LLM-data-augment1
LLM数据增强
基于LLM的数据增强论文合集1。
GPT3Mix
GPT3Mix: Leveraging Large-scale Language Models for Text Augmentation
EMNLP 2021 Findings,NAVER AI lab,代码。
Large-scale language models such as GPT3 are excellent few-shot learners, allowing them to be controlled via natural text prompts. Recent studies report that prompt-based direct classification eliminates the need for fine-tuning but lacks data and inference scalability. This paper proposes a novel data augmentation technique that leverages large-scale language models to generate realistic text samples from a mixture of real samples. We also propose utilizing soft-labels predicted by the language models, effectively distilling knowledge from the large-scale language models and creating textual perturbations simultaneously. We perform data augmentation experiments on diverse classification tasks and show that our method hugely outperforms existing text augmentation methods. We also conduct experiments on our newly proposed benchmark to show that the augmentation effect is not only attributed to memorization. Further ablation studies and a qualitative analysis provide more insights into our approach.
作者声称是首个用LLM来进行数据增强工作的文章。
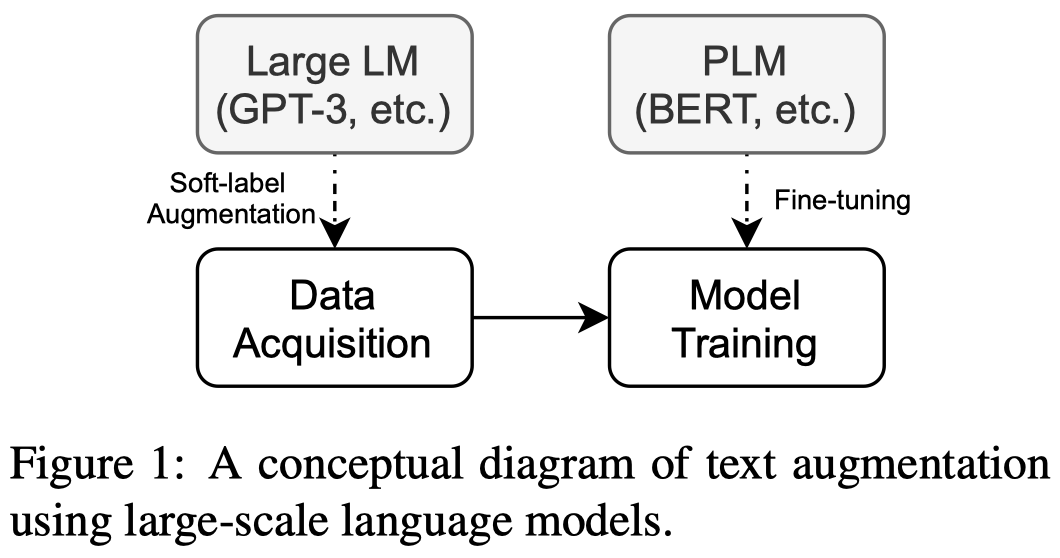
作者认为的需要用LLM来做数据增强,而不是直接执行特定任务的理由:
- First, the number of incontext training examples is hard limited by the maximum prompt length enabled by the inherent language model architecture.
- Second, prompt-based approaches require online inference on the expensive large-scale language models. The inference may not be scalable in real-world use cases, because it is slow and incurs huge memory overhead.
- Lastly, the prompt-based approaches do away with conventional machine learning techniques, making it mostly incompatible with existing established fine-tuning methods.
提出的GPT3Mix方法图:
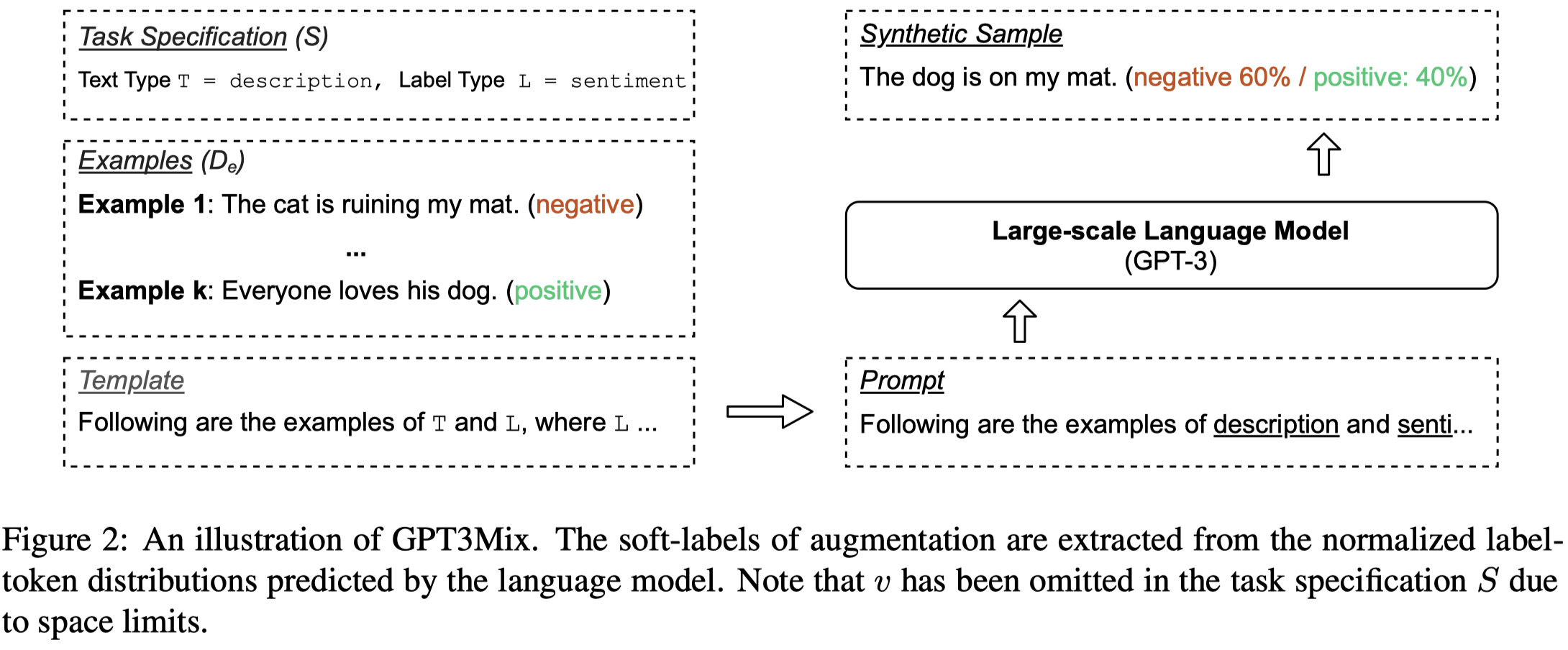
作者构造的生成训练数据的prompt template包括:
- Text Type:输入的text的类型,比如movie review
- Label Type:label class的类型,比如情感分类中是sentiment
- Label-token Verbalizer:将label转化为text tokens
构造数据的ICL prompt示例(不指定生成数据的label、prompt中一次性提供所有的label信息只适用于label数量较少的情况):


生成数据的时候,注意两点:
- 同时生成data和label,并且label在data之后出现,这样保证label是依赖于生成的data的
- 不是简单的生成label,还使用LLM对label tokens的conditional probability来作为soft-label。带有soft-label的GPT生成的text加入到原来的数据中,获得效果的提升。
上下文的demonstrations是从训练集中随机采样,默认使用的样例数量是2。
作者在实验部分针对text classification,主要基于GPT-3(davinci)。还自己构造了一个RT20 binary sentiment classification数据集(关于movie reviews),收集的是GPT3使用的最新data之后出现的新评论。下面是实验结果:
Data Augmentation for Intent Classification
Data Augmentation for Intent Classification with Off-the-shelf Large Language Models. ACL 2022 Workshop NLP4ConvAI 2022,代码。
Data augmentation is a widely employed technique to alleviate the problem of data scarcity. In this work, we propose a prompting-based approach to generate labelled training data for intent classification with off-the-shelf language models (LMs) such as GPT-3. An advantage of this method is that no task-specific LM-fine-tuning for data generation is required; hence the method requires no hyper-parameter tuning and is applicable even when the available training data is very scarce. We evaluate the proposed method in a few-shot setting on four diverse intent classification tasks. We find that GPT-generated data significantly boosts the performance of intent classifiers when intents in consideration are sufficiently distinct from each other. In tasks with semantically close intents, we observe that the generated data is less helpful. Our analysis shows that this is because GPT often generates utterances that belong to a closely-related intent instead of the desired one. We present preliminary evidence that a prompting-based GPT classifier could be helpful in filtering the generated data to enhance its quality.
作者认为之前的GPT3Mix工作,由于每次prompt会直接提供所有的label,并且不限制生成数据的label类型,只使用与label数量少的任务。而意图分类Intent Classification(IC)任务可能有上百个不同的intent,并且可能存在非常相近的intent,导致GPT3Mix不适用于意图分类task。
an intent is a type of request that the conversational agent supports; e.g. the user may want to change the language of the conversation, play a song, transfer money between accounts, etc.
作者的方法主要有两点:
每次只生成一类label的数据(但同样是随机找的demonstrations)

提出可以用LLM分类的能力,过滤掉text和label不对应的生成数据

作者实验基于GPT-3。发现GPT3无法准确的理解相似label,导致生成数据质量差,然后作者尝试了简单的使用GPT-3再来重新分类生成句子的方法。
We hypothesize that one limiting factor can be GPT-3’s inability to understand fine-grained differences in the meanings of utterances.
InPars
InPars: Unsupervised Dataset Generation for Information Retrieval. SIGIR 2022 Short paper,代码。
The Information Retrieval (IR) community has recently witnessed a revolution due to large pretrained transformer models. Another key ingredient for this revolution was the MS MARCO dataset, whose scale and diversity has enabled zero-shot transfer learning to various tasks. However, not all IR tasks and domains can benefit from one single dataset equally. Extensive research in various NLP tasks has shown that using domain-specific training data, as opposed to a general-purpose one, improves the performance of neural models [45, 56]. In this work, we harness the few-shot capabilities of large pretrained language models as synthetic data generators for IR tasks. We show that models fine-tuned solely on our synthetic datasets outperform strong baselines such as BM25 as well as recently proposed self-supervised dense retrieval methods. Code, models, and data are available at https://github.com/zetaalphavector/inpars.
大模型可以直接用来判断query和document之间的相关性,但是由于候选document的数量过多,在实践中,要用LLM来进行检索还是不实际的。
传统的dense retriever通过提前计算document的embedding,利用现有的搜索框架,可以高效的寻找相关documents。但是训练dense retriever需要足够的domain-specific training data。
因此,作者提出使用LLM来生成IR任务的数据 \((query, document)\) pairs:
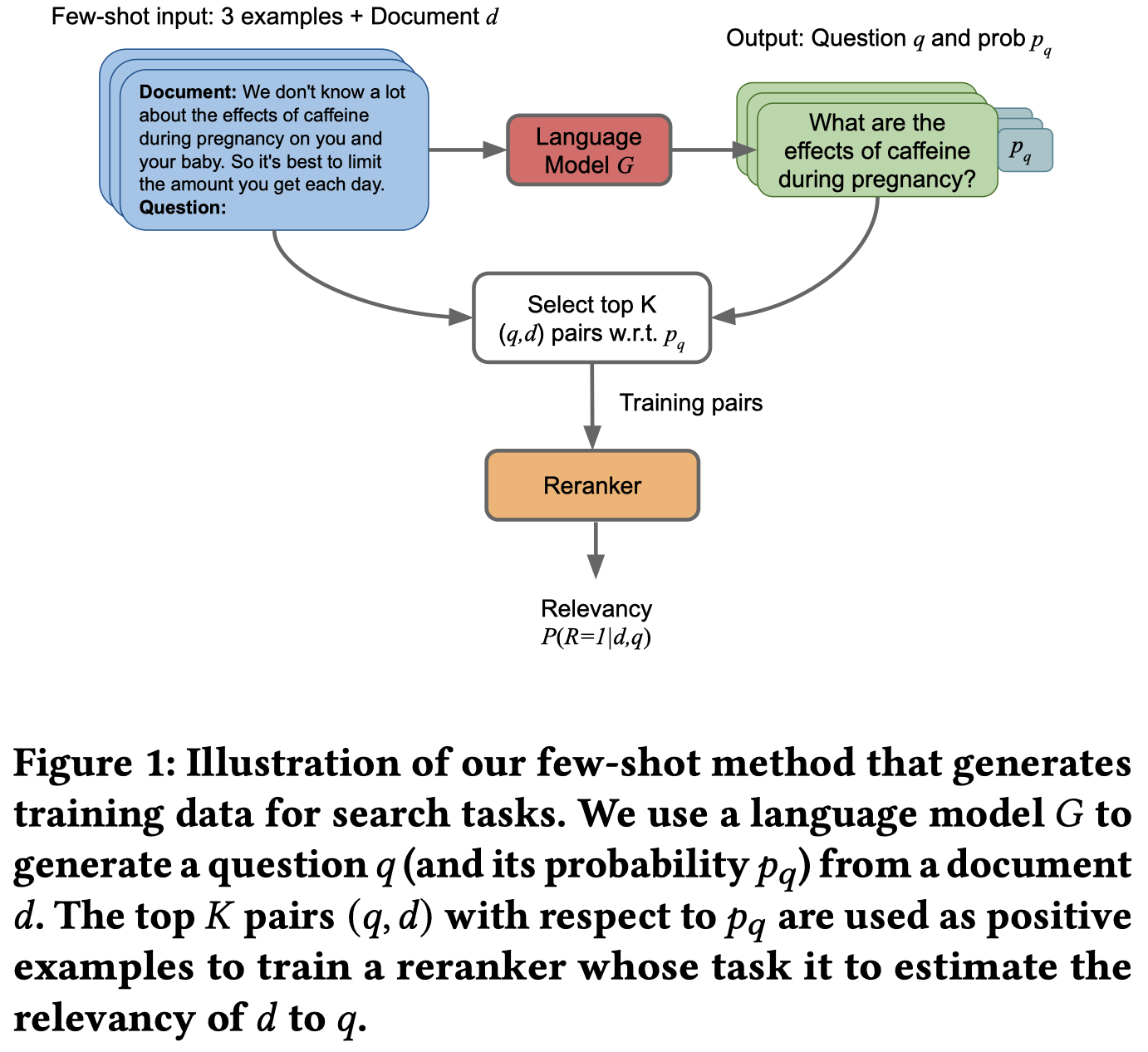
步骤:
通过corpus-level ICL,人工构造3个样例,实现利用LLM为document生成对应的问题
从语料库中采样\(100,000\)个documents,让LLM针对documents生成一个初步相关question,生成question用了两个模板:

第一个模板是原始的训练集中document和对应的question,第二个模板是作者提出的Guided by Bad Questions(GBQ)模板,将原来的question作为bad question,然后人工写一个更加复杂的question作为good question,让LLM生成good question。
利用LLM的conditional probability估计document-question之间的相关性:

依据相关性排序,从\(100,000\)个document-question pairs中,选择\(1,000\)个topK的数据作为训练数据。
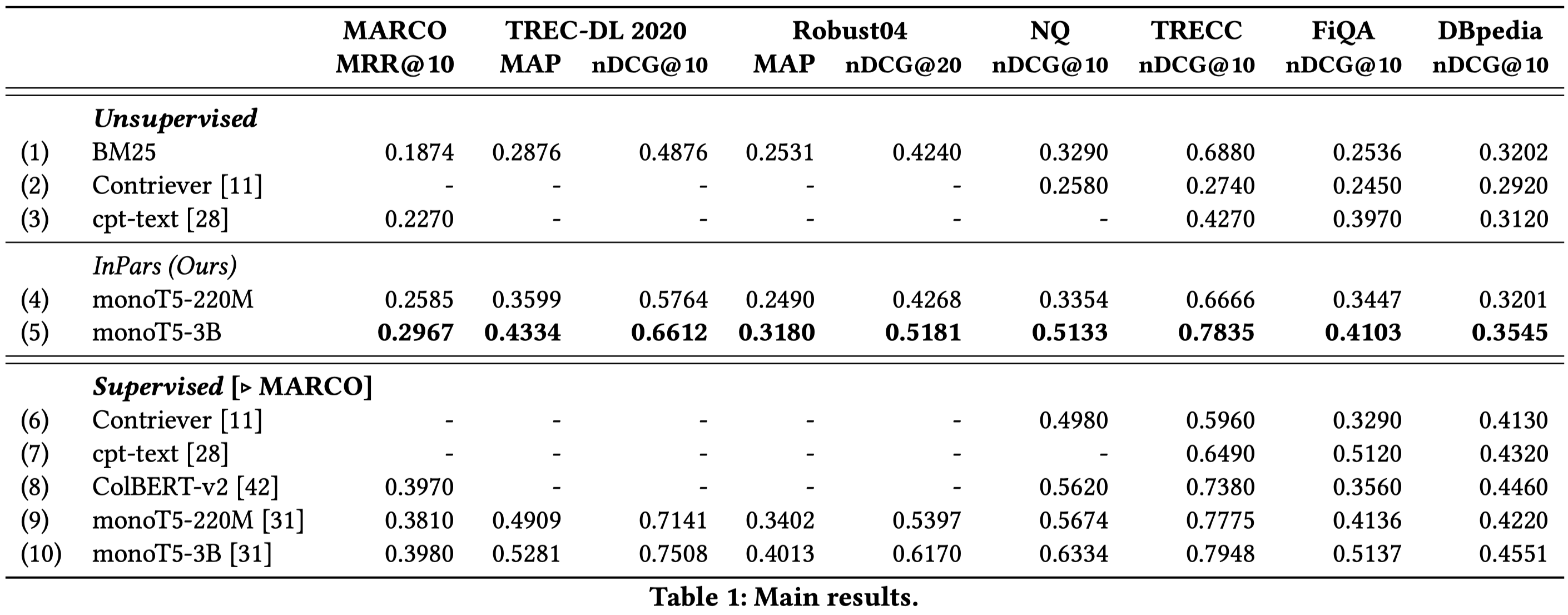
实验基于GPT-3,从实验结果中发现,在无监督的IR方法上效果不错,但是距离有监督的IR方法还有差距:
AugGPT
AugGPT: Leveraging ChatGPT for Text Data Augmentation
arXiv 2023-03
Text data augmentation is an effective strategy for overcoming the challenge of limited sample sizes in many natural language processing (NLP) tasks. This challenge is especially prominent in the few-shot learning scenario, where the data in the target domain is generally much scarcer and of lowered quality. A natural and widely-used strategy to mitigate such challenges is to perform data augmentation to better capture the data invariance and increase the sample size. However, current text data augmentation methods either can’t ensure the correct labeling of the generated data (lacking faithfulness) or can’t ensure sufficient diversity in the generated data (lacking compactness), or both. Inspired by the recent success of large language models, especially the development of ChatGPT, which demonstrated improved language comprehension abilities, in this work, we propose a text data augmentation approach based on ChatGPT (named AugGPT). AugGPT rephrases each sentence in the training samples into multiple conceptually similar but semantically different samples. The augmented samples can then be used in downstream model training. Experiment results on few-shot learning text classification tasks show the superior performance of the proposed AugGPT approach over state-of-the-art text data augmentation methods in terms of testing accuracy and distribution of the augmented samples.
基于改写方法的利用LLM生成text classification task的训练数据。作者认为LLM适合用来做数据增强的两点理由:
- LLM通过预训练,在大规模语料中进行预训练,在自己的参数空间中学习编码到了很多隐式的factual knowledge
- LLM经过RLHF等训练阶段,能够produce more informative and impartial responses to input
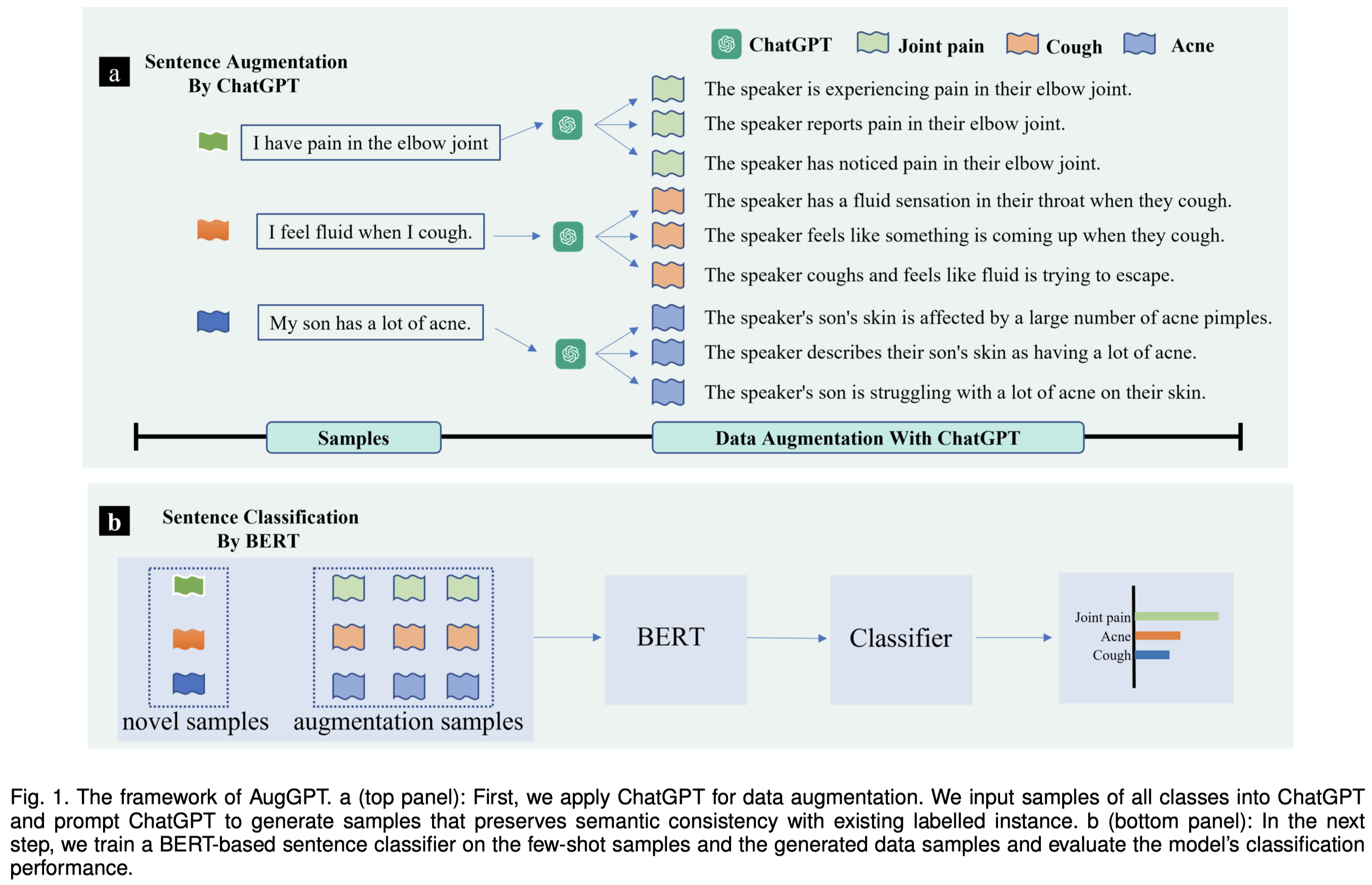
作者的实验是用clinical NLP tasks来进行评估,因为Data augmentation is particularly in demand in clinical NLP, because the significant burden of expert annotation and stringent privacy regulations make large-scale data labeling infeasible.
改写用的prompt:

