MCR-Collection1
Multimodal Coreference Resolution
多模态共指消解调研。
Who’s Waldo?
Who’s Waldo? Linking People Across Text and Images. ICCV 2021. 康奈尔大学. 代码.
We present a task and benchmark dataset for personcentric visual grounding, the problem of linking between people named in a caption and people pictured in an image. In contrast to prior work in visual grounding, which is predominantly object-based, our new task masks out the names of people in captions in order to encourage methods trained on such image–caption pairs to focus on contextual cues, such as the rich interactions between multiple people, rather than learning associations between names and appearances. To facilitate this task, we introduce a new dataset, Who’s Waldo, mined automatically from image–caption data on Wikimedia Commons. We propose a Transformer-based method that outperforms several strong baselines on this task, and release our data to the research community to spur work on contextual models that consider both vision and language. Code and data are available at: https://whoswaldo.github.io
Issue:之前的visual grounding评估,侧重于根据人的name来进行定位,这会导致一定程度的bias;
we observe that inferring associations based on expressions in person-centric samples—i.e. people’s names—could lead to problematic biases (e.g. with regards to gender)
而人类擅长重建text人物和视觉上的关联,即使不熟悉这个提到的具体人。
Solution:作者构造了一个benchmark,Who’s Waldo,强调如何根据context去推测被mask的person name 和visual objects的对应,注意下面case的name实际上都不会提供给model:

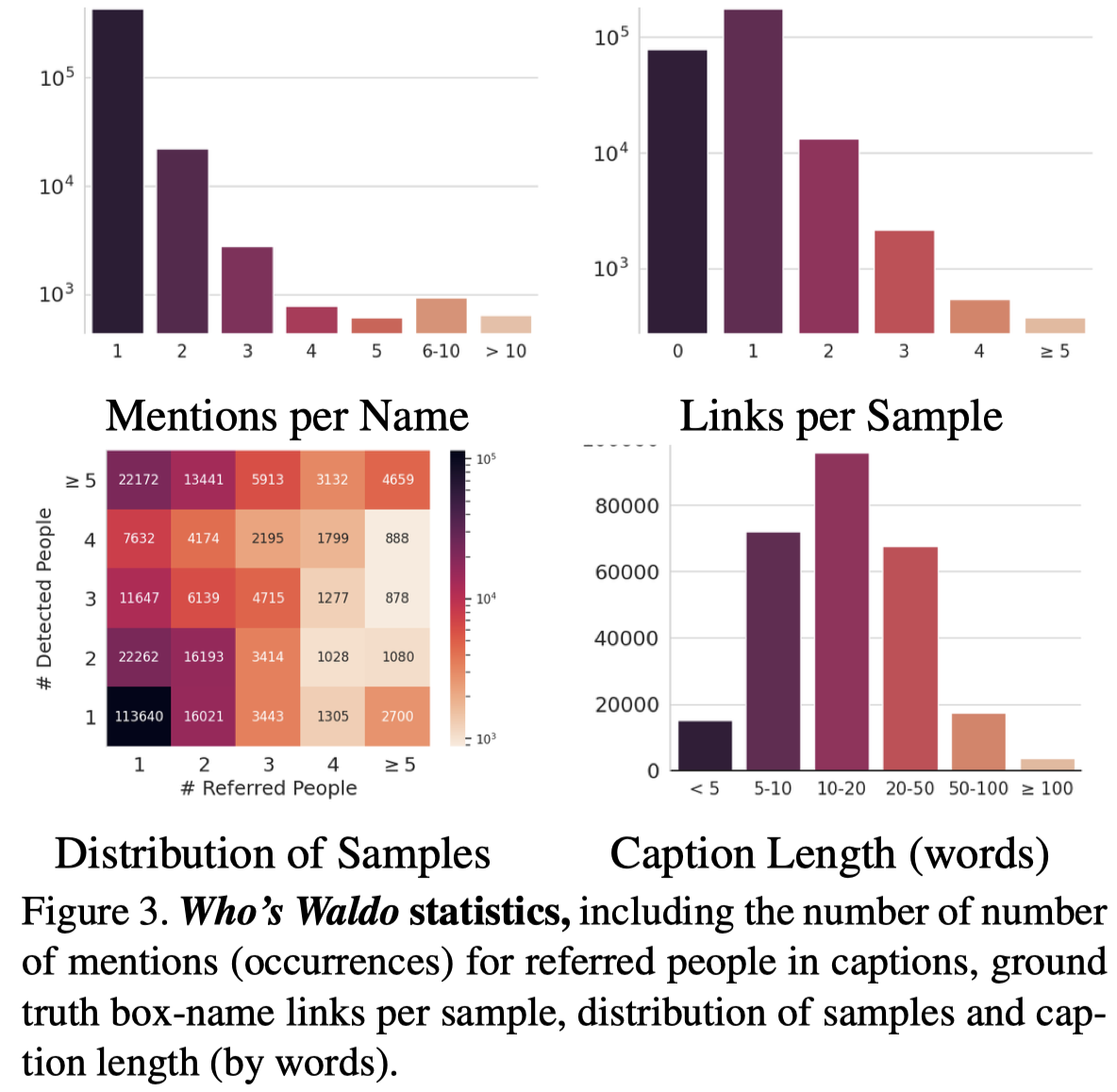
这个数据集使用image caption作为text,通常比较短。person name存在共指的情况,但是不是很频繁:
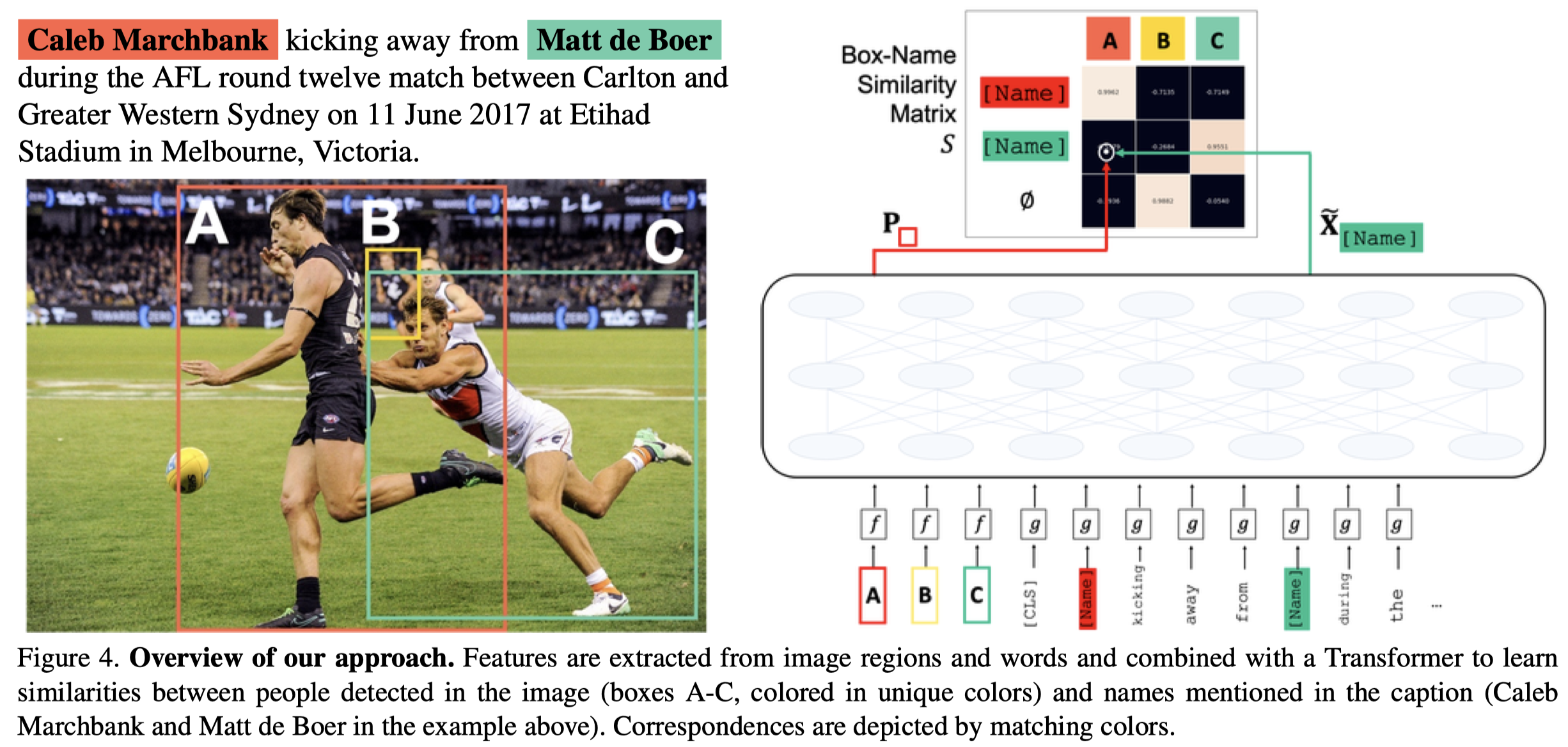
作者也提出了自己的方法:
VALSE
VALSE: A Task-Independent Benchmark for Vision and Language Models Centered on Linguistic Phenomena. 海德堡大学. ACL 2022. 代码.
We propose VALSE (Vision And Language Structured Evaluation), a novel benchmark designed for testing general-purpose pretrained vision and language (V&L) models for their visio-linguistic grounding capabilities on specific linguistic phenomena. VALSE offers a suite of six tests covering various linguistic constructs. Solving these requires models to ground linguistic phenomena in the visual modality, allowing more fine-grained evaluations than hitherto possible. We build VALSE using methods that support the construction of valid foils, and report results from evaluating five widely-used V&L models. Our experiments suggest that current models have considerable difficulty addressing most phenomena. Hence, we expect VALSE to serve as an important benchmark to measure future progress of pretrained V&L models from a linguistic perspective, complementing the canonical taskcentred V&L evaluations.
提出了一个新的benchmark VALSE用来评估pretrained V-L models对于不同粒度的语言学特征进行grounding的能力。
we lack detailed understanding of the extent to which such models are able to ground linguistic phenomena—from morphosyntax to semantics—in the visual modality.
从6个不同的方面进行评估,统计V-L model是否能够给出正确的答案:
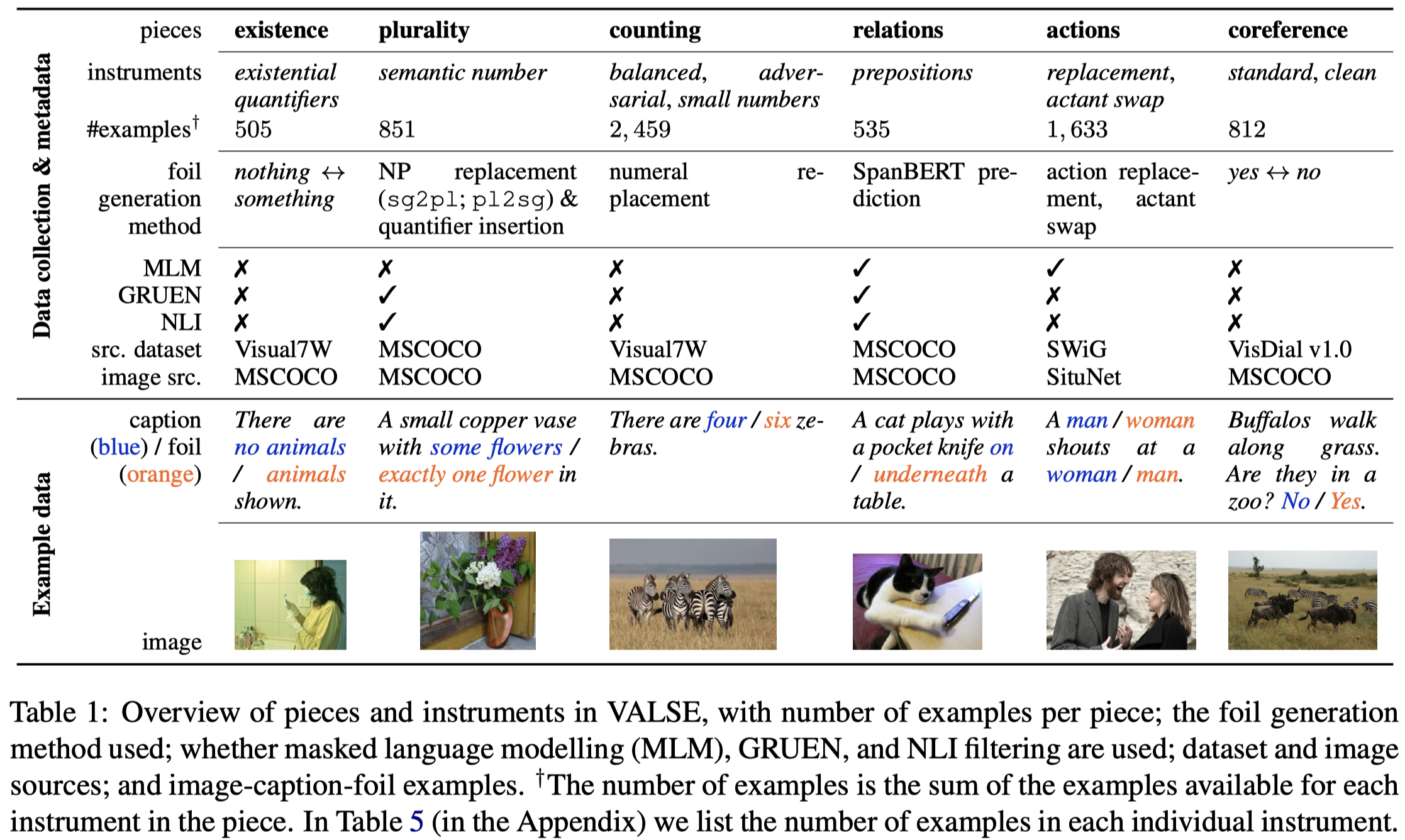
这里CR作为了benchmark的一个评估子任务,构造包括了共指场景的问题,让V-L model回答Yes/No,判断其是否能够理解共指任务。但是并没有要求V-L给出对应的bounding box,也没有真的判断代词和名词短语是否是指向同一object。
GRAVL-BERT
GRAVL-BERT: Graphical Visual-Linguistic Representations for Multimodal Coreference Resolution. COLING 2022. University of California. 代码.
Learning from multimodal data has become a popular research topic in recent years. Multimodal coreference resolution (MCR) is an important task in this area. MCR involves resolving the references across different modalities, e.g., text and images, which is a crucial capability for building next-generation conversational agents. MCR is challenging as it requires encoding information from different modalities and modeling associations between them. Although significant progress has been made for visual-linguistic tasks such as visual grounding, most of the current works involve single turn utterances and focus on simple coreference resolutions. In this work, we propose an MCR model that resolves coreferences made in multi-turn dialogues with scene images. We present G RAVL-BERT, a unified MCR framework which combines visual relationships between objects, background scenes, dialogue, and metadata by integrating Graph Neural Networks with VL-BERT. We present results on the SIMMC 2.0 multimodal conversational dataset, achieving the rank-1 on the DSTC-10 SIMMC 2.0 MCR challenge with F1 score 0.783. Our code is available at https: //github.com/alexa/gravl-bert.
Issue:MCR任务比纯文本的CR,以及一般的VQA任务、visual grounding任务更难。因为会使用不同的角度去描述objects,并且相比较visual grounding任务,具有更复杂的query:

作者关注的是多轮对话场景下task-oriented dialogues的MCR,关注query能够对应到那个image上的object。除了一般的textual conversation、scene image输入外,作者还考虑输入后端数据库内可能存在的object对应的metadata,比如商品的品牌、size、价格等。
Solution:作者方法的重点在于如何较好的对不同multimodal data进行编码:
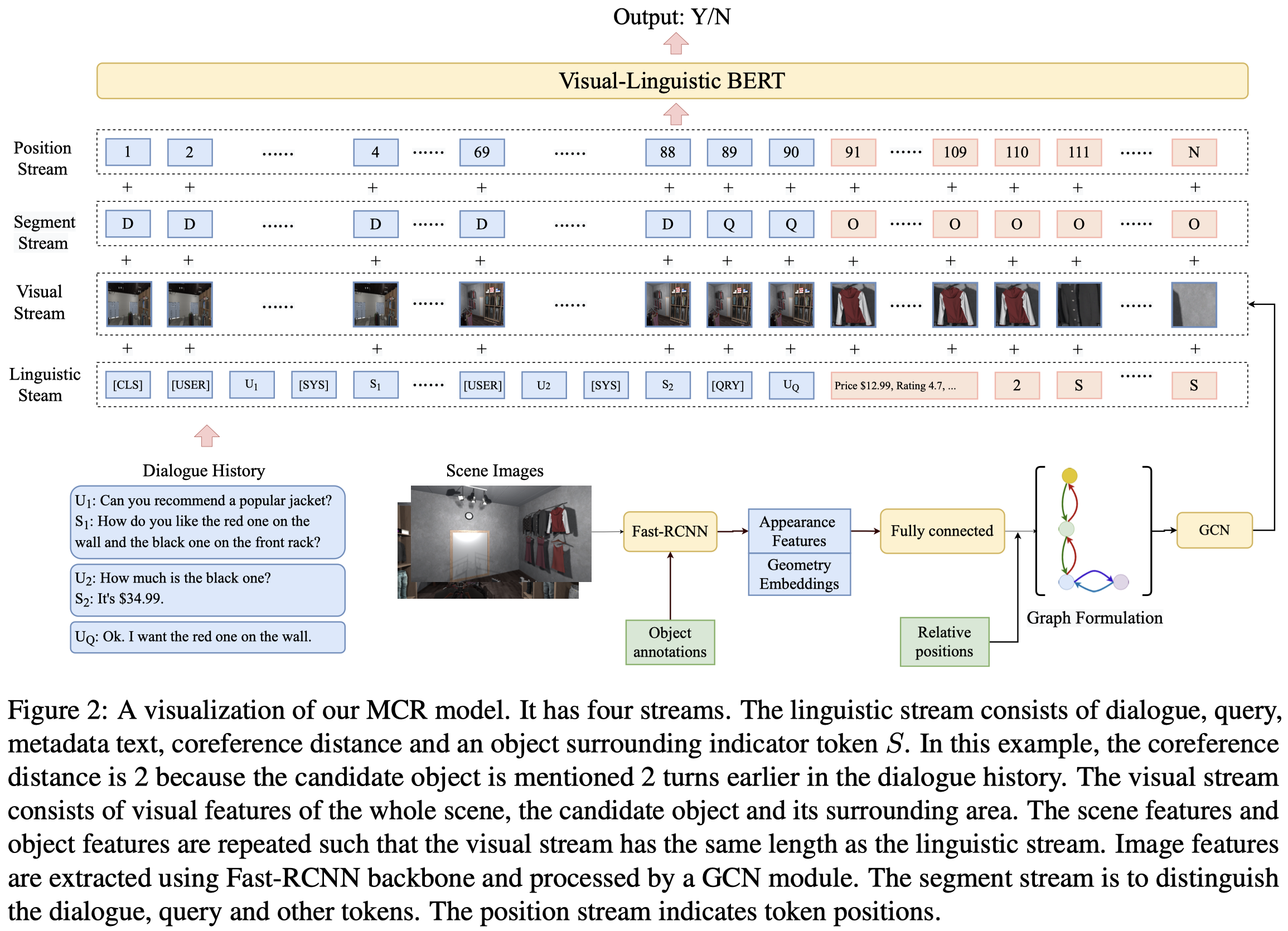
任务定义:


简单说是多轮文本对话输入,每一轮对话都有对应的图片,最后回答query是否提及某个visual object的0/1 binary classification task。
作者的输入有三个部分:
- The visual stream consists of the visual features from the whole scene, the candidate object and its surroundings.
- The linguistic stream includes the dialogue context, user query and candidate object’s metadata.
- The segment stream is used to distinguish the dialogue context, user query and object metadata inputs.
作者的模型每个单独判断1个visual object是否被最后的用户query提及。这样做的原因是因为在作者的任务场景image中,可能包括hundreds of objects,不可能把所有的objects都一起输入model。
对于image的处理是重点,作者先利用Faster-RCNN进行object detection,然后根据objects之间的上下左右空间关系建立一个graph。引入一个额外的节点node表示global image:
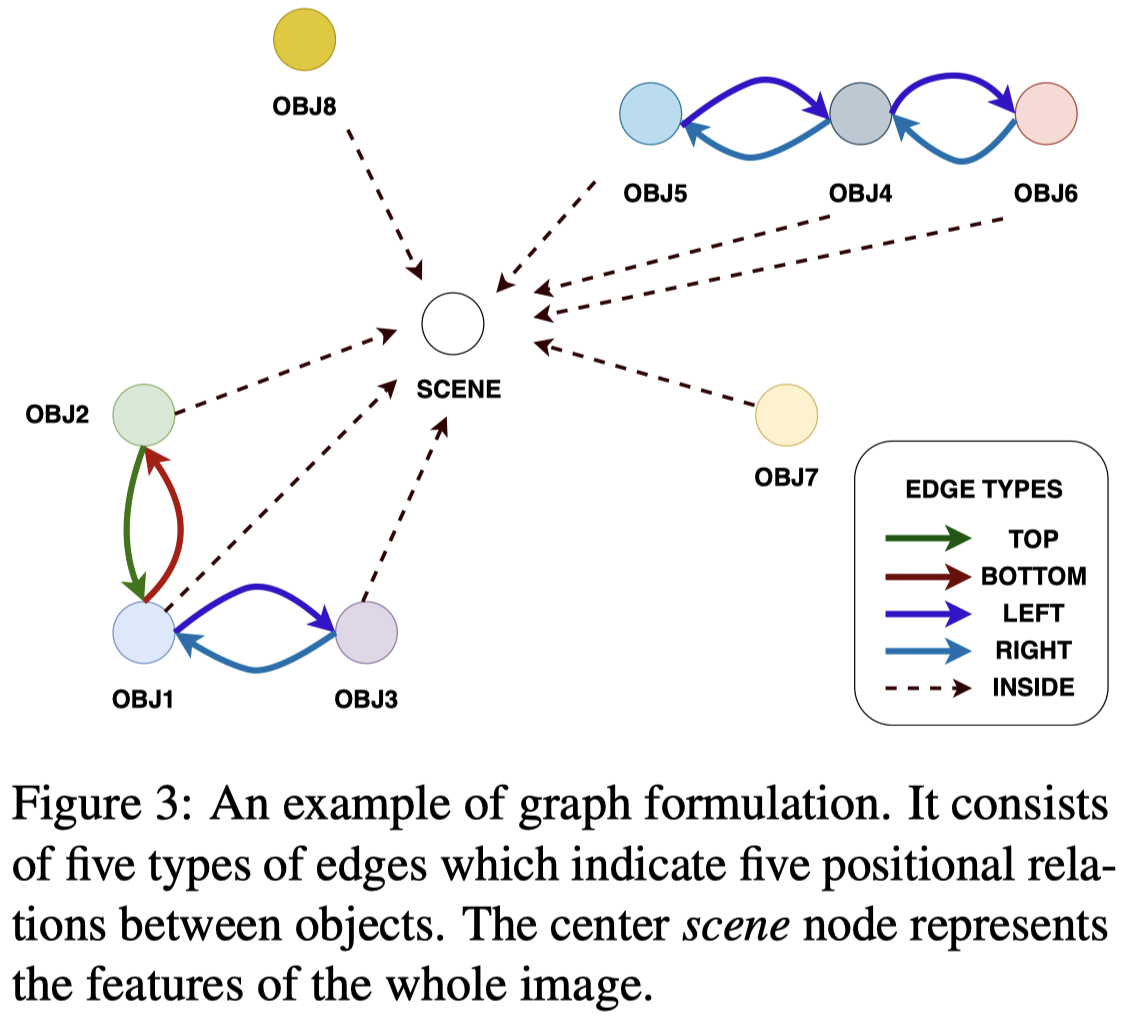
利用这个graph,作者使用FiLM-GCN (Brockschmidt, 2020)方法进行建模,学习node的表示。
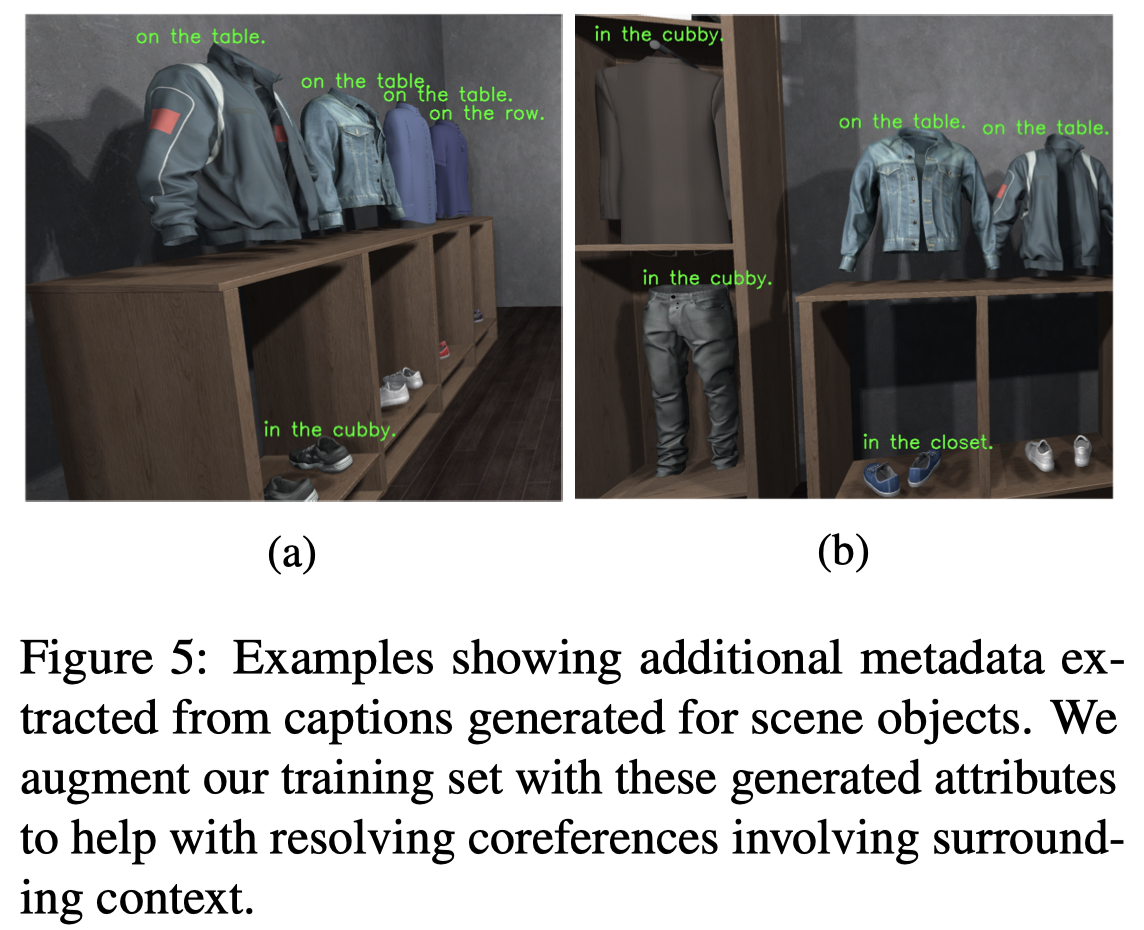
考虑到对于要查询的visual object周围的环境区域可能会被忽略,而在text描述的又常常用到,比如table、wall这些因素。作者使用两种方法策略来增强:
Object Surrounding: 作者从8个不同方向采样固定size的周围图像区域作为输入:

Image Captioning: 作者微调了一个Alexnet-LSTM captioning model来为每个object生成对应的caption来导出surrounding context,这些context会作为metadata一部分输入:
作者实验使用的数据集是Multimodal Conversations (SIMMC) 2.0 dataset(Kottur et al., 2021),里面是user-agent对话的,在家具店/服装店的VR图像下的对话。下面是一些case:

CIN/WS-MCR
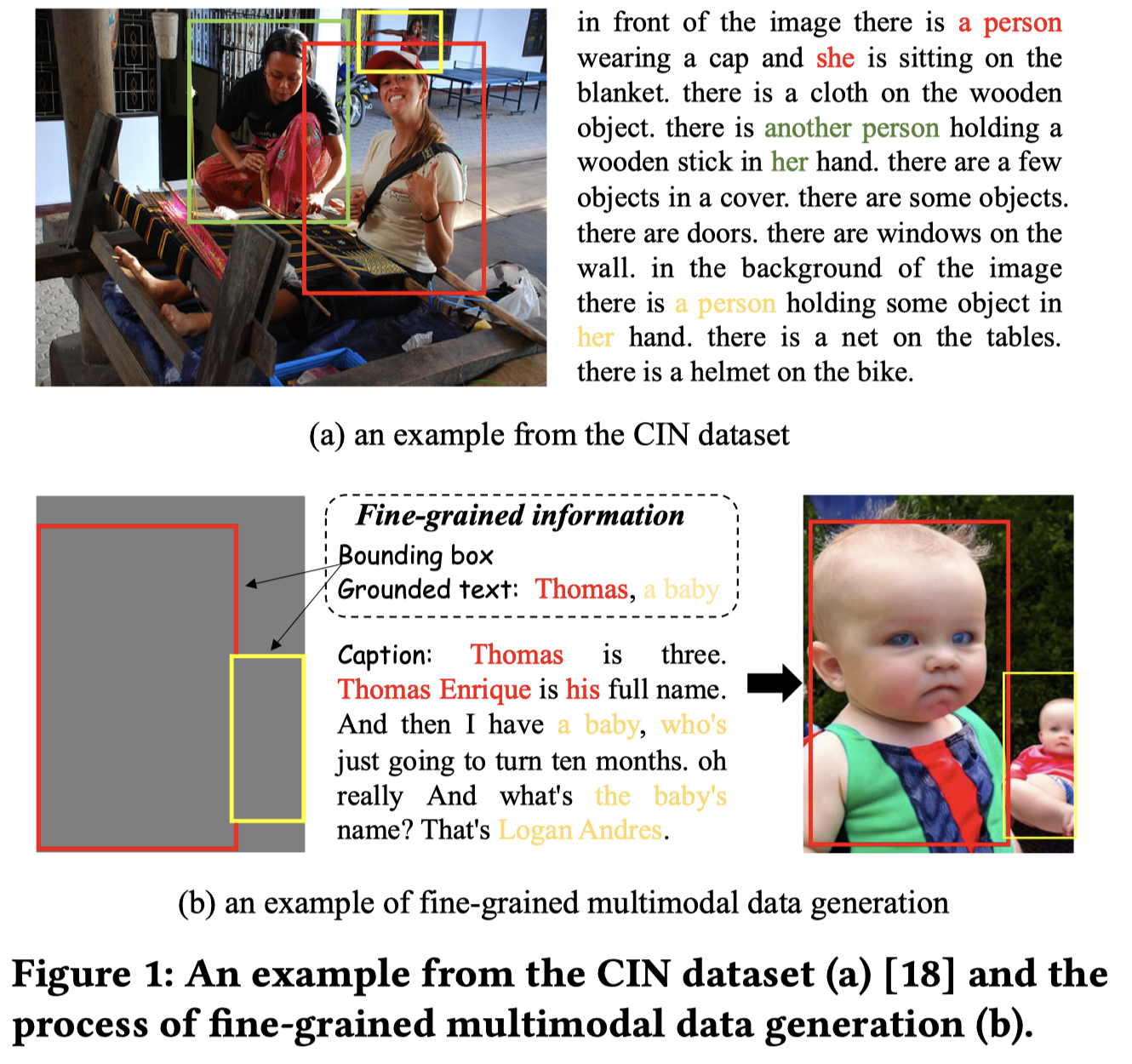
Who are you referring to? Coreference resolution in image narrations. 爱丁堡大学. ICCV 2023. 代码.
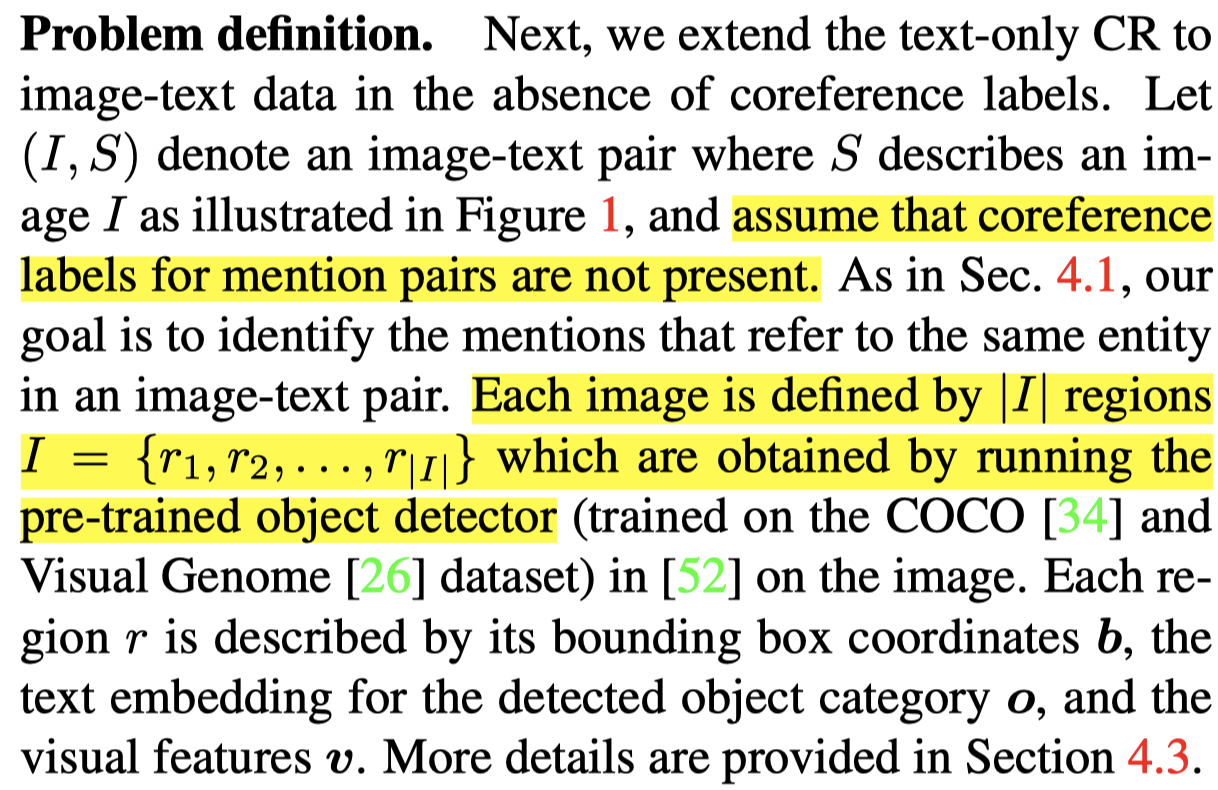
Coreference resolution aims to identify words and phrases which refer to the same entity in a text, a core task in natural language processing. In this paper, we extend this task to resolving coreferences in long-form narrations of visual scenes. First, we introduce a new dataset with annotated coreference chains and their bounding boxes, as most existing image-text datasets only contain short sentences without coreferring expressions or labeled chains. We propose a new technique that learns to identify coreference chains using weak supervision, only from imagetext pairs and a regularization using prior linguistic knowledge. Our model yields large performance gains over several strong baselines in resolving coreferences. We also show that coreference resolution helps improve grounding narratives in images.
Issue:现有的text-only的CR方法无法解决在image narrations图像描述的共指问题:
- image narrations通常需要理解image,仅仅依赖于text的描述是unstructured、noisy的
- 现有的text-image数据集通常文本较短,没有很多共指的实例

上图中的the woman需要有对应的image才能够和前面的a peron, her, she对应起来。
少数一些工作开始关注带有image的CR问题,但是他们依赖于有限的object categories,无法适应image narrations中存在的各种开放式的objects。
Solution:作者创建了一个新的数据集Coreferenced Image Narratives,CIN。
创建过程是从现有的数据集Localized Narratives dataset [47]的子集Flickr30k进行标注。这个数据集中的文本是对于image的描述,并且有speaker描述image时,鼠标在图像上移动的轨迹。
Tuset et al. [48] proposed the Localized Narratives dataset, new form of multimodal image annotations connecting vision and langauge. In particular, the annotators describe an image with their voice while simultaneously hovering their mouse over the region they are describing
由于标注cost比较高,作者只标注了对应的validation set (880)和test set (1000)用于评估,在训练集中是没有真实标注的。
标注过程中,mention包括pronouns (she), common nouns (another woman), or proper nouns (Peter),不包括第一人称代词。
作者的问题定义:指向相同objects的mention组成coreference chains,并有有对应的bounding box。
由于训练集中没有标注,作者把自己的实验设置称为weak supervision:
We use ‘weak supervision’ to refer to a setting where no coreference label for mention pairs and no grounding of mentions (i.e., bounding boxes are not linked to phrases in the text) are available.
由于训练过程缺少标注,就需要寻找某种替代策略。作者假设,共指mention应该大致对应到相同的image regions。
作者定义了一个辅助函数auxiliary function \(g(m,r)\)来评估mention \(m\)和image region \(r\)之间的相关性。通过平均,能够获得相对于全部region的分布:
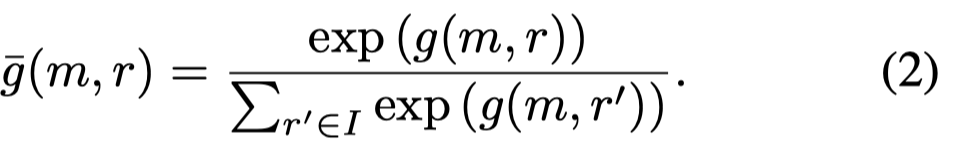
接下来评估两个mention之间的相关性,作者引入compatibility function \(f\):
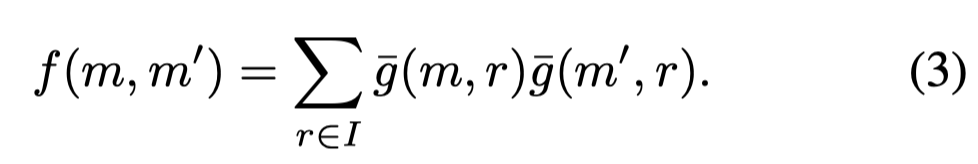
如果两个mention的auxiliary function分布越一致,compatibility function \(f\)越大。就更有可能共指。上面的过程中,image作为了推测共指关系的anchors。
由于没有真实对应的bounding box,作者把grounding task看做是一个weakly supervised localization task,把最大auxiliary function的值的image region,就看做是某个mention \(m\)对应的region \(r_m\):

优化loss是期望在当前样本的image上的\(r_m\)有最大的匹配度,而不是其它样本的image上有更高的匹配度:
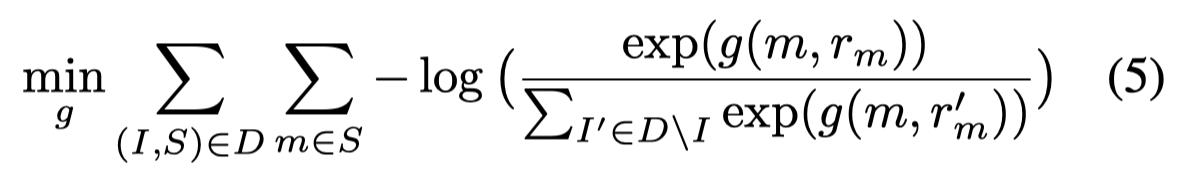
仅仅依赖于视觉信息去解决共指是不够的,因为可能存在视觉上相似的不同共指情况,比如plant、tree这些可能视觉上是相似的,但是利用语言特点可以将其分开。因此作者还引入共指规则来作为优化目标Linguistic constraints。下面是使用的共指规则,共指规则如果成立,\(q(m, m^\prime)\)的值会为1:
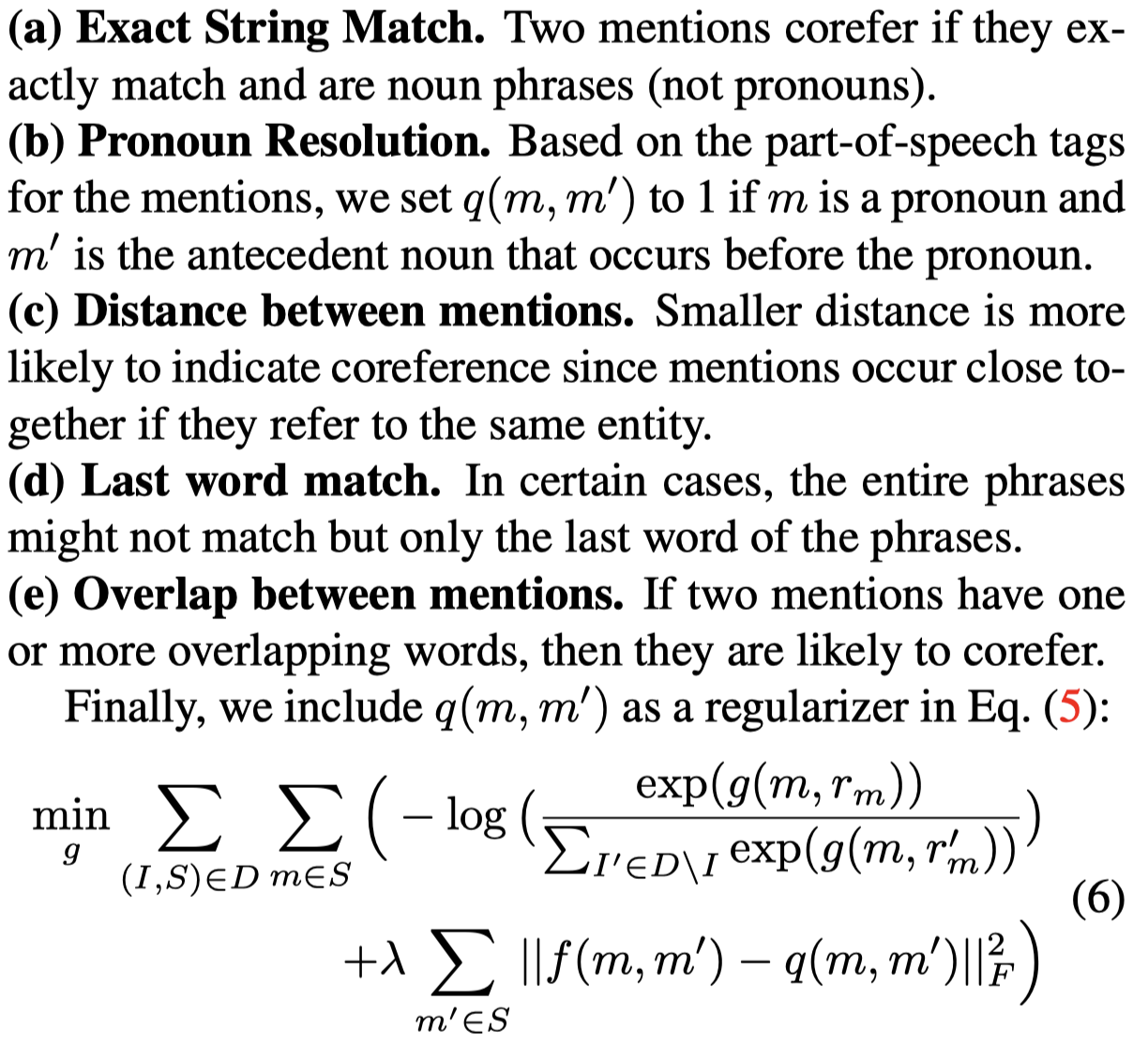
即期望利用语言规则推出的共指,和通过视觉信息推出的共指是相似的。
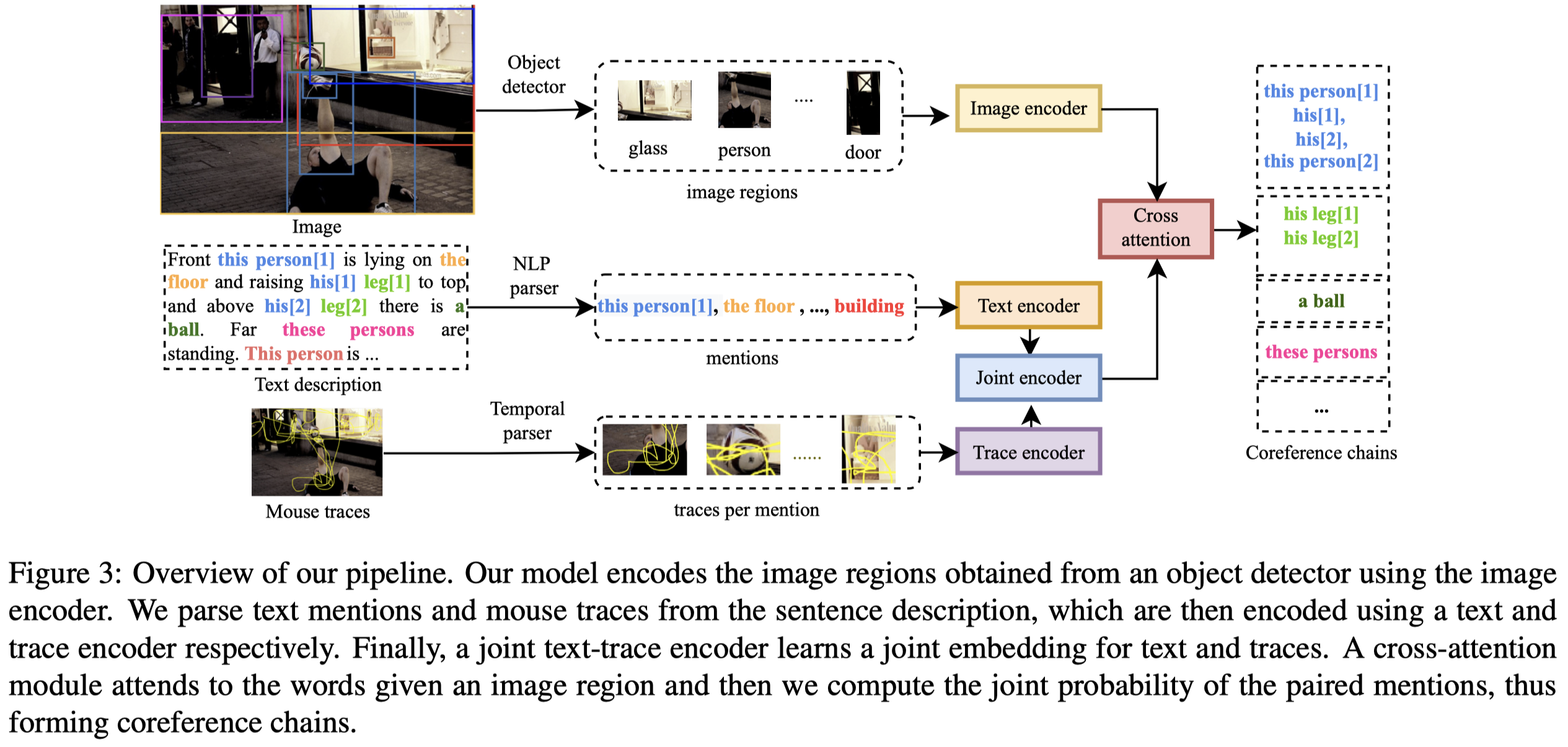
作者的整体方法架构上重点在于如何处理输入的特征:
- Image encoder:基于Faster-RCNN构造向量,拼接的包括bounding box coordinates、text embedding for the detected object category(使用Glove embedding)以及visual features
- Text encoder:利用现有NLP parser [2]找到的mention,以及对应的Glove word embedding
- Mouse trace encoder:For the mouse traces, we follow [47] and extract the trace for each word in the sentence and then convert it into bounding box coordinates for the initial representation.
把上面的三种模态融合,作者使用了一个跨模态机制,word embedding和mouse trace embedding拼接作为新的word embedding。计算mention的单个word在image上最大匹配度的region,
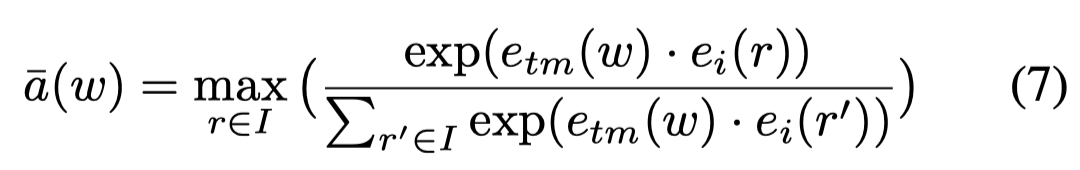
然后根据匹配度加权求和所有word对应的embedding,得到mention embedding:
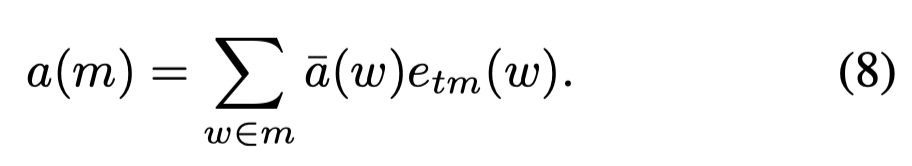
在得到mention embedding和region embedding之后,就可以用点积计算相似度:
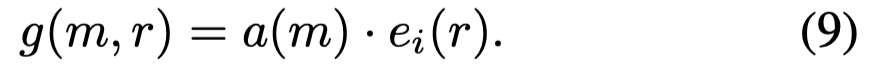
在实验部分,作者在Flickr30k数据集上训练,有30k的image-narration pairs。
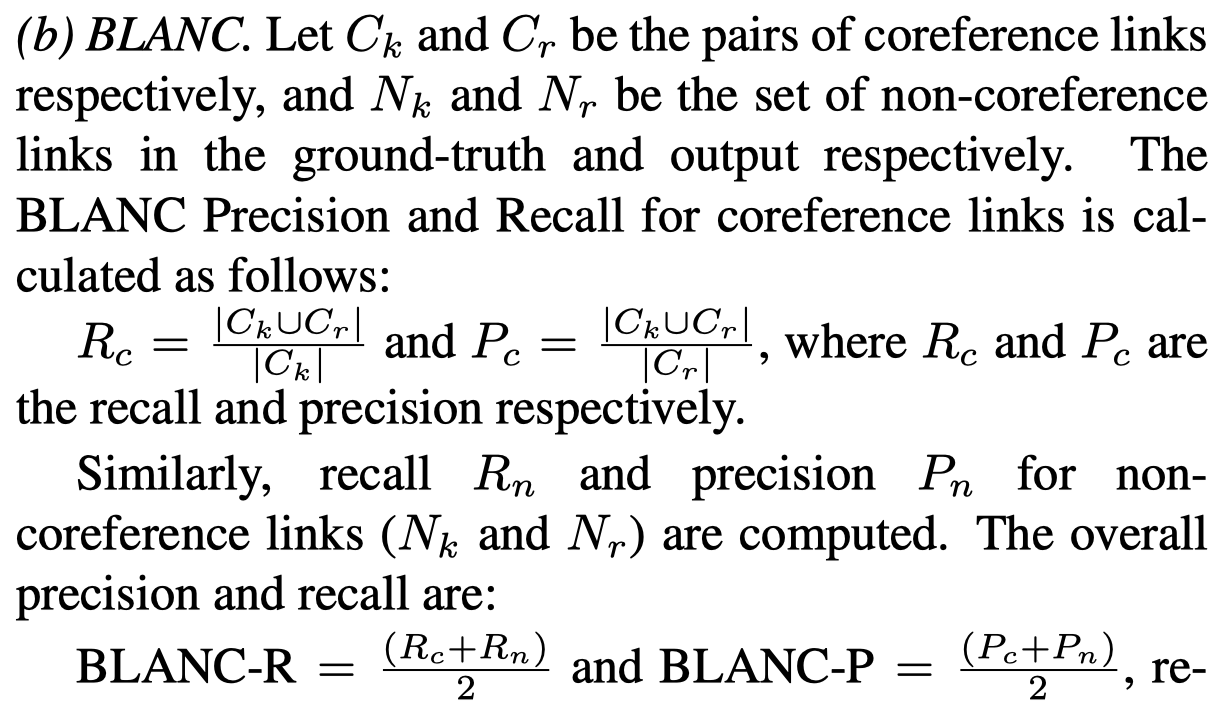
评估metric采用了两种,MUC和BLANC。
MUC measures the number of coreference links (pairs of mentions) common to the predicted \(R\) and ground-truth chains \(K\).
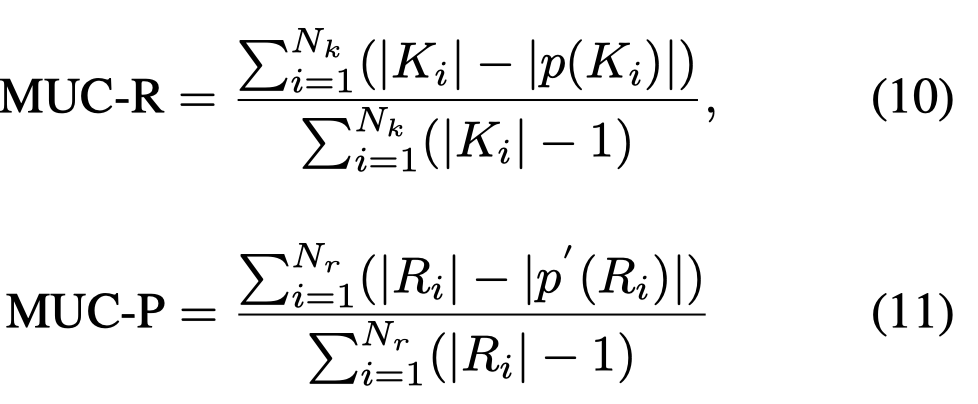
BLANC指标额外考虑了非共指的情况,
为了评估grounding的效果,使用IoU (Intersection over Union),如果预测的bounding box和真实的bounding box重合度超过0.5,就认为预测正确。
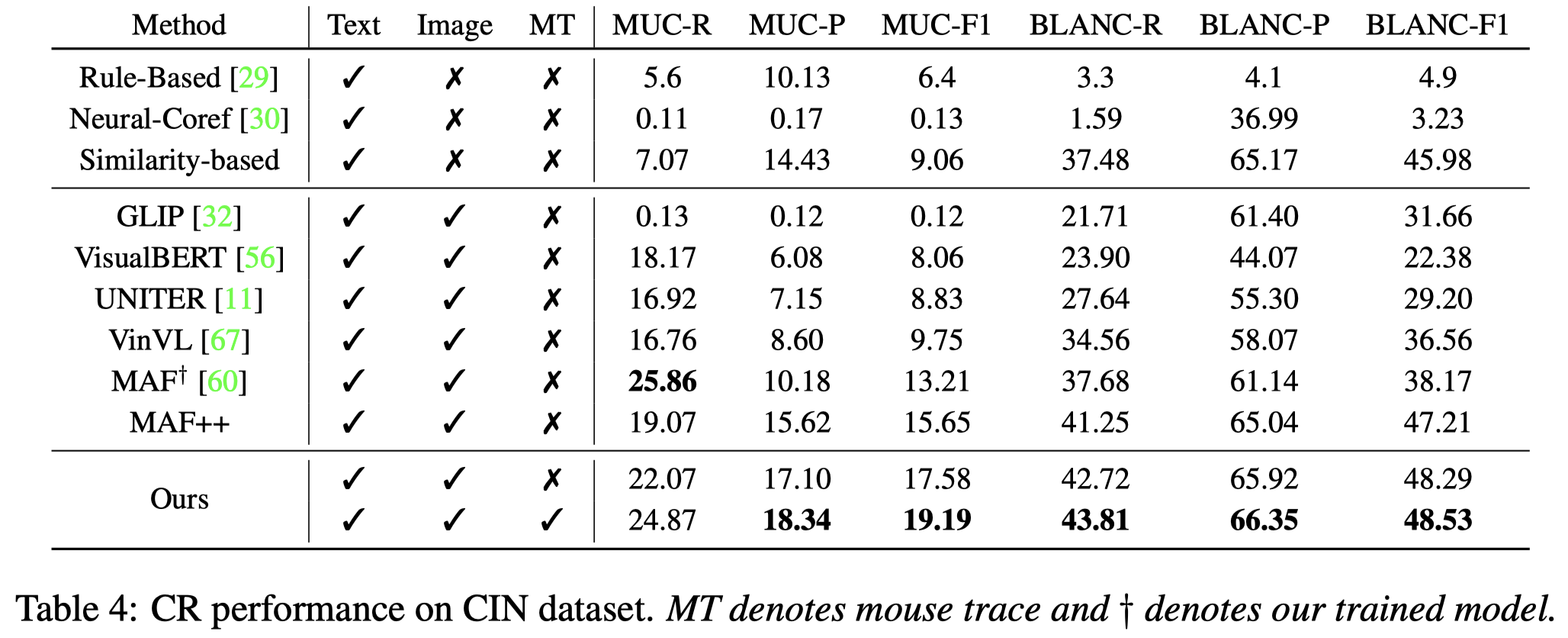
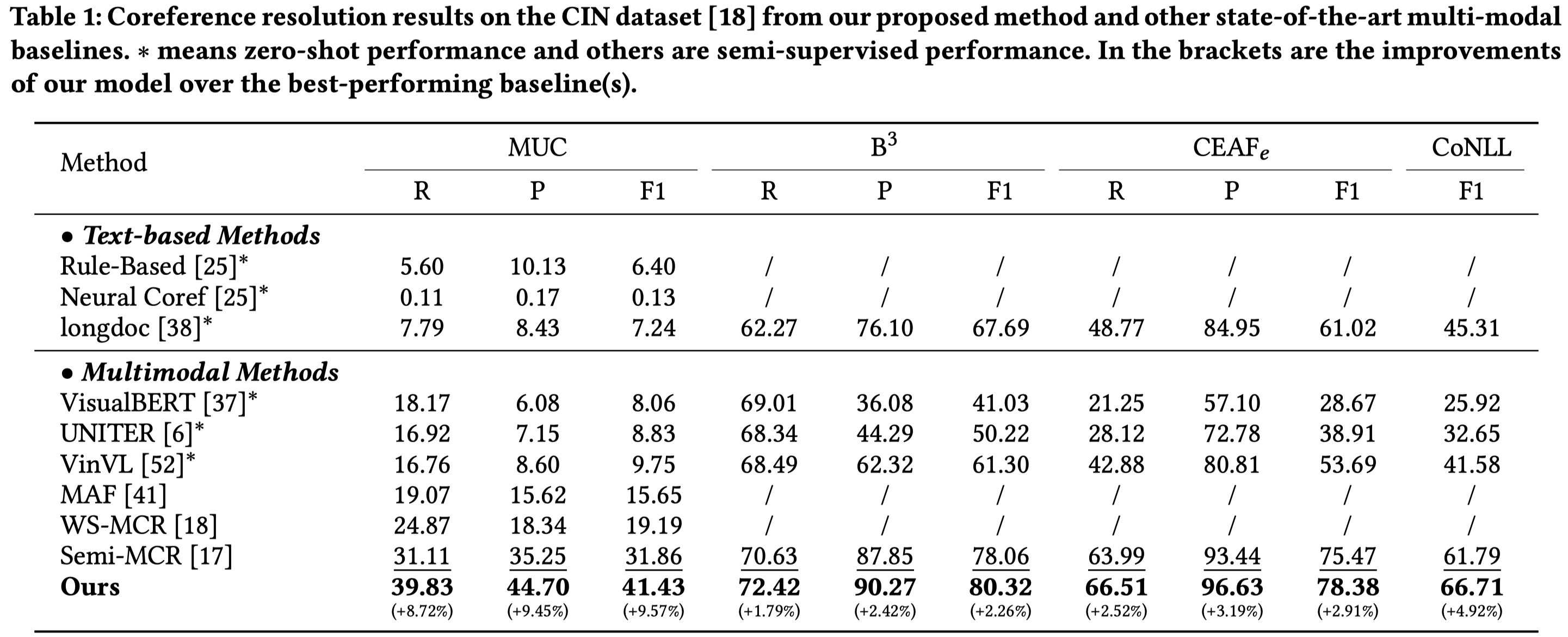
共指实验结果:
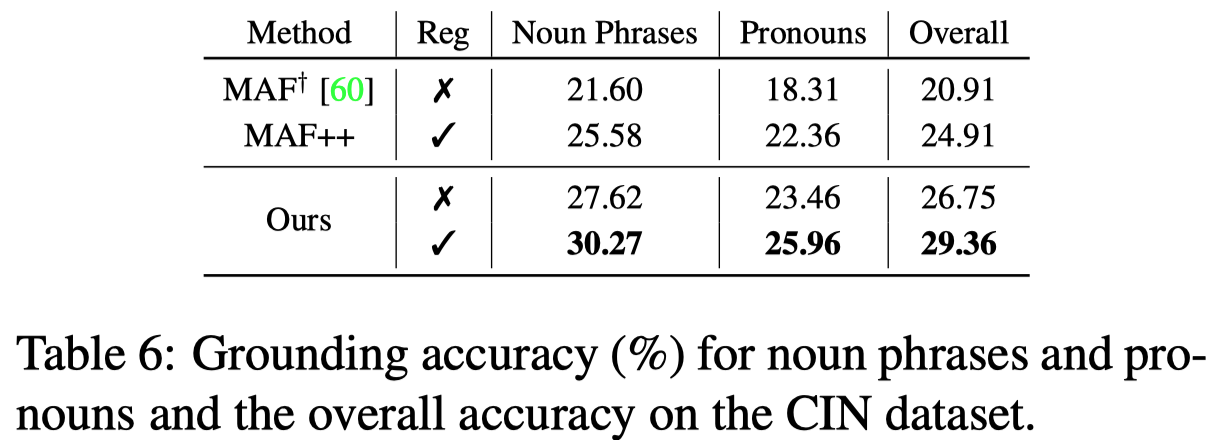
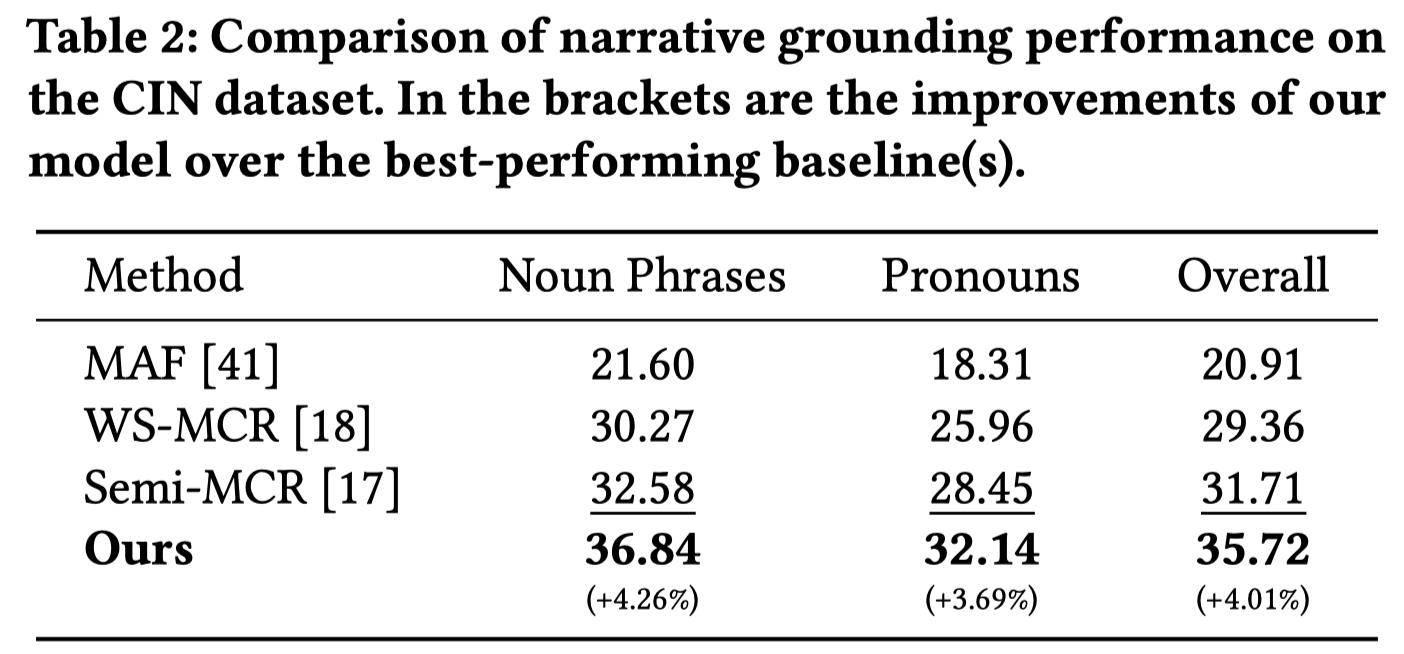
grounding结果:
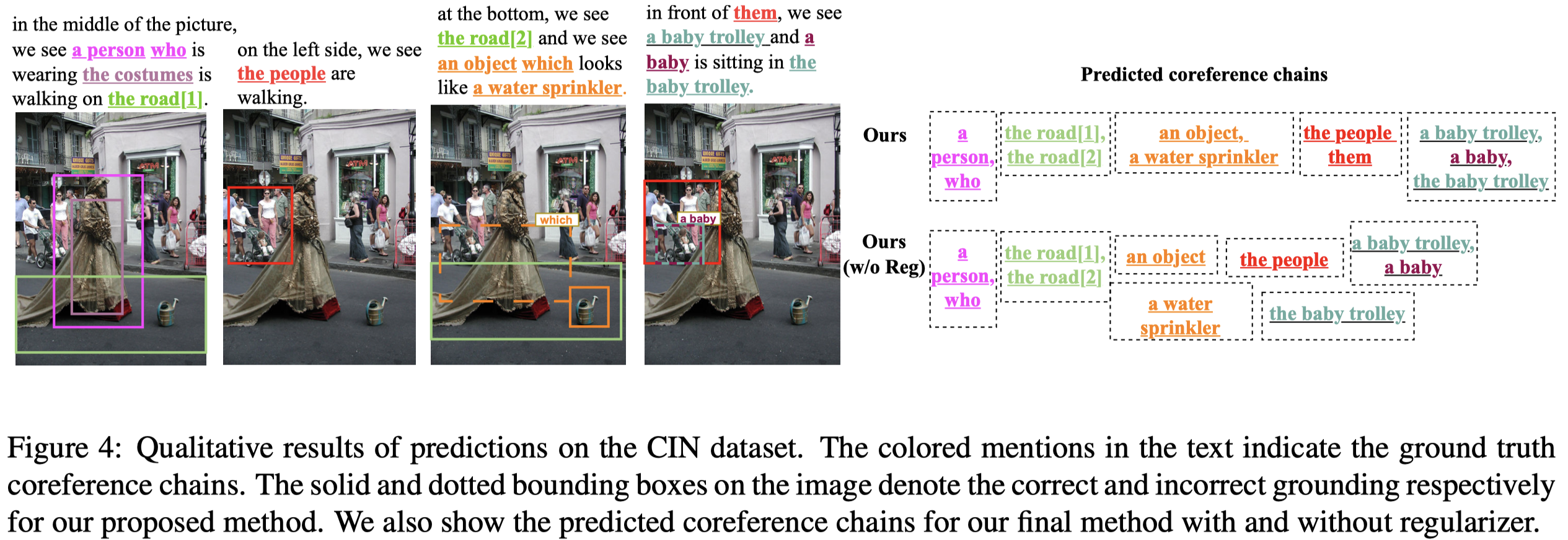
Semi-MCR
Semi-supervised Multimodal Coreference Resolution in Image Narrations. EMNLP 2023. 爱丁堡大学. 代码.
In this paper, we study multimodal coreference resolution, specifically where a longer descriptive text, i.e., a narration is paired with an image. This poses significant challenges due to fine-grained image-text alignment, inherent ambiguity present in narrative language, and unavailability of large annotated training sets. To tackle these challenges, we present a data efficient semi-supervised approach that utilizes image-narration pairs to resolve coreferences and narrative grounding in a multimodal context. Our approach incorporates losses for both labeled and unlabeled data within a crossmodal framework. Our evaluation shows that the proposed approach outperforms strong baselines both quantitatively and qualitatively, for the tasks of coreference resolution and narrative grounding.
Issue:与前面提出CIN数据集是同一作者。认为MCR任务的挑战有:
- 需要捕获细粒度的视觉信息
- 需要捕获跨句子的依赖
大规模的标注数据获取是很困难的。
Solution:采用了半监督的模式,直接联合labeled data和unlabeled data进行训练导致过拟合,因此作者提出了robust loss和thresholding-based training策略。
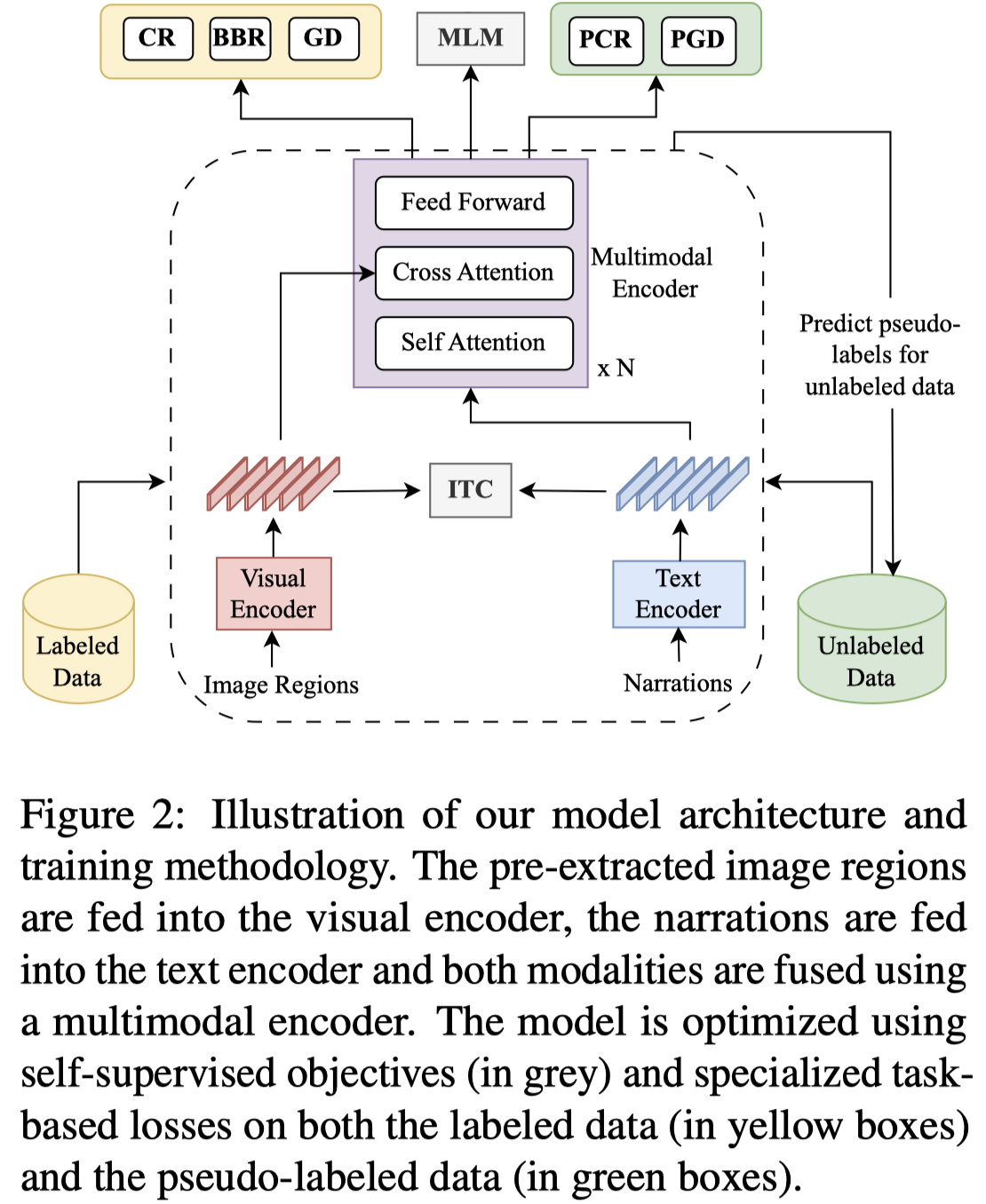
核心任务是学习两个function,\(f\)能够将mention编码为embedding;\(g\)函数评估mention \(m\)和某个图像区域的匹配score:

视觉编码器和检测初始objects使用Faster-RCNN;文本编码器使用BERT的前4层;某个mention embedding是组成的word embedding的平均。
跨模态注意力就是使用mention embedding作为query,visual embedding作为key和value。
为了利用无标注数据,作者采用了三类不同的损失。下面是在有标注数据集上的loss:
(S1) Coreference loss (CR):让共指正样本靠近,让负样本远离:
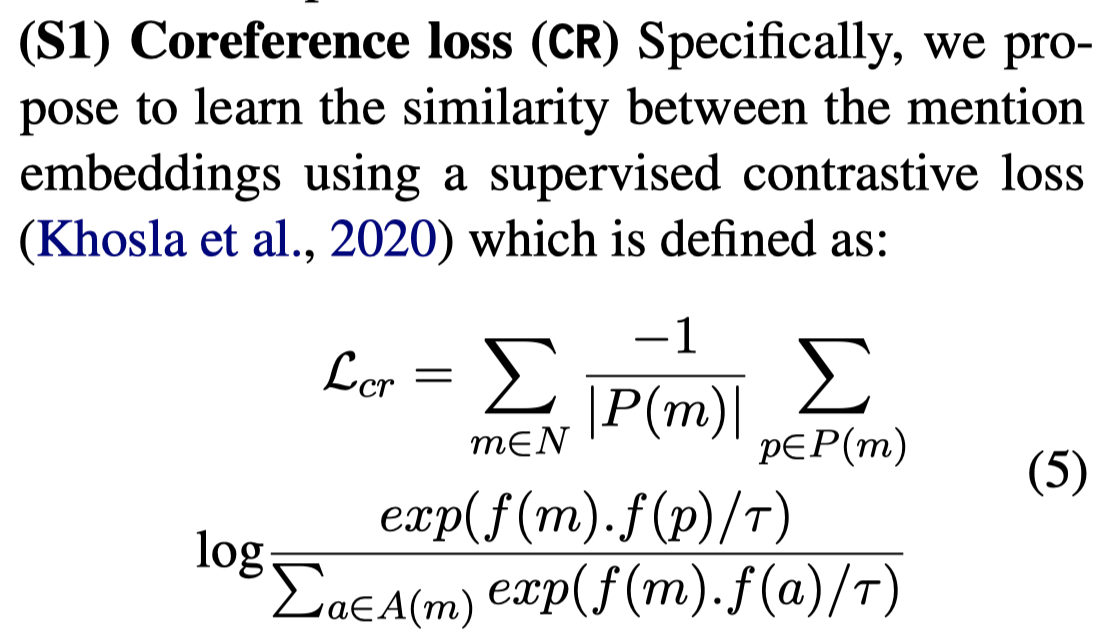
(S2) Grounding loss (GD):选择正确box的loss
注意这个loss,需要选择Faster-RCNN导出的boxes中,和ground-truth box有最大的IoU的box,作为需要被mention匹配的图像区域\(r\)。上面loss中的\(h(m,r)\)只对于选择的box值是1。
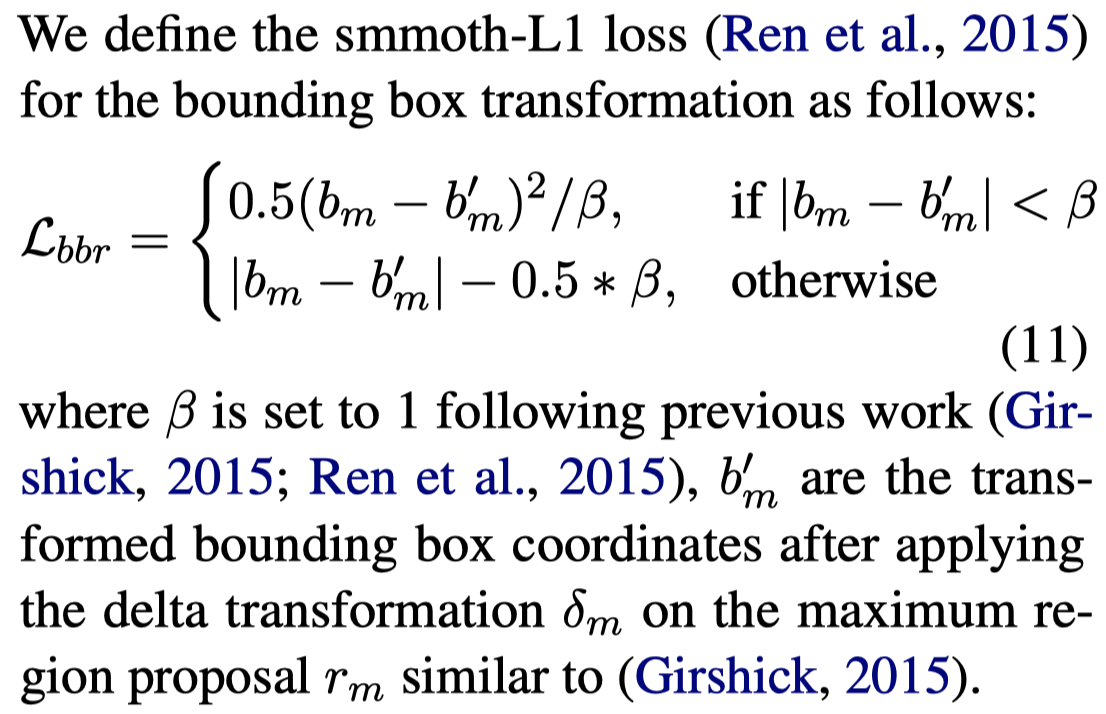
(S3) Bounding box regression loss (BBR):根据box位置的loss
接下来是使用伪标注的无标注数据集。
(U1) Pseudo coreference loss (PCR):计算某个mention和其它mention之间的embedding余弦相似度,选择大于阈值的作为positive samples,小于阈值的作为negative samples。然后分别采用平均值作作为集合中间值,以更加适应label noise:
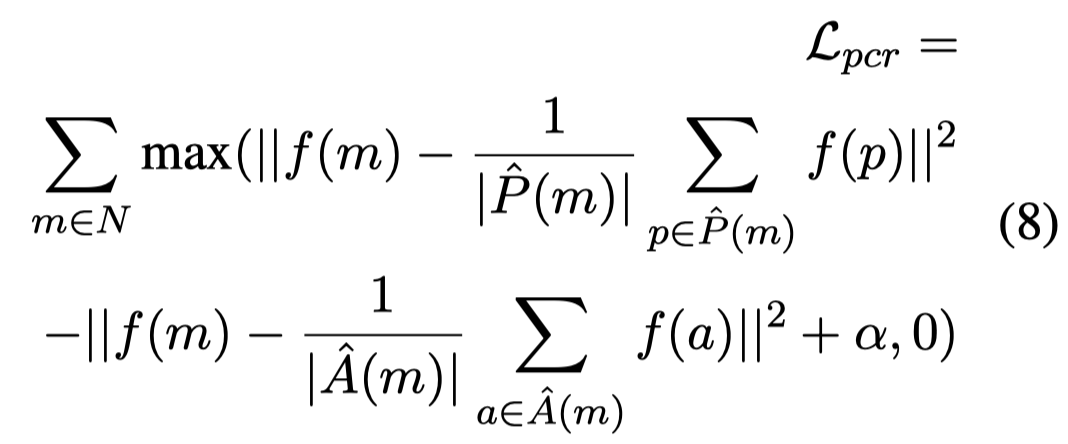
(U2) Pseudo grounding loss (PGD):把grounding score>0.9的认为是真的对应的image region,然后计算loss:
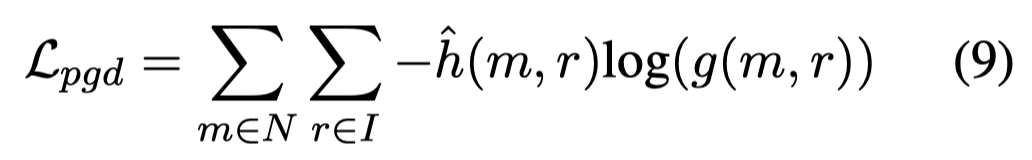
接下来,作者采用了两个预训练过程中用到的loss来更好的学习单模态表征:
(U3) Image-Text contrastive loss (ITC):在进入跨模态注意力之前的,单模态编码器的输出,计算image region 和mention之间的匹配度:
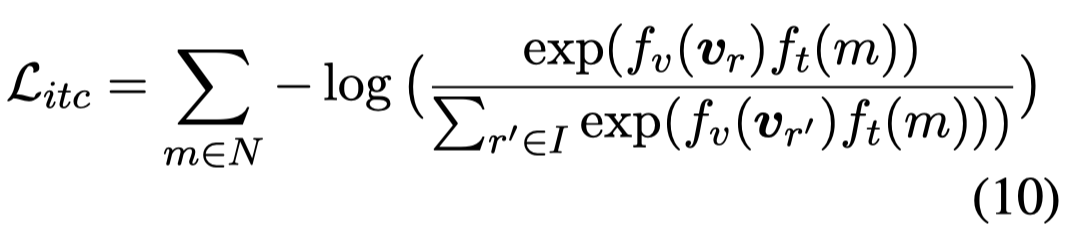
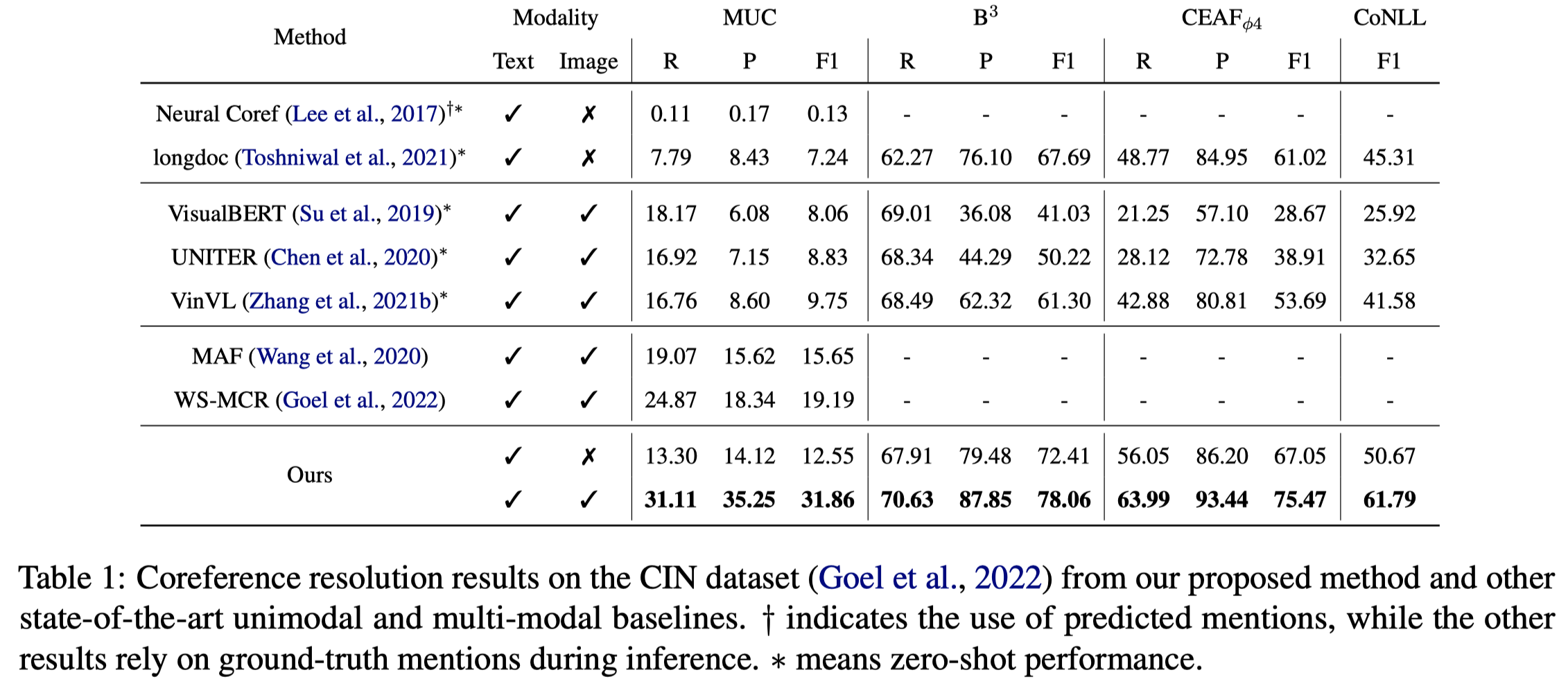
实验采用CIN的validation set作为labeled set,在Flickr30k的50k image-narration pairs作为无标注数据。
SLUMA
Self-Adaptive Fine-grained Multi-modal Data Augmentation for Semi-supervised Muti-modal Coreference Resolution. ACM MM 2024. 武大
Coreference resolution, an essential task in natural language processing, is particularly challenging in multi-modal scenarios where data comes in various forms and modalities. Despite advancements, limitations due to scarce labeled data and underleveraged unlabeled data persist. We address these issues with a self-adaptive fine-grained multi-modal data augmentation framework for semisupervised MCR, focusing on enriching training data from labeled datasets and tapping into the untapped potential of unlabeled data. Regarding the former issue, we first leverage text coreference resolution datasets and diffusion models, to perform fine-grained textto-image generation with aligned text entities and image bounding boxes. We then introduce a self-adaptive selection strategy, meticulously curating the augmented data to enhance the diversity and volume of the training set without compromising its quality. For the latter issue, we design a self-adaptive threshold strategy that dynamically adjusts the confidence threshold based on the model’s learning status and performance, enabling effective utilization of valuable information from unlabeled data. Additionally, we incorporate a distance smoothing term, which smooths distances between positive and negative samples, enhancing discriminative power of the model’s feature representations and addressing noise and uncertainty in the unlabeled data. Our experiments on the widely-used CIN dataset show that our framework significantly outperforms state-of-the-art baselines by at least 9.57% on MUC F1 score and 4.92% on CoNLL F1 score. Remarkably, against weakly-supervised baselines, our framework achieves a staggering 22.24% enhancement in MUC F1 score. These results, underpinned by in-depth analyses, underscore the effectiveness and potential of our approach for advancing MCR tasks.
Issue:多模态共指消解需要判断文本中的mention是否指向同一实体,还要划出其在图像image上对应的bounding box。之前的多模态共指消解MCR方法更多是关注模型优化和特征学习,忽略了:
- Scarcity of labeled data
- Under-exploitation of unlabeled data:利用unlabeled data常常是基于model confidence进行过滤,这种固定的做法的缺陷:(1) Loss of useful information (2) Limitation on the quantity of training data (3) Ignoring the model’s learning status
之前的DA方法是纯文本的。
Solution:作者基于文生图,依据有标注文本数据来生成新的图片;为了利用无标注数据,提出self-adaptive threshold的方法。
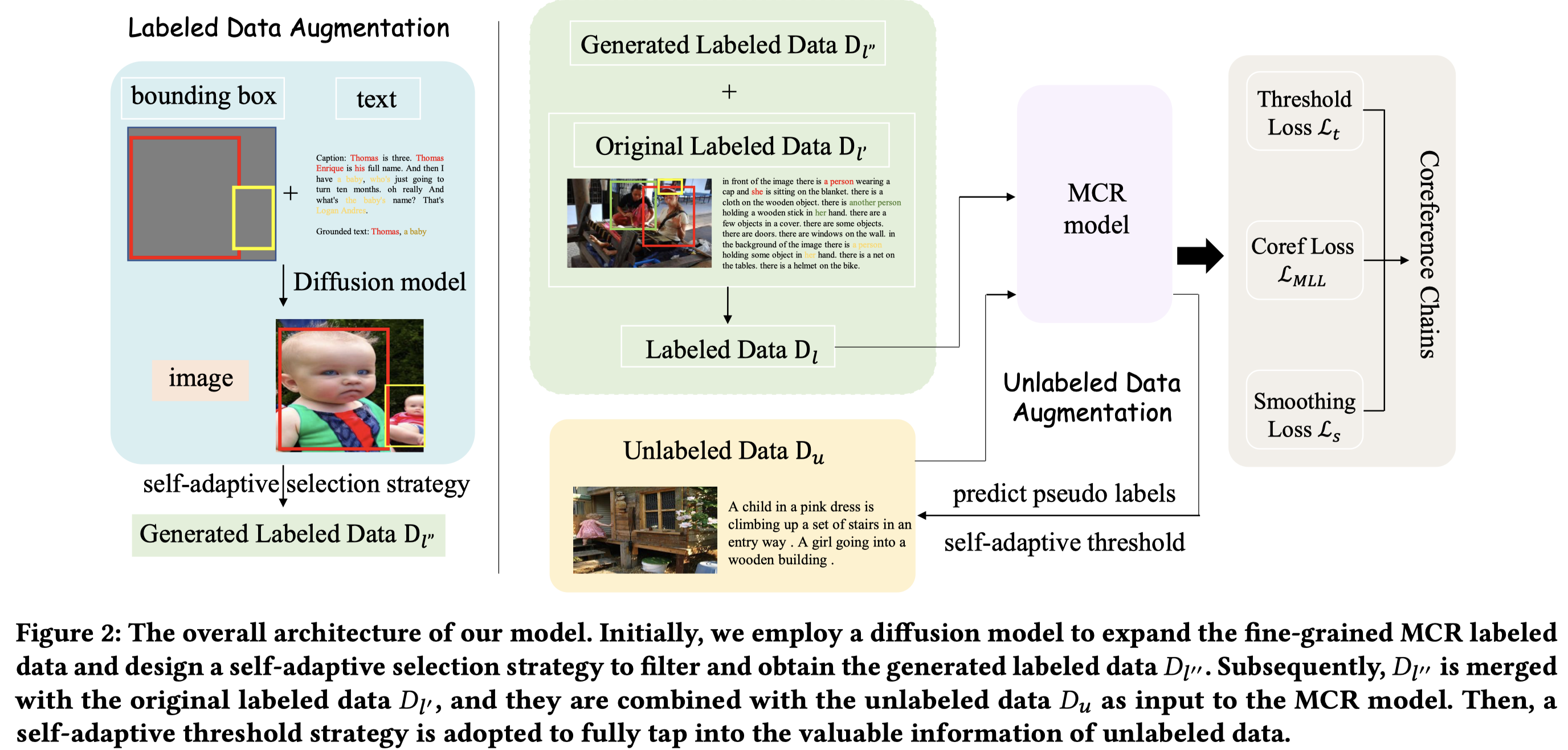
作者从纯文本的CR数据集,English OntoNotes 5.0获取文本,然后随机的构造bounding box,利用之前的方法GLIGEN [27]基于扩散模型生成新的image。
由于生成的image存在不确定性,作者使用一种自适应的数据选择策略,基于CLIPScore评估image和caption的匹配度。
一开始使用全部的训练样例确保多样性。随着训练过程,模型的性能逐渐增大,逐渐过滤掉生成的低score的数据。作者利用Exponential Moving Average (EMA)评估task model的学习状态:

当EMA值比较大的时候,task model效果比较好,过滤掉更多的生成数据以保证质量;当EMA比较小的时候,task model效果比较差,保留更多的生成数据用于训练。
利用训练的task model可以为unlabeled data进行标注,为了减小伪标注的noise,作者使用了self-adaptive threshold和distance smoothing两种技术。
self-adaptive threshold和上面过滤生成数据的思路一致,利用EMA(不同超参 \(\alpha\))评估model性能:
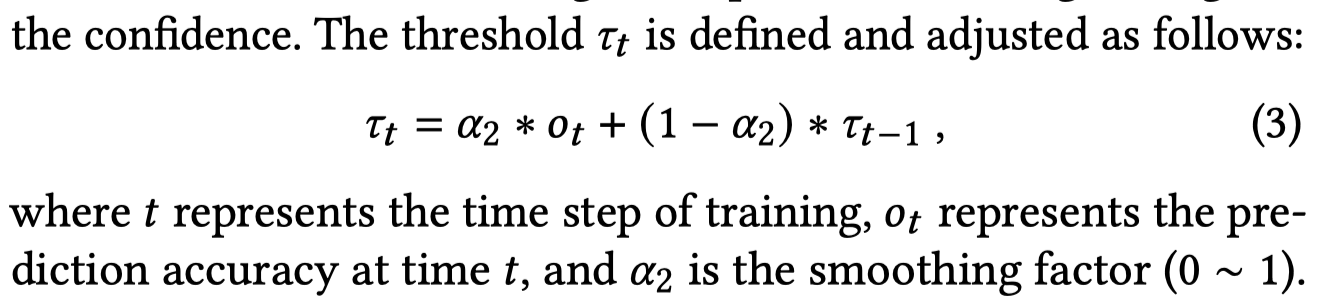
初期训练由于效果不太好,得到的阈值比较小,就会使用更多的无标注数据加速收敛;后期效果比较好,阈值比较大,就会过滤掉更多的无标注数据。利用无标注数据的训练loss是crossentropy loss with a confidence threshold:

Distance Smoothing是指作者在loss中,引入了正样本和负样本之间的差异大小的平滑系数。假设一个mention是\(m_i\),计算其和其它mention之间的余弦相似度,如果超过固定阈值(和前面的阈值应该不是一个),就认为是共指,属于positive mention;如果没有超过,就是negative mention。记positive mention是\(m_j\),记negative mention是\(m_k\)。分别计算正负样本对的特征欧式距离,然后评估差异大小作的平滑版本:
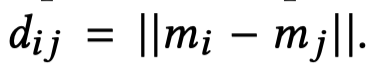
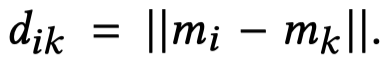
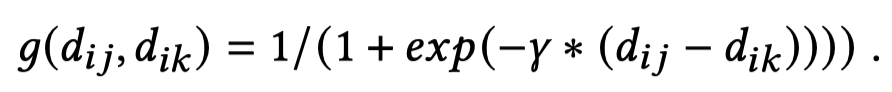
平滑系数把正负样本之间的差异平滑到0-1,起到了减小不同样本对之间差异大小的平滑作用。随后计算的loss:
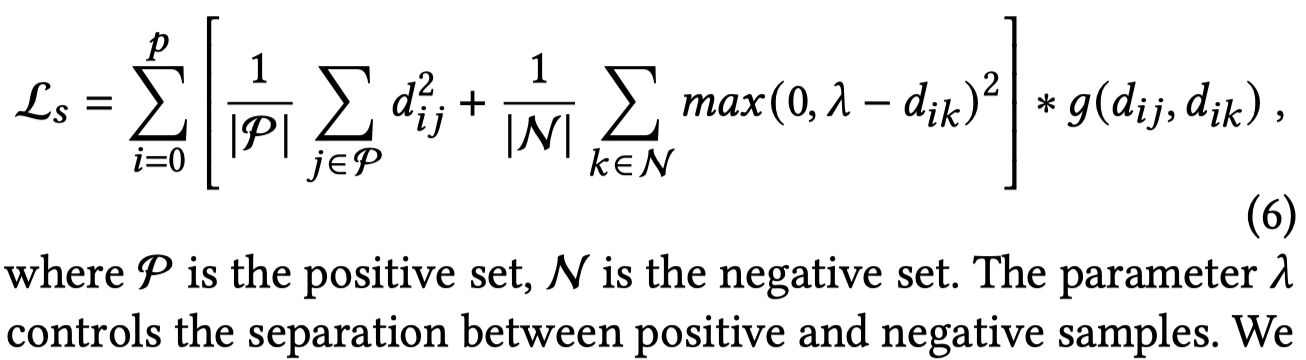
上述损失loss期望减小正样本之间的差异,增大正样本和负样本之间的差异。\(\lambda\)是正负样本对之间的差异距离。使得负样本的差异\(d_{ik}\)倾向于大于\(\lambda\),而\(d_{ij}\)倾向于变为0。
作者的MCR模型如图,使用BERT和RCNN作为编码器,然后单模态使用两个VAE,最后利用PoE的思想两个高斯分布相乘,得到多模态的高斯分布。
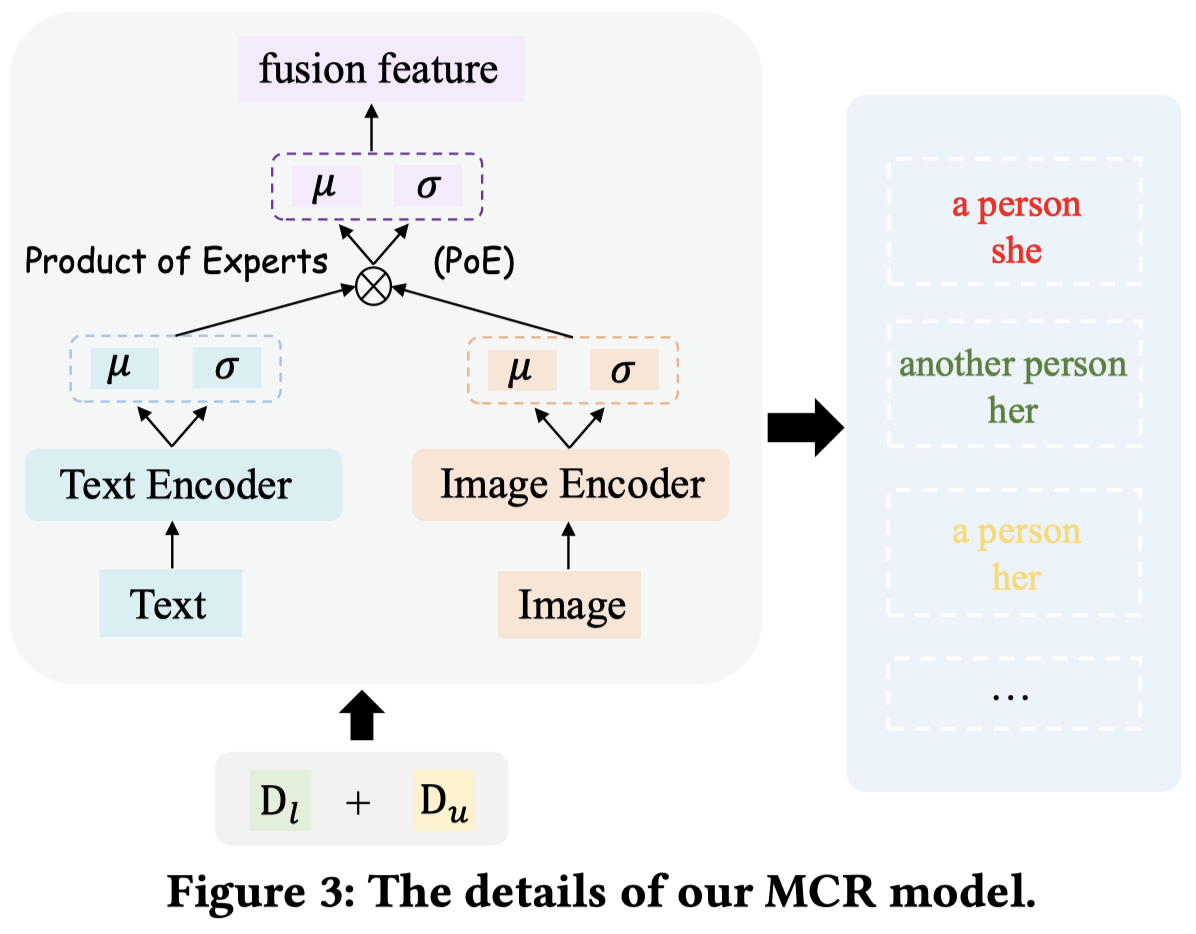
作者训练过程把CIN的validation set作为labeled set(感觉无法和其它baseline公平对比?)。
实验结果:
Parameter Augmentation LLM
Towards Multi-Modal Co-Reference Resolution in Conversational Shopping Agents. LREC-COLING 2024 Workshop. University of Massachusetts Amherst-Amazon
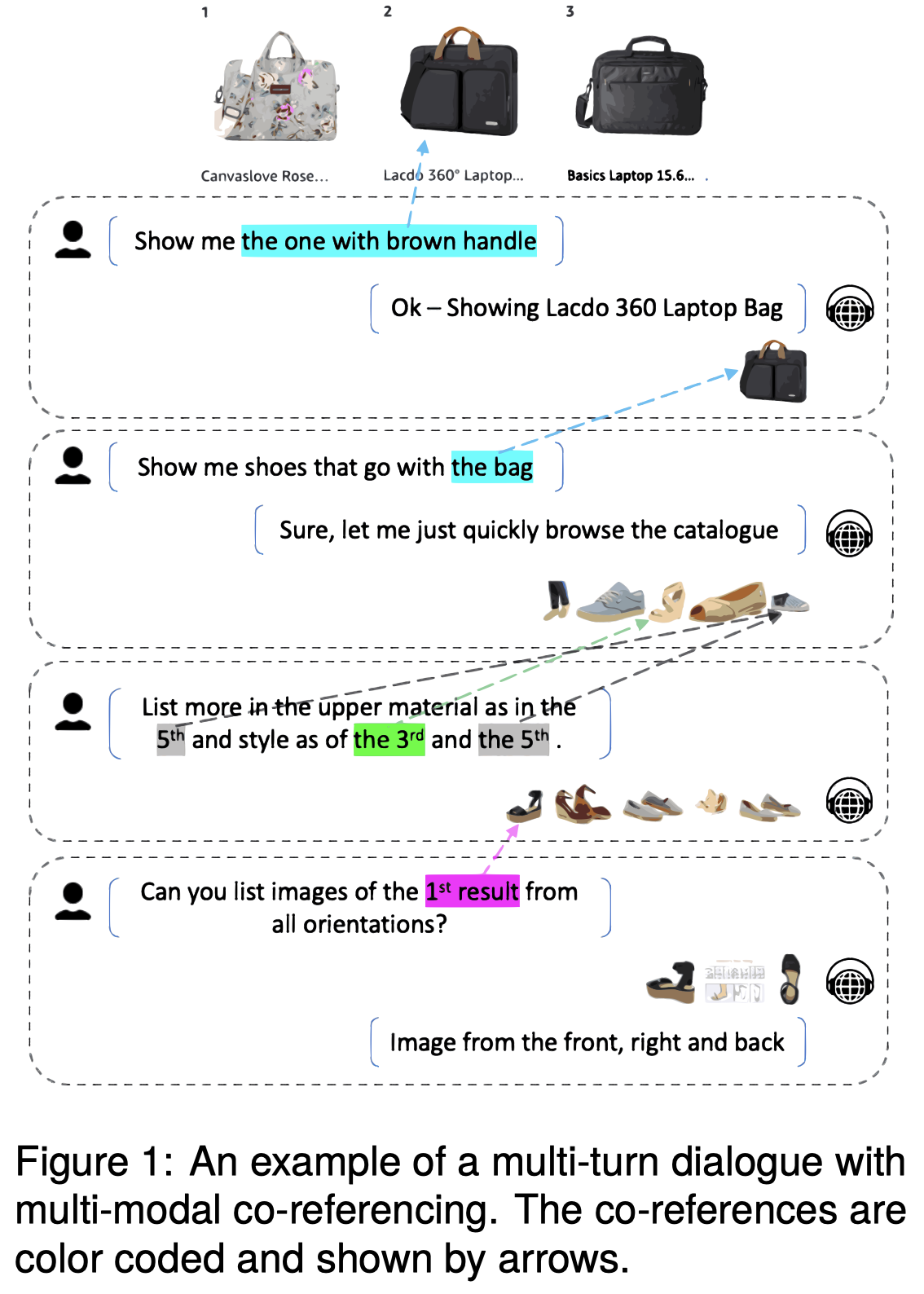
The context of modern smart voice assistants is often multi-modal, where images, audio and video content are consumed by users simultaneously. In such a setup, co-reference resolution is especially challenging, and runs across modalities and dialogue turns. We explore the problem of multi-modal co-reference resolution in multi-turn dialogues and quantify the performance of multi-modal LLMs on a specially curated dataset of long, image-interleaved conversations between a voice assistant and human in a shopping use case. We propose a custom architecture for multi-modal embedding alignment using a novel parameter augmentation technique. Our proposed Parameter Augmented LLM approach shows a 4.9% absolute F1 improvement above a cross-attention baseline while reducing the number of parameters being trained by 4×.
作者关注的是多轮对话场景下的共指消解问题,更多是image-level的grounding
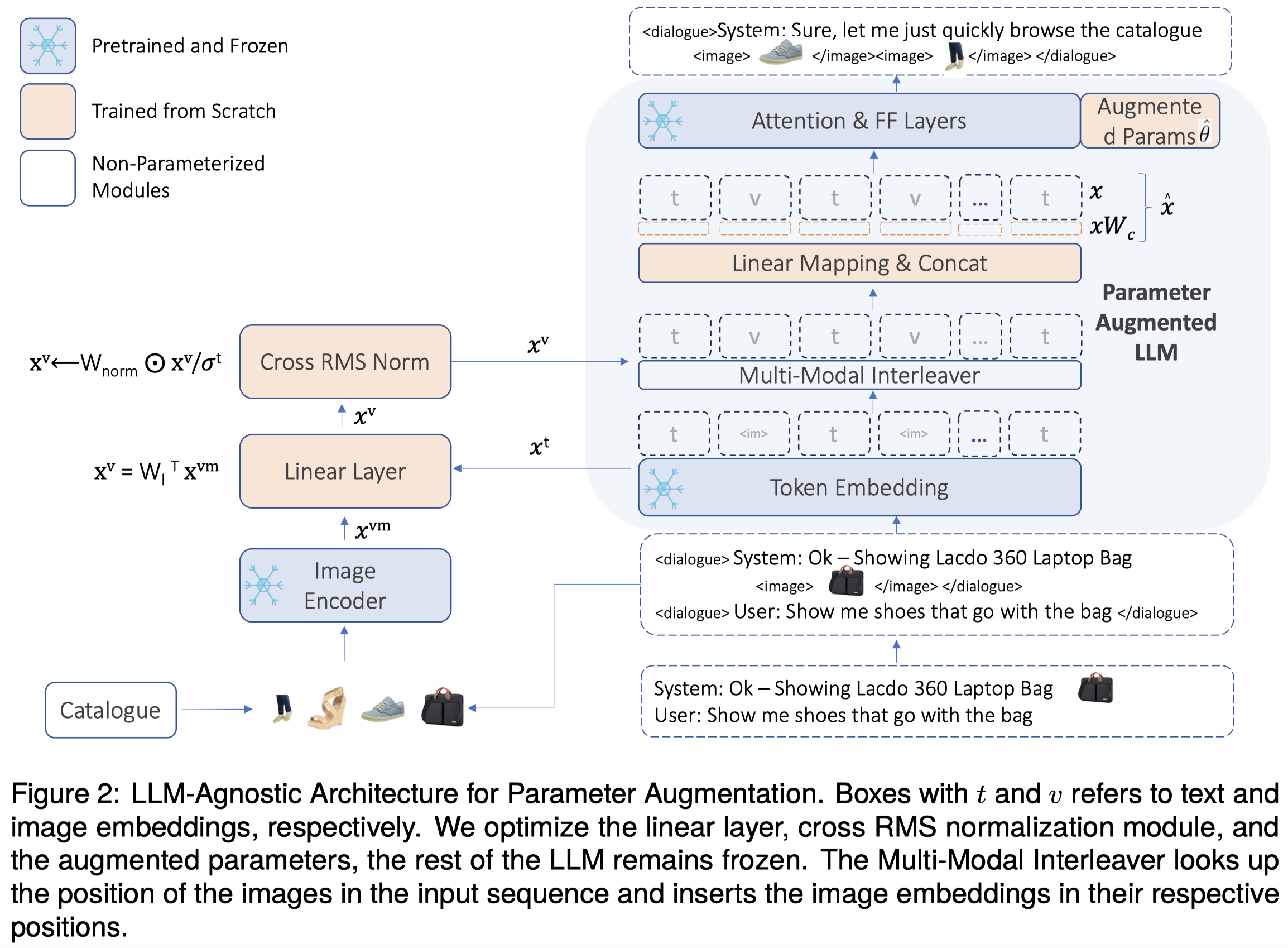
作者的方法类似于lora,微调了单模态LLM,Llama-7B,在权值矩阵上拼接新的权值矩阵,同时加入新投影操作改变token embedding的维度:
作者的实验包括两个,在Multi-Modal Context Carryover (MMCC) dataset上的image selection任务;以及Multi-Modal Domain-Aware (MMDA) (Saha et al., 2018) dataset.上的image retrieval任务。
