LLM-data-augment2
LLM数据增强
基于LLM的数据增强论文合集2。
PromptMix-emnlp23
PromptMix: A Class Boundary Augmentation Method for Large Language Model Distillation. University of Waterloo. EMNLP 2023. 代码.
Data augmentation is a widely used technique to address the problem of text classification when there is a limited amount of training data. Recent work often tackles this problem using large language models (LLMs) like GPT3 that can generate new examples given already available ones. In this work, we propose a method to generate more helpful augmented data by utilizing the LLM’s abilities to follow instructions and perform few-shot classifications. Our specific PromptMix method consists of two steps: 1) generate challenging text augmentations near class boundaries; however, generating borderline examples increases the risk of false positives in the dataset, so we 2) relabel the text augmentations using a prompting-based LLM classifier to enhance the correctness of labels in the generated data. We evaluate the proposed method in challenging 2-shot and zero-shot settings on four text classification datasets: Banking77, TREC6, Subjectivity (SUBJ), and Twitter Complaints. Our experiments show that generating and, crucially, relabeling borderline examples facilitates the transfer of knowledge of a massive LLM like GPT3.5-turbo into smaller and cheaper classifiers like DistilBERTbase and BERT base . Furthermore, 2-shot PromptMix outperforms multiple 5-shot data augmentation methods on the four datasets. Our code is available at https://github.com/ServiceNow/PromptMix-EMNLP-2023.