值得一提的是,作者在实验部分用生成句子和原来句子的embedding cosine相似度评估语义的一致性;然后用TransRate指标来评估生成的数据是否足够compactness,以至于能够方便对不同的类进行区分:
TransRate is a metric that quantifies transferability based on the mutual information between the features extracted by a pre-trained model and their labels, with a single pass through the target data. A higher TransRate could indicate better learnability of the data.
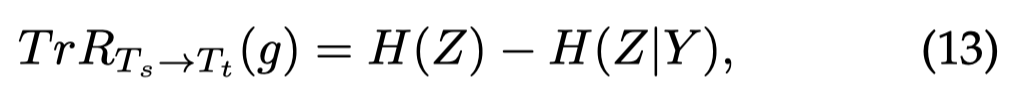
DISCO
DISCO: Distilling Counterfactuals with Large Language Models. ACL 2023,EPFL,代码。
Models trained with counterfactually augmented data learn representations of the causal structure of tasks, enabling robust generalization. However, high-quality counterfactual data is scarce for most tasks and not easily generated at scale. When crowdsourced, such data is typically limited in scale and diversity; when generated using supervised methods, it is computationally expensive to extend to new counterfactual dimensions. In this work, we introduce DISCO (DIStilled COunterfactual Data), a new method for automatically generating high-quality counterfactual data at scale. DISCO engineers prompts to generate phrasal perturbations with a large general language model. Then, a task-specific teacher model filters these generations to distill high-quality counterfactual data. While task-agnostic, we apply our pipeline to the task of natural language inference (NLI) and find that on challenging evaluations such as the NLI stress test, comparatively smaller student models trained with DISCO generated counterfactuals are more robust (6% absolute) and generalize better across distributions (2%) compared to models trained without data augmentation. Furthermore, DISCO-augmented models are 10% more consistent between counterfactual pairs on three evaluation sets, demonstrating that DISCO augmentation enables models to more reliably learn causal representations. Our repository are available at: https://github.com/eric11eca/disco
首个利用LLM生成counterfactual data的工作。
Counterfactual data augmentation (CAD) [Learning the difference that makes a difference with counterfactually-augmented data. 2019]是一种移除spurious correlation,提升模型robustness的数据增强技术。它修改原来数据中的重要组成部分,让原始的label改变:
Counterfactual data augmentation (CAD) (Kaushik et al., 2019) is one general approach to improve model robustness by training on edited instances that systematically alter the critical or causally salient parts of dataset instances that contributes to the label assignment.
一个不够鲁棒的model,对于反事实,可能由于在训练过程学习到了伪相关的特征,从而导致反事实的data还是预测的原来的label。
作者针对NLI任务进行实验,NLI任务的输入是premise-hypothesis pair \(<P,H>\),标签\(l\in \{ Entailment, Contradiction, Neutral \}\)。作者的反事实数据增强方法就是修改前提premise的部分描述,新的前提\(P^{\prime}\)能够让label变更为新\(l^{\prime}\)。
作者提出方法的大致流程:
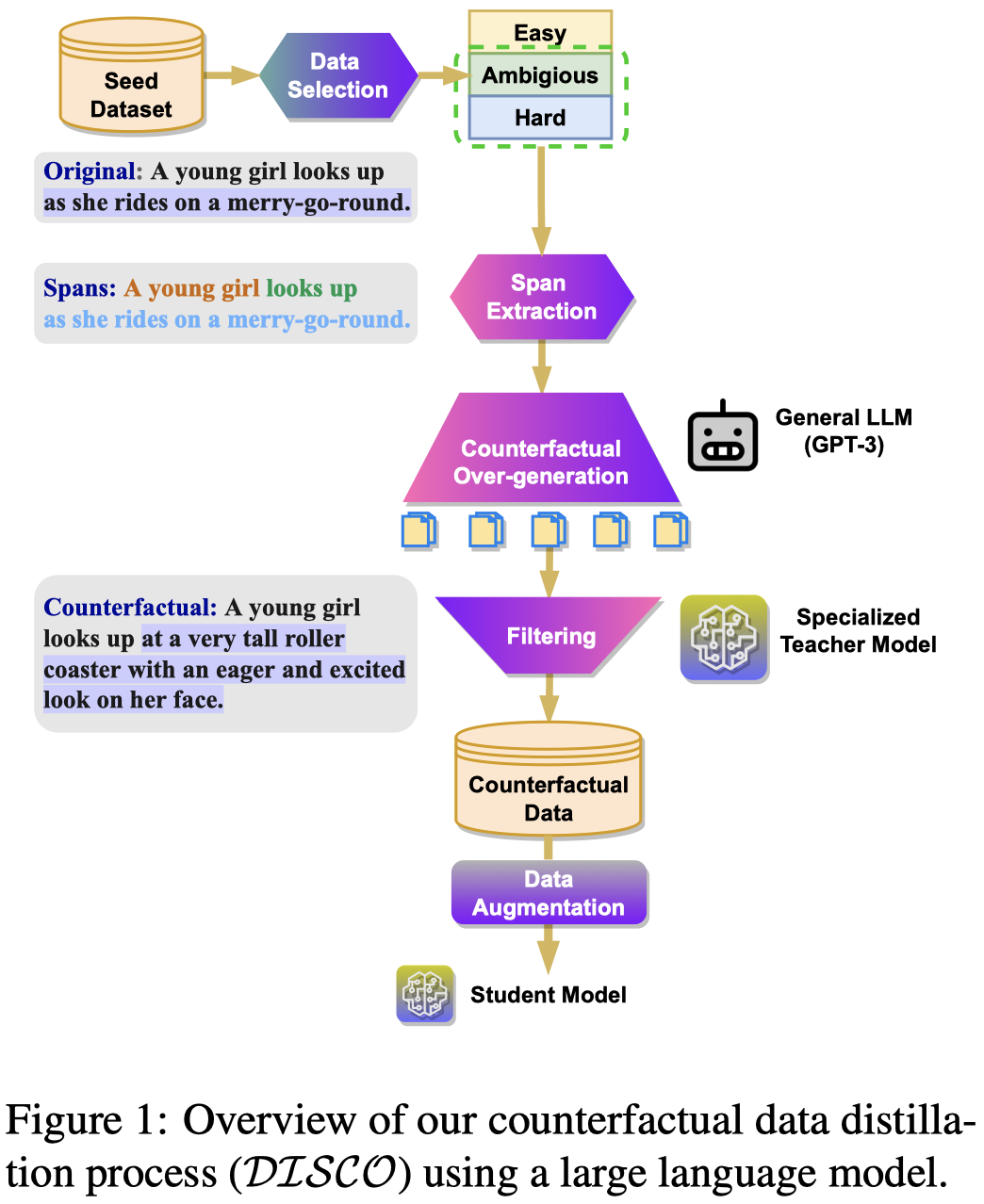
首先,作者只选择了部分训练集中的数据进行训练,利用dataset cartography技术[Dataset cartography: Mapping and diagnosing datasets with training dynamics. 2020],选择ambiguous和hard samples作为之后进行增强的对象;
然后,作者利用之前的一个neural syntactic parser[FLAIR: An easy-to-use framework for state-of-the-art NLP. NAACL 2019]将前提premise句子转化为span的集合;
由于不知道修改哪个span能够导致label的改变,迭代地用
[blank]去替换每个span,然后让LLM填补[blank]以至于对应的label变为新的label。作者提出了两种prompt,一种是让LLM补全[blank],是最常见的GPT的completing mode;一种是利用GPT3的insert mode,让GPT直接回复中间确实内容: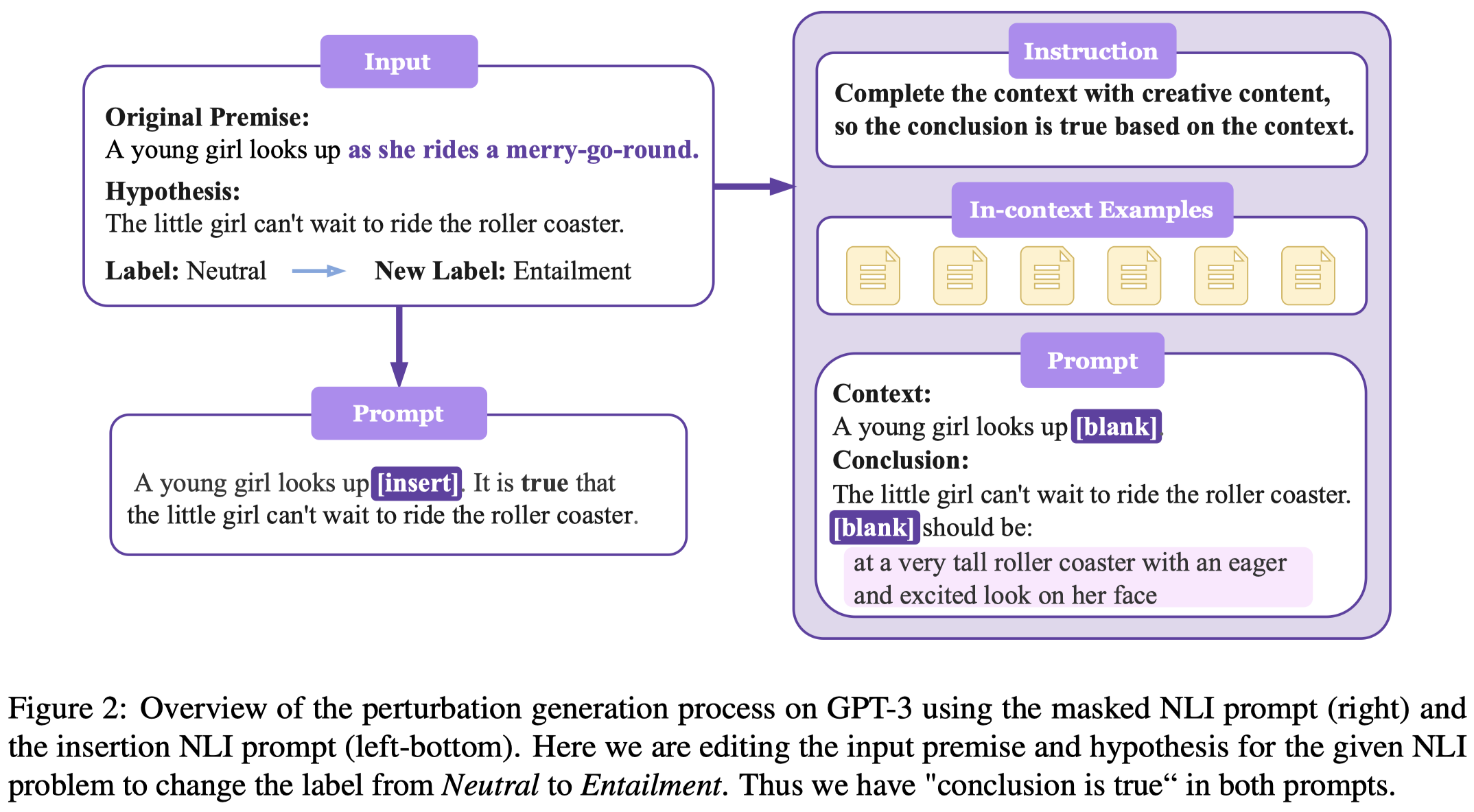
最后,过滤质量比较低的data;首先是用一系列预定义规则进行过滤heuristic-based automatic filter,如是不是和原来的数据有较多的重叠、是不是使用了negation words作为捷径以反转label。然后用一个现有的SOTA NLI模型,给定原始数据和新数据,确定预测的label分布是否发生了大的变化。
作者实验基于GPT-3(DaVinci-002),微调RoBERTa-large进行NLI任务。
实验部分内容较多,具体参考论文。有2个衡量多样性的metric可以注意下:
- Self-BLEU [Texygen: A benchmarking platform for text generation models. 2018]:评估lexical and syntactic diversity
- Dataset Distance:计算新data和旧data的信息多样性,使用OTDD (optimal transport dataset distance) [Geometric dataset distances via optimal transport. 2020]作为指标
GenRead
Generate rather than Retrieve: Large Language Models are Strong Context Generators
[详细博客]。
University of Notre Dame和Microsoft,ICLR 2023,代码。
Knowledge-intensive tasks, such as open-domain question answering (QA), require access to a large amount of world or domain knowledge. A common approach for knowledge-intensive tasks is to employ a retrieve-then-read pipeline that first retrieves a handful of relevant contextual documents from an external corpus such as Wikipedia and then predicts an answer conditioned on the retrieved documents. In this paper, we present a novel perspective for solving knowledge-intensive tasks by replacing document retrievers with large language model generators. We call our method generate-then-read (GenRead), which first prompts a large language model to generate contextual documents based on a given question, and then reads the generated documents to produce the final answer. Furthermore, we propose a novel clustering-based prompting method that selects distinct prompts, in order to generate diverse documents that cover different perspectives, leading to better recall over acceptable answers. We conduct extensive experiments on three different knowledge-intensive tasks, including open-domain QA, fact checking, and dialogue system. Notably, GenRead achieves 71.6 and 54.4 exact match scores on TriviaQA and WebQ, significantly outperforming the state-of-the-art retrieve-thenread pipeline DPR-FiD by +4.0 and +3.9, without retrieving any documents from any external knowledge source. Lastly, we demonstrate the model performance can be further improved by combining retrieval and generation. Our code and generated documents can be found at https://github.com/wyu97/GenRead.
作者提出了使用LLM生成的question的documents,作为question的background来回答问题,generate-then-read。
knowledge-intensive tasks如开放域QA任务等,常常需要大量的word knowledge / domain knowledge。之前的常常通过检索外部知识源Wikipedia等来获得relevant contextual documents。
retrieve-then-read来解决knowledge-intensive tasks存在的问题:
- First, candidate documents for retrieval are chunked (e.g., 100 words) and fixed, so the retrieved documents might contain noisy information that is irrelevant to the question.
- Second, the representations of questions and documents are typically obtained independently in modern two-tower dense retrieval models (Karpukhin et al., 2020), leading to only shallow interactions captured between them (Khattab et al., 2021).
- Third, document retrieval over a large corpus requires the retriever model to first encode all candidate documents and store representations for each document.
而作者认为,LLM生成的document比传统的检索结果更加和query question更加相关,原因是:LLM的生成结果是通过基于question的token,然后经过attention等机制生成的,而一般的检索只是利用question和document的embedding相似度去检索的。显然LLM的生成结果会和question更加相关。
We believe this is because large language models generate contextual documents by performing deep token-level cross-attention between all the question and document contents, resulting in generated documents that are more specific to the question than retrieved documents.
在检索方法中,检索的答案越多,能够提供更多的不同角度/方面的knowledge,从而增加最后回答答案的准确率。
但是如果是相同的prompt,LLM会倾向不断输出重复的内容。因此作者提出从不同的聚类中选择上下文样例,从而产生更多样的输出documents。
作者提出clustering-based prompt方法,提取不同的上下文样例,构造不同的prompt,生成的多个结果文档,一起再来辅助回答问题。核心包括3步:
- 初始化:先用LLM给训练集中的每个question生成一个document。也可以使用检索的方法,为每个question从外部知识源中检索一个相关document;
- 编码document,基于K-means无监督聚类:作者使用GPT-3这类LLM为每个question-document进行编码,然后进行K-means聚类。聚类的数量K,和要生成的documents数量一致
- 采样并且生成K个documents:对每一个聚类,采样n个样例作为上下文,然后生成query question的一个document,最终生成的K个documents。这些documents作为background,和query question组合成一个prompt,获得最终的答案。

Increasing diversity and accuracy
Increasing Diversity While Maintaining Accuracy: Text Data Generation with Large Language Models and Human Interventions. 密歇根大学与Microsoft. ACL 2023. [详细博客]。
Large language models (LLMs) can be used to generate text data for training and evaluating other models. However, creating high-quality datasets with LLMs can be challenging. In this work, we explore human-AI partnerships to facilitate high diversity and accuracy in LLM-based text data generation. We first examine two approaches to diversify text generation: 1) logit suppression, which minimizes the generation of languages that have already been frequently generated, and 2) temperature sampling, which flattens the token sampling probability. We found that diversification approaches can increase data diversity but often at the cost of data accuracy (i.e., text and labels being appropriate for the target domain). To address this issue, we examined two human interventions, 1) label replacement (LR), correcting misaligned labels, and 2) out-of-scope filtering (OOSF), removing instances that are out of the user’s domain of interest or to which no considered label applies. With oracle studies, we found that LR increases the absolute accuracy of models trained with diversified datasets by 14.4%. Moreover, we found that some models trained with data generated with LR interventions outperformed LLM-based few-shot classification. In contrast, OOSF was not effective in increasing model accuracy, implying the need for future work in human-in-the-loop text data generation.
作者讨论了2种在解码阶段增加多样性的方法:
Logit Suppression:decreases the probability of high-frequency tokens。之前生成的tokens,根据频率,降低它在下一次采样中的概率。这里叫做logit的原因应该是,作者通过调用OpenAI的logit bias API来实现这一点。
High Temperature:增大temperature \(T\),更大的temperature意味着最终的概率分布更加平滑flat:
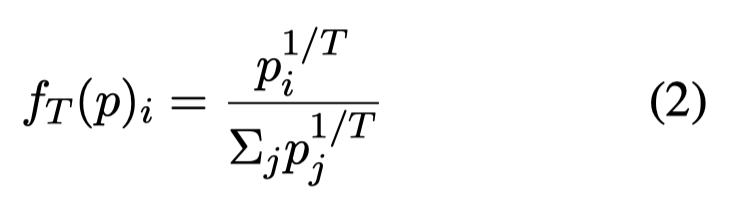
示意图:
作者调用GPT生成数据的时候,考虑的是短文本分类任务,构造的prompt主要考虑text type和label:

Vote-k
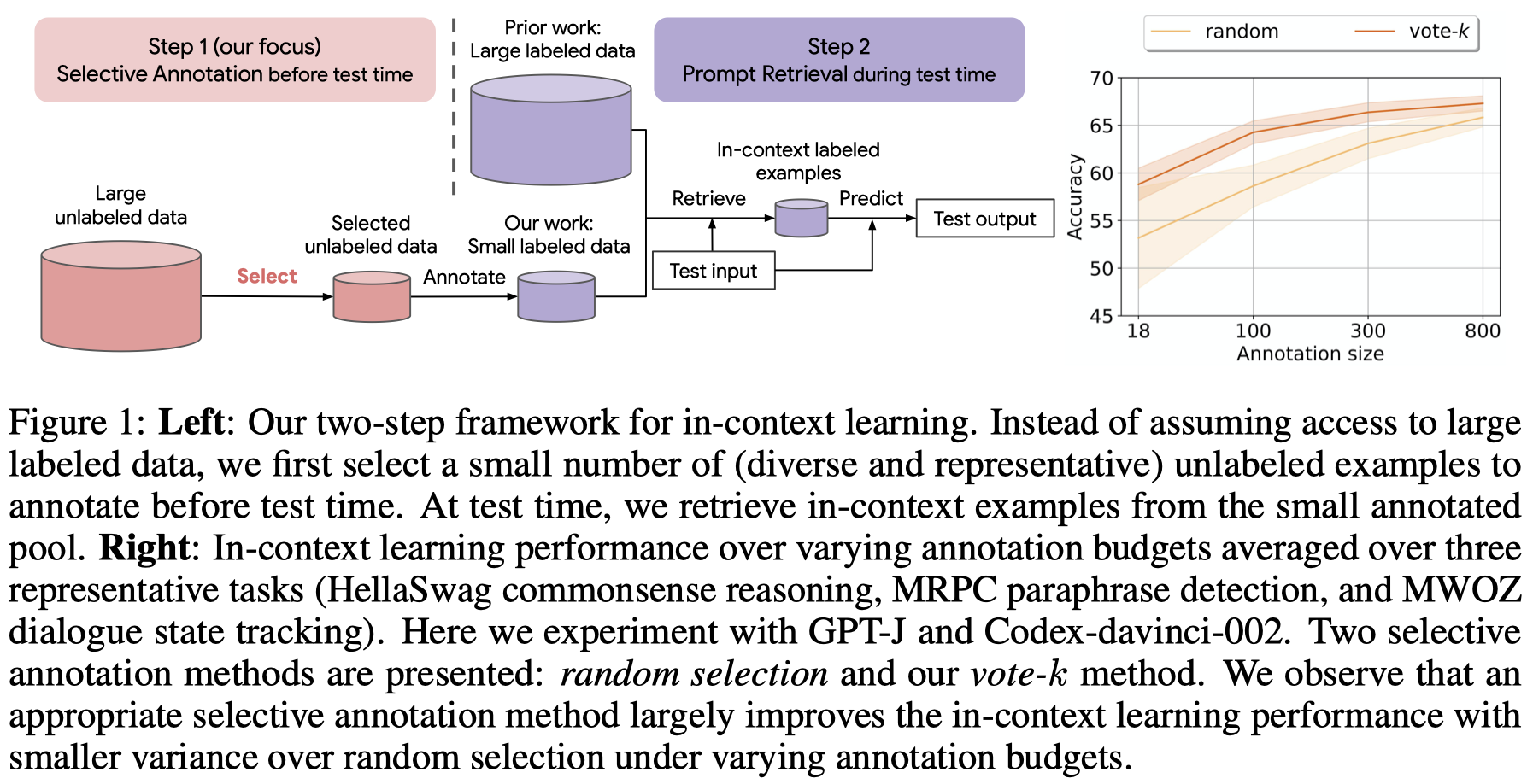
Selective Annotation Makes Language Models Better Few-Shot Learners.
香港大学,ICLR 2023,代码。
Many recent approaches to natural language tasks are built on the remarkable abilities of large language models. Large language models can perform in-context learning, where they learn a new task from a few task demonstrations, without any parameter updates. This work examines the implications of in-context learning for the creation of datasets for new natural language tasks. Departing from recent in-context learning methods, we formulate an annotation-efficient, two-step framework: selective annotation that chooses a pool of examples to annotate from unlabeled data in advance, followed by prompt retrieval that retrieves task examples from the annotated pool at test time. Based on this framework, we propose an unsupervised, graph-based selective annotation method, vote-k, to select diverse, representative examples to annotate. Extensive experiments on 10 datasets (covering classification, commonsense reasoning, dialogue, and text/code generation) demonstrate that our selective annotation method improves the task performance by a large margin. On average, vote-k achieves a 12.9%/11.4% relative gain under an annotation budget of 18/100, as compared to randomly selecting examples to annotate. Compared to state-of-the-art supervised finetuning approaches, it yields similar performance with 10-100× less annotation cost across 10 tasks. We further analyze the effectiveness of our framework in various scenarios: language models with varying sizes, alternative selective annotation methods, and cases where there is a test data domain shift. We hope that our studies will serve as a basis for data annotations as large language models are increasingly applied to new tasks.
利用LLM的ICL能力,为每个instance寻找相似的demonstrations能够极大的提升性能。但是这潜在的要求存在一个规模较大的标注数据能够提供上下文,之前很少有工作讨论LLM的ICL需要的demonstrations的标注代价。
作者提出,不需要为很多的data进行标注而作为候选demonstrations,可以选择representativeness和diversity的少量无标注data进行标注:
- representativeness will help many test instances to find similar demonstrations
- diversity increases the total coverage
作者提出的方法vote-k来选择合适的无标注数据进行标注:
步骤:
首先,通过Sentence-BERT将所有的无标注data编码为embedding,然后计算一个data point和其它data point的余弦相似度,选择\(k\)个最相似的data points(实验中发现\(k=150\)通常比较合适),创造一条有向边,构造出一个graph \(G=(V,E)\);
然后,有两个集合\(\mathcal{L}\)代表需要被标注的data,\(\mathcal{U}\)代表剩下的无标注data。初始\(\mathcal{L}=\empty\),然后迭代的从\(\mathcal{U}\)中选择degree score最大的一个data point \(u\)加入到\(\mathcal{L}\)中:
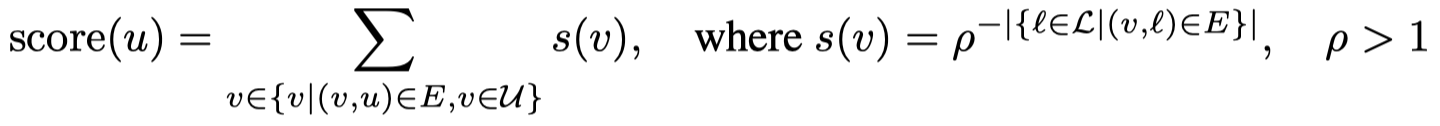
上面的公式通过超参\(\rho\)降低了和已经被标注的data相似的无标注data的权重(实验中发现\(\rho=10\)通常比较合适),从而鼓励多样性;选最大的score鼓励代表性。迭代一直进行\(M/10\)次;
为了进一步增加多样性,以标注好的\(M/10\)个data作为上下文样例,使用LLM为剩余的无标注数据进行预测,并且按照预测probability排序的划分为\(M\)个buckets,选择前\(9M/10\)个buckets的结果加入到\(\mathcal{L}\)中,不选择那些可以被最confident预测出来的无标注数据,最终\(|\mathcal{L}|=M\);
在实验中,对于这些选择出来的有标注数据,还是使用基于相似度的kNN方法作为demonstrations,提升LLM的ICL能力。
Distilling Step-by-Step
Distilling Step-by-Step! Outperforming Larger Language Models with Less Training Data and Smaller Model Sizes
华盛顿大学与Google,ACL 2023 Findings,代码。
Deploying large language models (LLMs) is challenging because they are memory inefficient and compute-intensive for practical applications. In reaction, researchers train smaller task-specific models by either fine-tuning with human labels or distilling using LLM-generated labels. However, finetuning and distillation require large amounts of training data to achieve comparable performance to LLMs. We introduce Distilling step-by-step, a new mechanism that (a) trains smaller models that outperform LLMs, and (b) achieves so by leveraging less training data needed by finetuning or distillation. Our method extracts LLM rationales as additional supervision for training small models within a multi-task framework. We present three findings across 4 NLP benchmarks: First, compared to both finetuning and distillation, our mechanism achieves better performance with much fewer labeled/unlabeled training examples. Second, compared to few-shot prompted LLMs, we achieve better performance using substantially smaller model sizes. Third, we reduce both the model size and the amount of data required to outperform LLMs; our finetuned 770M T5 model outperforms the few-shot prompted 540B PaLM model using only 80% of available data on a benchmark, whereas standard finetuning the same T5 model struggles to match even by using 100% of the dataset.
作者从540B的PaLM中导出rationales,然后让小模型T5学会输出对应的rationales。
部署大模型需要很高的代价:
Serving a single 175 billion LLM requires at least 350GB GPU memory using specialized infrastructure (Zheng et al., 2022). To make matters worse, today’s state-of-the-art LLMs are composed of over 500B parameters (Chowdhery et al., 2022), requiring significantly more memory and compute.
为了避免这一点,有两种做法,一种是传统的在下游task的现有数据集上进行训练,这要求有人工标注;另一种是用LLM为无标注的data进行标注,蒸馏到小模型上,这种做法需要的大规模无标注数据可能是比较难的requires large amounts of unlabeled data which can be hard to obtain (Tang et al., 2019; Liang et al., 2020).
作者提出的Distilling Step-by-Step方法是通过导出LLM的推理rationales,减少小模型训练所需要的训练数据量:

rationales提供了更多的为什么input能够被输出为output的信息,并且是通常很难仅仅从input上找到的:
Intuitively, rationales provide richer, more detailed information about why an input is mapped to a specific output label, and often contain relevant task knowledge that may be hard to infer solely from the original inputs.
rationale可以用来做什么?这一点已经有比较多的研究工作: 1. rationale可以用来规范model behavior;human rationales can be used to regularize model behavior (Ross et al., 2017) 2. rationale可以用来作为输入的一部分,提高预测性能;it can be used as additional inputs to guide a model’s predictions (Rajani et al., 2019); it can be used to improve overall model performance (Zaidan et al., 2007; Zhang et al., 2016; Camburu et al., 2018;Hancock et al., 2019; Pruthi et al., 2022); 3. rationale可以直接作为目标输出的一部分,提升模型预测的可解释性;human rationales can be used as gold standard labels to make models more interpretable by generating similar rationales (Wiegreffe et al., 2021; Narang et al., 2020; Eisenstein et al., 2022).
作者的方法很简单,第一步就是用人工写的CoT prompting模板从LLM中导出rationales;第二步是将rationales作为预测objective,用多任务学习机制加入一个额外的loss,让小模型学会输出rationales:
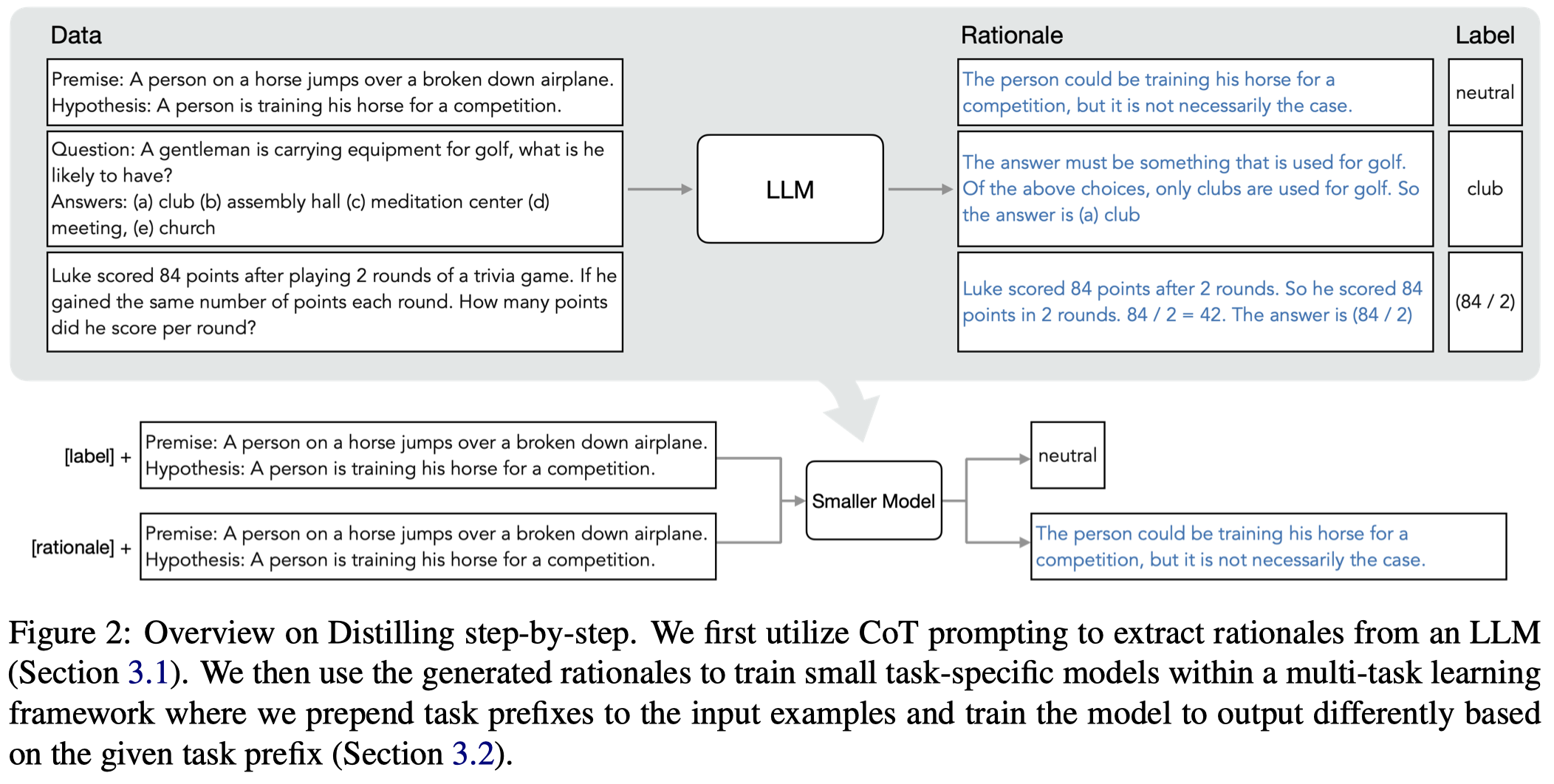
导出rationales的prompt如下:

将rationales看做是一种多任务,而不是和原来的label拼接在一起进行输出是必要的:

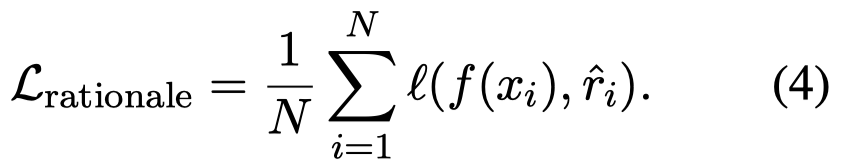
作者在实验中发现,如果是用单任务的方法让模型同时输出label和rationales,有时候会反而减低性能,这一点在前人的工作中也有发现相似的规律。
LM-CPPF
LM-CPPF: Paraphrasing-Guided Data Augmentation for Contrastive Prompt-Based Few-Shot Fine-Tuning
德兰黑大学与Google,ACL 2023 Short Paper,代码。
In recent years, there has been significant progress in developing pre-trained language models for NLP. However, these models often struggle when fine-tuned on small datasets. To address this issue, researchers have proposed various adaptation approaches. Promptbased tuning is arguably the most common way, especially for larger models. Previous research shows that adding contrastive learning to prompt-based fine-tuning is effective as it helps the model generate embeddings that are more distinguishable between classes, and it can also be more sample-efficient as the model learns from positive and negative examples simultaneously. One of the most important components of contrastive learning is data augmentation, but unlike computer vision, effective data augmentation for NLP is still challenging. This paper proposes LM-CPPF, Contrastive Paraphrasing-guided Prompt-based Fine-tuning of Language Models, which leverages promptbased few-shot paraphrasing using generative language models, especially large language models such as GPT-3 and OPT-175B, for data augmentation. Our experiments on multiple text classification benchmarks show that this augmentation method outperforms other methods, such as easy data augmentation, back translation, and multiple templates.
作者用LLM改写原有的句子,利用有监督对比学习拉近改写前和改写后的小模型的特征距离。
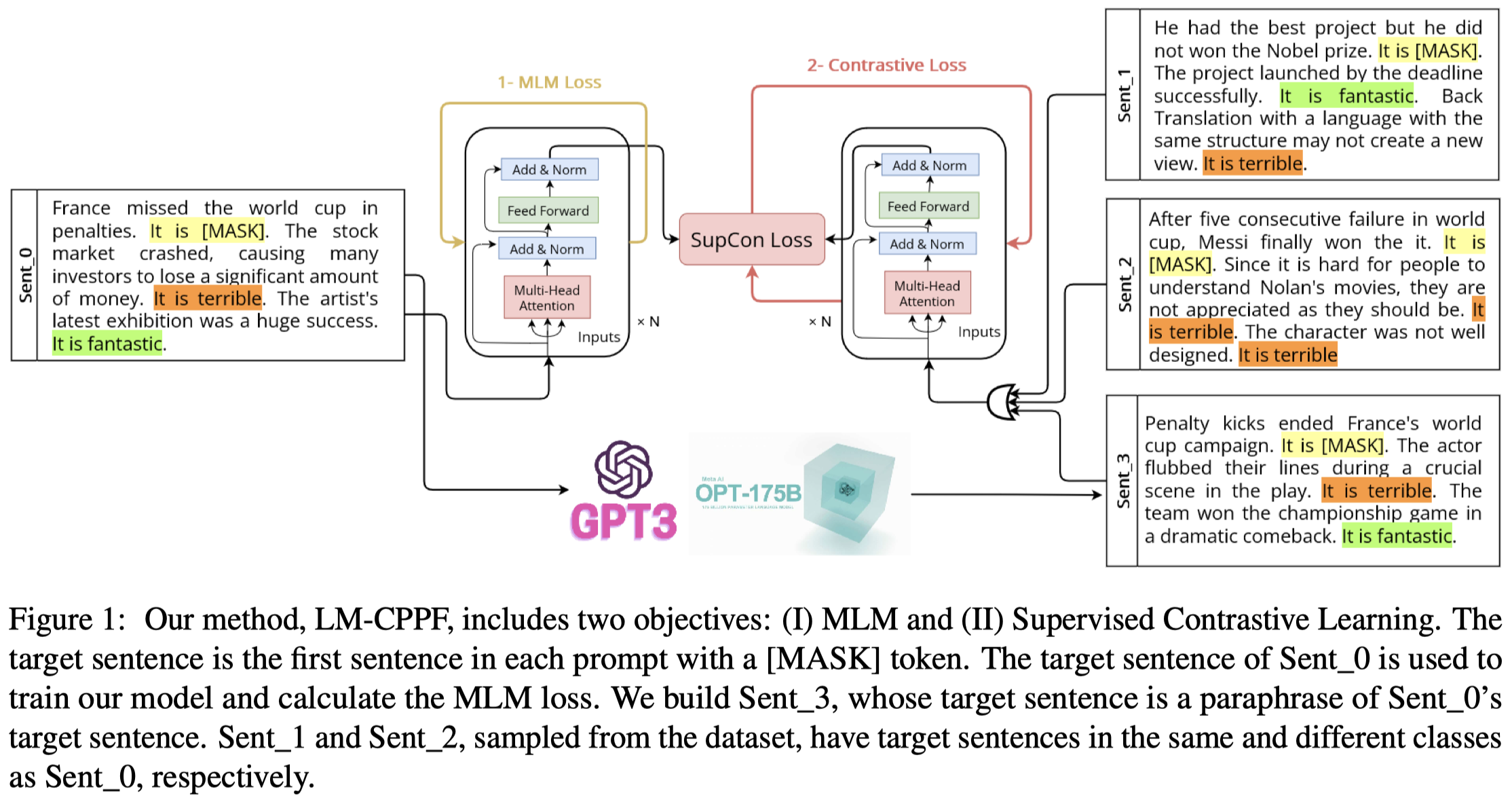
- 第一步是对于要改写的target sentence,mask掉label,然后随机采样几个样例作为demonstrations拼接为一个text。作者微调的小模型是Roberta-base,用其计算被mask的label的loss,Masked Language Modeling (MLM) loss;
- 第二步是利用GPT-3或者OPT改写target sentence,作者尝试了几种不同的方法,发现了下面最合适的instruction:
Generate a paraphrase of the following text using different words and sentence structures while still conveying the same meaning和demonstration format:<Original Text>, in other words <Paraphrased>。改写后的句子在图中对应的是Sent_3。改写的句子同样随机采样几个demonstrations,作为增强数据; - 第三步是增强的数据同样输入到Roberta-base中,利用Supervised Contrastive Learning loss [Supervised Contrastive Learning. NeurIPS 2020]去优化;
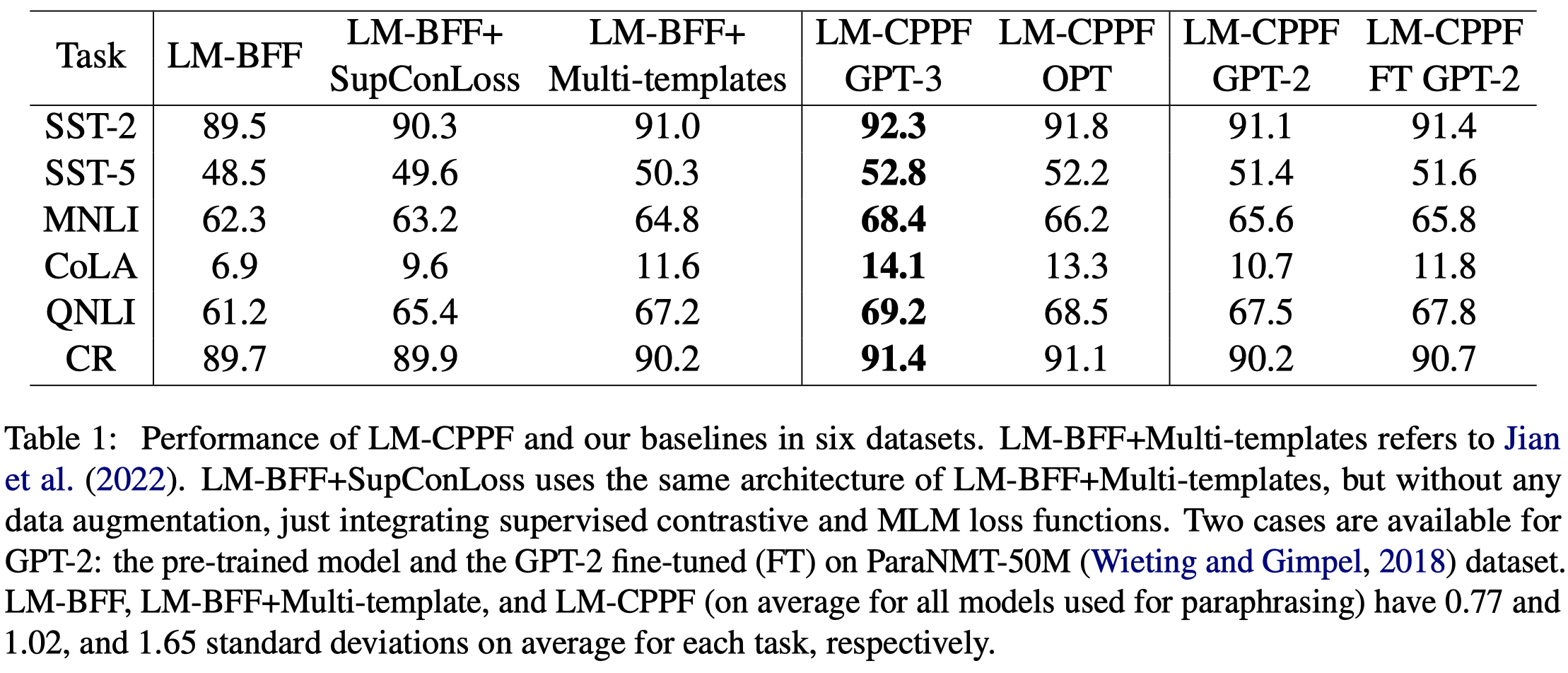
实验结果:
CoTAM
Generating Efficient Training Data via LLM-based Attribute Manipulation
University of California,arXiv 2023-07,代码。
In this paper, we propose a novel method, Chain-of-Thoughts Attribute Manipulation (CoTAM), to guide few-shot learning by carefully crafted data from Large Language Models (LLMs). The main idea is to create data with changes only in the attribute targeted by the task. Inspired by facial attribute manipulation, our approach generates label-switched data by leveraging LLMs to manipulate task-specific attributes and reconstruct new sentences in a controlled manner. Instead of conventional latent representation controlling, we implement chainof-thoughts decomposition and reconstruction to adapt the procedure to LLMs. Extensive results on text classification and other tasks verify the advantage of CoTAM over other LLMbased text generation methods with the same number of training examples. Analysis visualizes the attribute manipulation effectiveness of CoTAM and presents the potential of LLMguided learning with even less supervision.
作者从LLM部署所需要的巨大资源出发,考虑用数据增强训练一个更好的小模型。作者认为之前的LLM数据增强方法没有考虑可控的文本生成,可能影响了生成数据的信息有效性以及可能包含spurious correlation,variance比较大,让小模型比较难去学习

作者收到了attribute manipulation in computer vision (Shen et al., 2020; Shen and Zhou, 2021)方法的启发,这些方法通过修改latent space中的embedding,重新生成新的image。作者提出,使用LLM可以为text生成不同的attributes,通过修改attributes,让生成的text的label发生改变:
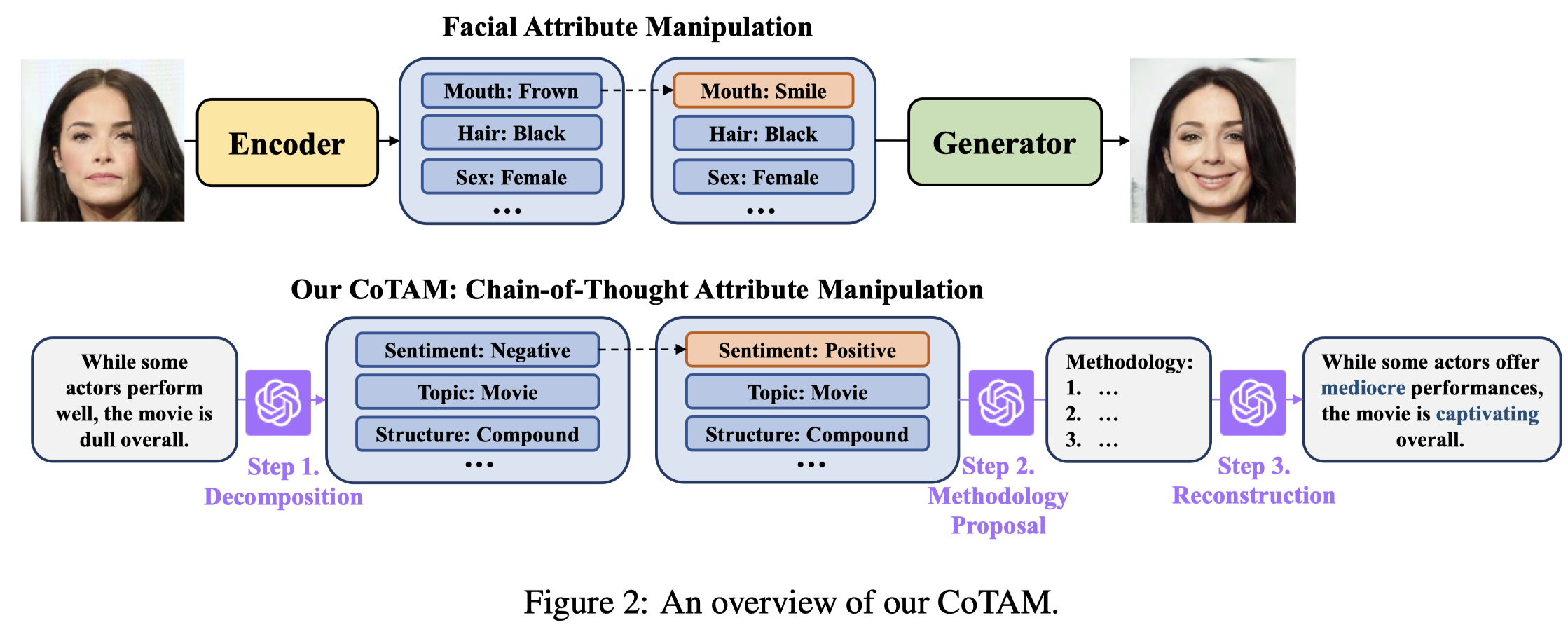
主要就是利用LLM进行3步prompt:
第一步是让label作为一个attribute,然后让LLM提出更多的其它attributes:
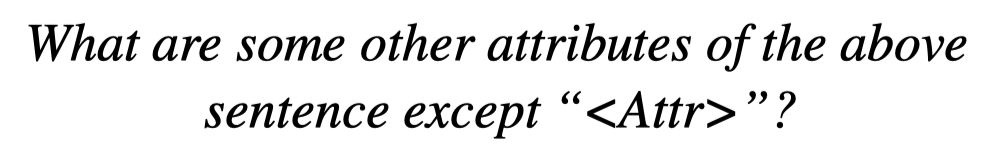
第二步是只改变label attribute,让LLM提出能够包括这些attributes句子的方法:
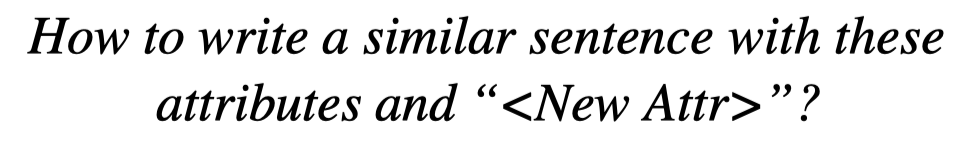
第三步是让LLM根据上面的方法,写一个新句子:

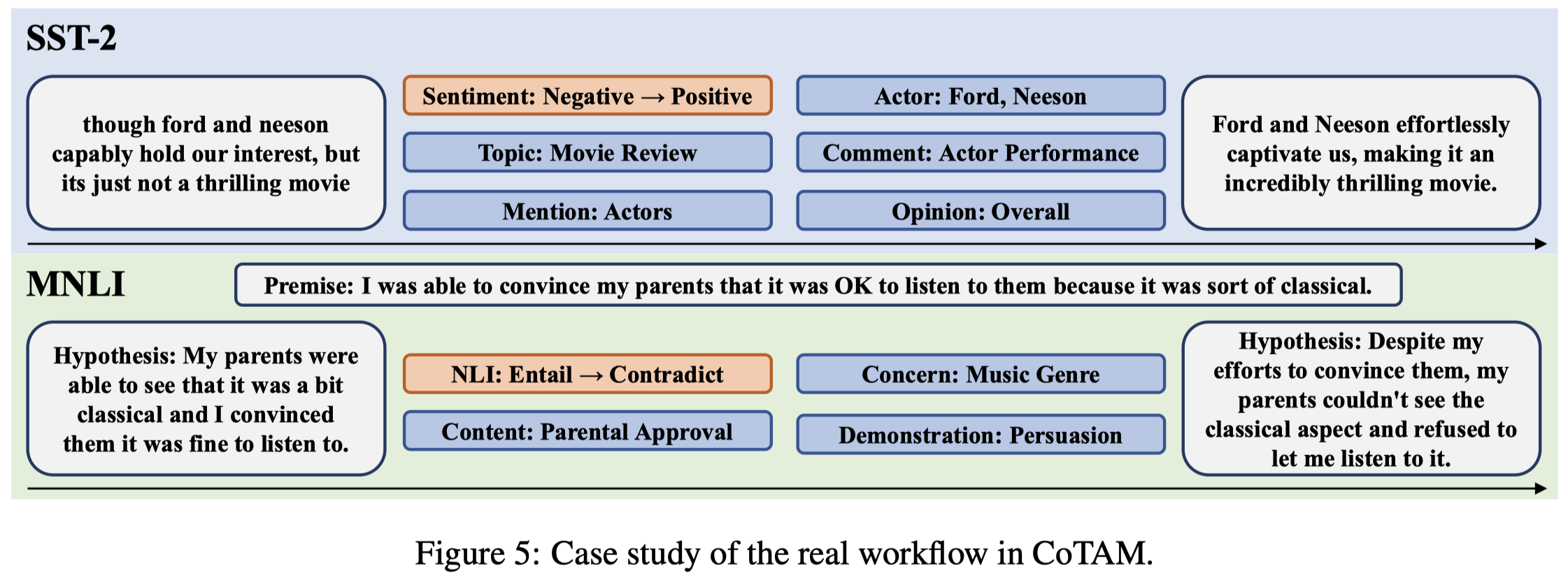
作者生成句子的实例:
PVI
Selective In-Context Data Augmentation for Intent Detection using Pointwise V-Information
EACL 2023,台湾大学与Amazon
This work focuses on in-context data augmentation for intent detection. Having found that augmentation via in-context prompting of large pretrained language models (PLMs) alone does not improve performance, we introduce a novel approach based on PLMs and pointwise Vinformation (PVI), a metric that can measure the usefulness of a datapoint for training a model. Our method first fine-tunes a PLM on a small seed of training data and then synthesizes new datapoints – utterances that correspond to given intents. It then employs intent-aware filtering, based on PVI, to remove datapoints that are not helpful to the downstream intent classifier. Our method is thus able to leverage the expressive power of large language models to produce diverse training data. Empirical results demonstrate that our method can produce synthetic training data that achieve state-of-the-art performance on three challenging intent detection datasets under few-shot settings (1.28% absolute improvement in 5-shot and 1.18% absolute in 10-shot, on average) and perform on par with the state-of-the-art in full-shot settings (within 0.01% absolute, on average).
作者利用ICL基于OPT-66B生成intent classification task的更多数据:

然后,为了选择什么样的生成数据适合用来训练小模型,作者提出了一种选择模型生成data的方法,利用Pointwise V-Information (PVI) [Understanding dataset difficulty with V-usable information. ICML 2022]:
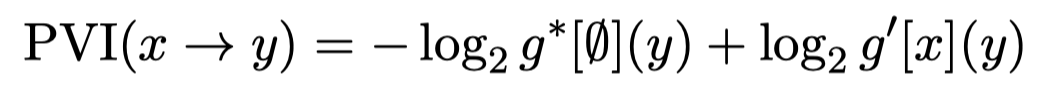
也就是有没有用data \(x\)微调前后,预测分布class \(y\)的概率的变化。如果PVI score越大,代表当前这一data对于class \(y\)的信息越多,越应该被挑选出来。
作者为每个intent class在validation set下测试出来PVI的平均值,作为PVI threshold,大于阈值的生成数据才会被使用。
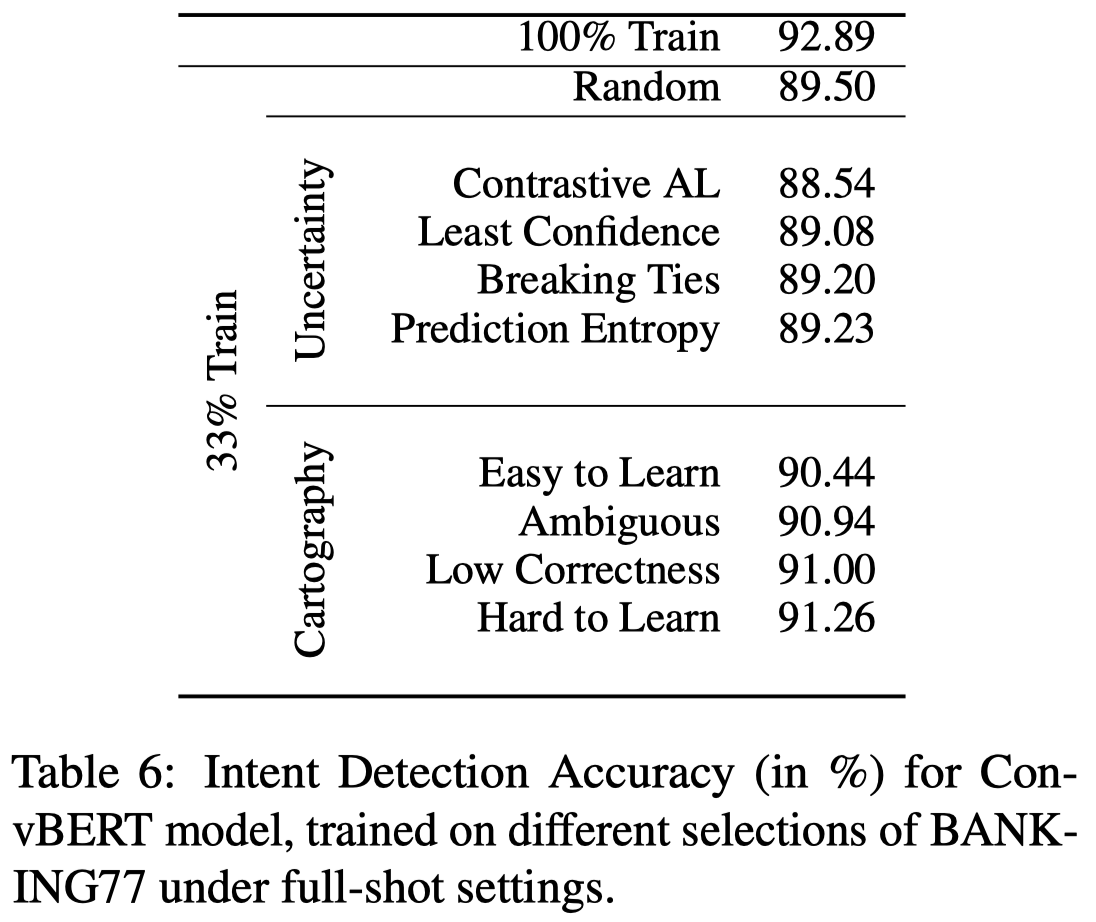
作者在附录中,还尝试了使用data cartography技术[Dataset cartography: Mapping and diagnosing datasets with training dynamics. EMNLP 2020]和classification uncertainty相关metric去选择生成的数据,但是发现还是直接应用全部的生成数据效果最好:
Synthetic data: subjectivity
Synthetic Data Generation with Large Language Models for Text Classification: Potential and Limitations
Purdue University, 作者评论接收至EMNLP 2023。[详细博客]。
The collection and curation of high-quality training data is crucial for developing text classification models with superior performance, but it is often associated with significant costs and time investment. Researchers have recently explored using large language models (LLMs) to generate synthetic datasets as an alternative approach. However, the effectiveness of the LLM-generated synthetic data in supporting model training is inconsistent across different classification tasks. To better understand factors that moderate the effectiveness of the LLM-generated synthetic data, in this study, we look into how the performance of models trained on these synthetic data may vary with the subjectivity of classification. Our results indicate that subjectivity, at both the task level and instance level, is negatively associated with the performance of the model trained on synthetic data. We conclude by discussing the implications of our work on the potential and limitations of leveraging LLM for synthetic data generation.
Issue: 目前在不同的task里,对于使用LLM生成的data是否能够和真实人工标注的data相比,没有定论。
Solution: 作者认为出现这种现象的原因之一和具体text classification任务的主观程度subjectivity有关,实验发现主观性越强的分类任务,LLM生成数据的效果也会越差。
作者采用了zero-shot和few-shot ICL两种设置。
对于zero-shot ICL prompt:
- “context prompt” relevant to the targeted domain of interest is used to set the context. 与具体task context相关的prompt
- the “data generation prompt”, is provided to the LLM, instructing the model to generate texts with a specific style, label (with respect to the classification task of interest), and word limit. 提供具体的label、生成字数限制等要求的prompt
- a “diversity prompt” to the LLM—“Can you provide something more diverse compared to the previously generated data?”—aiming to increase the diversity of the synthetic data generated. 生成具体的几个text data后,提示LLM生成更多不同的text data
对于few-shot ICL prompt:
- “context prompt”与前面zero-shot ICL一样
- 随机采样的几个demonstrations,其中说明了对应的label
- 还强制限制了不允许仅仅是修改原来的句子,而是期望生成更多的具体data,比如
You should imitate the example I have provided, but you cannot simply modify or rewrite the example I have given
下面是不同task用到的具体prompt:
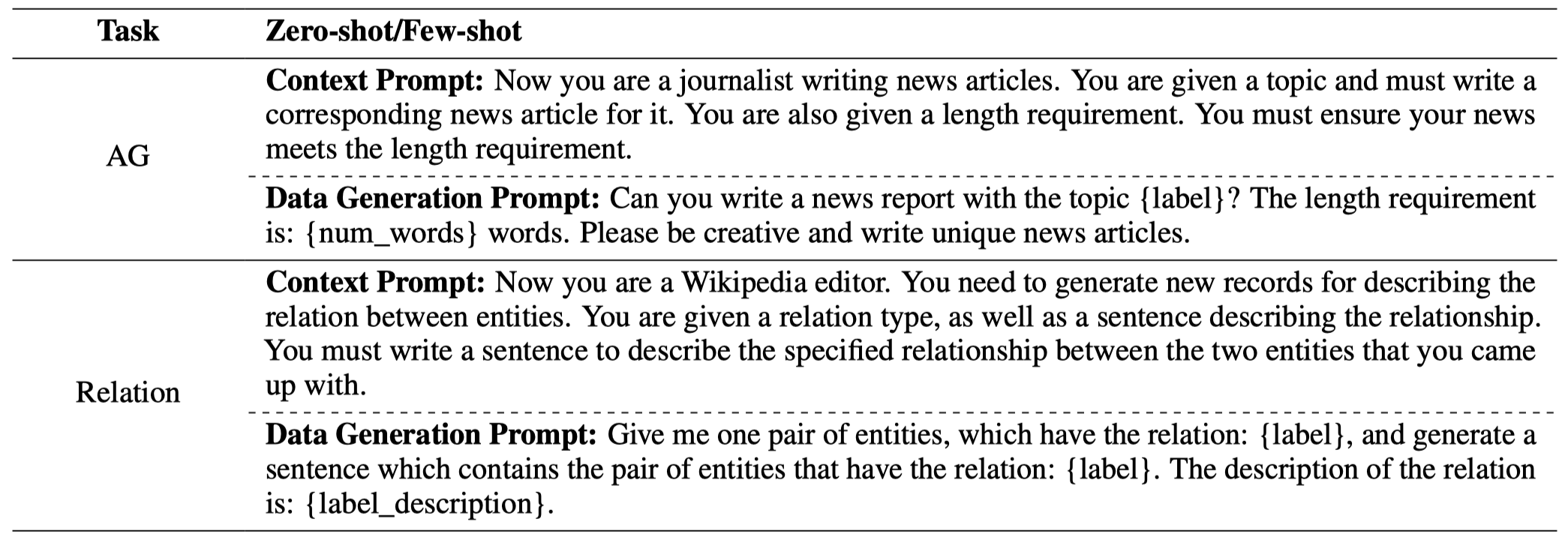
分别独立的在真实数据、生成数据上进行训练的实验结果(对于关系分类任务,只讨论了FewRel 2.0数据集中‘country’, ‘league’, ‘screenwriter’, and ‘tributary’的4种relation。每种relation生成3000条数据):
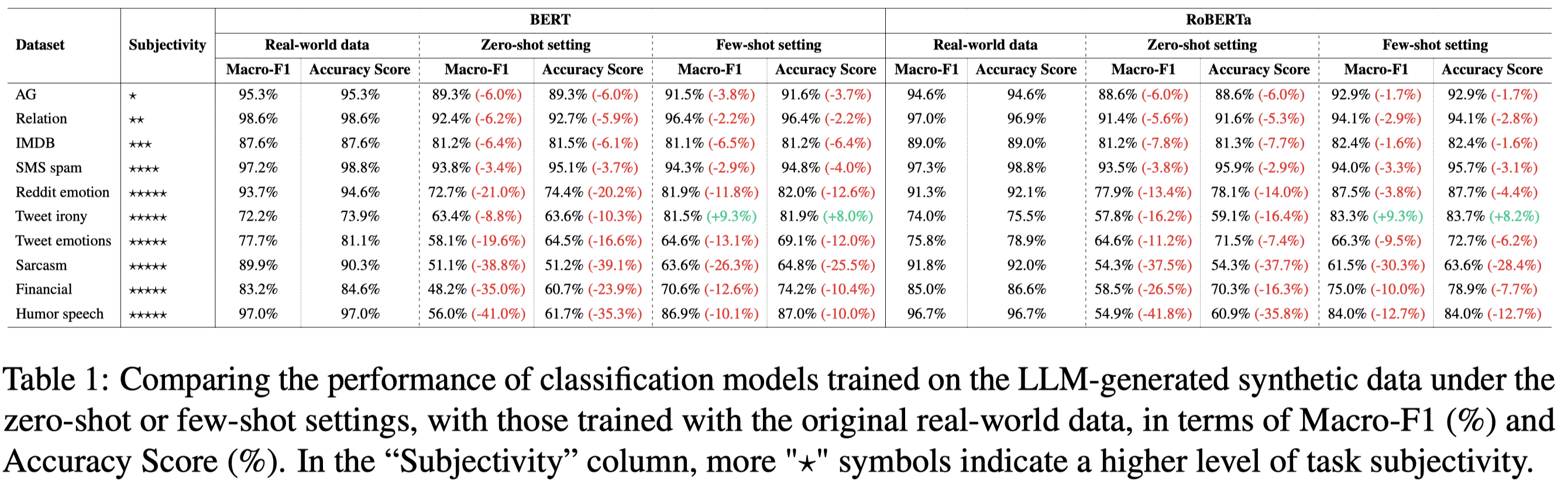
观察:
- 直接使用真实数据训练的效果最好
- few-shot ICL生成数据效果比zero-shot ICL效果好
- LLM在生成带有更多人类主观性的数据上,效果更差
为什么任务的主观程度会增大LLM生成数据的效果?作者提供了两个解释:
- highly subjective tasks often require a deep understanding of nuanced human emotions and contextual subtleties, as well as the ability to discern and accurately interpret different perspectives. 越主观,越要求对于人类情感等有非常微妙的理解
- it may be challenging for LLMs to generate synthetic data to recover such potentially biased “majority view,” especially if the LLMs are trained to maintain neutrality. 大多数的任务实例是利用众包标注的,也就是说在数据集里的gold label可能只反映了多个人的主要投票意见。对于LLM来说,要生成反映这种majority view的句子可能比较难。
使用一小部分真实数据进行训练,然后拿这一小部分真实数据作为demonstrations进行数据增强的实验结果:
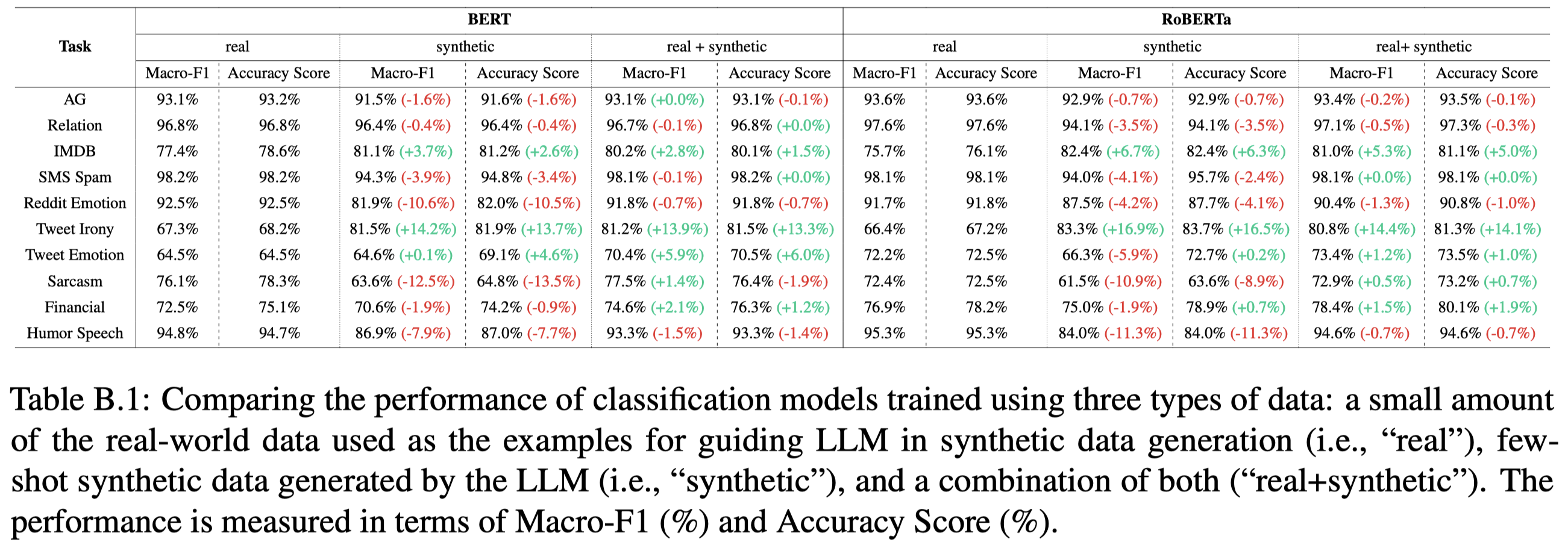
观察:
- 在关系抽取任务上,作者的这种比较简单的生成数据的方法,没有明显提升效果
AttPrompt
Large Language Model as Attributed Training Data Generator: A Tale of Diversity and Bias. NeurIPS 2023. Georgia Tech. 代码.
Large language models (LLMs) have been recently leveraged as training data generators for various natural language processing (NLP) tasks. While previous research has explored different approaches to training models using generated data, they generally rely on simple class-conditional prompts, which may limit the diversity of the generated data and inherit systematic biases of LLM. Thus, we investigate training data generation with diversely attributed prompts (e.g., specifying attributes like length and style), which have the potential to yield diverse and attributed generated data. Our investigation focuses on datasets with high cardinality and diverse domains, wherein we demonstrate that attributed prompts outperform simple class-conditional prompts in terms of the resulting model’s performance. Additionally, we present a comprehensive empirical study on data generation encompassing vital aspects like bias, diversity, and efficiency, and highlight three key observations: firstly, synthetic datasets generated by simple prompts exhibit significant biases, such as regional bias; secondly, attribute diversity plays a pivotal role in enhancing model performance; lastly, attributed prompts achieve the performance of simple class-conditional prompts while utilizing only 5% of the querying cost of ChatGPT associated with the latter. We release the generated dataset and used prompts to facilitate future research 2 .
Issue: LLM已经在一些工作上被用于生成task-specific的data,但是他们主要是利用simple class-conditional prompt去query LLM来生成新的训练数据,不能保证diversity of the generated data [7, 47, 56] and inheriting systematic biases inherent in LLMs [60, 21]. 比如,作者在利用之前简单的class-conditional prompt对NYT数据集新闻领域的数据进行生成的时候,在生成数据里,对于location这个属性,68.01%都是North America。相反的,描述了Africa的只有0.69%。
Solution: 作者主要通过data attributes来缓解LLM生成训练中存在的bias和diversity问题。
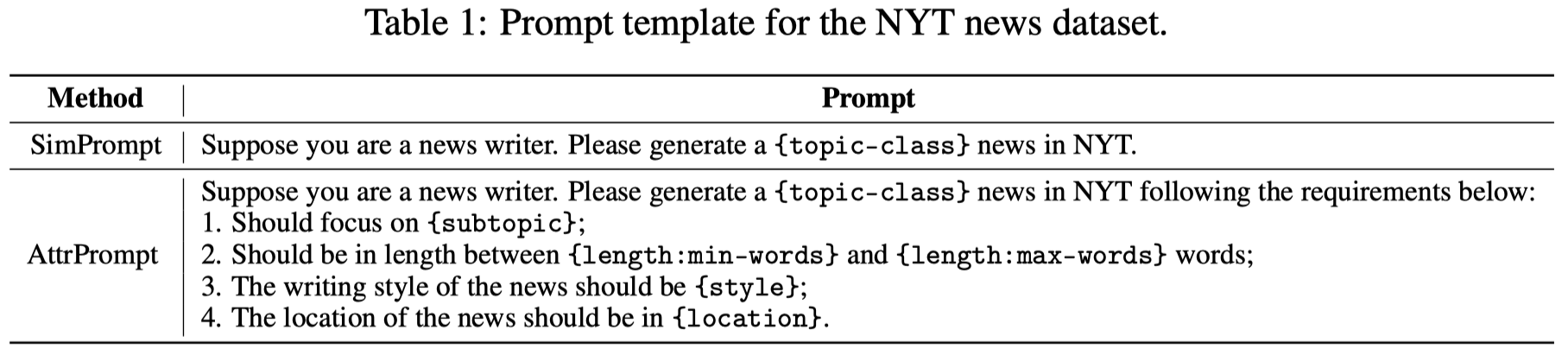
下面是作者提出的用于生成具有不同属性的passage的prompt,和之前简单的class-conditional prompt的对比:
作者提出的利用ChatGPT半自动构造数据集方式:
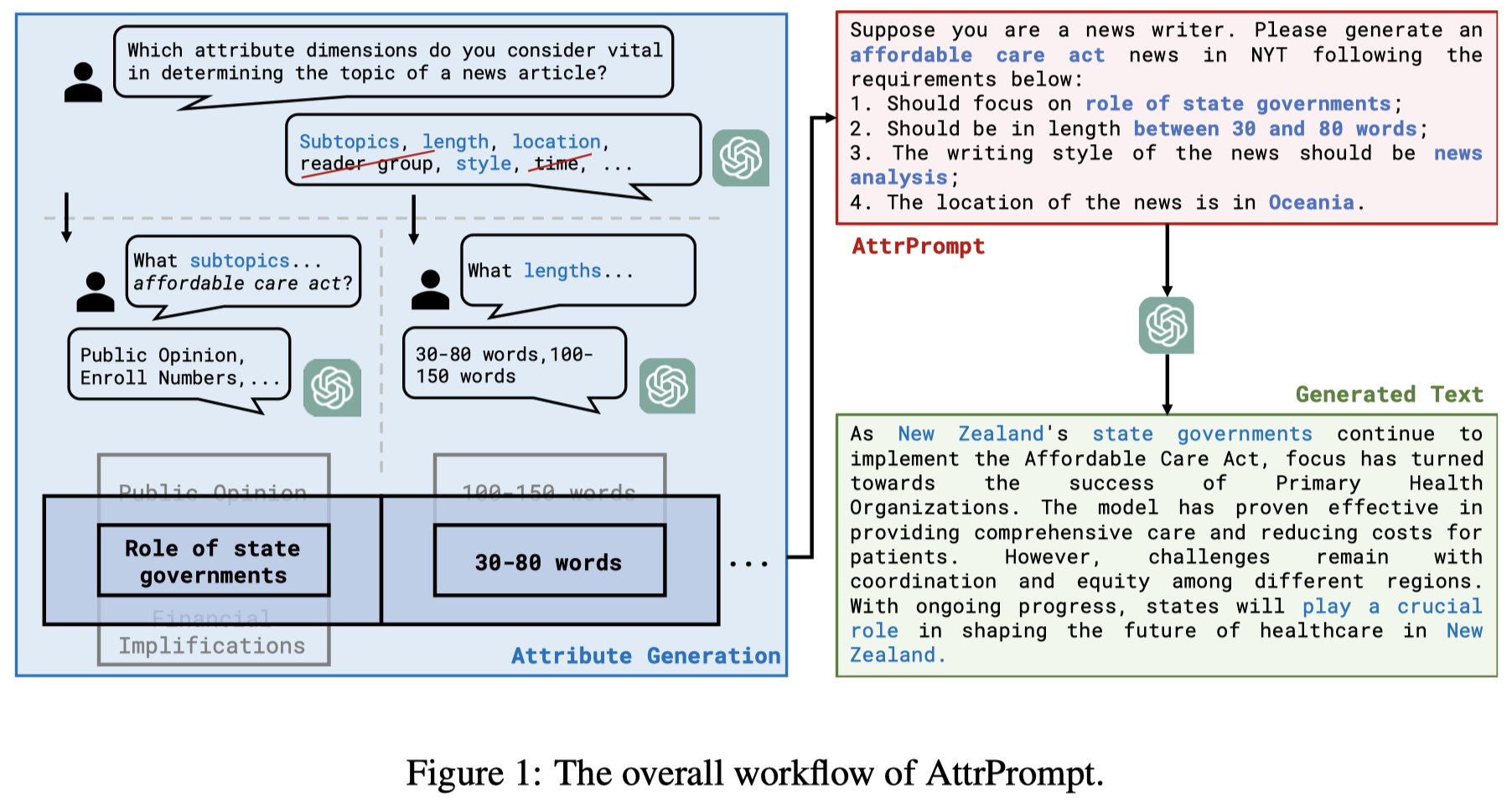
首先,利用ChatGPT询问在生成不同类型text data的时候,不同的属性可能是什么?下面以生成NYT news数据为例:

然后,人工的选择部分合适data attributes,human-ai collaboration scheme [26, 50, 57]:

其值attribute values也可以由GPT提供,比如下面询问attribute subtopic的values:

对于每种data attributes,可以分为class-independent attributes和class-dependent attributes。class-independent比如length,和具体class无关;class-dependent属性比如subtopic,就和具体的class有关。例如subtopic如果取值是effect of trade tariffs on manufacturing companies,那么可以对应于NYT数据集里的international business类,也可以对应于economy类。为了避免这种模糊的attribute values,作者利用Class-Dependent Attribute Value Filtering (CAF)策略,通过query ChatGPT 5个和当前class最相似的其它class,然后用ChatGPT检查各个class-dependent attribute的values是否和这5个相似的class相关。如果是,就移除这个特定的attribute value。

然后对于不同class,通过组合不同的data attribute的values,就可以让LLM生成不同的text。
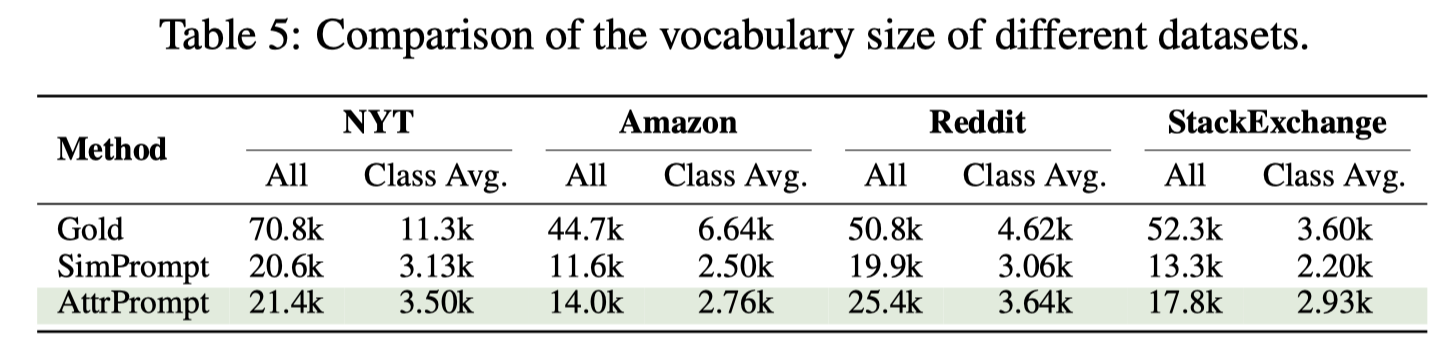
接下来,作者针对生成数据的diversity进行了分析。下面是统计vocabulary size:
下面是计算same-class内text pairs的sentence embedding相似度分布:
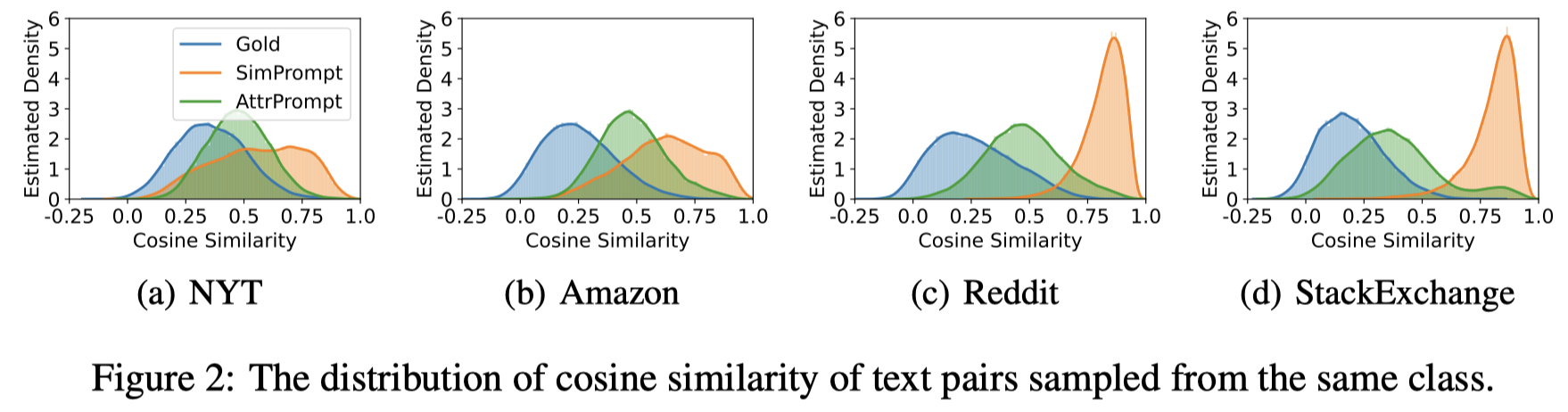
可以看到gold data有最大的多样性,而LLM生成的text和real data还是有差距。
下面是作者人工检查的100个句子,分析句子中的bias:
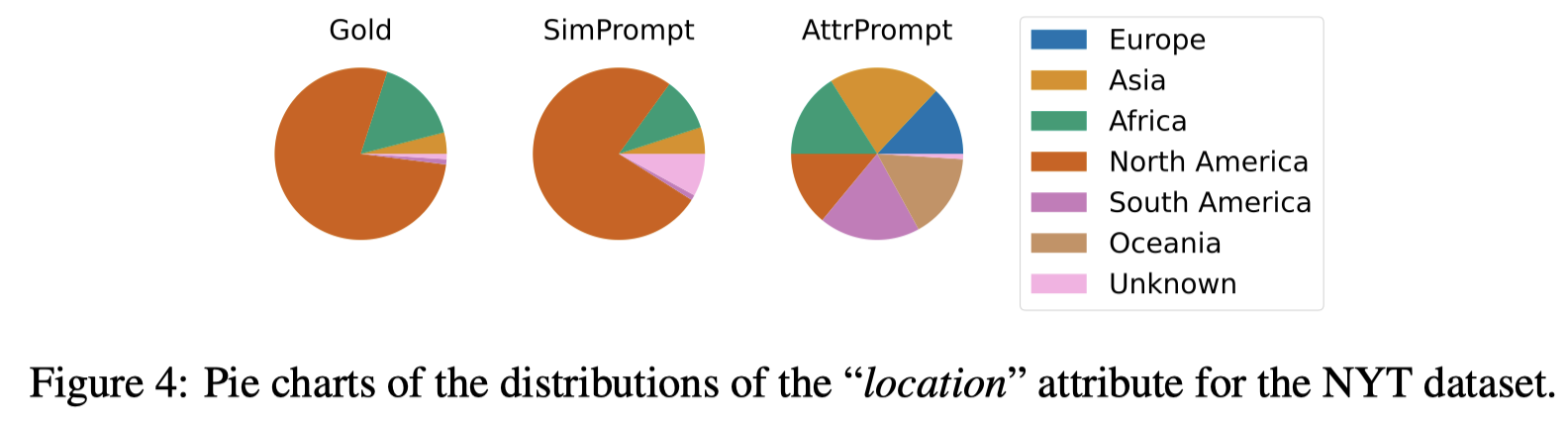
可以看到,如果是简单的让LLM生成新数据,LLM生成的句子有很大的偏差。
下面的表格是作者将生成的数据(和原来数据集数据量一样)加入到gold training data中的效果:
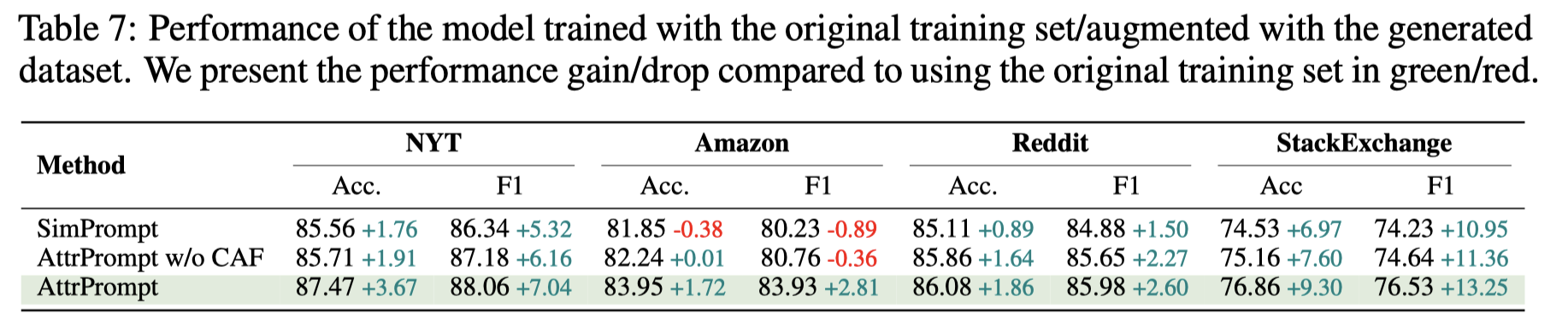
作者在实验里还比较了不同生成数据的prompt在budget(即调用ChatGPT的花费cost与性能比)和sample efficiency(使用更多数据带来的性能变化):

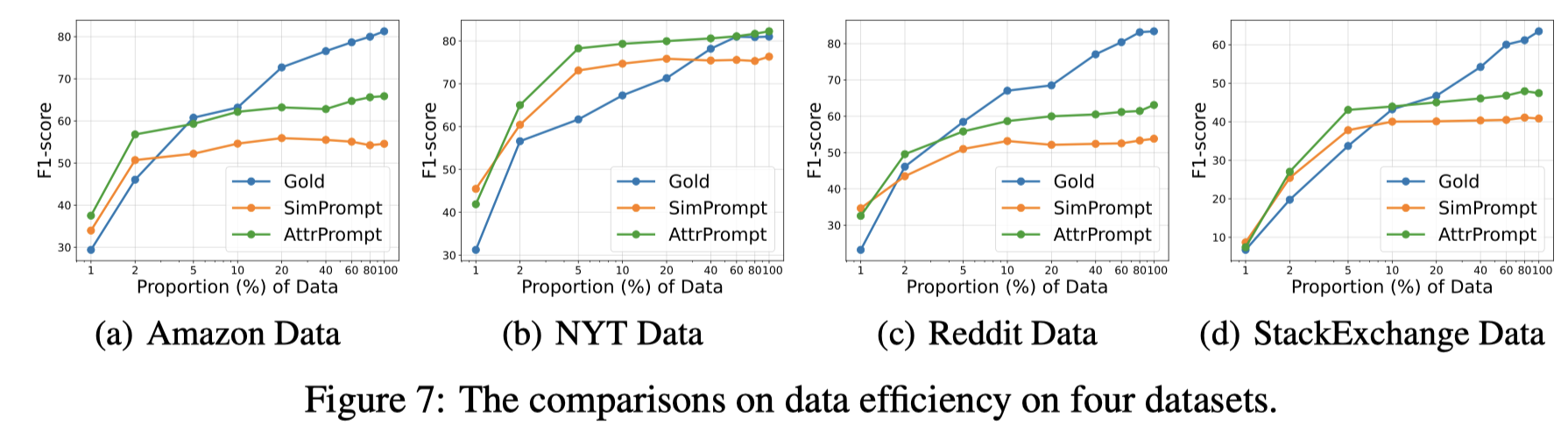
Figure 7有个很重要的启发,增加生成数据的多样性是必要的,这样才能够让生成数据越多,性能也一直随着增加。如果生成的数据是原来数据的重复,那么更多的新数据就没有意义了。
Overall, AttrPrompt renders better sample efficiency than SimPrompt, which suggests that increasing the diversity of the prompts could be an effective way to improve the unsatisfactory data scaling trend of using LLM as data generator [52].
最后,作者实验了将AttPrompt和以前构造训练数据方法结合:
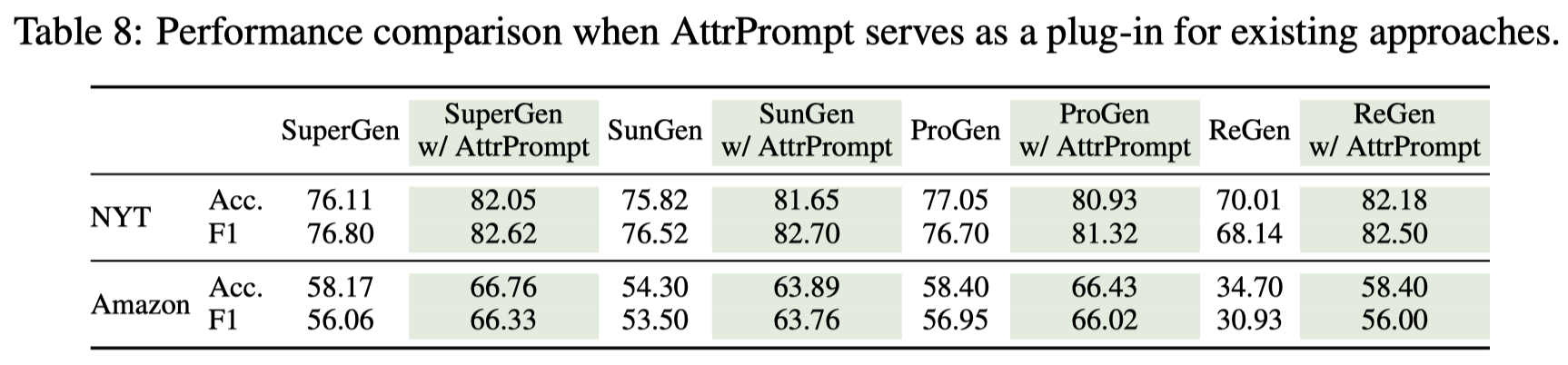
Grammar Prompting
Grammar Prompting for Domain-Specific Language Generation with Large Language Models. MIT. NeurIPS 2023.
Large language models (LLMs) can learn to perform a wide range of natural language tasks from just a handful of in-context examples. However, for generating strings from highly structured languages (e.g., semantic parsing to complex domain-specific languages), it is challenging for the LLM to generalize from just a few exemplars. We explore grammar prompting as a simple approach for enabling LLMs to use external knowledge and domain-specific constraints, expressed through a grammar expressed in Backus–Naur Form (BNF), during incontext learning. Grammar prompting augments each demonstration example with a specialized grammar that is minimally sufficient for generating the particular output example, where the specialized grammar is a subset of the full DSL grammar. For inference, the LLM first predicts a BNF grammar given a test input, and then generates the output according to the rules of the grammar. Experiments demonstrate that grammar prompting can enable LLMs to perform competitively on a diverse set of DSL generation tasks, including semantic parsing (SMCalFlow, Overnight, GeoQuery), PDDL planning, and even molecule generation (SMILES).
Issue: 由于预训练过程,LLM的上下文学习能力已经得到了证明。但是上下文学习不适用于无法通过几个例子就能够说清楚的task,比如特定领域语言生成Domain-Specific Language Generation任务。
This approach is however inadequate for applications where the task specifications cannot be fully delineated through just a handful of exemplars, for example in semantic parsing where an LLM must translate a natural language utterance to an executable program in a domainspecific language (DSL)
领域特定的语言,并不是一般的编程语言,因此LLM可能在预训练过程中没有见过很多,也因此无法简单的通过几个demonstrations就学会如何输出领域特定语言。下面是为calendar assistant生成一个预定会议调用API流程对应的DSL:

Soluation: 为了解决这个问题,作者提出了使用Backus–Naur Form (BNF)重新描述demonstrations的grammar prompting方法。BNF是一种标准元语言,metalanguages,能够用来描述某个语言的语法。比如对于上面的例子,有下面对应的BNF:
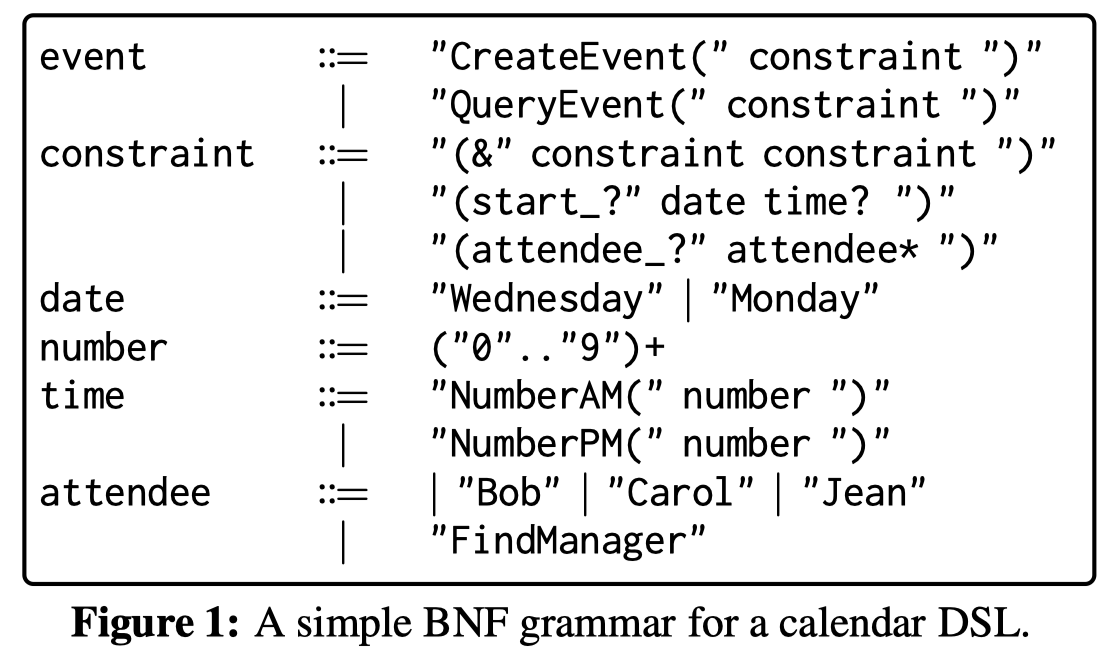
DSL是由专家定义的特定领域的特定语言,因此LLM在预训练阶段大概率较少遇到。而BNF是通用的元语言,因此LLM在预训练阶段更有可能见过,比如在cs教科书上有对应的介绍。因此作者利用BNF来描述所有的DSL语言。
作者的prompt先是让LLM输出对应的BNF语法grammar,然后再query转化为对应的DSL语言:
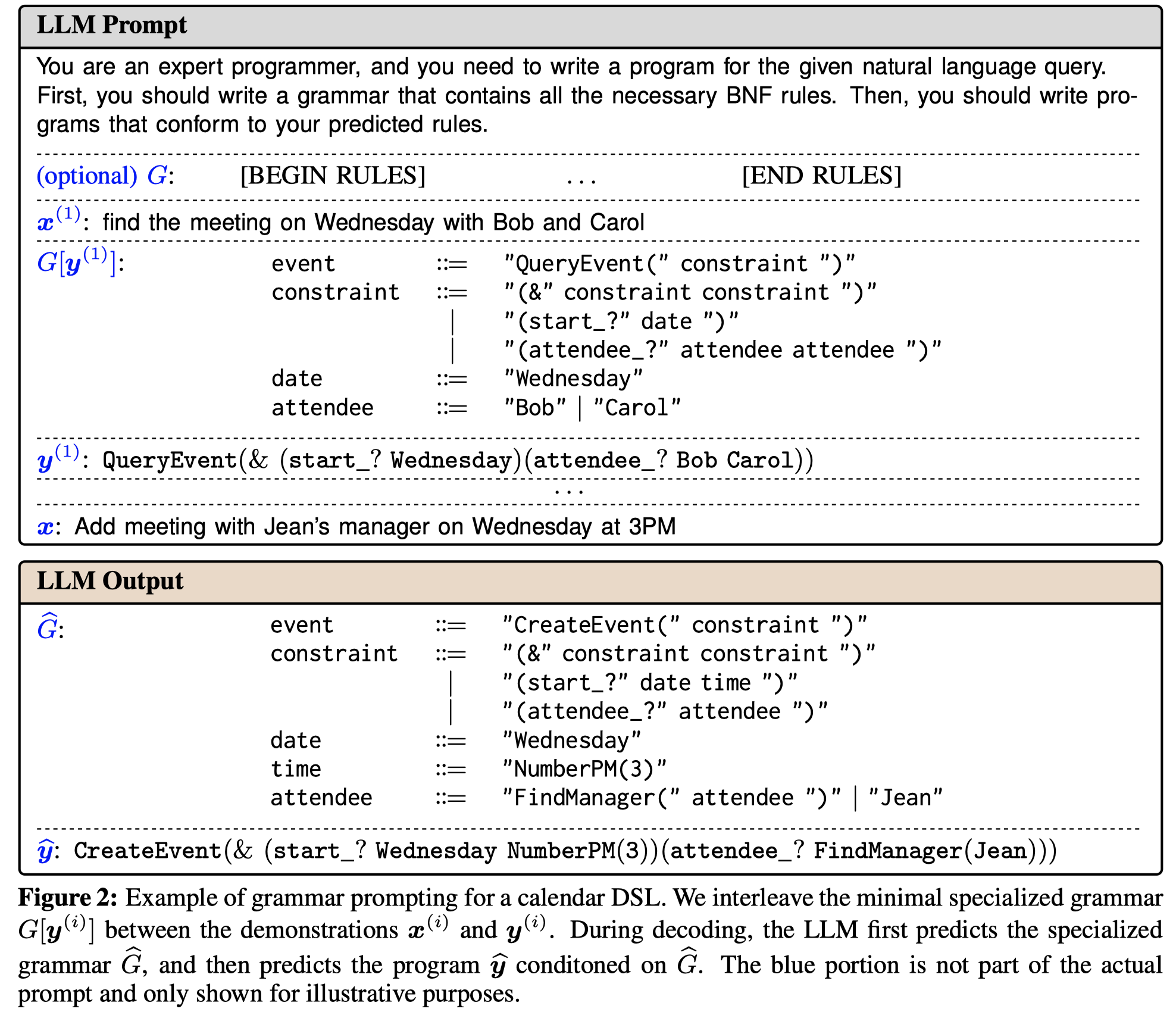
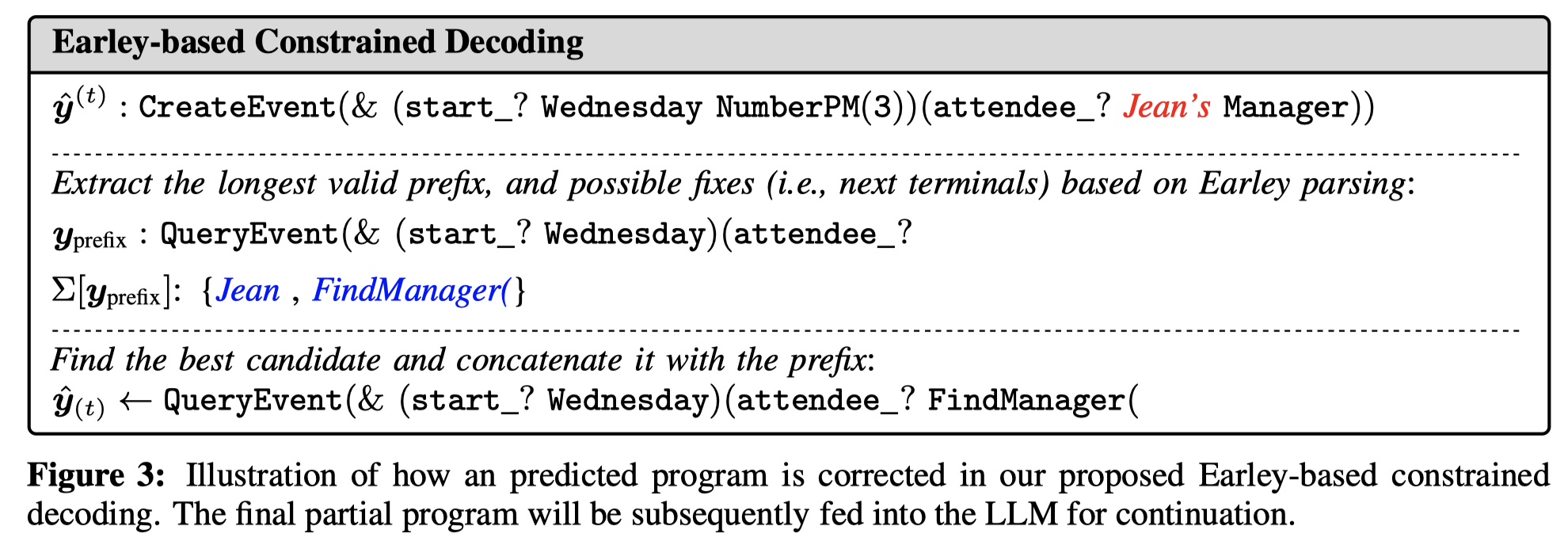
顺便一提,从BNF到最后的DSL有可能转化错误,比如DSL没有遵循BNF进行生成。因此,作者还提出了一个Earley-based Constrained Decoding策略(这部分没有太看懂,总体上理解是调用外部Earley解析器,找到目前的DSL中有效valid的最长前缀,然后让其提供几个可能的后续,再让LLM从后续当中做选择)。下面是一个修正生成的DSL中可能存在错误的例子:
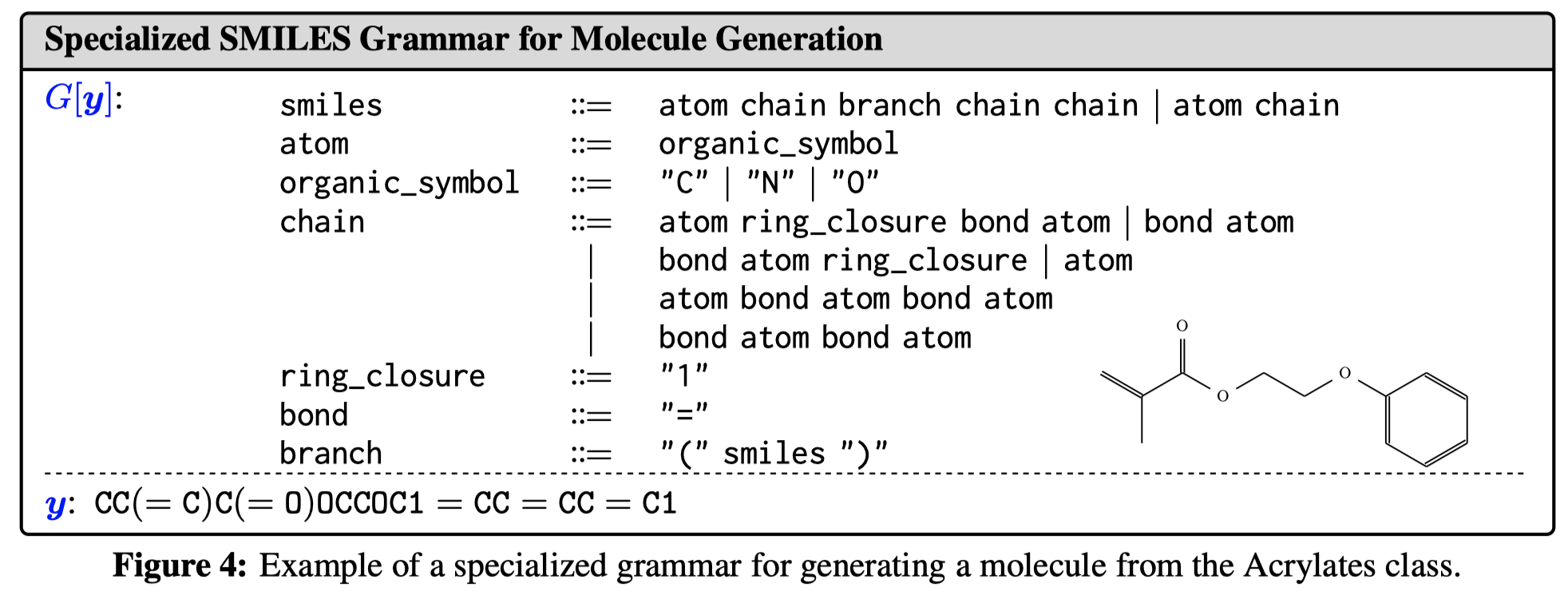
实验是基于Codex, GPT-3.5和GPT-4,针对DSLs for semantic parsing (SMCalFlow, Overnight, GeoQuery), an action DSL (PDDL planning), and a molecule generation DSL (SMILES)三种任务进行了实验。
下面是分子预测任务的一个case:
SunGen
Self-Guided Noise-Free Data Generation for Efficient Zero-Shot Learning. ICLR 2023. 香港大学. 代码.
There is a rising interest in further exploring the zero-shot learning potential of large pre-trained language models (PLMs). A new paradigm called data-generationbased zero-shot learning has achieved impressive success. In this paradigm, the synthesized data from the PLM acts as the carrier of knowledge, which is used to train a task-specific model with orders of magnitude fewer parameters than the PLM, achieving both higher performance and efficiency than prompt-based zero-shot learning methods on PLMs. The main hurdle of this approach is that the synthesized data from PLM usually contains a significant portion of low-quality samples. Fitting on such data will greatly hamper the performance of the taskspecific model, making it unreliable for deployment. Previous methods remedy this issue mainly by filtering synthetic data using heuristic metrics(e.g., output confidence), or refining the data with the help of a human expert, which comes with excessive manual tuning or expensive costs. In this paper, we propose a novel noise-robust re-weighting framework SunGen to automatically construct high-quality data for zero-shot classification problems. Our framework features the ability to learn the sample weights indicating data quality without requiring any human annotation. We theoretically and empirically verify the ability of our method to help construct good-quality synthetic datasets. Notably, SunGen-LSTM yields a 9.8% relative improvement than the baseline on average accuracy across eight different established text classification tasks.
Issue: 利用PLM生成训练数据,然后微调小模型的范式已经在很多如下游任务上得到了研究。更进一步的,出现了generation-based zero-shot learning,直接让PLM生成zero-shot labels对应的training data,然后微调小的任务模型tiny task model(TAM)。这种做法和经典的和直接利用PLM进行zero-shot任务比较起来,有两个优点:
- since the task model has orders-of-magnitude fewer parameters than the PLM, it demonstrates much lower inference latency
- with the large amount of PLM-generated training data, the task model often shows better performance than prompt-based zero-shot PLM counterparts.
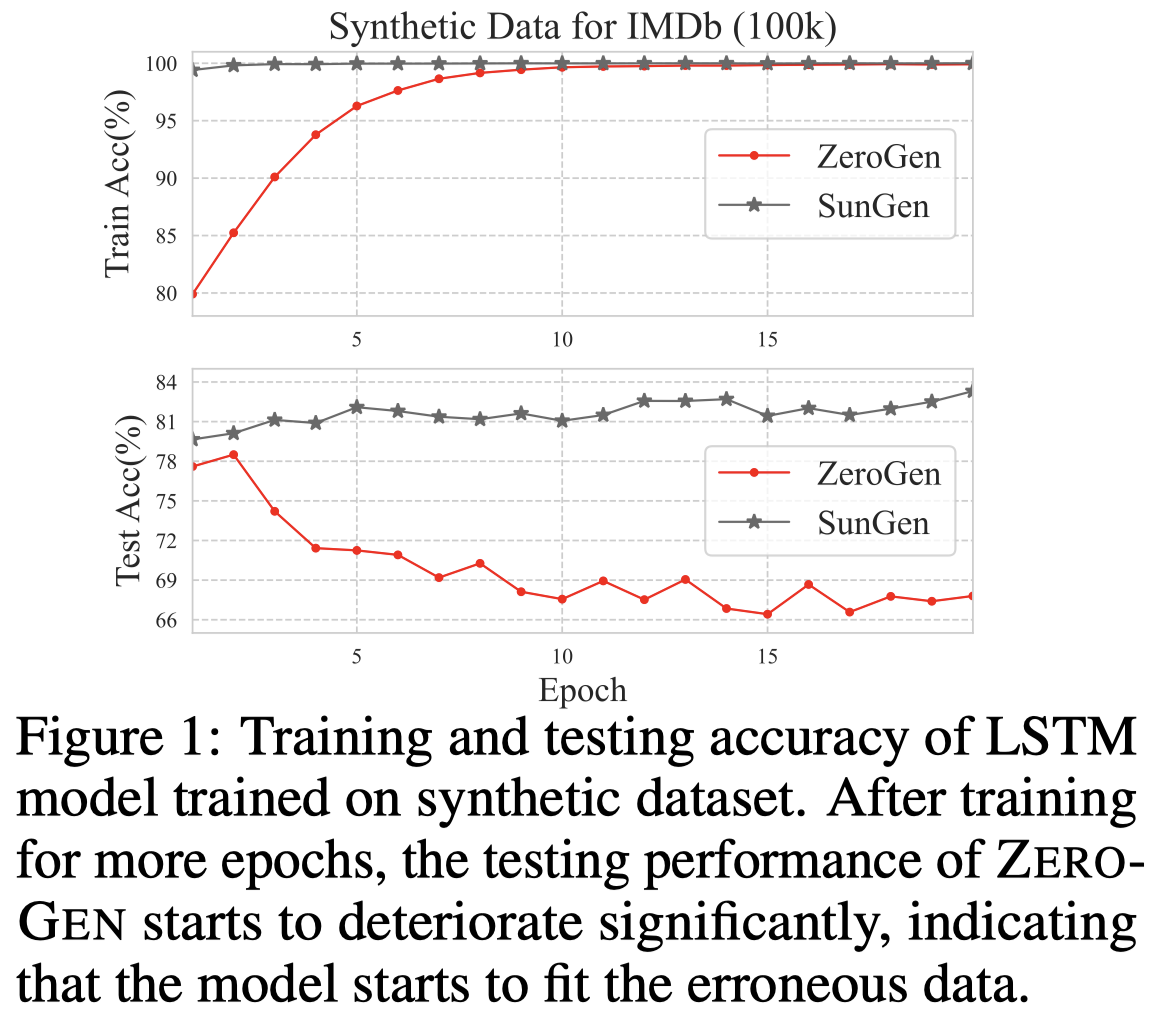
对于generation-based zero-shot learning来说,利用PLM可以生成无限数量的训练数据,需要重点关心的问题是生成数据的质量。比如作者观察到的,前人方法ZeroGen,随着生成数据增多,在测试集上的效果下降。这说明其生成数据的质量降低,模型过拟合这些低质量生成数据:
经典的自动解决noisy data的影响的方法是re-weighting samples:
To avoid human intervention, the classic approach to eliminate the effect of noisy data is to re-weight the samples. The core idea is to design a weighting function \(w\), such that the correct samples are associated with larger weights and the noisy ones with smaller weights.
re-weighting samples方法有两种,一种是基于启发式规则的,例如基于生成数据的confidence、loss等,需要提前根据task-specific knowledge定义好,而且效果也不稳定[Metaweight-net: Learning an explicit mapping for sample weighting. NeurIPS 2019];另一种是adaptive method自动学习sample weight \(w\),这种方法通常是bi-level optimization problem,需要一个已有的clean validation set作为outer loop来知道inner loop学习\(w\)。但问题是,在zero-shot场景下,没有这样的validation set。
can we design an objective such that the sample weights can be optimized with only access to the noisy synthetic data?
Solution: 作者的解决方案是在adaptive re-weighting方法的基础上,在outer loop里加入noise-robust loss,通过其优化samples的weights。
作者提出的Self-gUided Noise-free data GENeration(SunGen)方法:
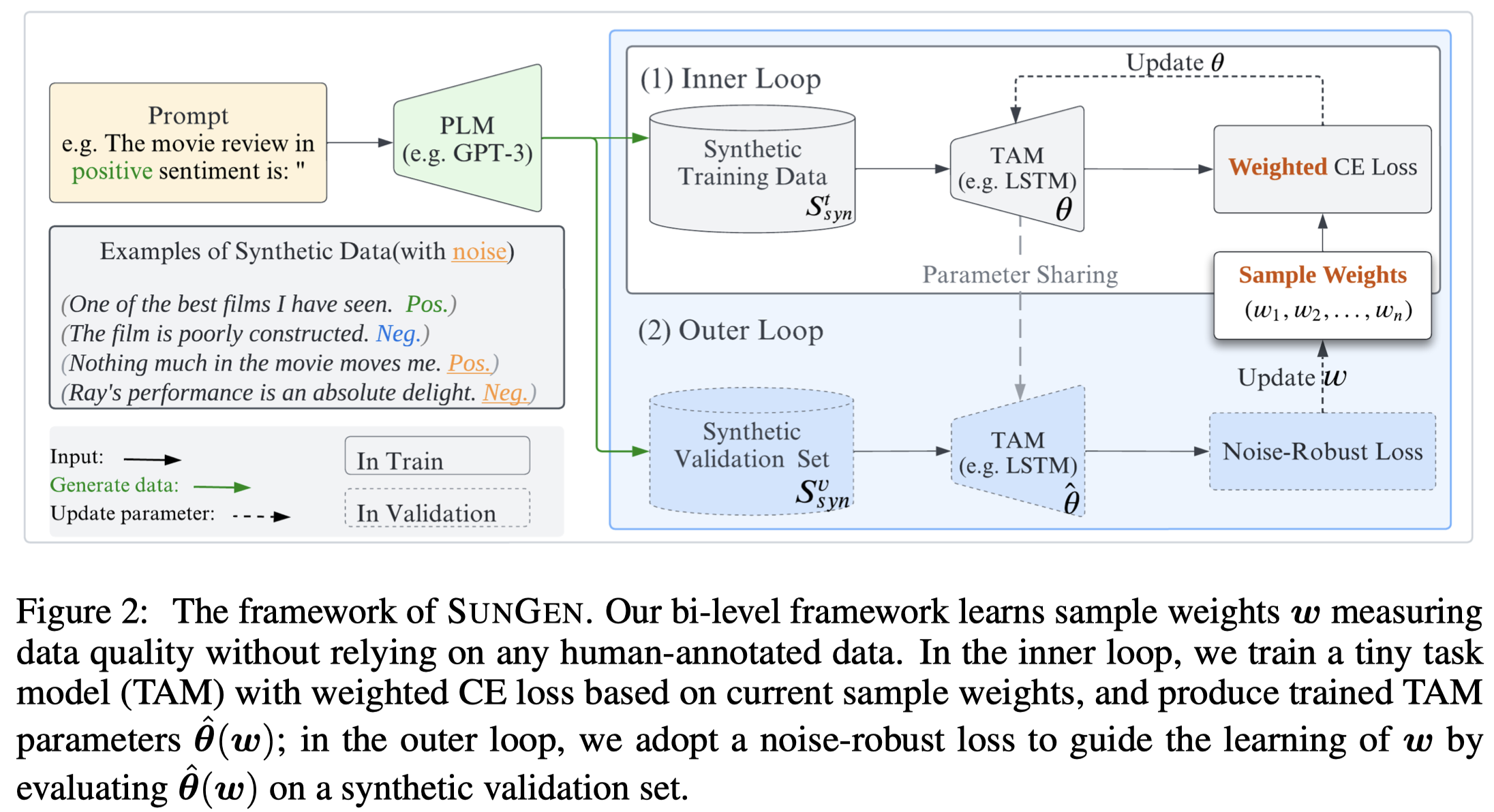
核心是inner loop和outer loop。inner loop基于cross-entropy(CE) loss,在synthetic training data上,根据sample weights,优化TAM参数:
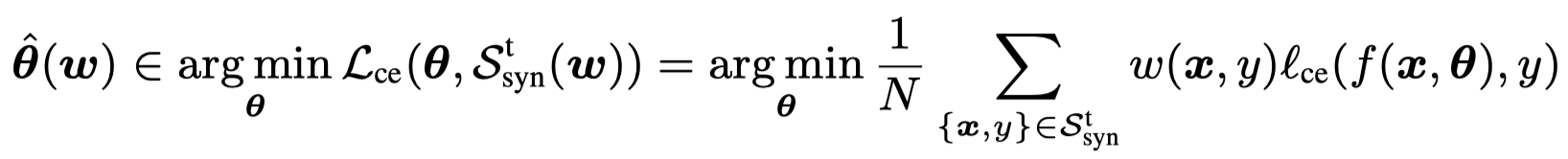
outer loop基于noise-robust loss,在synthetic validation data上,优化sample weights \(\mathbf{w}\):
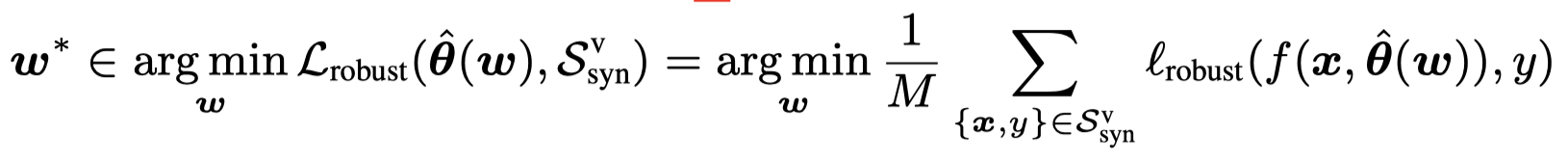
noise-robust loss拥有特殊的property:
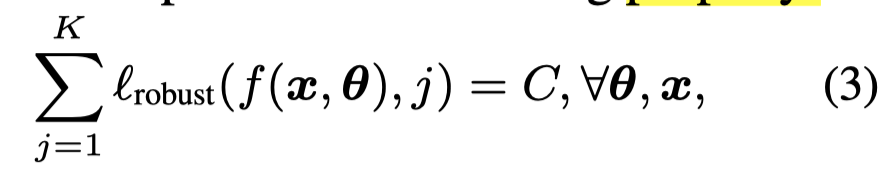
对于拥有这样property的loss,之前的研究证明了在大部分labels是正确的情况下,有部分noisy labels和全部正确的labels有一致的global minimum。
More formally, when the majority of the training samples are correctly labelled, the global minimizer (\(\mathbf{\theta}^*\) ) of \(\ell_{robust}\) robust is the same regardless of whether the training data is clean or noisy.
具体,作者使用的是reversed cross-entropy loss \(\ell_{rce}\),即将ground-truth label和predicted probability互换:
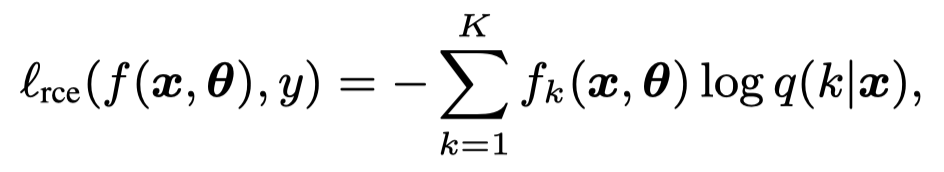
上面公式里如果\(k\)是ground truth label,那么\(q(k|x)=1\),否则\(q(k|x)=0\)。因此对应的\(log\ q(k|x)=0\)和\(log\ q(k|x)=A\)。\(A\)是一个估计常量。可以判断出来,上面的reversed cross-entropy loss \(\ell_{rce}=C=-(K-1)A\)。
在根据\(\ell_{robust}\)优化sample weights \(\mathbf{w}\)的时候,采用的是truncated back-propagation:
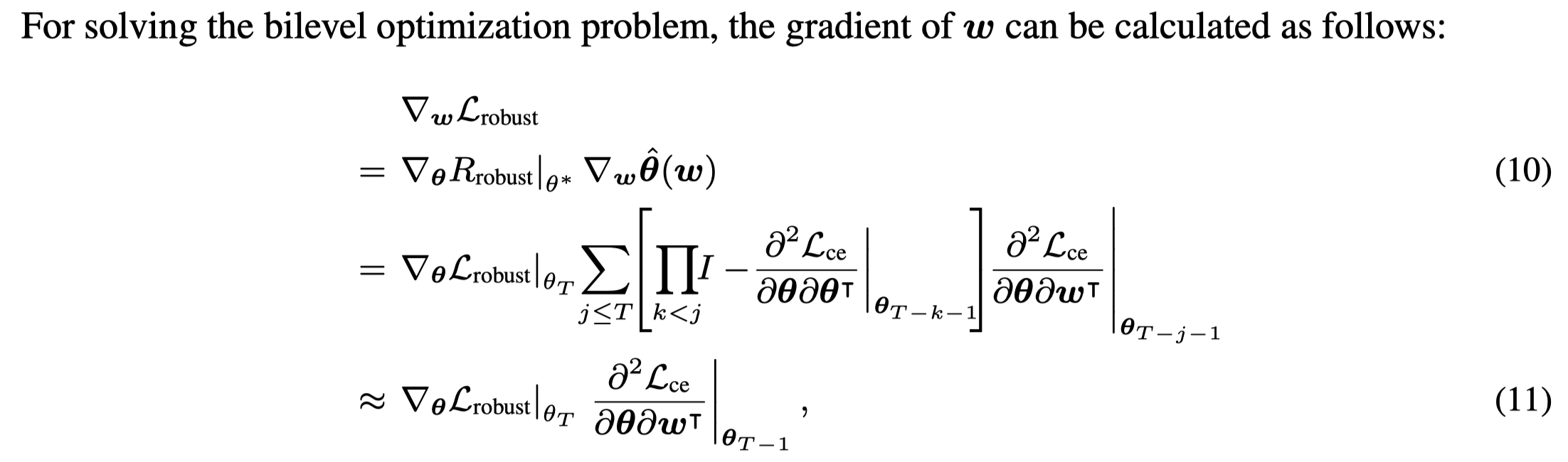
具体优化流程,先inner loop再outer loop:
在实验部分,基于GPT2-XL(1.5B)对8个text classification tasks进行实验。下面是作者在不同数据集里使用的数据生成的prompt:

ProGen
ProGen: Progressive Zero-shot Dataset Generation via In-context Feedback. The University of Hong Kong. EMNLP 2022 Findings. 代码.
Recently, dataset-generation-based zero-shot learning has shown promising results by training a task-specific model with a dataset synthesized from large pre-trained language models (PLMs). The final task-specific model often achieves compatible or even better performance than PLMs under the zero-shot setting, with orders of magnitude fewer parameters. However, synthetic datasets have their drawbacks. They have long been suffering from low-quality issues (e.g., low informativeness and redundancy). This explains why the massive synthetic data does not lead to better performance – a scenario we would expect in the humanlabeled data. To improve the quality of dataset synthesis, we propose a progressive zero-shot dataset generation framework, ProGen, which leverages the feedback from the task-specific model to guide the generation of new training data via in-context examples. Extensive experiments on five text classification datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach. We also show ProGen achieves onpar or superior performance with only 1% synthetic dataset size compared to baseline methods without in-context feedback.
Issue: 之前PLM已经被利用于数据生成,但还是需要有监督数据。ZeroGen方法首先提出利用task description作为prompt进行Dataset-generation-based Zero-shot Learning。但是这种zero-shot数据增强方法最大的问题是生成数据的low-quality。由于low-quality data(low informativeness,redundancy等),生成更多的数据不一定带来性能提升。
Solution: 作者的方法是从tiny task model中学习feedback,选择作者定义的高质量的data,然后作为新的demonstrations,生成新的数据。
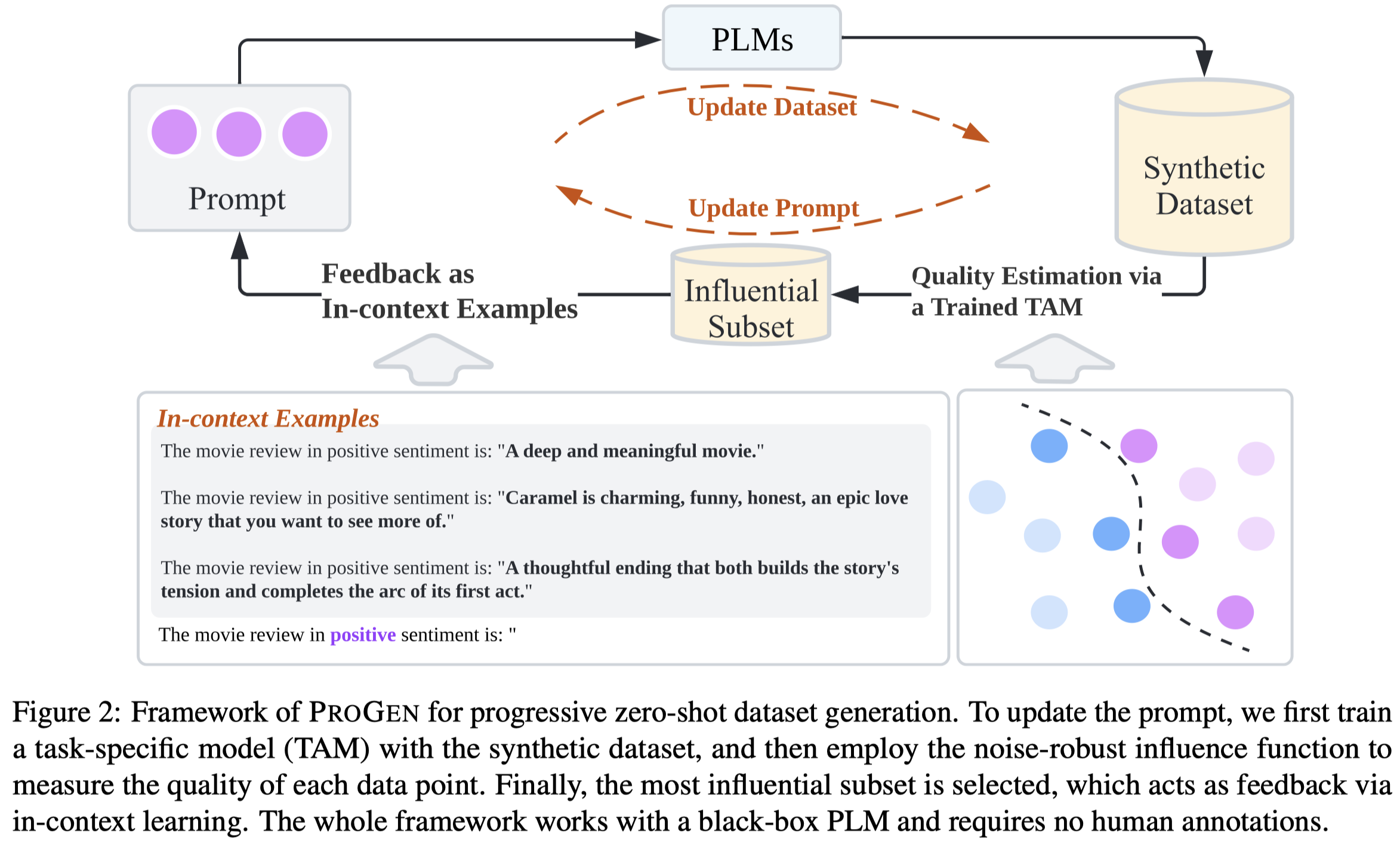
最大的难点是如何对生成的数据进行评估,作者提出来利用下游task model的influence function (Koh and Liang, 2017)作为评估质量的标准:

但是这需要一个验证集,而作者的验证集只能由生成数据构成,因此作者提出使用Reverse Cross-Entropy (RCE) loss作为noise-tolerant loss:
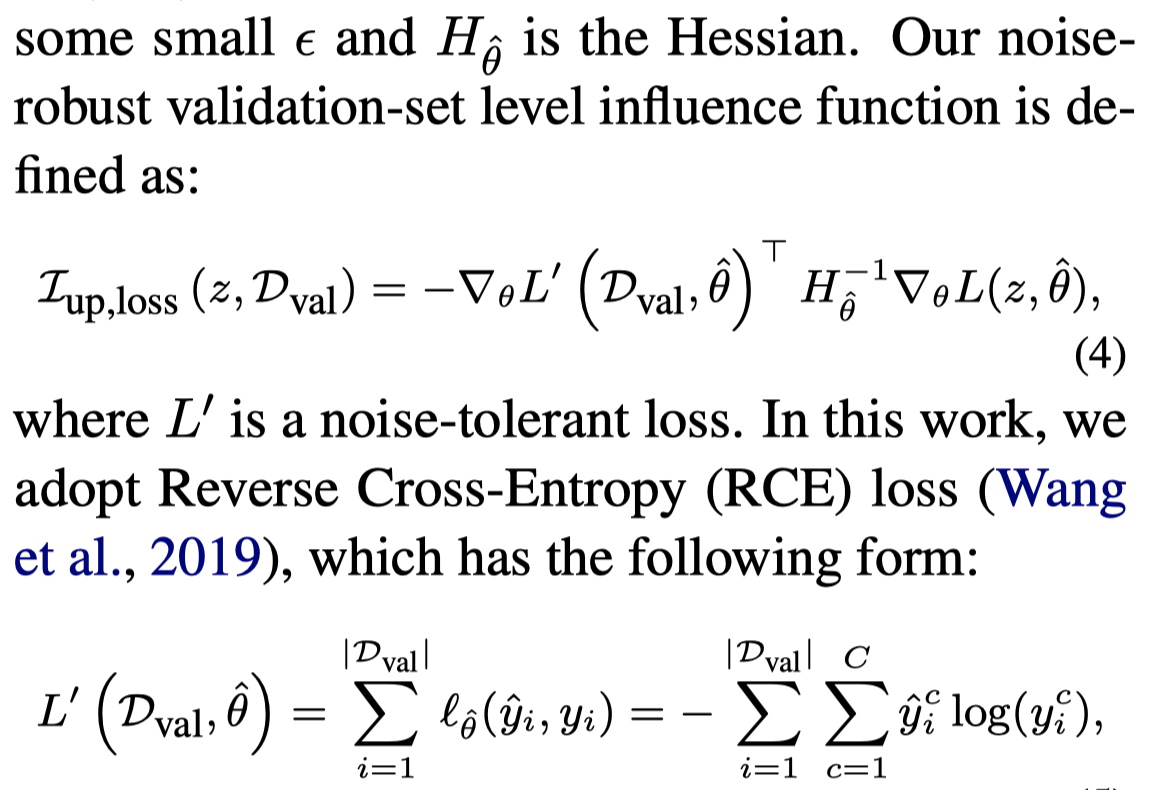
最后,计算出来的influence function负值越小,代表着对应生成的数据越可能减小在validation set上的权重,越应该看做是高质量生成数据。
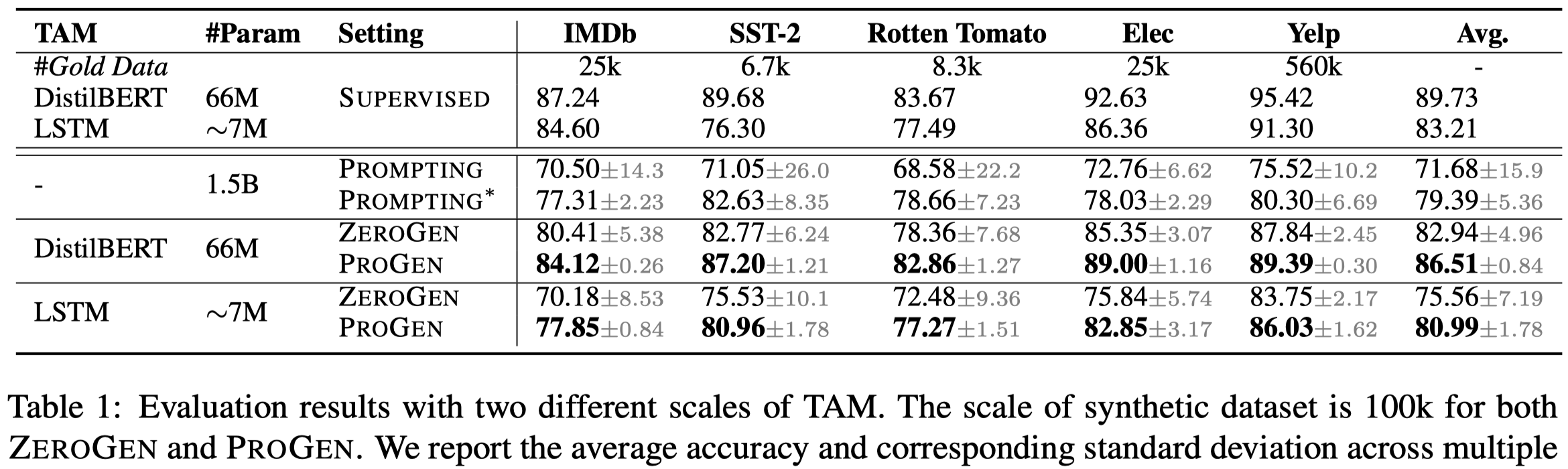
作者的实验是基于GPT2-XL,在text classification任务上进行实验。尽管不是LLM,但是仍然可以适用于各种LLM。
FewGen
Tuning Language Models as Training Data Generators for Augmentation-Enhanced Few-Shot Learning. University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign. ICML 2023. Code. [详细博客]
Recent studies have revealed the intriguing few-shot learning ability of pretrained language models (PLMs): They can quickly adapt to a new task when fine-tuned on a small amount of labeled data formulated as prompts, without requiring abundant task-specific annotations. Despite their promising performance, most existing few-shot approaches that only learn from the small training set still underperform fully supervised training by nontrivial margins. In this work, we study few-shot learning with PLMs from a different perspective: We first tune an autoregressive PLM on the few-shot samples and then use it as a generator to synthesize a large amount of novel training samples which augment the original training set. To encourage the generator to produce label-discriminative samples, we train it via weighted maximum likelihood where the weight of each token is automatically adjusted based on a discriminative meta-learning objective. A classification PLM can then be fine-tuned on both the few-shot and the synthetic samples with regularization for better generalization and stability. Our approach FewGen achieves an overall better result across seven classification tasks of the GLUE benchmark than existing few-shot learning methods, improving no-augmentation methods by 5+ average points, and outperforming augmentation methods by 3+ average points.
Issue: 之前的微调PLM进行数据生成的方法,没有显式地建模不同label之间的区别,可能导致在生成相似label对应的训练数据时,生成数据的质量难以保证。
Soluation: 作者认为在生成的时候,应该考虑token对于label的独特性。
作者提出的方法的总体结构图:
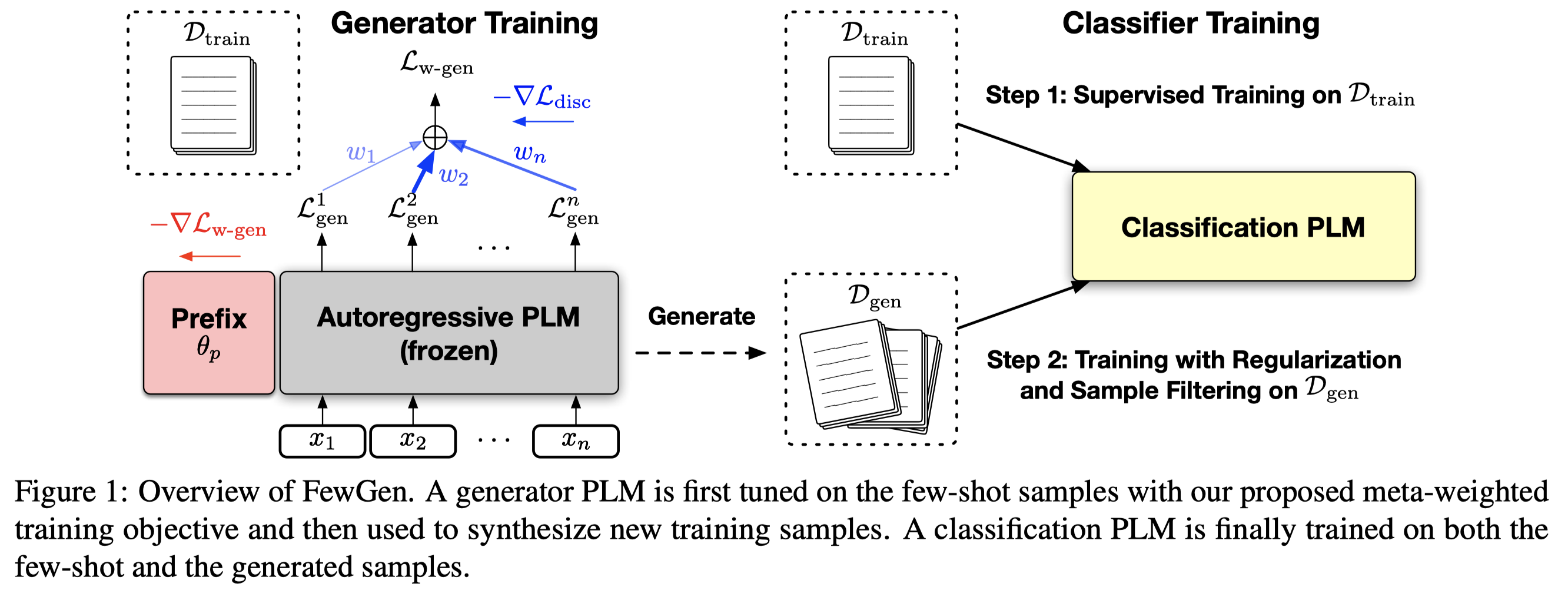
假定存在\(L\)个label,每个类型有\(K\)个训练数据,\(K\)是一个很小的值,如\(K=16\)。组成了训练集\(D_{train} = \{(\mathbf{x}, y)_i\}\)。其中,\(\mathbf{x} = [x_1,x_2,\dots,x_n]\)表示长度为\(n\)个tokens的text。类似的,还有\(D_{dev}\)和\(D_{test}\)。
我们要在训练集上训练一个data generator,\(G_{\mathbf{\theta}}\),来构造新的数据,所有新的生成数据构成了新的数据集合\(D_{gen}=\{ (\tilde{\mathbf{x}},\tilde{y})_i \}\)。
我们用\(C_\phi\)表示训练出来执行downstream task的分类器模型。
之前常见的训练数据生成器的方法是利用autoregressive PLM \(G_{\mathbf{\theta}}\)在\(D_{train}\)上按照maximum likelihood generation loss:
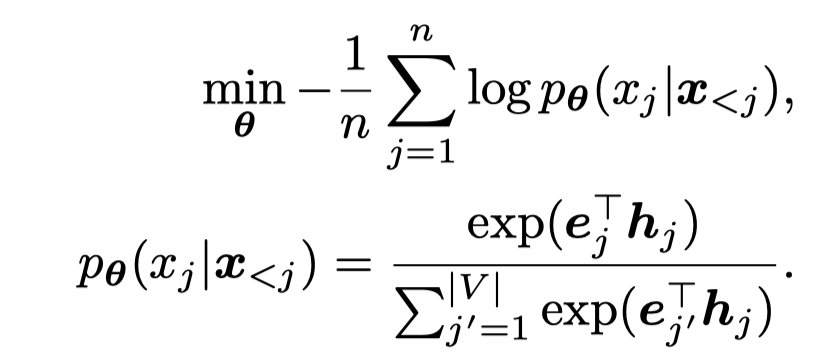
其中,\(\mathbf{h}_j\)表示是对于第\(j\)个位置PLM编码输出的embedding,\(\mathbf{e}_{j}\)表示正确的原来token \(j\)的token embedding,一共有\(V\)个候选token。期望正确token的输出概率\(p_\theta\)最大。训练结束后,就可以利用\(G_\theta\)按照学习到的概率不断采样新的tokens,获得新的生成数据。
但是如果直接在一个很小的训练集上,更新所有的PLM参数\(\mathbf{\theta}\)是不必要的。作者这里是利用prefix-tuning的方法,固定model整体的参数,只更新prefix vectors \(\mathbf{\theta}_p\),即最后学习到的data generator是\(G_{\mathbf{\theta}_p}\)。
对于带有label的任务来说,能够让生成的数据和label匹配是必要的。不同的label对应的数据可能有自己特有的pattern。而要学习conditional text generation probability \(p(\mathbf{x}|y_l)\)。最直接的方法是针对不同的label \(l\)有自己的参数\(\mathbf{\theta}_{p_l}\),直接优化generative likelihood:
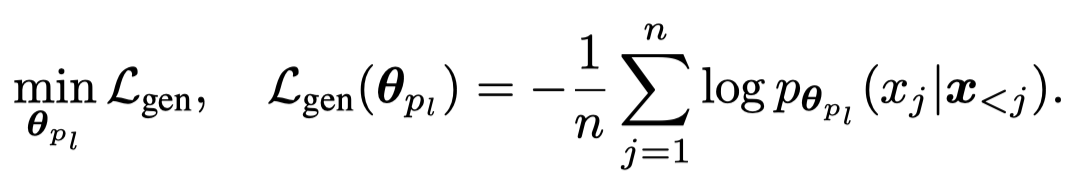
上面的方法没有考虑到label discriminativeness (/dɪˈskrɪmənətɪv/) \(p(y_l|\mathbf{x})\)也就是期望被downstream能够学习到的到的真实/理想分布。最理想的情况下,是期望生成的新数据:
- \(y_l\)是正确的
- 理论上,一个有足够能力的task model,可以根据\(\mathbf{x}\)非常confidence/明确的输出\(y_l\)
如果生成的数据从理论上/让人类去判断,根据\(\mathbf{x}\)既可以被分类为\(y_1\),又可以被分类为\(y_2\),很明显这个不是我们期望的理想数据。
对于很多challenging NLP tasks,是存在不同label之间有很相似的distributions的,不同label之间的差别很微妙。比如对于一个movie review:a movie where the ending feels like a cop-out,根据最后的cop-out可以判断这个是一个negative review(认为这个电影的结尾是个逃避式的结尾,比如作者选择了一种非常简单没法让人满意的方式结束了剧情,对于很多情节没有交代清楚);但如果仅仅是调整下最后的表达,换为revelation,就变为了一个positive review(认为电影的结尾有新意,出乎人的意料)。
为了评估label-discriminativeness,作者定义了一个新的loss,也就是某个text token \(j\),在使用label \(l\)时的对应参数 \(\mathbf{\theta}_p\)的情况下出现的概率和使用其它labels的对应参数时生成的概率的比值:
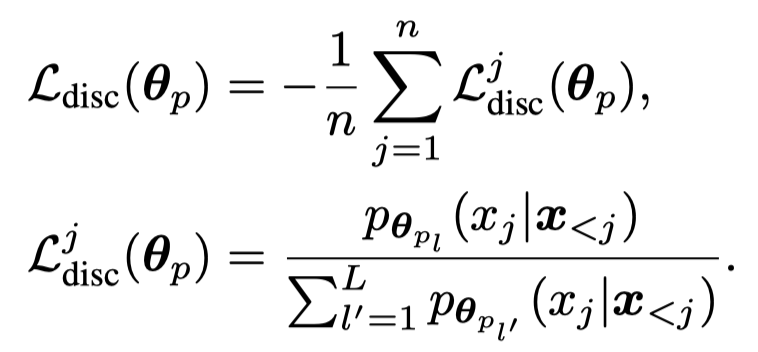
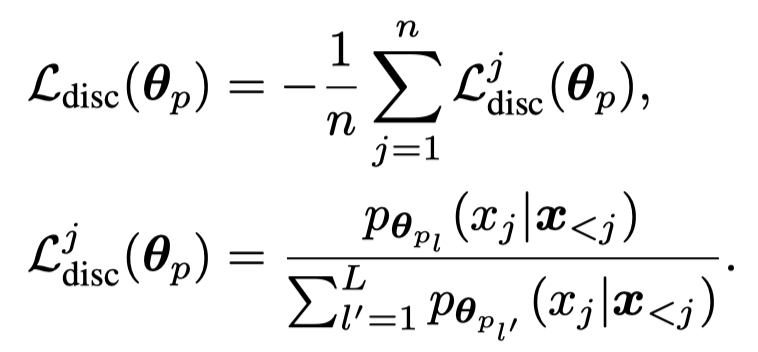
在优化生成式loss的过程中,每个token对于最后的loss有相同的loss weight \(1\)。而大多数的token是label-indiscriminate,那么优化\(\mathcal{L}_{gen}\)只需要让大多数的token,在无论输入参数\(\mathbf{\theta}_{p_l}\)的情况下,都进行输出。就能够让\(\mathcal{L}_{gen}\)在全局上越来越小。例如输入a movie,接下来的that在输入任意\(\mathbf{\theta}_{p_l}\)的情况下,出现概率都差不多。让更多的token出现概率不会随着输入参数\(\mathbf{\theta}_{p_l}\)变化,可能是让\(\mathcal{L}_{gen}\)不断减小的较优解。
那么如何让PLM学会针对不同的label,生成的data有区别呢?
最直接的做法是同时优化label-discriminative loss \(\mathcal{L}_{disc}\)。但这么做可能不会带来理想的结果,可能会让PLM倾向于对每个位置上的tokens都针对不同label用独特的描述。但是想到the这些词实际上是不需要随着label变化的。
也就是说我们需要让PLM能够学会将不同的token区分出来,关注到其中是label-discriminative的tokens。我们可以给每个token赋予不同的loss weight \(w_j\),如果一个位置上的token是label-discriminative的,那么就增大它的loss weight \(w_j\)。这样实现让PLM在优化生成loss的时候,要更多的关注根据当前输入的label参数\(\mathbf{\theta}_{p_l}\)和输出的label-discriminative的对应。比如输入的label是negative,输出的关键token是cop-out这样的词;输入的label是positive,输出的关键token是revelation这样的词。再比如如果出现bad/good这样的word,很明显也应该关注。

\(w_j\)是随着不同的text变化的,要想提前人工设定好是不实际的。那么就需要某种方法来自动学习\(w_j\)。
首先,如果让\(w_j\)看做是一个可学习的参数,赋值给输入的\(\mathbf{x}\)上的不同tokens,然后通过优化上面的\(\mathcal{L}_{w-gen}\)学习不同的token loss weight。但这意味着我们需要给每个训练数据的每一个token都学习一个参数\(w_j\)。虽然这种做法可以实现,但很明显这种做法很笨拙,并且仅仅在样本量非常小的情况下可以应用。
作者的做法是借鉴了meta-learning的思想,将这个优化问题看做是bi-level optimization问题。
对于generator要优化的参数,还是通过optimize生成loss来获得:
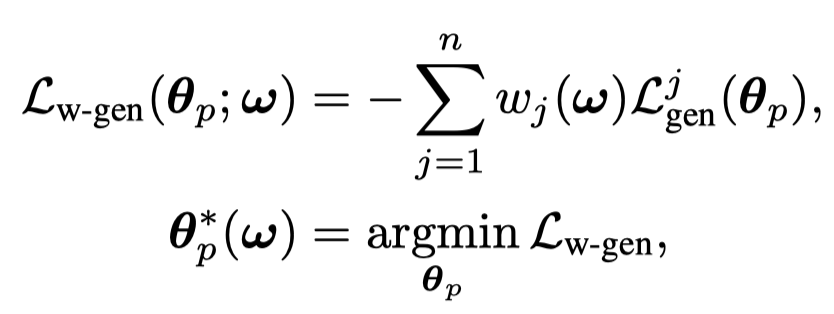
这里每个token的loss weight是通过\(w_j(\mathbf{\omega})\)函数计算得到的,它是一个带有softmax的feedforward network,输入是每个token计算得到的discriminative loss \(\mathcal{L}_{disc}^j\): \[ g_{\mathbf{\omega}} (\mathcal{L}_{disc}^j) = FFN(\mathcal{L}_{disc}^j) \\ w_j(\mathbf{\omega}) = \frac{exp(g_{\mathbf{\omega}} (\mathcal{L}_{disc}^j))}{\sum_{j^\prime = 1}^n exp(g_{\mathbf{\omega}} (\mathcal{L}_{disc}^{j^\prime}))} \] 这样输入的一个text不同位置的所有token的loss weight和是\(1\)。
对于要优化的weighting parameters \(\omega\)是通过优化outer objective \(\mathcal{L}_{disc}\):
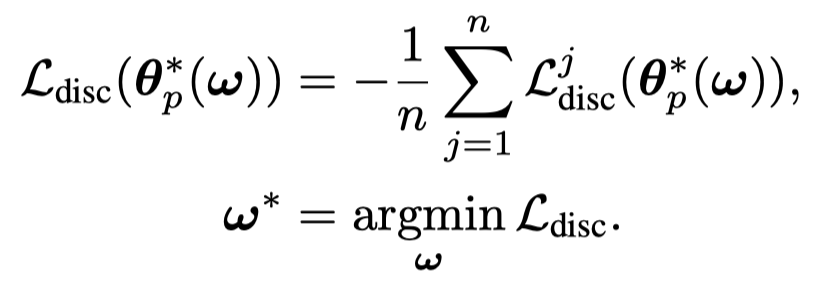
在优化生成式loss的过程中,每个token对于最后的loss有相同的loss weight \(1\)。而大多数的token是label-indiscriminate,那么优化\(\mathcal{L}_{gen}\)只需要让大多数的token,在无论输入参数\(\mathbf{\theta}_{p_l}\)的情况下,都进行输出。就能够让\(\mathcal{L}_{gen}\)在全局上越来越小。例如输入a movie,接下来的that在输入任意\(\mathbf{\theta}_{p_l}\)的情况下,出现概率都差不多。让更多的token出现概率不会随着输入参数\(\mathbf{\theta}_{p_l}\)变化,可能是让\(\mathcal{L}_{gen}\)不断减小的较优解。
那么如何让PLM学会针对不同的label,生成的data有区别呢?
最直接的做法是同时优化label-discriminative loss \(\mathcal{L}_{disc}\)。但这么做可能不会带来理想的结果,可能会让PLM倾向于对每个位置上的tokens都针对不同label用独特的描述。但是想到the这些词实际上是不需要随着label变化的。
也就是说我们需要让PLM能够学会将不同的token区分出来,关注到其中是label-discriminative的tokens。我们可以给每个token赋予不同的loss weight \(w_j\),如果一个位置上的token是label-discriminative的,那么就增大它的loss weight \(w_j\)。这样实现让PLM在优化生成loss的时候,要更多的关注根据当前输入的label参数\(\mathbf{\theta}_{p_l}\)和输出的label-discriminative的对应。比如输入的label是negative,输出的关键token是cop-out这样的词;输入的label是positive,输出的关键token是revelation这样的词。再比如如果出现bad/good这样的word,很明显也应该关注。
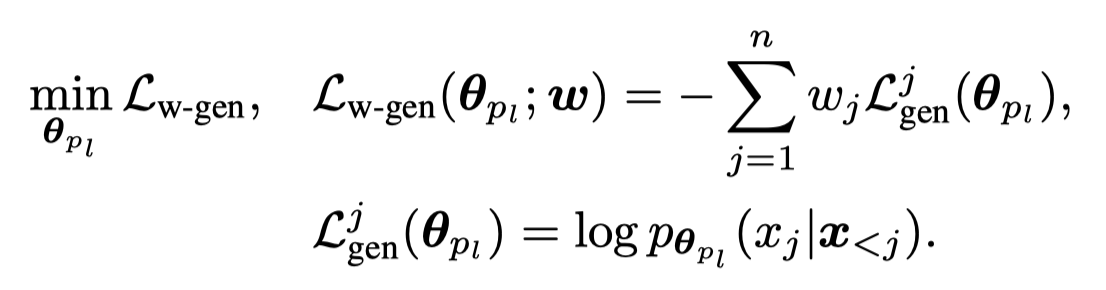
\(w_j\)是随着不同的text变化的,要想提前人工设定好是不实际的。那么就需要某种方法来自动学习\(w_j\)。
首先,如果让\(w_j\)看做是一个可学习的参数,赋值给输入的\(\mathbf{x}\)上的不同tokens,然后通过优化上面的\(\mathcal{L}_{w-gen}\)学习不同的token loss weight。但这意味着我们需要给每个训练数据的每一个token都学习一个参数\(w_j\)。虽然这种做法可以实现,但很明显这种做法很笨拙,并且仅仅在样本量非常小的情况下可以应用。
作者的做法是借鉴了meta-learning的思想,将这个优化问题看做是bi-level optimization问题。
对于generator要优化的参数,还是通过optimize生成loss来获得:
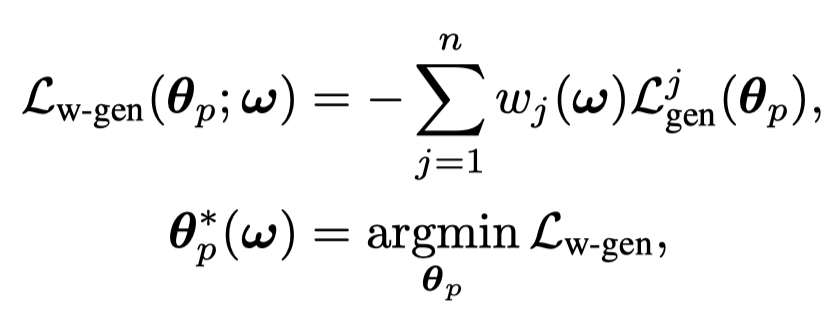
这里每个token的loss weight是通过\(w_j(\mathbf{\omega})\)函数计算得到的,它是一个带有softmax的feedforward network,输入是每个token计算得到的discriminative loss \(\mathcal{L}_{disc}^j\): \[ g_{\mathbf{\omega}} (\mathcal{L}_{disc}^j) = FFN(\mathcal{L}_{disc}^j) \\ w_j(\mathbf{\omega}) = \frac{exp(g_{\mathbf{\omega}} (\mathcal{L}_{disc}^j))}{\sum_{j^\prime = 1}^n exp(g_{\mathbf{\omega}} (\mathcal{L}_{disc}^{j^\prime}))} \] 这样输入的一个text不同位置的所有token的loss weight和是\(1\)。
对于要优化的weighting parameters \(\omega\)是通过优化outer objective \(\mathcal{L}_{disc}\):
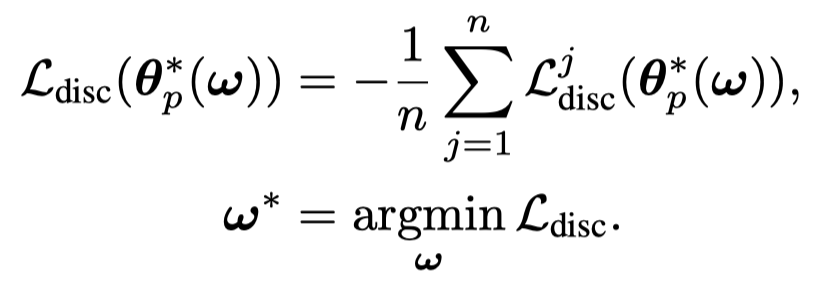
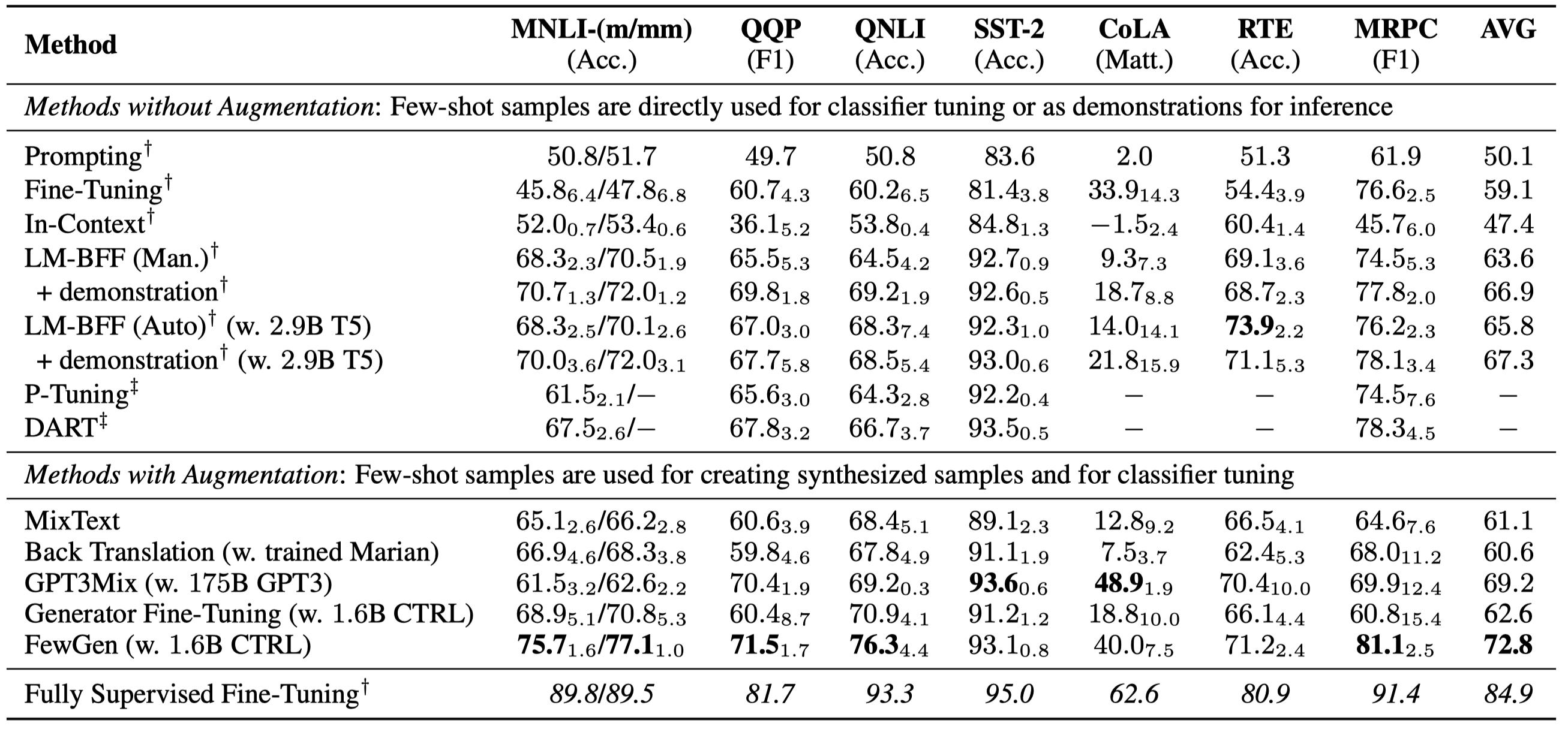
主要实验结果:
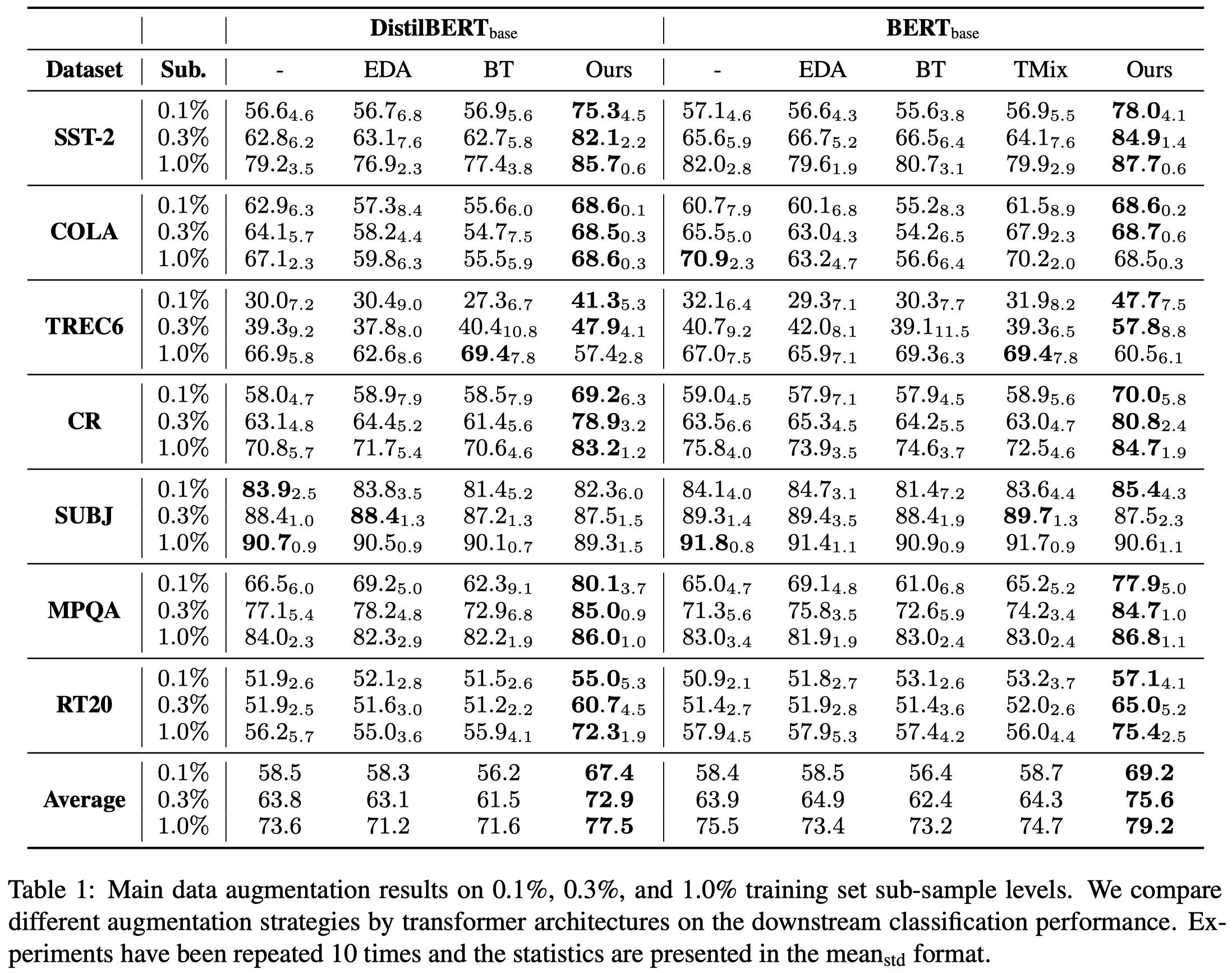
消融实验: