MIE-Collection2
MRE and MNER 1
多模态信息抽取相关论文总结集合2。
GMNER/H-Index
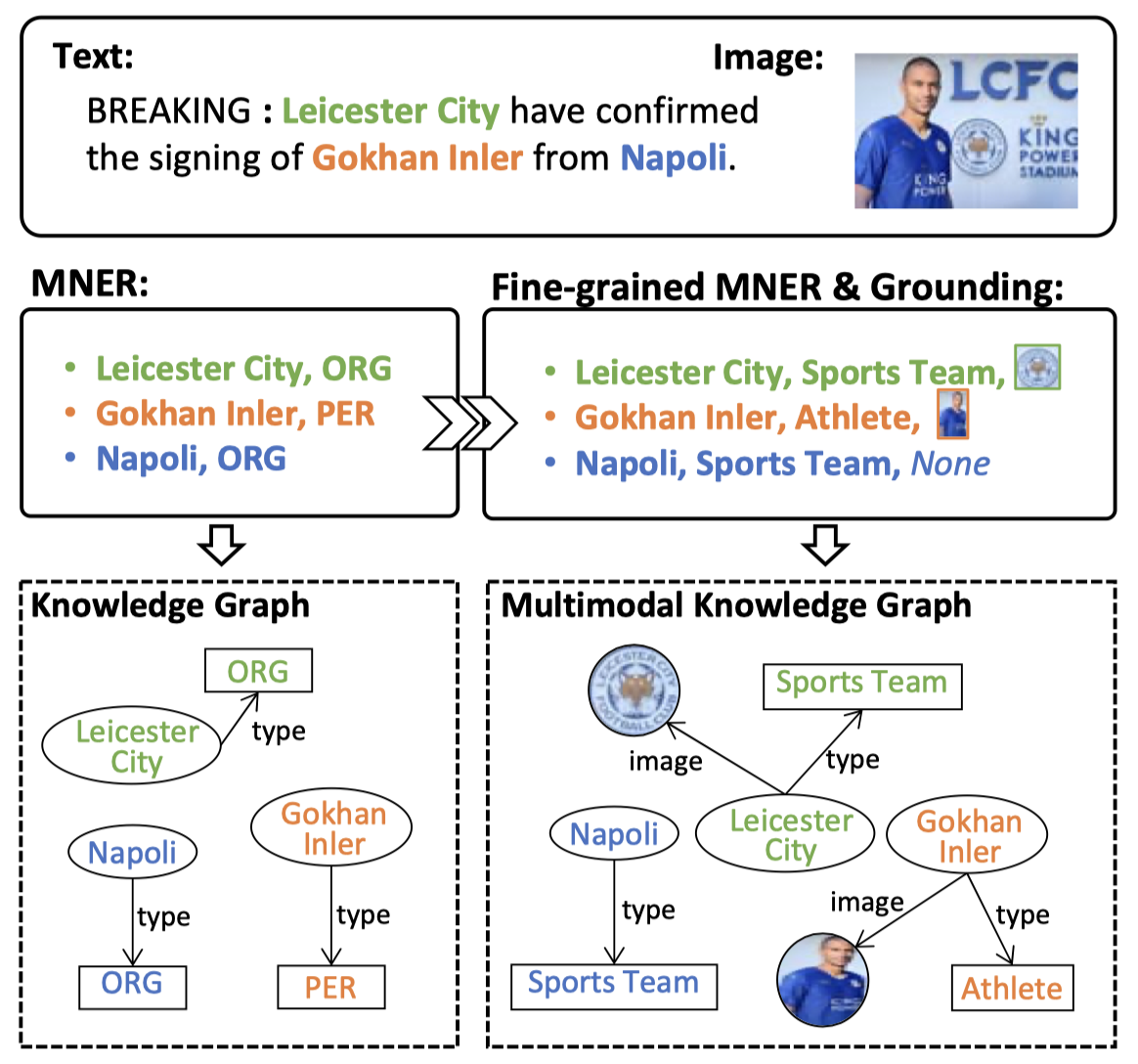
Grounded Multimodal Named Entity Recognition on Social Media. 南京科大. ACL 2023. 代码.
In recent years, Multimodal Named Entity Recognition (MNER) on social media has attracted considerable attention. However, existing MNER studies only extract entity-type pairs in text, which is useless for multimodal knowledge graph construction and insufficient for entity disambiguation. To solve these issues, in this work, we introduce a Grounded Multimodal Named Entity Recognition (GMNER) task. Given a text-image social post, GMNER aims to identify the named entities in text, their entity types, and their bounding box groundings in image (i.e., visual regions). To tackle the GMNER task, we construct a Twitter dataset based on two existing MNER datasets. Moreover, we extend four well-known MNER methods to establish a number of baseline systems and further propose a Hierarchical Index generation framework named H-Index, which generates the entity-type-region triples in a hierarchical manner with a sequence-tosequence model. Experiment results on our annotated dataset demonstrate the superiority of our H-Index framework over baseline systems on the GMNER task. Our dataset annotation and source code are publicly released at https://github.com/NUSTM/GMNER.
Issue:之前的多模态NER方法只是把image看做是additional clues,输出的是entity-type pairs。这有两个局限:
- The extracted entity-type pairs are solely useful for constructing text-only knowledge graph rather than multimodal knowledge graph. 不能帮助构建多模态知识图谱
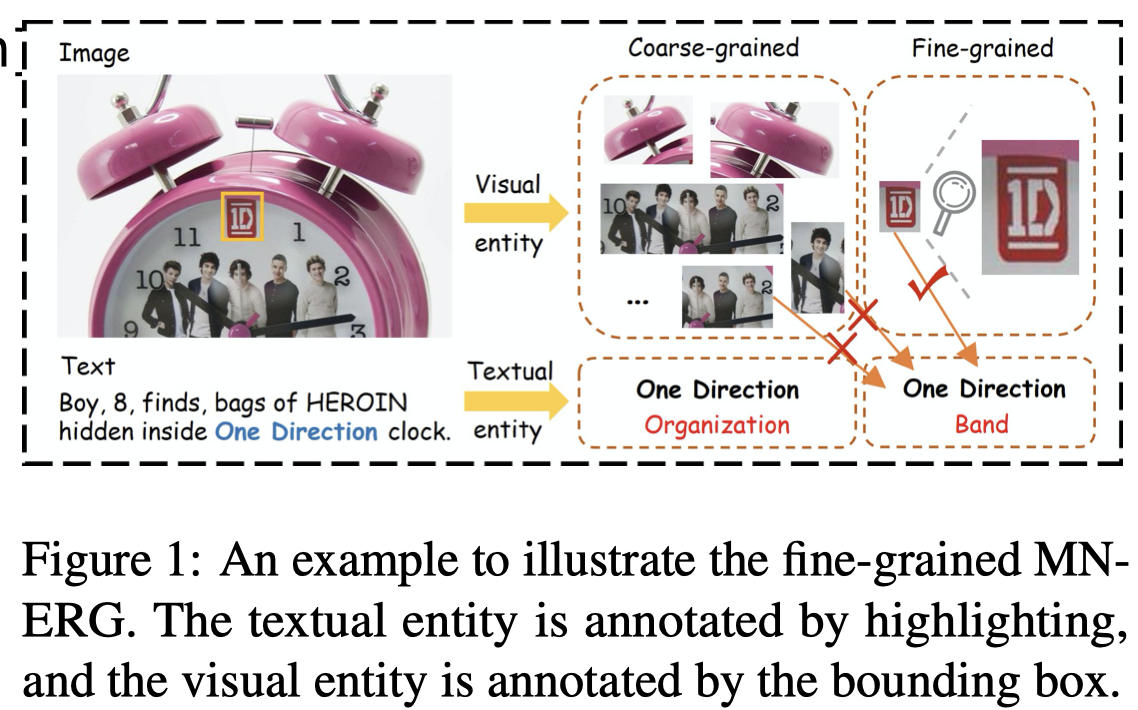
- Moreover, only identifying entity-type pairs in text is often insufficient for entity disambiguation. For example, in Fig. 1, without the grounded yellow bounding box, it is hard to infer the (Michael Jordan, PER) pair refers to the professor in UC Berkeley rather than the famous basketball player. 带有image信息能够帮助实体消歧

Solution:因此,作者提出了新任务,Grounded Multimodal Named Entity Recognition (GMNER) task。任务定义为:

首先,作者基于Twitter-2015和Twitter-2017数据集,人工标注了entity对应的bounding box。需要注意两点:
- 没有image的data被过滤掉
- 属于同一类型的多于3个的实体的data被过滤掉
作者找了3个研究生进行人工标注,统计结果为:
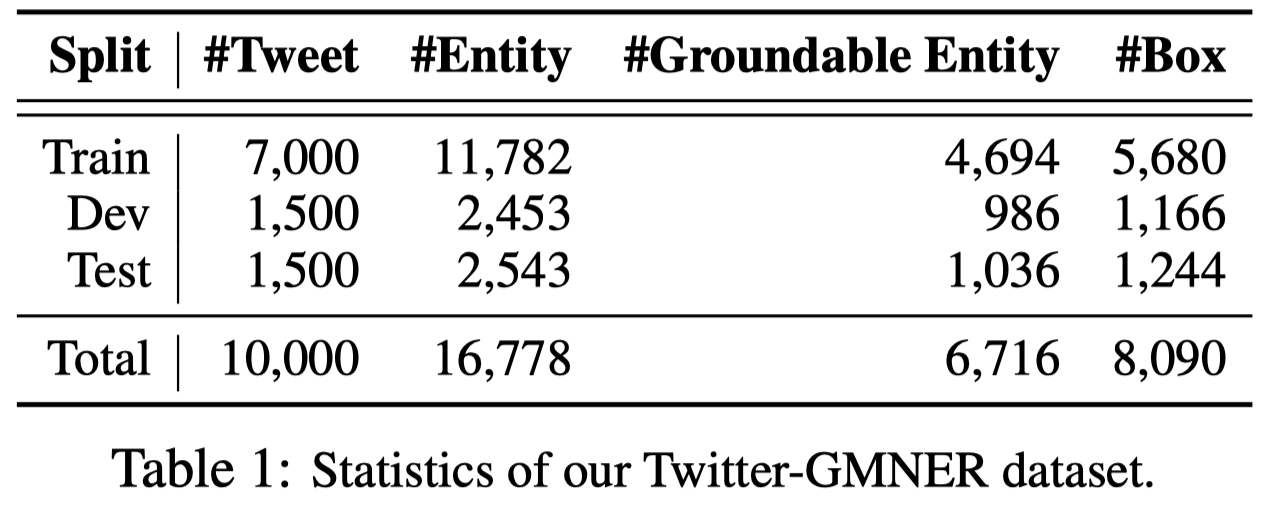
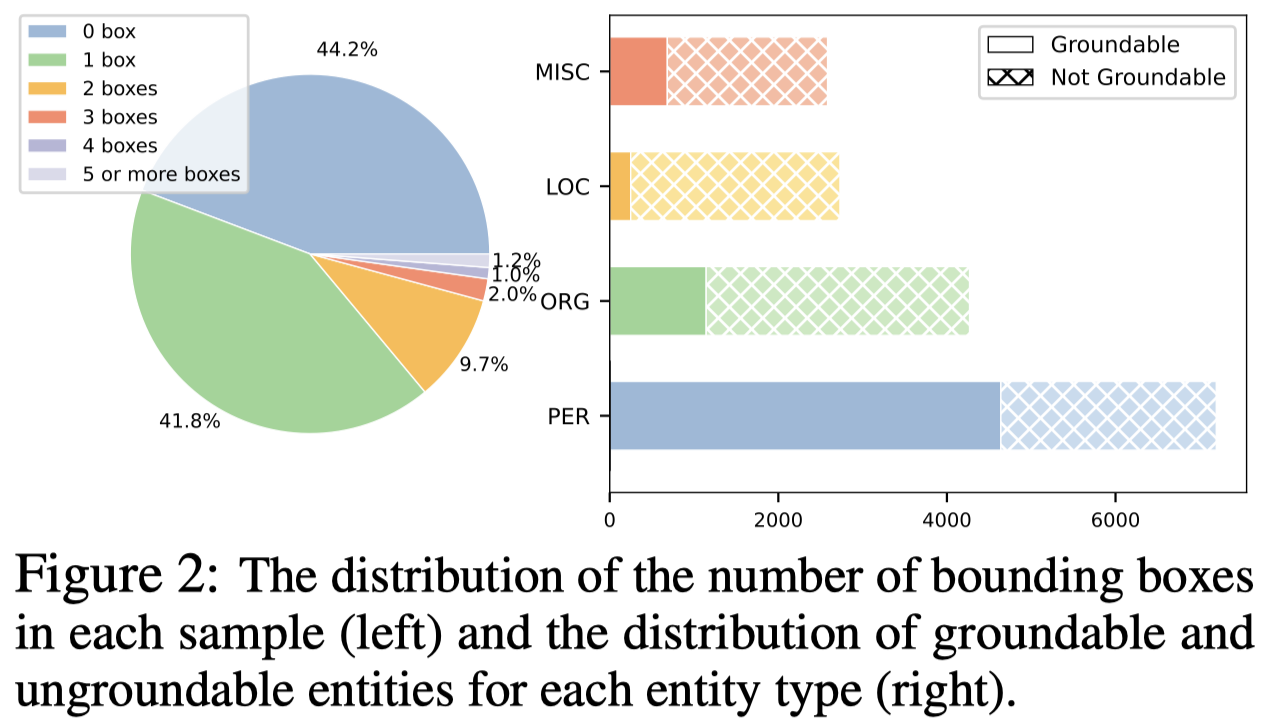
在数据集中,不是所有entity都可以被grounding的,60%的entity没有bounding box,40%的text没有对应的entity bounding box。另外,有的entity有多个ground-truth bounding box。
为了解决GMNER任务,作者提出了一个H-Index的方法,基于BART-base:
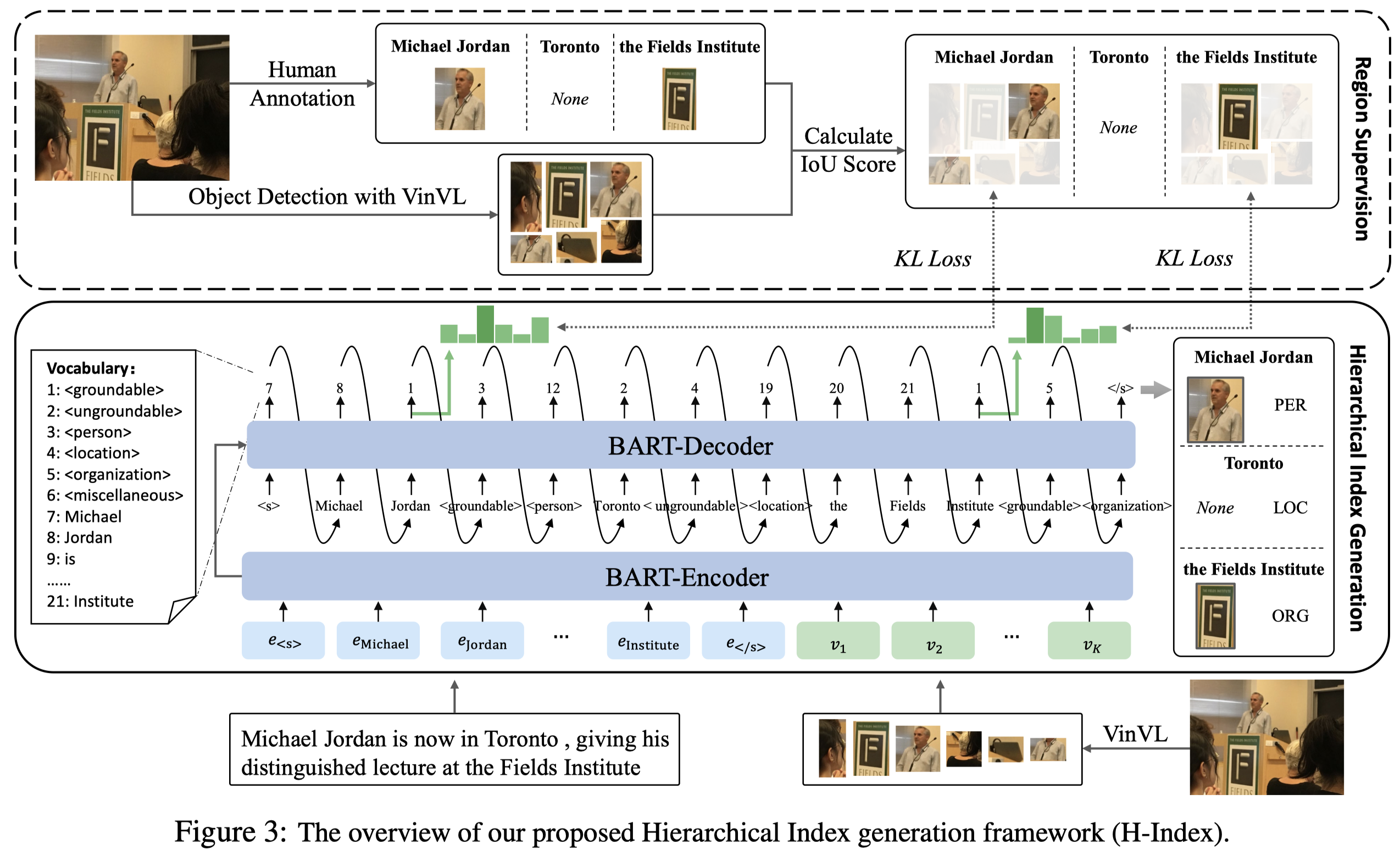
对于image,作者利用VinVL (Zhang et al., 2021b)方法提前识别\(K\)个objects,每个object使用VinVL学习到的特征再经过mean-pooling之后的embedding表示。VinVL识别的objects就是最后模型会选择的可以对应不同entity的候选项。
为了统一输出space,作者使用不同index进行表示。例如使用1和2表示entity是否groundable;使用3-6表示entity types,6之后的数字表示entity的boundary。

随后,作者利用BART对输出结果进行建模。
为了进行entity grounding,作者使用index 1的embedding来输入到一个额外的输出层,用于计算和VinVL导出的objects的匹配度:

由于VinVL导出的objects和grounding-truth bounding box不一致,因此衡量每个VinVL的objects的IoU度数,少于0.5的设为0,归一化后作为目标预测分布概率。使用KL散度拉近预测分布和ground-truth分布的差距。
在inference阶段,直接选择最大的\(p(z_k)\)对应的image region作为预测bounding box。
在实验阶段,只有entity、entity type和bounding box全部预测正确才认为正确。一个entity有多个ground-truth bounding box,只要最大的IoU大于0.5即可。

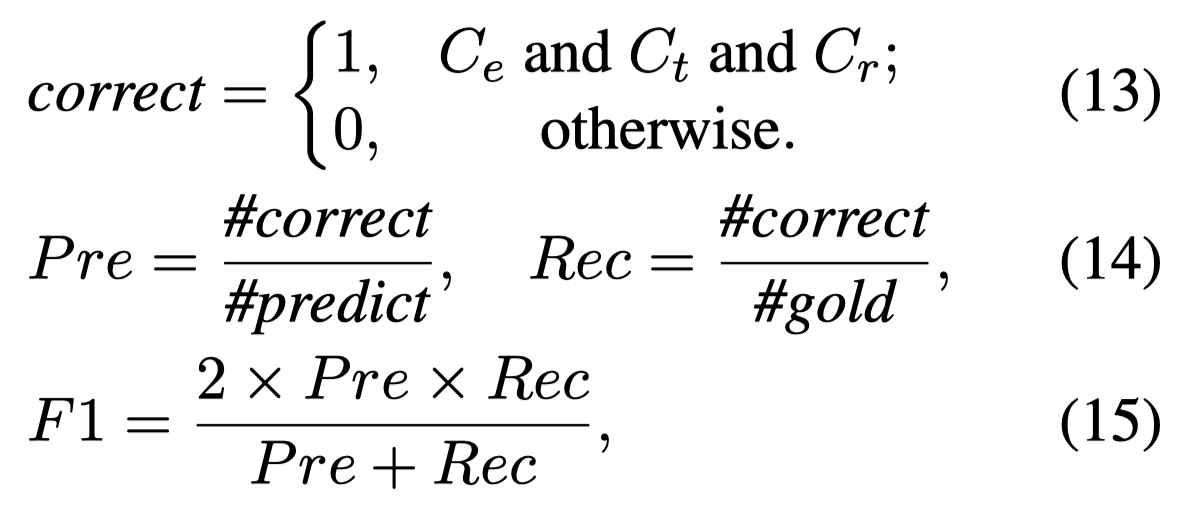
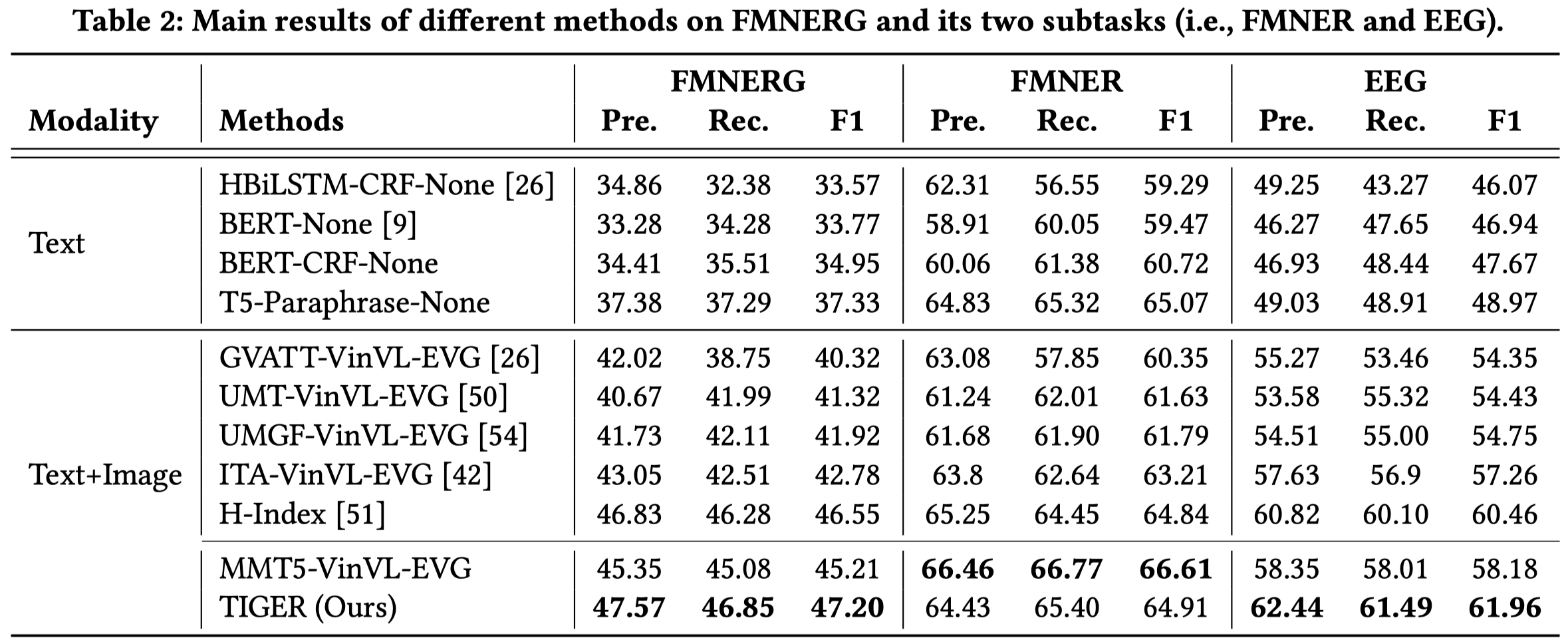
实验结果:
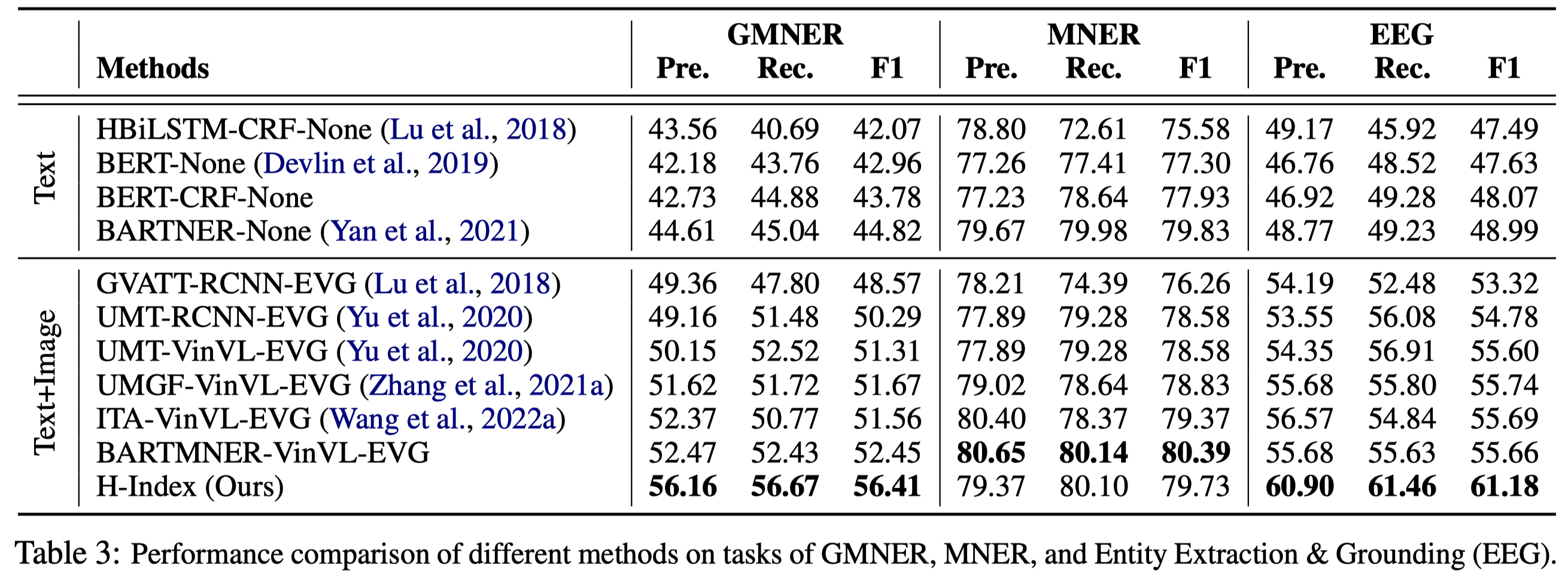
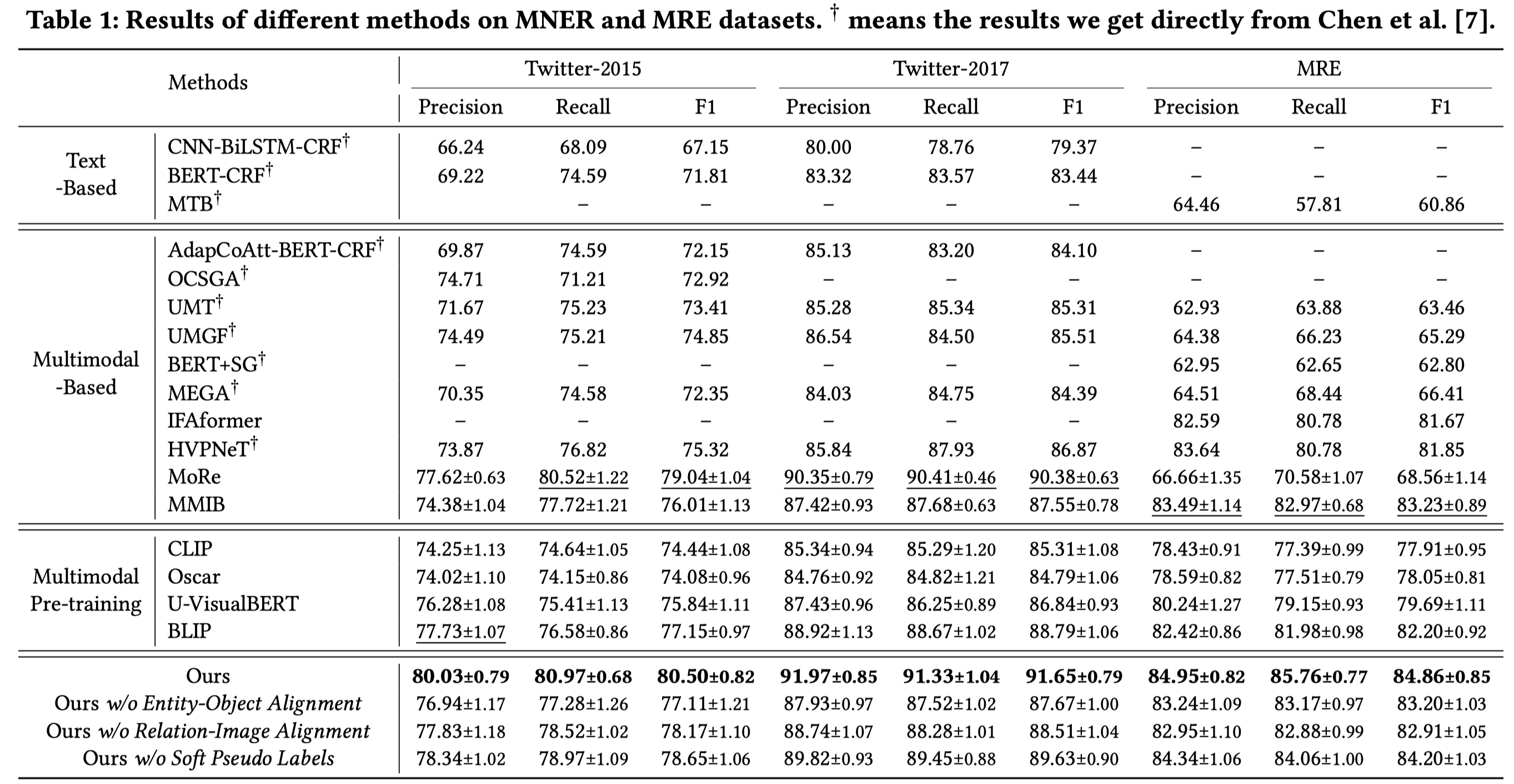
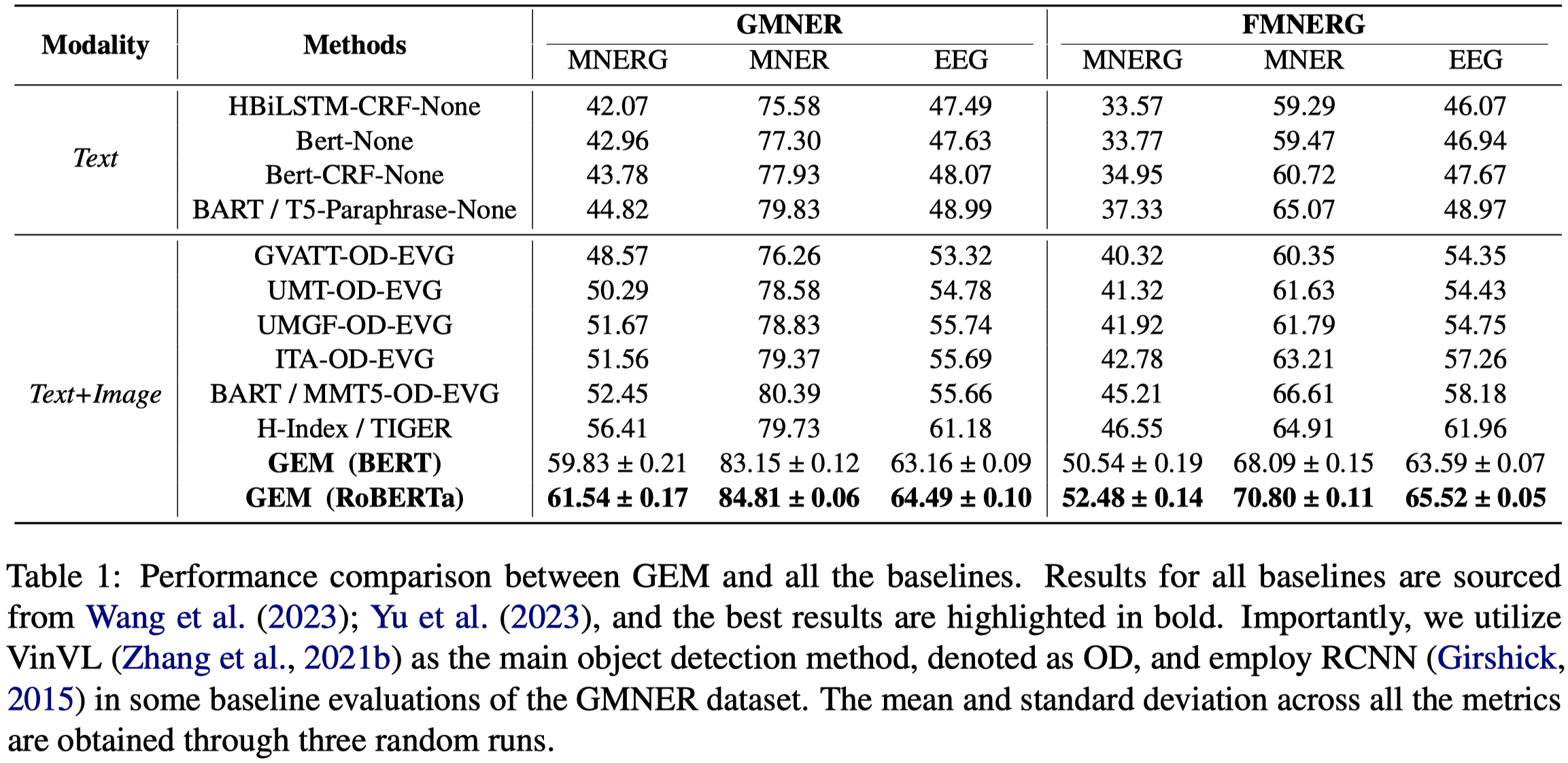
上面表格中的MNER和EEG是GMNER的两个子任务,MNER只评估entity和entity type正确性;EEG只评估entity和bounding box正确性。
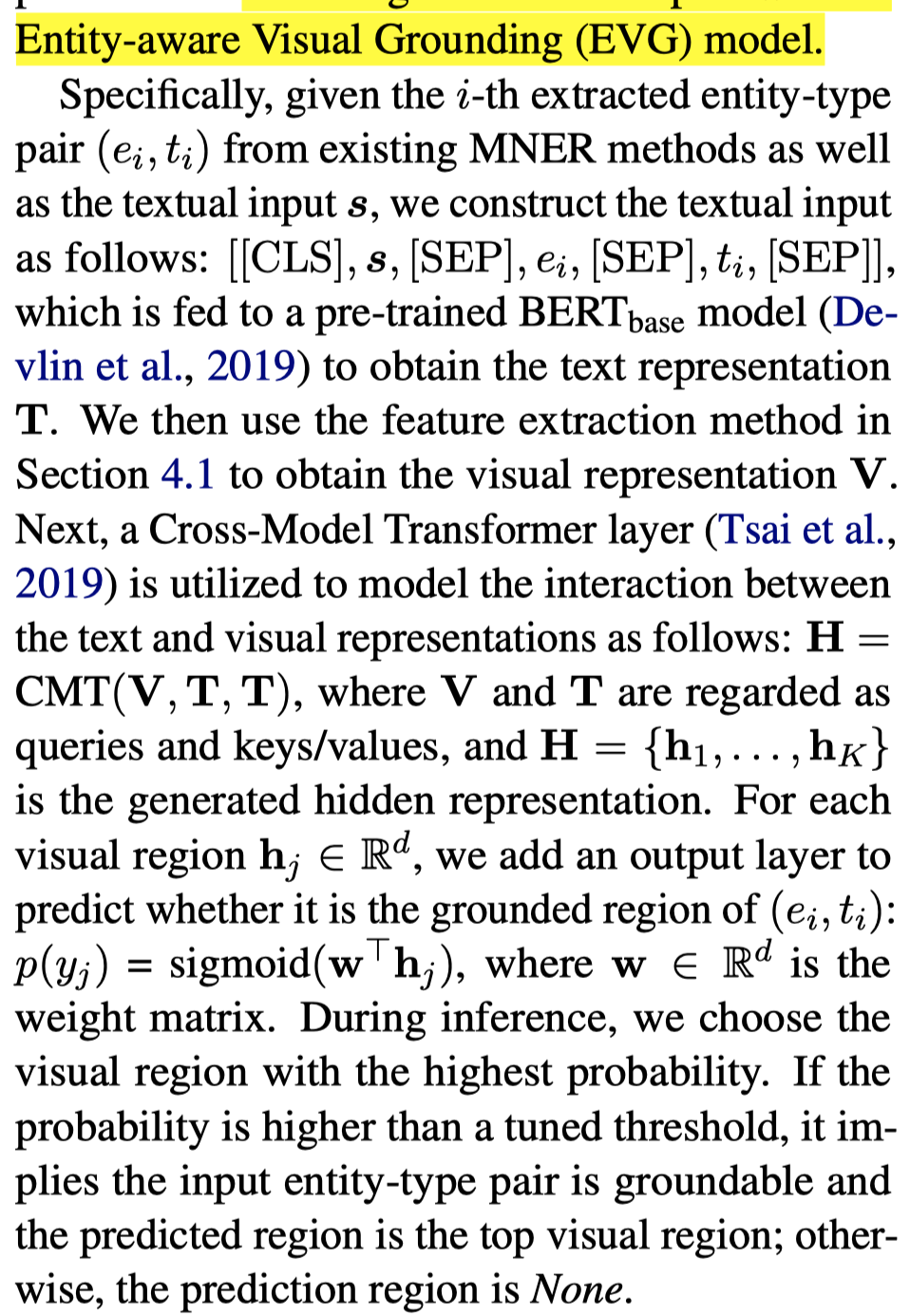
为了构造baseline方法,作者利用现有的MNER models预测得到entity和entity type,然后输入到作者构建的EVG方法来获得对应的bounding box。具体的EVG方法如下:利用现有MNER模型抽取候选entity,构造text,输入BERT得到text embedding,利用跨模态注意力,VinVL找到的objects作为query,text作为key/value,得到object embedding,输入到sigmoid输出层,判断其是否是对应的object,超过阈值就认为是entity对应的object。
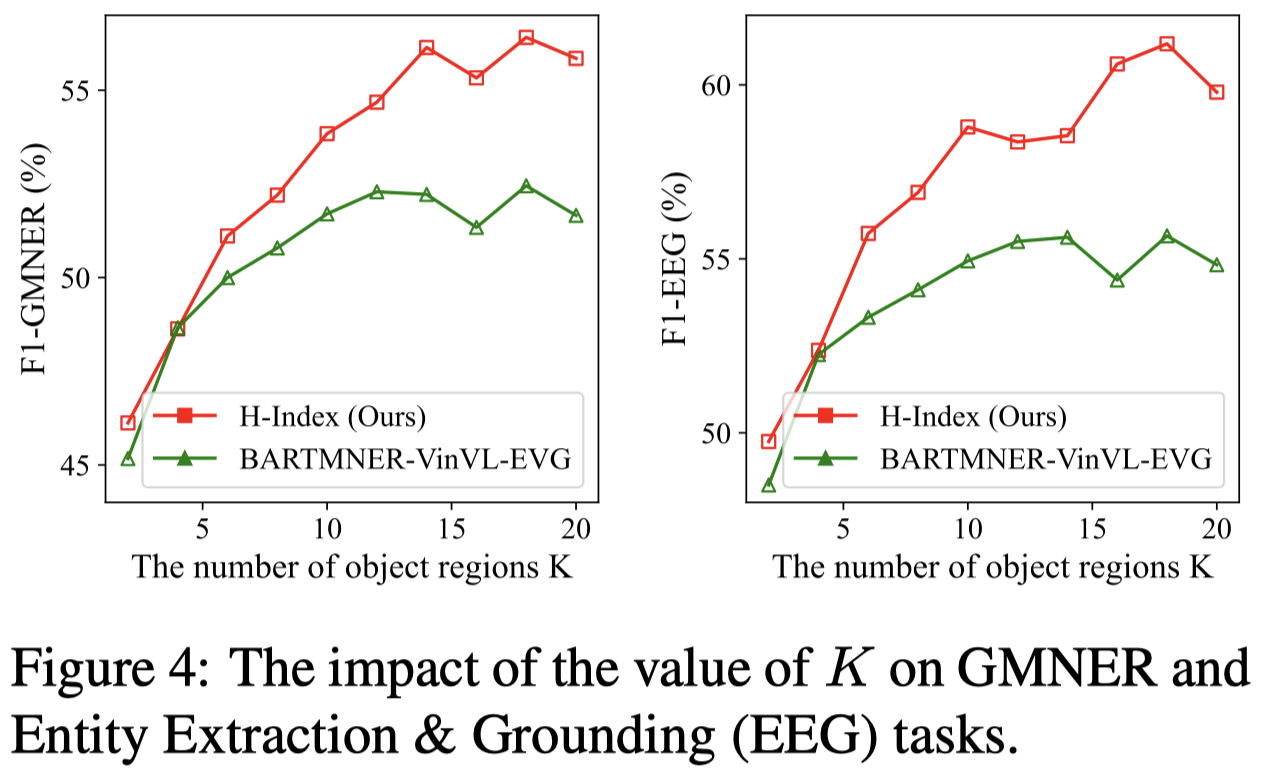
模型的性能受限于VinVL:
FMNERG/TIGER
Fine-Grained Multimodal Named Entity Recognition and Grounding with a Generative Framework. ACM MM 2023. 南京科大. 代码.
Multimodal Named Entity Recognition (MNER) aims to locate and classify named entities mentioned in a pair of text and image. However, most previous MNER works focus on extracting entities in the form of text but failing to ground text symbols to their corresponding visual objects. Moreover, existing MNER studies primarily classify entities into four coarse-grained entity types, which are often insufficient to map them to their real-world referents. To solve these limitations, we introduce a task named Fine-grained Multimodal Named Entity Recognition and Grounding (FMNERG) in this paper, which aims to simultaneously extract named entities in text, their fine-grained entity types, and their grounded visual objects in image. Moreover, we construct a Twitter dataset for the FMNERG task, and further propose a T5-based multImodal GEneration fRamework (TIGER), which formulates FMNERG as a generation problem by converting all the entity-type-object triples into a target sequence and adapts a pre-trained sequence-to-sequence model T5 to directly generate the target sequence from an image-text input pair. Experimental results demonstrate that TIGER performs significantly better than a number of baseline systems on the annotated Twitter dataset. Our dataset annotation and source code are publicly released at https://github.com/NUSTM/FMNERG.
Issue:识别带有image区域信息的意义:This weakens the capability of machines to ground text symbols to their corresponding visual objects in images, which is crucial for multimodal knowledge graph (MKG) construction [62] and many vision-language tasks such as knowledge-intensive visual question answering [18, 31] and entity-aware image captioning [59].
之前的MNER方法集中在考虑粗粒度的NER,不能够帮助具有相同name的entity消歧。例如given the entity Gokhan Inler and its type PER, it is hard to infer whether it refers to the football player or the singer in the real world.
Solution:作者在GMENR数据集基础上,进行了细粒度标注,获得数据集FMNERG,包括8个粗粒度type和51个细粒度type:
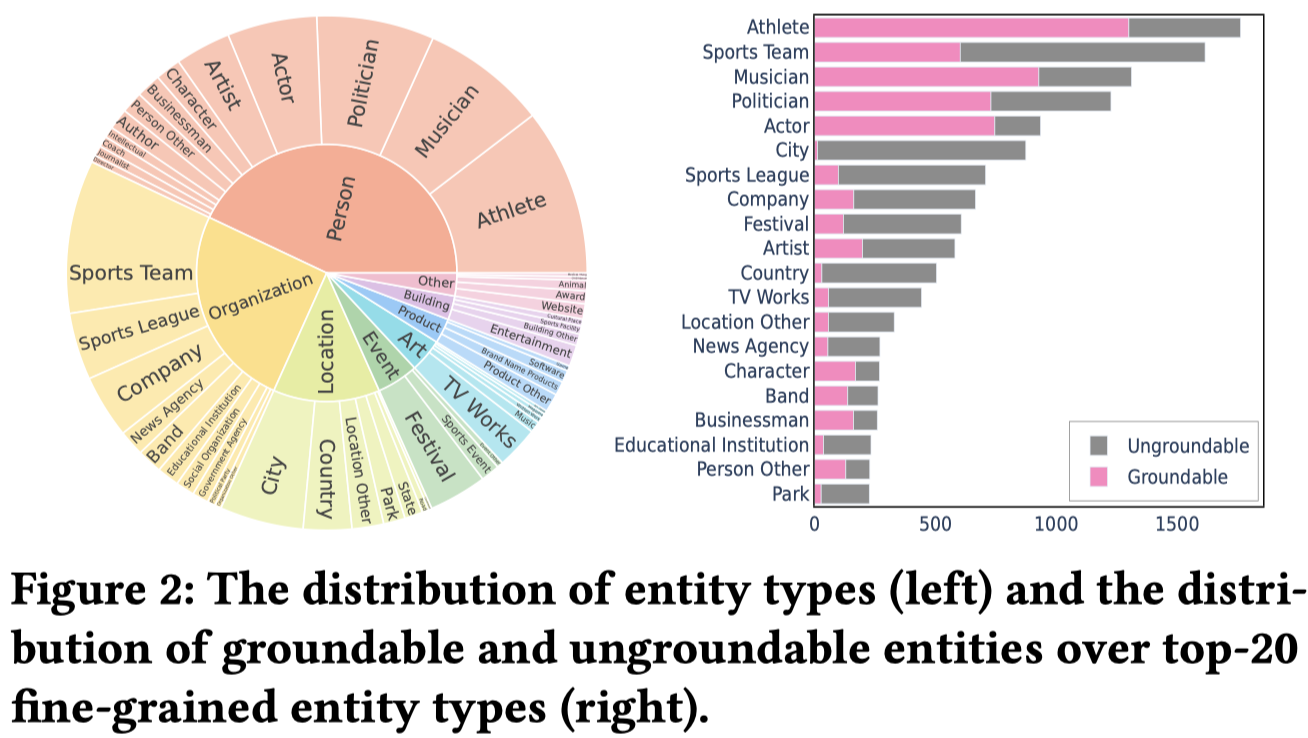
注意很多的细粒度entity type是长尾分布的;81%的entity属于PER、ORG或LOC;PER entity是最容易grounding的。
作者的方法:
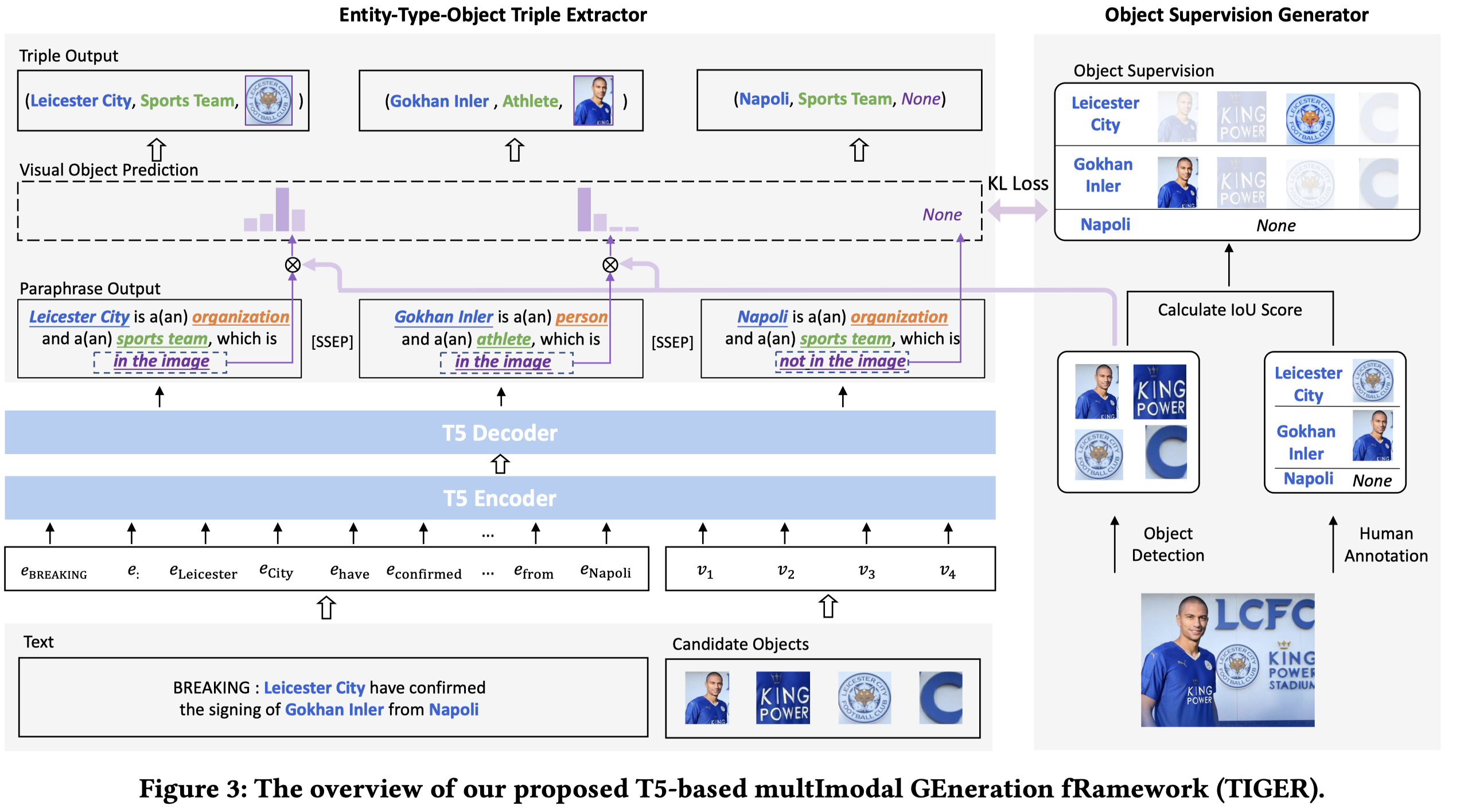
处理输入过程与H-Index一致,利用VinVL提前识别objects,然后每个object对应的mean pooling得到的embedding作为visual embedding。
训练T5-base输出包括粗粒度entity type和细粒度type:
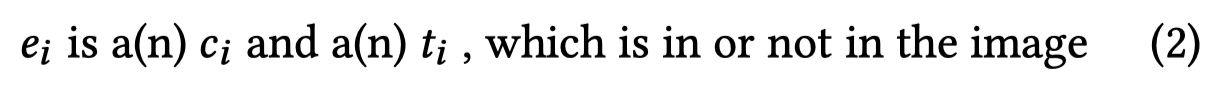
输出的"in the image"三个token embedding被用来和objects计算相似度:

同时使用H-Index中利用KL散度拉近objects和ground-truth bounding box之间的差距。下面实验结果:

Multimodal Pretraining
Prompt Me Up: Unleashing the Power of Alignments for Multimodal Entity and Relation Extraction. ACM MM 2023. 清华. 代码.
How can we better extract entities and relations from text? Using multimodal extraction with images and text obtains more signals for entities and relations, and aligns them through graphs or hierarchical fusion, aiding in extraction. Despite attempts at various fusions, previous works have overlooked many unlabeled image-caption pairs, such as NewsCLIPing. This paper proposes innovative pretraining objectives for entity-object and relation-image alignment, extracting objects from images and aligning them with entity and relation prompts for soft pseudo-labels. These labels are used as self-supervised signals for pre-training, enhancing the ability to extract entities and relations. Experiments on three datasets show an average 3.41% F1 improvement over prior SOTA. Additionally, our method is orthogonal to previous multimodal fusions, and using it on prior SOTA fusions further improves 5.47% F1.
Issue: 之前的MIE方法会受到有标注的multimodal data数量限制。利用一般的text-image pairs进行预训练可以提升模型的能力,但是一般的这种预训练数据缺少实体和关系的标注信息。
Solution:作者提出了一种基于伪entity和relation标注的对齐预训练方法:
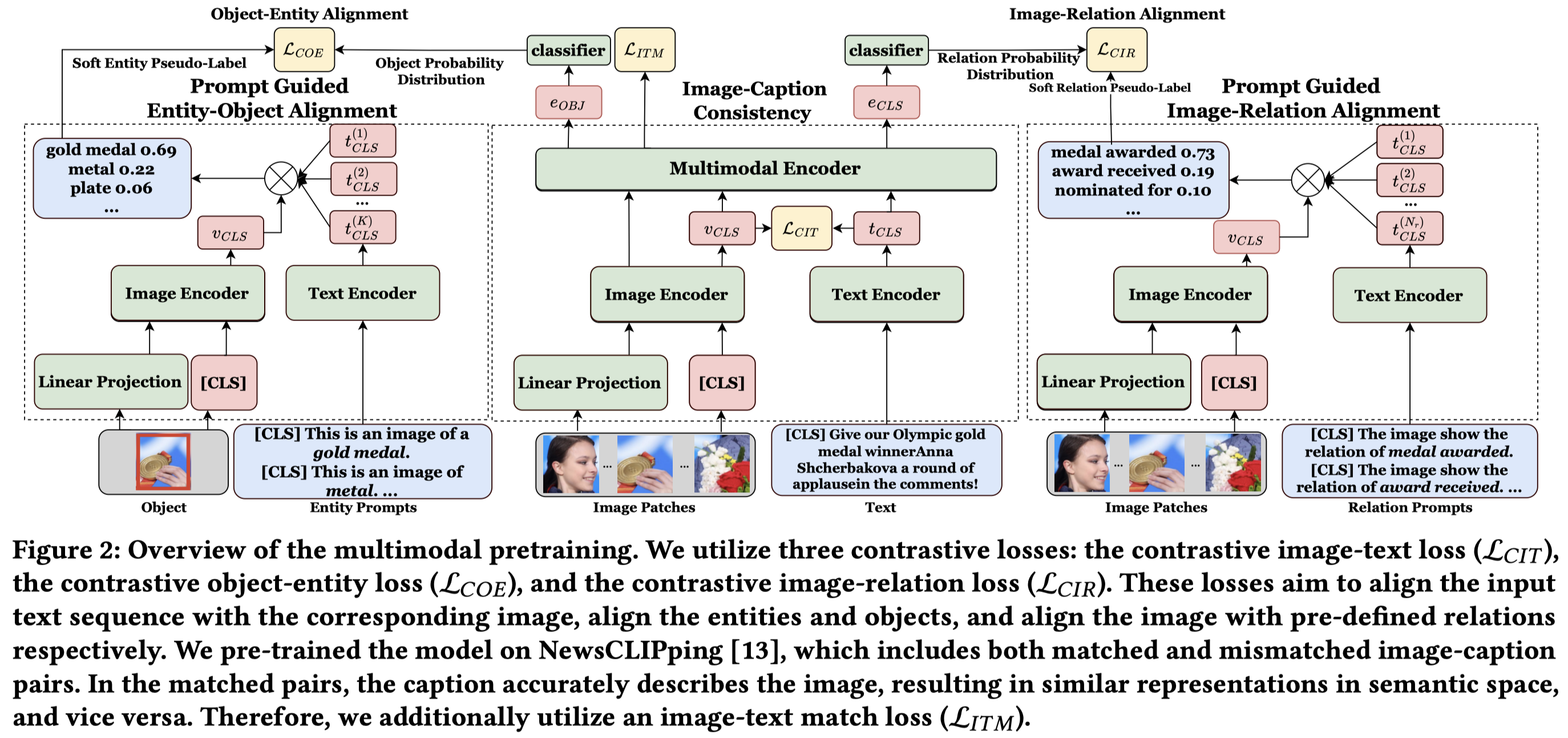
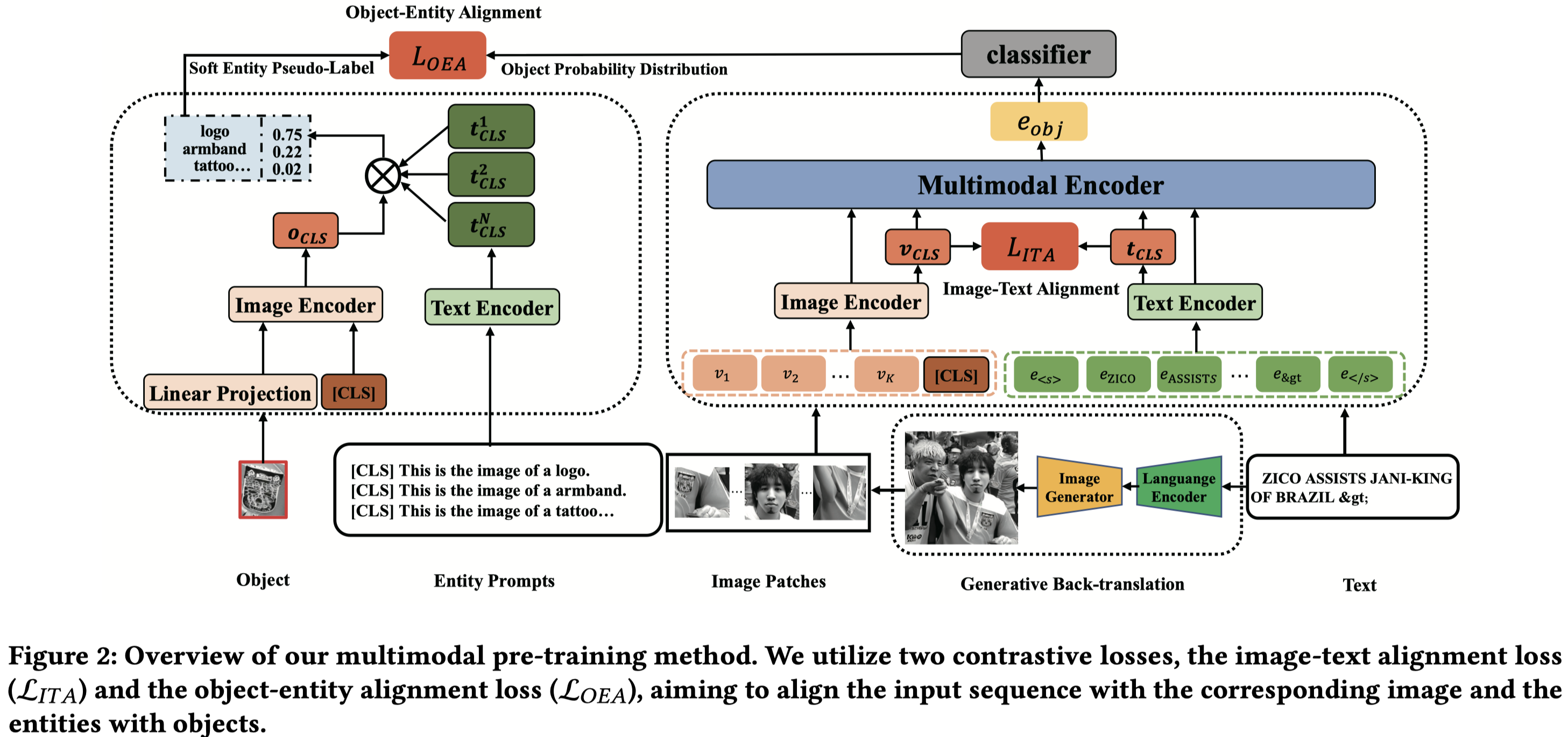
有三个对齐,text-image的对齐、entity-object对齐以及relation-image的对齐。
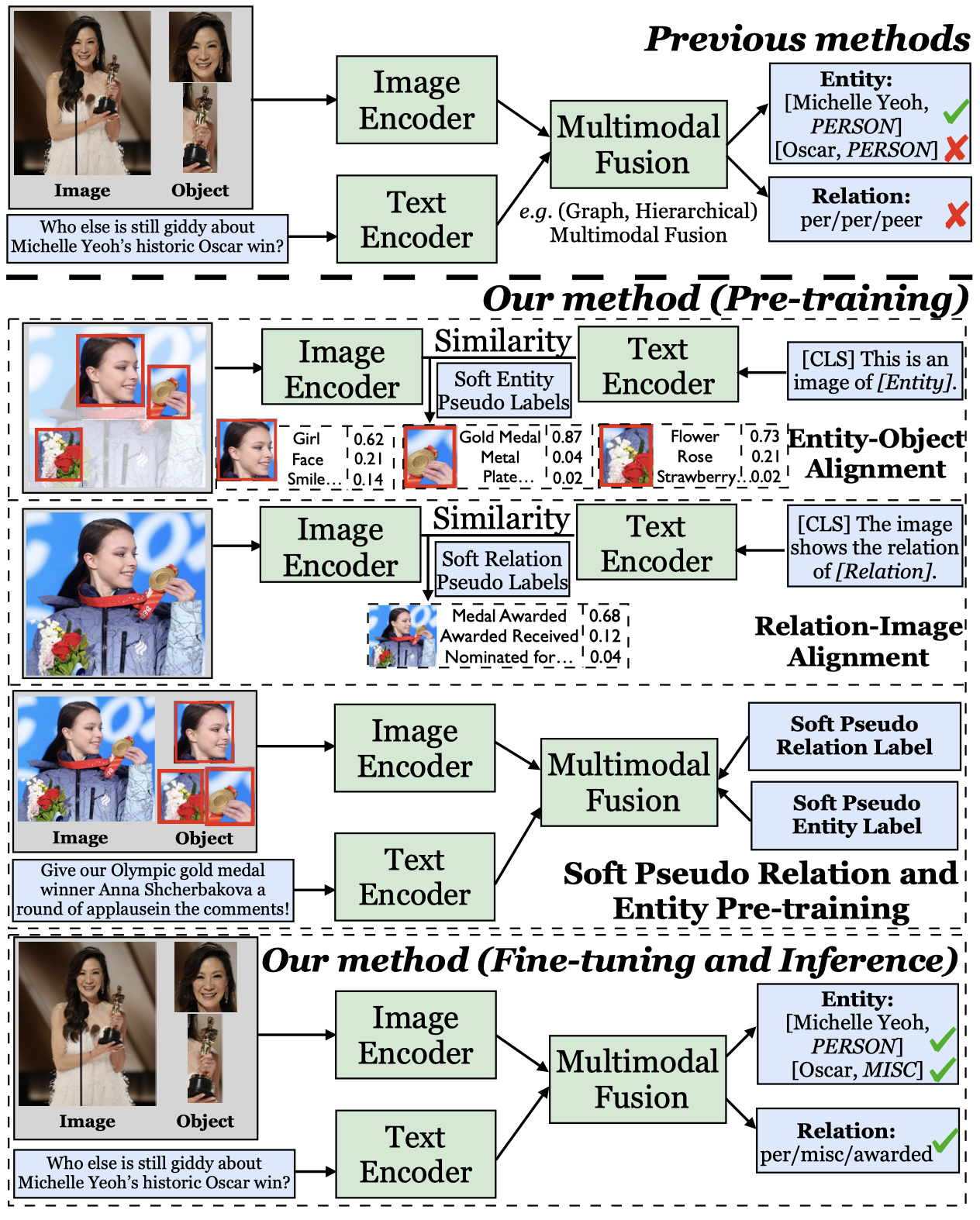
作者的总体结构是,利用BERT作为text encoder,ViT作为image encoder,两者的编码再输入到BERT中获得多模态的标注。
伪对齐标注的生成依赖于单模态的编码,多模态的编码用来逼近单模态的预估结果。
作者基于的预训练数据是NewsCLIPping,包括对齐的图文对和未对齐的图文对。
text-image的对齐:利用[CLS]的多模态表示,输入到预测层,判断text是否和image匹配,计算:
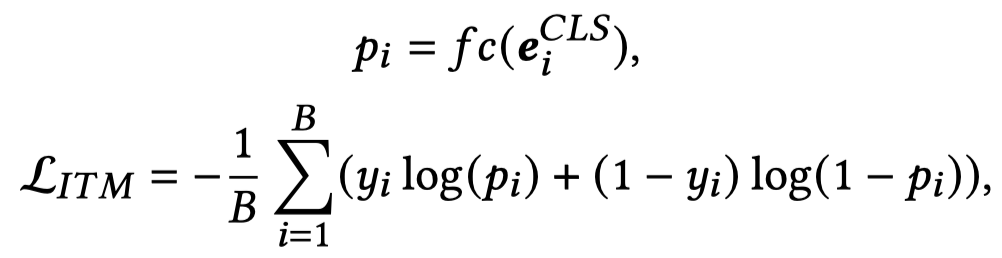
由于上述loss不意味着切换其它image,得到的score也是很低的,即不能完全描述对齐。因此,计算对比loss:
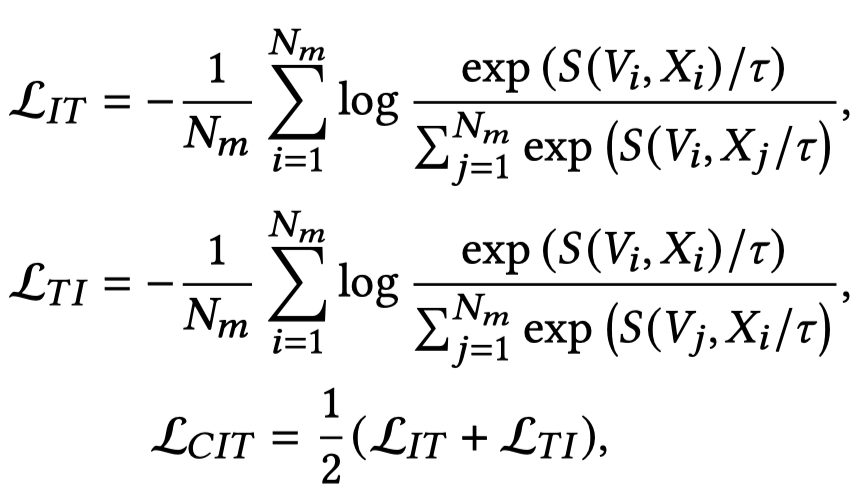

entity-object对齐:作者利用YOLO导出image中的objects,然后输入到ViT获得对应的object表示。利用spaCY找到文本中最频繁的\(M\)个名词,作为候选entites。每个entity构造对应的prompt,输入到BERT获得对应的entity表示。然后,计算soft entity pseudo-labels:
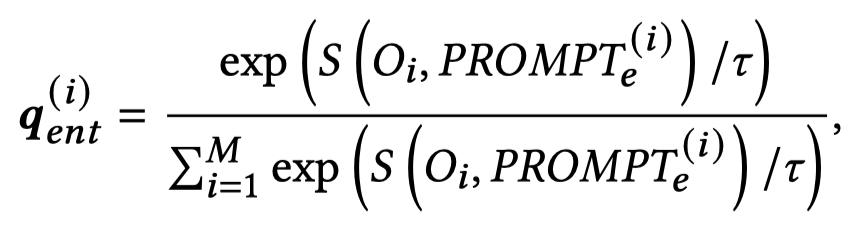
使用object每个patch的多模态表示,取平均值,经过预测层计算其与候选entity匹配度。
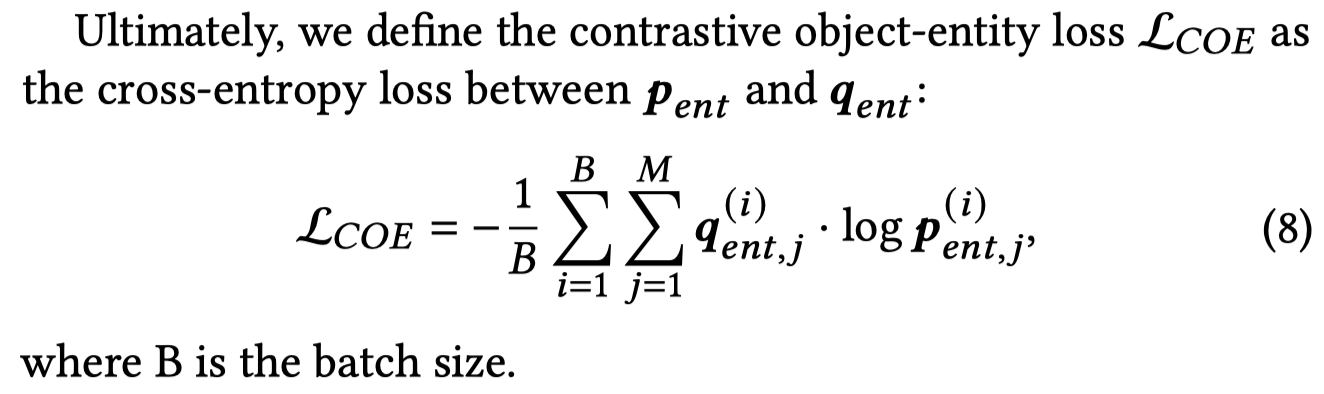
Image-Relation对齐:与entity-object对齐类似,区别在于是从Wikidata中找到的类型为“data”的relation作为预定义的关系集合。每个relation构造prompt,输入BERT得到表征,计算其与整个image的伪标注匹配度:
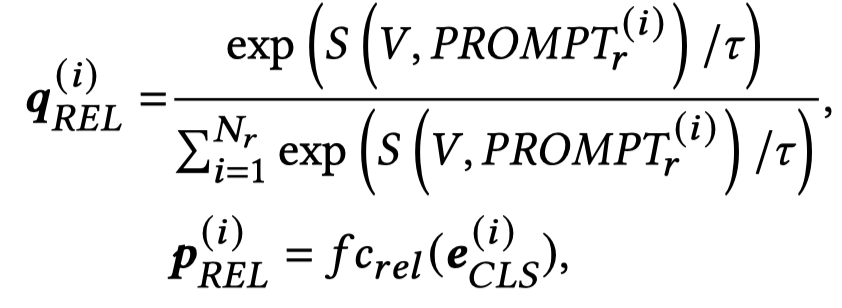
利用[CLS]的多模态表示,输入到预测层,判断relation prompt和image的匹配度:
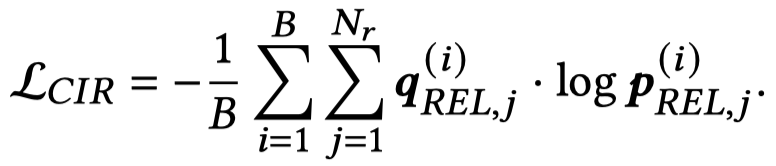
预训练结束后,会针对MNER和MRE任务分别微调。
H-Index+Pre-training
Contrastive Pre-training with Multi-level Alignment for Grounded Multimodal Named Entity Recognition. ICMR 2024. 人大
Recently, Grounded Multimodal Named Entity Recognition (GMNER) task has been introduced to refine the Multimodal Named Entity Recognition (MNER) task. Existing MNER studies fall short in that they merely focus on extracting text-based entity-type pairs, often leading to entity ambiguities and failing to contribute to multimodal knowledge graph construction. In the GMNER task, the objective becomes more challenging: identifying named entities in text, determining their entity types, and locating their corresponding bounding boxes in linked images, necessitating precise alignment between the textual and visual information. We introduce a novel multi-level alignment pre-training method, engaging with both text-image and entity-object dimensions to foster deeper congruence between multimodal data. Specifically, we innovatively harness potential objects identified within images, aligning them with textual entity prompts, thereby generating refined soft pseudo labels. These labels serve as self-supervised signals that pre-train the model to more accurately extract entities from textual input. To address misalignments that often plague modality integration, our method employs a sophisticated diffusion model that performs back-translation on the text to generate a corresponding visual representation, thus refining the model’s multimodal interpretative accuracy. Empirical evidence from the GMNER dataset validates that our approach significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art models. Moreover, the versatility of our pre-training process complements virtually all extant models, offering an additional avenue for augmenting their multimodal entity recognition acumen.
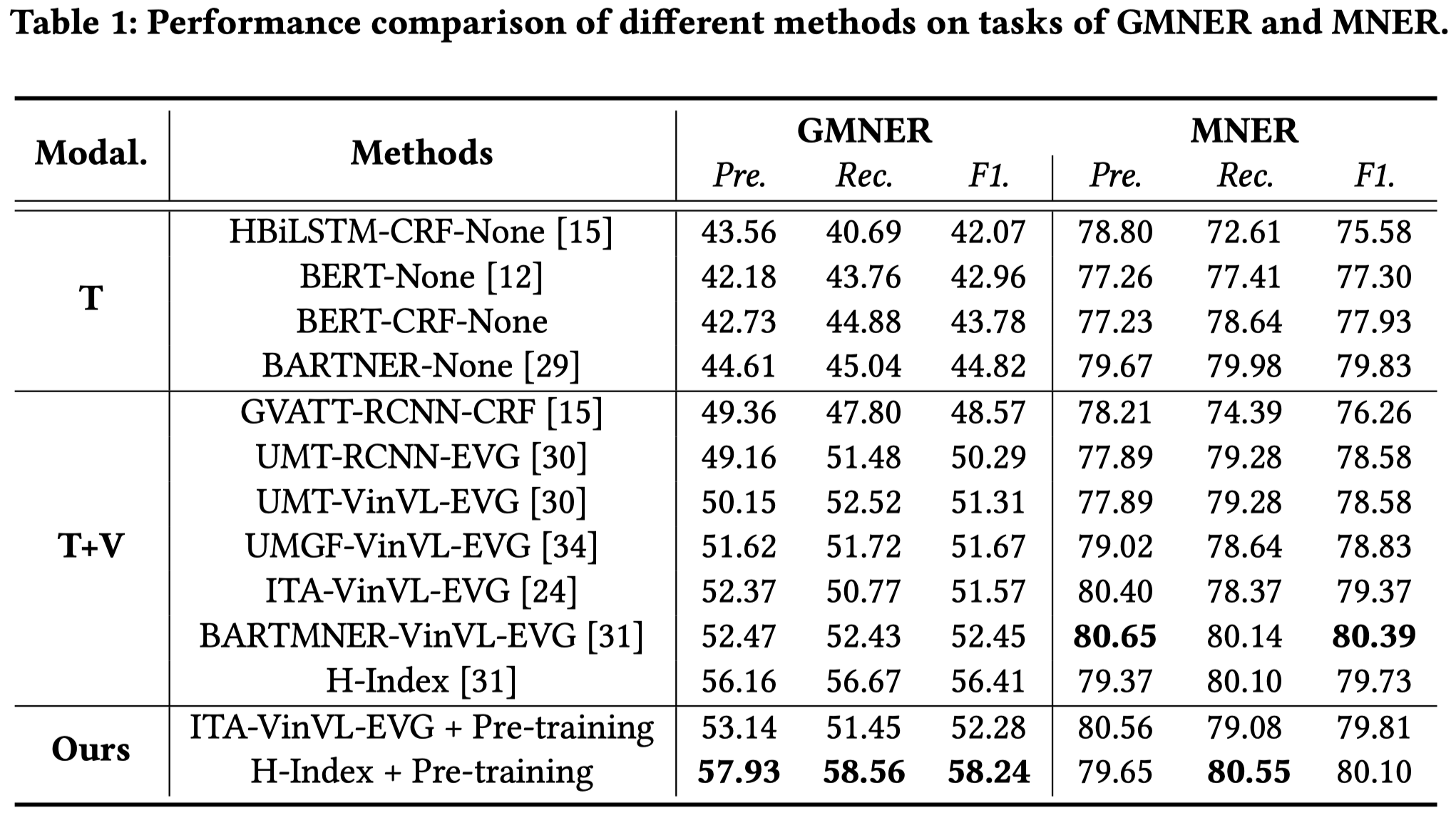
基本上是follow了前一篇MM 2023 pretraining的工作,区别在于作者利用Twitter-2015、Twitter-2015和TwitterSnap进行pretraining,然后利用GMNER进行微调。不是直接利用一般的图文对的原因是为了能够利用相同领域相同特征的数据进行预训练。
另一个区别点在于,作者实际上只使用了这些数据中的text数据,不使用原始image,而是利用stable diffusion模型生成新image,从而保证更好的对齐。
作者的预训练策略与前一篇一模一样。利用BERT和ViT进行编码;对于图像会先使用VinVL识别objects,再分别有ViT进行编码;输入到BART encoder获得multimodal embedding。
对比学习的策略也一样,利用spaCY寻找候选entity,构造prompt,计算object和entity prompt之间的匹配度作为soft label。使用BART得到的多模态表征,取值平均获得object的多模态表示,输入预测层计算匹配度。
在GMENR上微调的过程与H-Index一致,同样利用index token统一输出格式,使用KL散度训练entity grounding。
MUIE/Reamo
Recognizing Everything from All Modalities at Once: Grounded Multimodal Universal Information Extraction. 哈工深. ACL 2024 Findings. 代码. (已开源,但是无checkpoints,需要重新训练)
In the field of information extraction (IE), tasks across a wide range of modalities and their combinations have been traditionally studied in isolation, leaving a gap in deeply recognizing and analyzing cross-modal information. To address this, this work for the first time introduces the concept of grounded Multimodal Universal Information Extraction (MUIE), providing a unified task framework to analyze any IE tasks over various modalities, along with their fine-grained groundings. To tackle MUIE, we tailor a multimodal large language model (MLLM), Reamo, capable of extracting and grounding information from all modalities, i.e., ‘recognizing everything from all modalities at once’. Reamo is updated via varied tuning strategies, equipping it with powerful capabilities for information recognition and fine-grained multimodal grounding. To address the absence of a suitable benchmark for grounded MUIE, we curate a high-quality, diverse, and challenging test set, which encompasses IE tasks across 9 common modality combinations with the corresponding multimodal groundings. The extensive comparison of Reamo with existing MLLMs integrated into pipeline approaches demonstrates its advantages across all evaluation dimensions, establishing a strong benchmark for the follow-up research. Our resources are publicly released at https://haofei.vip/MUIE.
Issue:作者认为之前的多模态IE工作存在问题:
- 不同任务都有IE model导致资源浪费,需要一个one-for-all的通用型model来进行处理
- 不同模态数据都能够携带有用信息,但是之前的方法只输出纯文本
- 之前的方法常关注modality-aligned的data,但是不同模态间的信息可以是关联的,也可以是不关联的
Solution: 作者训练的Reamo(Recognizing Everything from All Modalities at Once)方法架构:
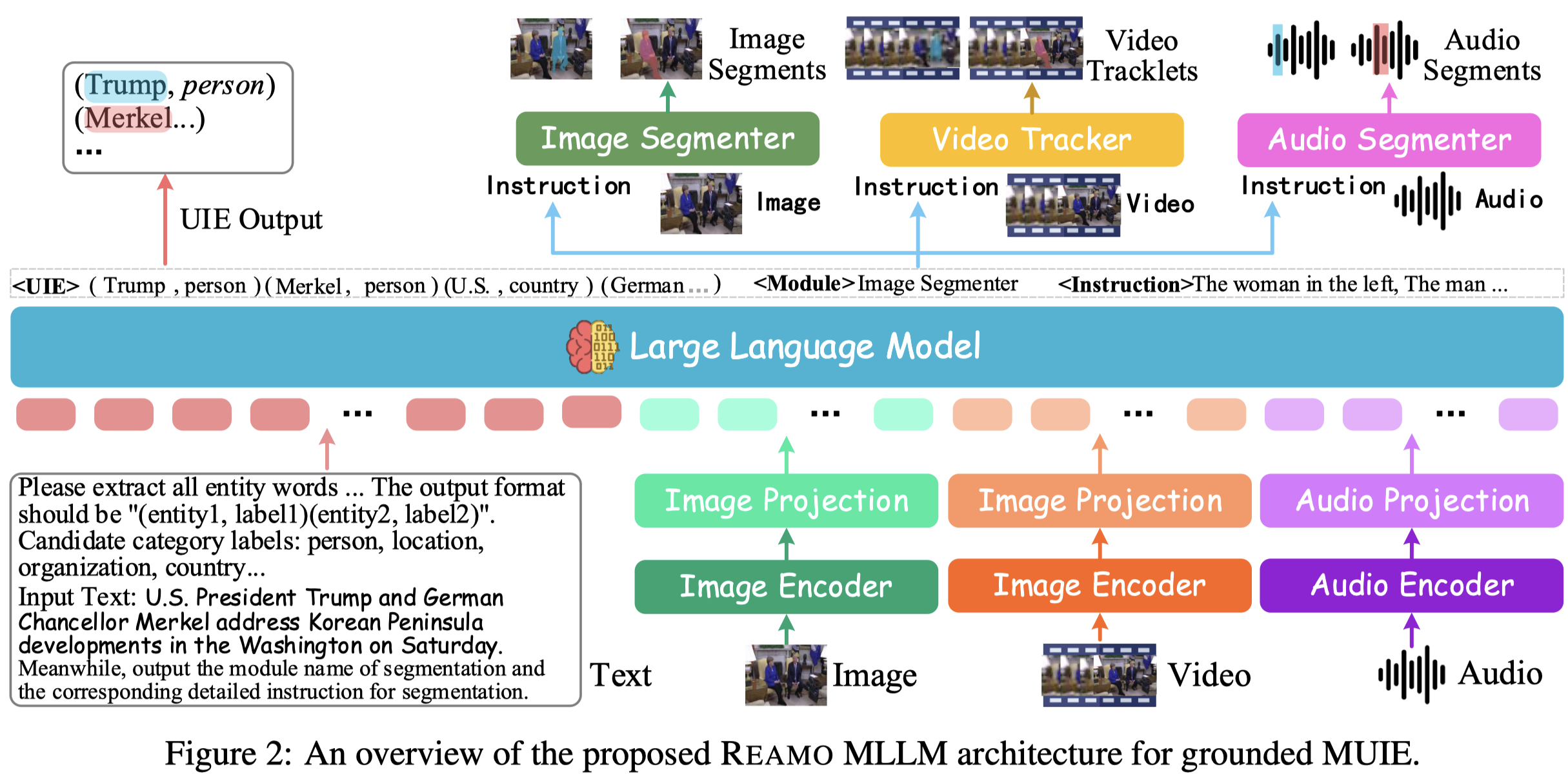
输入的多模态数据使用ImageBind处理,LLM采用Vicuna-v1.5。输出解码器SEEM model (Zou et al., 2023) for image segmentation and video tracking、SHAS model (Tsiamas et al., 2022) for audio segmentation。
LLM会直接输出UIE的结果,同时还会输出调用哪个外部工具进行grounding的instruction:


作者方法的训练过程:
UIE Instruction Tuning:follow instructUIE方法,使用LoRA微调LLM让其学会textual UIE。
Multimodal Alignment Learning:粗粒度的对齐,只微调projection layer,输入其它模态数据,让LLM输出对应的text描述。使用数据Webvid-2M、CC3M、AudioCaps。
Fine-grained Cross-modal Grounding-aware Tuning:细粒度的对齐,输入text phrase和and grounded regional modality features,让LLM判断是否match。使用数据MS-COCO、TAO和Speech NER。
Invocation-based Meta-response Tuning:使用前面的多个task数据,设计对话模板让LLM学会输出调用外部工具的指令,同时还利用GPT-4生成了更多的数据,一共得到10k的微调数据。
为了评估微调的MLLM的MUIE效果,作者在现有的数据集测试集上创建了新的标注数据集:
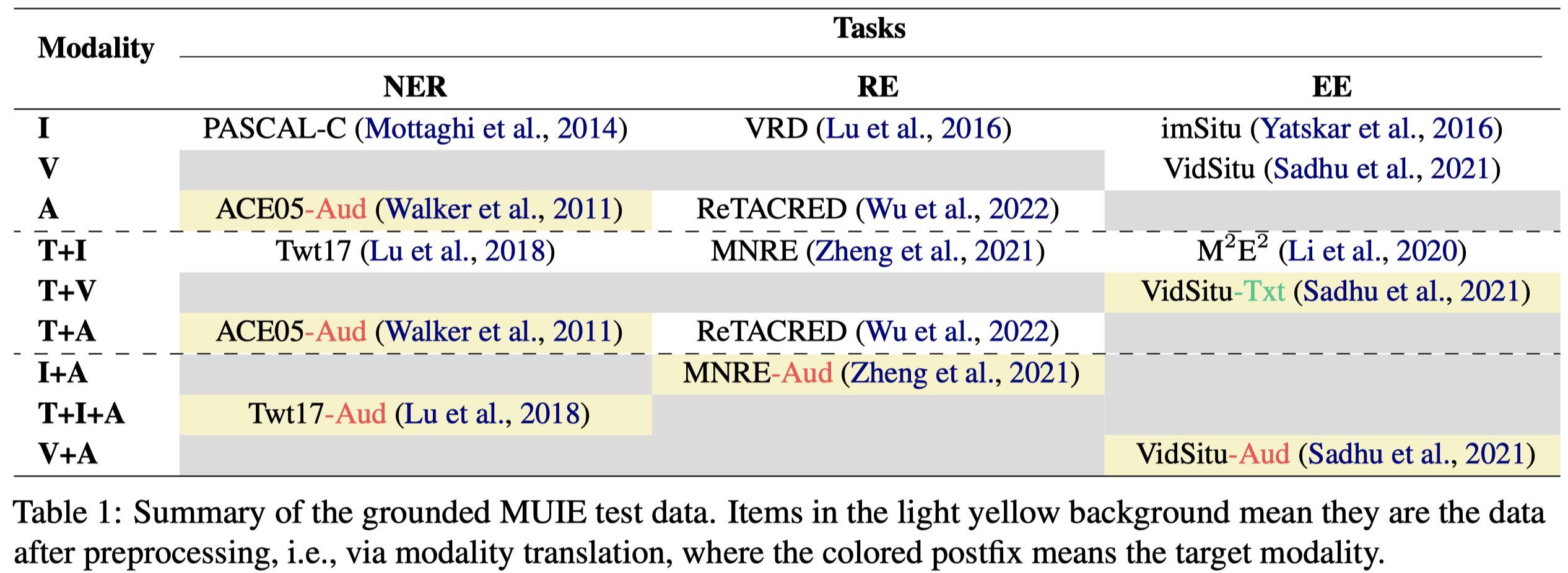
表格中的标黄的数据集,是作者在原有数据集上增加的新模态数据。比如对于MNRE数据集,使用Bark and Edge-TTS将text转换为语音。
作者还挑选了部分测试样例加入随机噪音,因此作者创建的评估数据集中,包括了modality-aligned和modality-specific的cases。
每个数据集选择200条数据,一共有3000条测试数据。
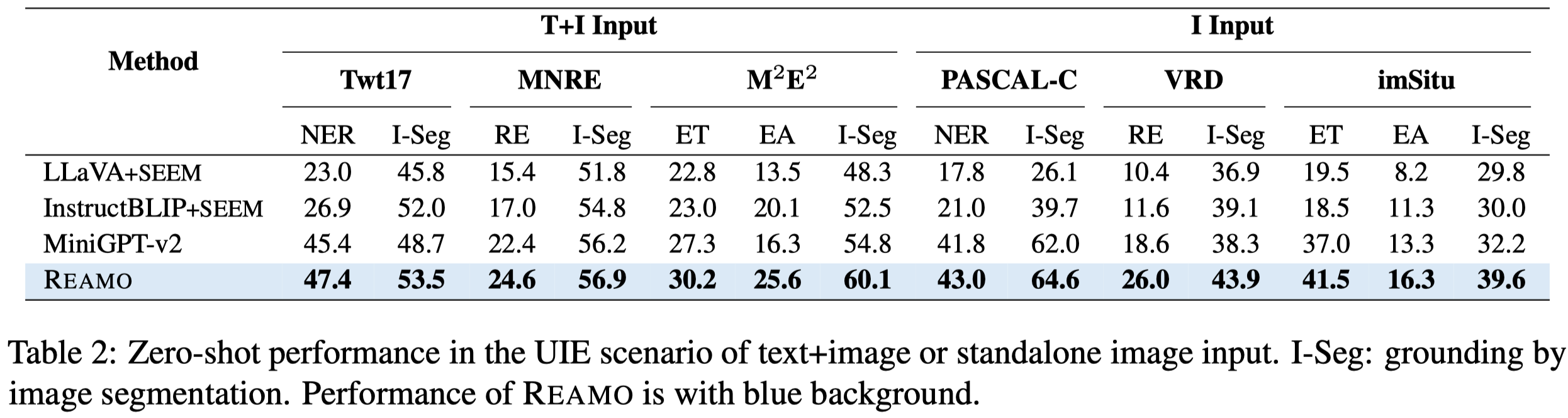
作者并没有使用MIE的数据进行训练,部分zero-shot的实验结果:

一些错误分析:Repetition of Extracted Content、Incomplete Information Extraction、Incorrect Grounding Match、Miss-grounding、Over-grounding、Error Propagation(由于作者的方法是pipeline形式的)
RiVEG
LLMs as Bridges: Reformulating Grounded Multimodal Named Entity Recognition. 天大. ACL 2024 Findings. 代码.
Grounded Multimodal Named Entity Recognition (GMNER) is a nascent multimodal task that aims to identify named entities, entity types and their corresponding visual regions. GMNER task exhibits two challenging properties: 1. The weak correlation between image-text pairs in social media results in a significant portion of named entities being ungroundable. 2. There exists a distinction between coarse-grained referring expressions commonly used in similar tasks (e.g., phrase localization, referring expression comprehension) and finegrained named entities. In this paper, we propose RiVEG, a unified framework that reformulates GMNER into a joint MNER-VE-VG task by leveraging large language models (LLMs) as a connecting bridge. This reformulation brings two benefits: 1) It maintains the optimal MNER performance and eliminates the need for employing object detection methods to pre-extract regional features, thereby naturally addressing two major limitations of existing GMNER methods. 2) The introduction of entity expansion expression and Visual Entailment (VE) module unifies Visual Grounding (VG) and Entity Grounding (EG). It enables RiVEG to effortlessly inherit the Visual Entailment and Visual Grounding capabilities of any current or prospective multimodal pretraining models. Extensive experiments demonstrate that RiVEG outperforms state-of-the-art methods on the existing GMNER dataset and achieves absolute leads of 10.65%, 6.21%, and 8.83% in all three subtasks. Code and datasets publicly available at https://github.com/JinYuanLi0012/RiVEG.
Issue:作者认为现在的GMNER方法存在两个缺陷:
- entity grounding和MNER两个任务可能互相干扰。预测效果最好的MNER不一定需要跨模态交互;而进行entity grounding使用多模态表征也不一定是最好的
- 现有的方法利用之前的object detection方法导出image regions特征,这限制了GMNER方法的上限
另一方面,现有的visual grounding方法也不一定能够很好的使用于entity grounding。作者发现即使微调现有的visual grounding方法,也不能够很好的定位named entity。主要有两个差异导致:
- 一般的visual grounding关注的是referring expressions,而named entity通常更加简洁。例如“A female superhero in the MCU”和“Black Widow”是不同的。
- 一般visual grounding会假设the input referring expression must match an object in the image,但是MNER任务中的image和text是weak correlation,很多entity并没有对应的image region。
Solution:作者利用LLM来减小named entity和visual grounding理想输入之间的差异。
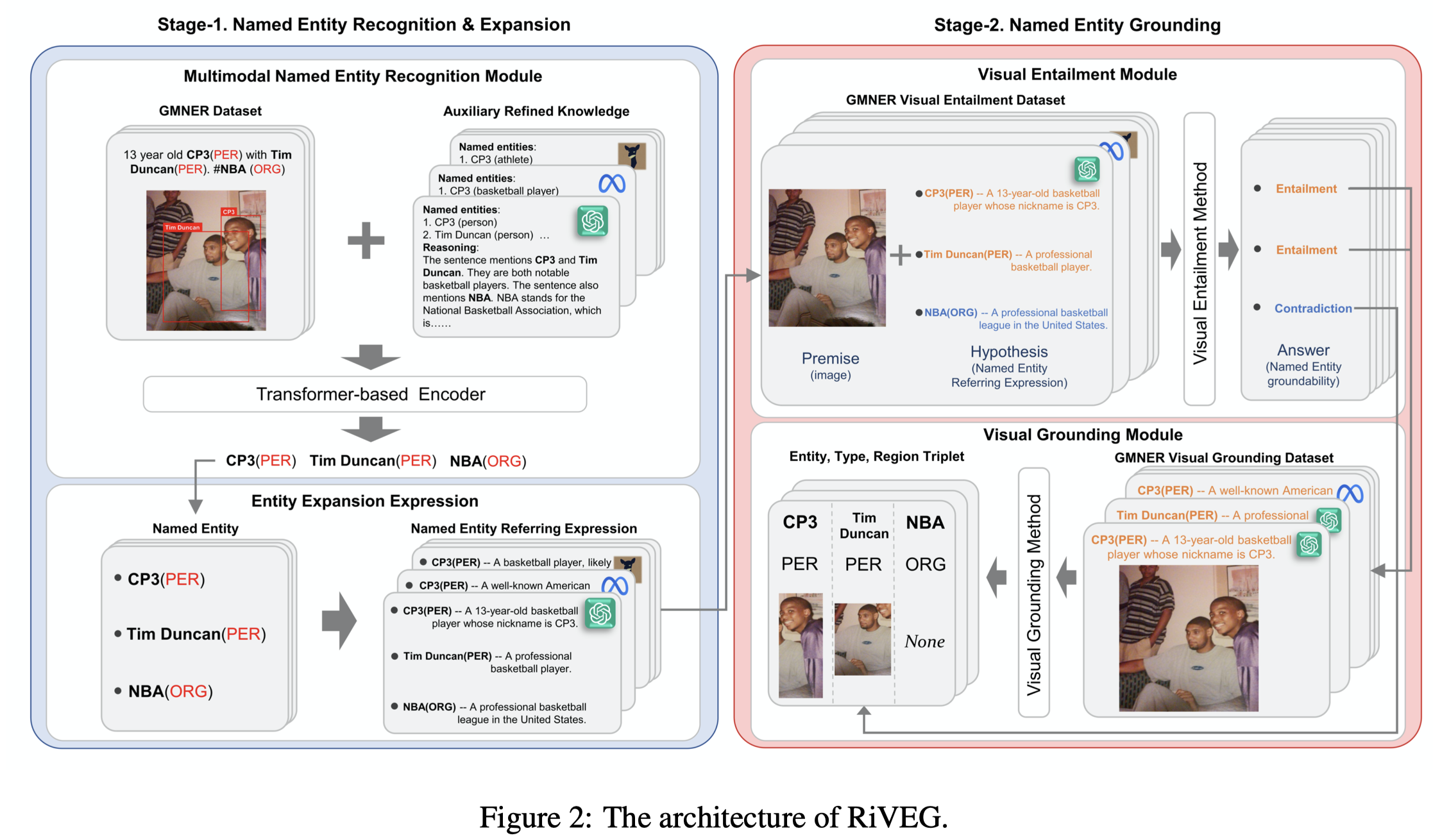 对于现有GMNER的问题,作者不同同时进行MNER和entity grounding,而是作为两步,第一步进行MNER,第二步进行entity grounding。
对于现有GMNER的问题,作者不同同时进行MNER和entity grounding,而是作为两步,第一步进行MNER,第二步进行entity grounding。
首先,作者进行了数据增强。利用mPLUG-Owl (Ye et al., 2023)将image 转换为caption,然后借助PGIM方法里的思路,让LLM提供额外的解释。区别在于,出了使用ChatGPT,作者还用了额外的4个LLM:vicuna-7b-v1.5, vicuna-13b-v1.5, llama-2-7b-chat-hf, llama-2-13b-chat-hf。生成的额外解释与原始文本拼接,然后输入到NER-CRF模型中。这样相当于训练集扩大了5倍。
随后,作者利用LLM将找到的命名entity,转化为coarse-grained entity expansion expressions:

获得了对应的entity描述之后,作者引入一个Visual Entailment Module,通过训练OFA-large(Wang et al., 2022a)方法,使其学会给定image,和entity描述,输出判断entity是否出现在image中。
如果判断出现在image中,再通过Visual Grounding Module来获得对应的bounding box。同样是微调OFA-large,使其学会给定image,和entity描述,输出entity的bounding box。
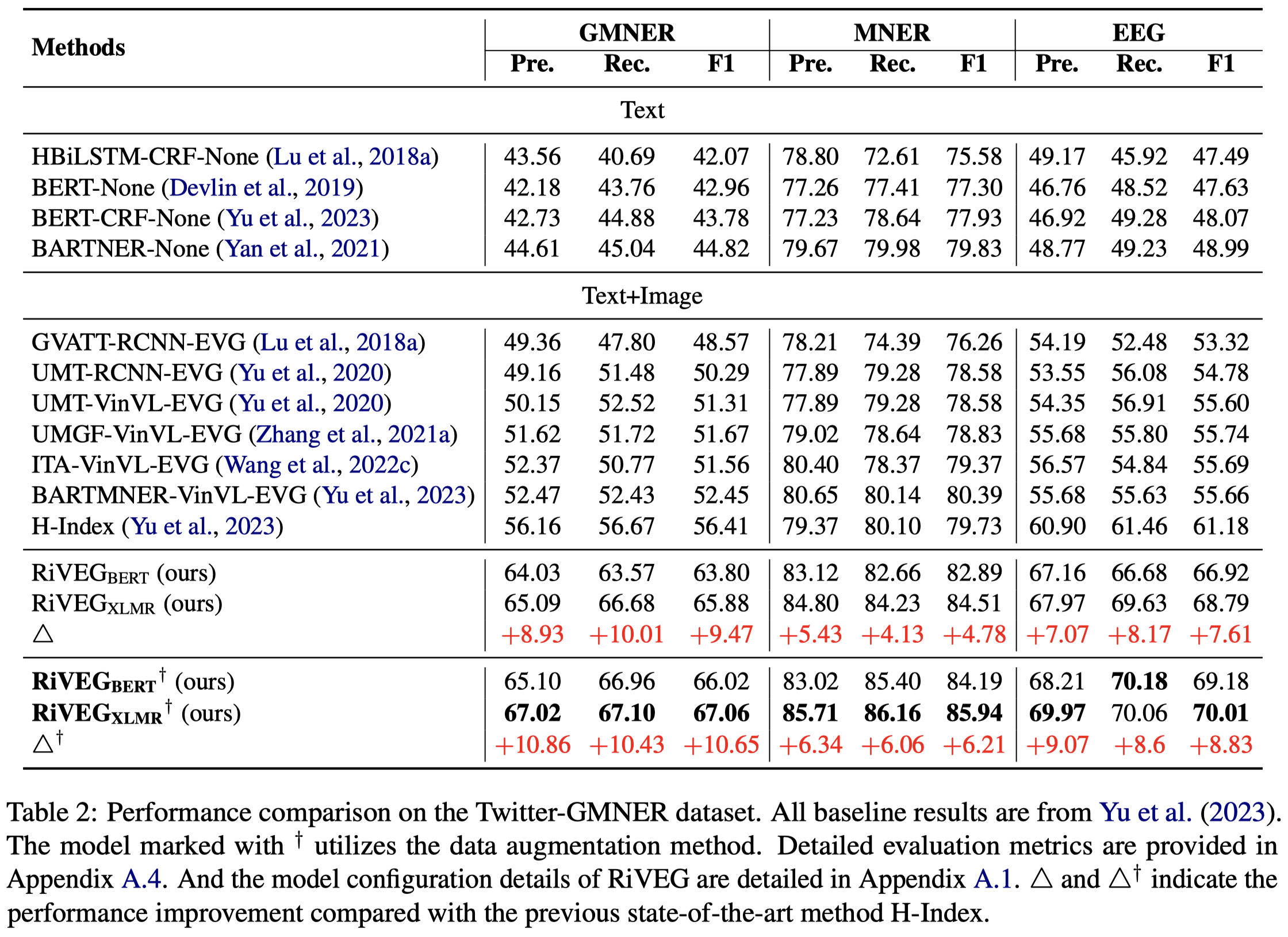
实验中选择的NER-CRF模型,同样与PGIM方法保持一致。
SCANNER
SCANNER: Knowledge-Enhanced Approach for Robust Multi-modal Named Entity Recognition of Unseen Entities. NAACL 2024. NAVER Cloud
Recent advances in named entity recognition (NER) have pushed the boundary of the task to incorporate visual signals, leading to many variants, including multi-modal NER (MNER) or grounded MNER (GMNER). A key challenge to these tasks is that the model should be able to generalize to the entities unseen during the training, and should be able to handle the training samples with noisy annotations. To address this obstacle, we propose SCANNER (Span CANdidate detection and recognition for NER), a model capable of effectively handling all three NER variants. SCANNER is a two-stage structure; we extract entity candidates in the first stage and use it as a query to get knowledge, effectively pulling knowledge from various sources. We can boost our performance by utilizing this entity-centric extracted knowledge to address unseen entities. Furthermore, to tackle the challenges arising from noisy annotations in NER datasets, we introduce a novel self-distillation method, enhancing the robustness and accuracy of our model in processing training data with inherent uncertainties. Our approach demonstrates competitive performance on the NER benchmark and surpasses existing methods on both MNER and GMNER benchmarks. Further analysis shows that the proposed distillation and knowledge utilization methods improve the performance of our model on various benchmarks.
Issue: 作者关注MNER的两个问题:
- 如何处理unseen entites,现有的方法很多不擅长处理
- NER标注中存在noise,特别是由于entity span的boundaries
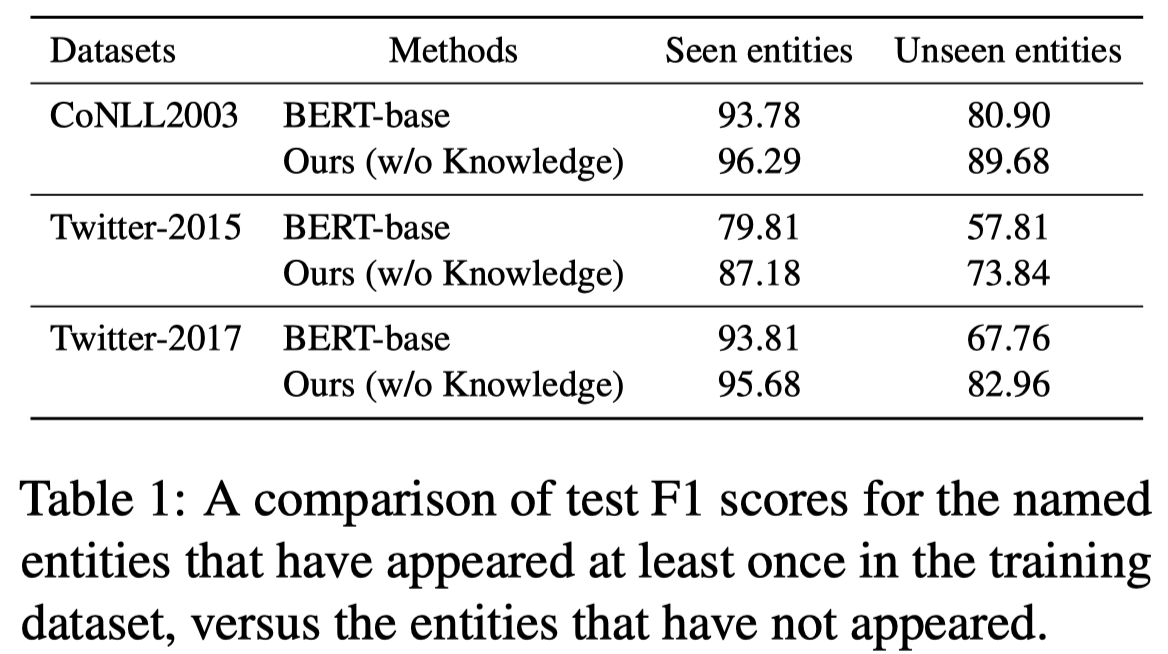
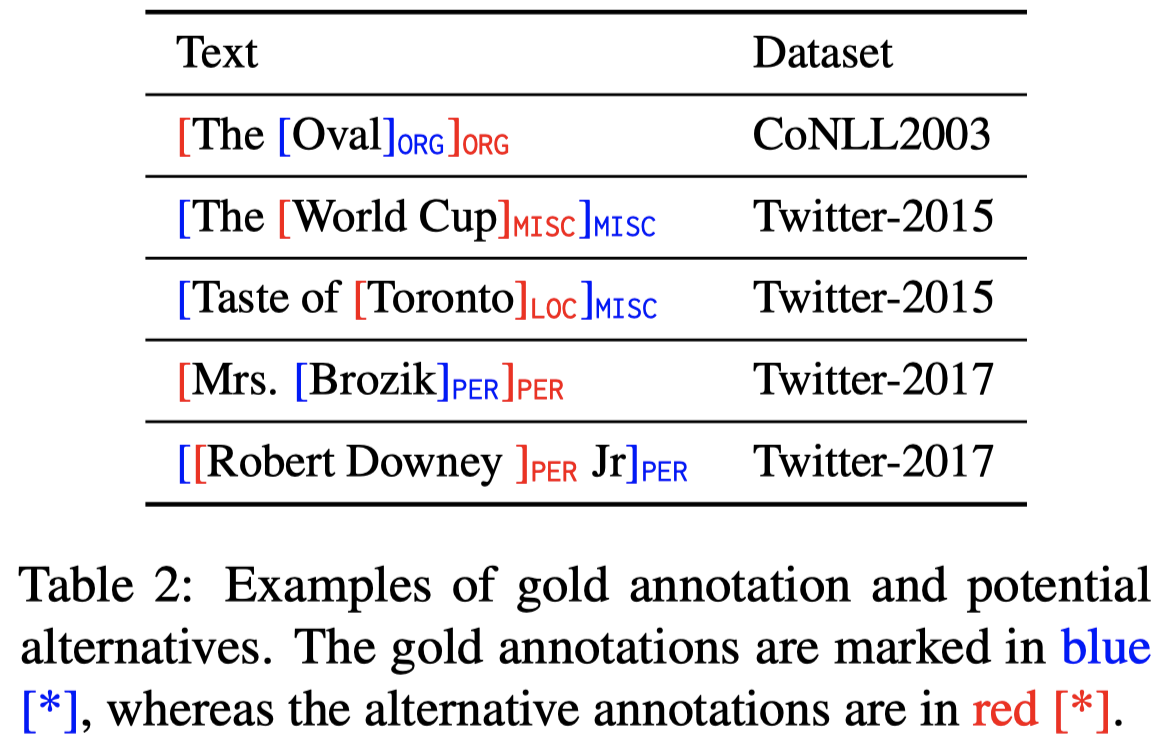
Solution:作者解决unseen entity的思路是寻找额外knowledge,包括internal (image-based) and external (e.g., Wikipedia) knowledge。而作者解决noise annotations的思路是,同时利用teacher model和ground-truth标注提供监督信号。
作者的方法包括两阶段:
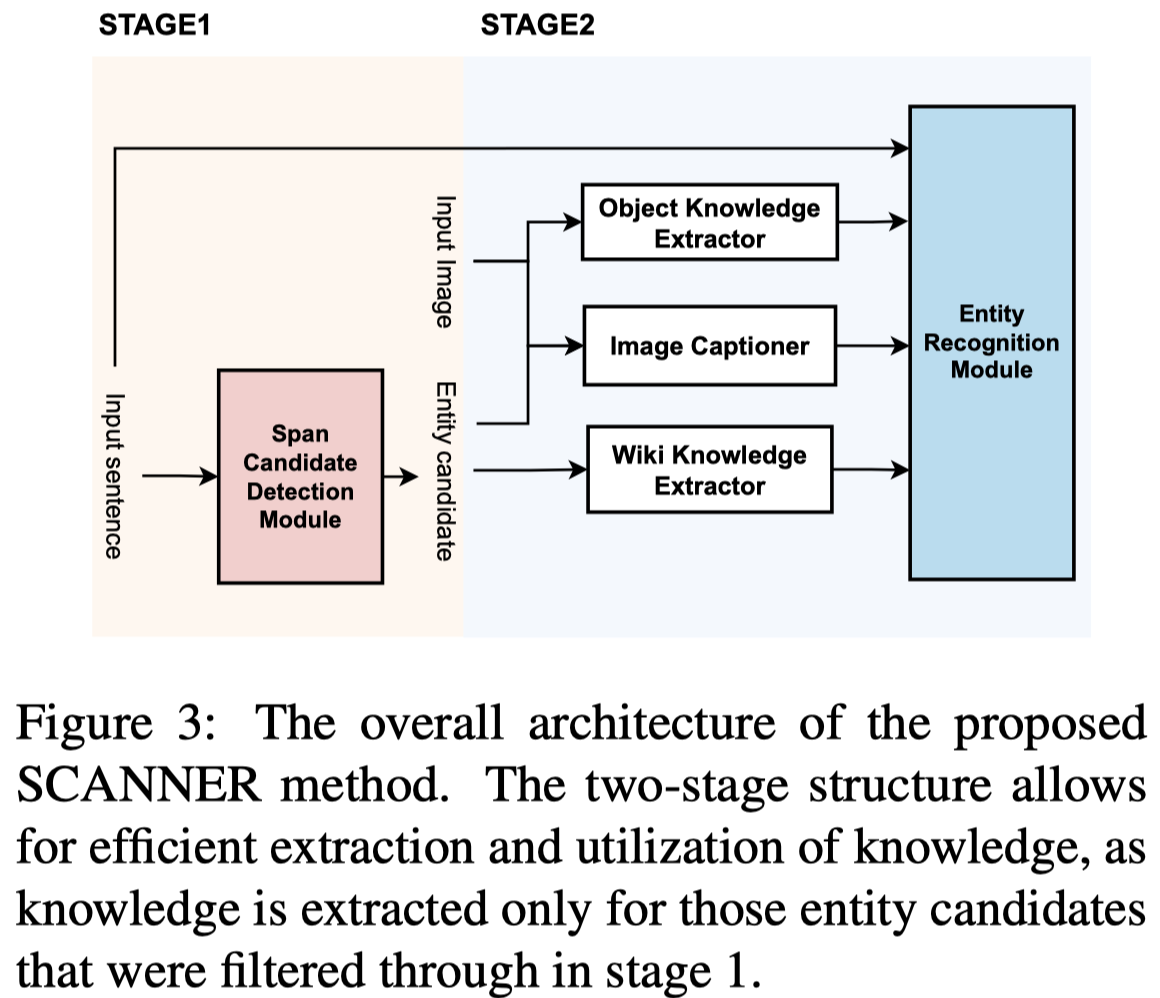
第一个阶段是利用NER model,根据B-I-O标注来判断哪些span可能是entity span。第二阶段会根据候选entity span在Wikipedia和image中寻找对应的knowledge,第二阶段图:
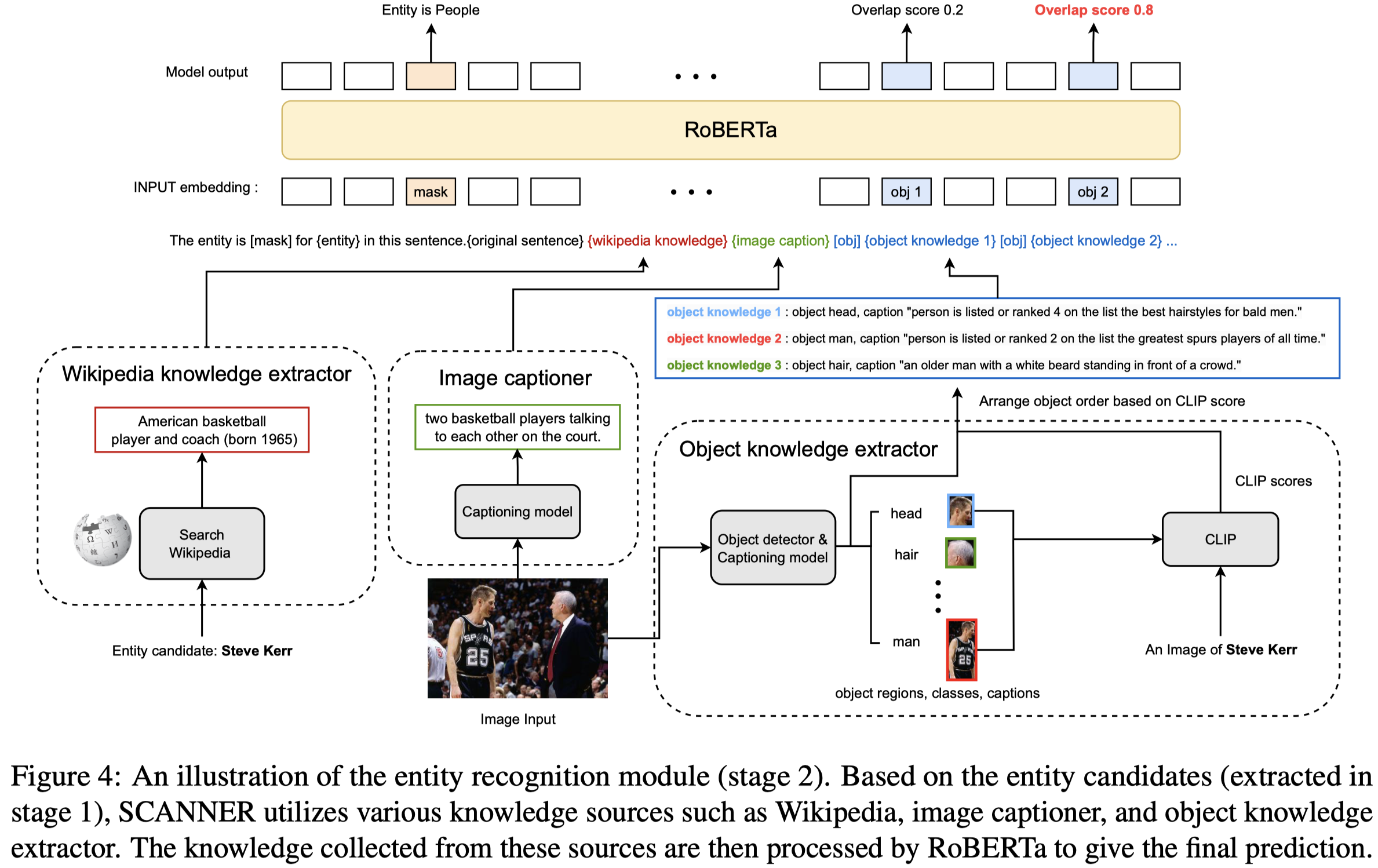 从Wikidata中获取knowledge,以entity作为query从Wikidata中查询相关信息。
从Wikidata中获取knowledge,以entity作为query从Wikidata中查询相关信息。
从image中寻找knowledge的时候,先利用BLIP-2将image 转化为caption;然后利用VinVL识别visual objects和其对应的class。visual objects也利用BLIP-2输出其对应的caption。
利用CLIP score计算候选entity和visual objects之间的相似度,然后排序。
所有object knowledge之间使用[obj] token间隔,与image caption,Wikipedia knowledge,原始text sentence进行拼接,输入到Transformer encoder模型中。
利用[mask] token计算候选entity对应的type;利用[obj] token经过linear projection层+sigmoid,判断其与entity之间的匹配度,用于grounding。
随后,为了应对noise annotations,作者提出Trust Your Teacher (TYT)。先利用ground-truth annotations监督微调出teacher model。teacher model对于训练sample的预测结果和ground-truth annotations一起监督微调student model:
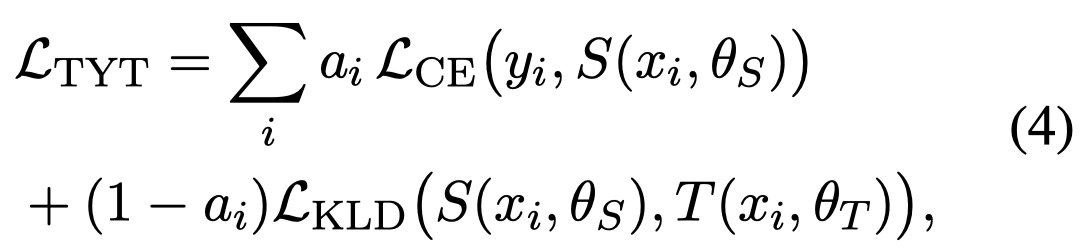
其中\(\alpha_i\)是第\(i\)个sample的weight。是根据teacher model在对应样本的ground-truth class上的预测score得到的。用来判断whether to trust the teacher model prediction or the ground truth. This implies that since the teacher model is well-trained, if the score for the ground truth class is high, then the sample is considered reliable and more weight is given to the cross-entropy with the ground truth label.
具体实现中,RoBERTa-large in NER, XLM-RoBERT-alarge (Conneau et al., 2020) for MNER, GMNER both in stage 1 and stage 2.
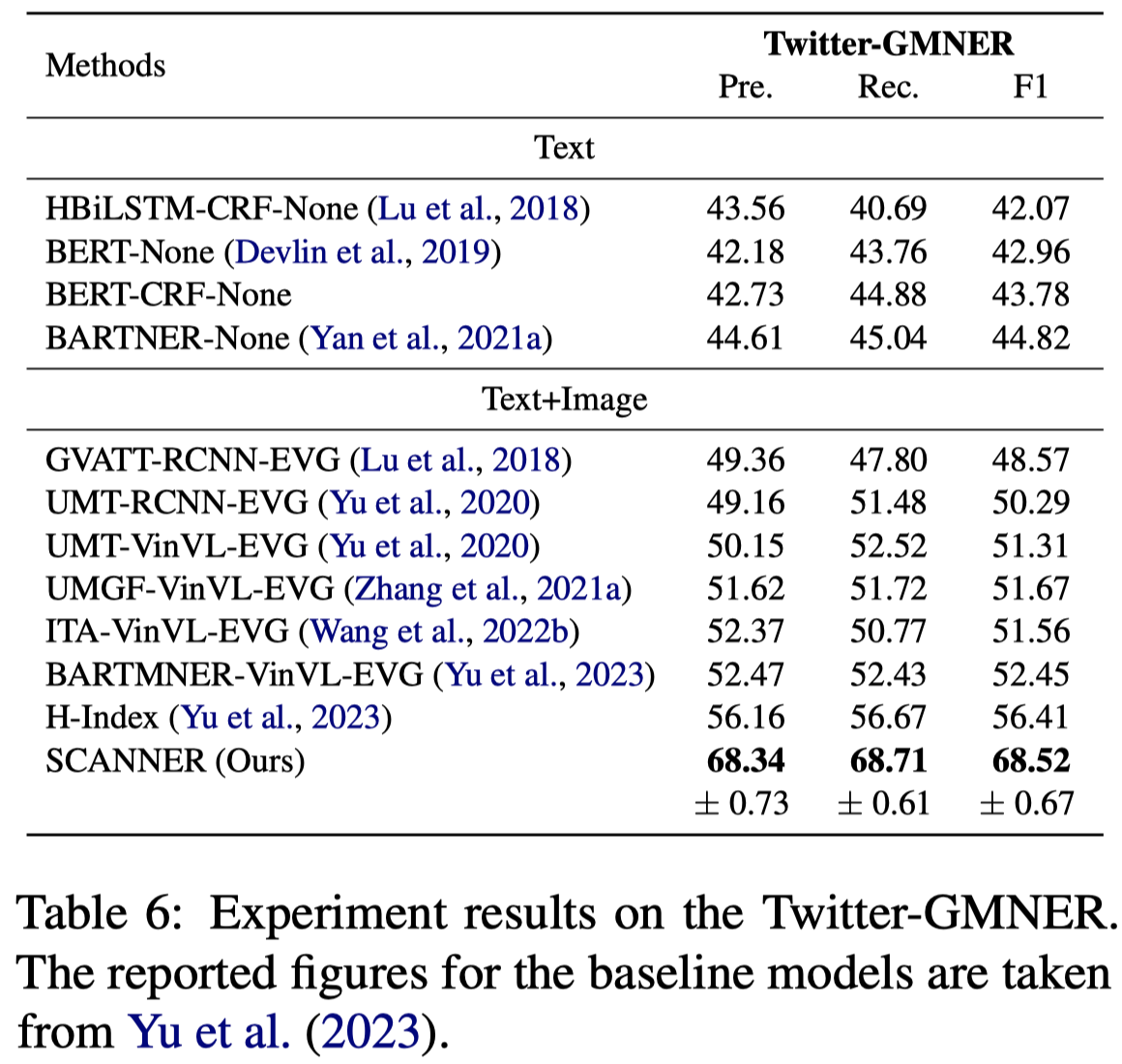
\(RE^2\)
\(RE^2\) : Region-Aware Relation Extraction from Visually Rich Documents. Adobe. NAACL 2024. 代码.
Current research in form understanding predominantly relies on large pre-trained language models, necessitating extensive data for pretraining. However, the importance of layout structure (i.e., the spatial relationship between the entity blocks in the visually rich document) to relation extraction has been overlooked. In this paper, we propose REgion-Aware Relation Extraction (\(RE^2\)) that leverages region-level spatial structure among the entity blocks to improve their relation prediction. We design an edge-aware graph attention network to learn the interaction between entities while considering their spatial relationship defined by their region-level representations. We also introduce a constraint objective to regularize the model towards consistency with the inherent constraints of the relation extraction task. To support the research on relation extraction from visually rich documents and demonstrate the generalizability of \(RE^2\) , we build a new benchmark dataset, DIVERSEFORM, that covers a wide range of domains. Extensive experiments on DIVERSEFORM and several public benchmark datasets demonstrate significant superiority and transferability of \(RE^2\) across various domains and languages, with up to 18.88% absolute F-score gain over all high-performing baselines.
Issue:什么是Visually Rich Documents?
Visually Rich Documents (VRDs) encompass various types such as invoices, questionnaire forms, financial forms, legal documents, and so on. These documents possess valuable layout information that aids in comprehending their content.
之前的从VRD中识别关系的方法忽略对relative spatial relationship among the entity blocks的学习
Solution: 作者的任务定义:

也就是说,作者的任务是识别question entity和answer entity之间是否存在关联的2分类问题。
具体作者的方法识别了三个层次的entity,构建2分图,这里图的edge考虑了entity的布局,例如左上、左下等。然后利用GNN进行建模。具体细节参考论文。

为了评估,作者创建了新benchmark DiverseForm,包括Veterans Affairs, visa applications, tax documents, air transport各种VRD文档。
GEM
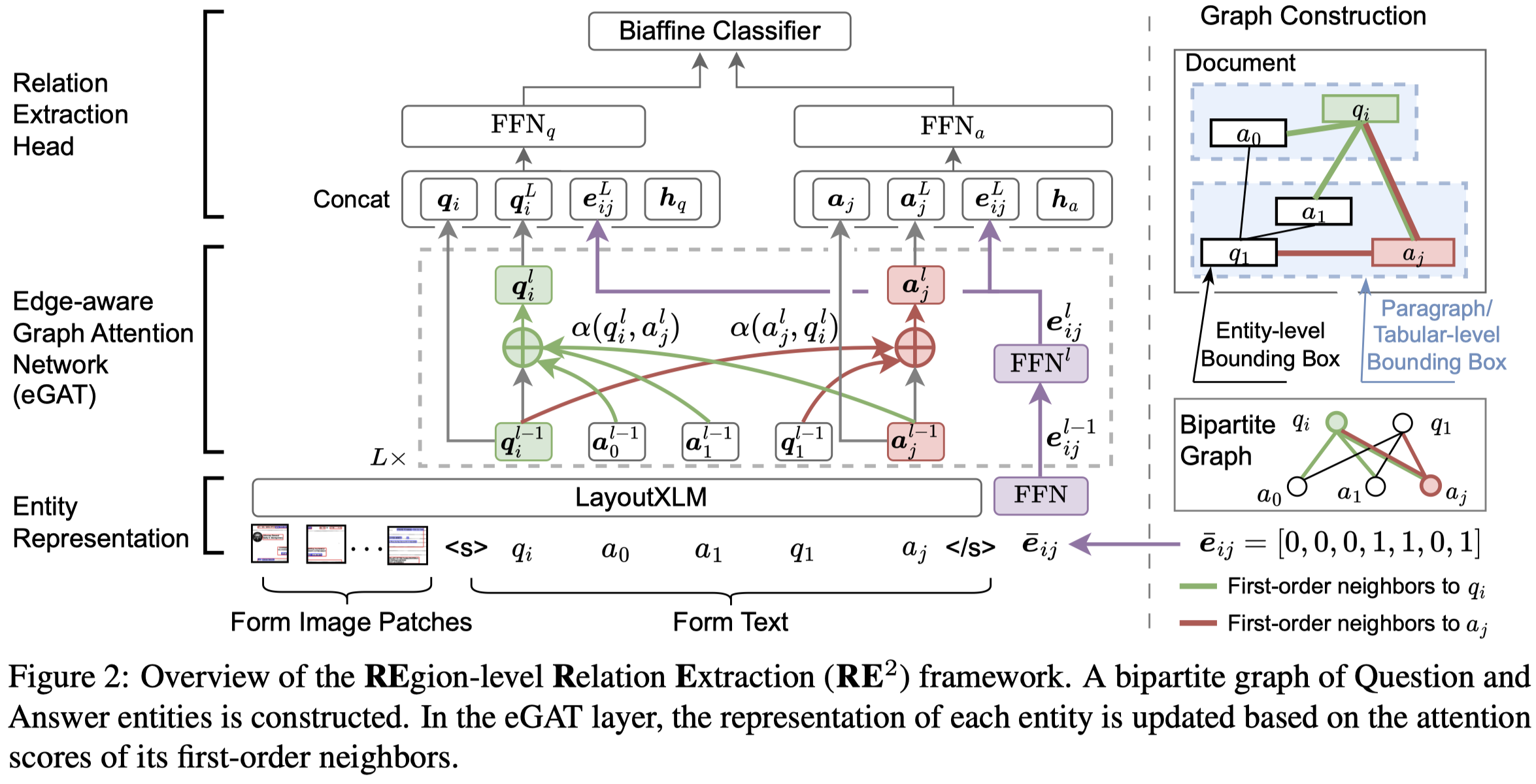
Granular Entity Mapper: Advancing Fine-grained Multimodal Named Entity Recognition and Grounding. 中科大. EMNLP 2024 Findings.
Multimodal Named Entity Recognition and Grounding (MNERG) aims to extract paired textual and visual entities from texts and images. It has been well explored through a two-step paradigm: initially identifying potential visual entities using object detection methods and then aligning the extracted textual entities with their corresponding visual entities. However, when it comes to fine-grained MNERG, the long-tailed distribution of textual entity categories and the performance of object detectors limit the effectiveness of traditional methods. Specifically, more detailed classification leads to many low-frequency categories, and existing object detection methods often fail to pinpoint subtle regions within images. To address these challenges, we propose the Granular Entity Mapper (GEM) framework. Firstly, we design a multi-granularity entity recognition module, followed by a reranking module based on the Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) to incorporate hierarchical information of entity categories, visual cues, and external textual resources collectively for accurate finegrained textual entity recognition. Then, we utilize a pre-trained Large Visual Language Model (LVLM) as an implicit visual entity grounder that directly deduces relevant visual entity regions from the entire image without the need for bounding box training. Experimental results on the GMNER and FMNERG datasets demonstrate that our GEM framework achieves state-of-the-art results on the fine-grained content extraction task.
Issue:进行细粒度的GMNER任务面临两个挑战:
- fine-grained textual entities often suffer from the problem of long-tailed distribution, necessitating external information sources to achieve precise recognition and classification of these textual entities. 细粒度的textual entity通常是长尾分布的,需要额外信息来实现精确预测
- On the other hand, fine-grained visual entities often exhibit a wide variety of sizes, which challenges traditional object detection methods in consistently recalling them and further hinders multimodal entity alignment. 细粒度的visual entity的size各不相同,一般的object detection方法不一定能够找到对应的细粒度标识
Solution:作者期望能够supplementing the valuable knowledge and clues and tracing relevant regions directly from the images is essential for fine-grained content extraction.
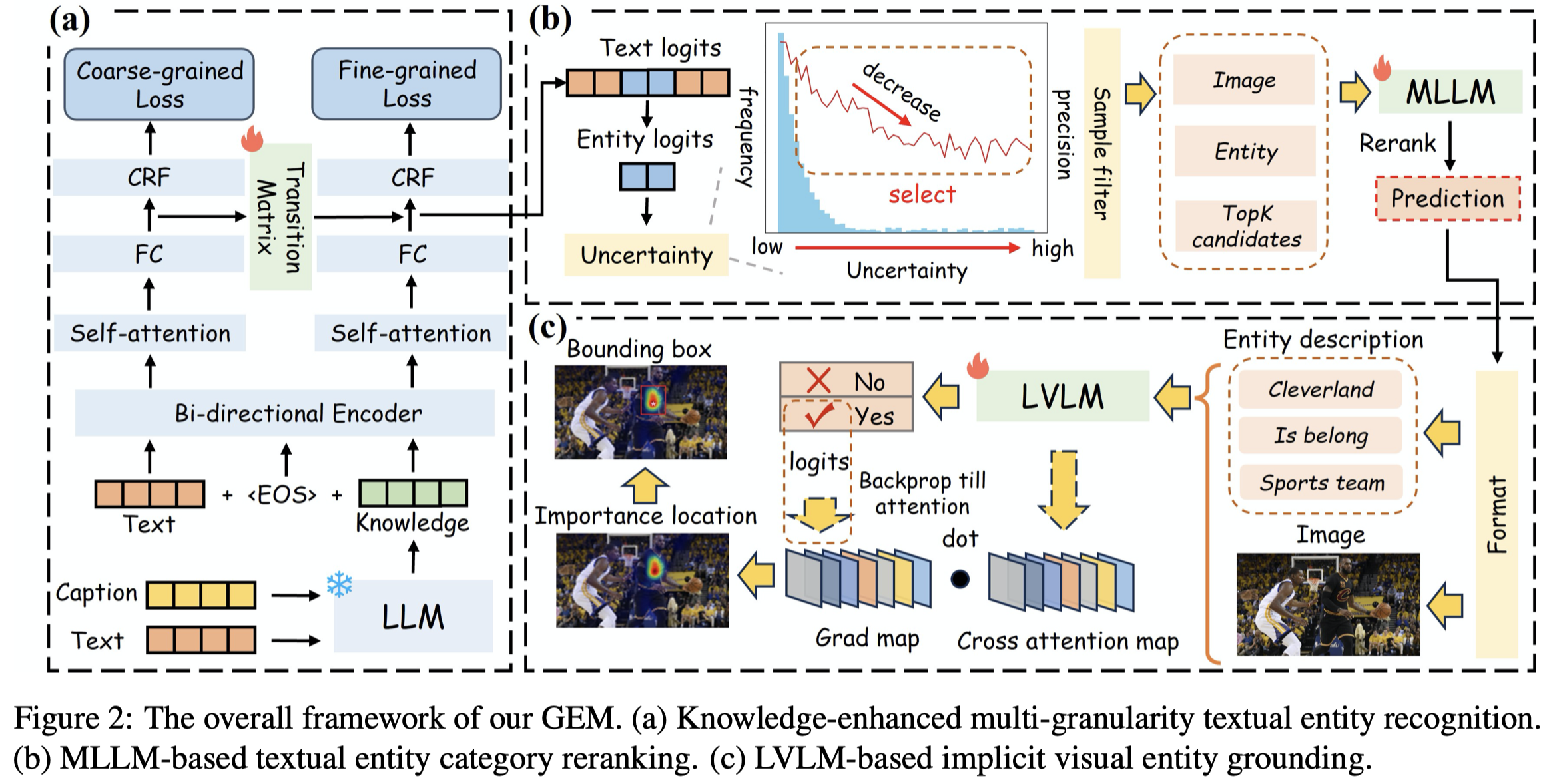
作者的方法包括三个模块。第一个模块是利用LLM来获得额外的knowledge,然后利用传统的NER-CRF方法分为两个branch进行粗粒度和细粒度的NER标注。
下面是利用LLM(ChatGPT)获得额外信息的示例,输入text以及利用BLIP-2生成的image caption,输出text的额外解释:

为了进一步增强长尾分布细粒度entity category的识别,对于CRF输出的粗粒度标注和细粒度标注,作者引入learnable transition matrix实现对\(i\)-th token的粗粒度预测概率\(y_i^c\)到细粒度预测概率的增强\(y_i^f\)。
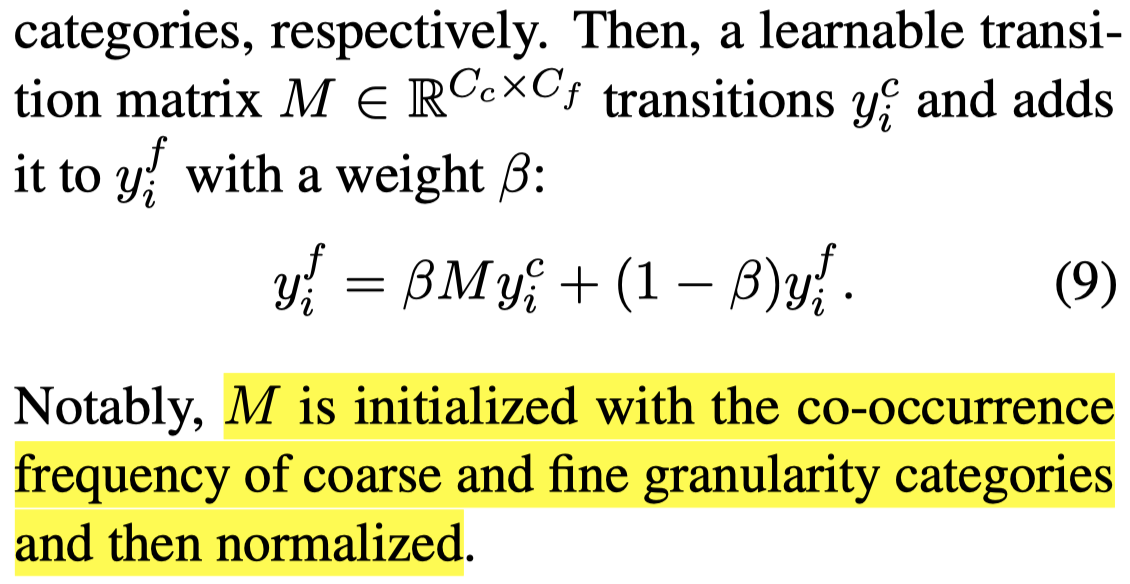
其中,\(\beta=0.1\)。
第二个模块是利用MLLM对不确定的entity预测结果进行进一步确认。首先,获得预测为entity的tokens的预测概率分布,把同一type的B-I的logits相加,再Softmax。
如果成为不同entity type的概率的信息熵越大,越不确定;超出阈值\(\gamma=0.2\)的entity认为需要进一步处理,没有超过的就认为已经得到较好的处理,不需要进行进一步确认。
随后,作者取image和top-K候选的entity categories,输入LLaVA,让llava选择最可能的实体分类。

需要注意的是,这里的LLaVA是作者经过了基于LoRA(rank=64)指令微调的,为了让其输出符合预期的结果。
第三个模块是进行grounding。作者训练BLIP用于判断一个textual entity是否出现在image中。下面是输入BLIP的文本描述,包括entity和预测的entity type:

为了实现grounding,作者利用了BLIP中隐含的特征分布,利用gradient-based weighting (Selvaraju et al., 2017; Tiong et al., 2022) 找到不同图像区域的重要度。考虑了梯度的跨模态注意力,如果梯度为负,则权重为0;如果梯度为正,取跨模态注意力的正值。
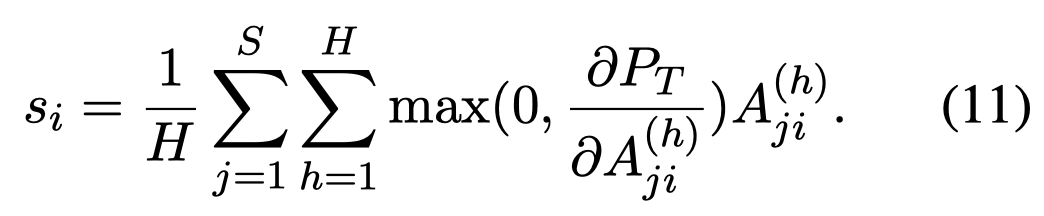
跨模态注意力图中带有最大权重的patch看做是有关的image region。为了得到对应的bounding box,作者把其看做是visual prompt,结合SAM和SEEM来获得对应的bounding box。
SeqGMPER
Grounded Multimodal Procedural Entity Recognition for Procedural Documents: A New Dataset and Baseline. 华南理工. LREC-COLING 2024. 代码(截止2024/11/17未开源)
Much of commonsense knowledge in real world is in the form of procudures or sequences of steps to achieve particular goals. In recent years, knowledge extraction on procedural documents has attracted considerable attention. However, they often focus on procedural text but ignore a common multimodal scenario in the real world. Images and text can complement each other semantically, alleviating the semantic ambiguity suffered in text-only modality. Motivated by these, in this paper, we explore a problem of grounded multimodal procedural entity recognition (GMPER), aiming to detect the procedural entity and the corresponding bounding box groundings in images (i.e., visual entities). A new dataset (Wiki-GMPER) is built and extensive experiments are conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of our proposed model.
Issue: 什么是Procedural Knowledge?
In our daily life, much of commonsense knowledge is in the form of sequences of actions to achieve particular goals (e.g., cooking recipes, crafting and maintenance manuals), which is called Procedural Knowledge (Georgeff and Lansky, 1986; Ren et al., 2023).
即一个为达到特定目的实施的步骤序列。在这种数据上自动抽取entity和一般的multimodal NER的区别有两点:
- the GMPER task is based on long multimodal procedural documents with multiple steps and complex interactions between procedural entities. 长文档的输入
- Secondly, the state of the same visual entity, such as shape, color and forms (e.g., solid, liquid and gaseous) will dynamically change as the procedure progresses. 视觉实体的状态会发生改变
Solution: 作者的方法:
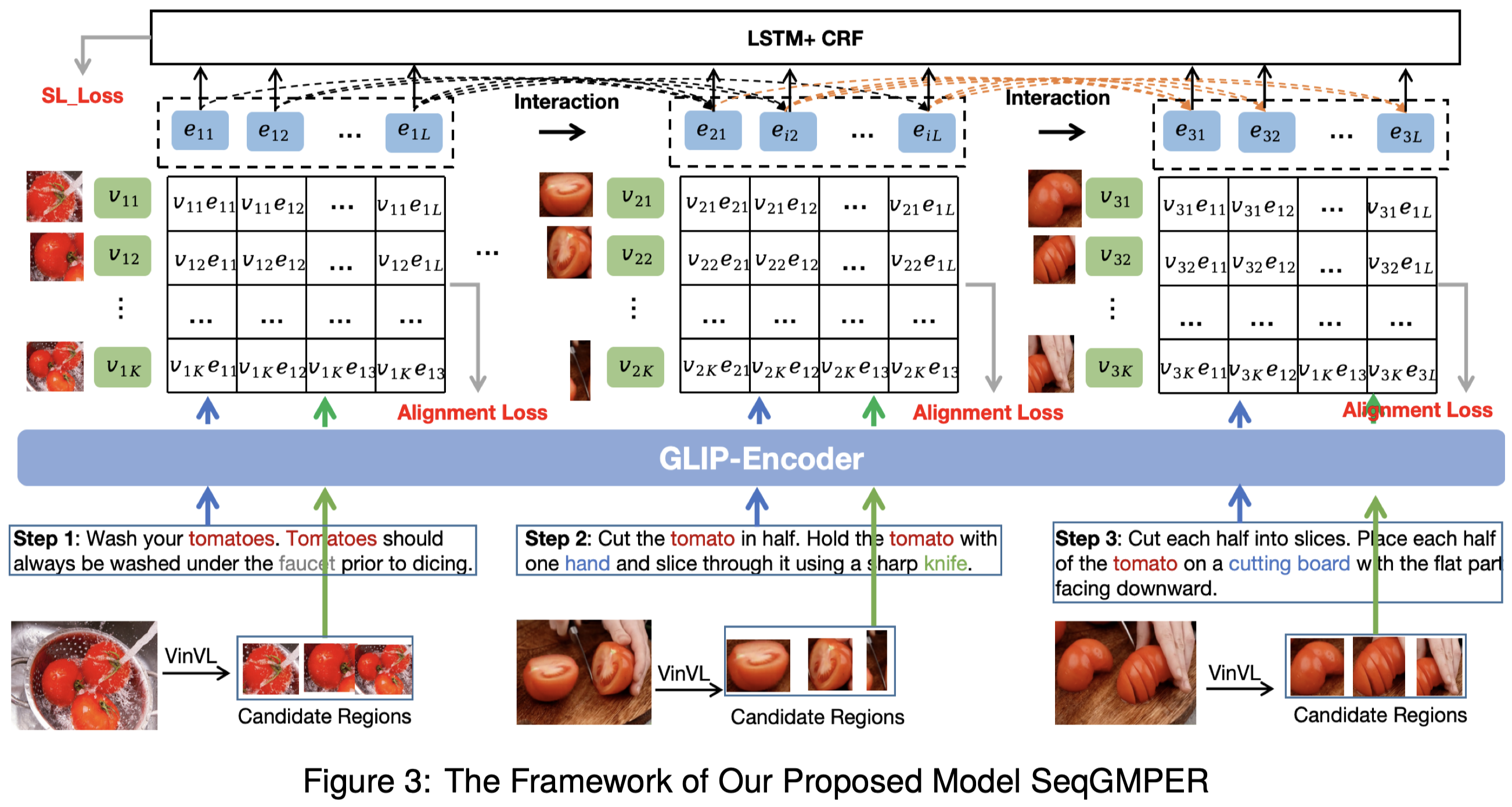
作者任务的定义:
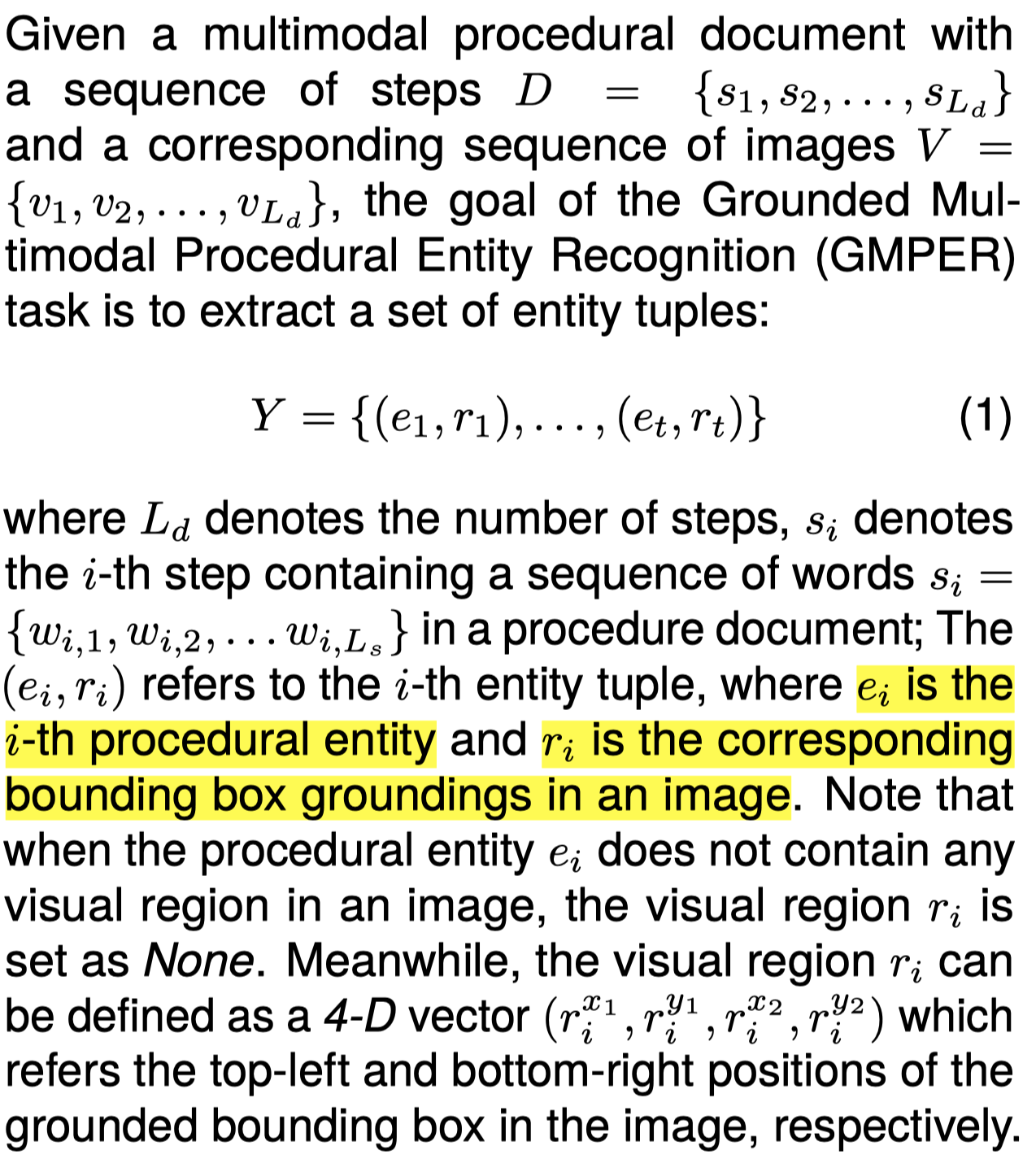
与GMNER任务类似,区别是不需要判断entity type。
利用GLIP的编码器对每个step的文本和图像分别进行处理。对于图像,额外采用和H-Index一样的步骤,使用VinVL识别top-K的objects,然后采用平均池化获得表征。
在GLIP的输出之后,为了建模实体状态的改变,作者提出Sequential Element Attention Mechanism。对于GLIP编码输出的每一step的文本和图像embedding,分别进行融合。本质上就是计算前一步中的文本/图像embedding与当前step的文本/图像embedding计算相似度,然后拼接:
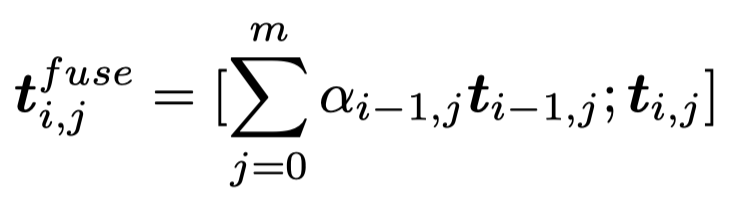
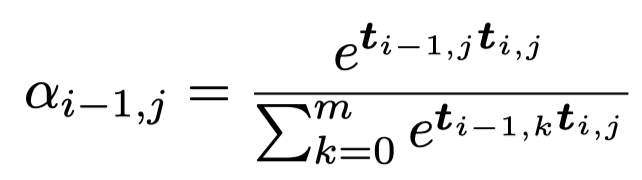
作者在输出阶段执行三个task:
- Procedural Entity Recognition:使用LSTM-CRF预测entity
- Binary Groundable Classification:获得预测entity token的融合embedding,然后平均,输入到带有softmax的预测层中,判断0/1,即entity是否groundable
- Grounded Procedural Entity:使用跨模态注意力融合文本和object embeddings,然后输出到维度是K的sigmoid预测层中,如果某个图像object对应的得分超过0.5,就认为该区域是对应entity的。
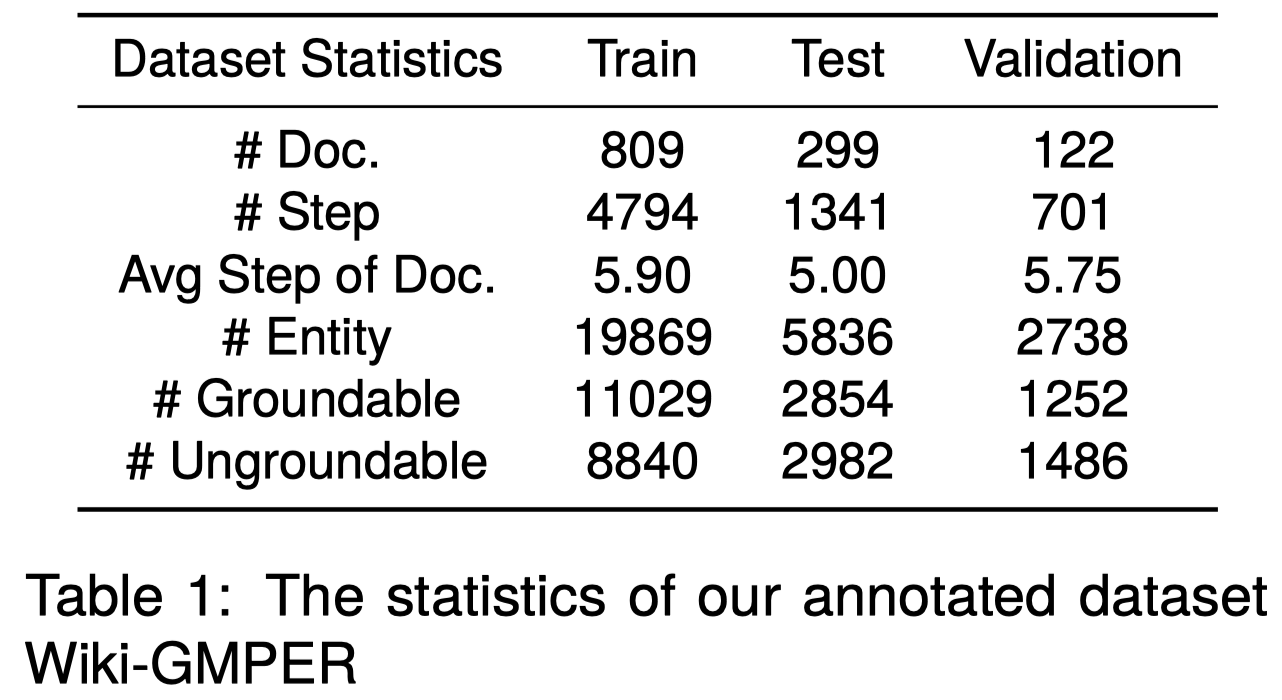
为了测试,作者基于wikihow,选择Crafts and Recipes两个主题作为数据源,创建了Wiki-GMPER数据集:
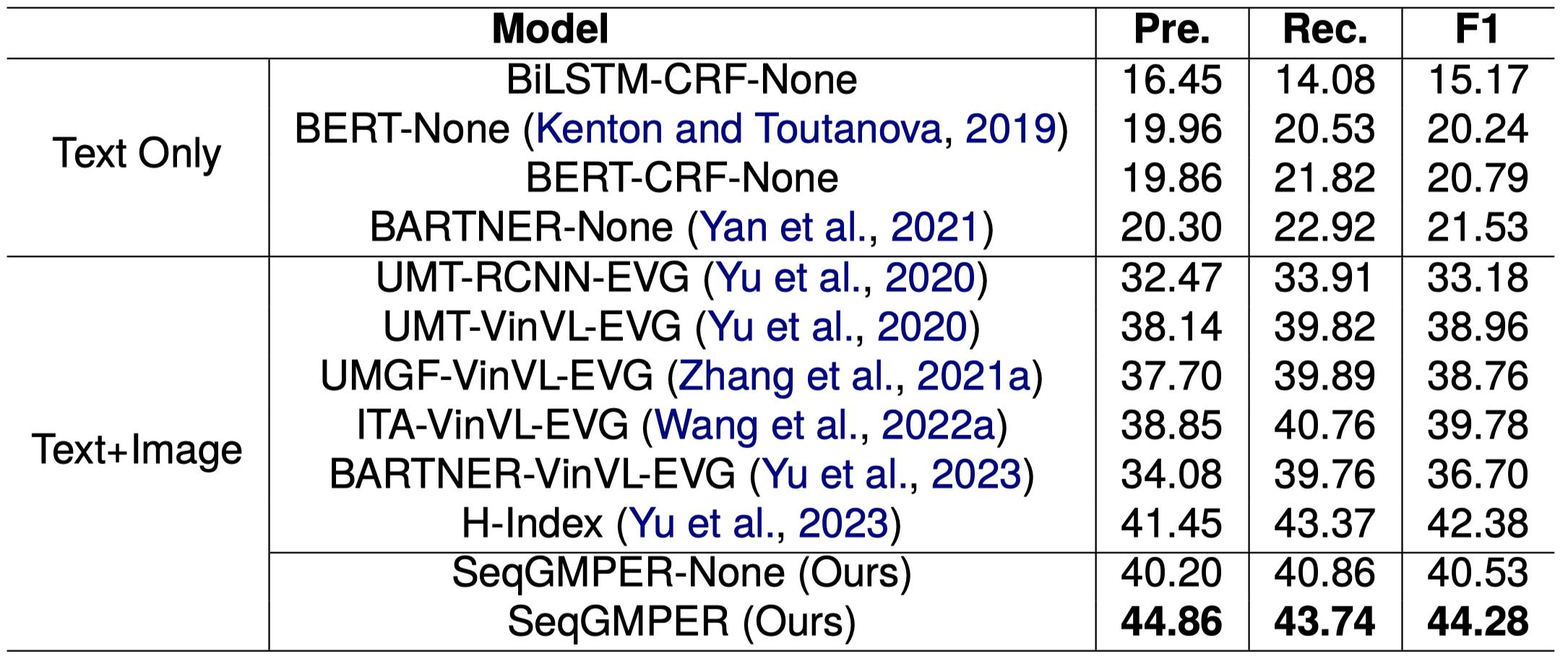
MQA
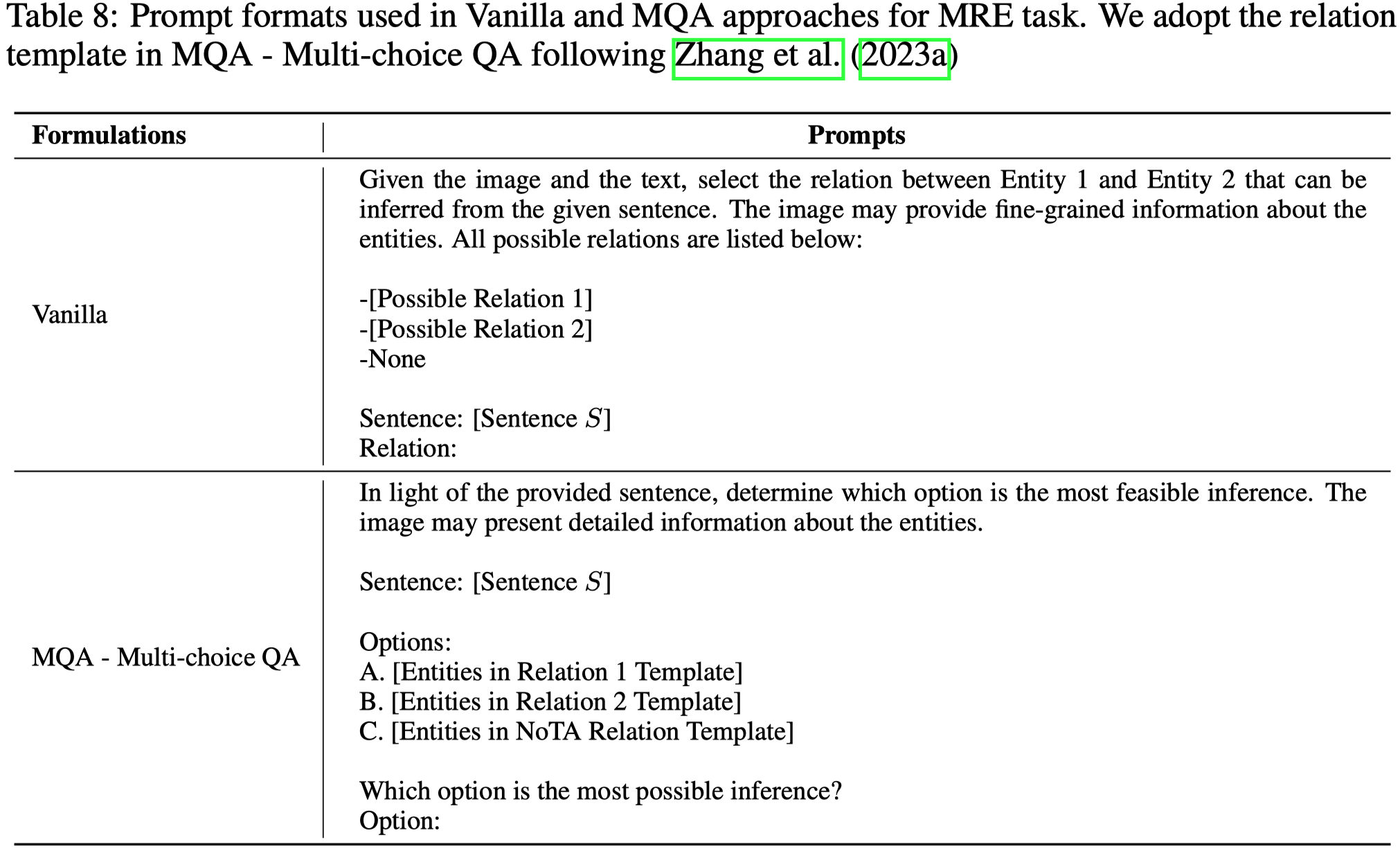
Multimodal Question Answering for Unified Information Extraction. 浙大. arXiv 2023. 代码.
Multimodal information extraction (MIE) aims to extract structured information from unstructured multimedia content. Due to the diversity of tasks and settings, most current MIE models are task-specific and data-intensive, which limits their generalization to real-world scenarios with diverse task requirements and limited labeled data. To address these issues, we propose a novel multimodal question answering (MQA) framework to unify three MIE tasks by reformulating them into a unified span extraction and multi-choice QA pipeline. Extensive experiments on six datasets show that: 1) Our MQA framework consistently and significantly improves the performances of various off-the-shelf large multimodal models (LMM) on MIE tasks, compared to vanilla prompting. 2) In the zero-shot setting, MQA outperforms previous state-of-the-art baselines by a large margin. In addition, the effectiveness of our framework can successfully transfer to the few-shot setting, enhancing LMMs on a scale of 10B parameters to be competitive or outperform much larger language models such as ChatGPT and GPT-4. Our MQA framework can serve as a general principle of utilizing LMMs to better solve MIE and potentially other downstream multimodal tasks.
Issue:为不同的MIE任务设计独立的model,需要很高时间成本,并且方法的泛化性也会受限。
Solution:作者探索了利用LMM进行MIE任务的prompt template设计。借鉴了QA4RE的思路。
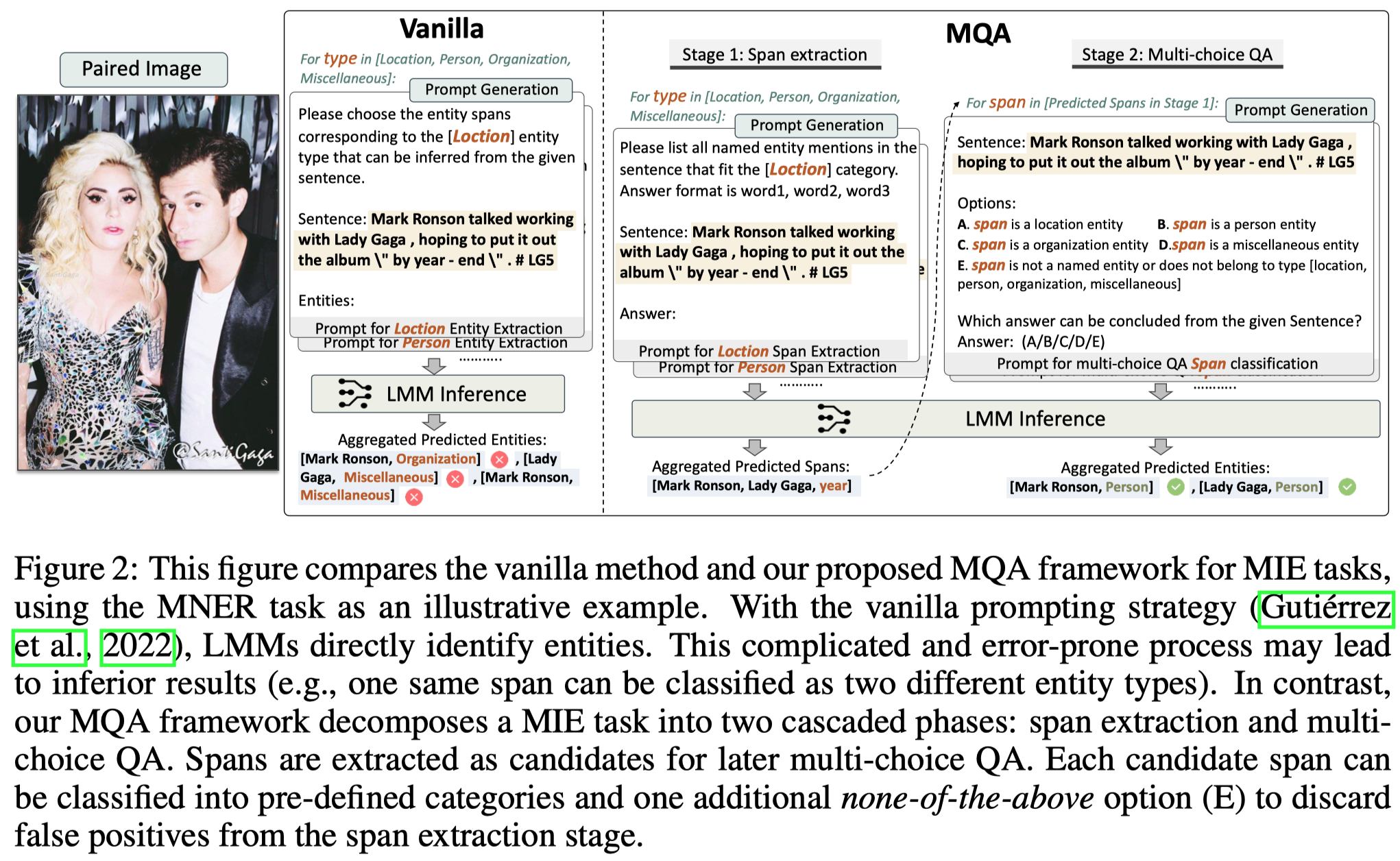
核心分为两步,第一步是span extraction,对于MNER和MED有用。第二步是classification,所有的任务都有。第二步里每个任务的label都组织为choice option的形式,并且加入了NOTA类。
作者的实验使用了BLIP-2和Instruct-BLIP两个模型,考虑在zero-shot和few-shot finetuning的形式。
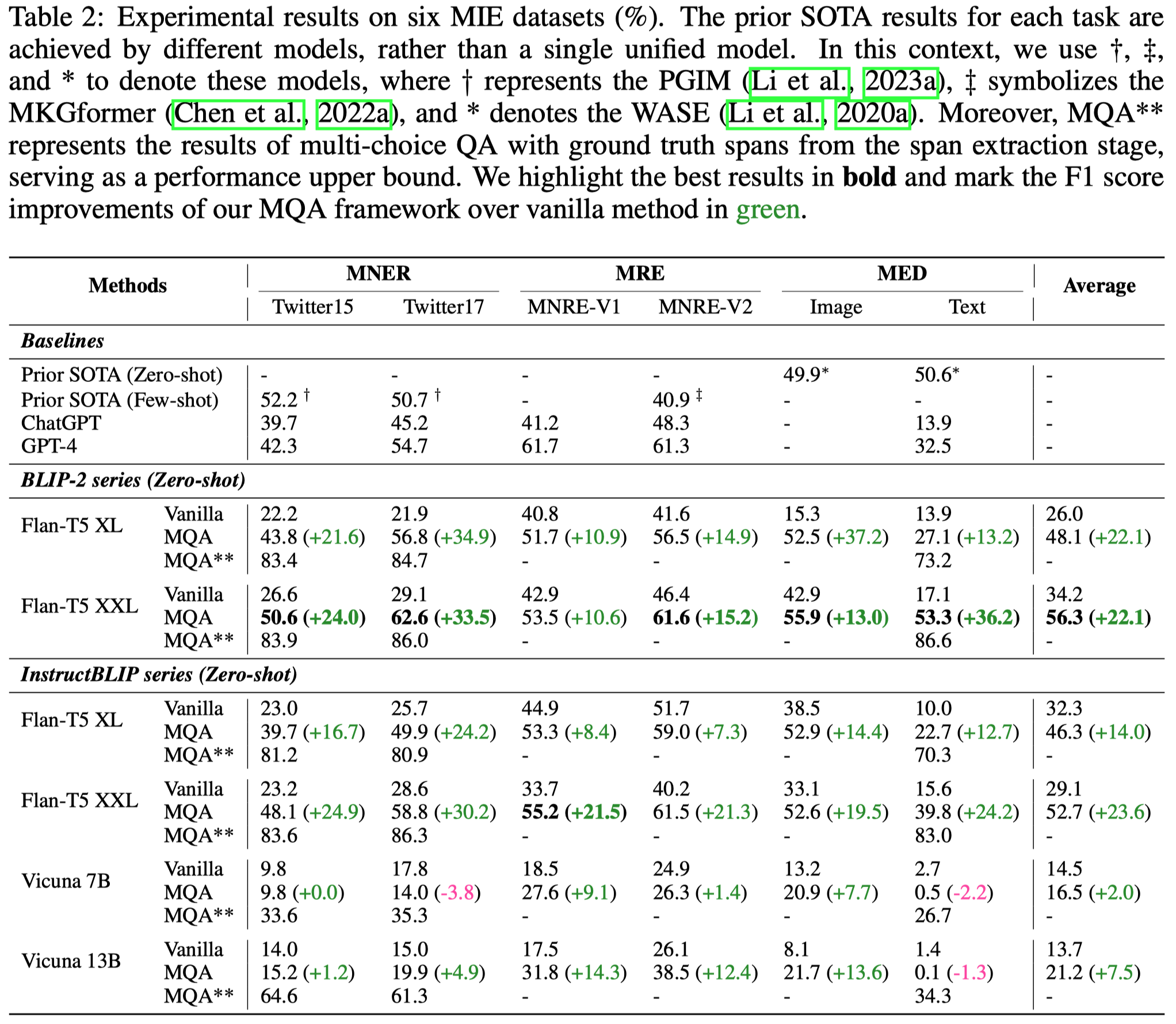
作者测试了ChatGPT和GPT-4的形式,但是是zero-shot,也没有使用作者的MQA prompt。如果采用的话效果应该能进一步提升。并且如果是使用ICL的策略应该会提升较多?
MORE
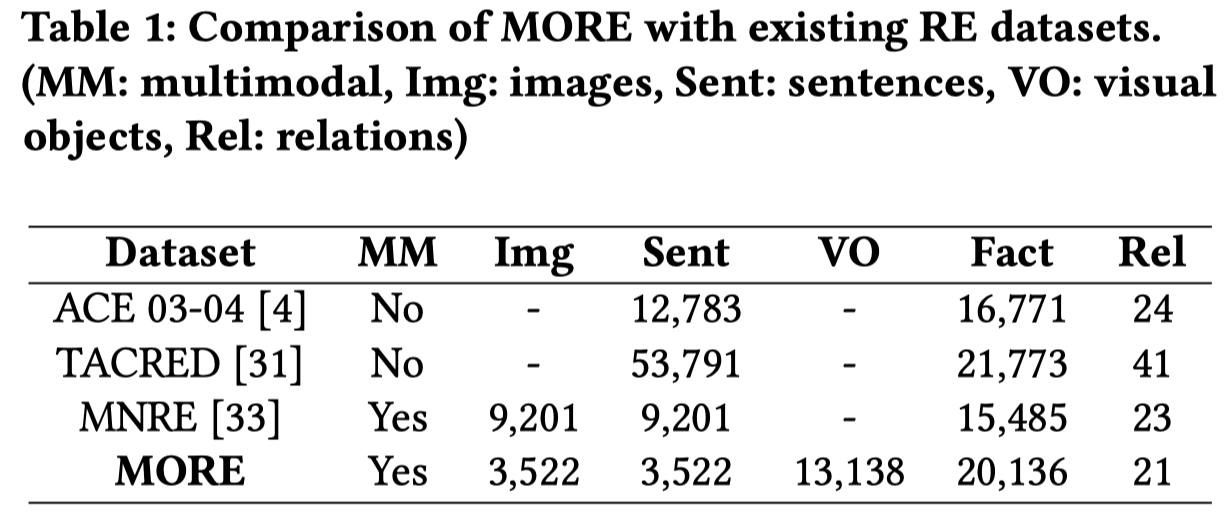
MORE: A Multimodal Object-Entity Relation Extraction Dataset with a Benchmark Evaluation. 南大. ACM MM 2023. 代码.
Extracting relational facts from multimodal data is a crucial task in the field of multimedia and knowledge graphs that feeds into widespread real-world applications. The emphasis of recent studies centers on recognizing relational facts in which both entities are present in one modality and supplementary information is used from other modalities. However, such works disregard a substantial amount of multimodal relational facts that arise across different modalities, such as one entity seen in a text and another in an image. In this paper, we propose a new task, namely Multimodal Object-Entity Relation Extraction, which aims to extract "object-entity" relational facts from image and text data. To facilitate research on this task, we introduce MORE, a new dataset comprising 21 relation types and 20,136 multimodal relational facts annotated on 3,522 pairs of textual news titles and corresponding images. To show the challenges of Multimodal Object-Entity Relation Extraction, we evaluated recent state-of-the-art methods for multimodal relation extraction and conducted a comprehensive experimentation analysis on MORE. Our results demonstrate significant challenges for existing methods, underlining the need for further research on this task. Based on our experiments, we identify several promising directions for future research. The MORE dataset and code are available at https://github.com/NJUNLP/MORE.
Issue:之前的方法关注的是单模态侧的关系识别,作者提出entity不在同一模态的跨模态关系抽取,Multimodal Object Entity Relation Extraction。这种情况在现实中是存在的,特别是对于text是title,image是新闻文章的图像。

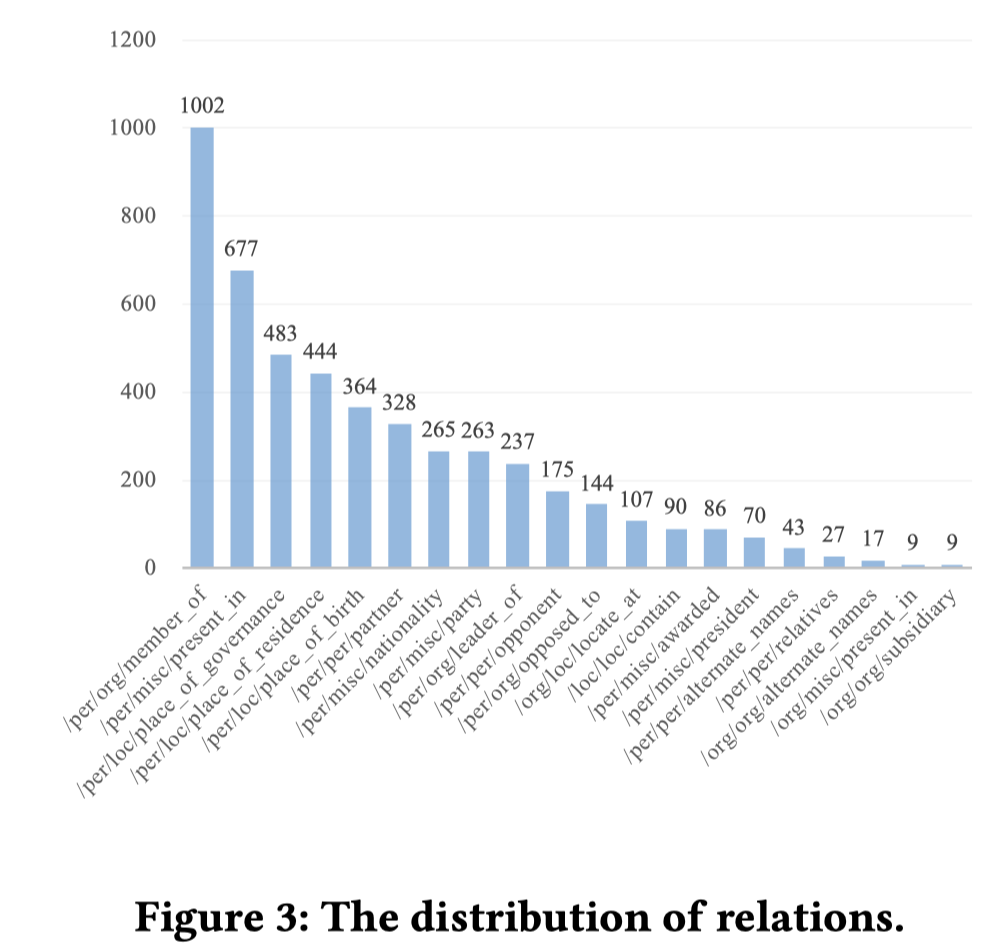
Solution: 作者从The New York Times English news and Yahoo News from 2019 to 2022获取新闻领域的数据,然后人工标注,获得新数据MORE。作者保证选择的数据中visual object不会作为textual entity出现。
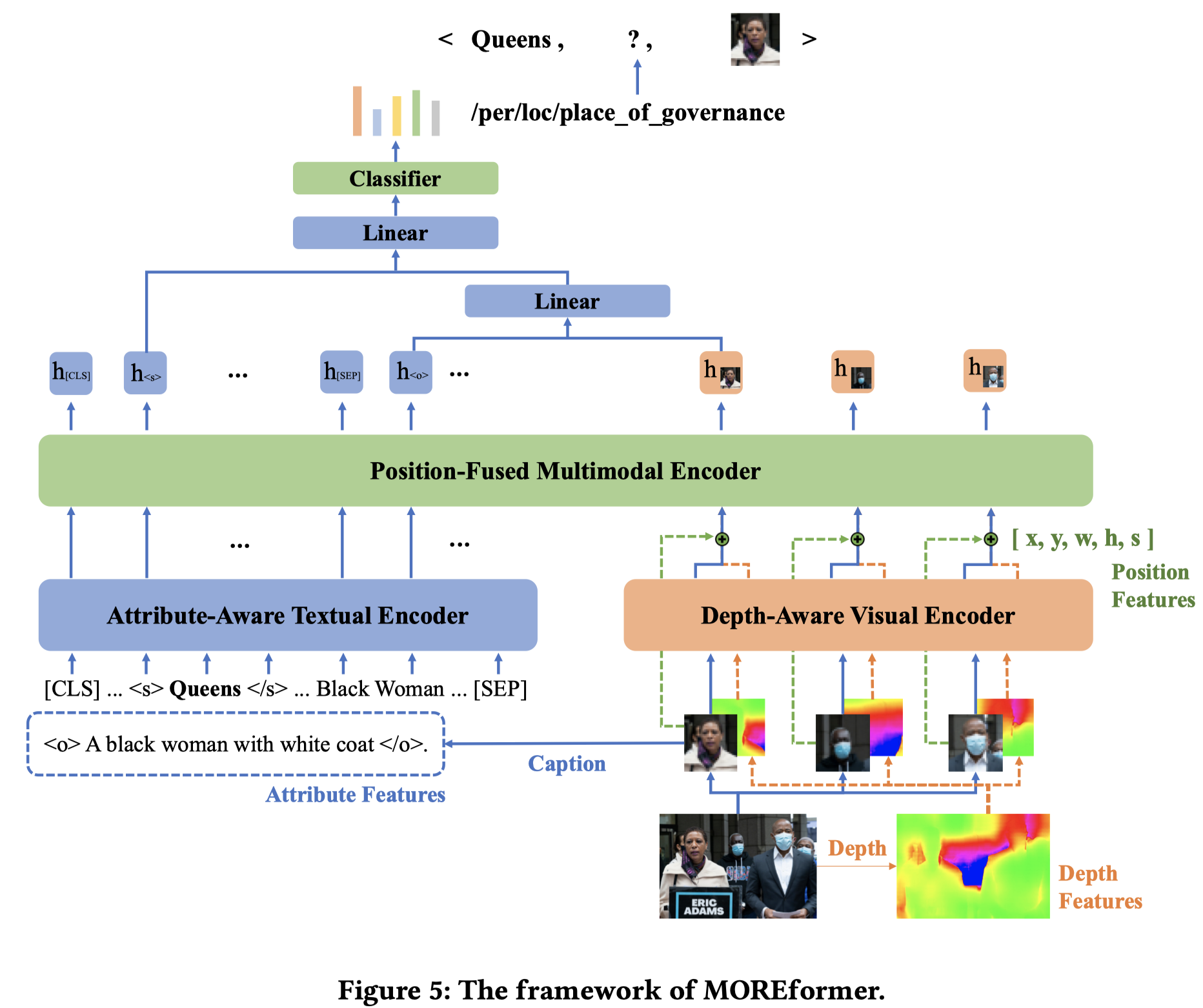
作者构造的新方法基于MKGformer,只是在文本、图像和多模态编码器中考虑了新的输入:

FocalMRE
Focus & Gating: A Multimodal Approach for Unveiling Relations in Noisy Social Media. 南大. ACM MM 2024. 代码.
Multimedia content’s surge on the internet has made multimodal relation extraction vital for applications like intelligent search and knowledge graph construction. As a rich source of image-text data, social media plays a crucial role in populating knowledge bases. However, the noisy information present in social media poses a challenge in multimodal relation extraction. Current methods focus on extracting relevant information from images to improve model performance but often overlook the importance of global image information. In this paper, we propose a novel multimodal relation extraction method FocalMRE, which leverages image focal augmentation, focal attention, and gating mechanisms. FocalMRE enables the model to concentrate on the image’s focal regions while effectively utilizing the global information in the image. Through gating mechanisms, FocalMRE optimizes the multimodal fusion strategy, allowing the model to select the most relevant augmented regions for overcoming noise interference in relation extraction. The experimental results on the public MNRE dataset reveal that FocalMRE exhibits robust and significant performance advantages in the multimodal relation extraction task, especially in scenarios with high noise, long-tail distributions, and limited resources. The code is available at https://github.com/NJUNLP/FocalMRE.
Issue: 作者认为之前的方法通常关注从image寻找和text相关的特征,而忽略了对图像全局信息的建模。图像的全局信息能够辅助理解相对位置、时空关系、object在image中的context等,能够辅助RE。
Nonetheless, these approaches overlook the importance of global image information crucial for understanding the relative positions, spatial relationships, and overall context of objects in the image, which can enhance the accuracy of relation extraction.
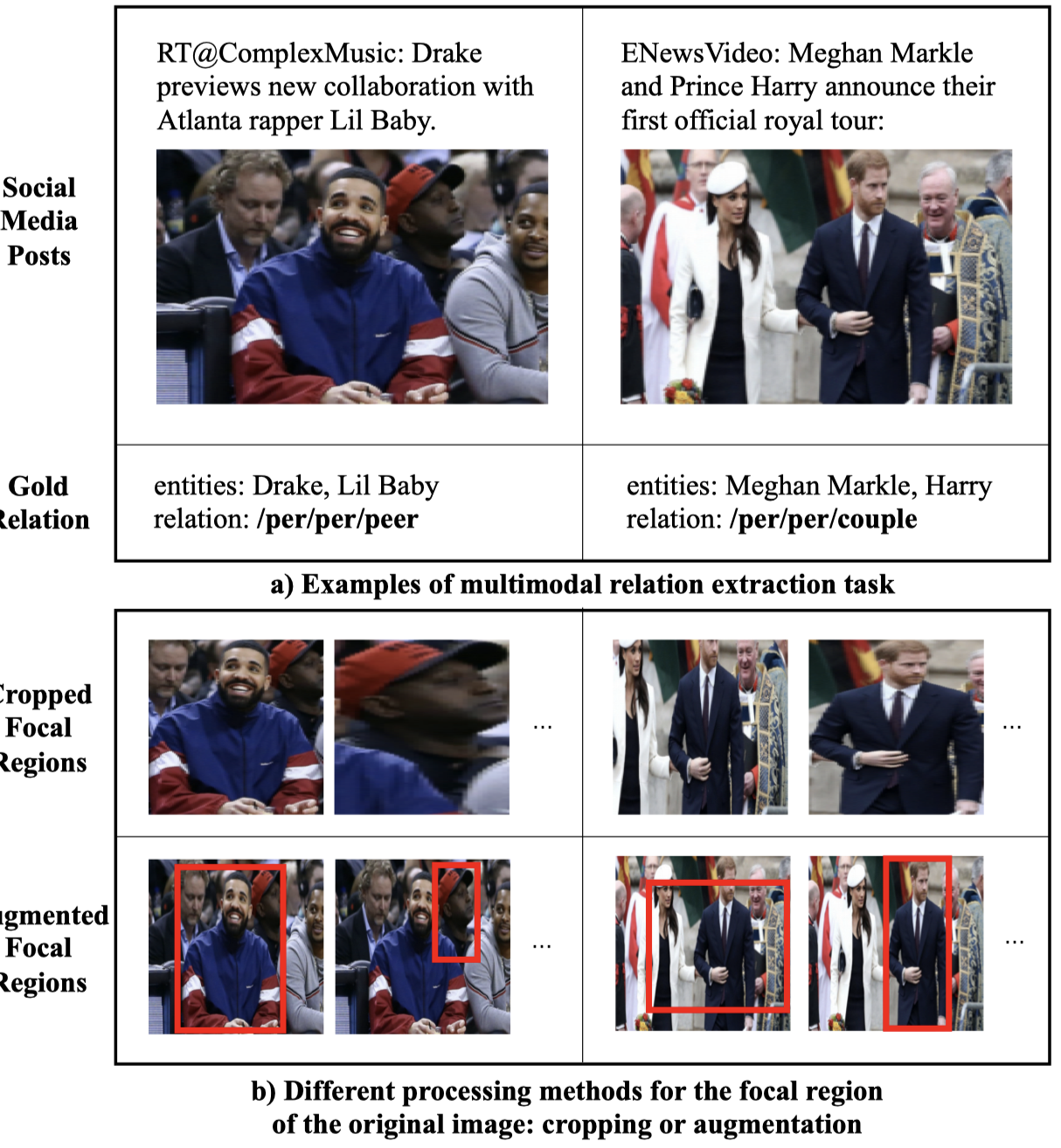
以前的方法利用object detection或者visual grounding方法找到重要的图像区域,然后切割出来,会丢失全局图像信息。
Solution: 作者的方法:
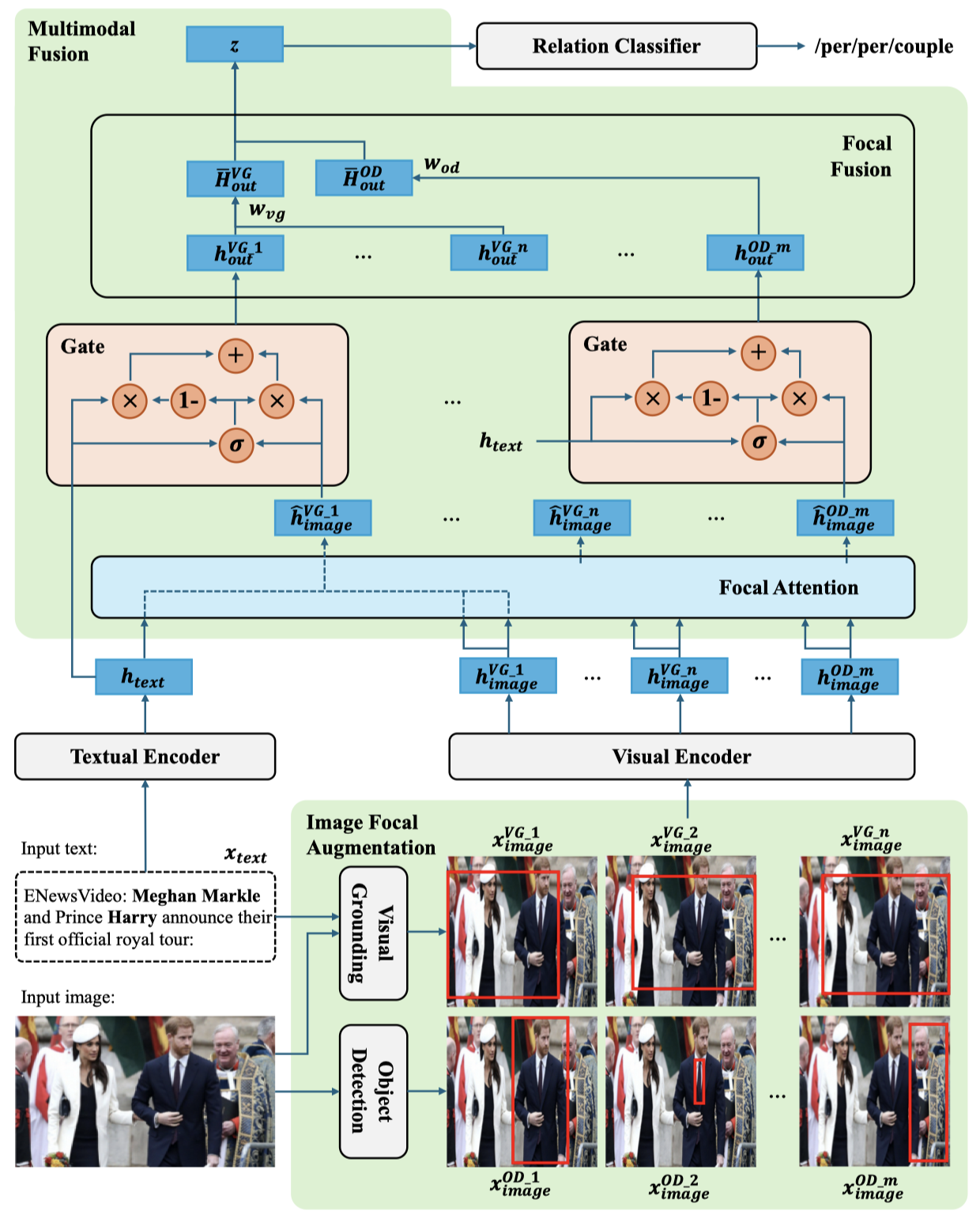
策略比较简单,就是直接把object detection或者visual grounding方法找到重要的图像区域分别在图像上用focal frame标记出来,然后分别作为模型输入。
作者使用BERT和ViT作为单模态编码器。
然后在图中的focal attention,使用text作为query,image作为key和value能够获得各个image对应的表示。为了融合text和image,使用gate进行融合:
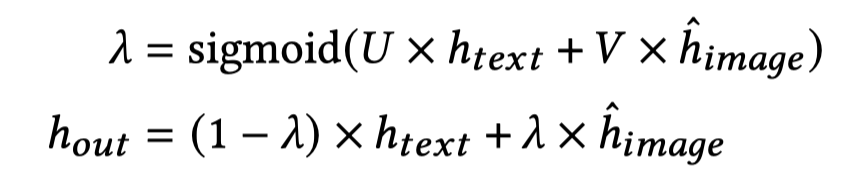
在Focal Fusion部分,对于object detection或者visual grounding方法增强的images,分别有独立的权重融合各个image的表征。例如对于visual grounding方法增强的images,所有images的embedding集成一个张量,然后有\(w_{vg}\),长度为images的数量:
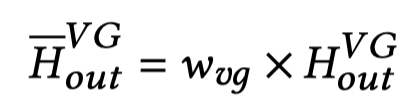
最后头尾实体分别拼接,用于关系分类:
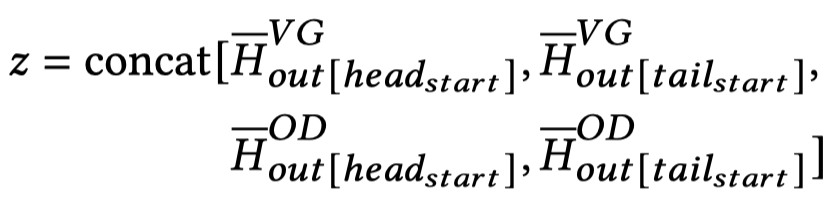
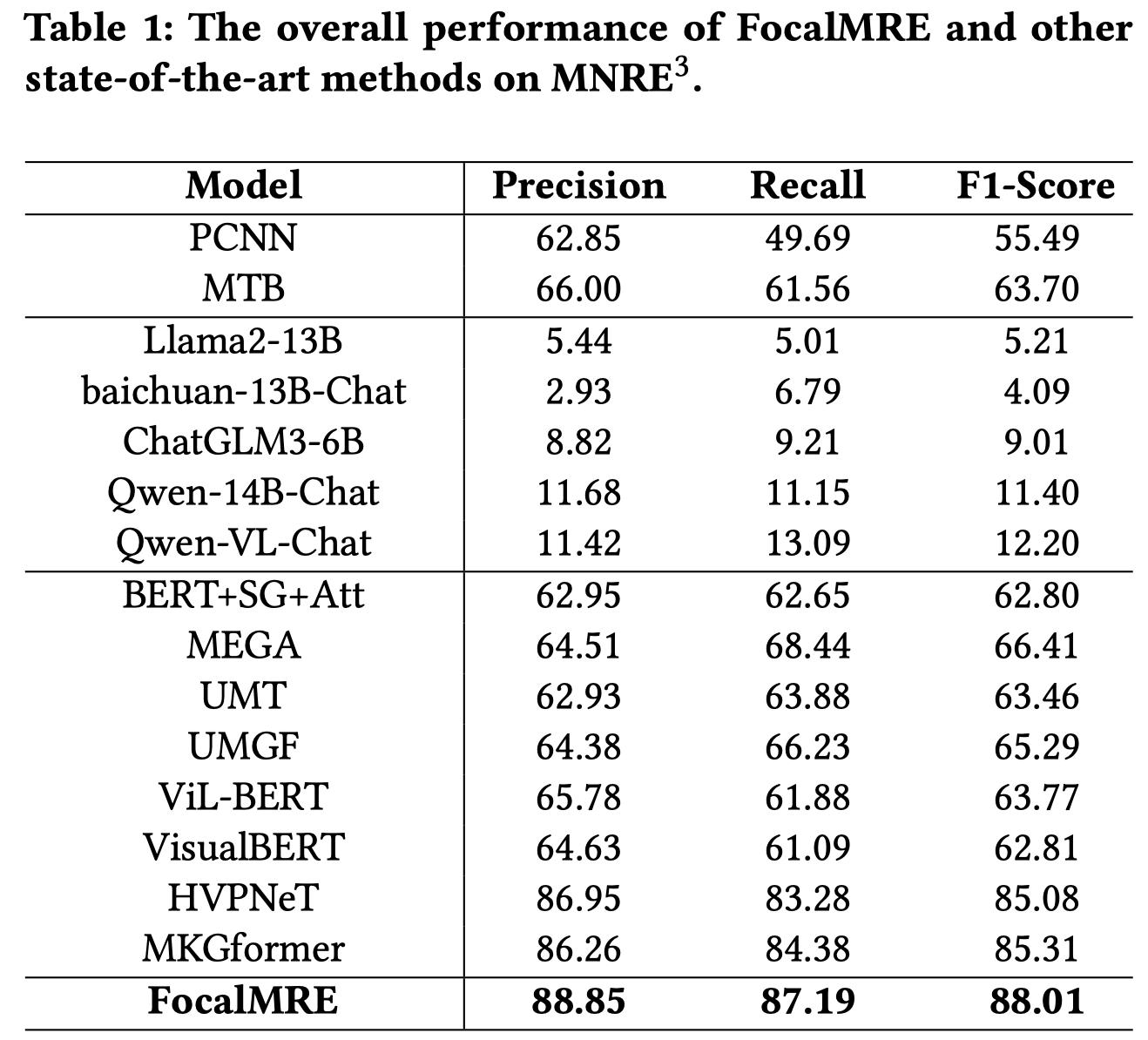
实验里尝试用LMM进行MRE,只有其中的Qwen-VL-Chat有处理图像的能力。
Shap-CA
Shapley Value-based Contrastive Alignment for Multimodal Information Extraction. 北大. ACM MM 2024.
The rise of social media and the exponential growth of multimodal communication necessitates advanced techniques for Multimodal Information Extraction (MIE). However, existing methodologies primarily rely on direct Image-Text interactions, a paradigm that often faces significant challenges due to semantic and modality gaps between images and text. In this paper, we introduce a new paradigm of Image-Context-Text interaction, where large multimodal models (LMMs) are utilized to generate descriptive textual context to bridge these gaps. In line with this paradigm, we propose a novel Shapley Value-based Contrastive Alignment (Shap-CA) method, which aligns both context-text and context-image pairs. Shap-CA initially applies the Shapley value concept from cooperative game theory to assess the individual contribution of each element in the set of contexts, texts and images towards total semantic and modality overlaps. Following this quantitative evaluation, a contrastive learning strategy is employed to enhance the interactive contribution within context-text/image pairs, while minimizing the influence across these pairs. Furthermore, we design an adaptive fusion module for selective cross-modal fusion. Extensive experiments across four MIE datasets demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods.
Issue:作者认为MIE任务中,存在两种gap,语义gap和模态gap。语义gap是指text和image描述的meaning存在差异,比如“Rocky”可以指一个dog、person或cat。模态gap是指即使语义一样,也是用不同模态数据表示的,比如dog单词和dog图像。
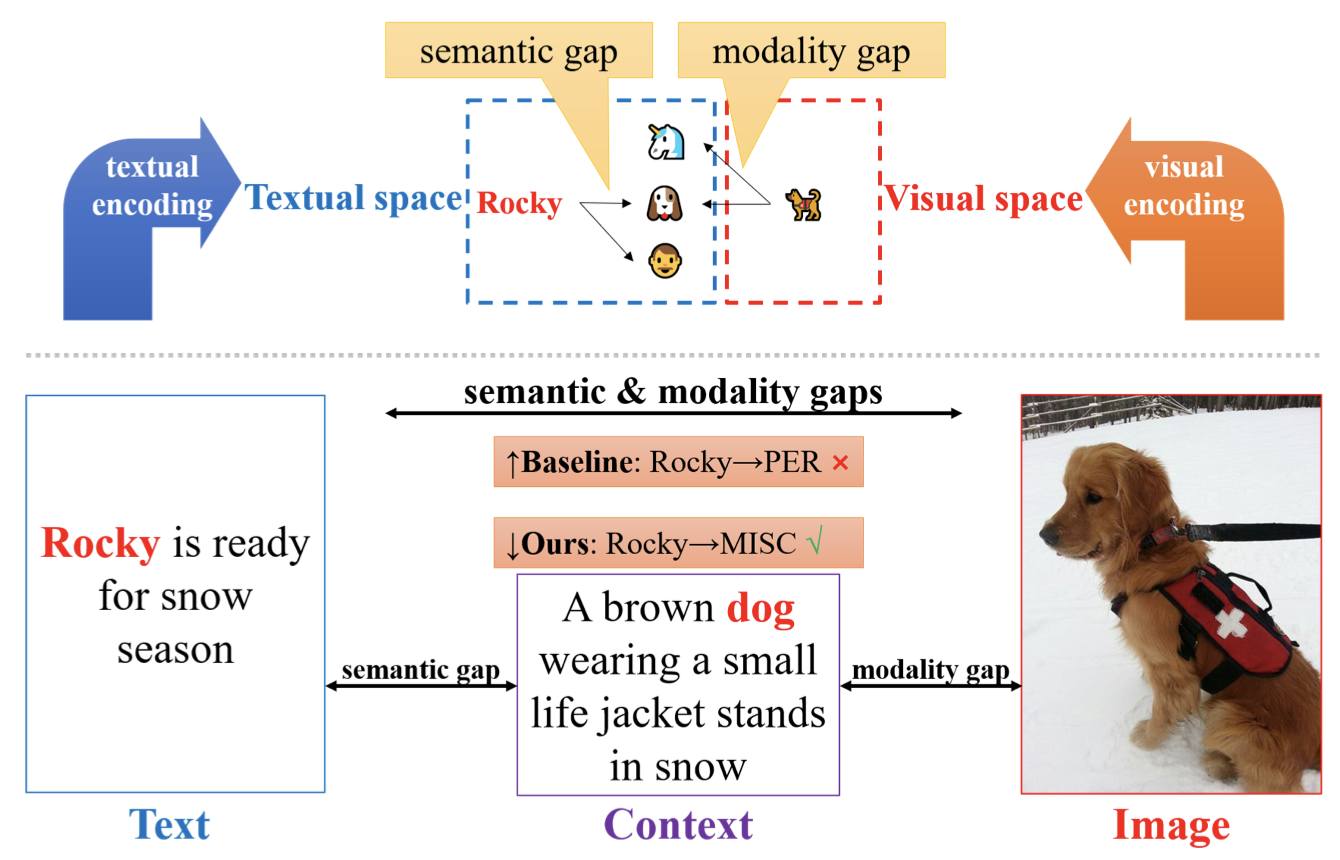
Solution: 作者最大的创新点在于引入博弈论cooperative game theory当中的Shapley Value概念来作为对比学习的监督目标。
由于存在两种gap,作者使用统一中介。由于文本是IE主要的来源,因此中介使用文本模态进行表示。使用LLaVA-1.5作为caption model来描述image内容,生成context。
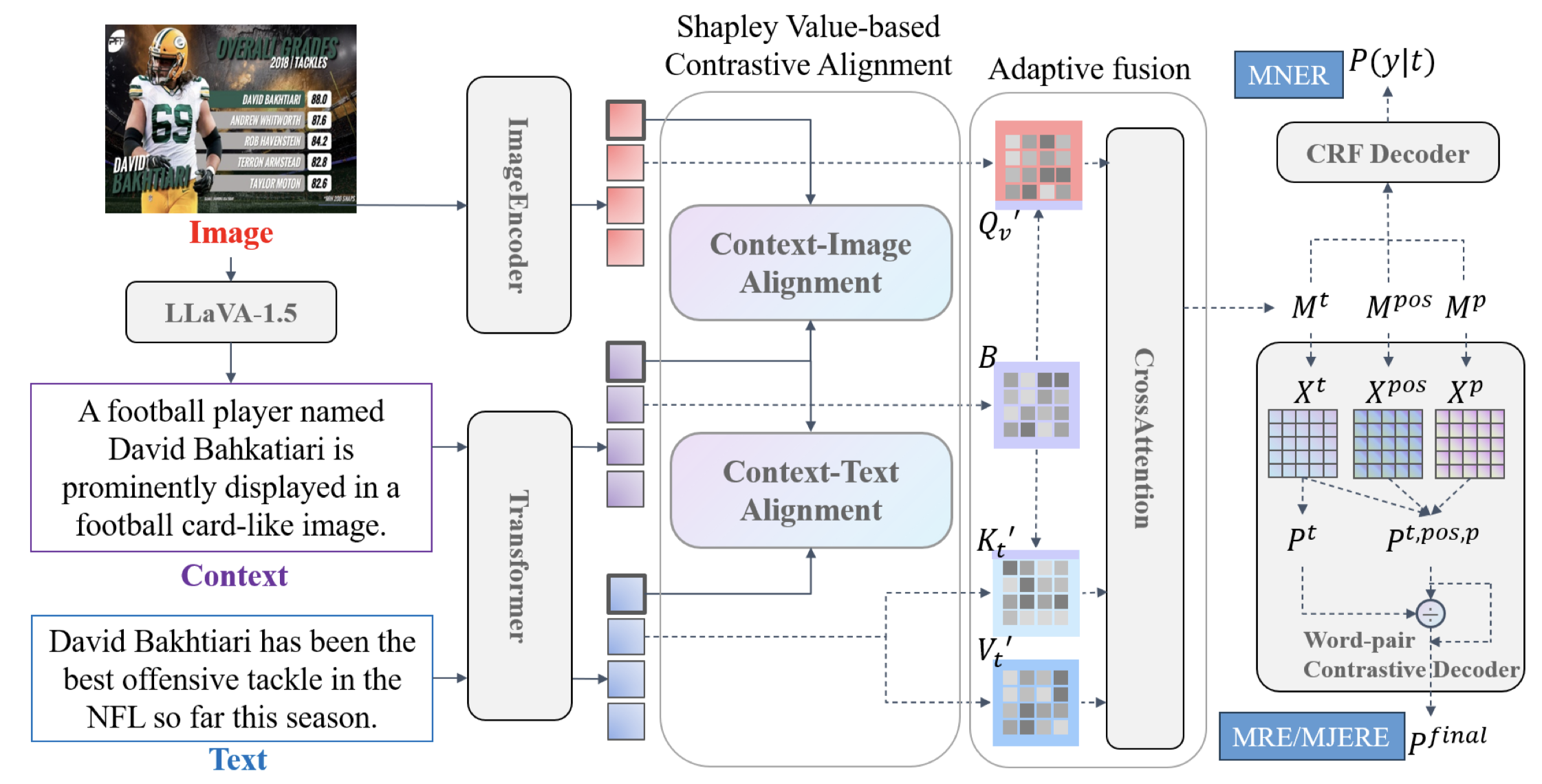
接下来,是如何对齐text、context以及image。
作者使用BERT编码context和text的拼接,获得token embedding和sentence embedding。使用ViT或ResNet152编码image。
下面是作者引入的Shaley value介绍:

本质上就是衡量某个参与者的效用大小。
作者的player是在一个batch中的\(k\)个text/context/image,比如一个batch中的context作为player,衡量其对于第\(j\)个text的效用。则先任意选择context的集合\(S\),如果有更强语义相似度的context对于text的效用应该更大。
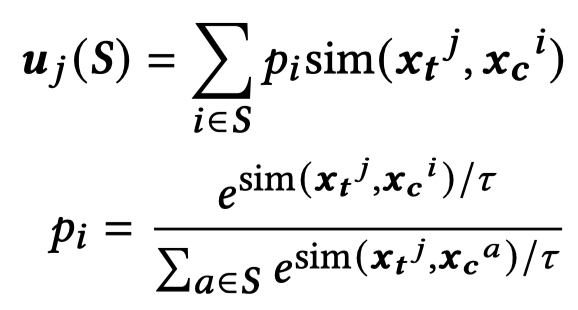
上面实际上是计算context集合\(S\)对于第\(j\)个text的语义相似度的期望。这样,只要不断的选择集合\(S\)就能够计算出来某个context对于第\(j\)个text的效用。
但是由于这样的计算量太大,因此作者考虑Monte-Carlo approximation methods [8, 33]进行估计。具体思想参考论文。
在获得了不同context对于第\(j\)个text的Shaley value估计值后,就可以计算对齐损失。也就是期望\(j\)-th context对于第\(j\)个text的效用最大:

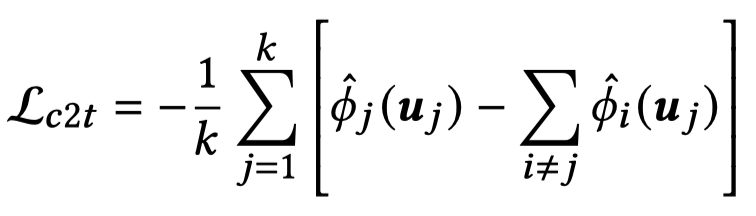
同样,作者计算text-to-context contrastive loss、context-to-image loss和image-to-context loss。
实验结果来看,作者的方法至少在MRE任务上并不是很突出:

UMIE
UMIE: Unified Multimodal Information Extraction with Instruction Tuning. 杭州城市大学. AAAI 2024. 代码.
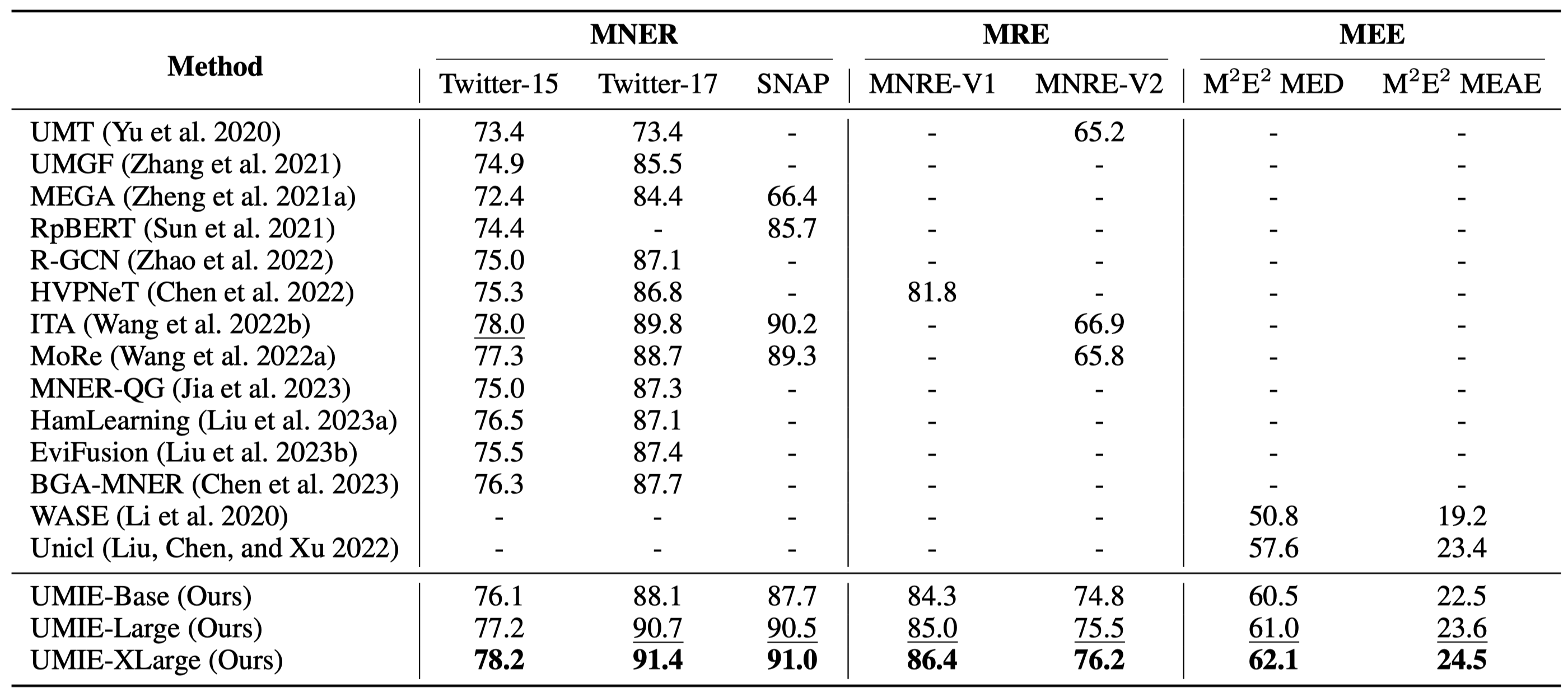
Multimodal information extraction (MIE) gains significant attention as the popularity of multimedia content increases. However, current MIE methods often resort to using task-specific model structures, which results in limited generalizability across tasks and underutilizes shared knowledge across MIE tasks. To address these issues, we propose UMIE, a unified multimodal information extractor to unify three MIE tasks as a generation problem using instruction tuning, being able to effectively extract both textual and visual mentions. Extensive experiments show that our single UMIE outperforms various state-of-the-art (SoTA) methods across six MIE datasets on three tasks. Furthermore, in-depth analysis demonstrates UMIE’s strong generalization in the zero-shot setting, robustness to instruction variants, and interpretability. Our research serves as an initial step towards a unified MIE model and initiates the exploration into both instruction tuning and large language models within the MIE domain. Our code, data, and model are available at https://github.com/ZUCC-AI/UMIE.
Issue:之前的MIE方法为每个task设计独立的mode:
- 容易过拟合特定任务
- 每个task一个model消耗更多时间
Solution: 首次提出统一多模态信息抽取unified multimodal information extractor (UMIE)。
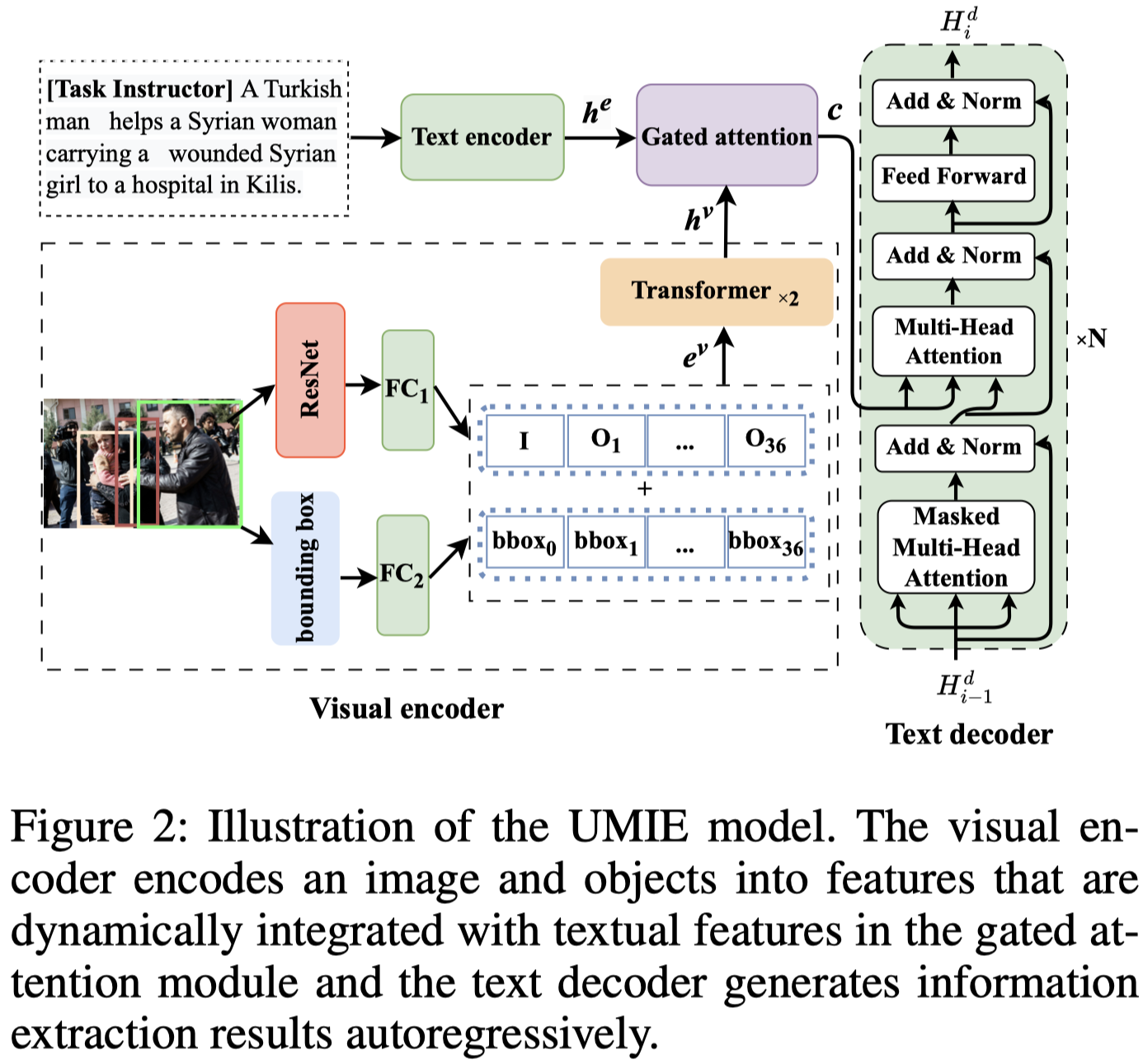
作者的结构是基于Flan-T5进行改造的。输入的文本经过Transformer encoder编码。而image是首先借助visual grounding工具,为每个image识别36个RoI及对应的bounding box(如果不够36个 ,用zero进行填充)。原始的image和objects经过Resnet-101编码得到对应的features,然后用全连接层转化embedding的维度与Transformer维度一致。对于objects还额外编码了bounding box:
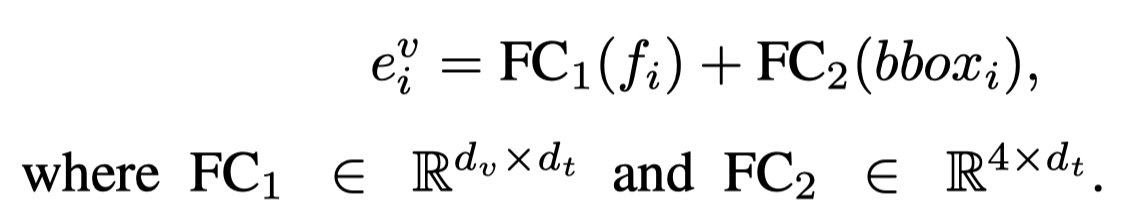
然后,再利用两层Transformer编码,得到最后的视觉表示\(h^v \in \mathbb{R}^{37\times d_t}\)。
后续利用跨模态注意力,使用文本表示作为query,获得text-aware visual embeddings。作者额外设计了一个gate来融合文本表示和视觉表示,也就是取所有token的平均值,与所有image embedding的平均值计算相似度:
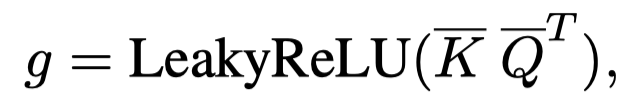
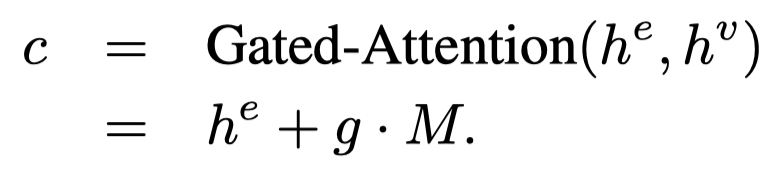
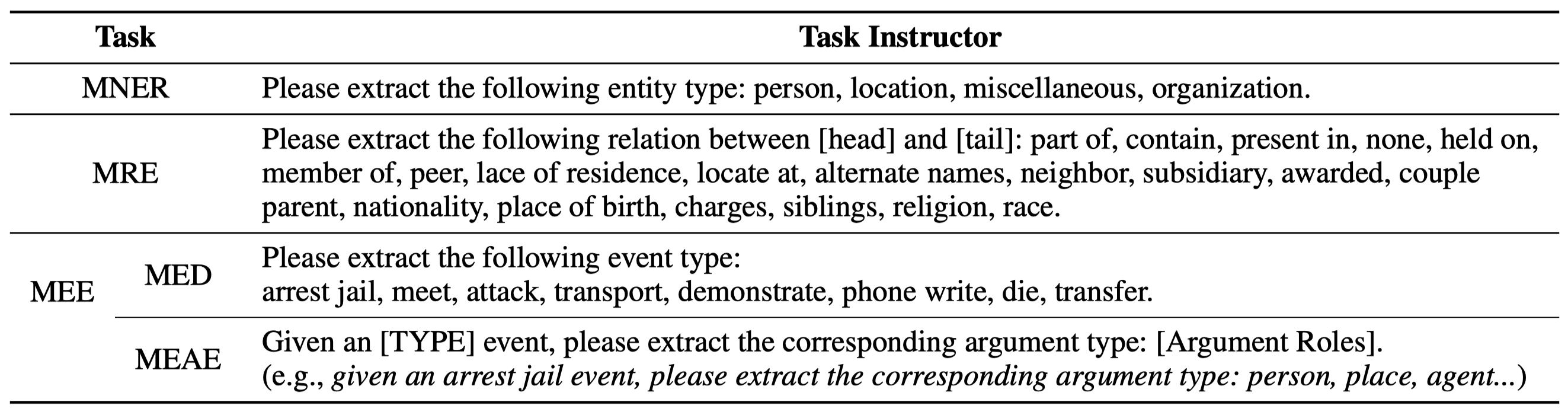
在微调过程中,作者直接使用现有的MIE数据集,不同task有不同的task instruction:
CAMIM
Caption-Aware Multimodal Relation Extraction with Mutual Information Maximization. ACM MM 2024. 吉大. 代码.
Multimodal Relation Extraction (MRE) has achieved great improvements. However, modern MRE models are easily affected by irrelevant objects during multimodal alignment which are called error sensitivity issues. The main reason is that visual features are not fully aligned with textual features and the reasoning process may suppress redundant and noisy information at the risk of losing critical information. In light of this, we propose a Caption-Aware Multimodal Relation Extraction Network with Mutual Information Maximization (CAMIM). Specifically, we first generate detailed image captions through the Large Language Model (LLM). Then, the Caption-Aware Module (CAM) hierarchically aligns the finegrained visual entities and textual entities for reasoning. In addition, for preserving crucial information within different modalities, we leverage a Mutual Information Maximization method to regulate the multimodal reasoning module. Experiments show that our model outperforms the state-of-the-art MRE models on the benchmark dataset MNRE. Further ablation studies prove the pluggable and effective performance of our Caption-Aware Module and Mutual Information Maximization method. Our code is available at https://github.com/zefanZhang-cn/CAMIM.
Issue:现有的MIE存在两个缺陷:
- Error sensitivity issues:不相关的visual objects可能会干扰multimodal推理过程,比如entity指向了不正确的object,relation预测可能出错
- Critical information loss issues:忽略了如何保存任务的关键信息
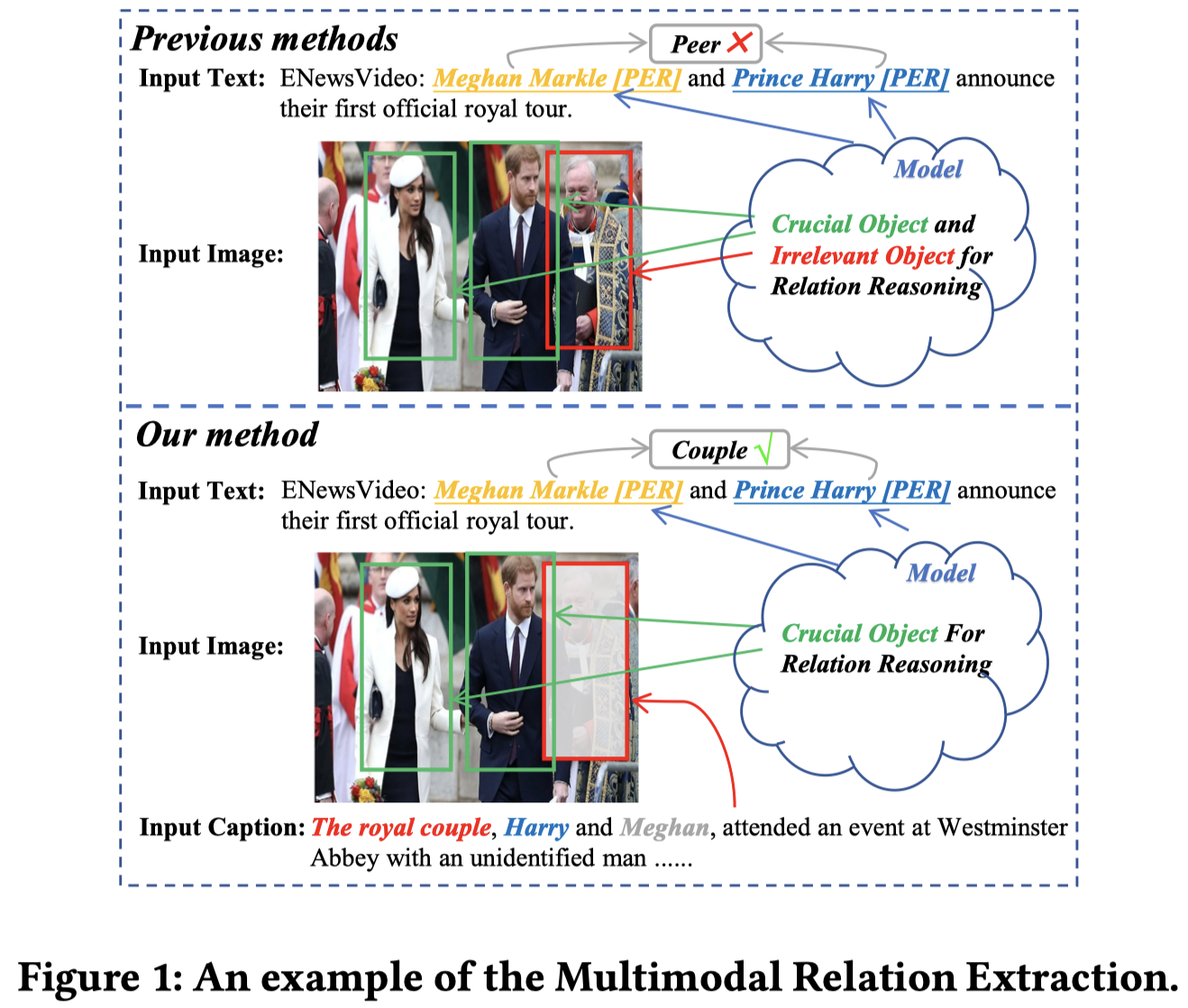
Solution:对于第一个问题,作者提出Caption-Aware Module来细粒度的融合多模态信息;对于第二个问题,引入互信息来尽量保留模态无关的重要信息。
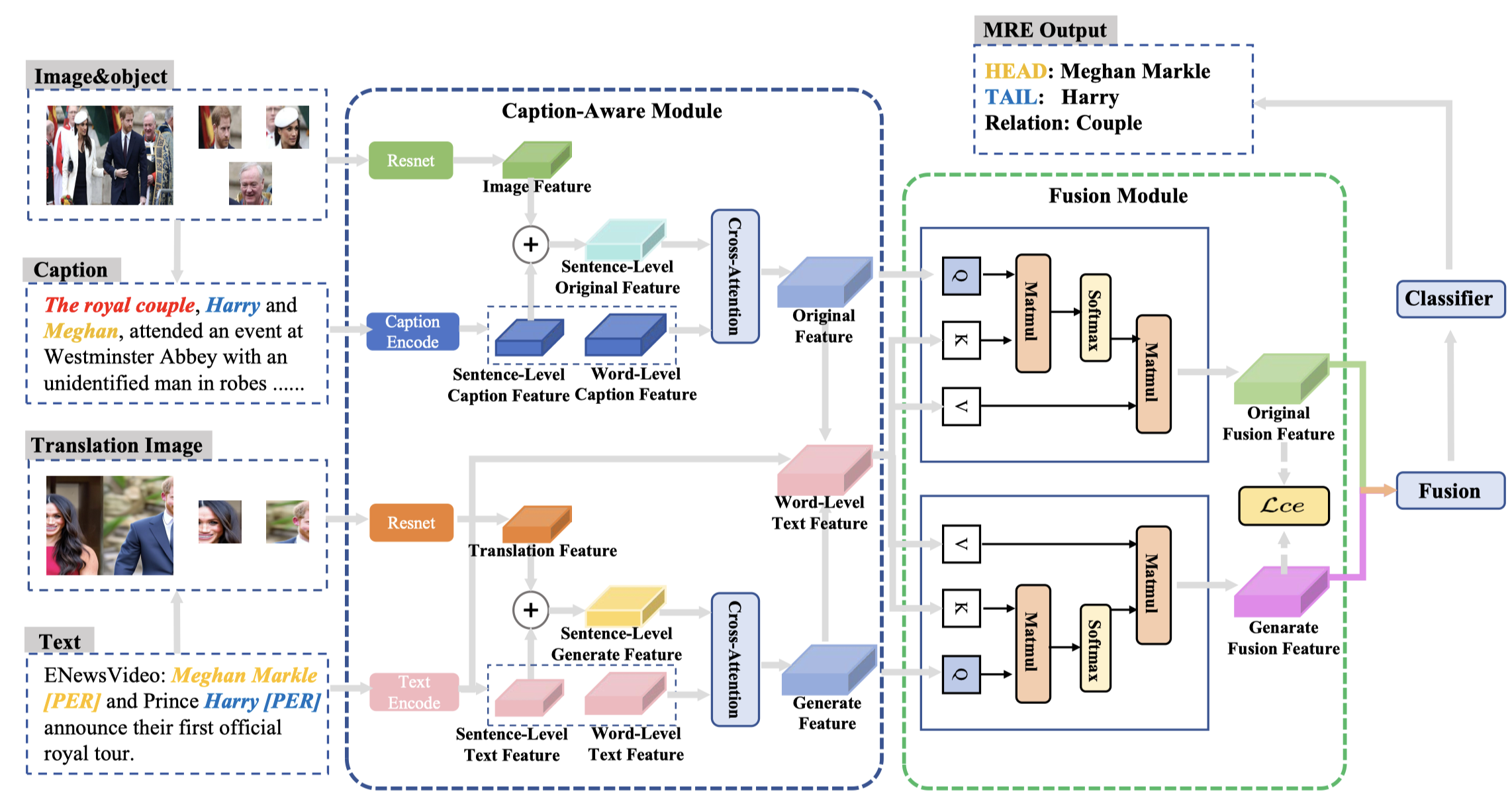
首先是输入部分,作者的输入包括两种:
利用原始image,借助LMM作为caption model生成的新caption(作者称为Original Feature)

利用原始text,借助TMR方法中得到的translation image(作者称为Generate Feature)
这两种输入的image,被ResNet50处理得到image embeddings;text部分由BERT处理得到sentence embedding和word embeddings。
句子级别的特征会与image embeddings拼接,作为Sentence-Level Features;然后会与word embeddings进行细粒度对齐融合。
具体过程是,Sentence-Level Features与word embeddings分别过一个self-attention层;再经过cross-attention层,结果再拼接,下面是对于Original Feature \(O_F\)的处理过程:
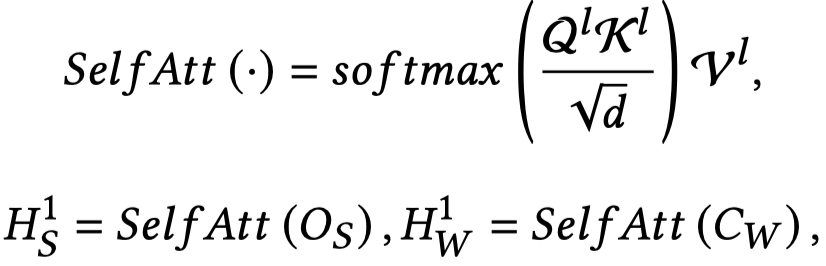

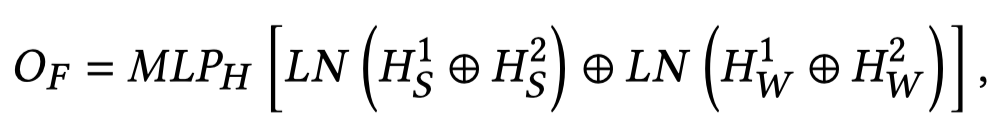
对于Generate Feature进行同样的处理流程,得到Generate Feature \(G_F\)。
Original Feature \(𝑂_𝐹\), Generate Feature \(𝐺_𝐹\), and Word-Level Text Feature \(𝑇_𝑊\)再输入到Fusion module,同样是cross-attention处理。可以得到融合了Text Feature \(𝑇_𝑊\)的Original Feature \(O_{final}\)和Generate Feature \(G_{final}\)。
在预测的时候,采用[CLS]的embedding预测relation。同时,作者引入互信息来捕获两个模态:Generate Fusion Feature \(O_{final}\)和Original Fusion Feature \(G_{final}\) 之间的模态无关信息:
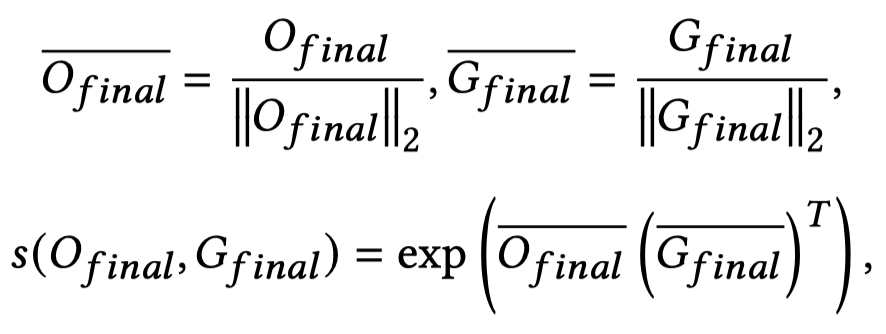
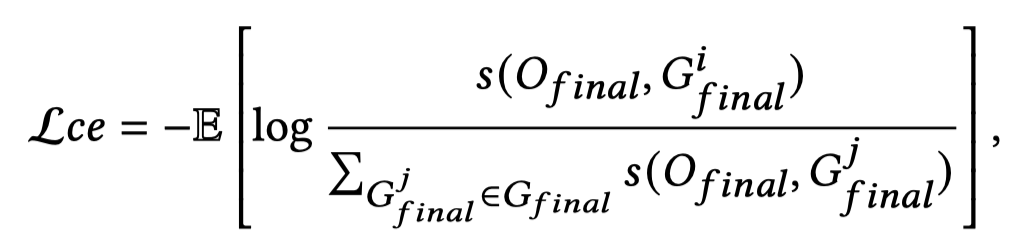
本质上,是要求一个batch中的成对的\(O_{final}\)与\(G_{final}\)关联度最大。
实验部分,作者的方法是基于HVPNeT [6] and TMR [64]进行实验:
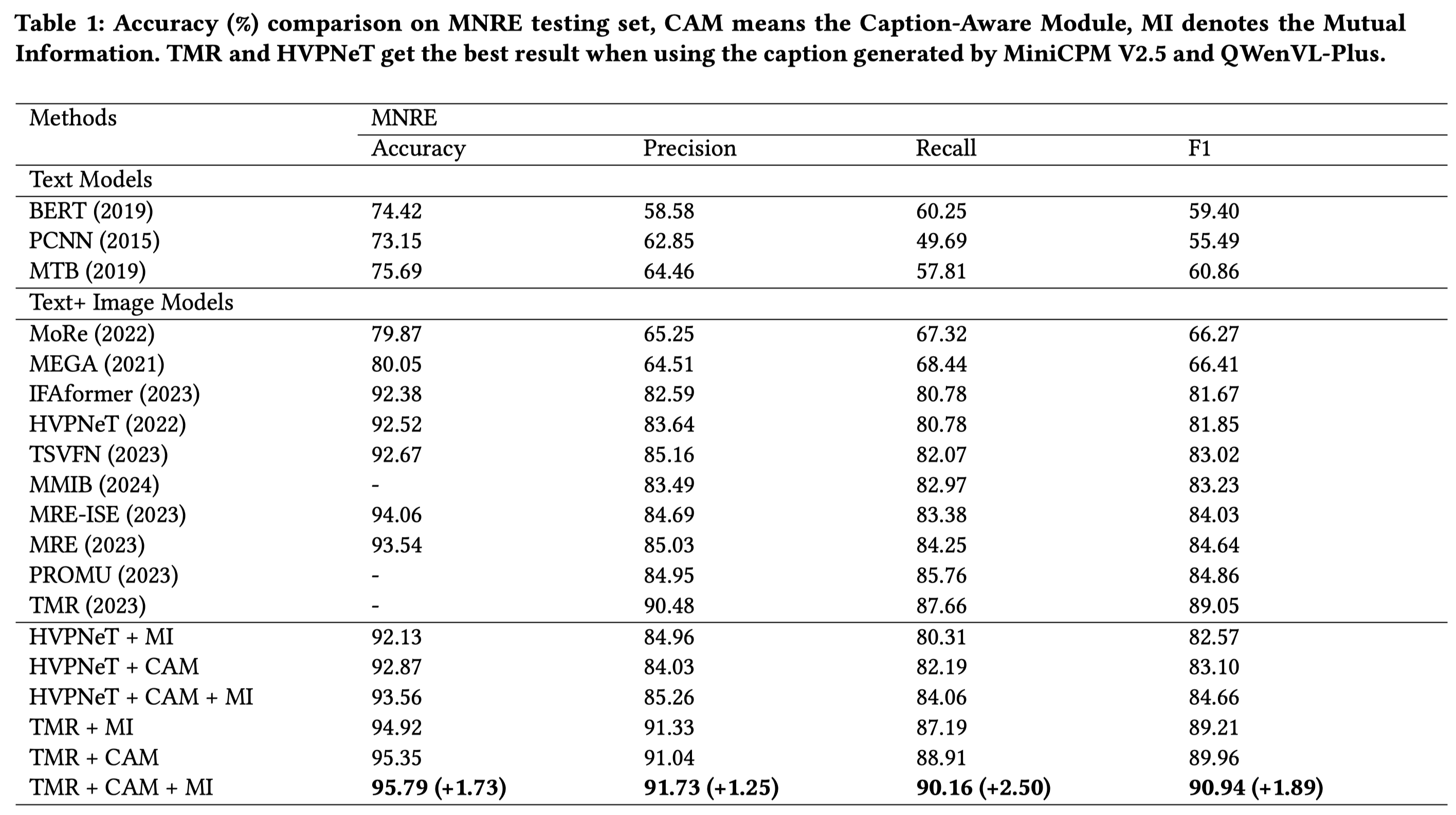
不同LMM作为caption model的对比:
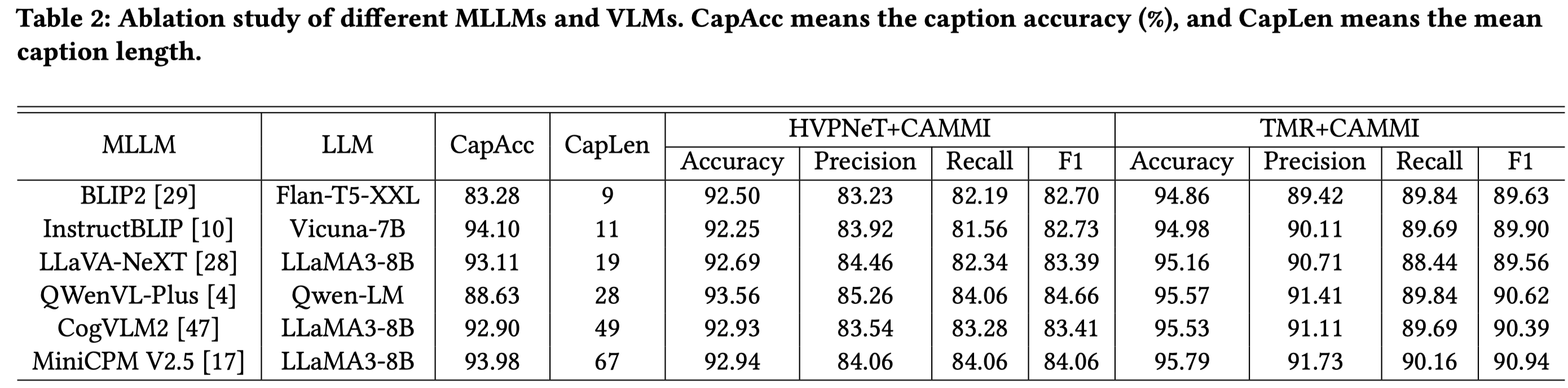
能够提供越长,越细粒度的caption效果越好。另外,caption不是完全正确的。
ISE-MRE
Information Screening whilst Exploiting! Multimodal Relation Extraction with Feature Denoising and Multimodal Topic Modeling. 新加坡国立. ACL 2023. 代码.
Existing research on multimodal relation extraction (MRE) faces two co-existing challenges, internal-information over-utilization and external-information under-exploitation. To combat that, we propose a novel framework that simultaneously implements the idea of internal-information screening and externalinformation exploiting. First, we represent the fine-grained semantic structures of the input image and text with the visual and textual scene graphs, which are further fused into a unified cross-modal graph (CMG). Based on CMG, we perform structure refinement with the guidance of the graph information bottleneck principle, actively denoising the less-informative features. Next, we perform topic modeling over the input image and text, incorporating latent multimodal topic features to enrich the contexts. On the benchmark MRE dataset, our system outperforms the current best model significantly. With further in-depth analyses, we reveal the great potential of our method for the MRE task. Our codes are open at https://github.com/ChocoWu/MRE-ISE.
Issue:作者认为之前的MRE模型存在两个缺陷:
- Internal-information over-utilization. 过于强调对image和text内部信息的全部利用,事实上存在很多噪音,只有一部分的context(无论是text还是image)对task是有帮助的
- External-information under-exploitation. 忽略了对外部信息的利用,有些case需要引入外部信息才能够准确预测
下面是作者的两个例子分别对应上面两个缺陷:
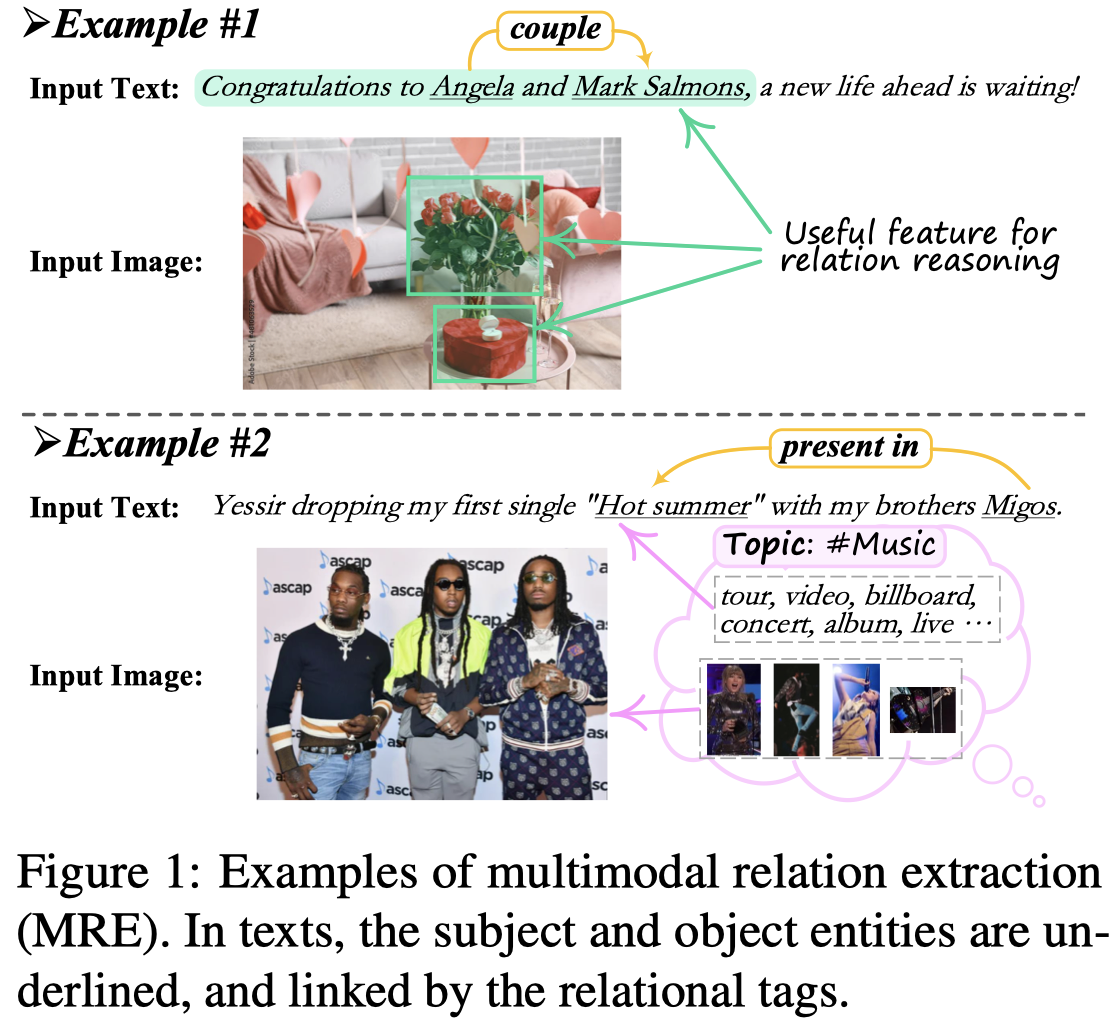
Solution:对于第一个缺陷,作者构造跨模态场景图,并且利用node过滤和edge调整方法寻找text-image pair中真正有用的部分;第二个缺陷,通过引入主题模型,为不同sample寻找符合的text和image主题。
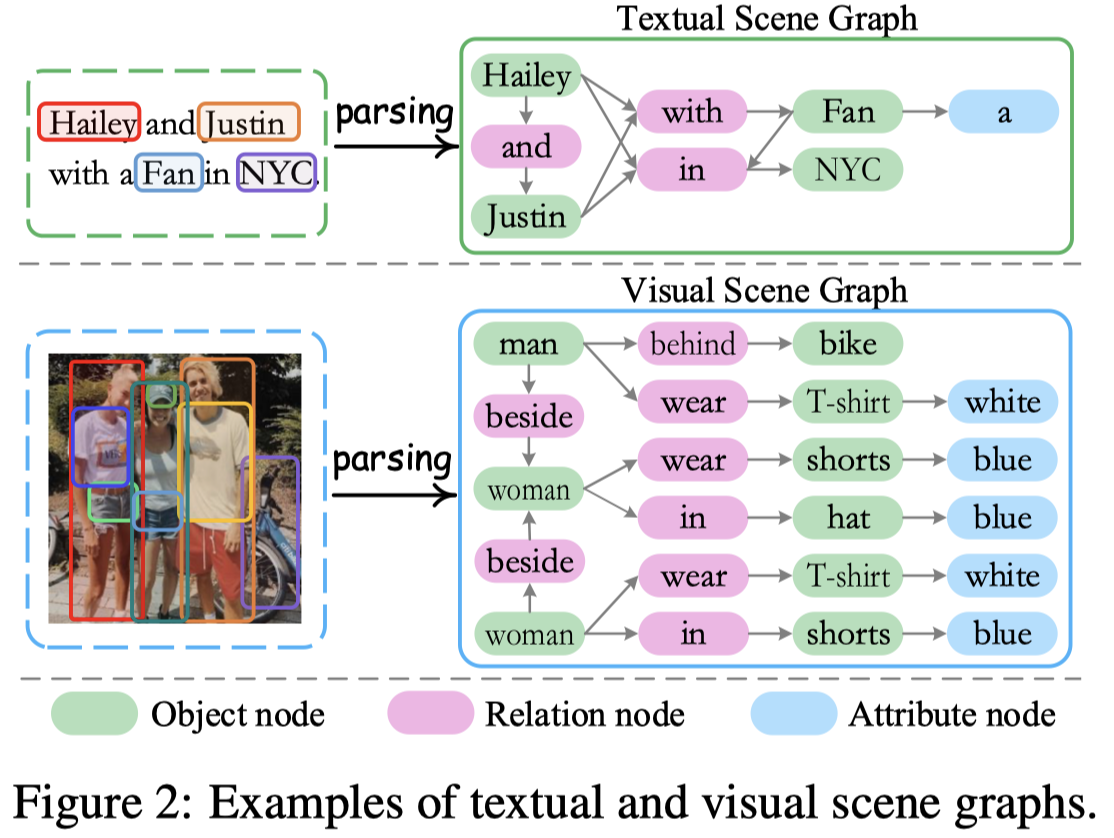
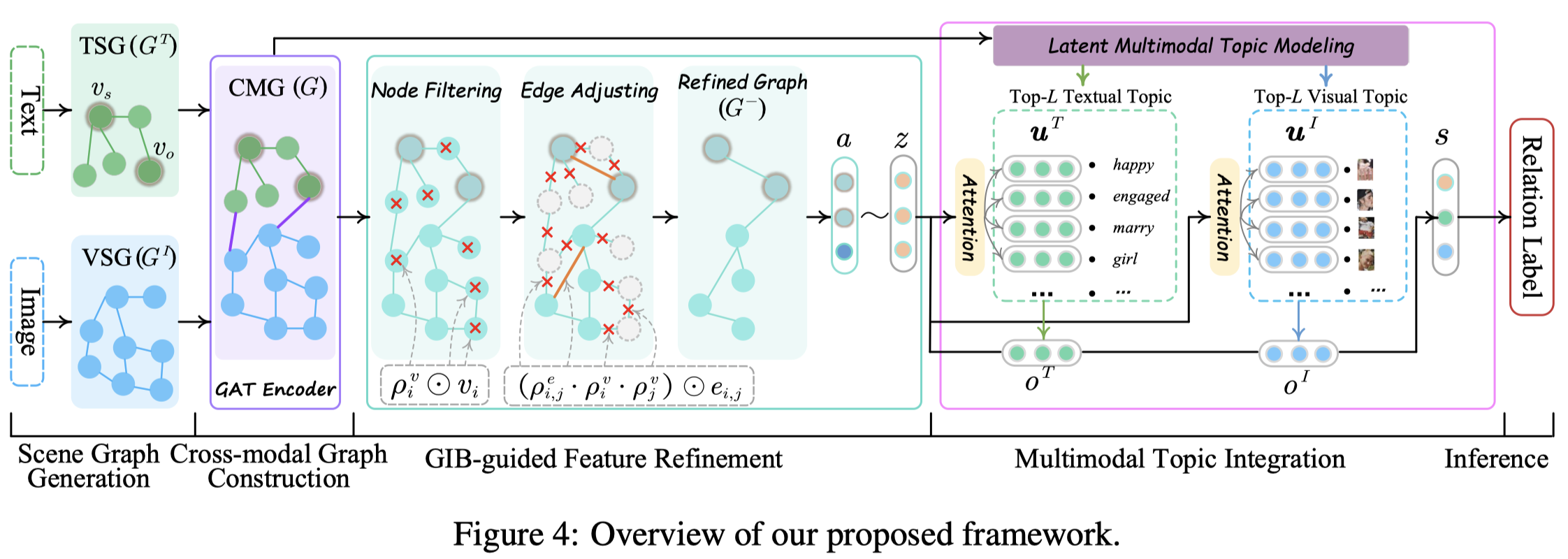
场景图包括三类node:object node, attribute node, and relationship node。
作者构造跨模态场景图Cross-modal Graph(CMG)的时候,先是调用外部工具分别处理image和text,然后基于相似度(超过阈值\(0.25\))进行跨模态链接。
作者使用2层GAT对graph进行建模。
为了保留有用的object,而去除噪音,作者引入信息瓶颈理论information bottleneck:
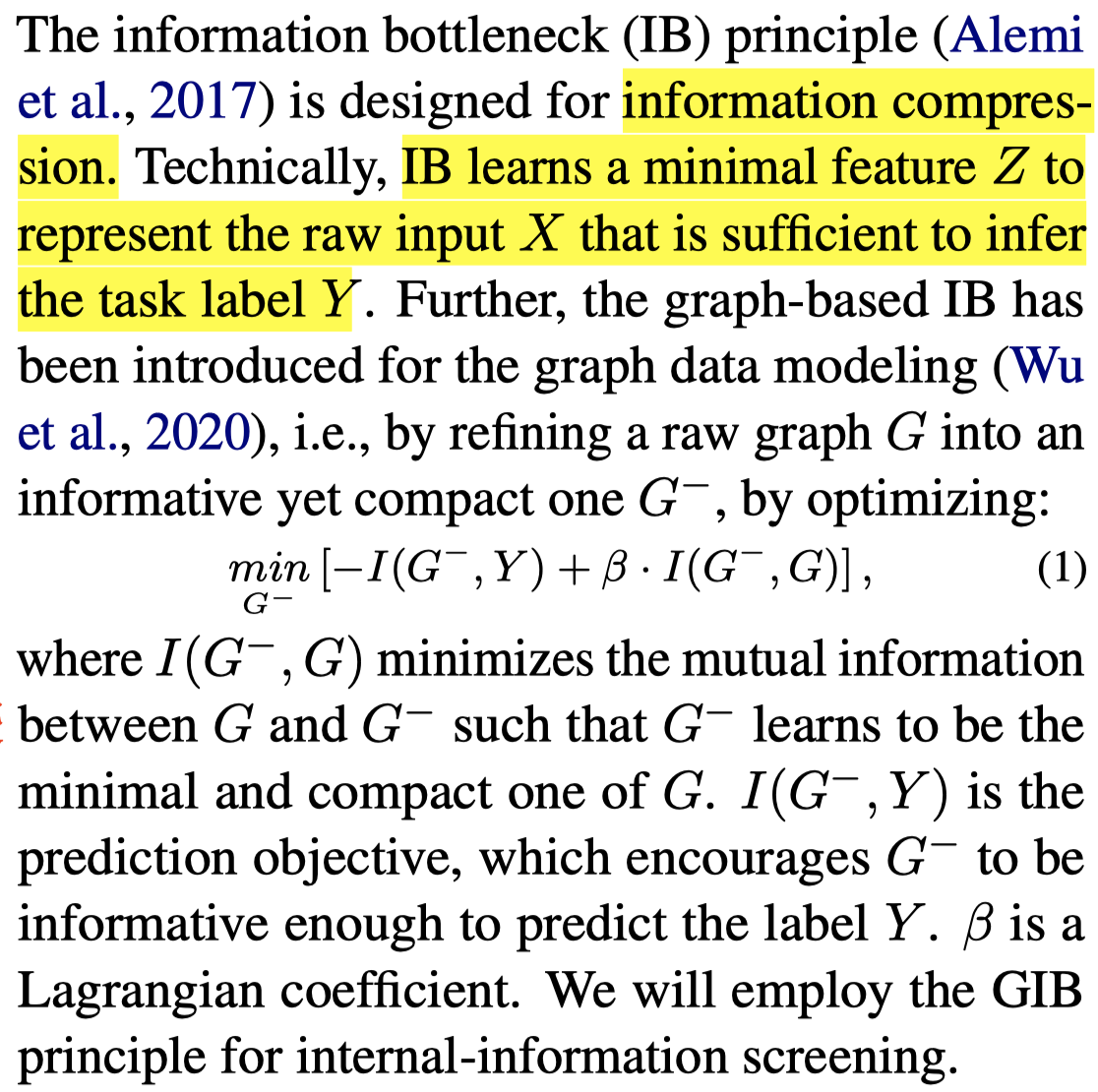
也就是学习新的缩减后的graph \(G^{-}\),期望它与原始graph的互信息最小,与预测目标\(Y\)互信息最大。
因此,需要对原始graph进行裁剪:
Node Filtering:作者使用了一个可微分的逼近伯努利分布的策略,使用考虑node的周围邻居以及目标entity pairs的上下文,从而计算\(\pi\)值:
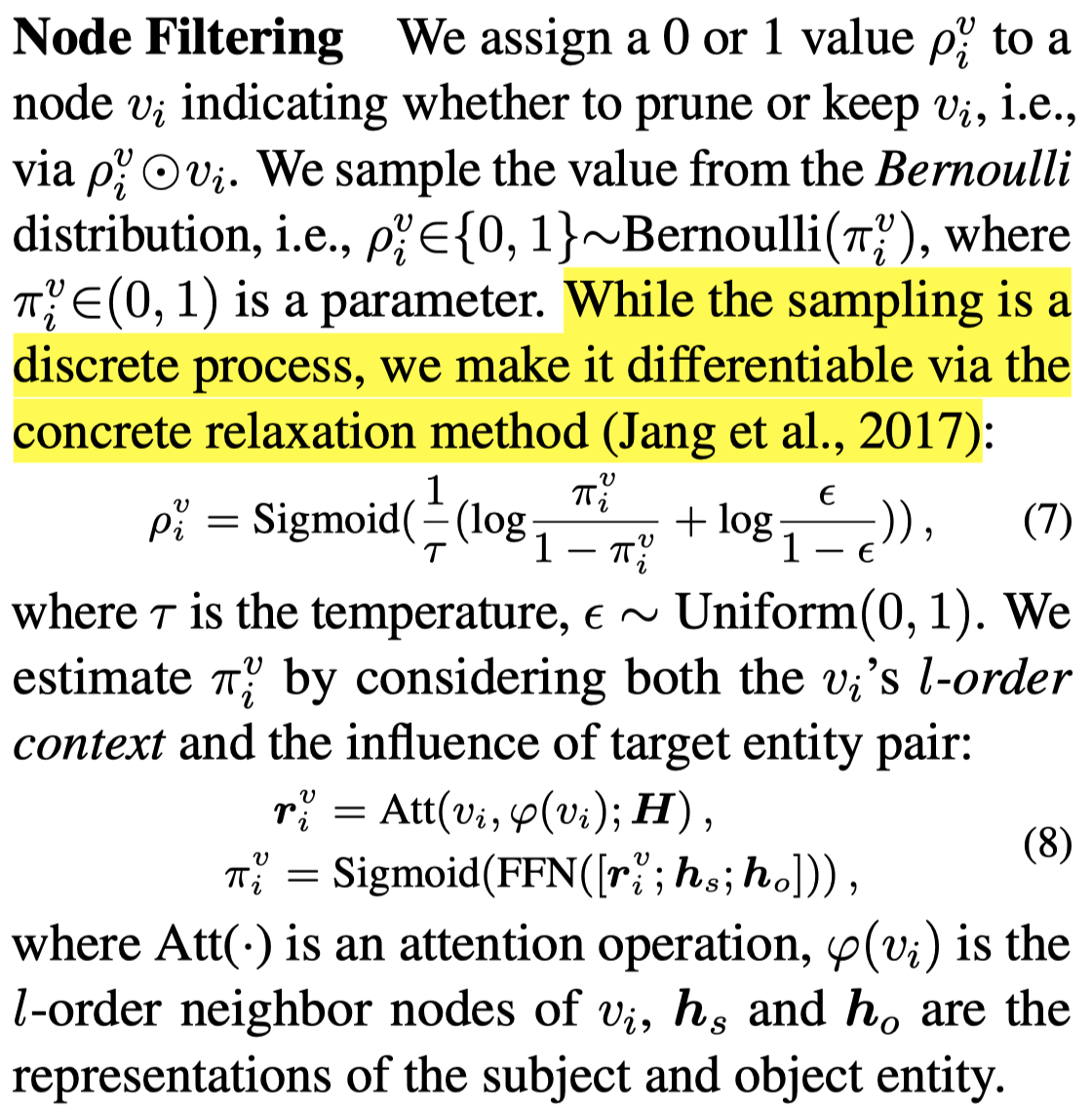
Edge Adjusting:采用同样的方法使用edge两端的node的表示估计\(\pi\)值判断edge是否存在。同时,如果任意端的node不存在,当然这个edge也不会存在。
利用GAT在裁剪后的graph \(G^-\)上学习新的图表示,用平均池化操作得到总体图的表示,再结合头尾实体的表示获得context feature:
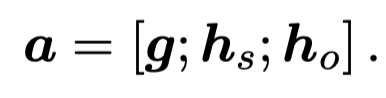
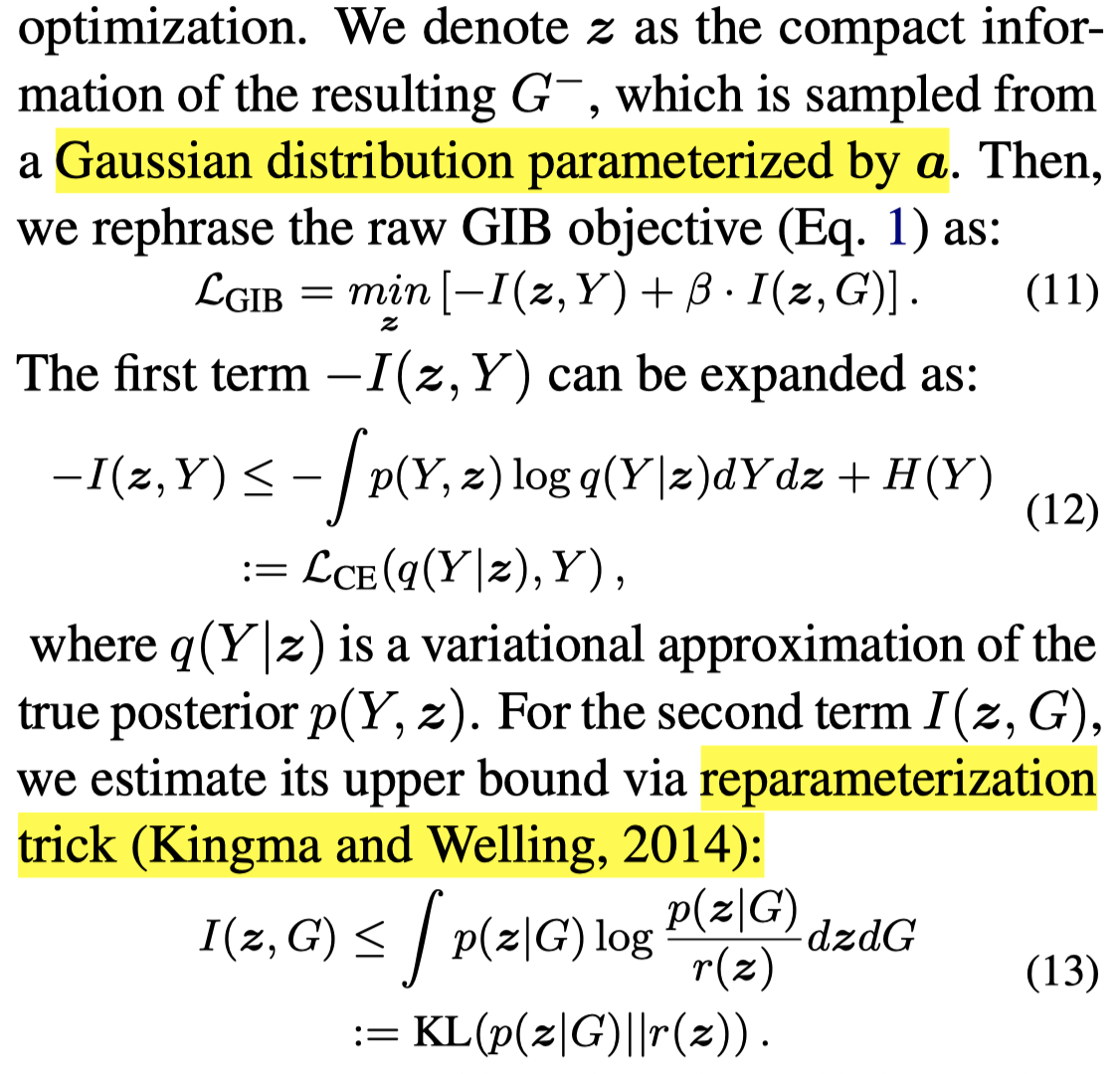
接下来就是如何在信息瓶颈理论下优化\(G^-\),作者利用context feature建立一个高斯分布,从中获得\(G^-\)的压缩表示\(z\),从而优化:
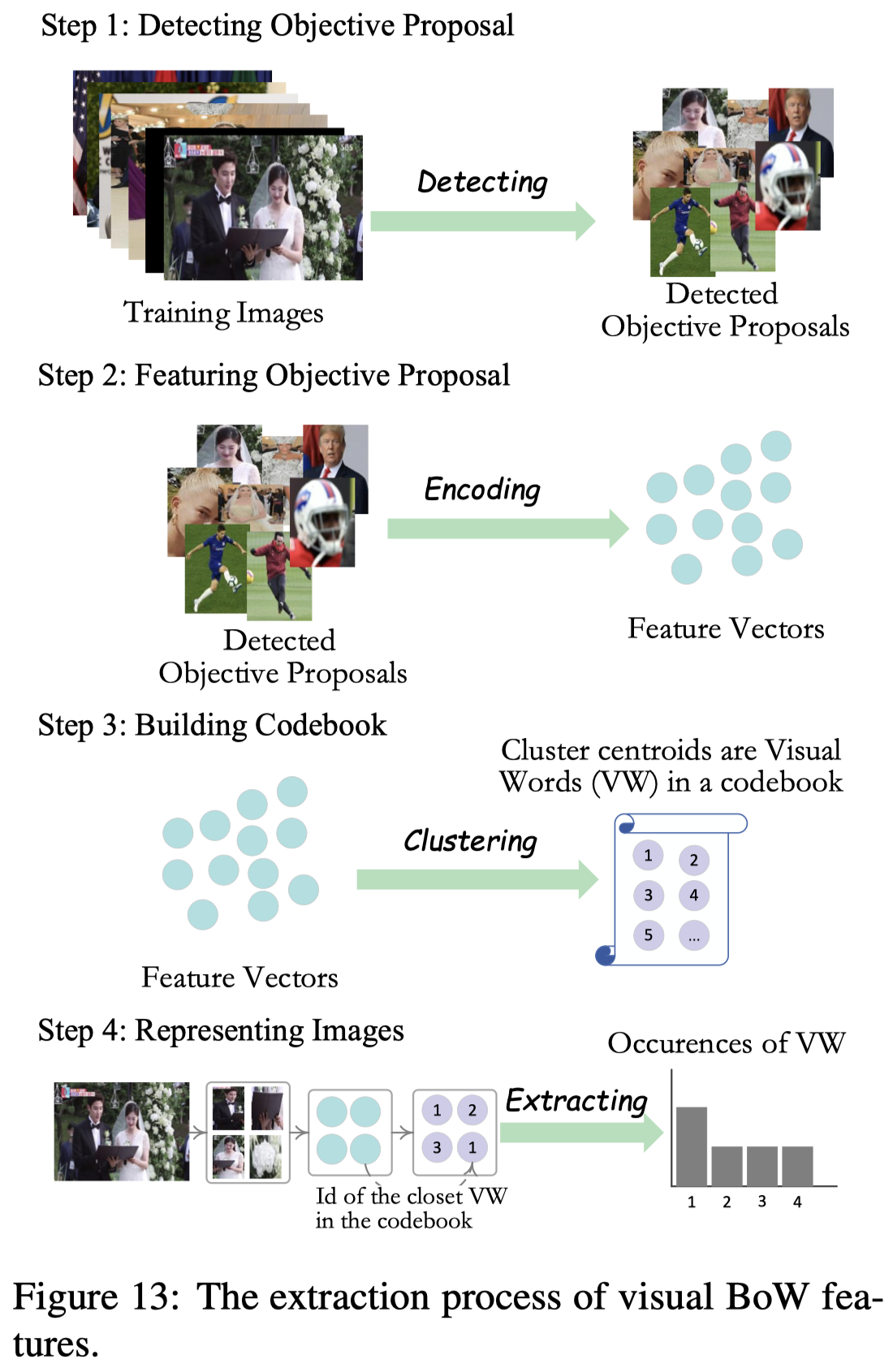
此外,为了获得额外的信息,作者使用隐式主题模型,通过所有训练集中的text和image,构造text词袋和visual词袋,聚类之后类的中心就作为对应的候选topic。下面是创建visual词袋的过程:
某个sample对应的主题的推算是基于Latent Multimodal Topic Modeling:
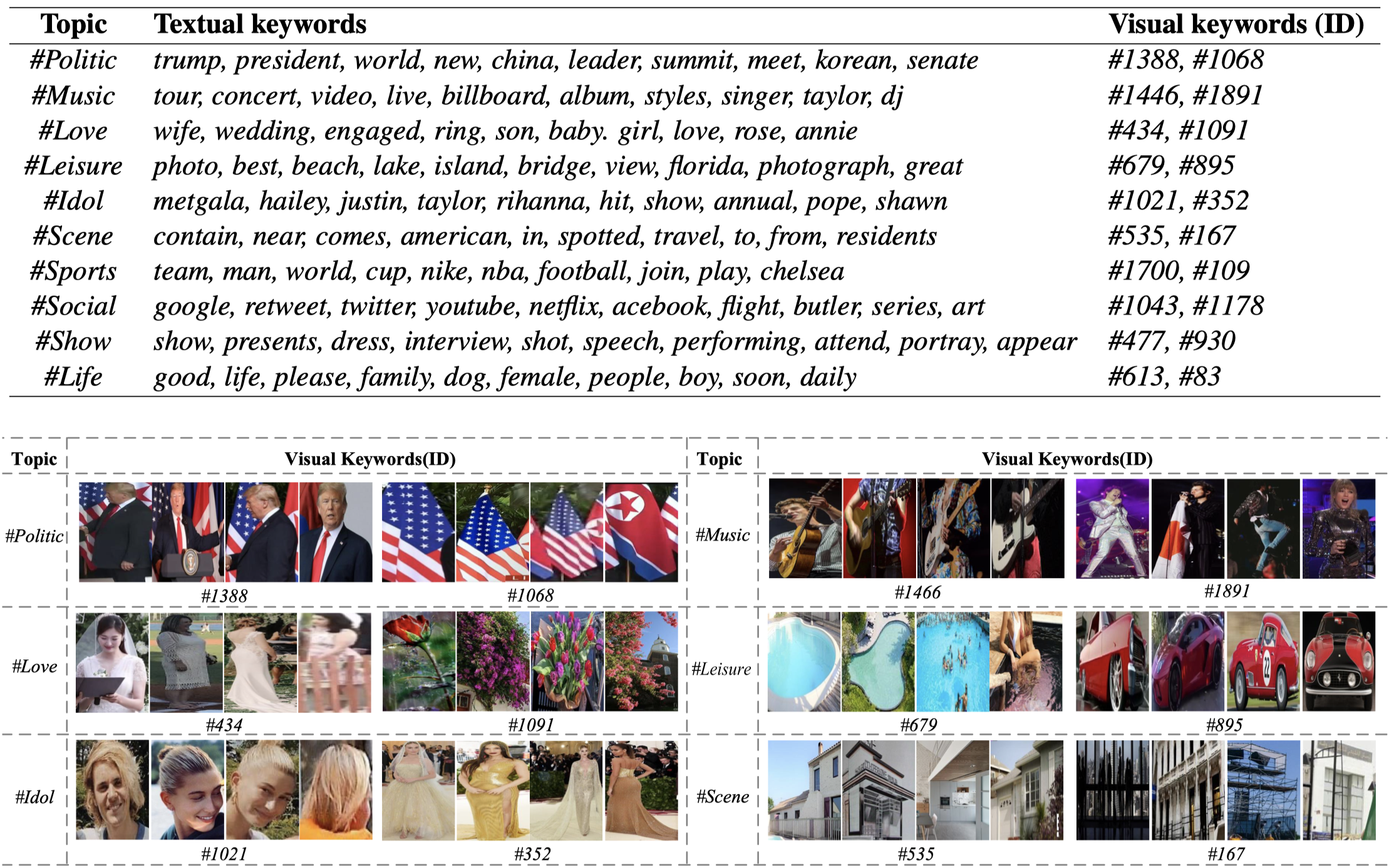
作者方法在MNRE数据集上的实验结果:

一些主题的case:
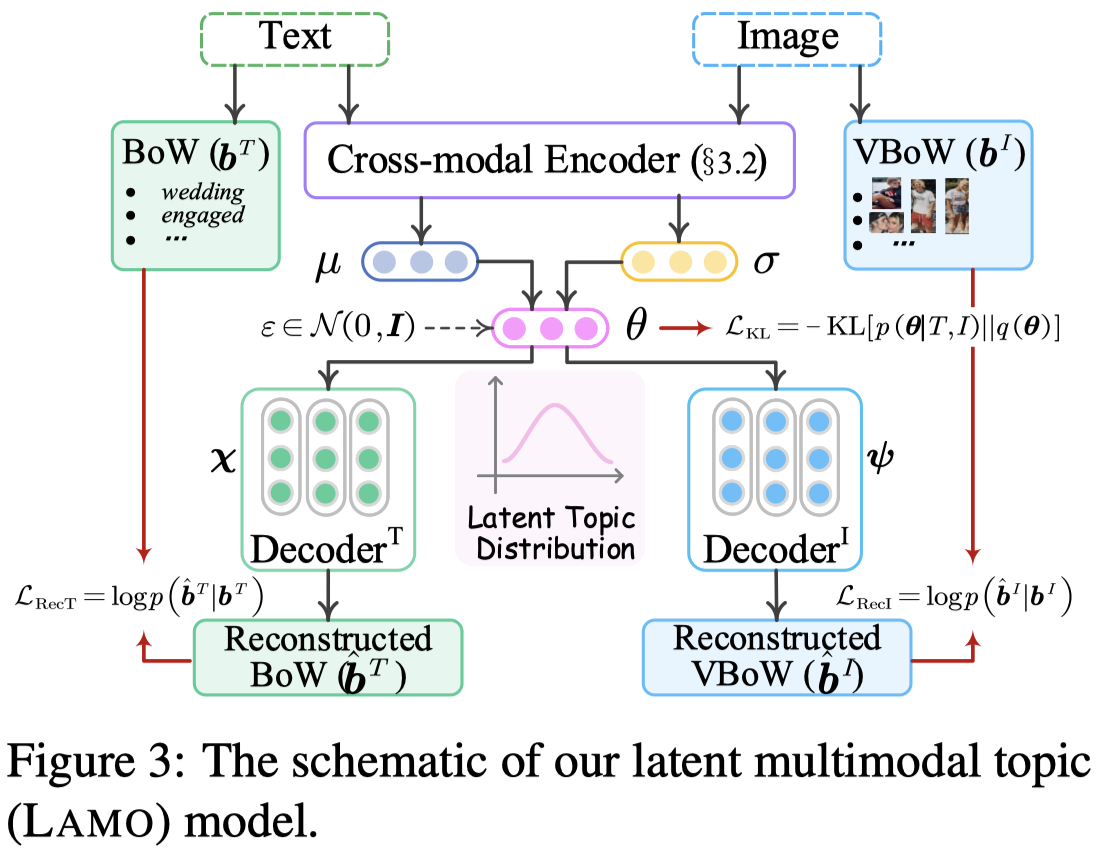
TMR
Rethinking Multimodal Entity and Relation Extraction from a Translation Point of View. 香港理工. ACL 2023. 代码.
We revisit the multimodal entity and relation extraction from a translation point of view. Special attention is paid on the misalignment issue in text-image datasets which may mislead the learning. We are motivated by the fact that the cross-modal misalignment is a similar problem of cross-lingual divergence issue in machine translation. The problem can then be transformed and existing solutions can be borrowed by treating a text and its paired image as the translation to each other. We implement a multimodal back-translation using diffusion-based generative models for pseudo-paralleled pairs and a divergence estimator by constructing a high-resource corpora as a bridge for low-resource learners. Fine-grained confidence scores are generated to indicate both types and degrees of alignments with which better representations are obtained. The method has been validated in the experiments by outperforming 14 state-of-the-art methods in both entity and relation extraction tasks. The source code is available at https://github.com/thecharm/TMR.
Issue: 作者认为MIE中的图文对存在两种misalignment:

对于部分misalignment,实体可能会被错误的对应到图像上的信息;而对于完全无关的image,image只能够提供无用的信息。
Solution: 作者首先提出,把text看做是image的target,借助back-translation的思想,再从text翻译回image。利用stable diffusion模型生成对齐程度更好的image:
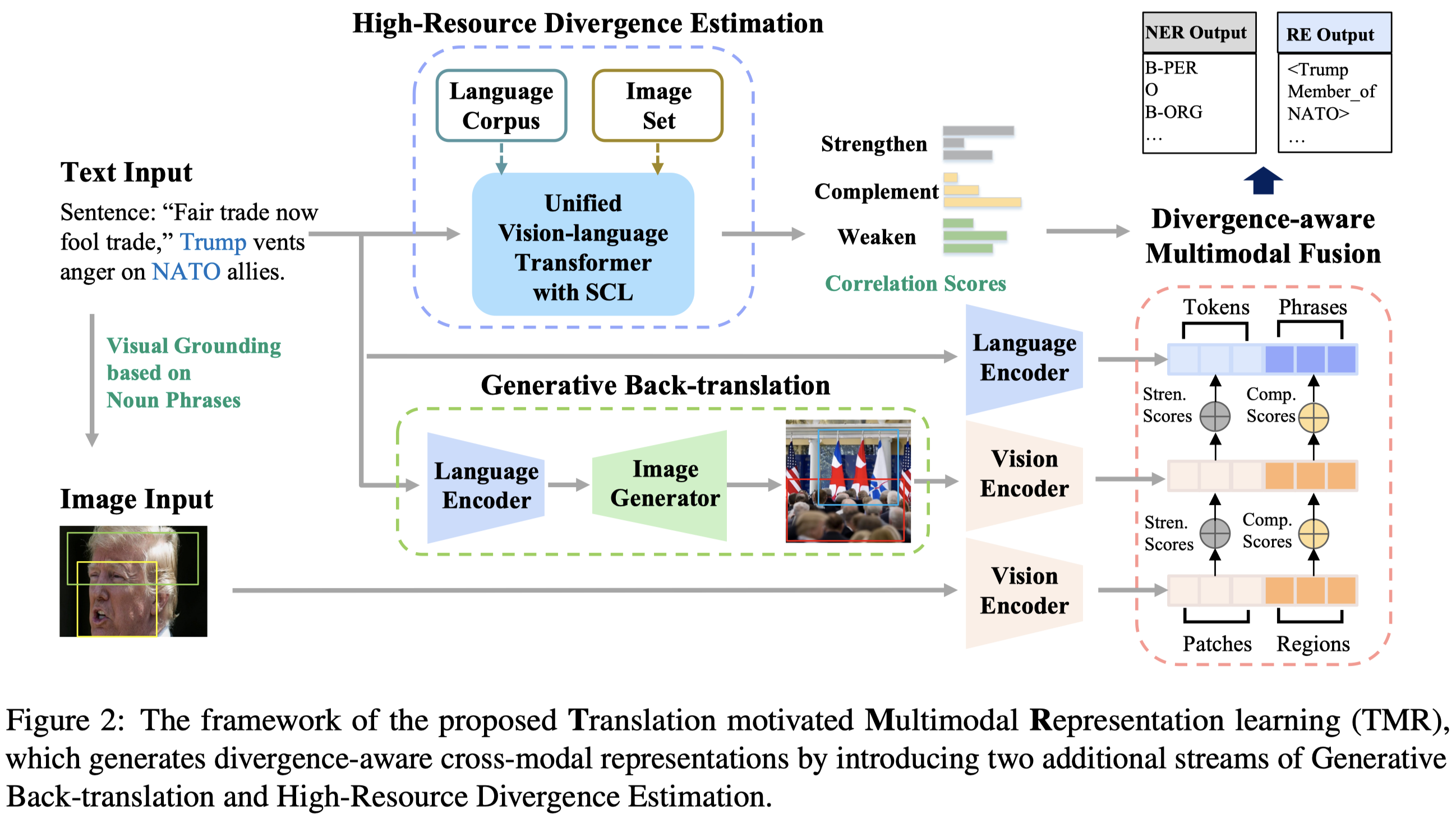
原始的image \(v\),生成的image \(v^\prime\)和原始文本 \(t\),分别组成图文对。
作者考虑了不同粒度的表示,对于文本a text is tokenized into words and phrases,对于图像an image is tokenized into patches and regions. 然后word-patch进行细粒度表示,phrase-region进行粗粒度表示。
文本的embedding是用BERT编码;图像的embedding使用ResNet50编码。
编码后,通过下面的Transformer可以获得多模态表示:
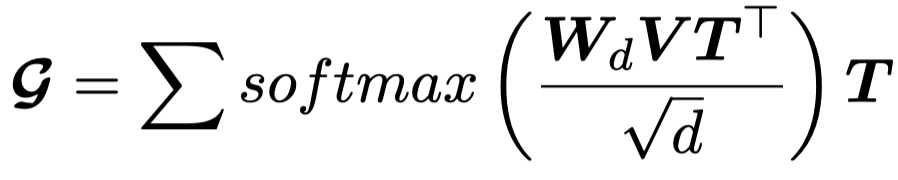
粗粒度表示与细粒度表示相加,就可以分别获得原始图文对的多模态表示\(G\)和生成图文对的多模态表示\(G^\prime\)。
作者额外建立了一个Multimodal Divergence Estimator(MDE),用来判断原始图文对的相关性:strengthen, complement, weaken。
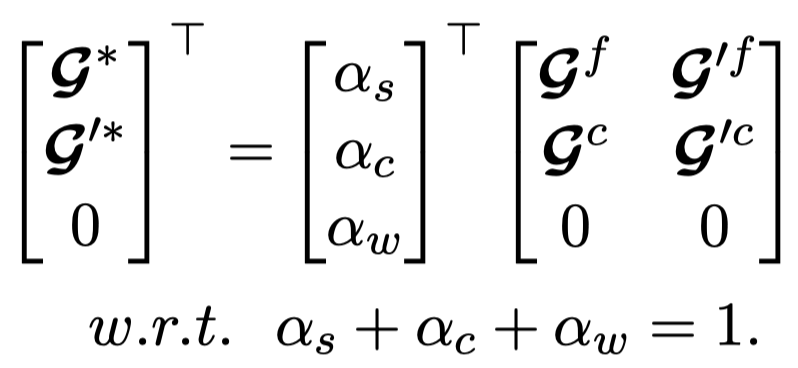
也就是说,如果判断图文关联属于strength,就更多采用细粒度多模态表示,否则就更多采用粗粒度表示。
为了训练MDE,作者利用外部数据构造训练集,利用MSCOCO的数据作为“strengthen”;利用LAION-400M的数据作为“complement”,利用随机替换前两者对应image作为“weaken”。
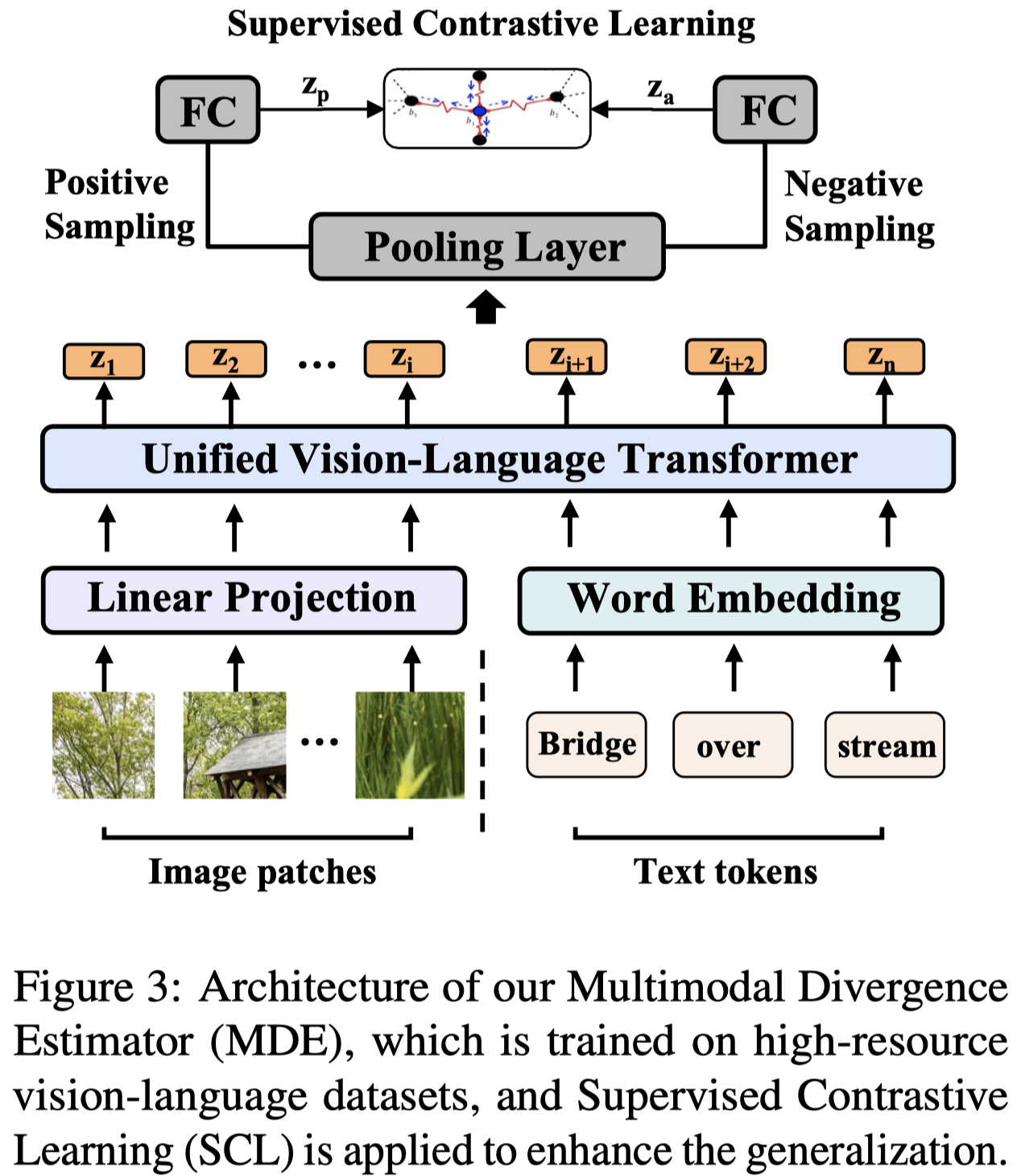
MDE的结构基于ViLT。由于作者的3个class是来自于2个不同的数据集,直接使用交叉熵可能会导致model直接根据领域特征预测class,例如总是对MSCOCO的数据预测Strengthen。因此作者训练过程使用对比损失训练,拉近positive之间的距离。
对于MNER任务,作者把最终的两种多模态表示,再利用多头机制进行融合,结合CRF进行预测。
对于MNRE任务,作者拼接the representations of textual entities, fine-grained and coarse-grained image-text pairs, as well as noun phrases to predict final relations,再进行预测:
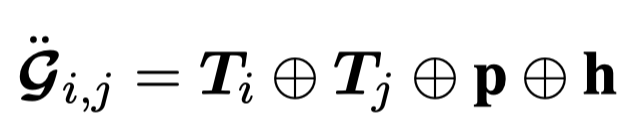
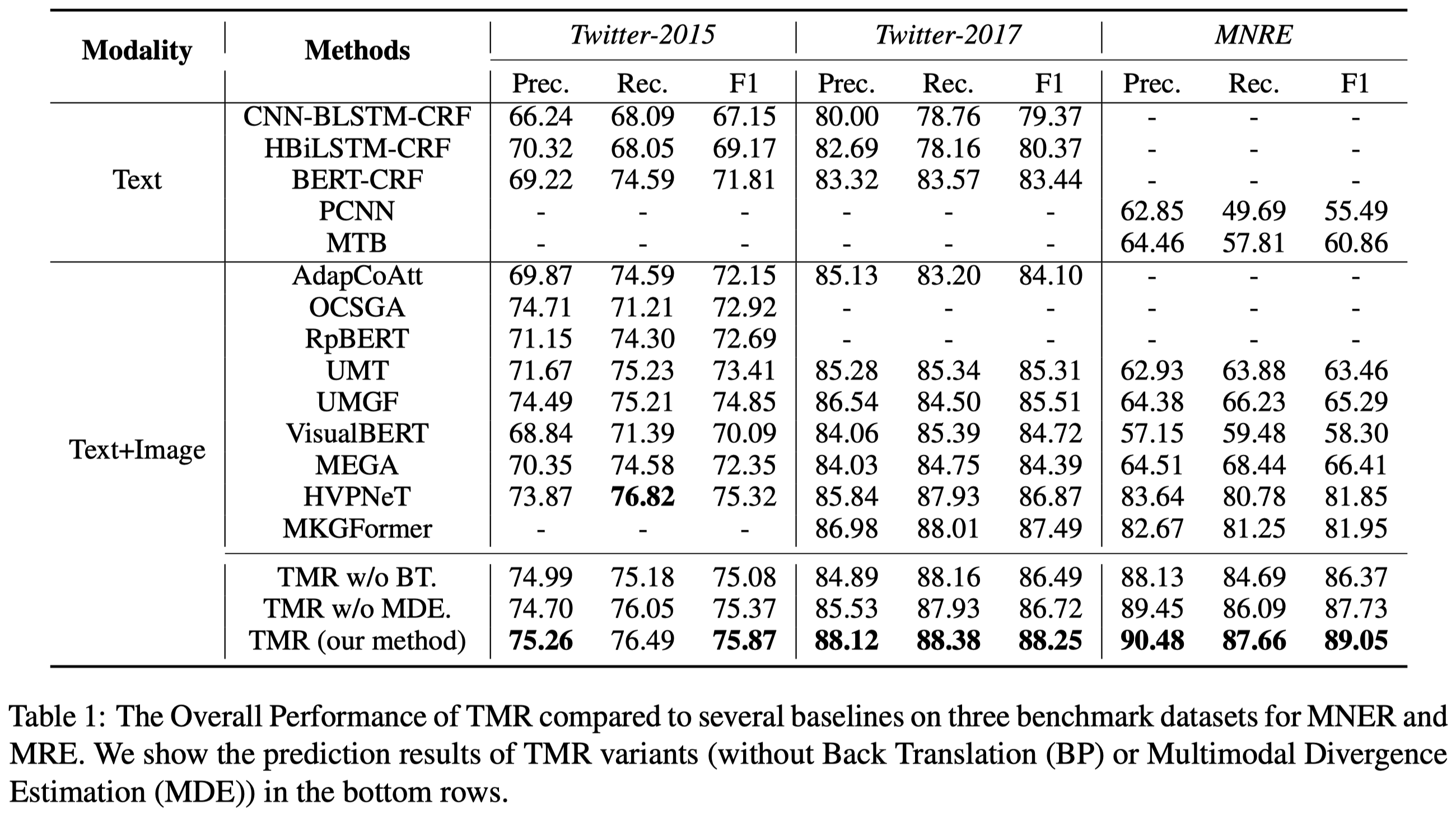
实验结果:
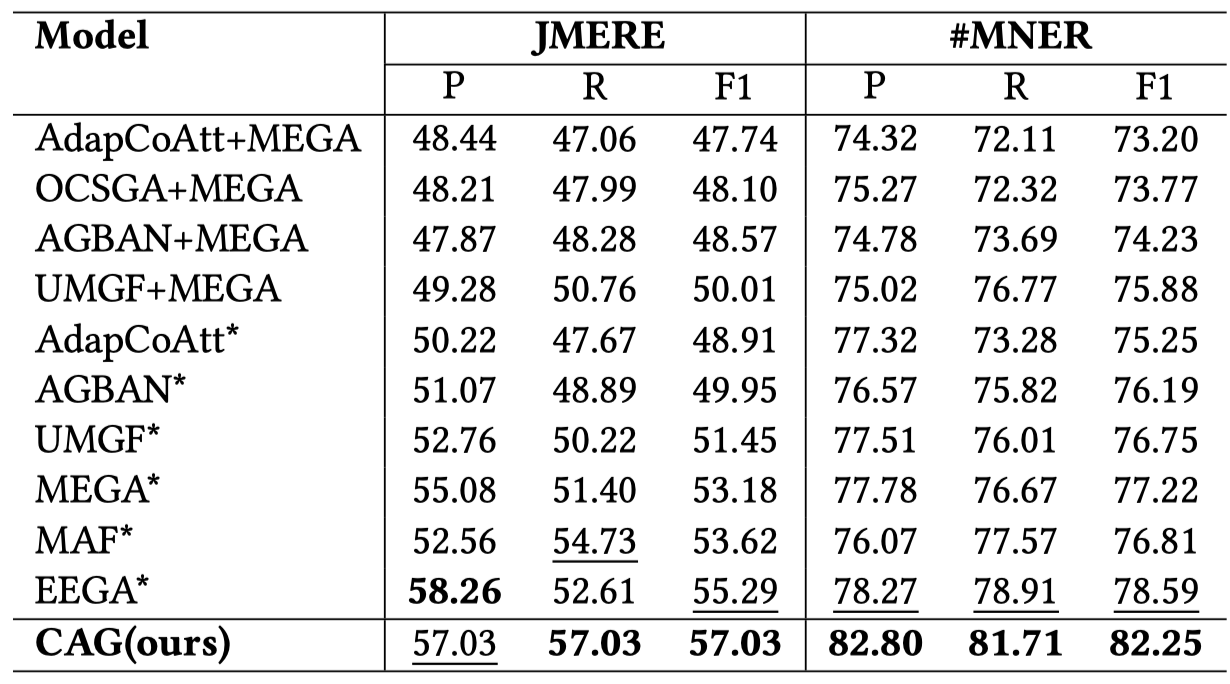
CAG
CAG: A Consistency-Adaptive Text-Image Alignment Generation for Joint Multimodal Entity-Relation Extraction. 北邮. CIKM 2024 Short. 代码.
Joint Multimodal Entity-Relation Extraction (JMERE) aims to extract entity-relationship triples in texts from given image-text pairs. As a joint multimodal information extraction task, it has attracted increasing research interest. Previous works of JMERE typically utilize graph networks to align textual entities and visual objects and achieve promising performance. However, these methods do not pay attention to the inconsistency between text and image and the straight alignment could limit the performance of JMERE models. In this paper, we propose a Consistency-adaptive text-image Alignment Generation (CAG) framework for various text-image consistency scenarios. Specifically, we propose a Consistency Factor (CF) to measure the consistency between images and texts. We also design consistency-adaptive contrastive learning based on CF, which can reduce the impact of inconsistent visual and textual information. Additionally, we adopt JMERE-specifical instruction tuning for better entity-relationship triplet generation. Experimental results on the JMERE dataset demonstrate that our proposed CAG is effective and achieves state-of-the-art performance.
Issue:作者认为以前的MIE方法直接把image投影到text空间中,忽略了text和image之间的不一致性:

对于弱一致的情况,如果直接把image投影到text可能造成错误的情况。
Solution:作者从embedding空间中,衡量text和image的一致性;然后利用对比损失,让强一致的text和image表示更加靠近;而弱一致的text和image相对没有那么靠近。
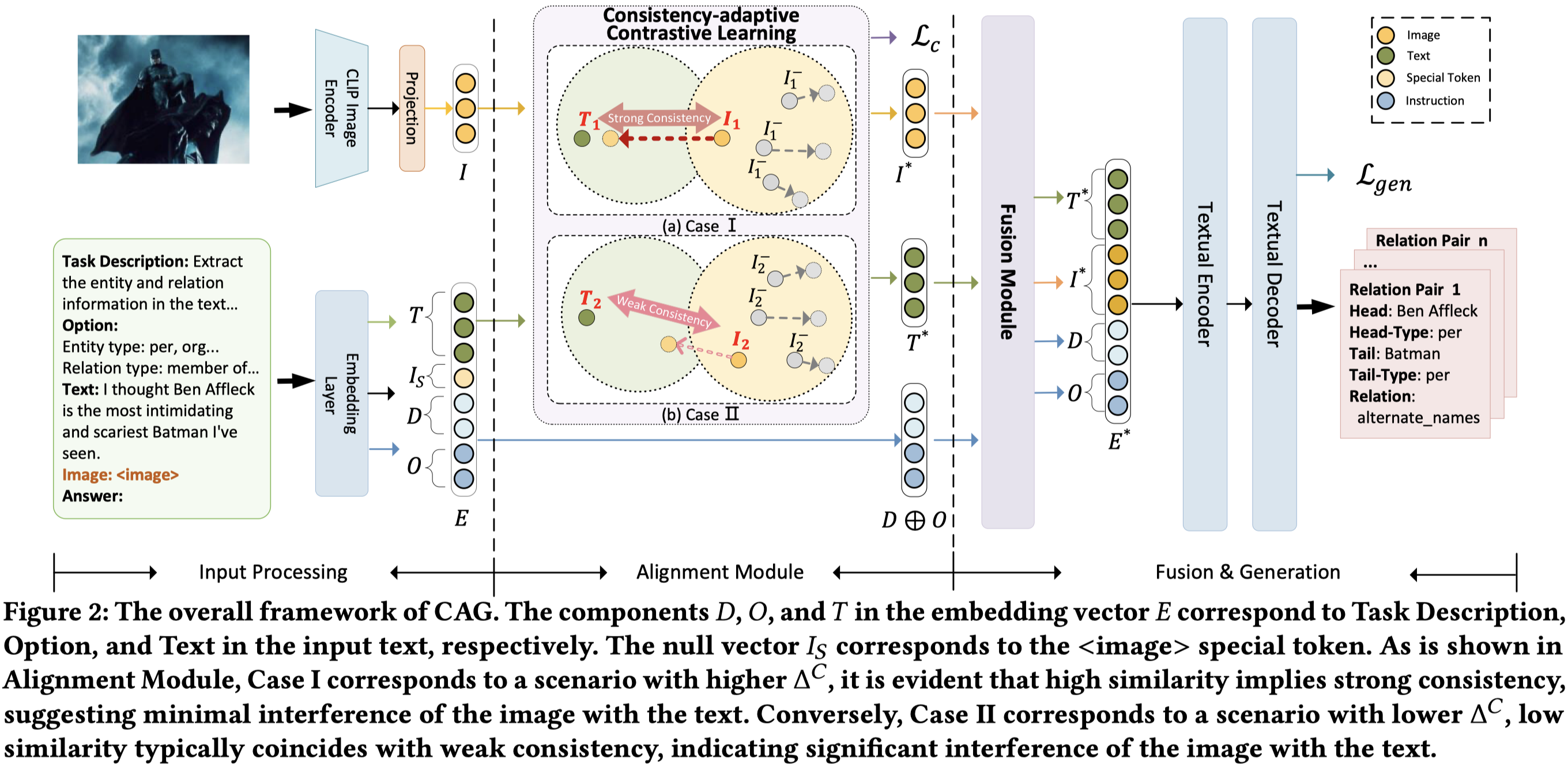
作者的方法基于Flan-T5,使用CLIP进行image编码。Flan-T5接收抽取task instruction、options包括所有头尾实体type、原始文本、以及image的placeholder。输入到T5 encoder中获得对应的embedding。
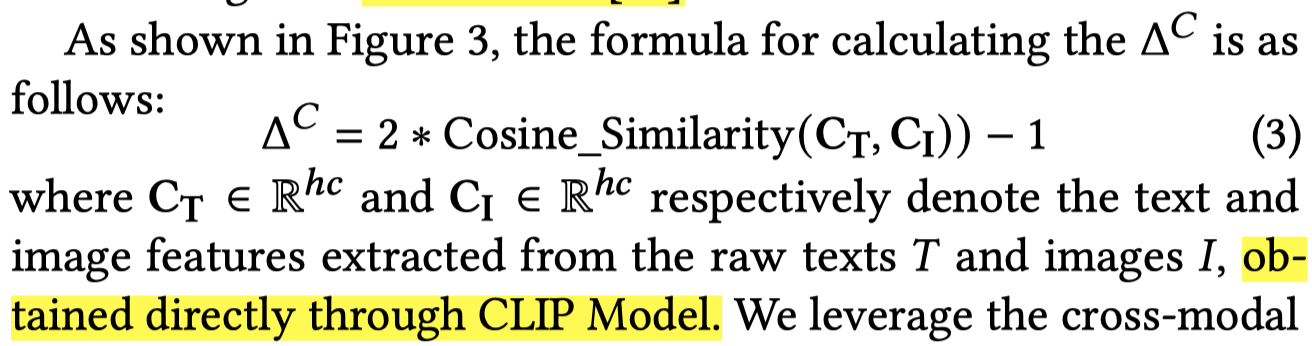
下面是作者衡量一致性的方法,直接借助CLIP的思想:
在估计了整体的一致性后,通过一致性来调整对比损失中的\(\tau\)值:
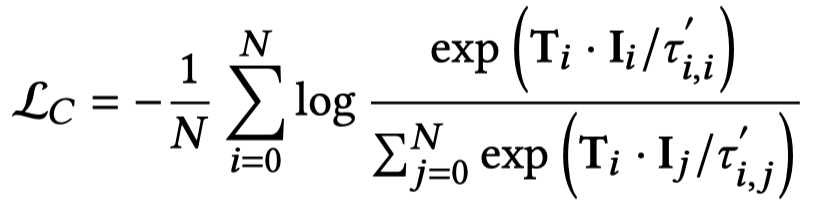 \[
\tau^\prime_{i,j}=\tau*(1-\alpha*\Delta_{i,j}^C)
\] 具有强一致性的最后\(\tau_{i,j}\)更小,相当于惩罚系数越大,loss越关注该图文对,要求其text和image embedding更加相似。
\[
\tau^\prime_{i,j}=\tau*(1-\alpha*\Delta_{i,j}^C)
\] 具有强一致性的最后\(\tau_{i,j}\)更小,相当于惩罚系数越大,loss越关注该图文对,要求其text和image embedding更加相似。
T5的输出embedding中的text和image使用CLIP优化后的embedding,再输入decoder,准备输出目标抽取结果。