Issue: 已经出现的prompt-based的LLM做数据增强的方法只考虑使用单个class的信息来进行生成,这样无法生成能够处于class boundary上的hard samples。
We hypothesize that training a robust text classifier requires the training data to have a good mix of borderline examples (Swayamdipta et al., 2020).
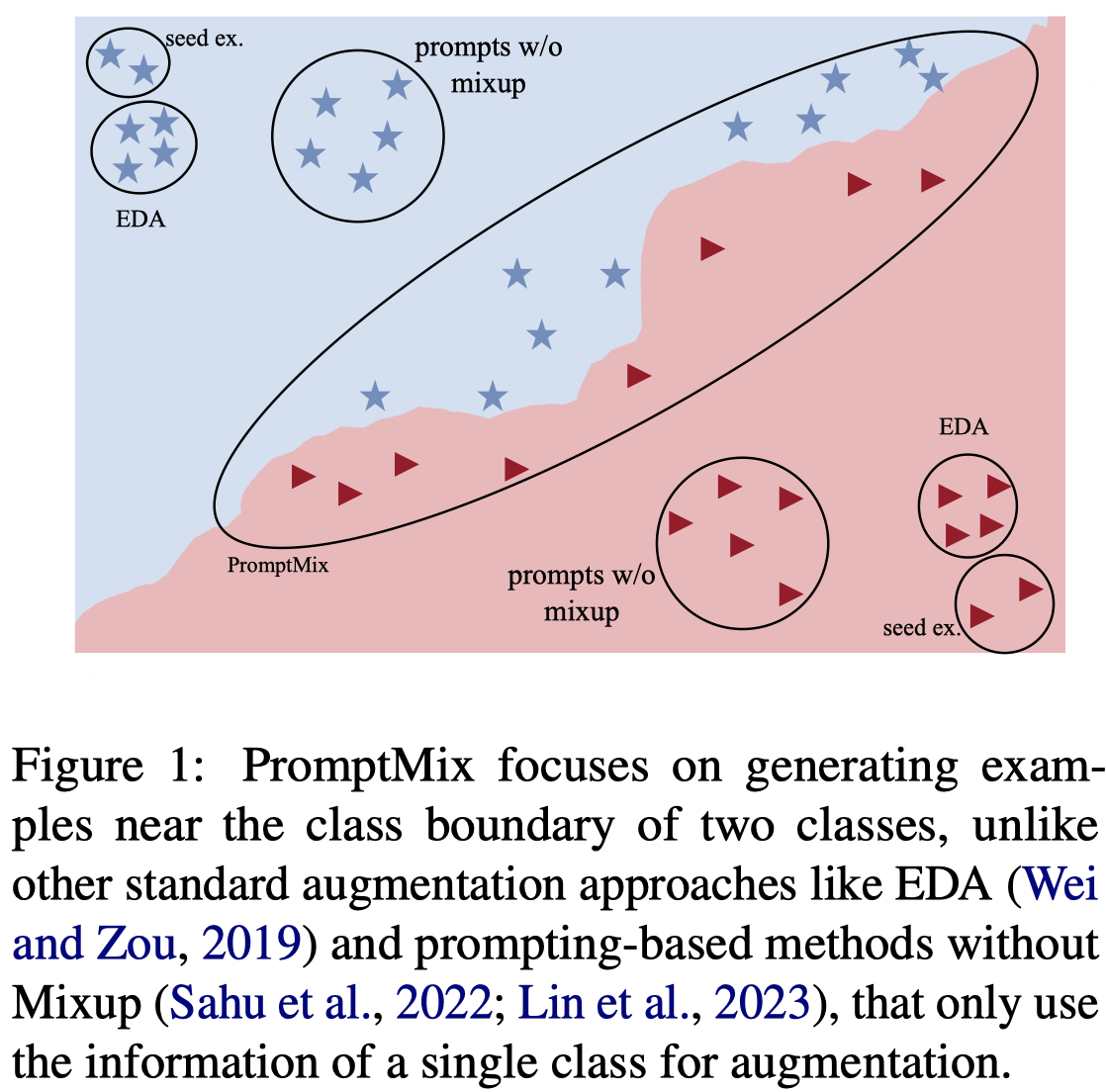
Solution:作者的策略是,一次给LLM提供多个class的信息,并且要求生成的data需要能够同时包含两个class的信息,让生成的数据能够处在class boundary上。
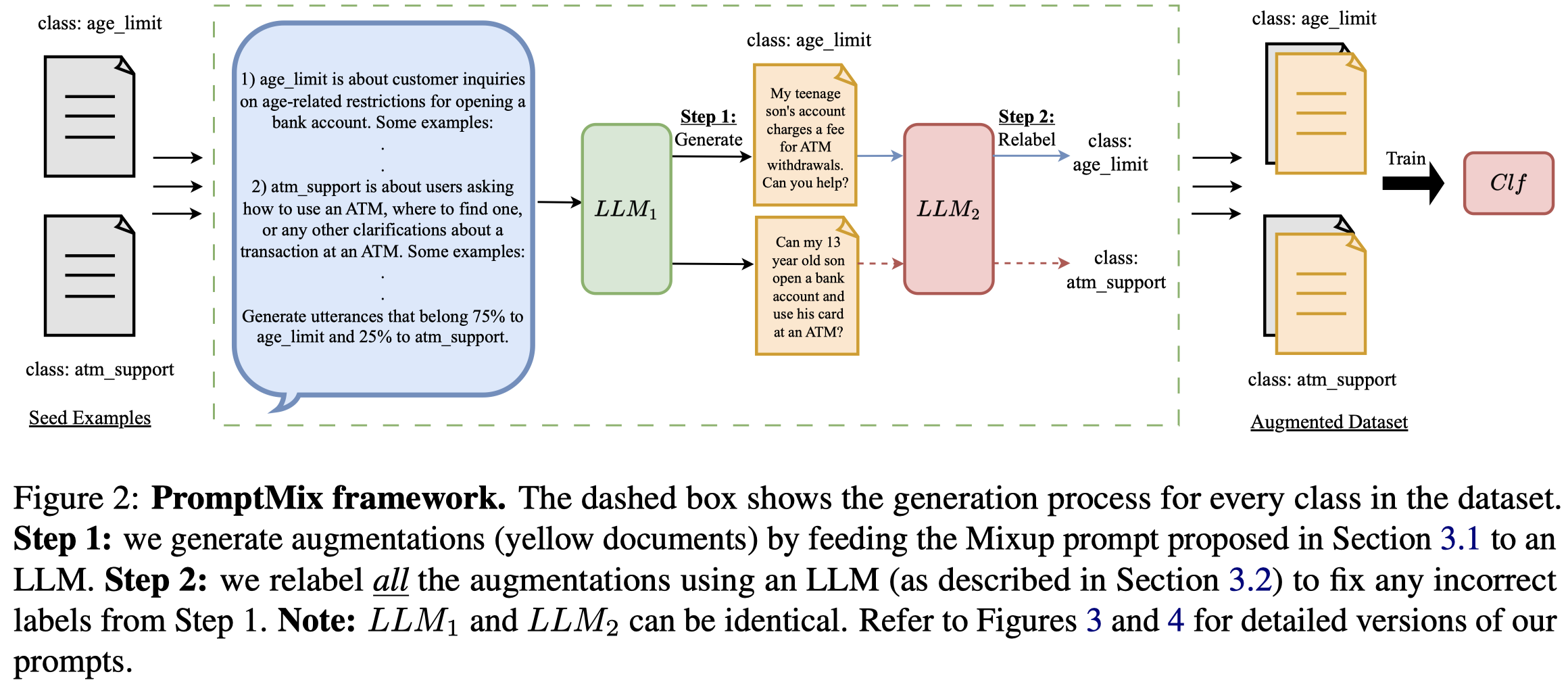
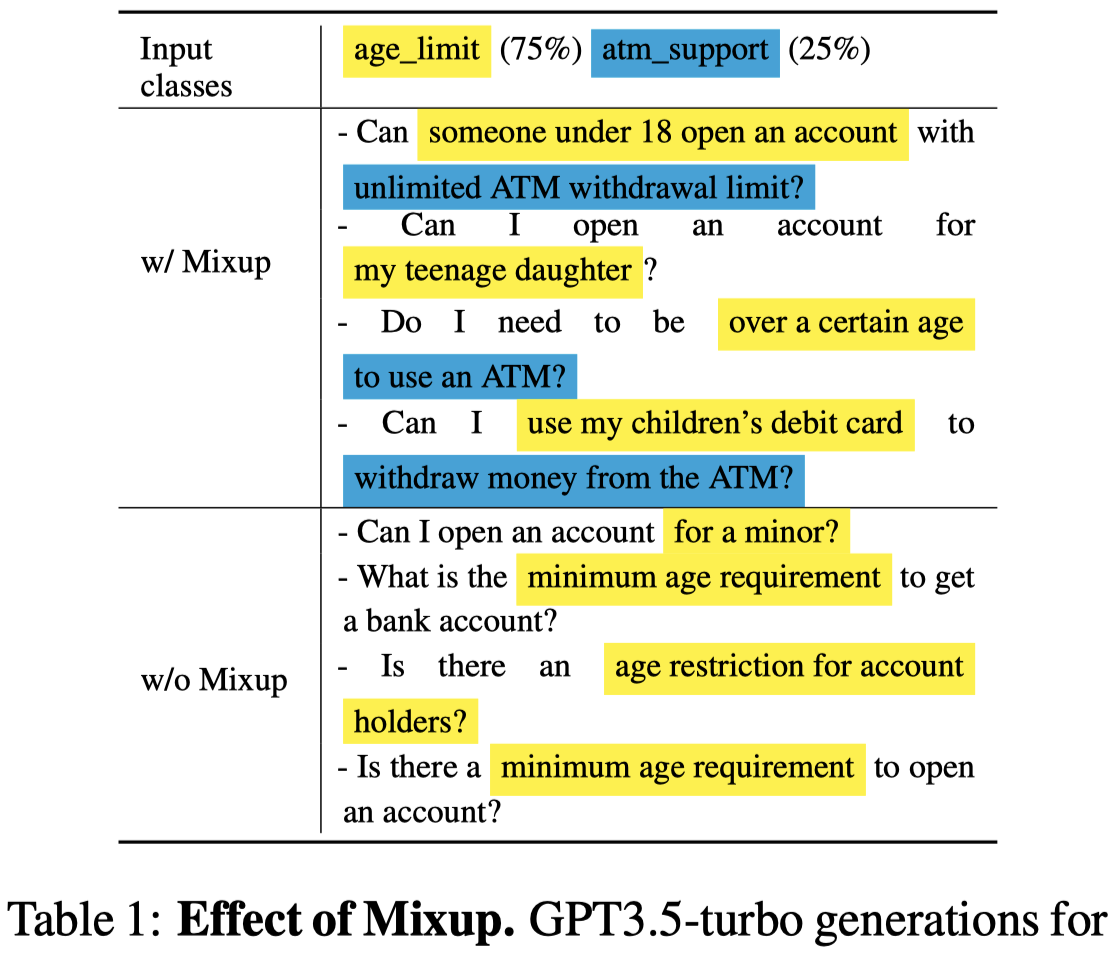
第一步,作者提出的用来生成hard samples的prompt。一次提供\(t=4\)个class的描述prompt(人工构造),每个class随机找\(k=0/2\)个样例,然后对于每个单独的class,要求生成的数据能够包括\(\alpha \%\)的class信息和\((1-\alpha) \%\)的另一种class的信息:
第二步,由于生成的句子包括了两个class的信息,无法保证最后生成的text到底是属于哪个class,因此需要用LLM进行relabelling。

作者的实验基于GPT-3.5-turbo进行生成,然后微调DistilBERT-base和BERT-base,进行text classification任务。
进行了class混合后的结果:
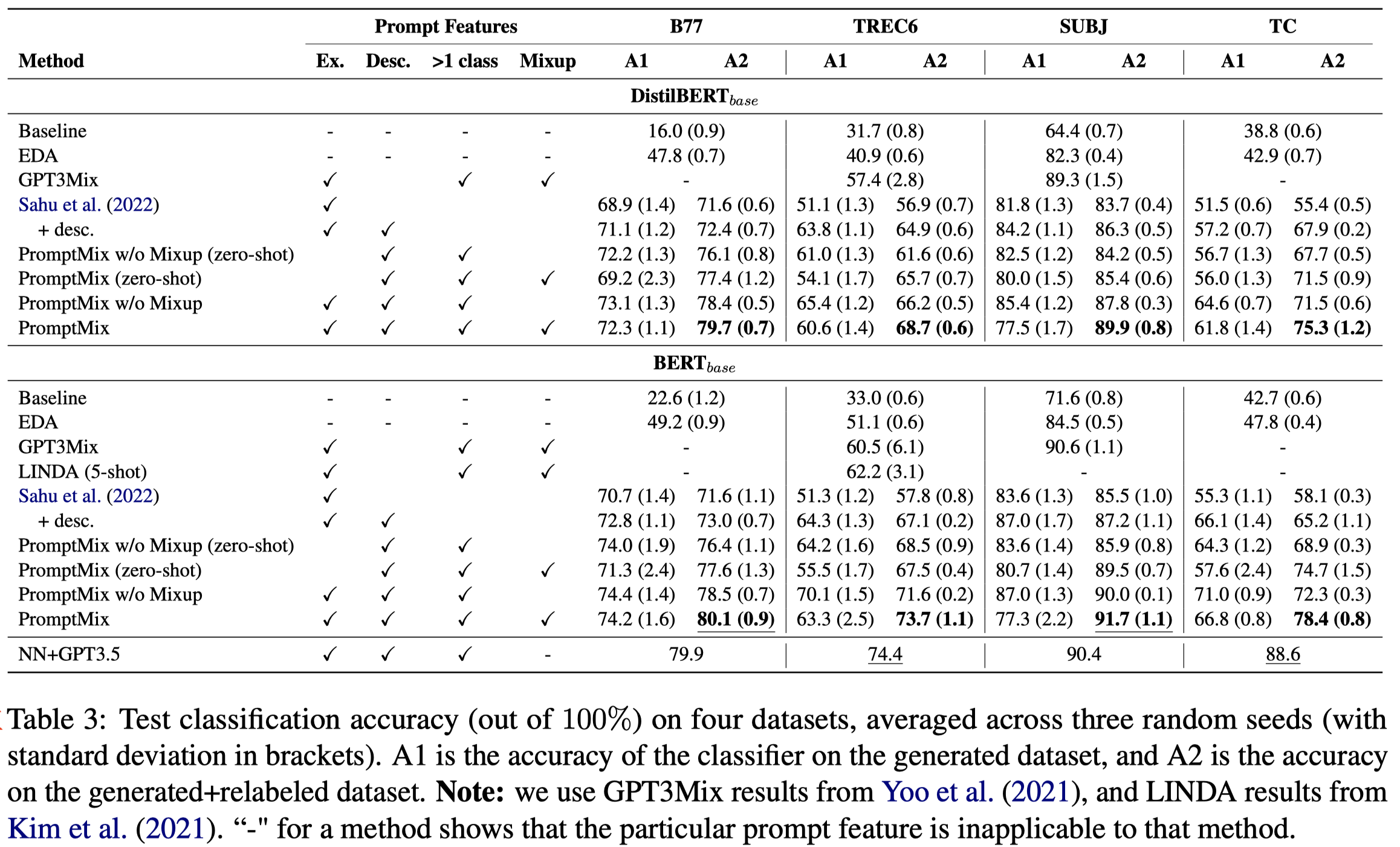
总体实验结果:
观察:
- 最后一行,在这些任务上,直接让GPT结合kNN ICL进行分类效果最好…作者这里提出的数据增强方法只是能够被声明为不到1%的参数量,达到了GPT类似的效果
- A1是只使用生成的数据;A2是使用real data和生成data;由于作者是生成的hard数据,因此如果完全使用生成数据训练的话,学习的分类器性能不好。只不过如果是同时使用,model的泛化性能够得到很好的提升
使用不同LLM对比的结果:
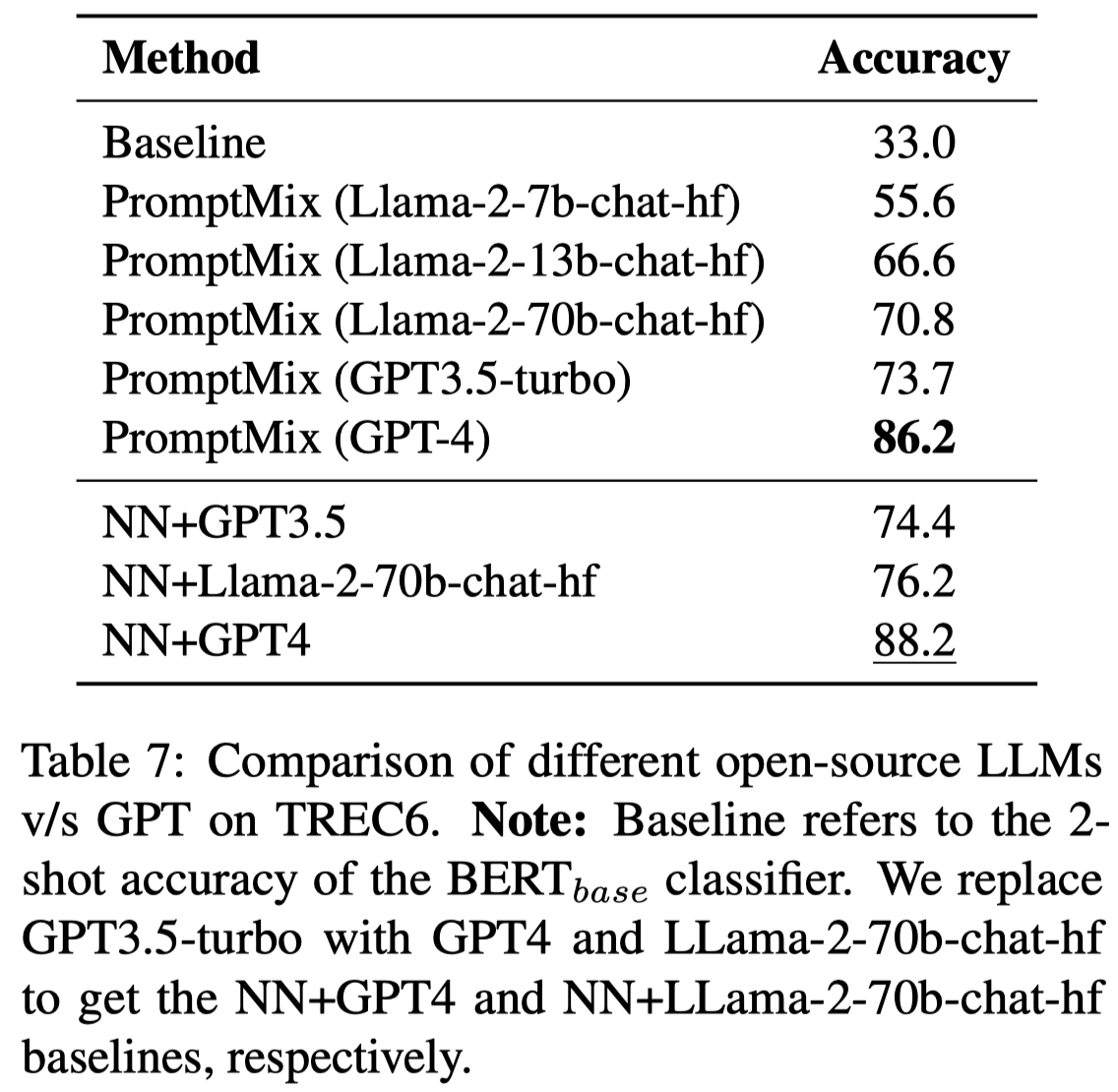
观察:
- GPT-4比起GPT3.5,效果又提升了接近10个点
- LLaMA2-70B接近GPT3.5
MSP-emnlp23
Mixture of Soft Prompts for Controllable Data Generation. Columbia University. EMNLP 2023. 代码.
Large language models (LLMs) effectively generate fluent text when the target output follows natural language patterns. However, structured prediction tasks confine the output format to a limited ontology, causing even very large models to struggle since they were never trained with such restrictions in mind. The difficulty of using LLMs for direct prediction is exacerbated in few-shot learning scenarios, which commonly arise due to domain shift and resource limitations. We flip the problem on its head by leveraging the LLM as a tool for data augmentation rather than a model for direct prediction. Our proposed Mixture of Soft Prompts (MSP) serves as a parameter-efficient procedure for generating multi-attribute data in a controlled manner. Denoising mechanisms are further applied to improve the quality of synthesized data. Automatic metrics show our method is capable of producing diverse and natural text, while preserving label semantics. Moreover, MSP achieves state-of-the-art results on three benchmarks when compared against strong baselines. Our method offers an alternate data-centric approach for applying LLMs to complex prediction tasks.
Issue: 直接利用LLM执行不同的低资源任务,在面临需要hierarchy or compositionality的NLU任务时,效果表现不好。
However, off-the-shelf LLMs have shown evidence of struggling with direct prediction in more complicated NLU tasks, such as those involving hierarchy or compositionality (Furrer et al., 2020; Qiu et al., 2022; Dziri et al., 2023). LLMs with ICL also exhibit problems when the target output requires a specific structure not represented in the training data (Reynolds and McDonell, 2021; Min et al., 2022).
另一种解决低资源问题的思路是数据增强,问题是缺少对于输出结果label preservation和diversity的控制。作者利用LLM来作为工具为数据增强生成更多fluent text。
Solution: 作者为数据集中的每一个attribute(在论文中的意思是指某种具体的type比如entity type)都学习一个对应的soft prompt;由于一个句子可能有多个attributes(比如多个entities),因此需要想办法混合soft prompts,根据混合后的soft prompt来生成最后的data。
作者的方法:
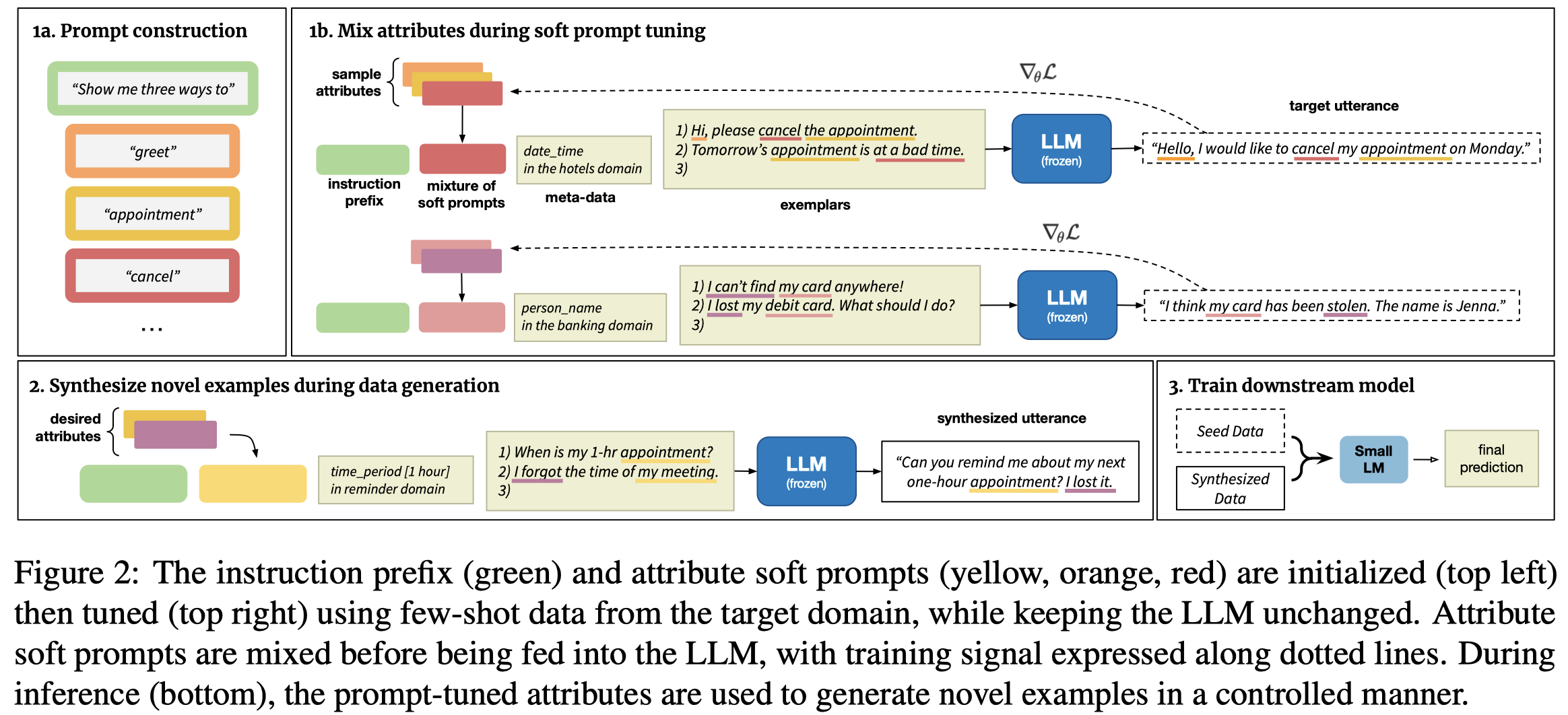
作者的prompt有如下几部分:
- an instruction prefix:
Show me three distinct utterances that all express the X; - soft prompts: 利用attributes的name和description来初始化,如"song is a musical song or melody";
- meta-data:和具体task相关的信息,比如domain name或slot-values
- exemplars:包括了前面attributes的样例\(k=2\)
由于一个句子可能对应多个attributes,比如"greet"和”change“ intents,就会有多个soft prompts,因此需要设计某种混合soft prompts的方法。具体来说作者设计了5种组合prompt的方法,比如concat:
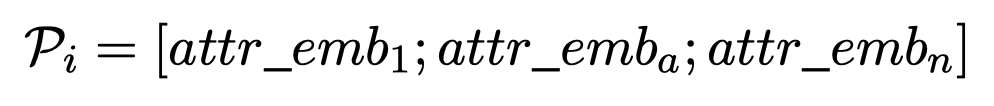
其它的还有pooling、Attention、Bottleneck和CNN的方法。
基于设计的prompt方法和attribute mixing方法,作者针对target domain的数据进行微调。微调后的LLM可以作为数据生成器。对于生成的数据,作者提出了两个Data Denoising的指标:
- 由于数据中存在数据不平衡的现象,作者采样生成数据的时候,按照某个attribute在数据集中出现的频率的进行反向采样
- 作者发现很多生成的错误数据和目标label之间有很大差异,因此作者只保留和原有数据sentence embedding相似的生成数据
作者的实验设置强调了从source domain到target domain的迁移。但实际上,作者生成target domain的数据时,只利用了target domain的数据,生成后的数据与原有的target domain真实数据,以及source domain的数据合并,训练下游任务模型。
作者在实验时,微调FLAN-T5-XXL(11B)来生成数据,下游任务使用GODEL。在实验时,作者使用了CrossNER数据集。
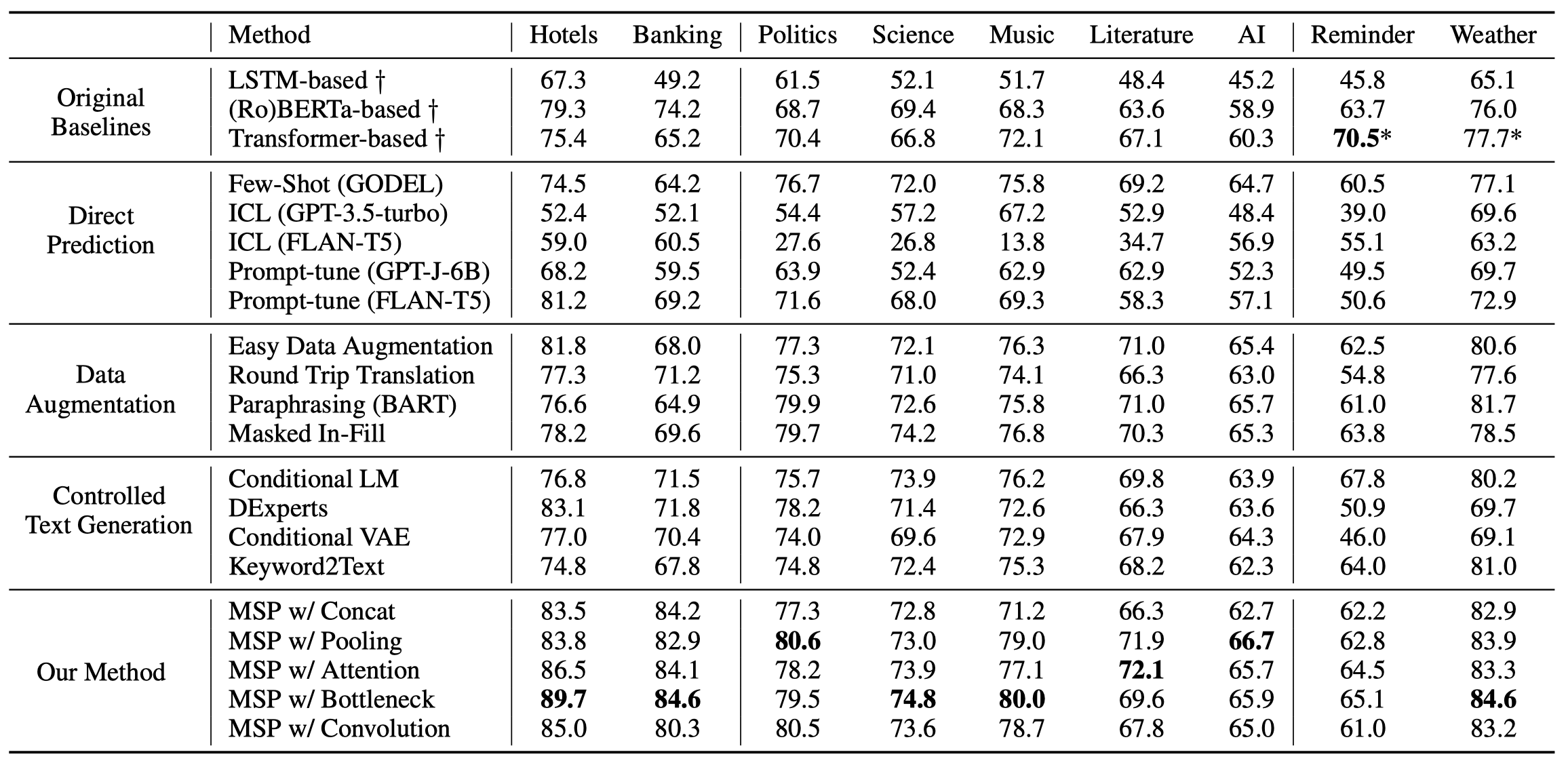
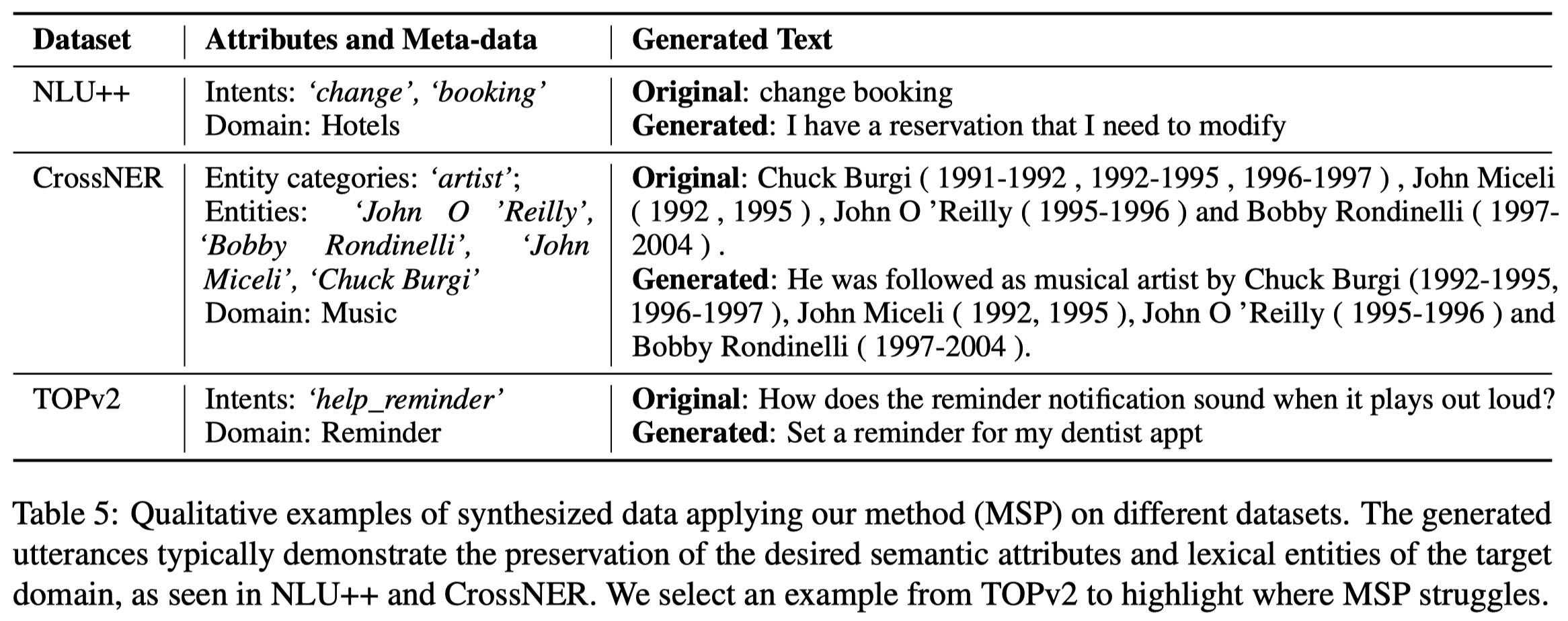
几个示例:
S3-emnlp23
Let’s Synthesize Step by Step: Iterative Dataset Synthesis with Large Language Models by Extrapolating Errors from Small Models. EMNLP 2023. 代码.
Data Synthesis is a promising way to train a small model with very little labeled data. One approach for data synthesis is to leverage the rich knowledge from large language models to synthesize pseudo training examples for small models, making it possible to achieve both data and compute efficiency at the same time. However, a key challenge in data synthesis is that the synthesized dataset often suffers from a large distributional discrepancy from the real task data distribution. Thus, in this paper, we propose Synthesis Step by Step (S3), a data synthesis framework that shrinks this distribution gap by iteratively extrapolating the errors made by a small model trained on the synthesized dataset on a small real-world validation dataset using a large language model. Extensive experiments on multiple NLP tasks show that our approach improves the performance of a small model by reducing the gap between the synthetic dataset and the real data, resulting in significant improvement compared to several baselines: 9.48% improvement compared to ZeroGen, 2.73% compared to GoldGen, and 15.17% improvement compared to the small model trained on human-annotated data.
Issue:虽然LLM已经在各类下游任务都已经取得了很好的效果。但受限于large model sizes and high inference latency,很难在实际中部署。也因此,在很多资源受限的任务中,使用small model仍然是收到偏好的。而要训练好一个small model关键是需要特定任务的大量有标注数据。但获取大量标注数据是很难的。
有一系列的方法讨论如何降低对人工标注数据的依赖:
- knowledge distillation (Hinton et al., 2015; Beyer et al., 2022; Hsieh et al., 2023; Xu et al., 2020; Zhou et al., 2020; Shridhar et al., 2023)
- data augmentation (DeVries and Taylor, 2017; Shorten and Khoshgoftaar, 2019; Li et al., 2022)
- module replacing (Xu et al., 2020; Zhou et al., 2023), semi-supervised learning (Chen et al., 2020; Wang et al., 2021; Smith et al., 2022)
- data synthesis (Anaby-Tavor et al., 2020; Puri et al., 2020).
data synthesis方法最大的问题在于生成的data和real data之间存在large distributional discrepancy。提高生成数据的质量能够使用更少的生成数据训练处更好的task model。减少让训练的模型取得比较好的效果所需要的生成数据的数量
如何提高生成数据的质量,减小和real data之间的distributional discrepancy。
Solution: 作者的方法思想核心是利用LLM生成数据,训练好的task model,在gold data上预测错误的samples,来反映生成data和real data之间的差异。让LLM模仿这些被错误预测的samples生成更多的数据,重新训练task model。
作者提出的Synthesis Step by Step (S3)方法图:

Seed Data Synthesis with Rationales. 作者首先考虑如何生成训练数据。作者的改进之处在于,首先利用LLM找出每个label可能对应的不同rationales;然后联合label和相应的rationales让LLM生成更加diverse, informative, and realistic examples。
Error Extrapolation-based Synthesis (EES). 作者提出Error Extrapolation-based Synthesis (EES)来找出只利用生成数据训练好的task model,在对应的real data上(实现中就是直接使用了对应task的training set来评估task model)被错误预测的samples,然后让LLM仿照这些被错误预测的samples生成更多的数据,加入到之前构造的seed data中。

作者对不同任务使用的prompt:
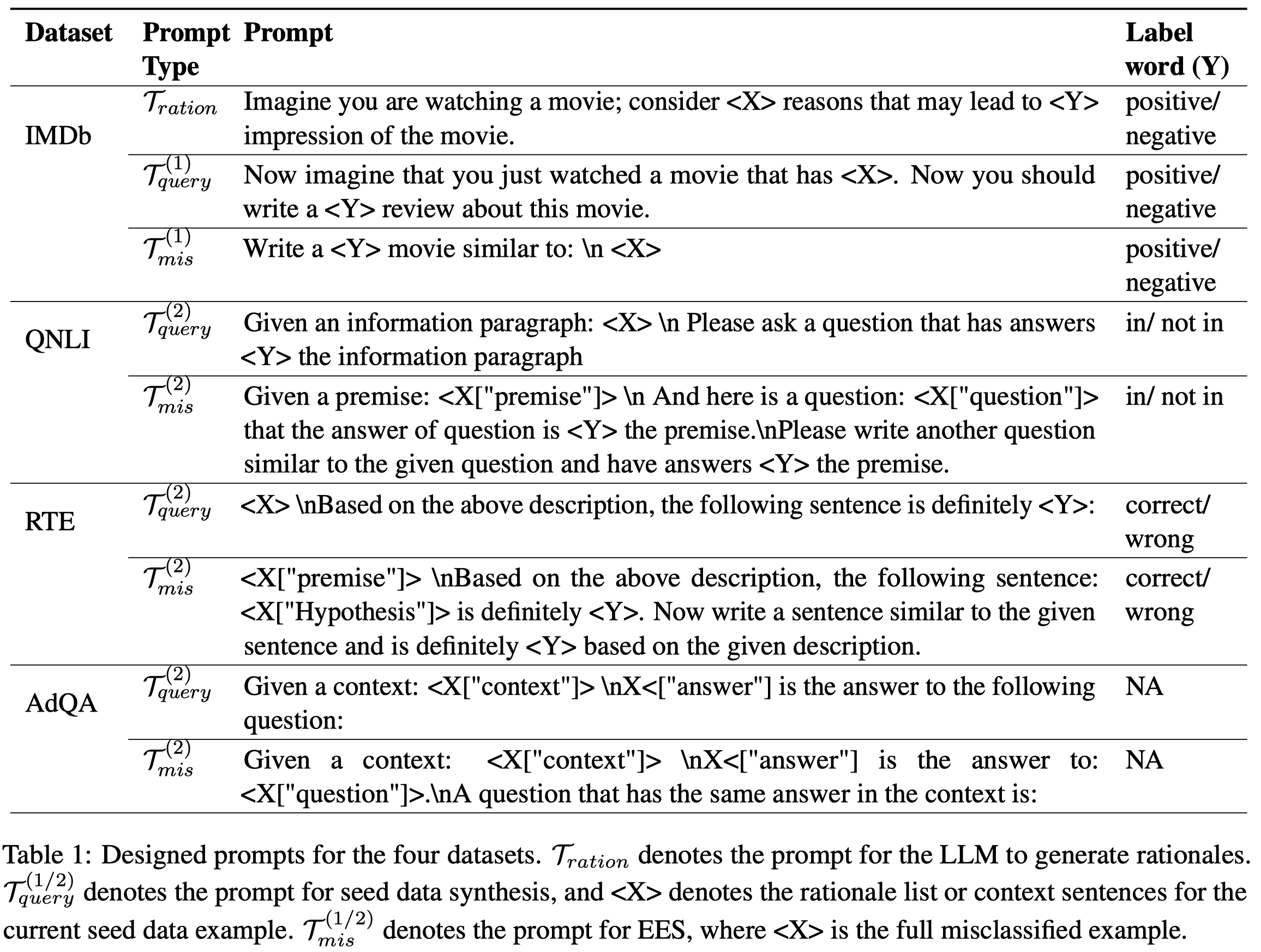
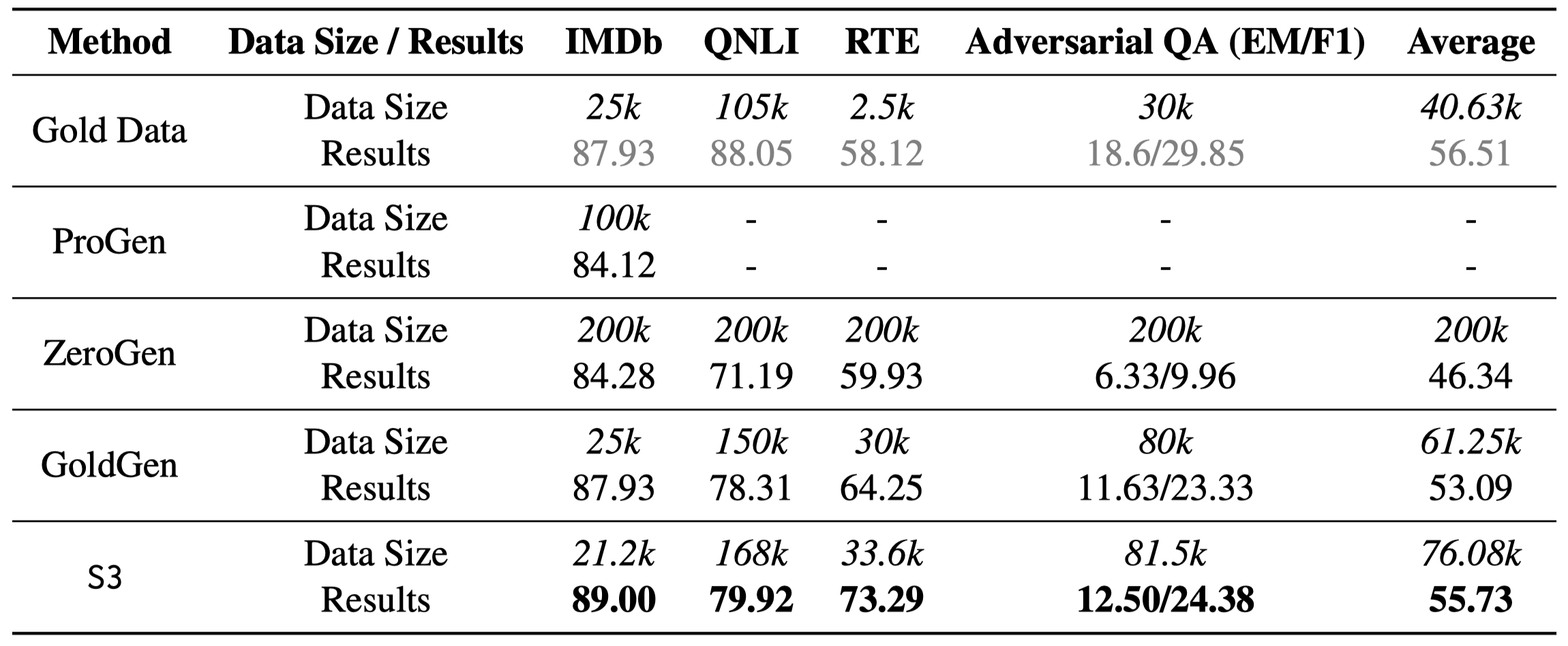
作者的实验使用了GPT3.5,temperature of 0.9;task model是DistilBERT-base-uncased。在text classification、Natural Language Inference (NLI)和QA三类task上进行了测试:
DOCTOR-emnlp23
Dialogue Chain-of-Thought Distillation for Commonsense-aware Conversational Agents. EMNLP 2023. Yonsei University. 代码。
Human-like chatbots necessitate the use of commonsense reasoning in order to effectively comprehend and respond to implicit information present within conversations. Achieving such coherence and informativeness in responses, however, is a non-trivial task. Even for large language models (LLMs), the task of identifying and aggregating key evidence within a single hop presents a substantial challenge. This complexity arises because such evidence is scattered across multiple turns in a conversation, thus necessitating integration over multiple hops. Hence, our focus is to facilitate such multi-hop reasoning over a dialogue context, namely dialogue chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning. To this end, we propose a knowledge distillation framework that leverages LLMs as unreliable teachers and selectively distills consistent and helpful rationales via alignment filters. We further present DOCTOR, a DialOgue Chain-of-ThOught Reasoner that provides reliable CoT rationales for response generation 1 . We conduct extensive experiments to show that enhancing dialogue agents with high-quality rationales from DOCTOR significantly improves the quality of their responses.
Issue:在Commonsense reasoning任务中,之前的方法大多是集中在对最后一轮对话中的context进行推理,而忽略了在之前多轮对话中会出现的evidence。
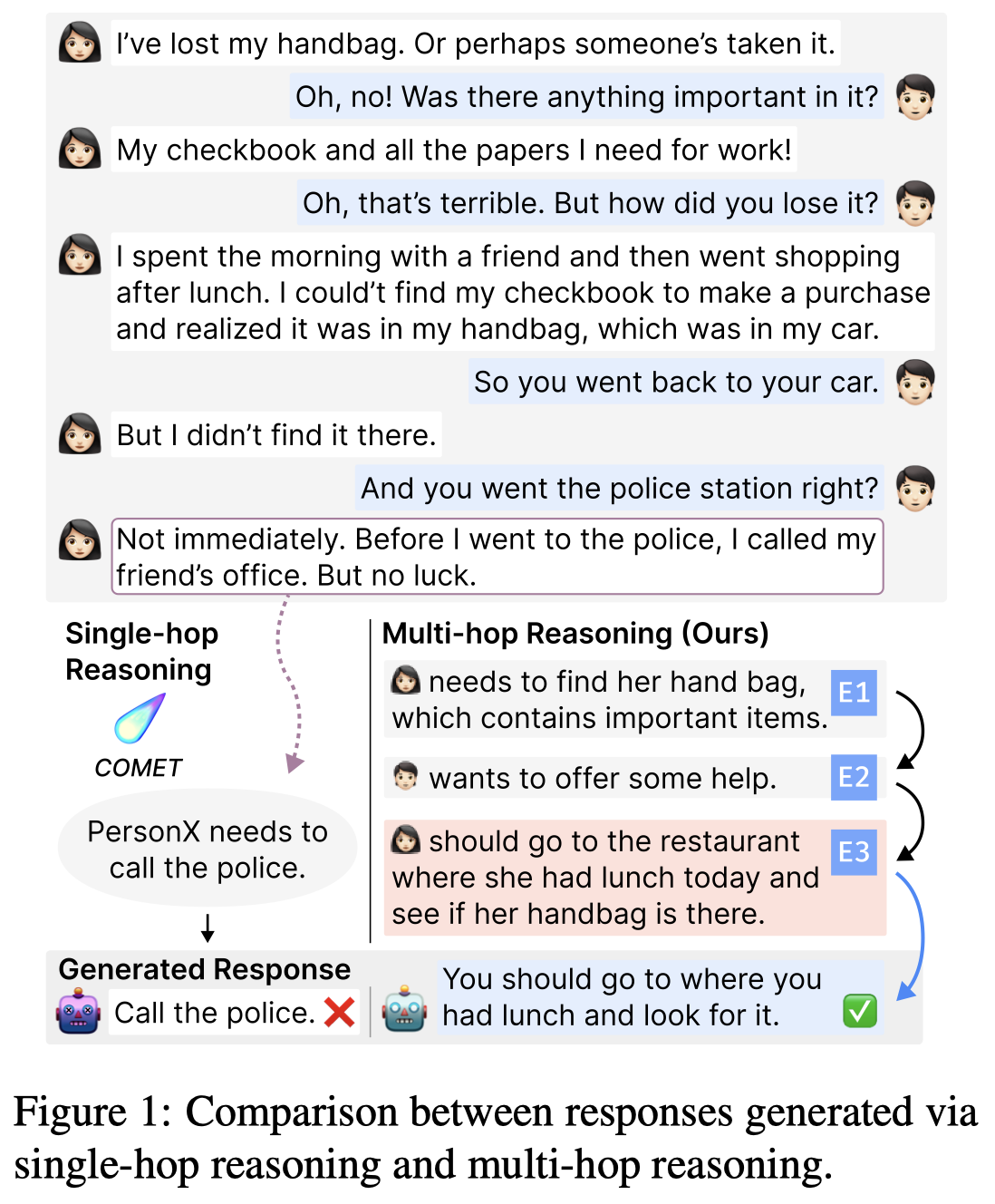
Solution: 作者将multi-hop commonsense reasoning看做是Chain-ofThought (CoT) reasoning (Wei et al., 2022) for dialogue response generation, namely Dialogue CoT。作者认为CoT生成的rationales能够帮助response generation。
但是LLM生成的rationales存在问题:
- LLMs tend to rely much on explicit cues, necessitating taskspecific constraints to seek implicit knowledge.
- LLMs exhibit poor alignment between rationales and dialogues, resulting in inconsistent and unhelpful rationales.
因此,作者将已有的LLM看做是unreliable reasoner,将其生成的rationales过滤后,作为好的rationales。尝试蒸馏一个新的LM让其能够直接输出过滤后的好的reliable rationales。
作者的方法图:
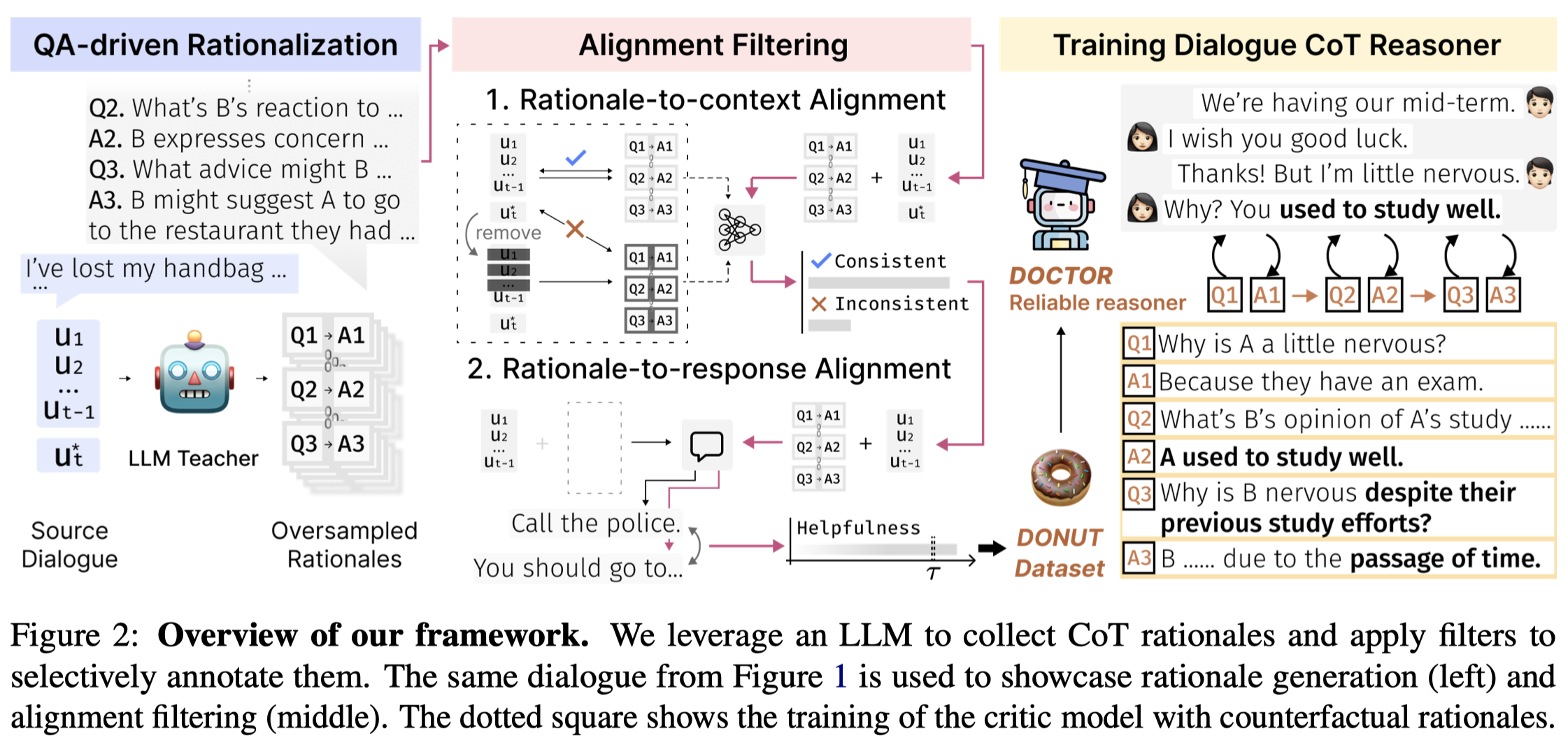
首先,是QA-driven Rationalization。作者给定LLM之前轮的context \(U_{<t}\)和下一步的real response \(u_{t}\),然后用不同的prompt提问,找到对应的rationales。每一轮对有对应的rationales集合,这样就实现了对于多轮问答中线索的搜寻。
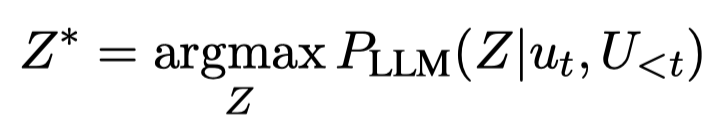
提问的prompt是作者从ATOMIC中选择的11种commonsense relations,然后构造问题,如:
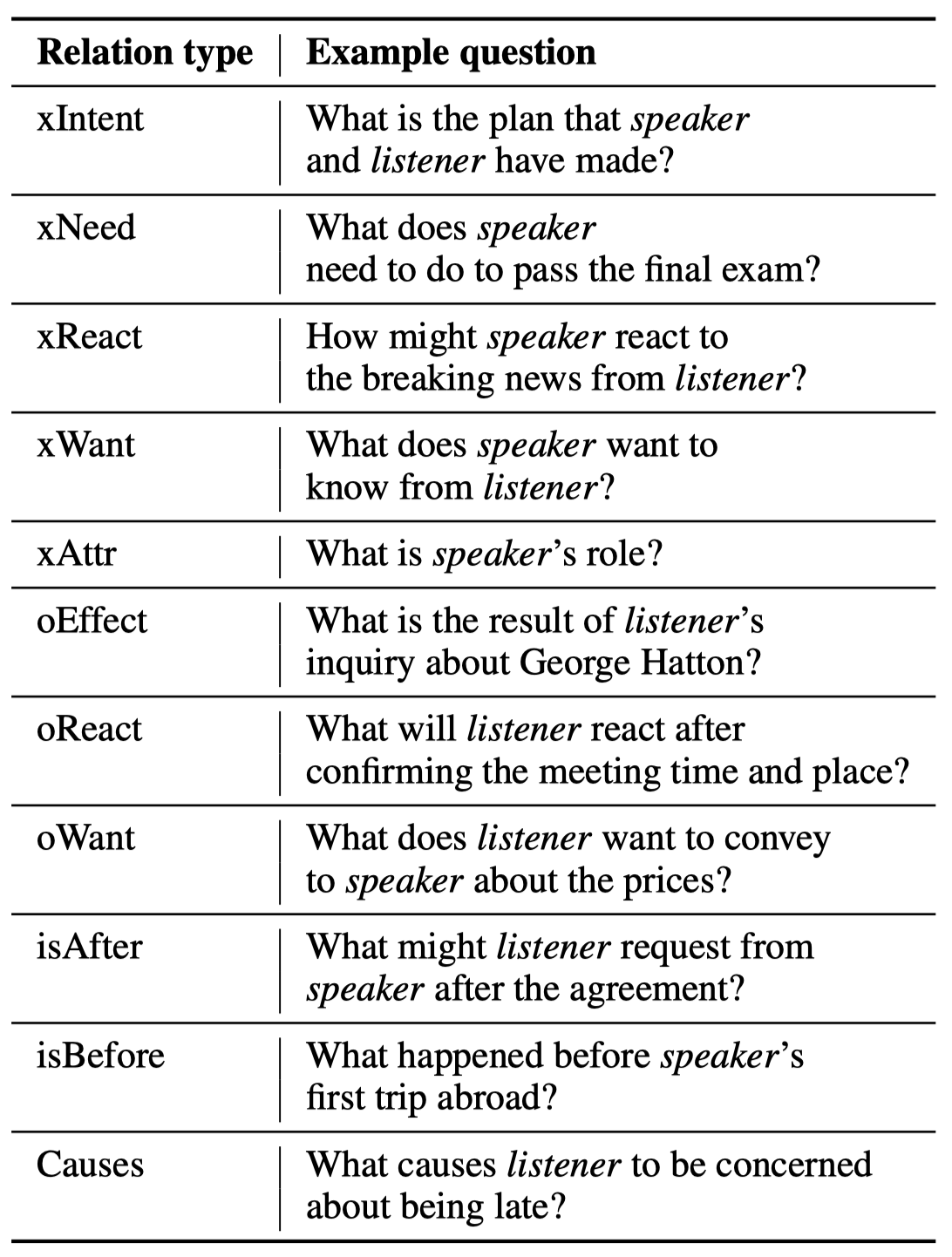
然后,为了保证生成的rationales的质量,作者利用了两个alignment filters:
Rationale-to-context alignment:为了判断rationales是否和给定的context是否一致,作者基于
RoBERTa-large训练了一个二元分类器。训练集的构造是一致的context和rationales、不一致的context和rationales。作者从SODA数据集中随机选择了6K个dialogues,输入给LLM完整的多跳问答的context,然后人工选择出和context一致的rationales。不一致的rationales是作者破坏完整的多轮问答,只给定最后一步的utterance,让LLM生成counterfactual rationales。作者训练出来的不一致分类器能够达到93%的测试准确度。Rationale-to-response alignment:为了判断rationales是否和后续的response一致,作者考虑在给定rationales的情况下,能够正确的输入后续的response。基于
Cosmo-3B,计算helpfulness ratio。具体是给定了rationales情况下,real utterance出现的perplexity和不给定rationales的perplexity比值: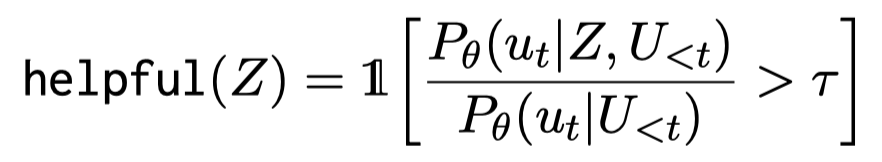
只有helpfulness ratio大于\(\tau=0.95\)的rationales会被选择。
为了蒸馏新的LM reasoner,作者构建了新的数据集DONUT。在其构造过程中,两个filters能够过滤掉近1/4的rationales。
在DONUT数据上,蒸馏出来的新的LM基于OPT-1.3B。
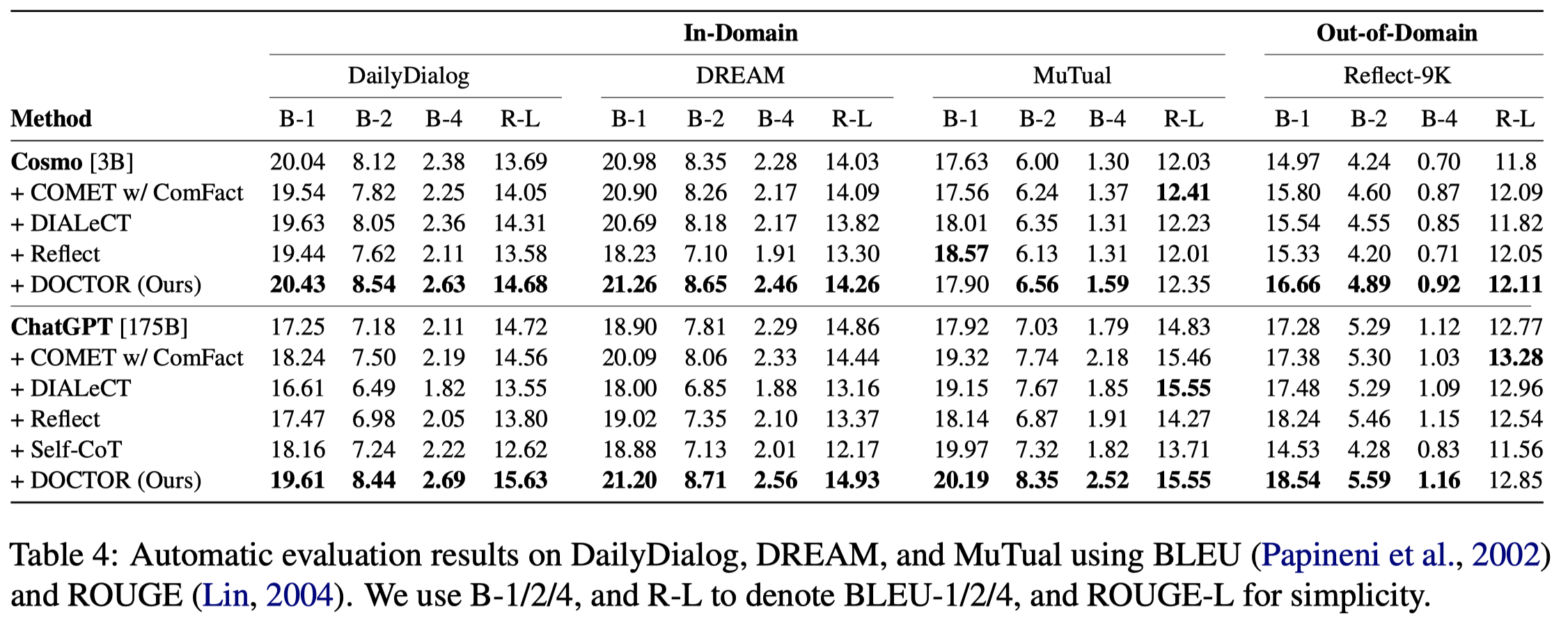
实验结果: