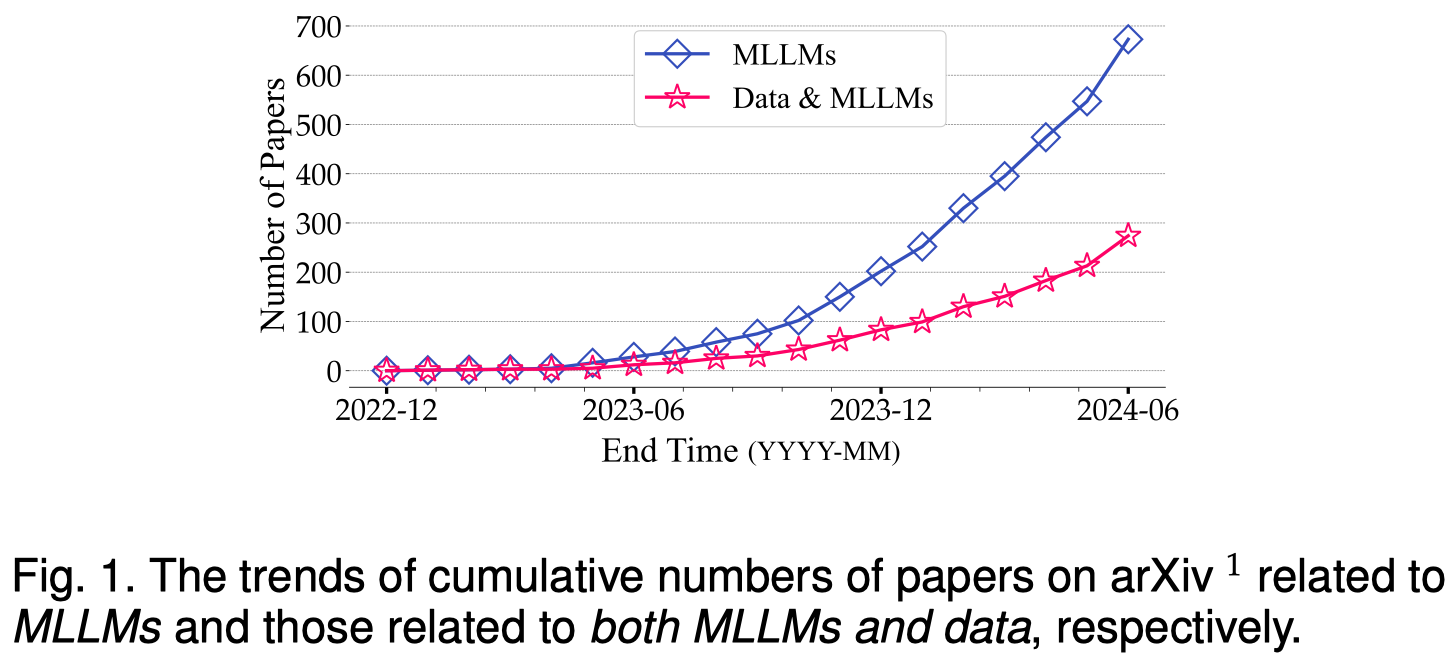
作者从数据和多模态大模型协同发展的角度进行了总结:
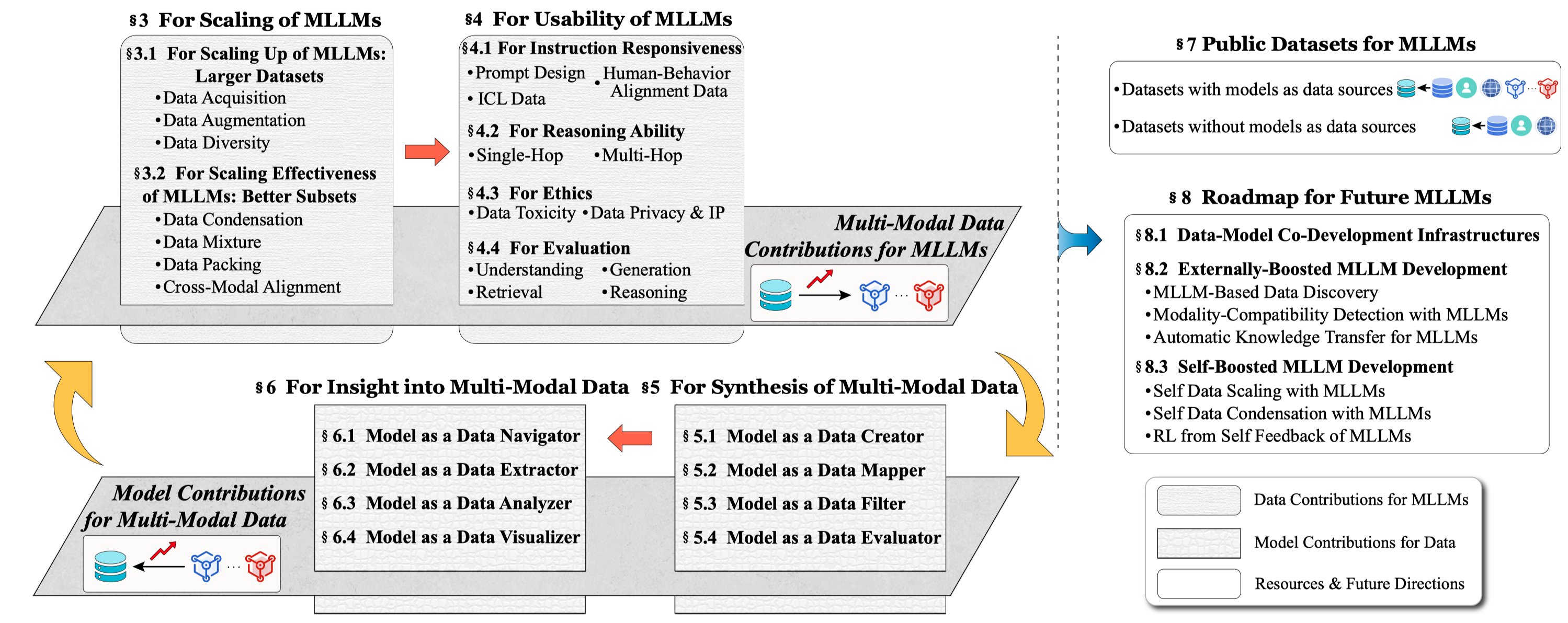
对于MLLM对data的作用,作者从data synthesis和data insights两个角度进行总结:
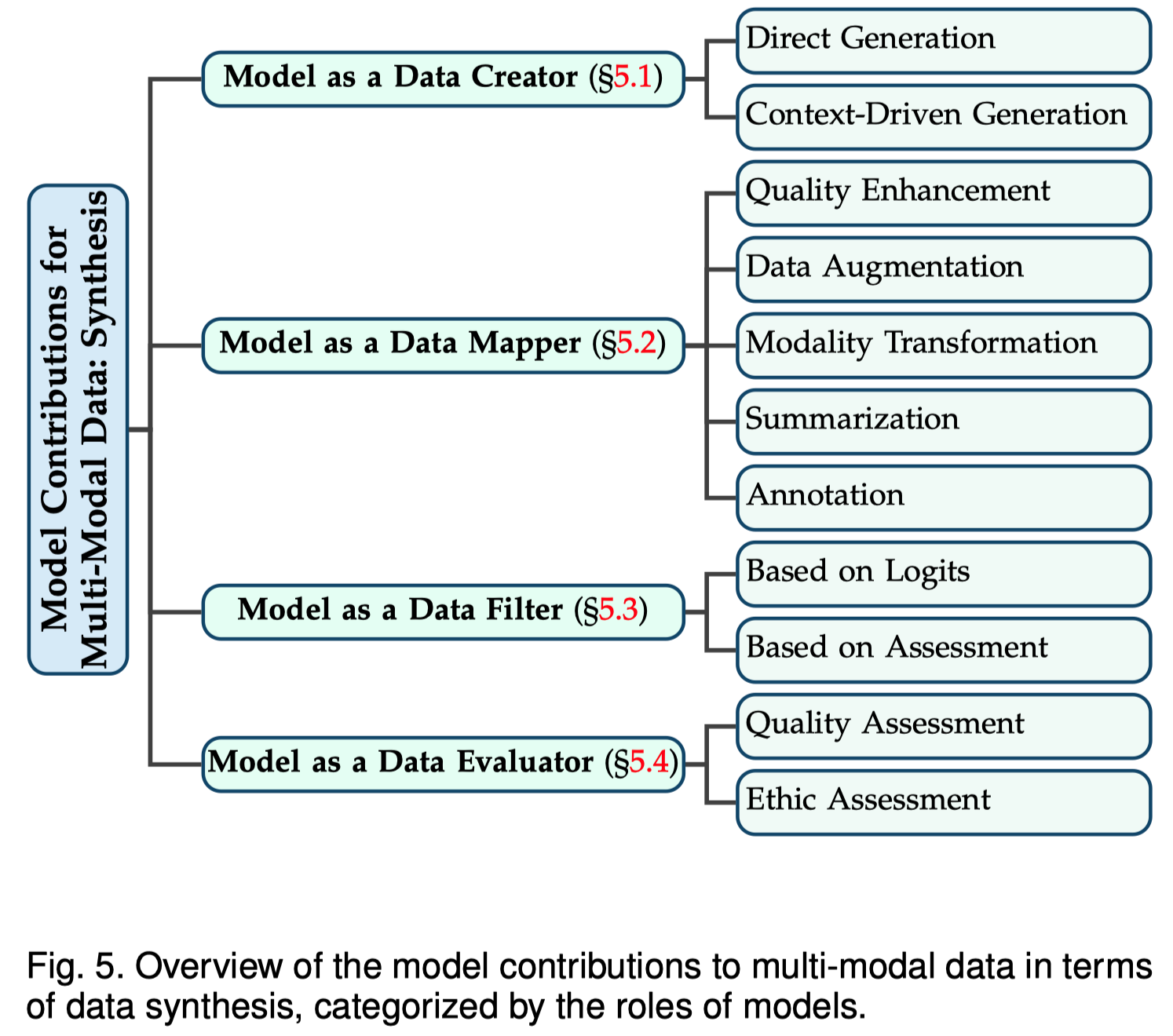
数据构造包括数据生成、数据转换、数据评估等。
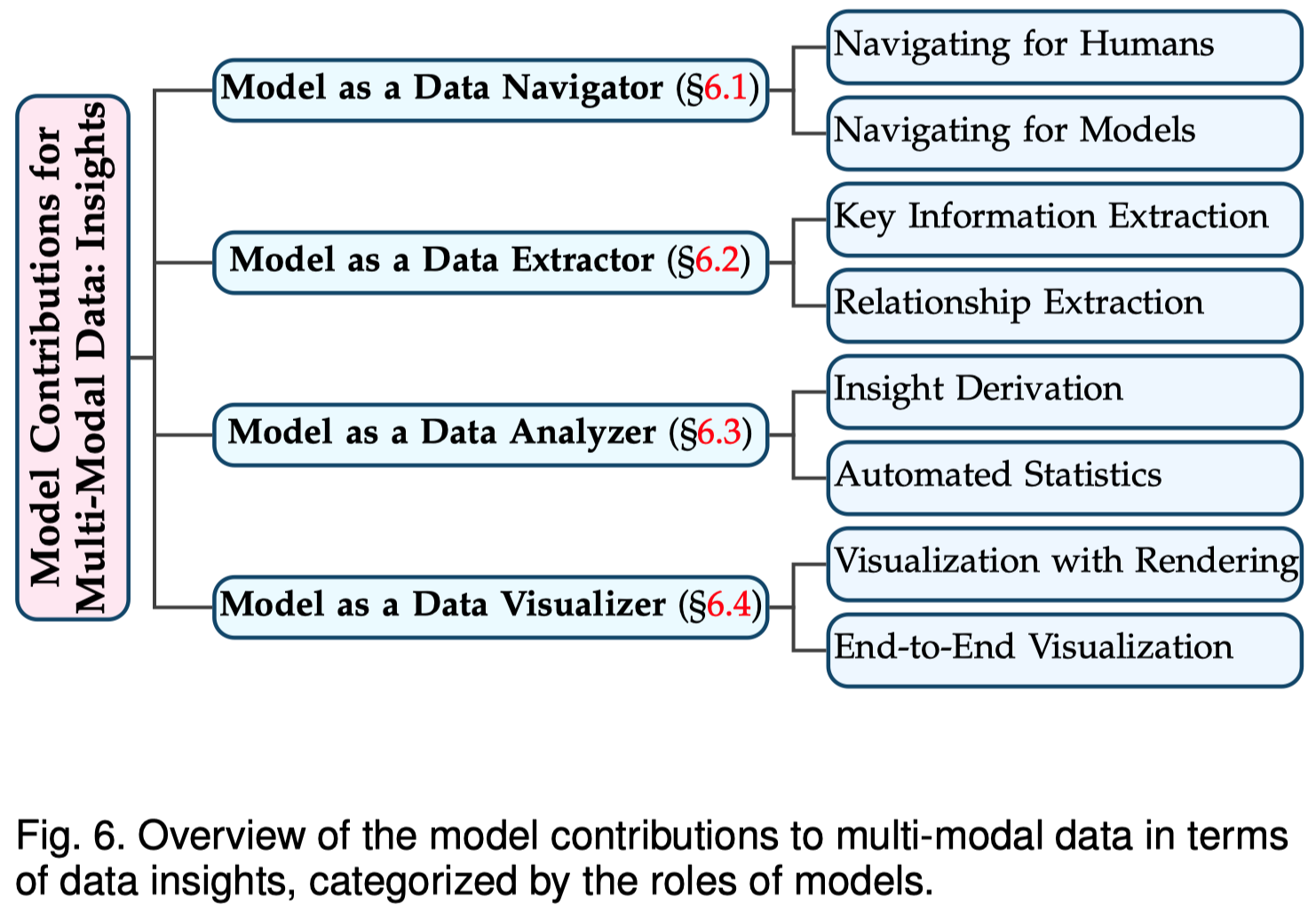
data insights包括利用MLLM进行数据处理(数据不一定用于MLLM,可能是其它task),比如数据检索、数据关键信息抽取等。
CFT-CLIP
Assessing News Thumbnail Representativeness: Counterfactual text can enhance the cross-modal matching ability. Soongsil University. ACL 2024 Findings. 代码.
This paper addresses the critical challenge of assessing the representativeness of news thumbnail images, which often serve as the first visual engagement for readers when an article is disseminated on social media. We focus on whether a news image represents the actors discussed in the news text. To serve the challenge, we introduce NEWSTT, a manually annotated dataset of 1000 news thumbnail images and text pairs. We found that the pretrained vision and language models, such as BLIP-2, struggle with this task. Since news subjects frequently involve named entities or proper nouns, the pretrained models could have a limited capability to match news actors’ visual and textual appearances. We hypothesize that learning to contrast news text with its counterfactual, of which named entities are replaced, can enhance the cross-modal matching ability of vision and language models. We propose CFT-CLIP, a contrastive learning framework that updates vision and language bi-encoders according to the hypothesis. We found that our simple method can boost the performance for assessing news thumbnail representativeness, supporting our assumption. Code and data can be accessed at https://github.com/ssu-humane/news-images-acl24.
Issue:作者关注评估新闻缩略图的代表性,主要关心一个缩略图是否描述了text的actors

由于text常常出现新的命名实体或专有名词,作者发现预训练的BLIP-2方法不能够很好的适应。
Solution:作者使用反事实生成,替换text中的实体来构造hard negative sample,结合对比学习进行训练。

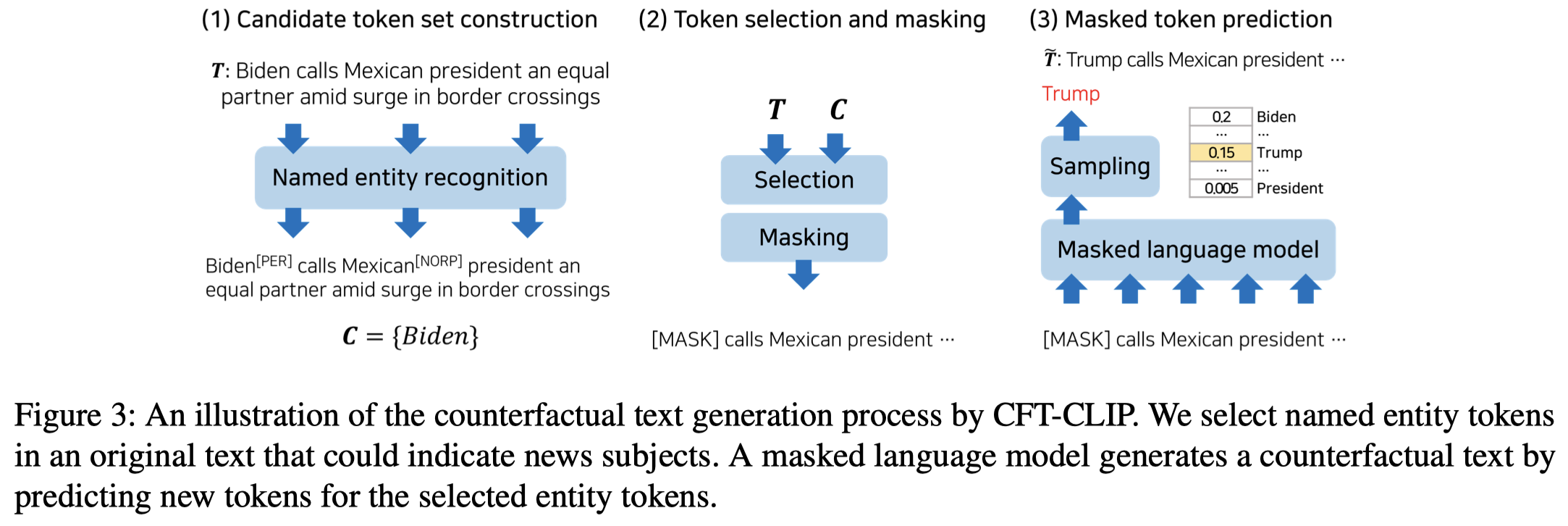
生成的方法很简单,就是先使用现有的NER model识别实体集合,然后mask。再利用BERT这类masked language model去预测mask token,直到获取到和原来不一样的entity tokens。
LaCLIP
Improving CLIP Training with Language Rewrites. google. NeurIPS 2023. 代码.
Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP) stands as one of the most effective and scalable methods for training transferable vision models using paired image and text data. CLIP models are trained using contrastive loss, which typically relies on data augmentations to prevent overfitting and shortcuts. However, in the CLIP training paradigm, data augmentations are exclusively applied to image inputs, while language inputs remain unchanged throughout the entire training process, limiting the exposure of diverse texts to the same image. In this paper, we introduce Language augmented CLIP (LaCLIP), a simple yet highly effective approach to enhance CLIP training through language rewrites. Leveraging the in-context learning capability of large language models, we rewrite the text descriptions associated with each image. These rewritten texts exhibit diversity in sentence structure and vocabulary while preserving the original key concepts and meanings. During training, LaCLIP randomly selects either the original texts or the rewritten versions as text augmentations for each image. Extensive experiments on CC3M, CC12M, RedCaps and LAION-400M datasets show that CLIP pre-training with language rewrites significantly improves the transfer performance without computation or memory overhead during training. Specifically for ImageNet zero-shot accuracy, LaCLIP outperforms CLIP by 8.2% on CC12M and 2.4% on LAION-400M. Code is available at https://github.com/LijieFan/LaCLIP.
Issue:在CLIP的训练过程中,DA方法只作用于image。实际上text的DA也应该被考虑,比如存在多个不同image使用相同text的情况。
Solution:由于CLIP的训练数据规模很大,使用商业的llm 改写百万上千万的caption代价很大,因此作者考虑使用开源LLM Llama进行改写。由于Llama没有经过instruction tuning,但是有ICL能力。因此作者先使用商业的LLM构造demonstrations,再利用Llama进行改写。
demonstration除了下面利用ChatGPT进行生成外,还有利用MSCOCO数据集、人工改写的方法:
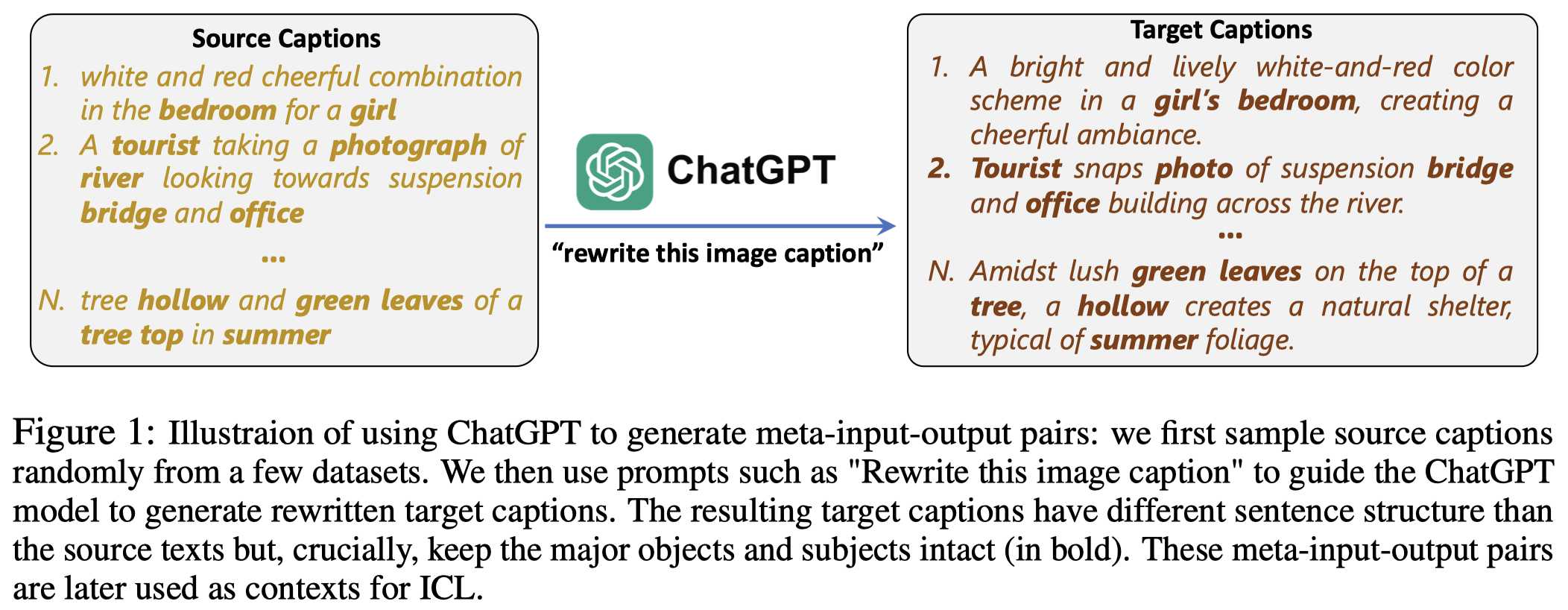
获得demonstrations后,作者调用Llama进行改写,ICL的prompt如下(注意其中的特殊符号=>是被实际定义的):

即使是使用Llama,作者改写CC3M数据集也在8块A100上运行了7h才完成。
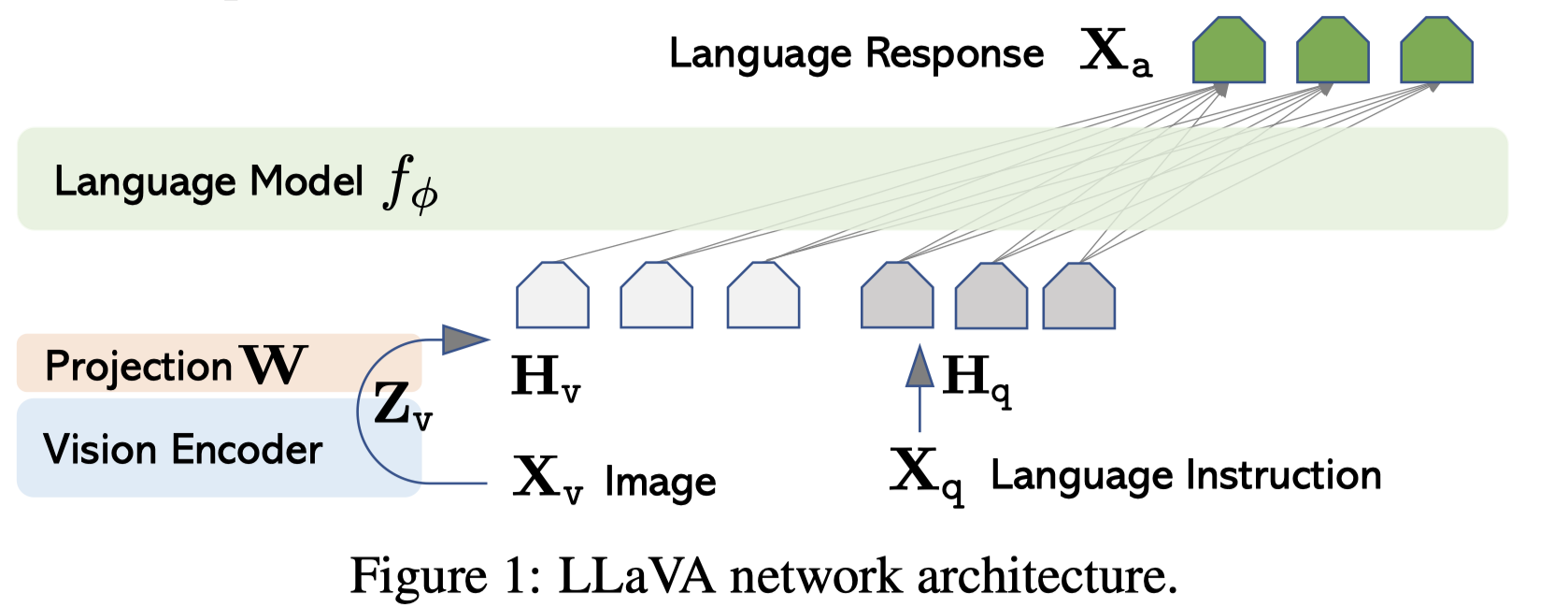
LLaVA
Visual Instruction Tuning. University of Wisconsin–Madison. NeurIPS 2023. 代码.
Instruction tuning large language models (LLMs) using machine-generated instruction-following data has been shown to improve zero-shot capabilities on new tasks, but the idea is less explored in the multimodal field. We present the first attempt to use language-only GPT-4 to generate multimodal language-image instruction-following data. By instruction tuning on such generated data, we introduce LLaVA: Large Language and Vision Assistant, an end-to-end trained large multimodal model that connects a vision encoder and an LLM for general-purpose visual and language understanding. To facilitate future research on visual instruction following, we construct two evaluation benchmarks with diverse and challenging application-oriented tasks. Our experiments show that LLaVA demonstrates impressive multimodal chat abilities, sometimes exhibiting the behaviors of multimodal GPT-4 on unseen images/instructions, and yields a 85.1% relative score compared with GPT-4 on a synthetic multimodal instruction-following dataset. When fine-tuned on Science QA, the synergy of LLaVA and GPT-4 achieves a new state-of-the-art accuracy of 92.53%. We make GPT-4 generated visual instruction tuning data, our model, and code publicly available.
应该是首个考虑multimodal instruction tuning的工作。为了减低人工设计multimodal instruction的代价,作者利用language-only GPT-4和ChatGPT生成多模态指令数据集。
输入是纯文本的prompt,为了描述image,使用image caption结合bounding box。GPT-4、ChatGPT生成的回复有三种类型:

原始的text-image pairs来源于现有数据集COCO。