IE-data-augment-collection1
Data Augment for IE papers 1
基于数据增强策略的信息抽取论文合集 1。
Cross-domain IE
CDA
Data Augmentation for Cross-Domain Named Entity Recognition
简写是Cross-domain Data Augmentation (CDA)方法。
EMNLP 2021,休斯顿大学与Snap,代码。
Current work in named entity recognition (NER) shows that data augmentation techniques can produce more robust models. However, most existing techniques focus on augmenting in-domain data in low-resource scenarios where annotated data is quite limited. In contrast, we study cross-domain data augmentation for the NER task. We investigate the possibility of leveraging data from highresource domains by projecting it into the lowresource domains. Specifically, we propose a novel neural architecture to transform the data representation from a high-resource to a low-resource domain by learning the patterns (e.g. style, noise, abbreviations, etc.) in the text that differentiate them and a shared feature space where both domains are aligned. We experiment with diverse datasets and show that transforming the data to the low-resource domain representation achieves significant improvements over only using data from high-resource domains.
应该是首个考虑用数据增强策略做跨域NER任务的方法。
之前的数据增强IE方法主要是利用in-domain data进行数据增强。作者发现不同domain有不同的patterns:
Based on our observations, the text in different domains usually presents unique patterns (e.g. style, noise abbreviations, etc.).
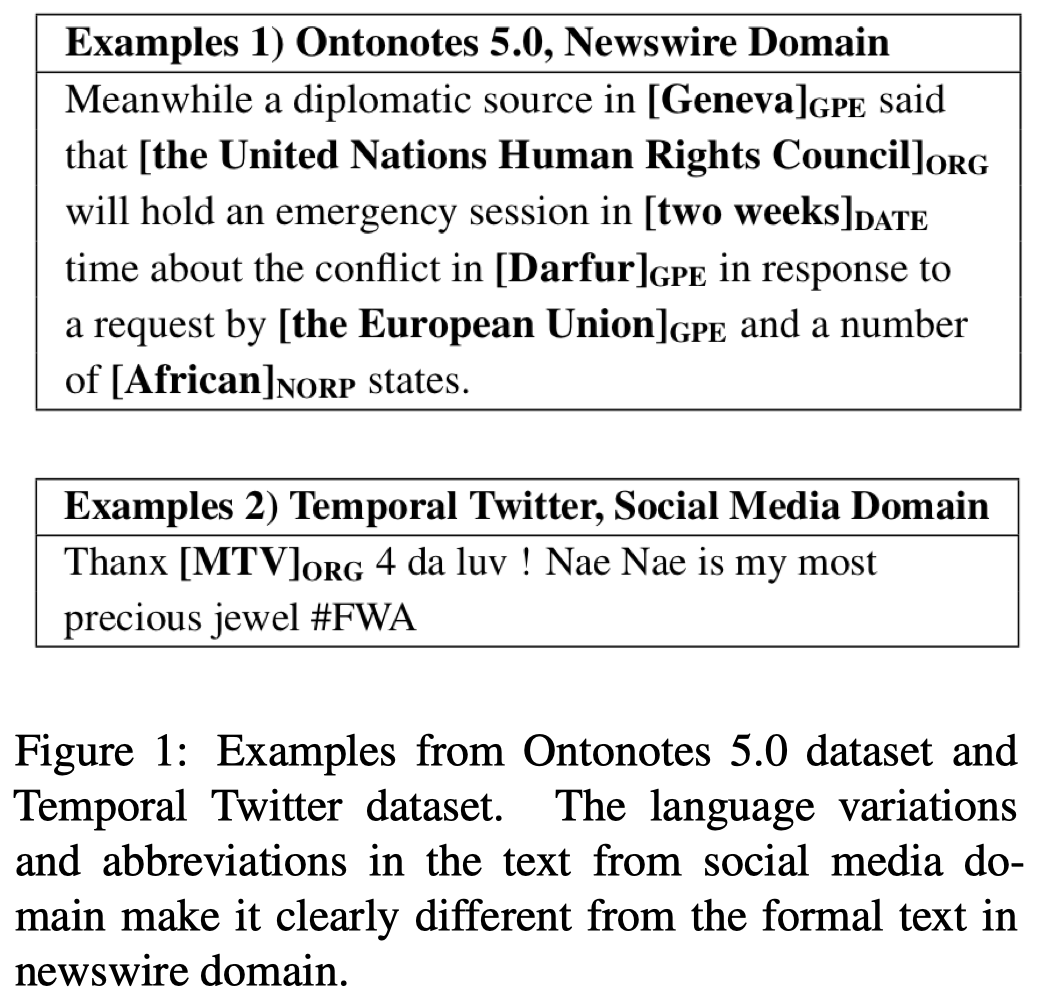
例如上面例子中新闻domain的句子更长,表达也更加正式;而social domain的句子有更多的噪音,句子更短,有更多口语/个性化的表达。
但是,作者认为不同domain的text的语义是可以迁移的,并且是存在领域不变量invariables的。作者研究从high-resource domain到low-resource domain数据增强NER方法。
和之前的数据增强方法一样,作者同样训练了一个LM来生成数据,编码器+解码器。编码器是biLSTM,解码器是另一层LSTM。
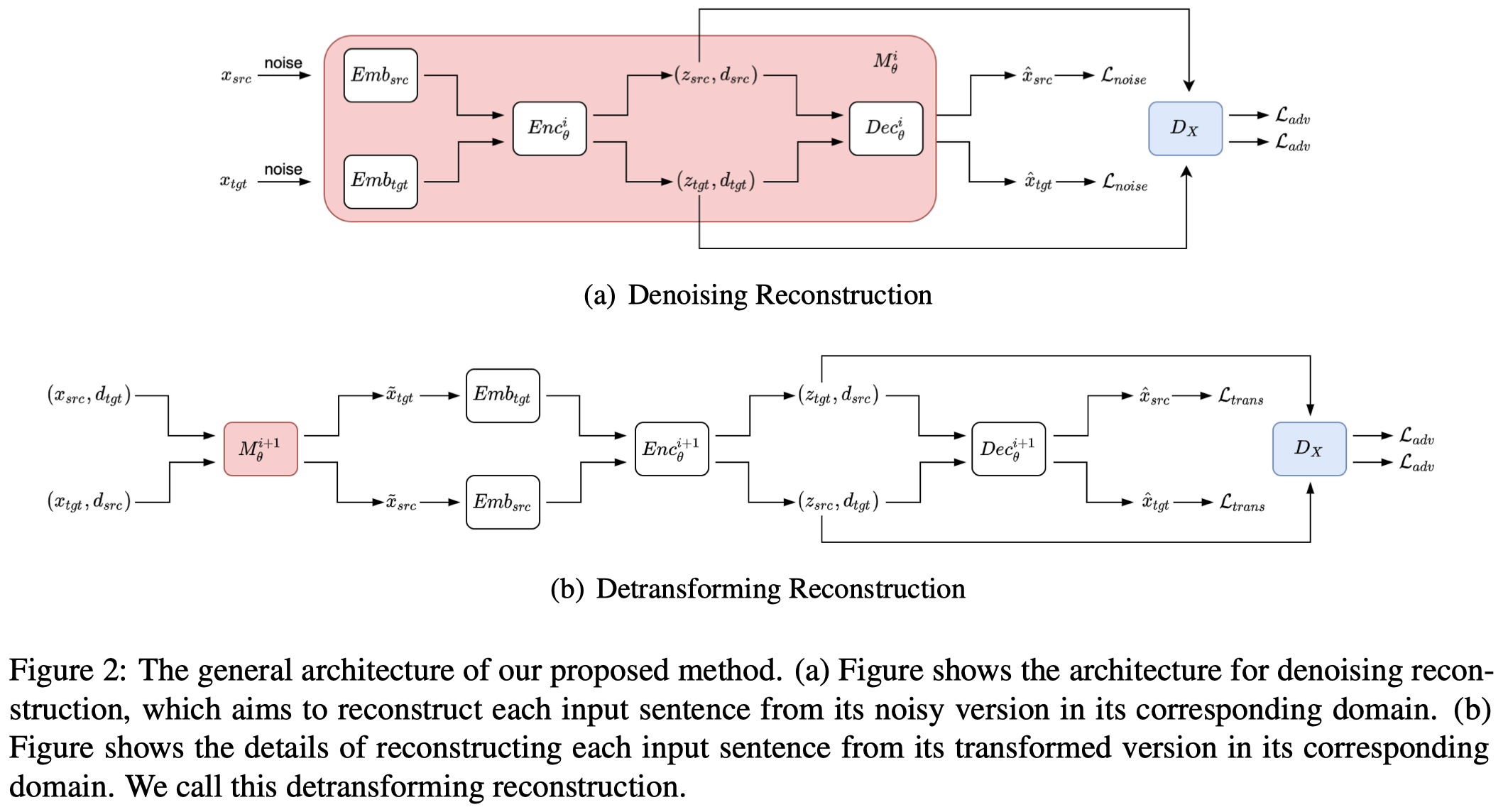
作者提出的训练模型包括两步:
Denoising Reconstruction:learn the textual pattern and generate compressed representations of the data from each domain
在输入的text中加入噪音,能够强迫model更加学会保留原始的数据结构信息,所以作者首先通过几种word-level operation来插入噪音:

使用相同参数的encoder和decoder去重建两个domain的input sentence。模型的参数可以看做是学习了隐式的领域对齐。loss是解码器输出和input text之间的差异。
这一步还额外训练了一个对抗式判别器discriminator用来判断编码器的输出是来自哪个领域,为下一步model学习domain mapping做准备。
Detransforming Reconstruction:align the compressed representations of the data from different domains so that the model can project the data from one domain to another
- 首先,用上一步学习好的encoder+decoder,把source domain的sentence转化为target domain style的sentence;把target domain的sentence转化为source domain style的sentence
- 然后,利用跨域转化后的句子,经过编码器和解码器,期望能够恢复在原来domain的句子
- 这一步继续训练对抗式判别器discriminator,如果判别器根据编码器的输出,判断领域变换后的sentence是原来domain的概率越小,则认为domain mapping效果越好
作者基于Ontonotes 5.0 Dataset(domains:Broadcast Conversation (BC), Broadcast News (BN), Magazine (MZ), Newswire (NW), and Web Data (WB).)和Temporal Twitter Dataset(Social Media (SM) domain)进行实验。基于source domain的data生成target domain的新training data。
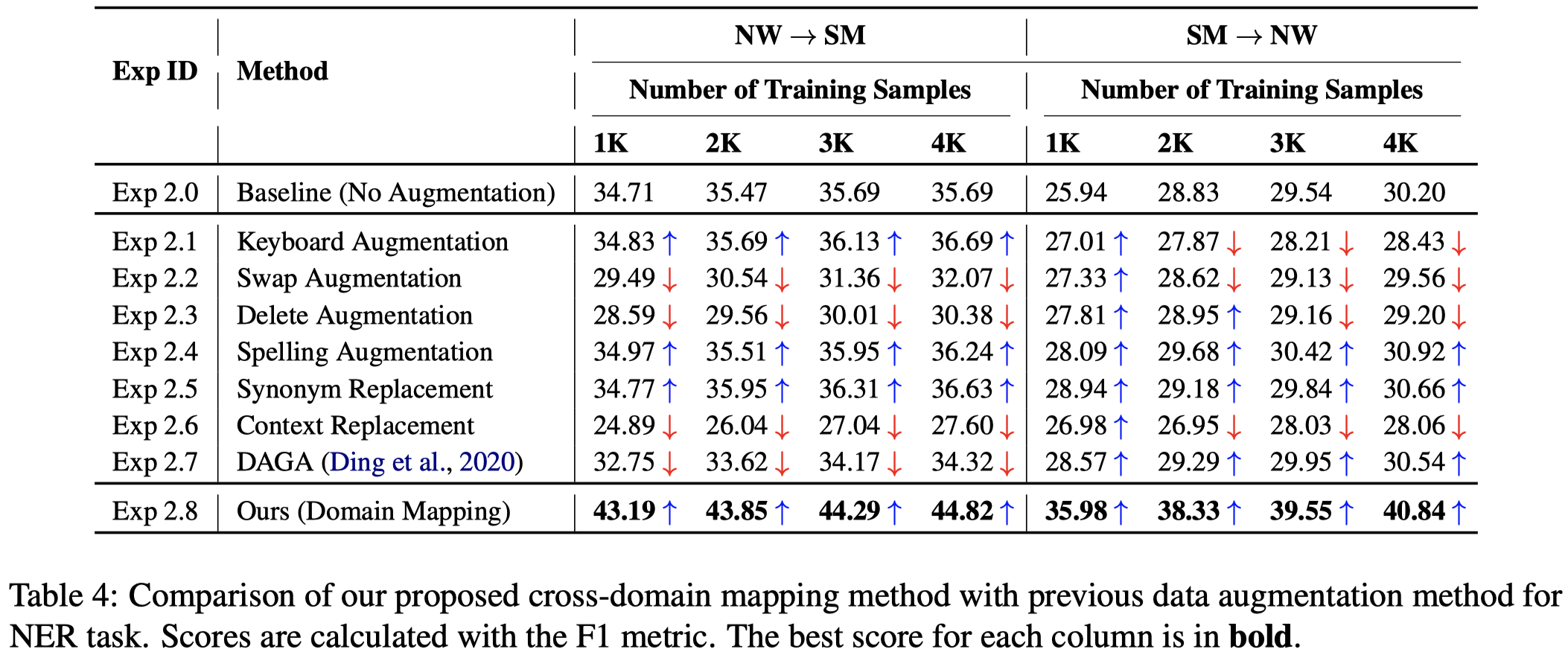
上面实验结果中能够看出,原来的in-domain的数据增强方法(如DAGA方法)无法很好的处理跨域问题。这说明原来数据增强方法无法直接生成对应domain的数据。
实验用的NER model是BERT+Linear Layer。
Style Transfer
Style Transfer as Data Augmentation: A Case Study on Named Entity Recognition
与前面CDA是同一作者。EMNLP 2022,代码。
In this work, we take the named entity recognition task in the English language as a case study and explore style transfer as a data augmentation method to increase the size and diversity of training data in low-resource scenarios. We propose a new method to effectively transform the text from a high-resource domain to a low-resource domain by changing its style-related attributes to generate synthetic data for training. Moreover, we design a constrained decoding algorithm along with a set of key ingredients for data selection to guarantee the generation of valid and coherent data. Experiments and analysis on five different domain pairs under different data regimes demonstrate that our approach can significantly improve results compared to current state-of-the-art data augmentation methods. Our approach is a practical solution to data scarcity, and we expect it to be applicable to other NLP tasks.
作者探究使用style transfer来为cross-domain NER任务做数据增强的方法。由于并没有带有NER label的style transfer数据集,因此作者提出可以利用非NER任务的style transfer数据集。(风格转换一定程度上不局限在特定任务,但是作者这种做法有个隐含的前提,就是NER的source domain和target domain中的styles已经包括在了非NER任务的style transfer数据集中)。
作者同样训练一个encoder+decoder的LM进行数据生成。这篇论文中作者使用的是T5-base。
第一步就是在非NER任务的style transfer数据集GYAFC (Rao and Tetreault, 2018)上进行训练。这个数据集包括了formal and informal的句子对。通过输入某个style的句子,让T5学会输出对应其它style的句子,优化重建loss \(L_{pg}\)。作者follow前人的工作,将style transfer看做是改写生成的问题paraphrase generation problem。和作者之前工作CDA中的domain判别器类似,这一步也额外训练了一个对抗性的style判别器,用来判断编码器输出的embedding是属于哪种style。
第二步是想办法让T5能够学会在NER的句子上进行风格转换。首先要把label注入到sentence中,这里作者把<START_ENTITY_TYPE> and <END_ENTITY_TYPE>插入到entity span的左右侧。然后就是作者提出的cycle-consistent reconstruction,简单说是输入某个sentence,让T5转化为另一种style的sentence,把这个转换后的sentence再输入到T5中,让T5重新回复原来style的sentence。第二步同样优化对抗性style判别器。
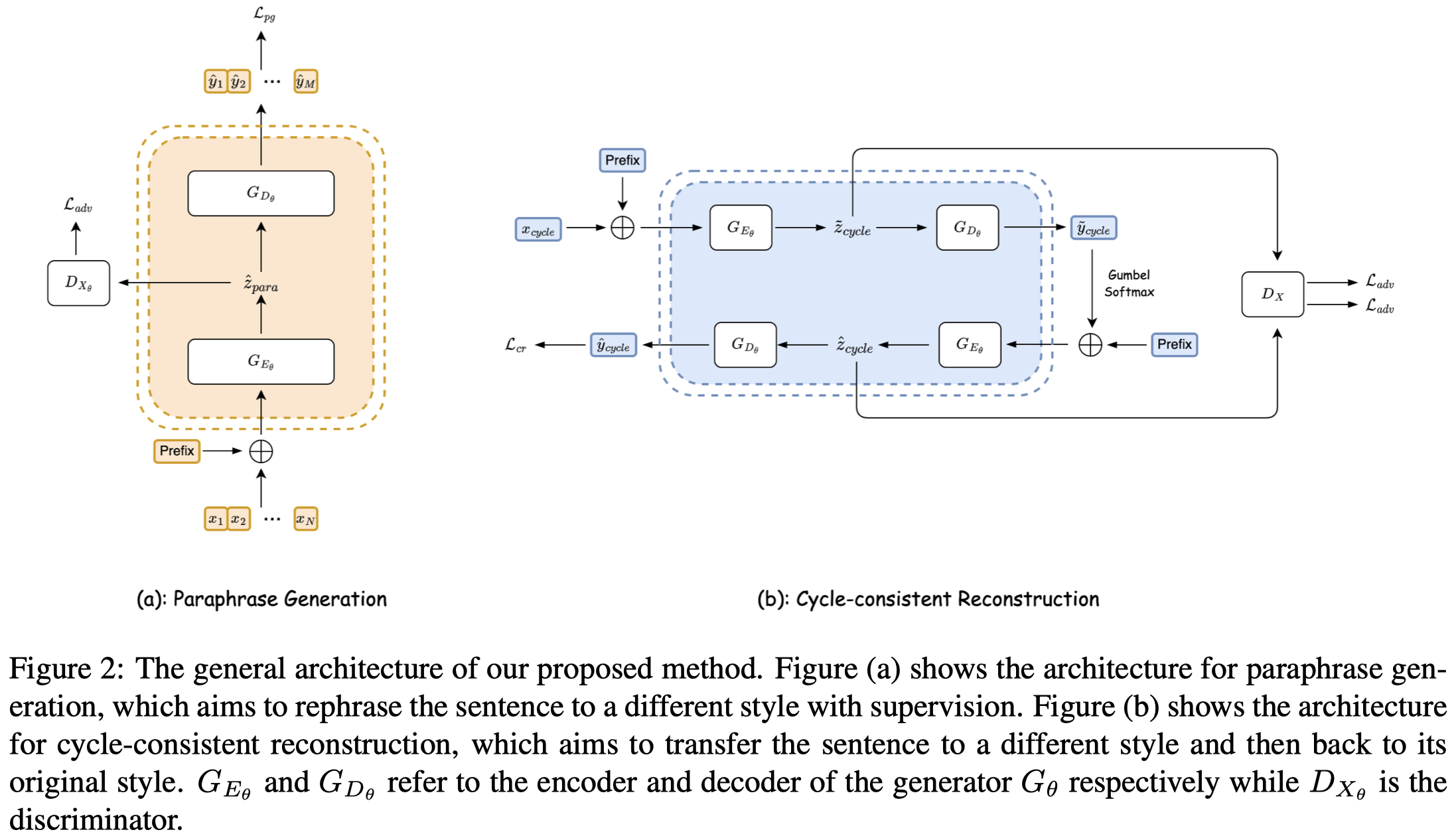
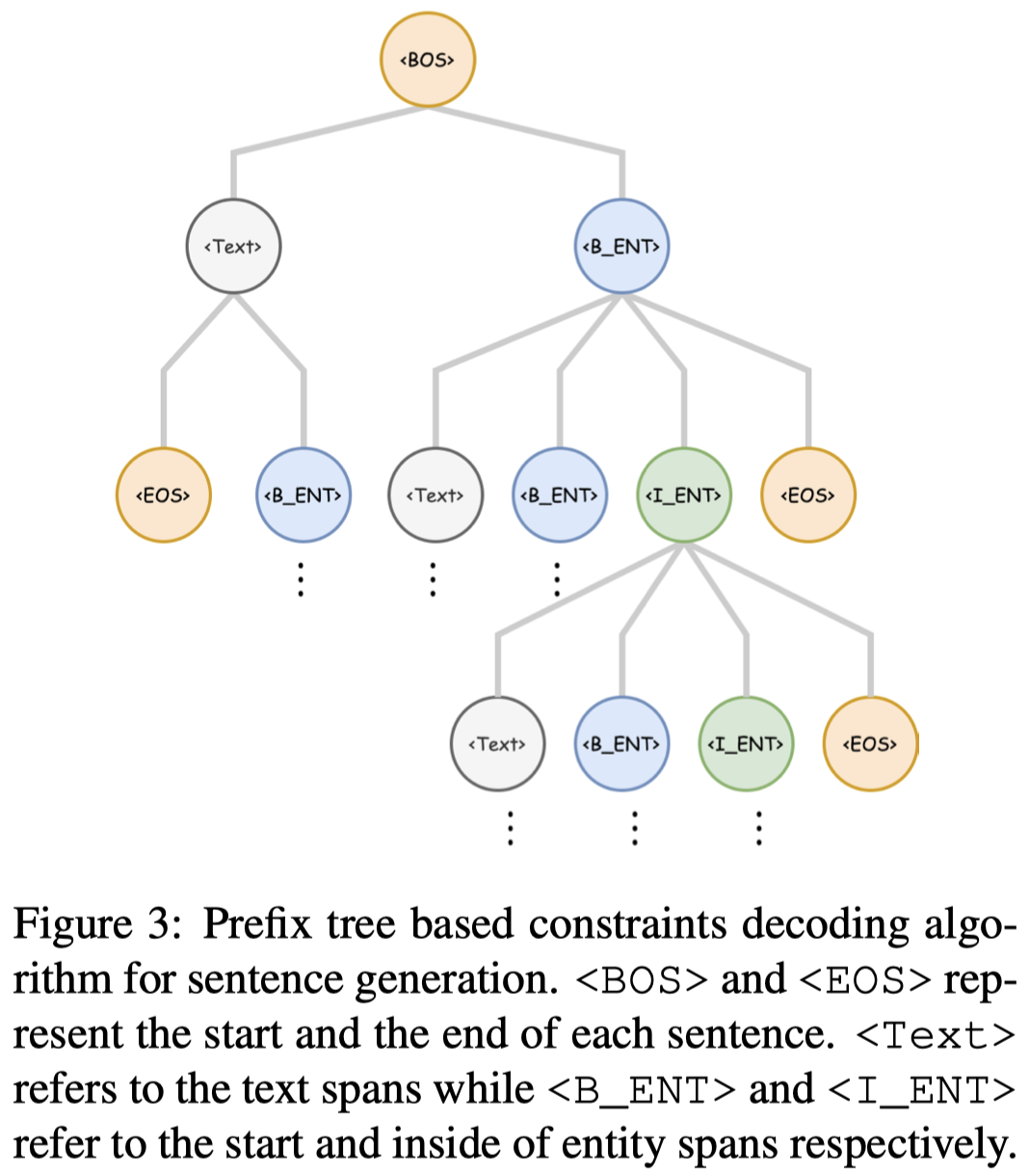
第三步是生成。为了保证生成数据是valid的,提出了基于prefix tree的Constrained Decoding策略,是保留top-K或top-p的token候选项,然后约束生成句子的输出范围,比如之前输出的span是属于<Text>,那么接下来输出的span就必须是<EOS> or <B_ENT>:
即使经过上一步,也不能保证生成数据是可靠的。为了进一步提升质量,比如过滤掉简单的重复、胡言乱语等生成的text,计算四个方法的4个metric,然后加权求和作为对于生成data质量的评估:
- Consistency: a confidence score from a pretrained style classifier as the extent a generated sentence is in the target style. 基于T5 base,用一个外部的model判断是否符合特定style
- Adequacy: a confidence score from a pretrained NLU model on how much semantics is preserved in the generated sentence. 基于开源model,判断生成句子保留的语义
- Fluency: a confidence score from a pretrained NLU model indicating the fluency of the generated sentence. 基于开源model,判断生成句子的流程程度
- Diversity: the edit distance between original sentences and the generated sentences at the character level. 利用原始sentence和生成sentence的编辑距离来衡量生成句子的多样性。
实验数据集与CDA中的一样,使用OntoNotes 5.0作为source domain和Temporal Twitter Corpus作为target domain。OntoNotes 5.0的domain style是formal的,Temporal Twitter Corpus的domain style是informal的。
作者的NER model是基于BERT base+Linear,与CDA的一致。
Fact-Mix
FactMix: Using a Few Labeled In-domain Examples to Generalize to Cross-domain Named Entity Recognition. COLING 2022,西湖大学 ,代码。
Few-shot Named Entity Recognition (NER) is imperative for entity tagging in limited resource domains and thus received proper attention in recent years. Existing approaches for few-shot NER are evaluated mainly under in-domain settings. In contrast, little is known about how these inherently faithful models perform in cross-domain NER using a few labeled in-domain examples. This paper proposes a two-step rationale-centric data augmentation method to improve the model’s generalization ability. Results on several datasets show that our model-agnostic method significantly improves the performance of crossdomain NER tasks compared to previous state-of-the-art methods, including the data augmentation and prompt-tuning methods. Our codes are available at https://github.com/lifan-yuan/FactMix.
作者主要从数据增强的角度解决跨域NER问题。作者认为跨域的NER任务要考虑两个核心问题:
- NER任务作为序列标注任务,它的label之间是相互依赖的,而不是相互独立的。不同领域这种label依赖不一样。it is essential to understand dependencies within the labels instead of classifying each token independently.
- 不同domain的文本中的non-entity tokens的语义是不一致的,这种不一致可能增大NER模型进行跨域NER的困难程度。non-entity tokens in NER do not hold unified semantic meanings, but they could become noisy when combined with entity tokens in the training set.
因此,作者认为NER模型学习到的non-entity token和要预测的label之间隐式联系可能影响跨域性能。比如在医学domain上的句子'Jane monitored the patient’s heart rate',Jane是一个person,在医学domain上训练好的一个NER model可能学习到Jane和monitored之间的潜在关联。但是如果迁移到关于movie review的跨域数据集上,Jane和monitor之间的在医疗领域的潜在关联就不再合适了。
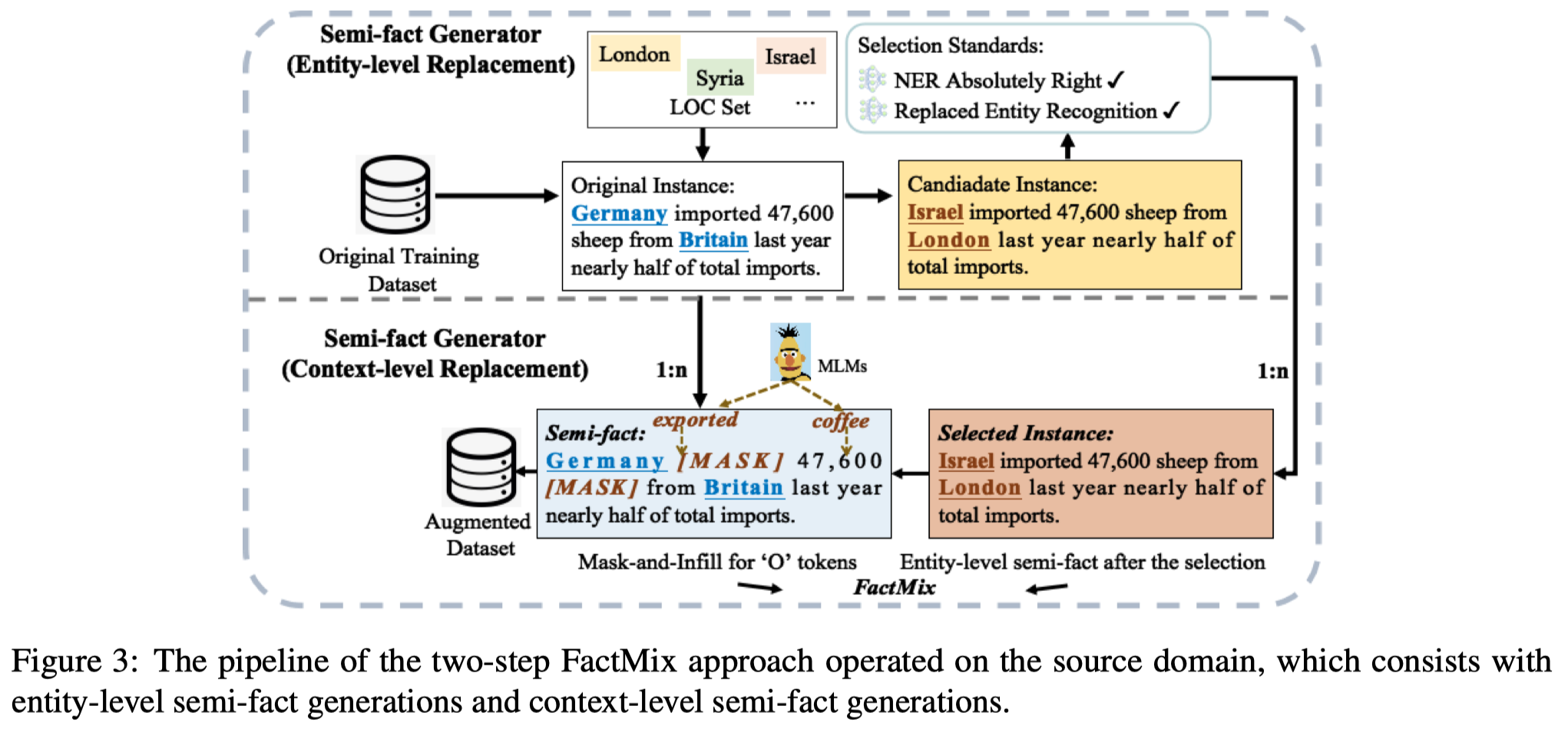
因此,作者提出了一种新的数据增强策略Context-level semi-fact generations:
- 随机使用MLM的[MASK] token代替source domain文本中的某个non-entity token,选择预测时概率最大的词进行替换。这样就引入了out-of-domain的context信息(被预训练model在预训练阶段学习到的信息)
- 为了避免替换后的词引起entity label标注的影响,作者只保留那些能够被NER模型正确预测所有token NER tag的替换后的样例
这种数据增强策略Context-level semi-fact generations和之前研究者提出的Entity-level semi-fact generations结合起来:
实验以CONLL2003作为source domain,CrossNER数据集下的多个子集作为target domain。训练的时候应用到了fine-tuning based和prompt-tuning based两种NER微调策略,具体参考论文。作者在BERT和RoBERT两类模型不同size的LM上进行了实验。
只使用source domain的数据来进行训练,然后测试在target domain上的效果,验证模型的领域泛化性。
In-domain IE
DAGA
DAGA: Data Augmentation with a Generation Approach for Low-resource Tagging Tasks
南洋理工与阿里达摩,EMNLP 2020,代码。
Data augmentation techniques have been widely used to improve machine learning performance as they enhance the generalization capability of models. In this work, to generate high quality synthetic data for low-resource tagging tasks, we propose a novel augmentation method with language models trained on the linearized labeled sentences. Our method is applicable to both supervised and semi-supervised settings. For the supervised settings, we conduct extensive experiments on named entity recognition (NER), part of speech (POS) tagging and end-to-end target based sentiment analysis (E2E-TBSA) tasks. For the semi-supervised settings, we evaluate our method on the NER task under the conditions of given unlabeled data only and unlabeled data plus a knowledge base. The results show that our method can consistently outperform the baselines, particularly when the given gold training data are less.
作者声称是首个在序列标注task上,引入LM做数据增强的文章。
数据增强是用来人造数据的一种在各个领域都被广泛应用的方法。NLP上的数据增强有它自己独特的特征:在image上简单的修改通常不会改变image本身的信息;但是在natural language上删除或替换一个词就可能完全改变整个sentence的意思。
而一般的NLP 数据增强方法包括synonym replacement, random deletion/swap/insertion, generation with VAE or pre-trained language models、back translation、systematically reordering the dependents of some nodes in gold data、leveraging knowledge base for question generation等等。
和上面的NLP任务相比,类似NER这类的token-level的sequence tagging任务对数据增强时引入的噪音更加敏感。序列标注有的3种尝试(2020年前):
- Annotating unlabeled data with a weak tagger [Automated phrase mining from massive text corpora. 2018] 使用已有的标注工具直接进行标注,需要标注工具已经提前具备了相应的domain knowledge,否则面临domain-shift problem [Multimix: A robust data augmentation framework for cross-lingual nlp. 2020]
- leveraging aligned bilingual corpora to induce annotation [Inducing multilingual text analysis tools via robust projection across aligned corpora. 2001] 要求有额外的外语语料,很多情况下不实际
- synonym replacement [Biomedical named entity recognition via reference-set augmented bootstrapping. 2019] 需要WordNet这类外部知识和人工设计的规则,难以覆盖所有的低资源场景
因此,作者提出使用生成式的数据增强方法。作者首先训练一个LM学会现有gold data中语言的特征:
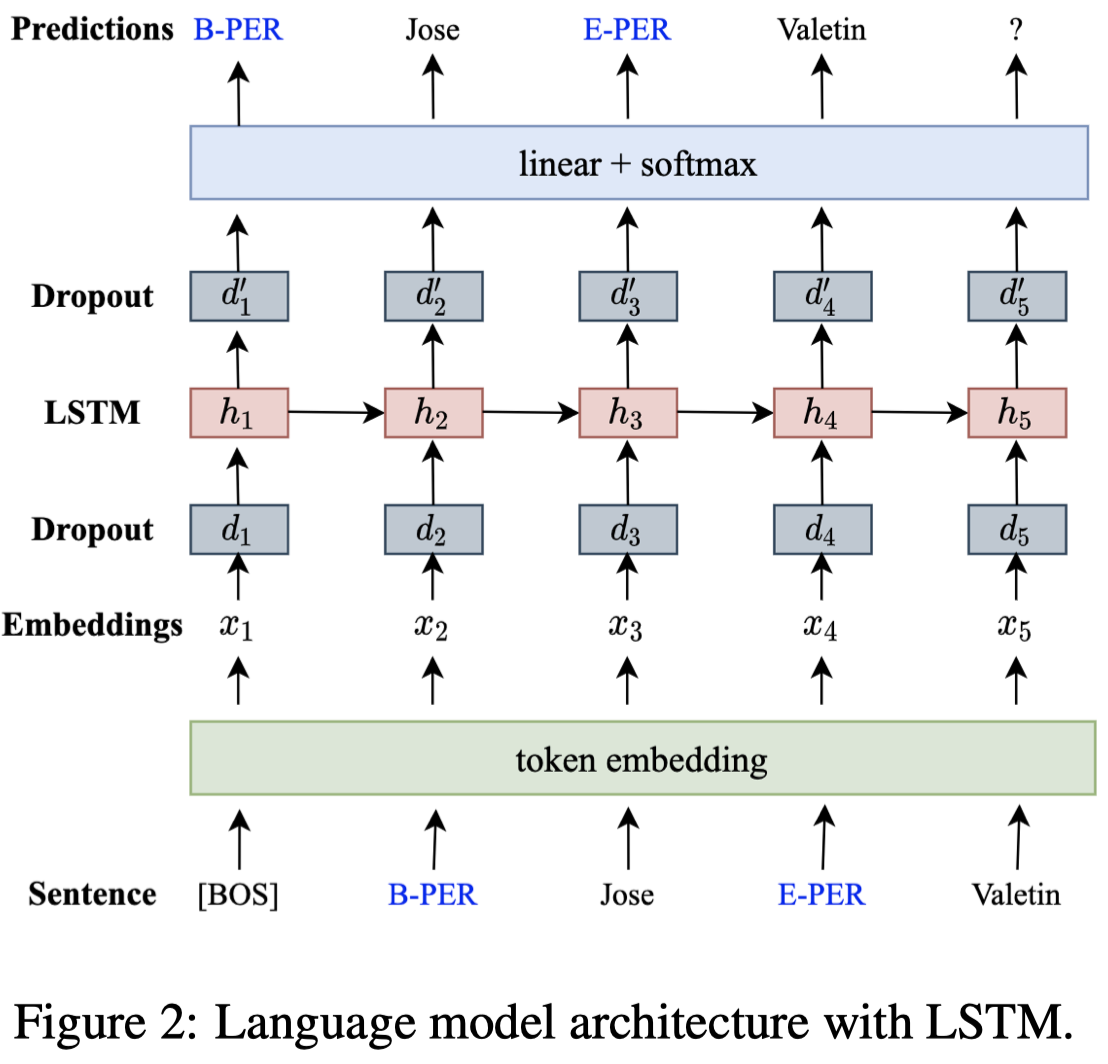
单层的LSTM作为语言模型,使用一般的单向language objectives进行优化。作者通过sentence linearization把所有的序列标注sentence都转换为带有tag的句子(NER任务中忽略tag \(O\)):
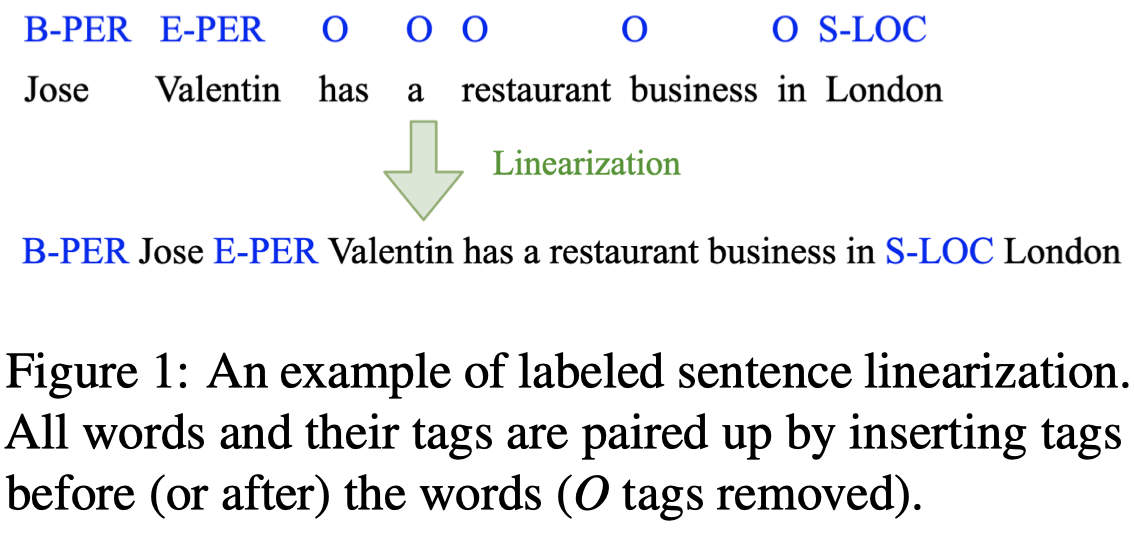
将tag放在对应的word前面,作者发现这样比tag在word后面效果好。推测原因是这样子可能更加符合一般的语言中形容词-名词的pattern(Modifier-Noun pattern)。
在生成的时候,输入是[BOS],让LSTM LM直接输出各种不同的句子。对于输出的句子进行后处理,比如删除没有tag的句子、删除有错误tag的情况等。
除了上面直接在gold data上让LM学习特征外,作者还提出了conditional generation method让LM能够利用unlabeled data or knowledge bases。从外部的数据源中获取更多的knowledge:

conditional generation本质就是在sentence之前添加condition tags:\(\{ [labeled], [unlabeled], [KB] \}\)。
在实验中,作者的NER使用BiLSTM-CRF模型在gold data和生成的data上进行训练,然后评估。作者使用了过采样gold data的策略,采样1个generated data,过采样4个gold data。
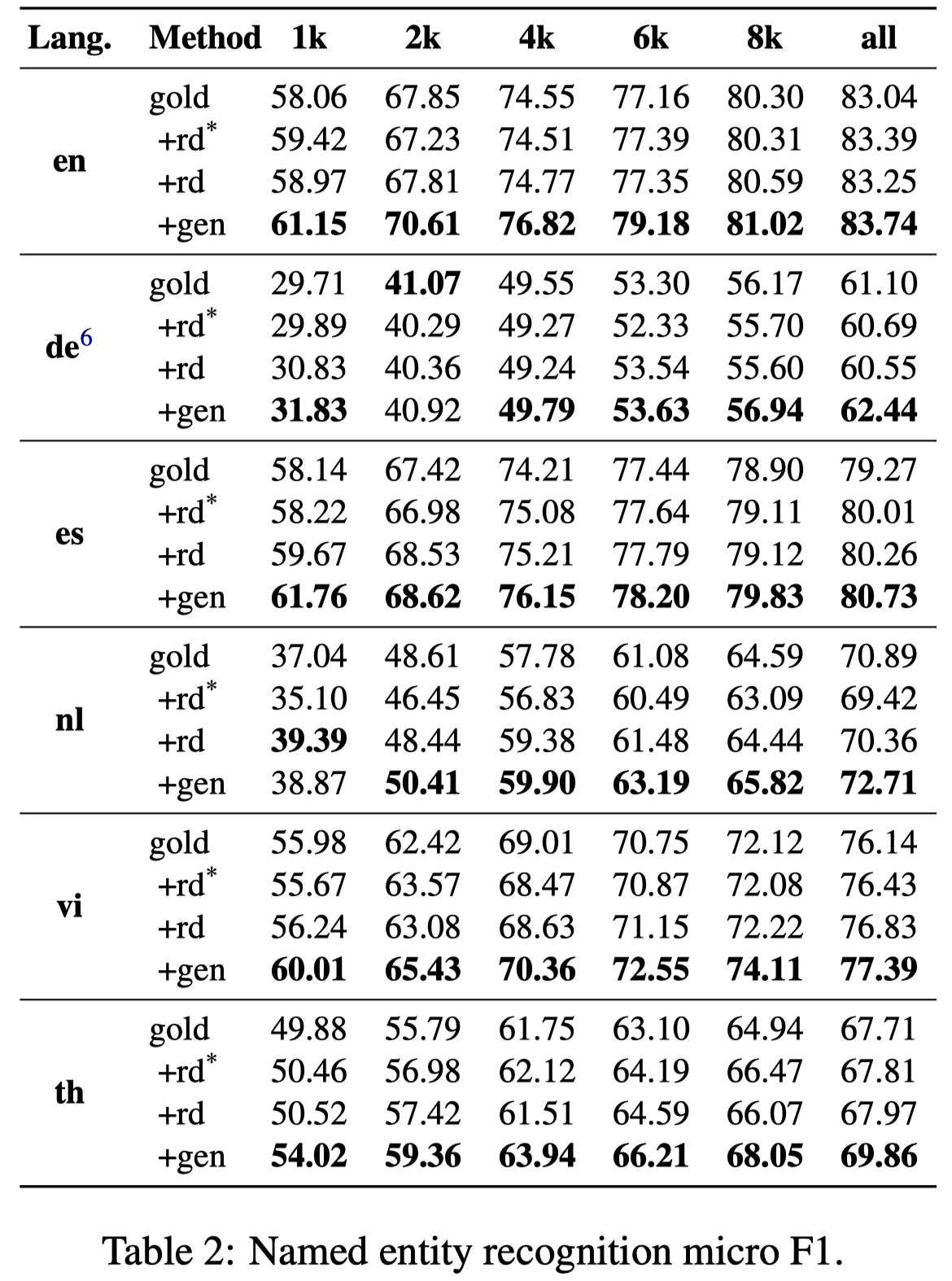
在CoNLL2002/2003 NER数据集的多个语言子集(English, German, Dutch and Spanish)上进行验证:
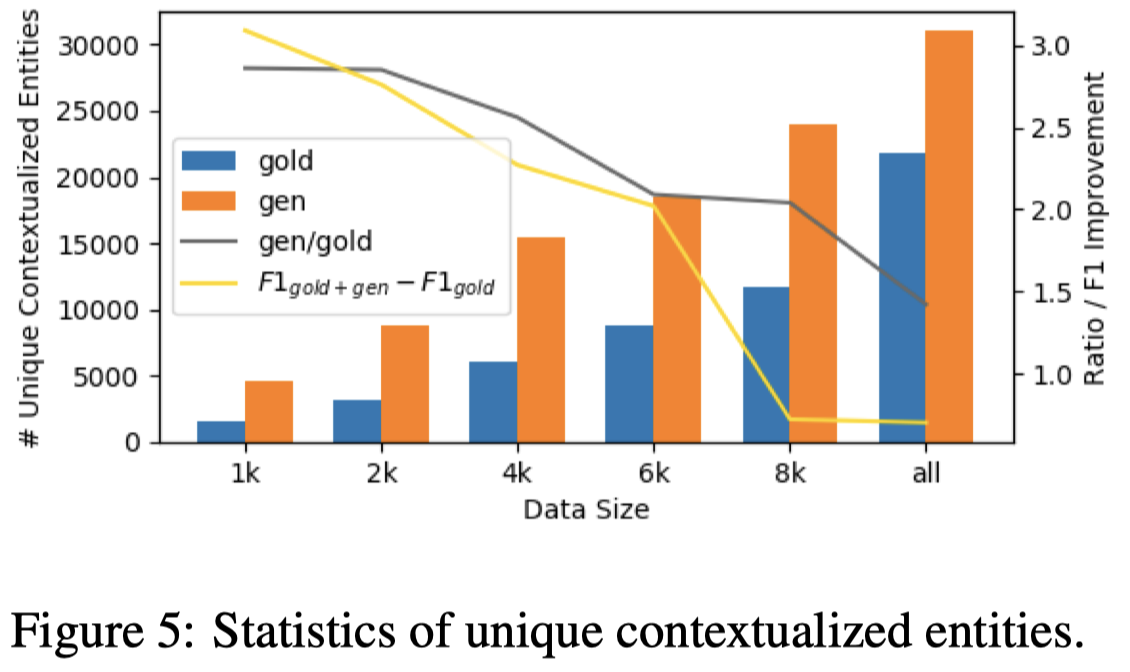
实验中有一个可以注意的是作者如何评估生成数据的多样性,一个是用entity出现的周围token作为上下文;计算unique上下文token数量;一个是统计unique entity的数量:
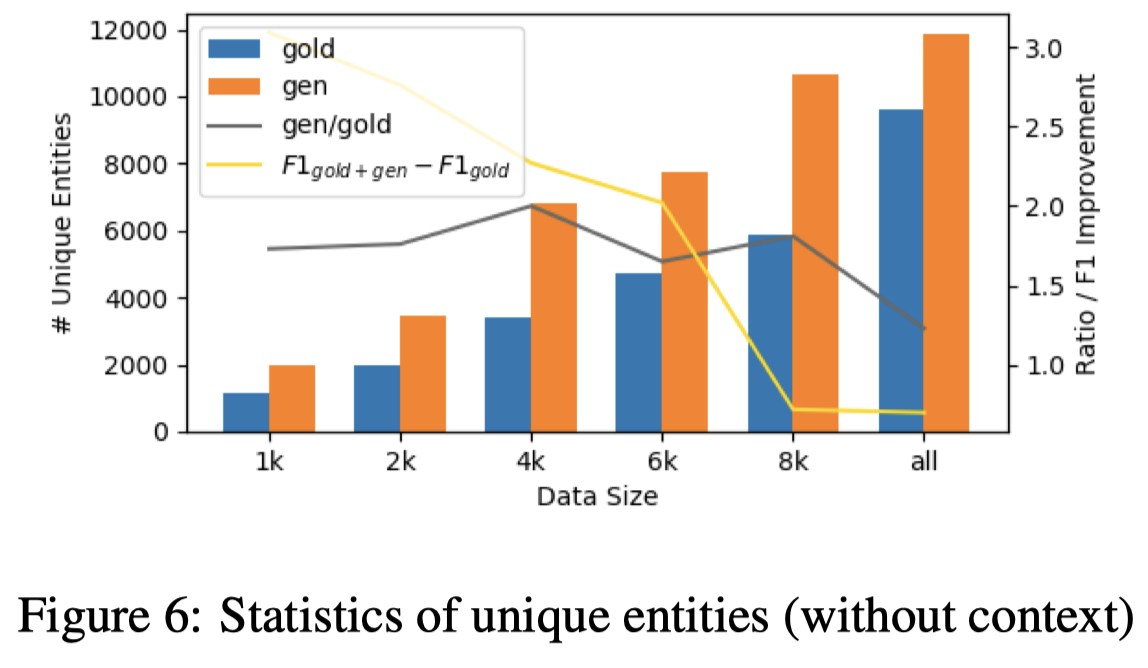
MELM
MELM: Data Augmentation with Masked Entity Language Modeling for Low-Resource NER
阿里达摩与南洋理工,ACL 2022,代码。
Data augmentation is an effective solution to data scarcity in low-resource scenarios. However, when applied to token-level tasks such as NER, data augmentation methods often suffer from token-label misalignment, which leads to unsatsifactory performance. In this work, we propose Masked Entity Language Modeling (MELM) as a novel data augmentation framework for low-resource NER. To alleviate the token-label misalignment issue, we explicitly inject NER labels into sentence context, and thus the fine-tuned MELM is able to predict masked entity tokens by explicitly conditioning on their labels. Thereby, MELM generates high-quality augmented data with novel entities, which provides rich entity regularity knowledge and boosts NER performance. When training data from multiple languages are available, we also integrate MELM with codemixing for further improvement. We demonstrate the effectiveness of MELM on monolingual, cross-lingual and multilingual NER across various low-resource levels. Experimental results show that our MELM presents substantial improvement over the baseline methods.
前人工作指出,增强上下文带来的提升比较少[A rigorous study on named entity recognition: Can fine-tuning pretrained model lead to the promised land? EMNLP 2020]。作者也发现,增强新entity多样性带来的效果要大于增强上下文patterns:
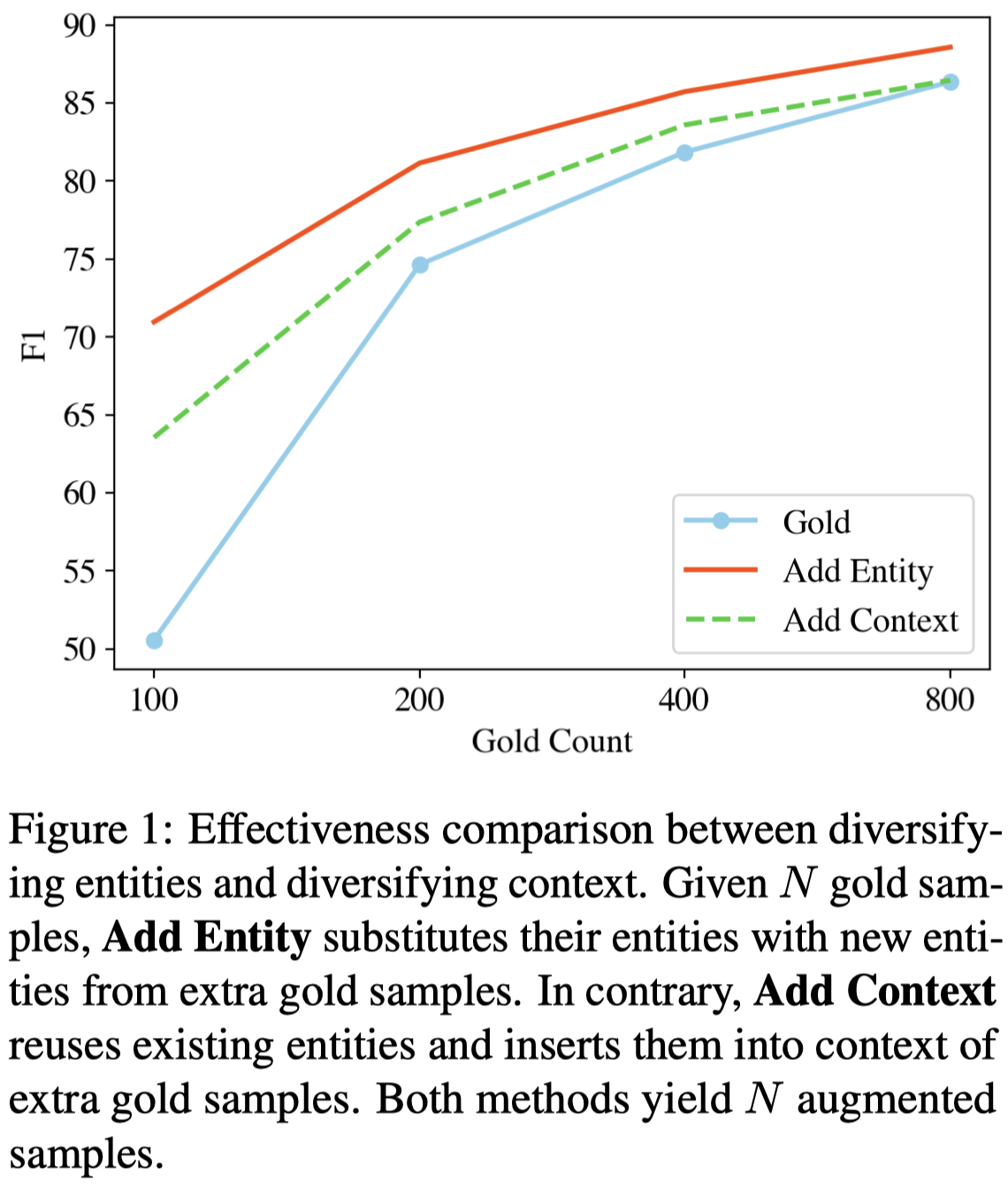
作者使用masked LM来给low-resource NER任务做数据增强。作者只会根据一定的概率mask entity的token。然后在mask data上fine-tuning pretrained MLM,让MLM学会根据context预测entity。
如果只是mask entity,然后让MLM预测,可能能够符合context,但是不一定符合原来的entity label。为了让生成的entity和原来的entity有相同的label,作者在原来的句子中插入entity type marker:
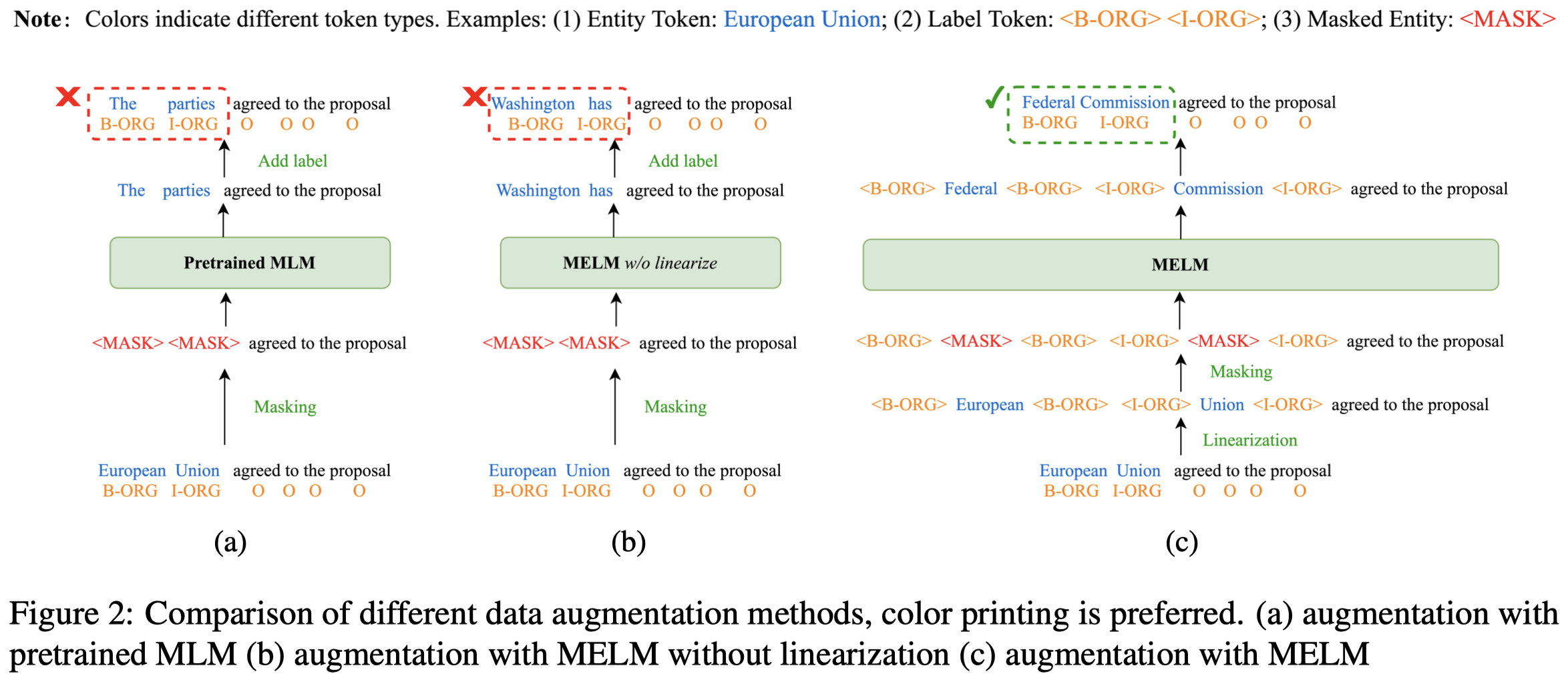
在进行数据生成的时候,输入masked sentence,为了增强生成数据的多样性。没有使用greedy decoding策略,而是在top-K的候选项上进行随机选择。
同时在生成的时候,采用了新的mask策略。每一次生成都有不同的mask阈值,这样进一步增大了mask结果的差异。
生成的数据需要经过处理以减低噪音,作者用一个训练好的NER模型,去处理增强的句子;只有NER model的标注和生成句子原来的entity label标注一致,才会被保留。
最后,作者在这篇论文中着重考虑多语言场景,引入code-mixing技术。随机从某个其它语言中,选择有相同label的entity作为候选项,之后选择在embedding space上余弦相似度的外语entity替换原来language entity(使用MUSE作为编码方法)。并且在替换后的entity前加入language tag表示替换后的entity原来的语言是什么。
增强的数据比例是3倍。作者实现中使用的LM是XLM-RoBERTa-base,使用的NER model是XLM-RoBERTa-Large+CRF。
在CoNLL 2002/2003数据集的不同语言子集上的实验结果:
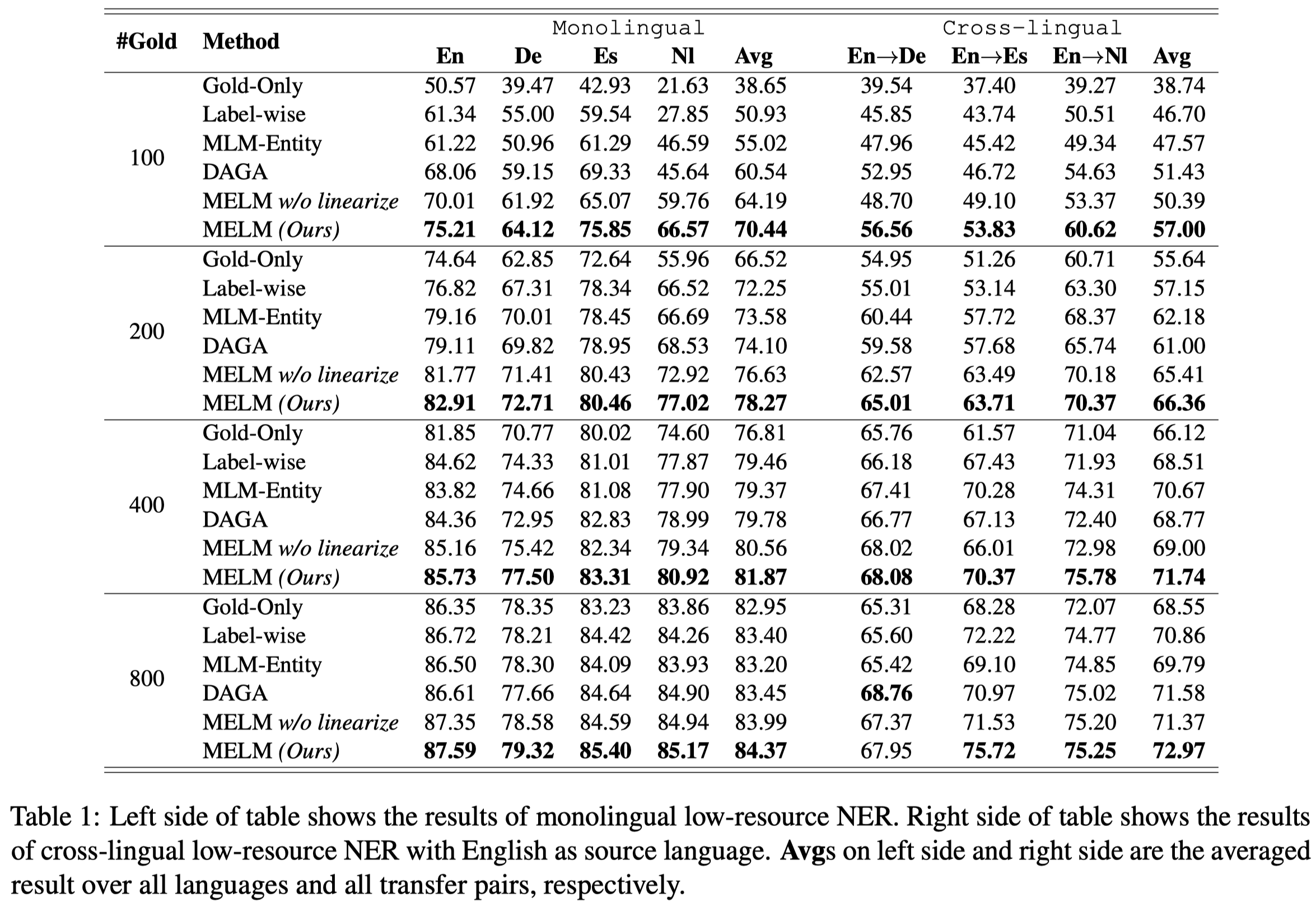
GPDA
Improving Low-resource Named Entity Recognition with Graph Propagated Data Augmentation
ACL 2023 short paper,上海科技与阿里达摩,代码。
Data augmentation is an effective solution to improve model performance and robustness for low-resource named entity recognition (NER). However, synthetic data often suffer from poor diversity, which leads to performance limitations. In this paper, we propose a novel Graph Propagated Data Augmentation (GPDA) framework for Named Entity Recognition (NER), leveraging graph propagation to build relationships between labeled data and unlabeled natural texts. By projecting the annotations from the labeled text to the unlabeled text, the unlabeled texts are partially labeled, which has more diversity rather than synthetic annotated data. To strengthen the propagation precision, a simple search engine built on Wikipedia is utilized to fetch related texts of labeled data and to propagate the entity labels to them in the light of the anchor links. Besides, we construct and perform experiments on a real-world lowresource dataset of the E-commerce domain, which will be publicly available to facilitate the low-resource NER research. Experimental results show that GPDA presents substantial improvements over previous data augmentation methods on multiple low-resource NER datasets.
data augmentation对于sentence-level NLP task两大思路:
- One is manipulating a few words in the original sentence, which can be based on synonym replacement (Zhang et al., 2015; Kobayashi, 2018; Wu et al., 2019; Wei and Zou, 2019), random insertion or deletion (Wei and Zou, 2019), random swap (¸Sahin and Steedman, 2018; Wei and Zou, 2019; Min et al., 2020). 修改原有句子的部分表述,获得新data。
- The other is generating the whole sentence with the help of back-translation (Yu et al., 2018; Dong et al., 2017; Iyyer et al., 2018), sequence to sequence models (Kurata et al., 2016; Hou et al., 2018) or pre-trained language models (Kumar et al., 2020). 构造完全新的data。
作者认为之前的 Data Augmentation会使用人造的数据,这可能inevitably introduces incoherence, semantic errors and lacking in diversity.
因此作者提出要直接使用已有的natural text作为辅助数据增强的来源。
方法:
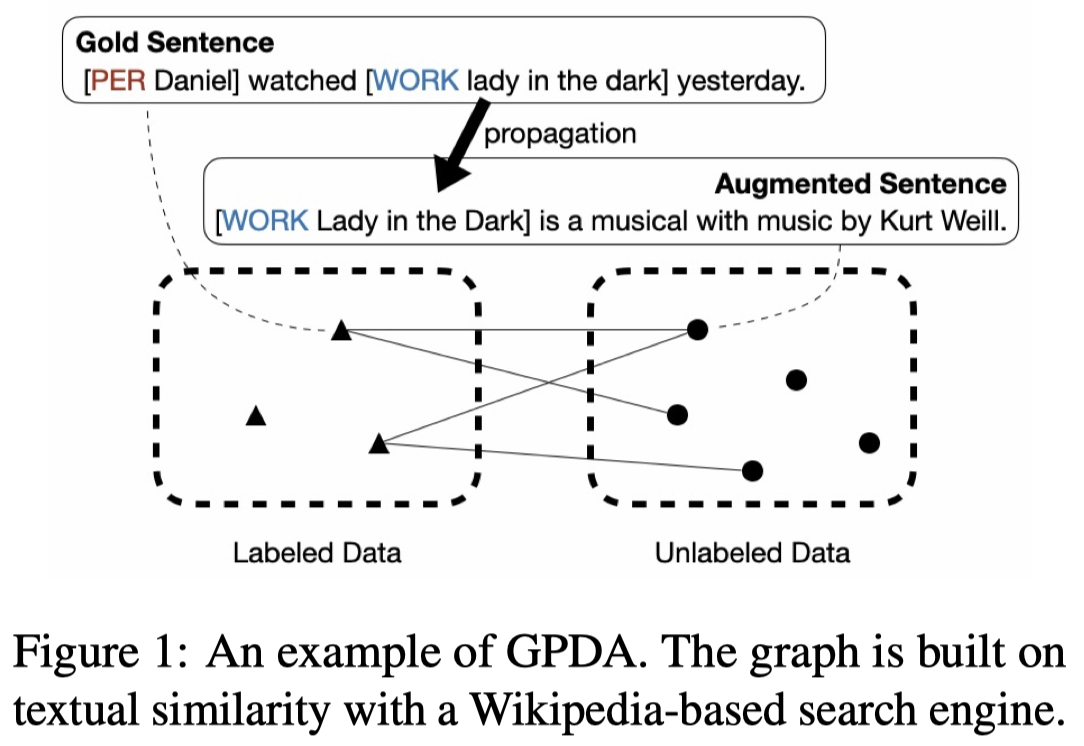
步骤:
- 从外部源如Wikipedia corpus中,通过BM25 sparse retrieval或者L2 dense retrieval的方法检索和句子相似的sentence
- 然后进行label propagation,在Wikipedia中带有链接的anchor text如果和有label的entity是完全匹配的,就赋值给anchor text对应的label。(但是完全一样text的entity就是相同的entity吗?)使用这样的新标注的数据和原有的有标注数据训练一个NER model
- 使用训练好的NER model,重新标注一次外部的text,然后使用重新标注后的数据和原有的有标注数据训练一个更好的NER model(Explored Entity Annotations,EEA)
实验:
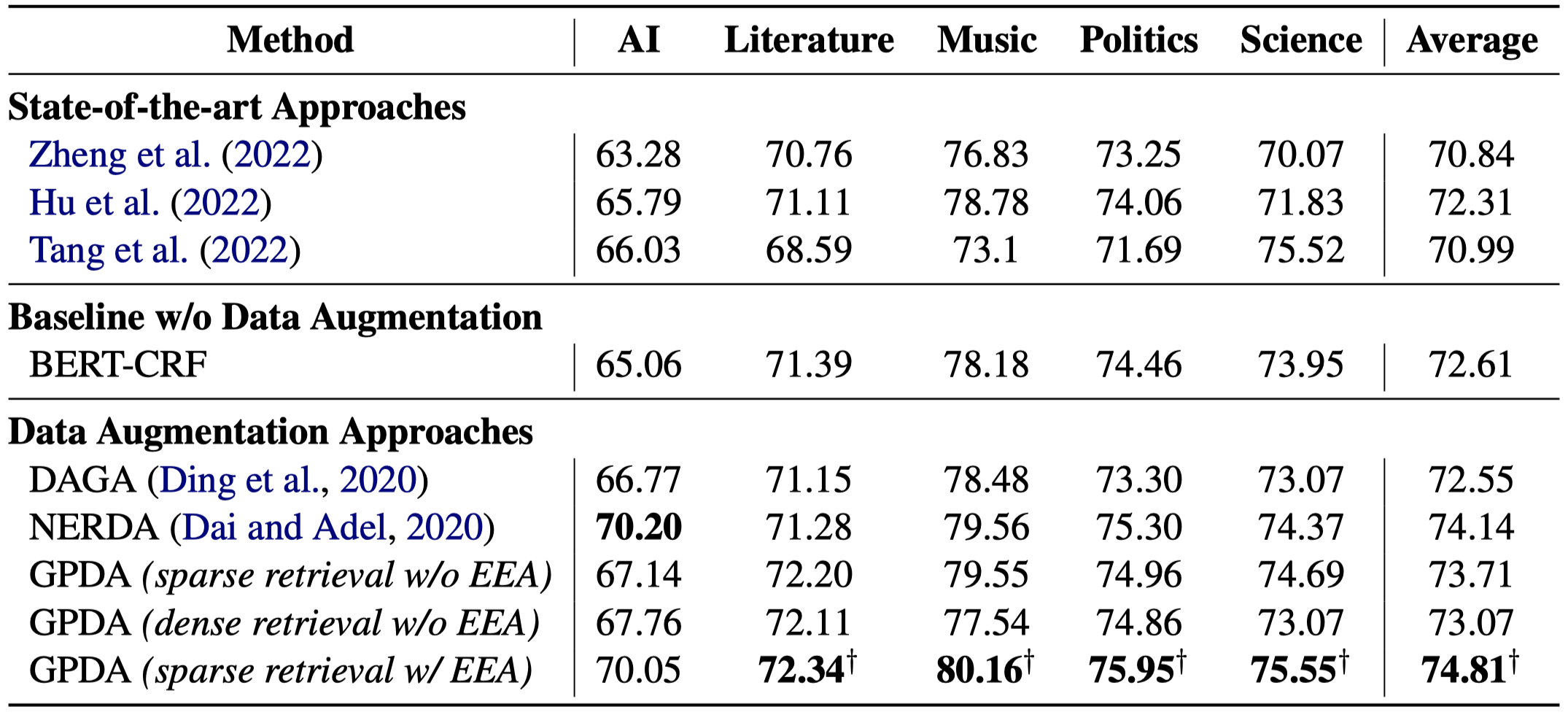

ENTDA
Entity-to-Text based Data Augmentation for various Named Entity Recognition Tasks
ACL 2023 Findings,清华与阿里达摩,[详细博客]
Data augmentation techniques have been used to alleviate the problem of scarce labeled data in various NER tasks (flat, nested, and discontinuous NER tasks). Existing augmentation techniques either manipulate the words in the original text that break the semantic coherence of the text, or exploit generative models that ignore preserving entities in the original text, which impedes the use of augmentation techniques on nested and discontinuous NER tasks. In this work, we propose a novel Entity-to-Text based data augmentation technique named ENTDA to add, delete, replace or swap entities in the entity list of the original texts, and adopt these augmented entity lists to generate semantically coherent and entity preserving texts for various NER tasks. Furthermore, we introduce a diversity beam search to increase the diversity during the text generation process. Experiments on thirteen NER datasets across three tasks (flat, nested, and discontinuous NER tasks) and two settings (full data and low resource settings) show that ENTDA could bring more performance improvements compared to the baseline augmentation techniques.
基于entity list生成对应的新data:
作者提出的方法:
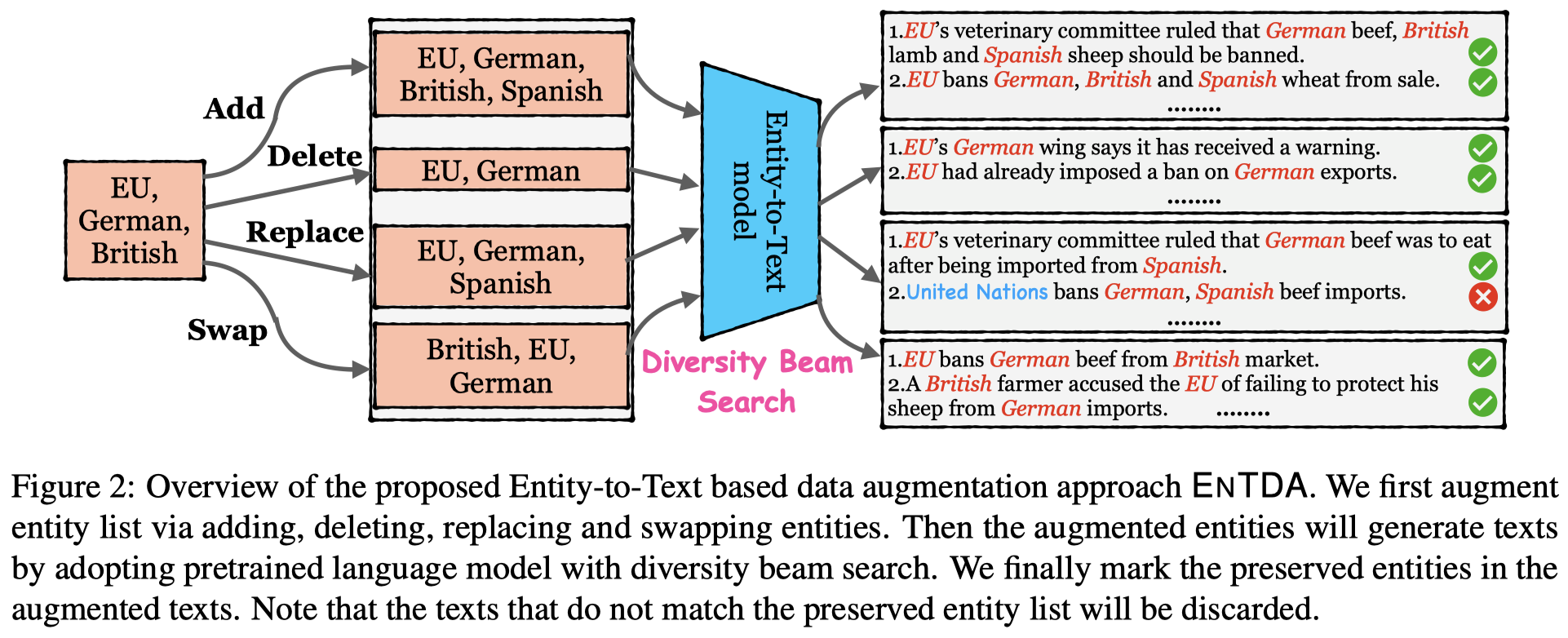
作者的生成data思路是根据entity list,让language model来直接生成相应的句子。
然后,让language model基于entity list生成对应的句子。为了提升生成句子的多样性diversity,作者提出了一种diversity beam search decoding策略:
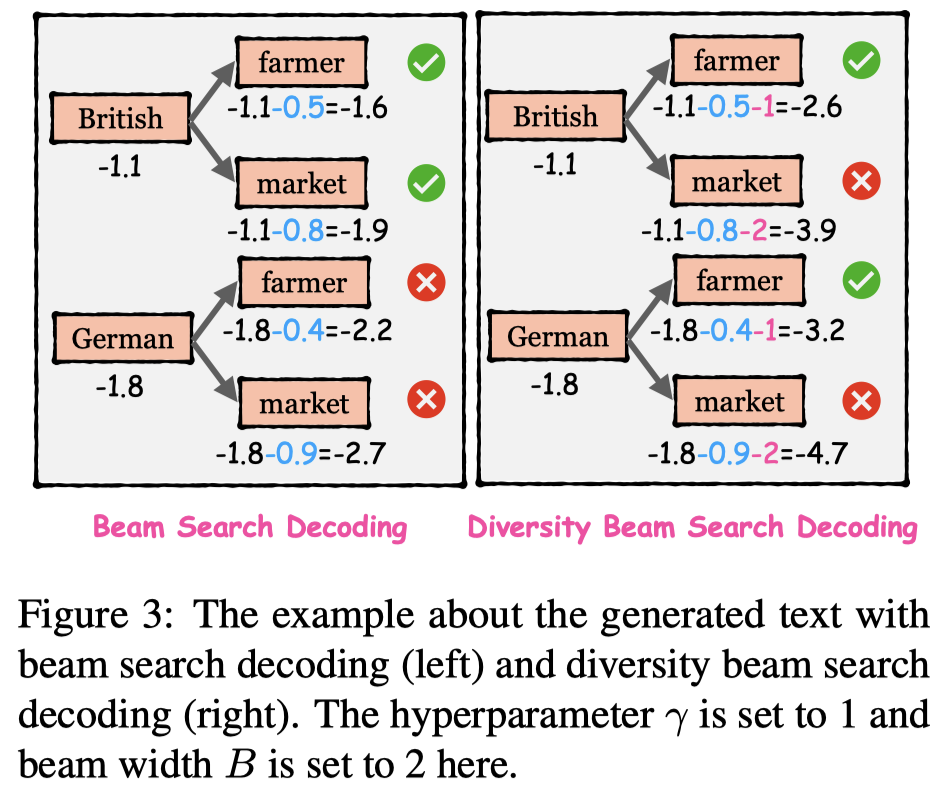
作者在flat, nested, and discontinuous NER tasks都进行了实验。在full data的情况下,提升不太大,但是在低资源的情况下提升很多。we randomly choose 10% training data from CoNLL2003/ACE2005/CADEC:
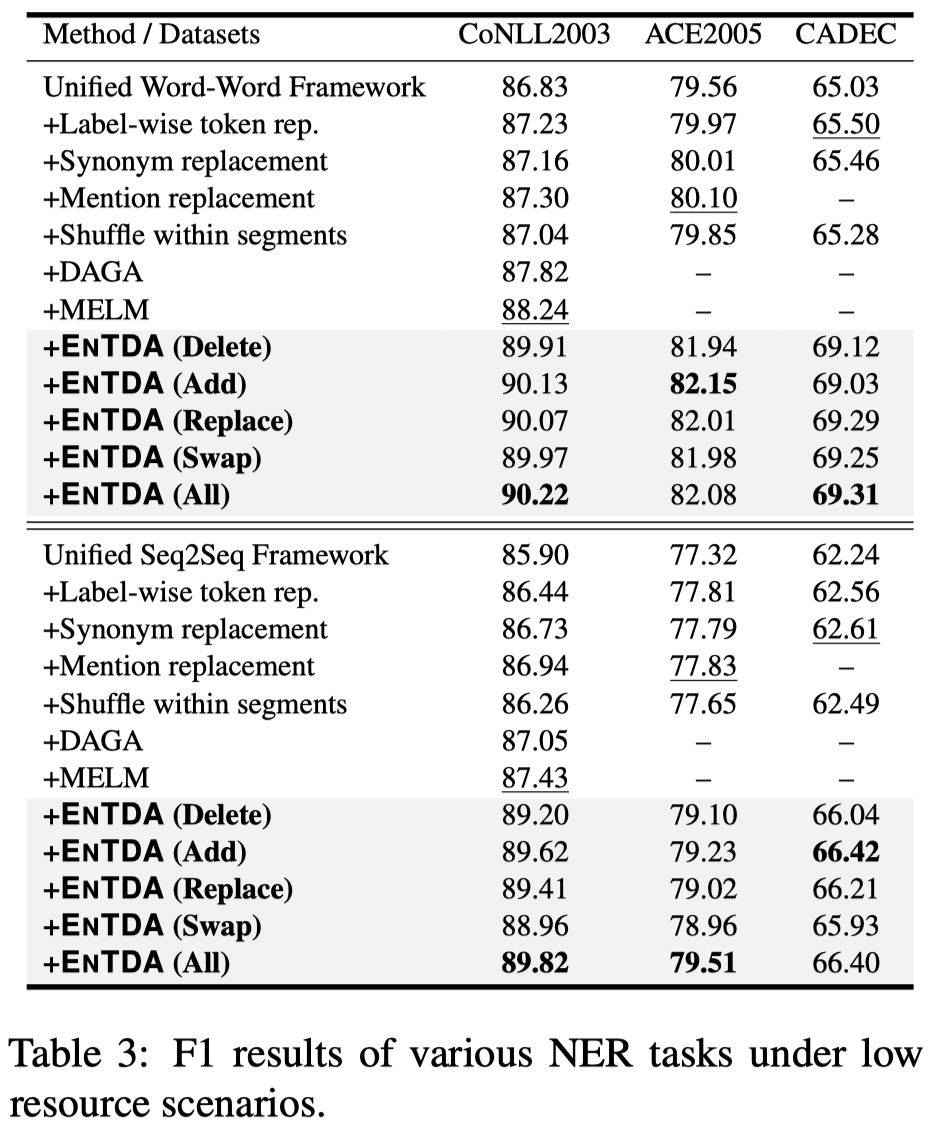
低资源的情况下,效果提升明显,有\(2\)%的提升幅度。
在真实的低资源NER数据集CrossNER的表现:
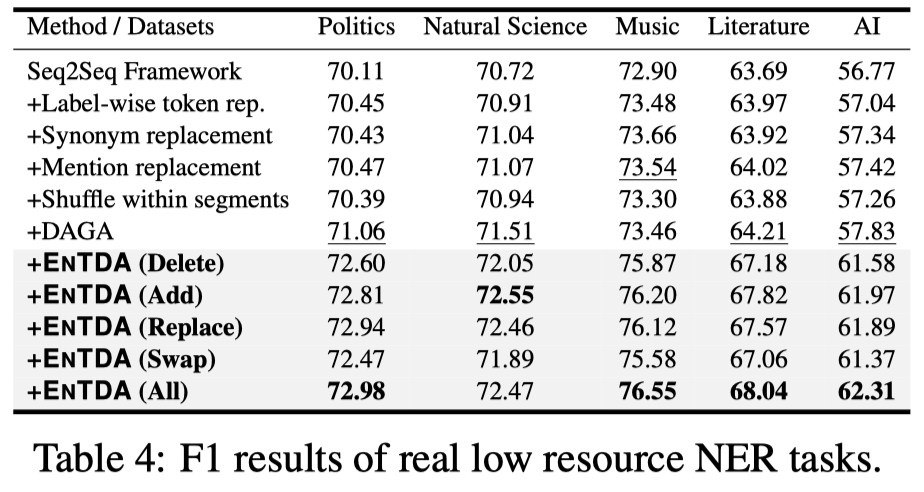
同样提升比较明显。
ACLM
ACLM: A Selective-Denoising based Generative Data Augmentation Approach for Low-Resource Complex NER
ACL 2023,University of Maryland,代码。
Complex Named Entity Recognition (NER) is the task of detecting linguistically complex named entities in low-context text. In this paper, we present ACLM (Attention-map aware keyword selection for Conditional Language Model fine-tuning), a novel data augmentation approach, based on conditional generation, to address the data scarcity problem in low-resource complex NER. ACLM alleviates the context-entity mismatch issue, a problem existing NER data augmentation techniques suffer from and often generates incoherent augmentations by placing complex named entities in the wrong context. ACLM builds on BART and is optimized on a novel text reconstruction or denoising task - we use selective masking (aided by attention maps) to retain the named entities and certain keywords in the input sentence that provide contextually relevant additional knowledge or hints about the named entities. Compared with other data augmentation strategies, ACLM can generate more diverse and coherent augmentations preserving the true word sense of complex entities in the sentence. We demonstrate the effectiveness of ACLM both qualitatively and quantitatively on monolingual, crosslingual, and multilingual complex NER across various low-resource settings. ACLM outperforms all our neural baselines by a significant margin (1%-36%). In addition, we demonstrate the application of ACLM to other domains that suffer from data scarcity (e.g., biomedical). In practice, ACLM generates more effective and factual augmentations for these domains than prior methods.
作者主要希望通过数据增强来解决complex NER任务:
complex NER benchmarks like MultiCoNER (Malmasi et al., 2022) present several contemporary challenges in NER, including short low-context texts with emerging and semantically ambiguous complex entities (e.g., movie names in online comments) that reduce the performance of SOTA methods previously evaluated only on the existing NER benchmark datasets.
作者认为之前SOTA的数据增强方法效果不好,因为对于complex NER任务来说,特定的entity要依赖于特定的context:
We first argue that certain types of complex NEs follow specific linguistic patterns and appear only in specific contexts (examples in Appendix 4), and augmentations that do not follow these patterns impede a NER model from learning such patterns effectively.
方法:
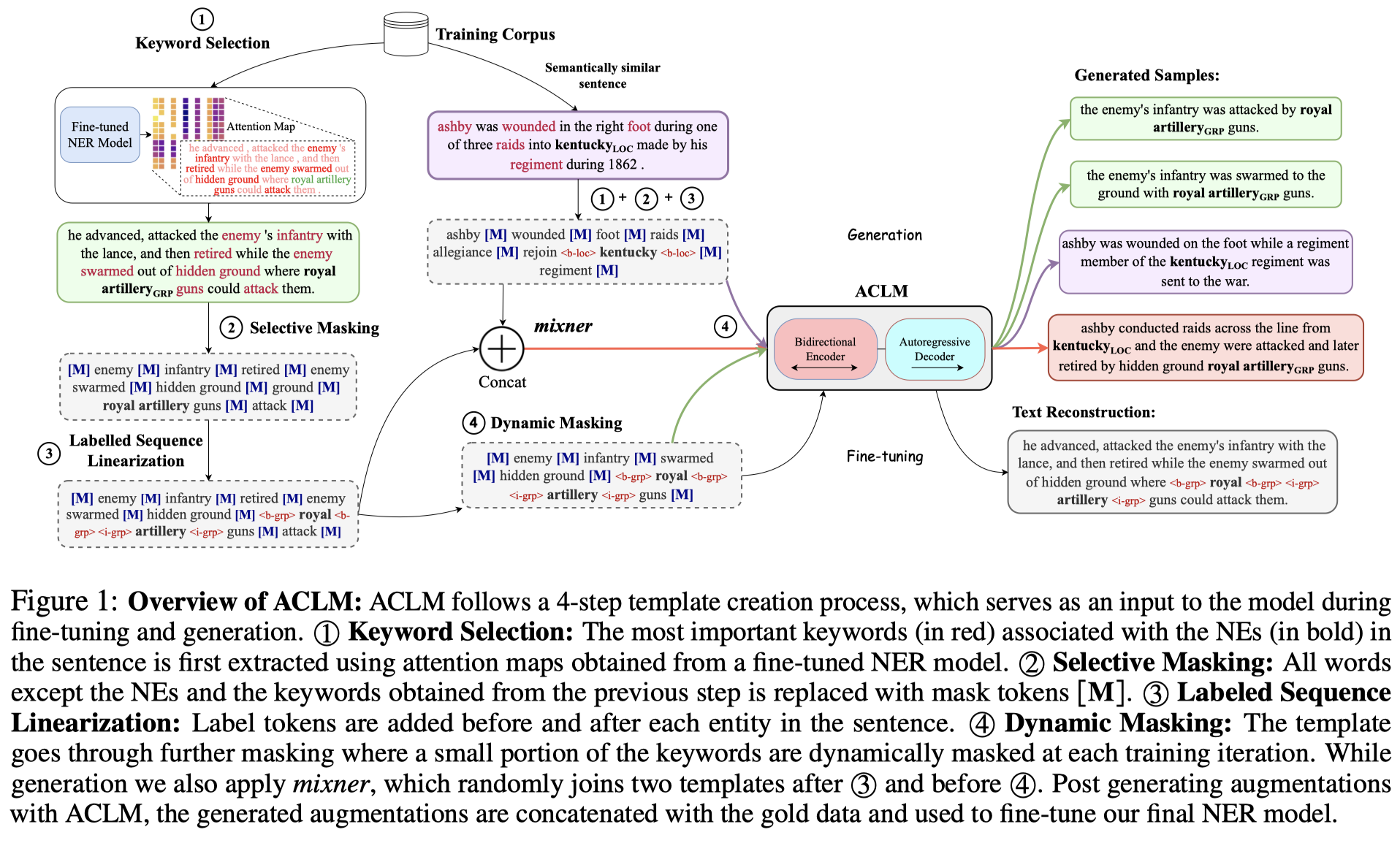
作者分为四步来获取corrupted sentence(paper里叫做template):
Keyword Selection:使用attention map寻找对entity最有意义的context tokens,然后将top-\(p\)%的context tokens用看做是keywords。具体来说,使用XLM-RoBERTa-large进行在训练集上进行训练,然后使用它最后4层所有Transformer attention head的注意力权重作为选择依据。
低资源的情况下,attention map可能是比较noisy的,所有head相加比较robust
BERT的低层更加关注其它token,而BERT的高层更加专注某个token
作者处理的entity可能有多个span或者1个span。对于1个span,每个token的attention score相加。对于有多个span的entity,每个span分别计算attention score获取重要tokens
Selective Masking:对于非entity和非重要keywords的其它tokens,用\([MASK]\) token进行替换。mask后的句子作为template。
Labeled Sequence Linearization:模仿MELM在entity token前后插入
<tag>。Dynamic Masking:动态的选择一部分keywords的token也进行替换,增加多样性
根据上面获取的corrupted sentence,微调mBart-50-large,让其重建原来的句子。
在进行数据生成的时候,对于每个sentence,创建\(R\)个corrupt text,生成\(R\)个augmented training samples(实现中\(R=5\))。
为了进一步增加多样性,作者在数据生成阶段,提出了一个mixer方法,根据一定的概率选择另外一个语义相似的句子生成的template进行拼接,然后生成新的句子:
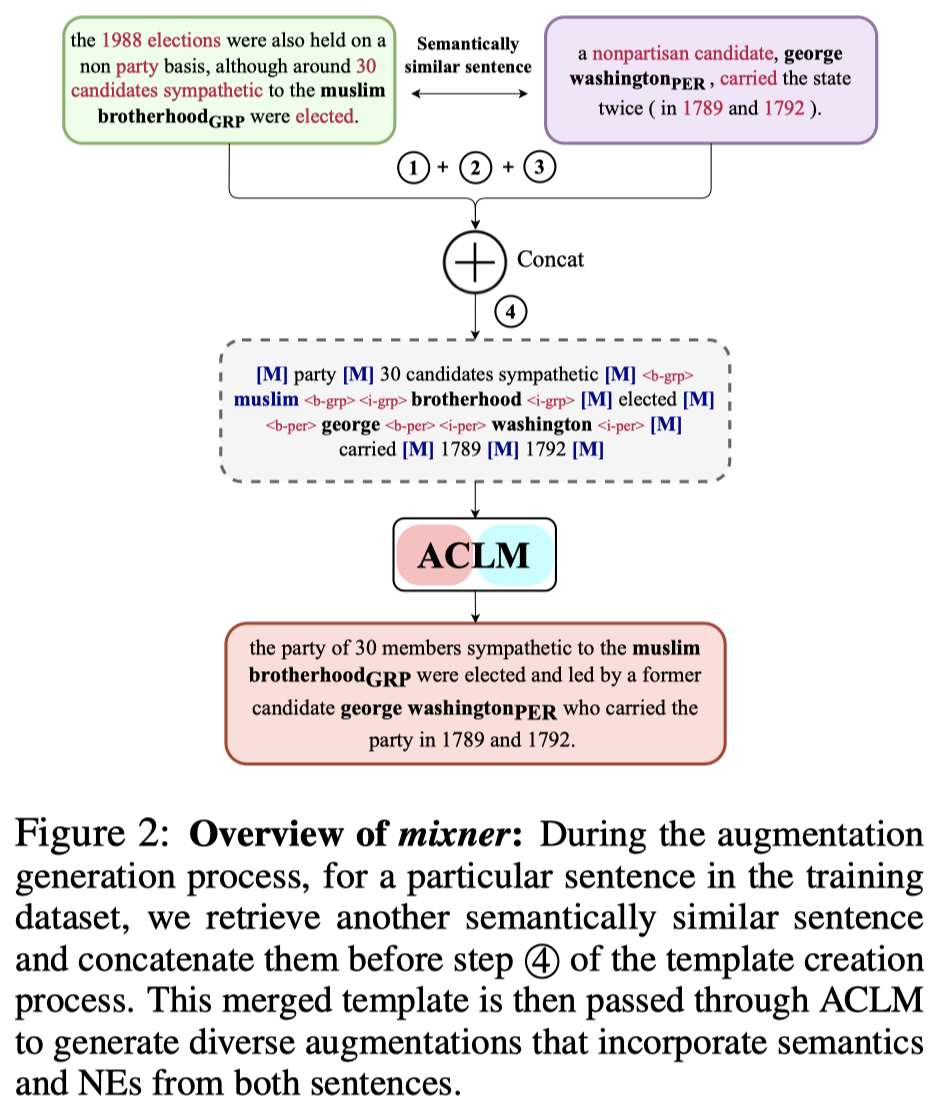
实现中基于multi-lingual Sentence-BERT的embedding计算不同句子之间的余弦相似度。
最后对生成的数据进行后处理,对与和原sentence非常相似的生成sentence等数据,进行移除。
作者在MultiCoNER上的实验结果:
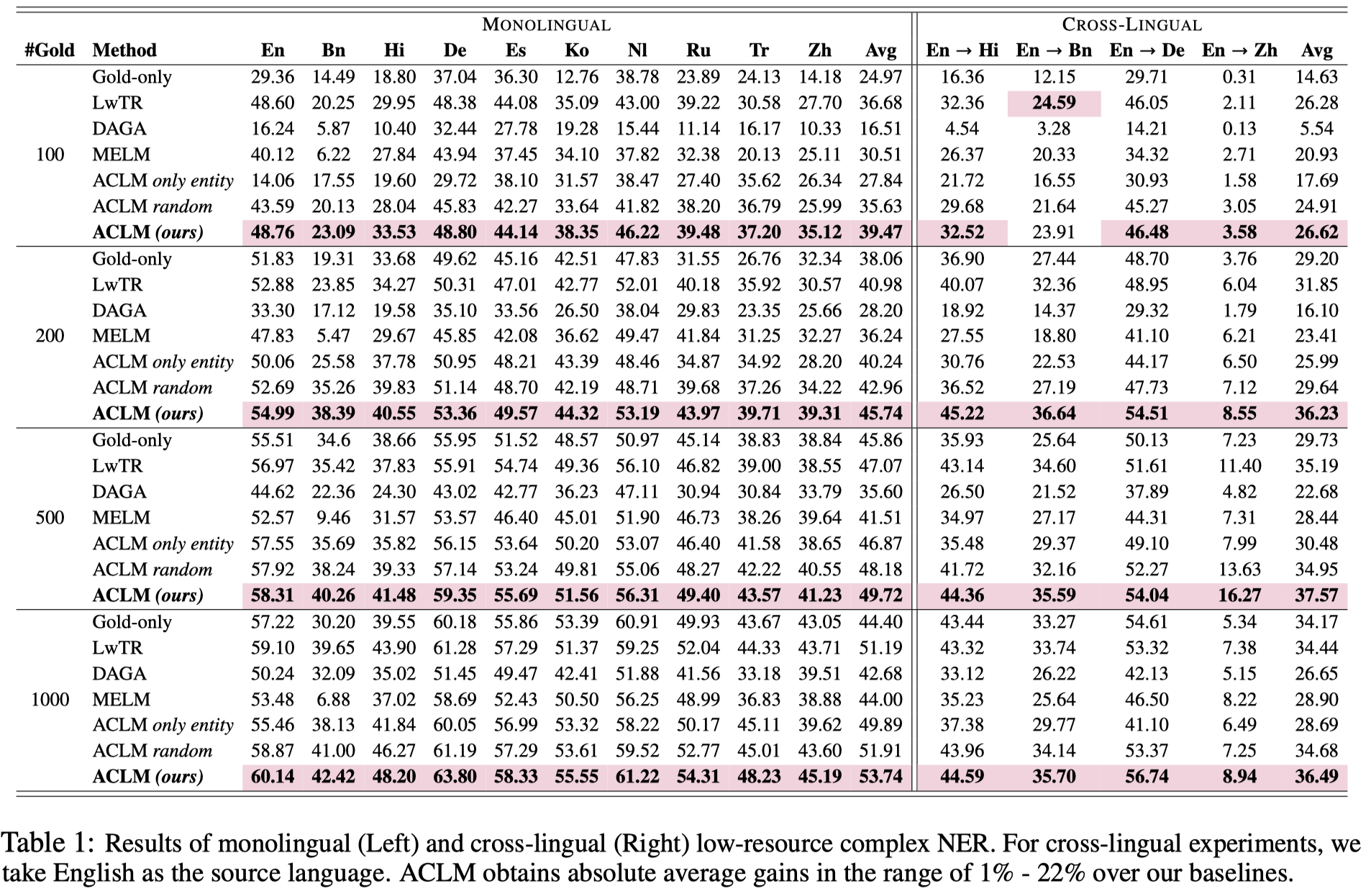
在其它NER数据集(CoNLL 2003 (Tjong Kim Sang and De Meulder, 2003) (news), BC2GM (Smith et al., 2008) (bio-medical), NCBI Disease (Do˘gan et al., 2014) (bio-medical) and TDMSci (Hou et al., 2021) (science))上的结果:
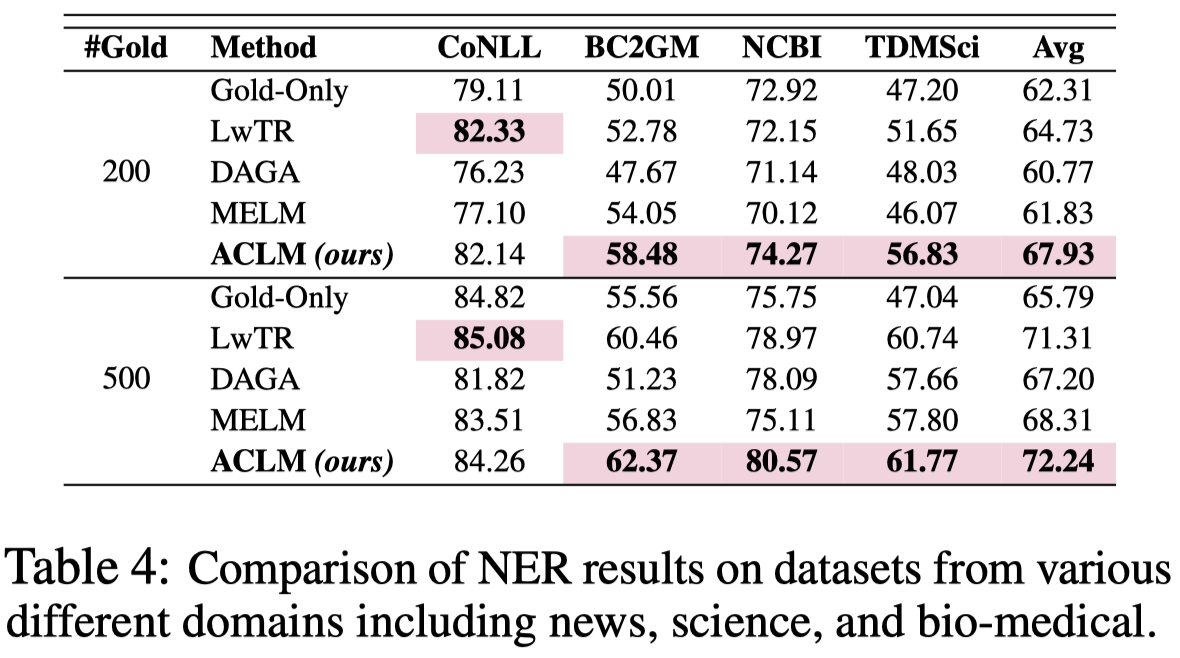
这个实验解释了一个重要的结论,在CoNLL2003这种entity和明确的数据集上,LwTR(替换相同entity type的其它entity)这种rule-based的方法反而取得了最好的结果。
对于生成数据的定量评估:
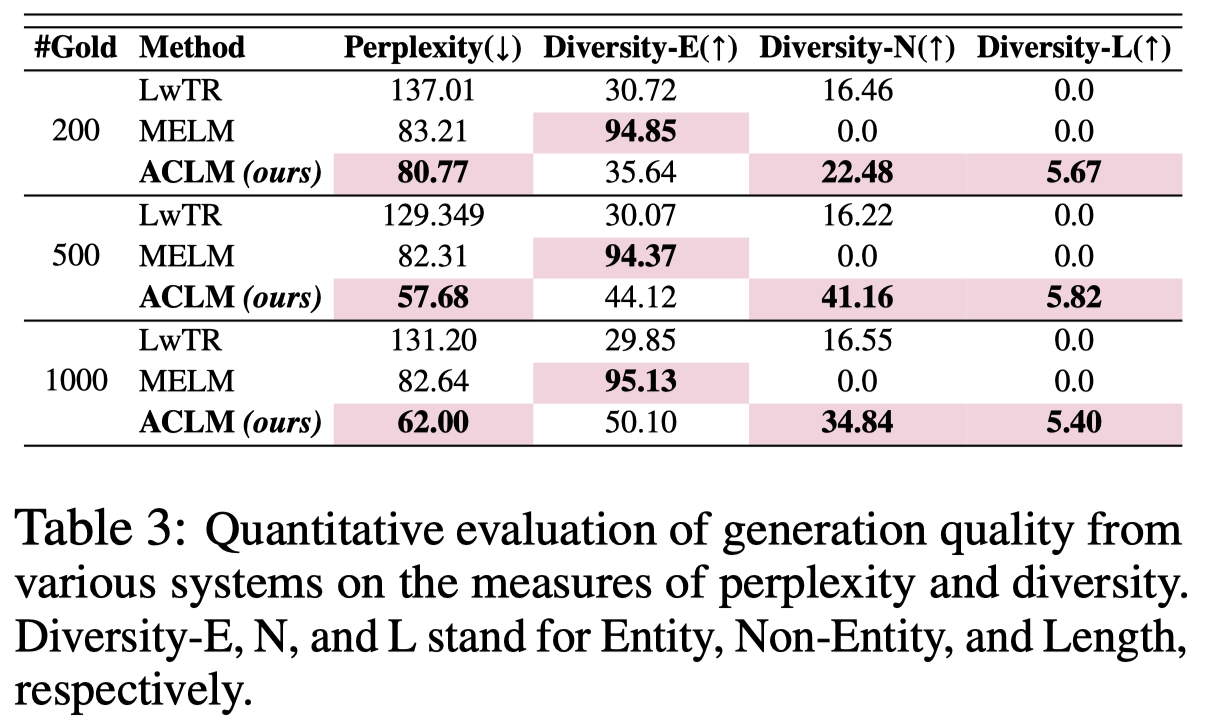
其中,Diversity-E指生成sentence中新出现的实体,Diversity-N指新出现的非entity的tokens,Diversity-L指新生成的句子长度与原来句子的比值。ACLM更擅长引入更多新的context tokens。
GDA
GDA: Generative Data Augmentation Techniques for Relation Extraction Tasks
ACL 2023 Findings,清华与浙大,代码。
Relation extraction (RE) tasks show promising performance in extracting relations from two entities mentioned in sentences, given sufficient annotations available during training. Such annotations would be labor-intensive to obtain in practice. Existing work adopts data augmentation techniques to generate pseudo-annotated sentences beyond limited annotations. These techniques neither preserve the semantic consistency of the original sentences when rule-based augmentations are adopted, nor preserve the syntax structure of sentences when expressing relations using seq2seq models, resulting in less diverse augmentations. In this work, we propose a dedicated augmentation technique for relational texts, named GDA, which uses two complementary modules to preserve both semantic consistency and syntax structures. We adopt a generative formulation and design a multi-tasking solution to achieve synergies. Furthermore, GDA adopts entity hints as the prior knowledge of the generative model to augment diverse sentences. Experimental results in three datasets under a low-resource setting showed that GDA could bring 2.0% F1 improvements compared with no augmentation technique. Source code and data are available.
Issue: 之前方法存在的问题:
- 之前的rule-based techniques的数据增强方法不能够保证构造出来的句子和原来的句子是语义一致的,并且由于忽略了语法结构还有可能扭曲原来的语义
- model-based techniques能够保持语义一致性 [Data augmentation in natural language processing: a novel text generation approach for long and short text classifiers. 2022],但是不能够生成多样性的表达。the model generates less diverse sentences – it includes similar entities and identical relational expressions under the same relation.
生成的数据既需要多样性,又需要和原来句子的语义一致性。
作者基于多任务学习提出的数据增强方法:
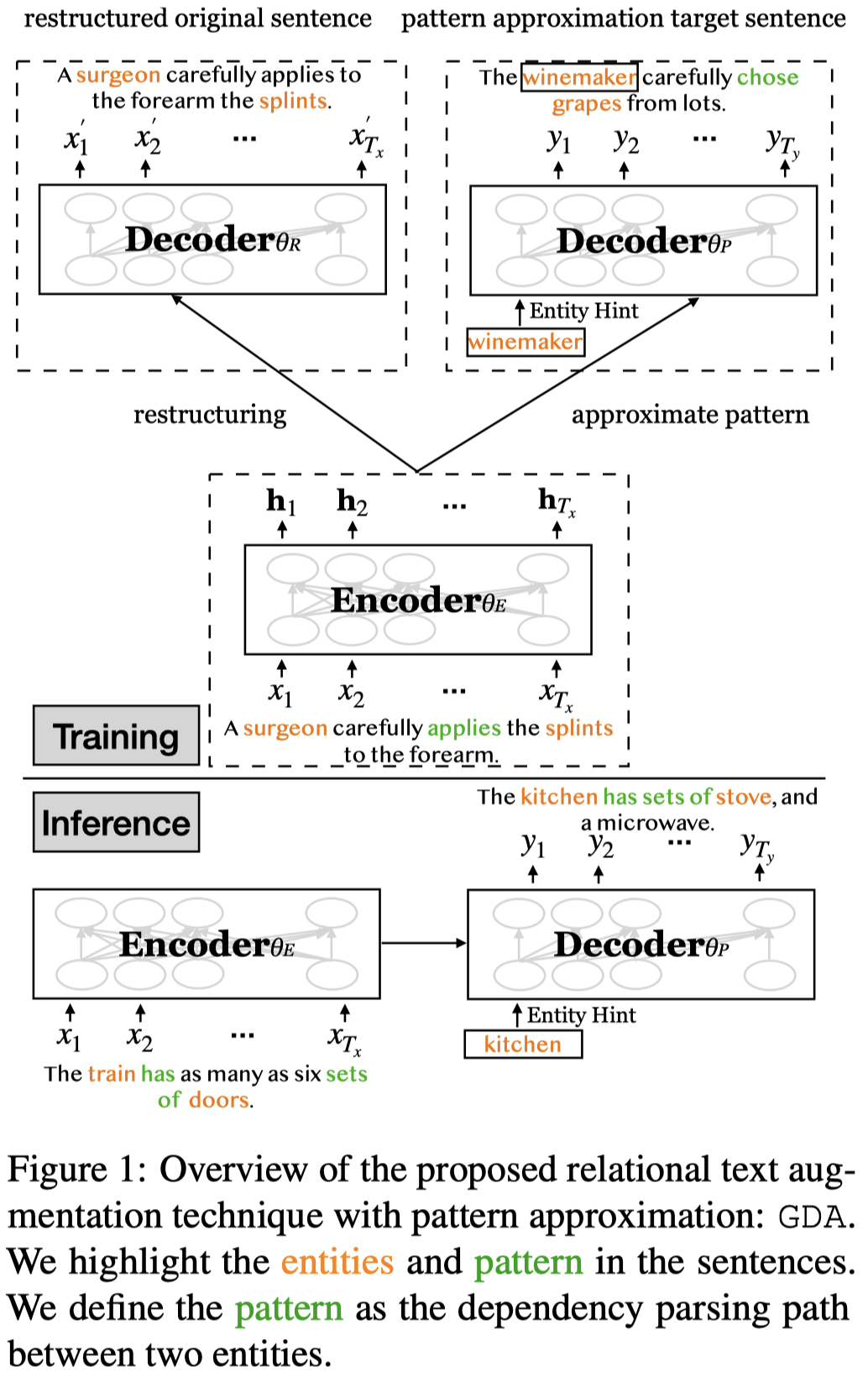
基于BART或T5这样的encoder+decoder结构,有两个decoder:
Original sentence restructuring. 左侧的decoder,重建原来的sentence,让模型学会产生和原来句子语义一致的句子:

Original sentence pattern approximation. 右侧的decoder用来生成新的sentence。由于归纳偏执,seq2seq decoder总是会倾向高频率出现的pattern,就失去生成数据的多样性。因此作者限制生成的新句子的pattern和原来的句子一致。具体做法是使用两个entity之间的语法路径作为relation pattern,生成句子的relation pattern和原来句子的relation pattern要接近:

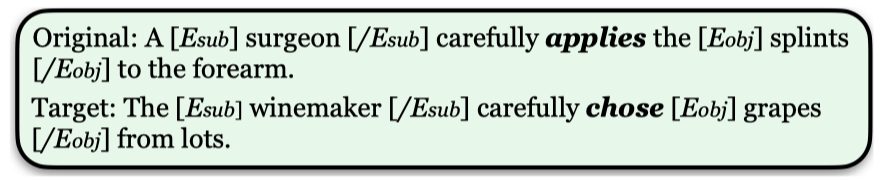
另外,为了进一步控制输出句子。作者会从数据集中同属于一个relation的样例中选择entity,输入解码器,让模型输出带有entity的句子。
训练的时候,先训练编码器和restructuring decoder;然后使用restructuring decoder的参数初始化pattern approximation decoder参数,和编码器一起训练;pattern approximation decoder参数继续用来初始化restructuring decoder。
两个decoder分别独立迭代优化;encoder一直进行优化。
实验结果:
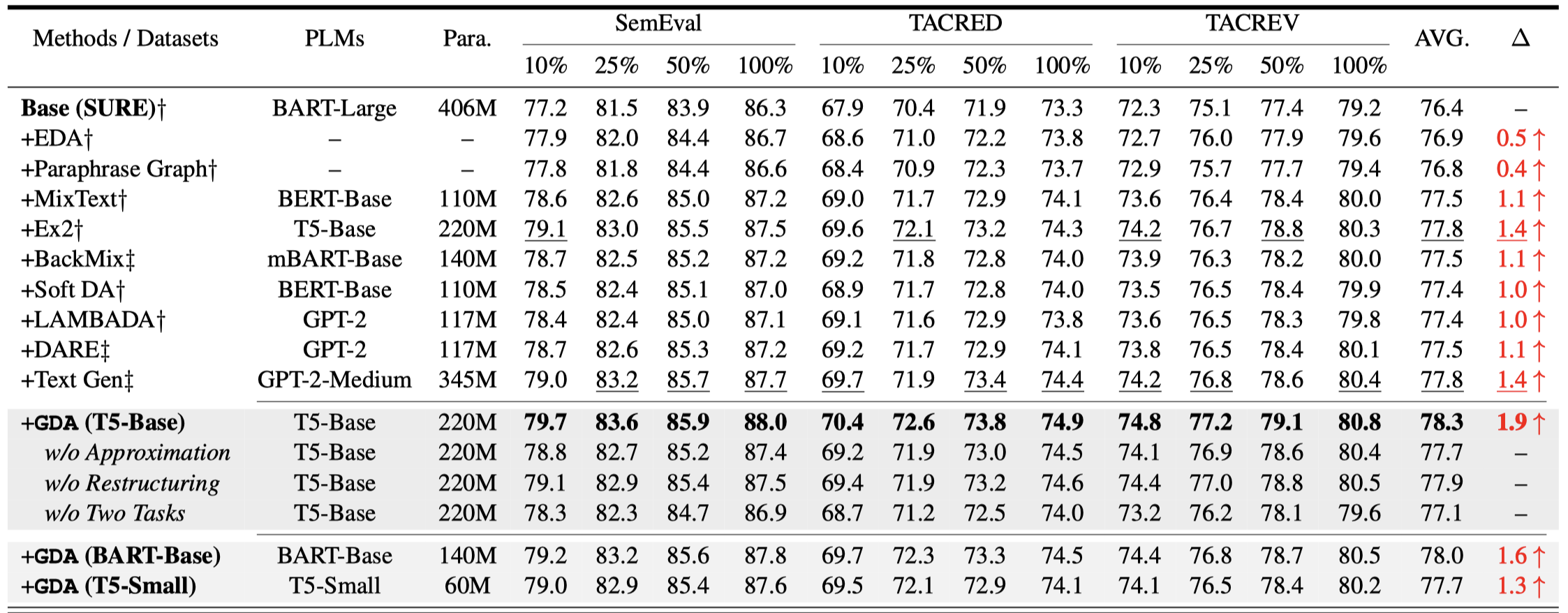
可以看到,利用作者的数据增强方法生成的数据来训练,能够有效提升Base model的效果。
不断增加数据增强数量:
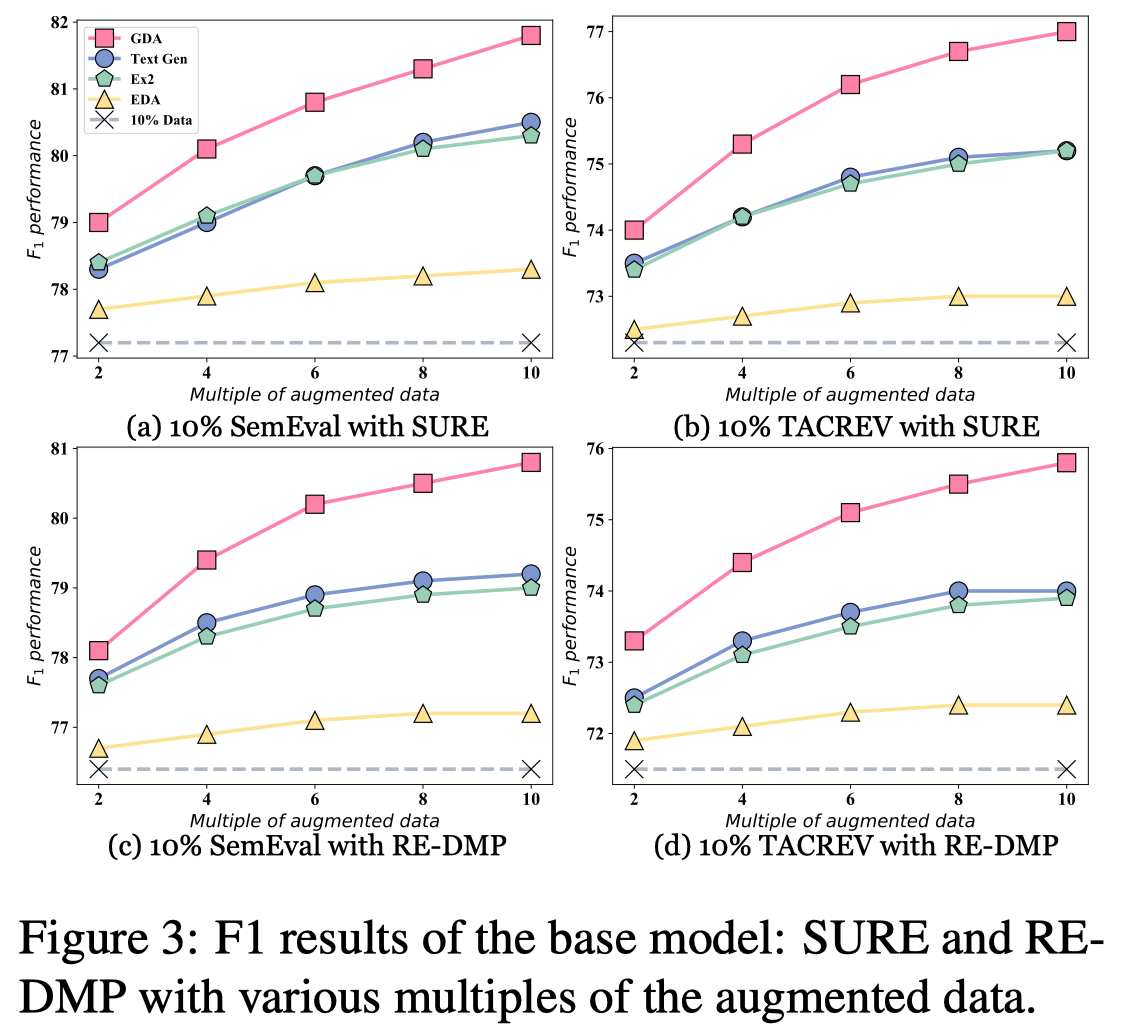
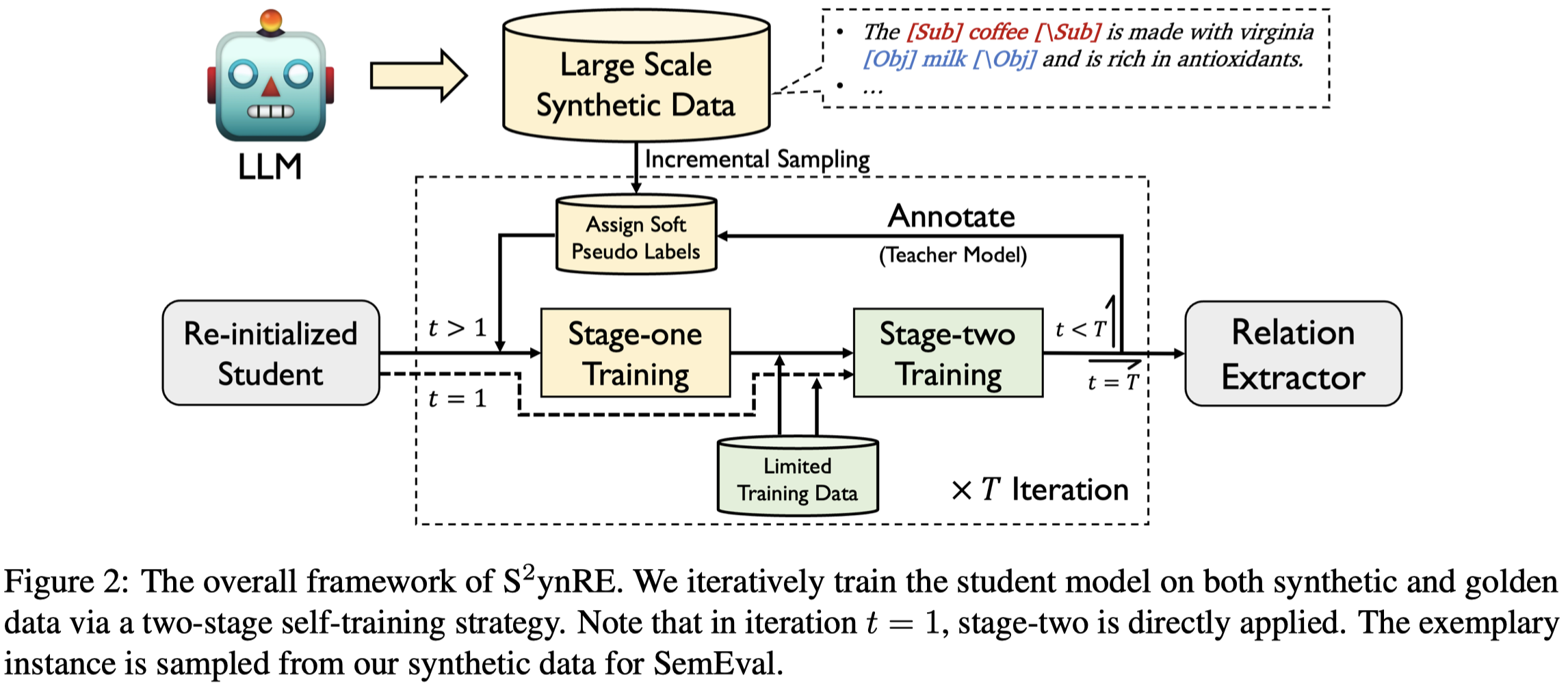
\(\mbox{S}^2\)ynRE
S2ynRE: Two-stage Self-training with Synthetic data for Low-resource Relation Extraction
中科大,ACL 2023,代码。
Current relation extraction methods suffer from the inadequacy of large-scale annotated data. While distant supervision alleviates the problem of data quantities, there still exists domain disparity in data qualities due to its reliance on domain-restrained knowledge bases. In this work, we propose S2ynRE, a framework of two-stage Self-training with Synthetic data for Relation Extraction. We first leverage the capability of large language models to adapt to the target domain and automatically synthesize large quantities of coherent, realistic training data. We then propose an accompanied two-stage self-training algorithm that iteratively and alternately learns from synthetic and golden data together. We conduct comprehensive experiments and detailed ablations on popular relation extraction datasets to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed framework. Code is available at https://github.com/BenfengXu/S2ynRE.
对于RE任务来说,高质量有标注的data获取很难,之前一种解决这个问题的思路是远监督distant supervision,尽管远监督获得了效果的提升,但是远监督的数据不能够保证和下游任务的schema、context分布特征等是相符的:
Although this line of methods have seen certain improvements, they still inevitably raise the concern that the distantly annotated data can vary considerably from downstream tasks both in target schema and in context distributions, thus may not be able to offer optimal transferability.
换句话说,要获得理想的领域特征一致的远监督数据本身也可能是比较难的。
因此,作者顺着最近的一些利用LLM生成text data的工作的思路,考虑使用LM来生成数据。作者的贡献主要有两点:
- 利用GPT-3.5和finetuned GPT-2 Large去适应target domain distribution,然后生成无label的RE data
- 提出了a two-stage self-training训练策略,更好的利用生成的无标注数据和原有标注数据
作者的RE任务是给定头尾实体,预测relation。
利用GPT-2 Large生成数据,首先按照language modeling的loss在训练集上微调;然后在推理阶段,输入<bos>开始进行采样生成new data。
利用GPT-3生成数据,采用5-shot ICL,随机找demonstrations的策略:
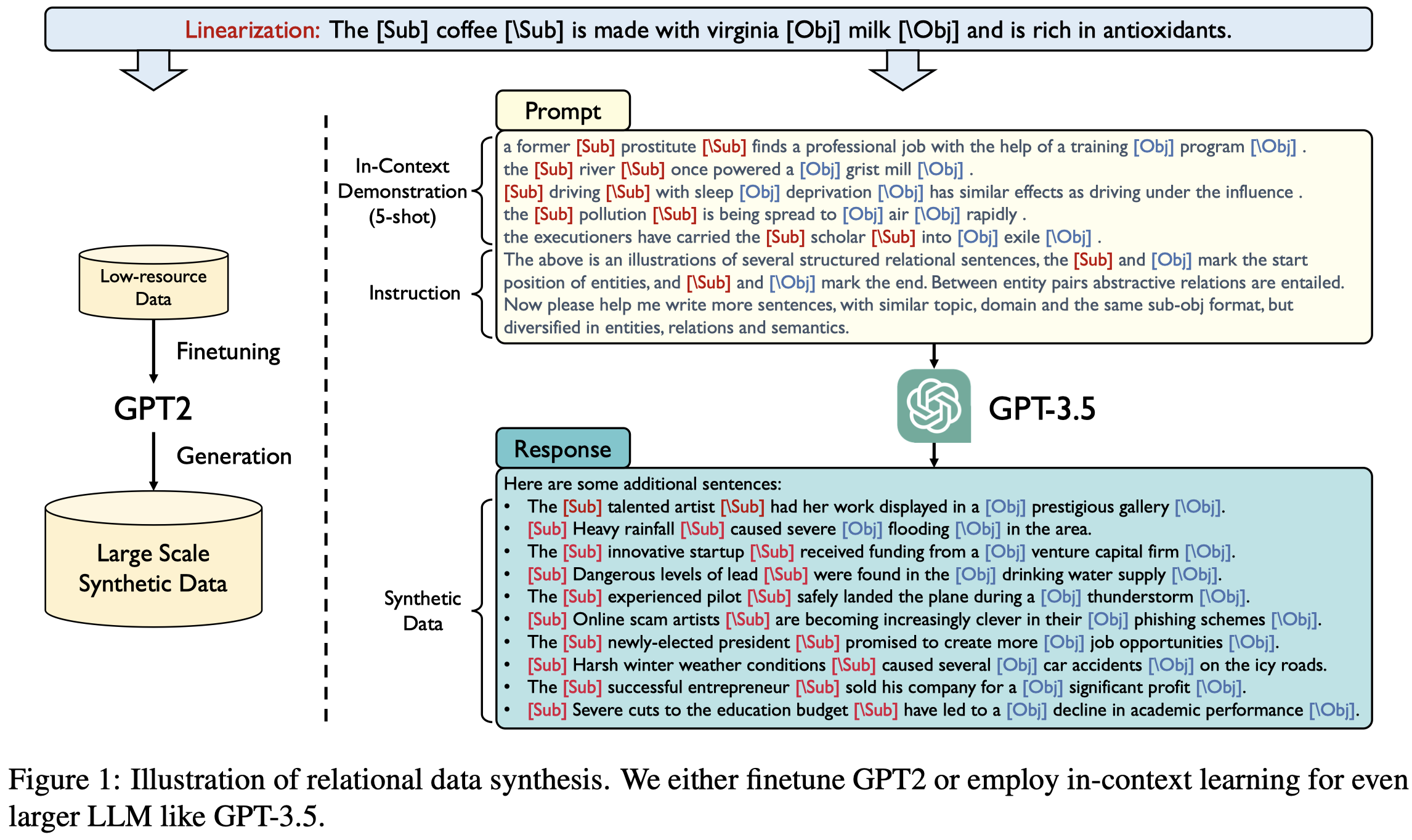
注意这里prompt对于结果的可控,只是通过一些指令性的表述,如similar topic, domain and the same sub-obj format。
然后是如何利用生成的无标注data,一般的策略是self-training,即给无标注data伪标注然后和原有data混合,训练小模型,训练好的小模型再重新标注无标注data。
作者认为这种直接将生成的数据加入到原有的数据方法前提是,要求生成的数据需要和原来的数据有一样的分布。
相反,作者将无标注数据和有标注数据分开,先使用gold data训练多个teacher model,然后标注生成的data,注意是soft label;然后用一个新初始化的student model在带有soft label的生成数据上训练,更新参数;之后继续在gold data上训练,更新后的model重新标注生成的data;这样迭代式的训练:
对于实验结果具体可以参考原paper,这里提供几个值得记录的结果:
作者使用BERT+Linear作为RE model。
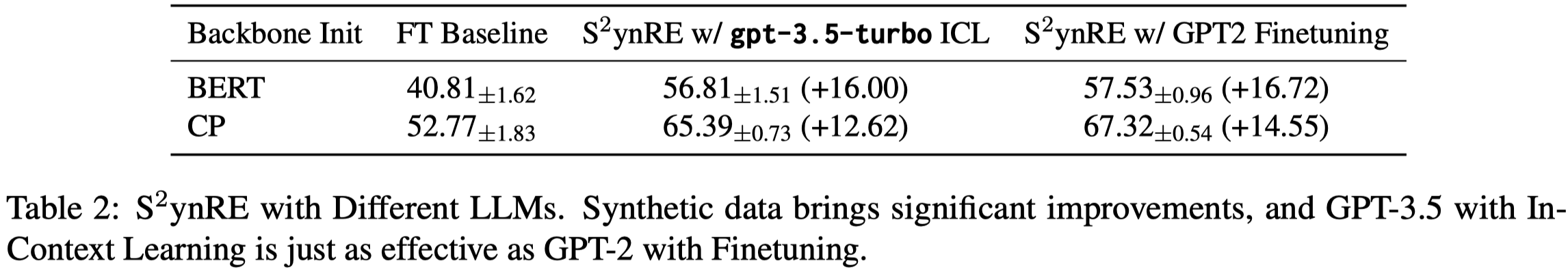
直接用GPT不一定能够超过finetuned LM来生成data,下面的结果没有找到是具体哪个dataset上的测试结果:
作者使用type-token ratio ([Evaluating story generation systems using automated linguistic analyses. 2017]; Data augmentation using pre-trained transformer models. 2020)来评估diversity。
DARE
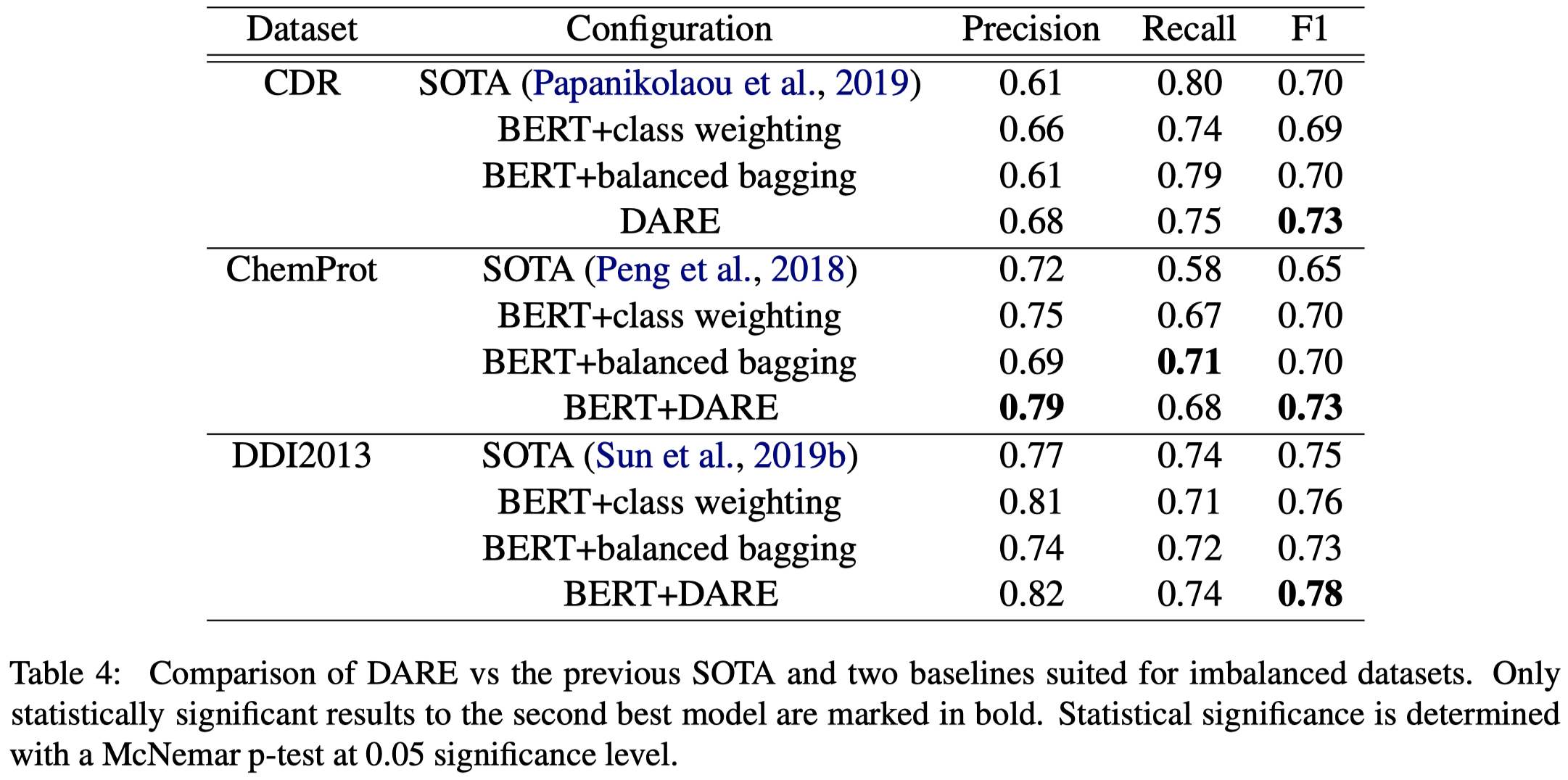
DARE: Data Augmented Relation Extraction with GPT-2. arXiv 2020
作者声明是首个利用GPT-2进行RE数据增强的工作:
Real-world Relation Extraction (RE) tasks are challenging to deal with, either due to limited training data or class imbalance issues. In this work, we present Data Augmented Relation Extraction (DARE), a simple method to augment training data by properly fine-tuning GPT-2 to generate examples for specific relation types. The generated training data is then used in combination with the gold dataset to train a BERT-based RE classifier. In a series of experiments we show the advantages of our method, which leads in improvements of up to 11 F1 score points against a strong baseline. Also, DARE achieves new state of the art in three widely used biomedical RE datasets surpassing the previous best results by 4.7 F1 points on average.
具体方法比较简单,对于头尾实体,用$符号进行标记,$ENTITY_A$和$ENTITY_B$;然后作者对于数据集中每个relation type对应的子数据集,都训练一个GPT2(774M)进行数据生成,原因是作者发现如果让一个GPT2直接生成所有的relation type的data,效果比较差。
同时,针对每个relation都生成对应的新数据,可以看做是一种过采样,作者认为这种过采样策略能够缓解class imbalance问题。

值得一提的是,为了缓解生成句子可能存在的噪音问题,作者采用了集成学习的策略。作者训练了20个基于BERT的classifier,每个classifier都是在full gold data和采样的生成数据的子集上进行了训练。
作者的RE任务是给定了头尾实体的RE,在3个biomedical RE数据集上进行了实验,实验结果:
RelationPrompt
RelationPrompt: Leveraging Prompts to Generate Synthetic Data for Zero-Shot Relation Triplet Extraction. ACL 2022 Findings. 阿里达摩. 代码。
Despite the importance of relation extraction in building and representing knowledge, less research is focused on generalizing to unseen relations types. We introduce the task setting of Zero-Shot Relation Triplet Extraction (ZeroRTE) to encourage further research in low-resource relation extraction methods. Given an input sentence, each extracted triplet consists of the head entity, relation label, and tail entity where the relation label is not seen at the training stage. To solve ZeroRTE, we propose to synthesize relation examples by prompting language models to generate structured texts. Concretely, we unify language model prompts and structured text approaches to design a structured prompt template for generating synthetic relation samples when conditioning on relation label prompts (RelationPrompt). To overcome the limitation for extracting multiple relation triplets in a sentence, we design a novel Triplet Search Decoding method. Experiments on FewRel and Wiki-ZSL datasets show the efficacy of RelationPrompt for the ZeroRTE task and zero-shot relation classification. Our code and data are available at github.com/declare-lab/RelationPrompt.
作者是提出的zero-shot relation extraction任务,
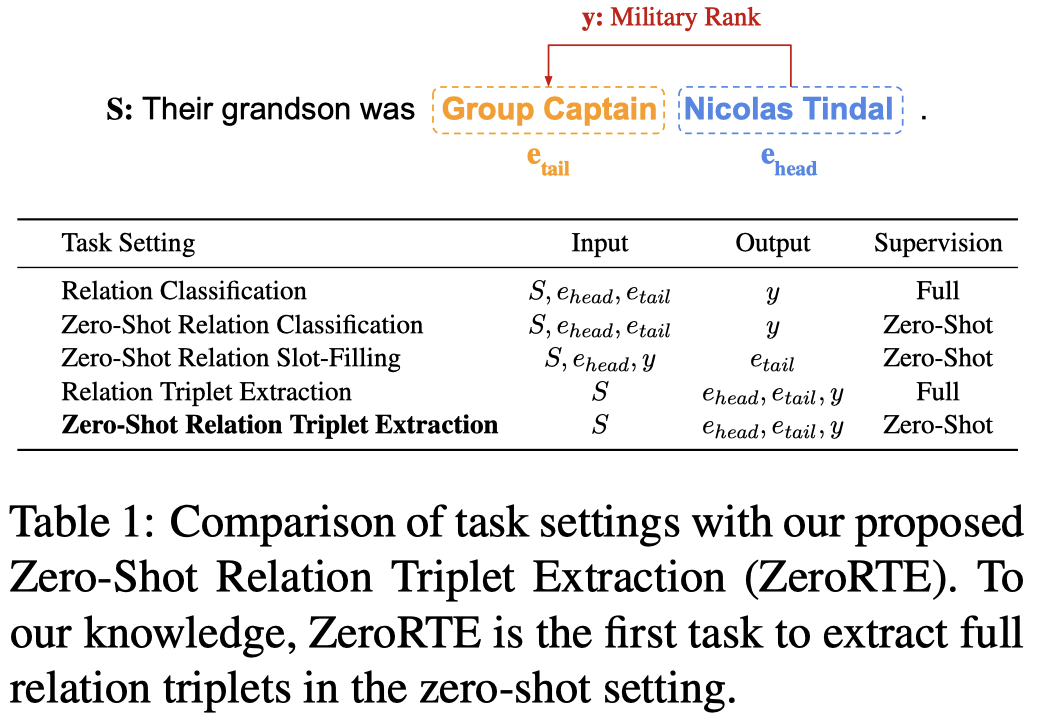
给定sentence,然后抽取triples。test set里包含没有在train set里出现的relation(但是entity type是都在train set里出现过的)。
作者解决zero-shot relation triple extraction任务的思路是,先为unseen relation生成sentence,构造一个人工训练集,然后用这个生成的人工训练数据集训练一个IE model,输出triples。作者没有考虑其它可能的解决zero-shot relation triple extraction任务的思路的原因:
- distant supervision:可能已有的外部knowledge base只包含了部分unseen relation的data
- 修改task objective,让model能够输出非提前定义好的label,
具体的训练流程如下:
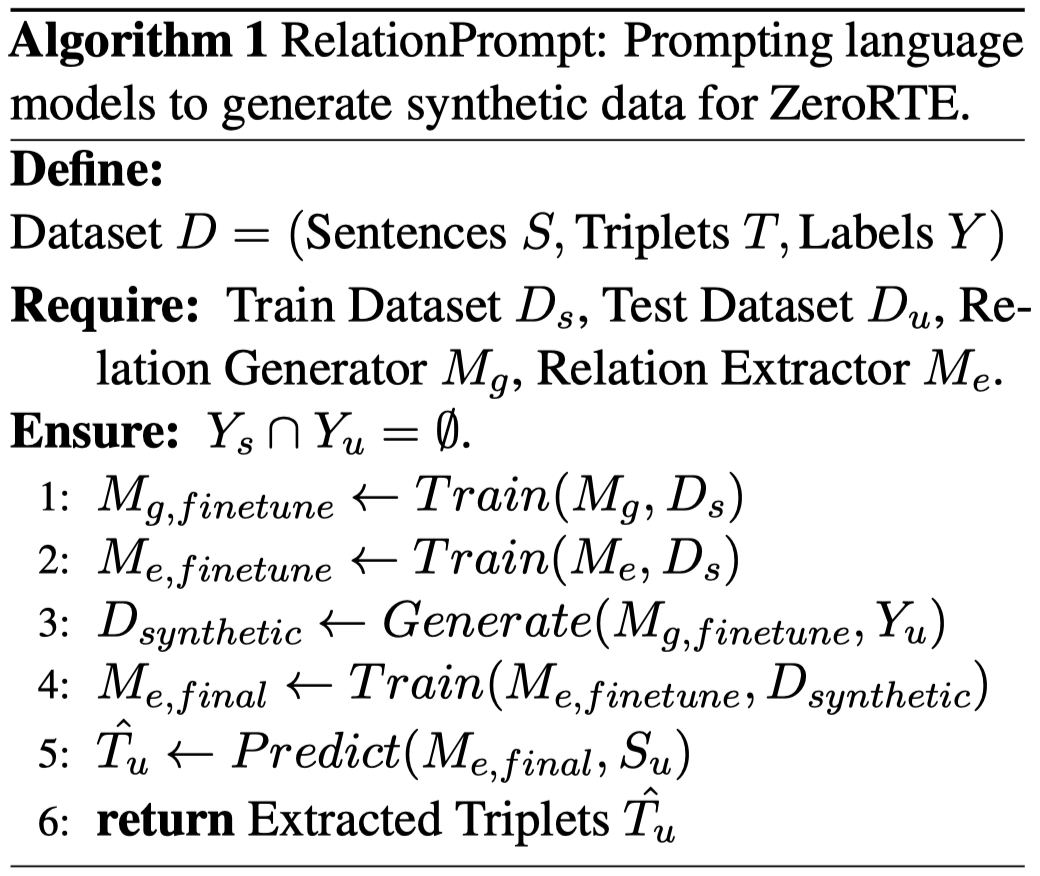
具体的实现细节:
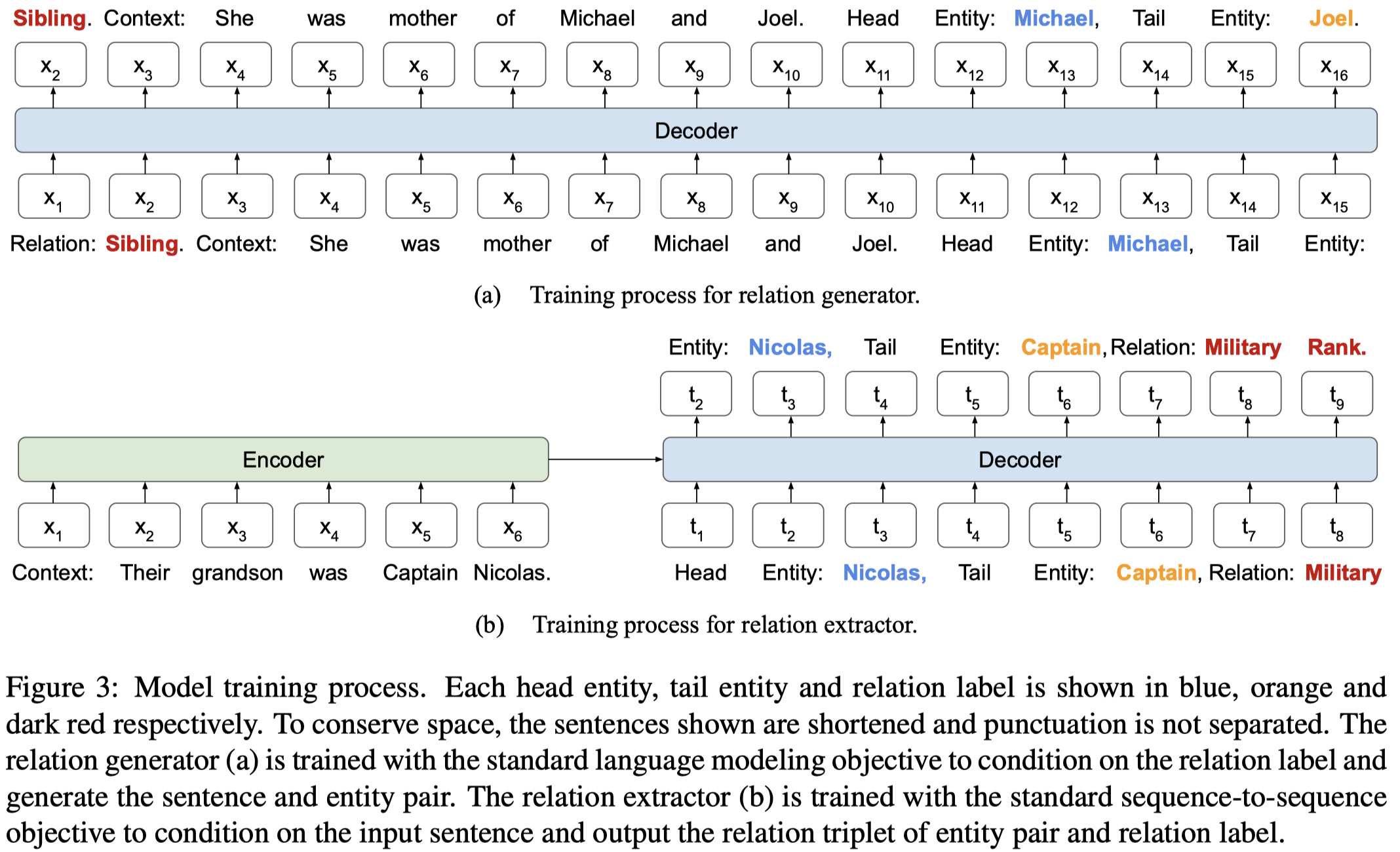
- Relation Gnerator:GPT-2(124M),输入
Relation:,输出Context: s. Head Entity: e head, Tail Entity: e tail,在training set上用language modeling objective进行finetune。然后用来为不同的unseen relation生成sentence。生成的sentence只包含一个triple,主要是考虑到如果让sentence直接包含多个triples,可能生成的句子质量难以保证; - Relation Extractor:BART(140M),输入
Context: s,生成Head Entity: e head, Tail Entity: e tail, Relation: y。先在training set上进行finetune,然后在Relation Gnerator生成的人造数据集上进行finetune,最后用于inference;
对于Relation Extractor,由于作者生成的sentence只包含一个triple,但是真实的sentence可能包含多个triples,一般的三元组抽取model都是假设text会抽取出多个triple,这样就和作者生成只包含一个triple的sentence不符了。为了解决这种training和testing过程中,sentences包含的triples不一致的问题,作者提出了一种Triplet Search Decoding方法:
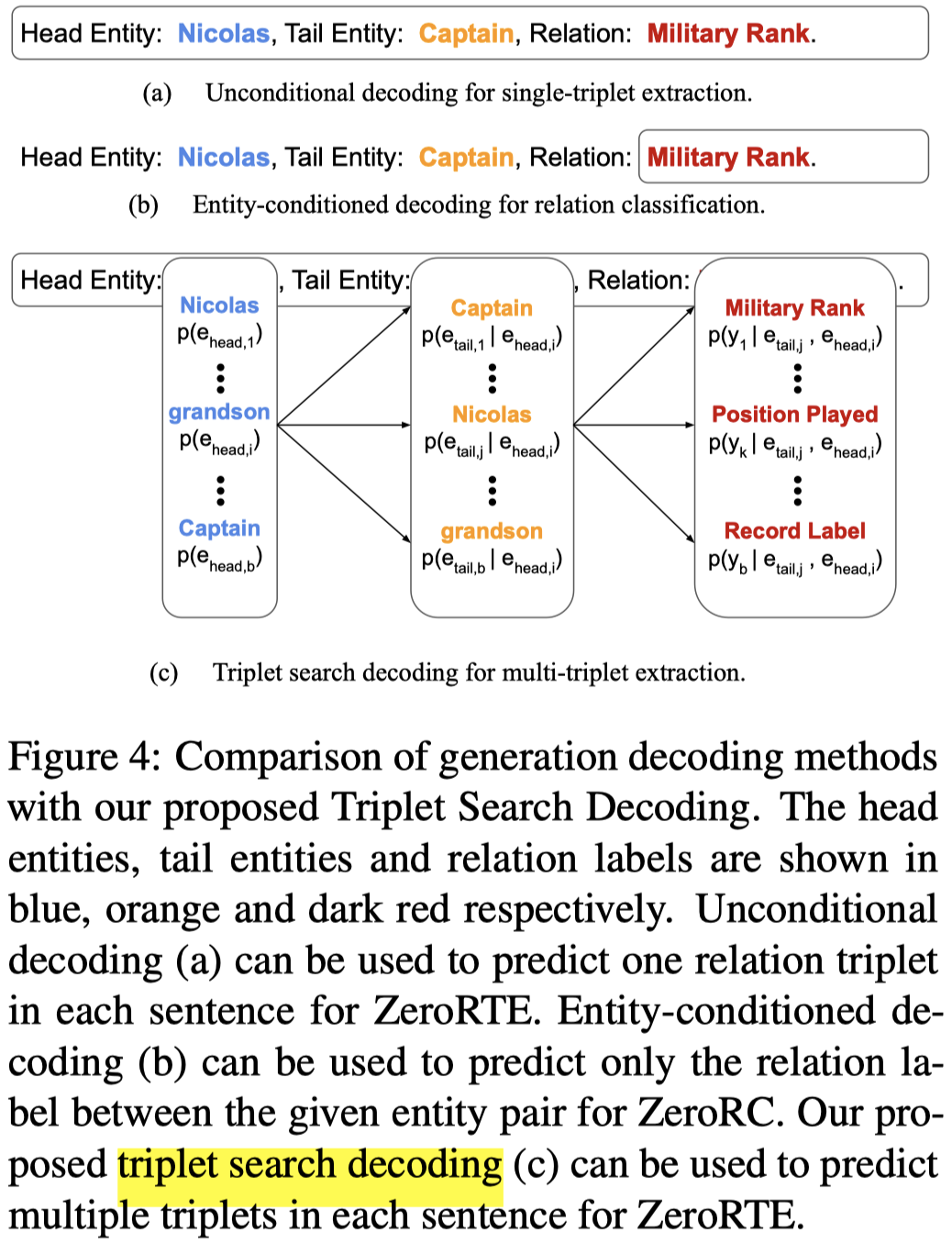
简单说,就是在输出head/tail/relation的第一个token的时候,保持前top-\(b\)的tokens,最后生成多个候选triples。这样即使在训练阶段,训练数据只有1个triples,在测试阶段也可以生成多个triples:
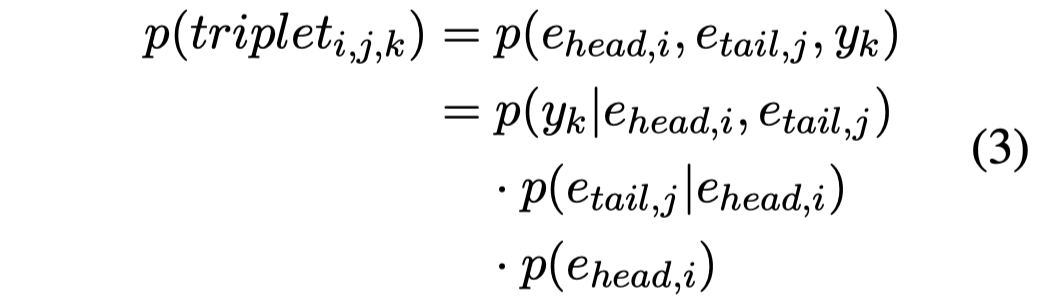
实验结果:
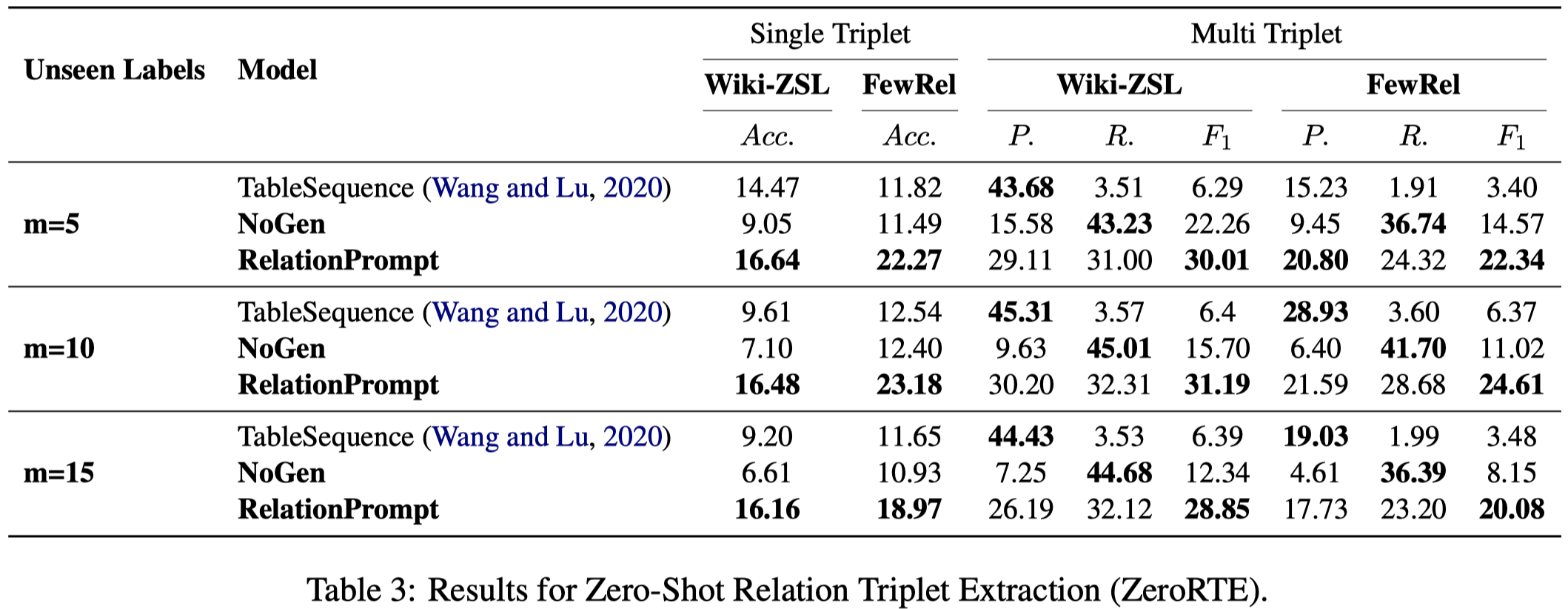
通过在Wiki-ZSL和FewRel两个数据集上,选择\(m\)个relation从训练集中拿出,作为unseen relations进行测试,实现zero-shot relation extraction。
DGRE
Generating Labeled Data for Relation Extraction: A Meta Learning Approach with Joint GPT-2 Training. ACL 2023. University of Oregon
Relation Extraction (RE) is the task of identifying semantic relation between real-world entities mentioned in text. Despite significant progress in RE research, a remaining challenge for RE concerns the lack of training data for data-hungry deep learning models. Cost of annotation and difficulty of the task are among hindrance to collect a large-scale RE dataset in different domains. To address this limitation, we propose a novel framework to automatically generate labeled data for RE. Our framework presents the pre-trained language model GPT-2 for data generation. In addition, to optimize the generated samples for an RE model, we introduce a meta learning approach to allow the GPT-2 model to be updated during the training process for RE. In particular, to leverage the feedback from the RE model to improve the data generation from GPT-2, we propose a novel reward function to update the GPT-2 model with REINFORCE, seeking to promote the similarity of the RE loss function’s gradients computed for generated data and a meta development set. We conduct extensive experiments on two benchmark datasets to produce state-of-the-art performance for RE.
Issue: 利用数据增强的技术,生成的data和RE model期望的data中间可能存在gap。
However, an issue with this approach involves the separation between the fine-tuning process of GPT-2 and the target RE model that might cause a mismatch between the generated data from GPT-2 and the data expected by the RE model (e.g., the generated data can be noisy or redundant for RE).
Solution: 为了解决这一点,作者提出要使得生成新数据的语言模型能够从执行具体RE任务的base model中学到反馈。
作者的生成模型是GPT-2,RE任务抽出模型是BERT-base。
对于GPT-2,首先是pre-training。通过在句子中的头尾实体tokens左右插入特殊符号,输入句子变为:\(T^\prime= [w_1, w_2, \dots , <SUB-l>w_s</SUB-l>, \dots , <OBJ-l>w_o</OBJ-l>, \dots , w_n]\)。这里的\(l\)是一个特殊标记,\(l=p\)表示头尾实体之间存在某种relation,\(l=n\)表示头尾实体之间不存在relation。通过language modeling的方式,让GPT-2适应领域data。
要注意,作者生成的sentence只通过\(<SUB-l><OBJ-l>\)表明了在两个entity之间存在某种relation,而没有说明具体是哪种relation type。
对于BERT-base,在进行抽取的时候,在预测层采用了Dynamic Pooling技术[Event extraction via dynamic multipooling convolutional neural networks. ACL 2015]。具体来说,最后一层的embedding,转化为:\(h = [e_{[CLS]}:f(e_1 ,\dots , e_{s−1} ) : e_s : f(e_{s+1} , \dots , e_{o−1} ) : e_o :f(e_{o+1}, \dots , e_n)]\),\(f\)表示Max Pooling操作,使用embedding \(h\)进行relation分类。
由于生成的数据没有relation type,BERT RE model上增加了一个额外的task head,判断实体之间是否存在某种relation的二元分类。这样就有针对原有标注数据和生成数据两种loss。
为了能够让GPT-2学会生成符合BERT RE model期望数据,接下来将GPT-2和BERT进行一起针对训练集,分batch进行训练,每次迭代同时更新GPT-2和BERT。
最直接的想法是利用performance metric的变化来评估generated data的好坏。这种做法需要提前划分出一个meta development set \(D_{meta}\)来计算reward,优化GPT-2参数。但是由于没有足够多的有标注数据,这种基于performance metric变化计算得到的reward,可能有很大的方差,非常不稳定。
因此,作者提出可以通过loss计算的梯度,来评估一条生成数据是否适合训练RE model:
Intuitively, a generated sample \(T_g\) is helpful for the RE model \(M_{\theta_t}\) if the gradient of \(L_{base}\) with this sample aligns with the steepest direction with the development data (i.e., similar gradients from \(T\) gand \(D_{meta}\))
一条生成数据与在meta development set上数据的平均梯度越相似/方向一致,认为这个生成数据质量越好,reward越大。然后reward作为这条生成数据梯度计算的权重,更新GPT-2参数。具体的训练过程如下:

实验结果:
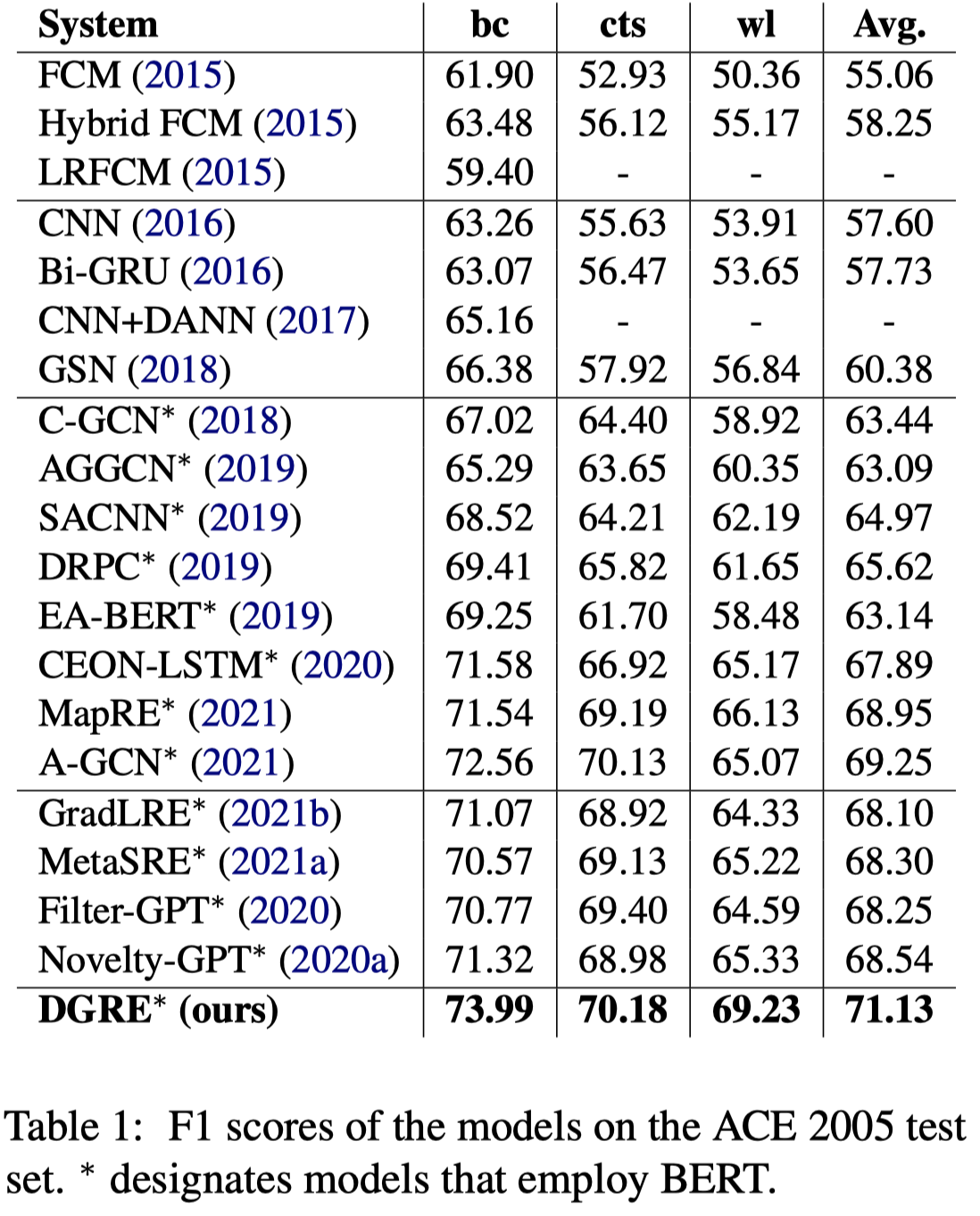
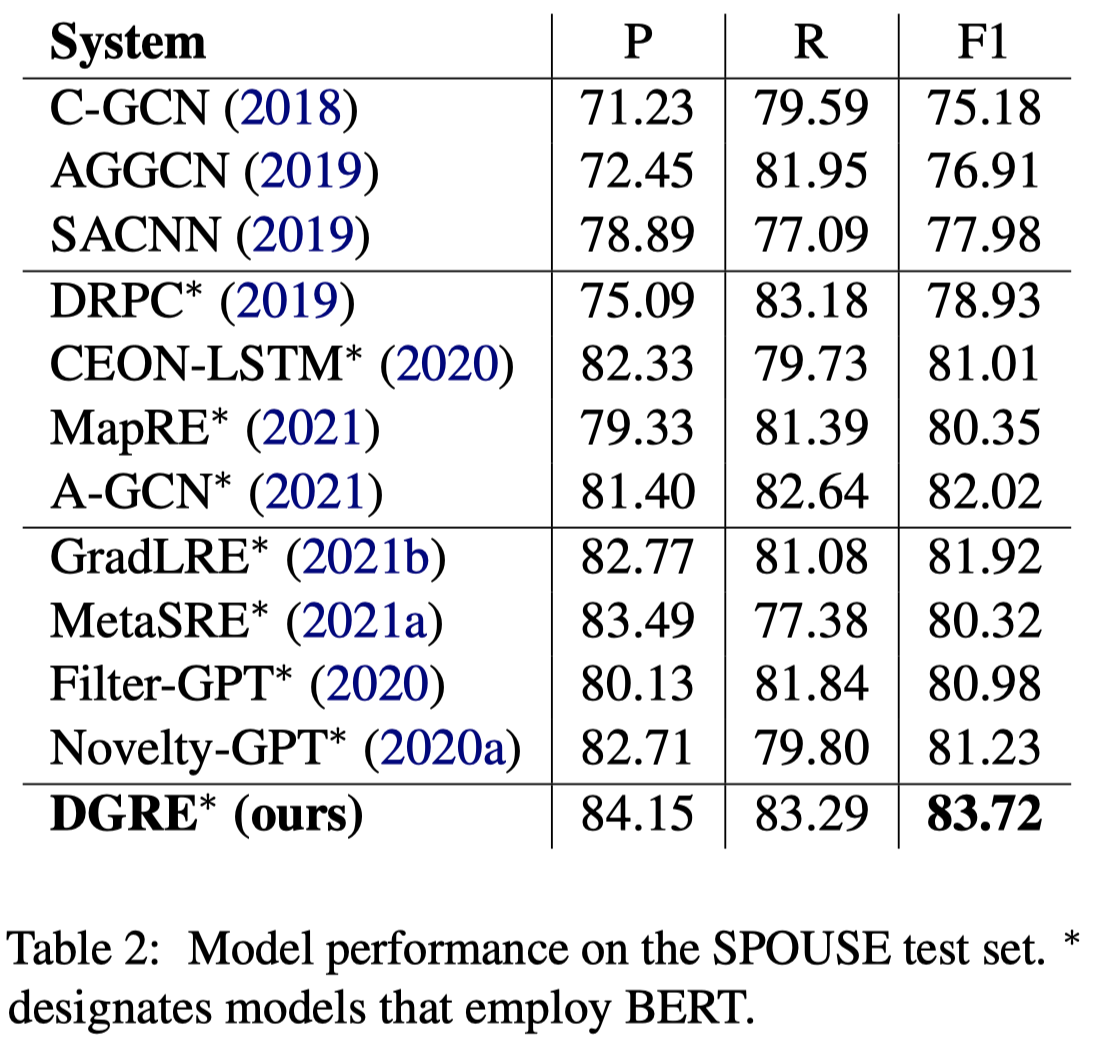
使用数据增强,大概给模型带来了1个点的提升:
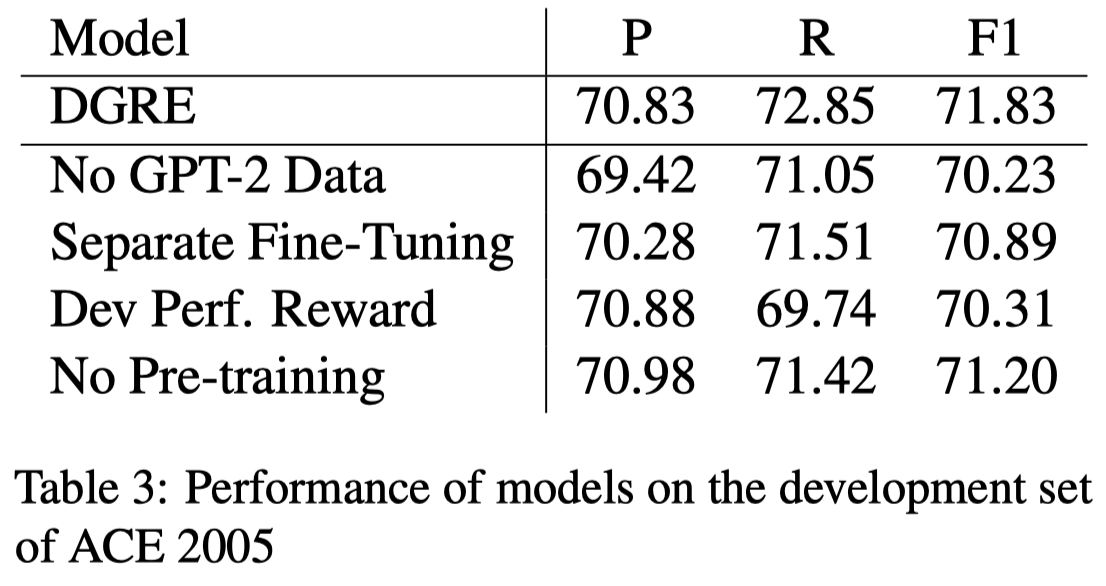
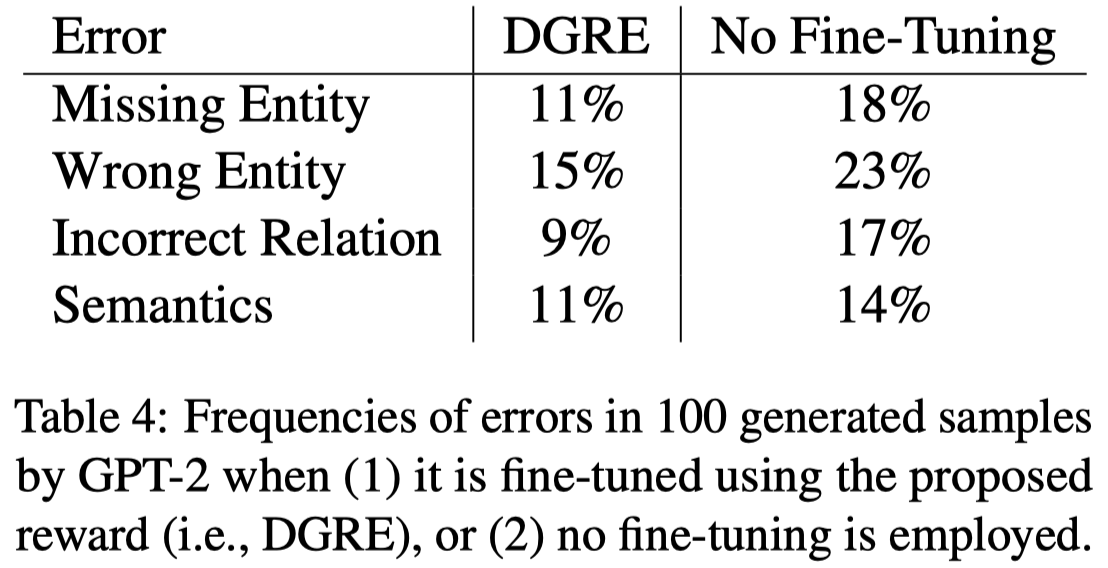
根据反馈,更新生成数据model的参数,能够减低各类错误:
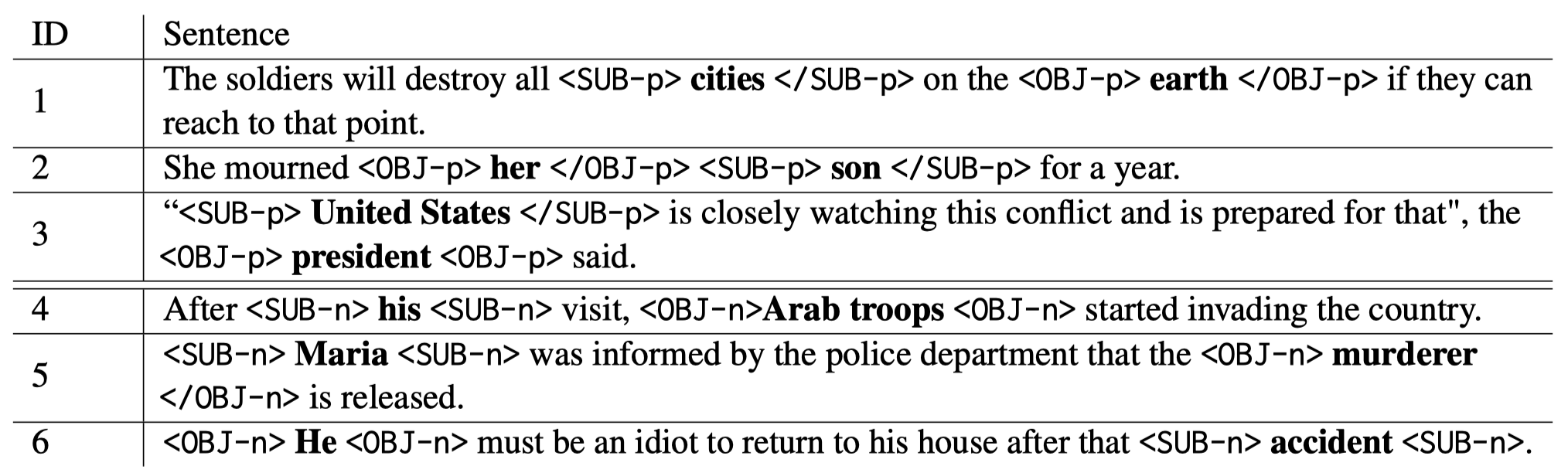
作者生成的具体cases:
DRNN
Improved Relation Classification by Deep Recurrent Neural Networks with Data Augmentation. COLING 2016. 北大. 代码.
Nowadays, neural networks play an important role in the task of relation classification. By designing different neural architectures, researchers have improved the performance to a large extent in comparison with traditional methods. However, existing neural networks for relation classification are usually of shallow architectures (e.g., one-layer convolutional neural networks or recurrent networks). They may fail to explore the potential representation space in different abstraction levels. In this paper, we propose deep recurrent neural networks (DRNNs) for relation classification to tackle this challenge. Further, we propose a data augmentation method by leveraging the directionality of relations. We evaluated our DRNNs on the SemEval-2010 Task 8, and achieve an F 1-score of 86.1%, outperforming previous state-of-the-art recorded results.
以前的RE方法常常利用浅层的神经网络,缺少对于不同层级表征空间的学习。
作者的方法是提出了利用多层级的RNN:
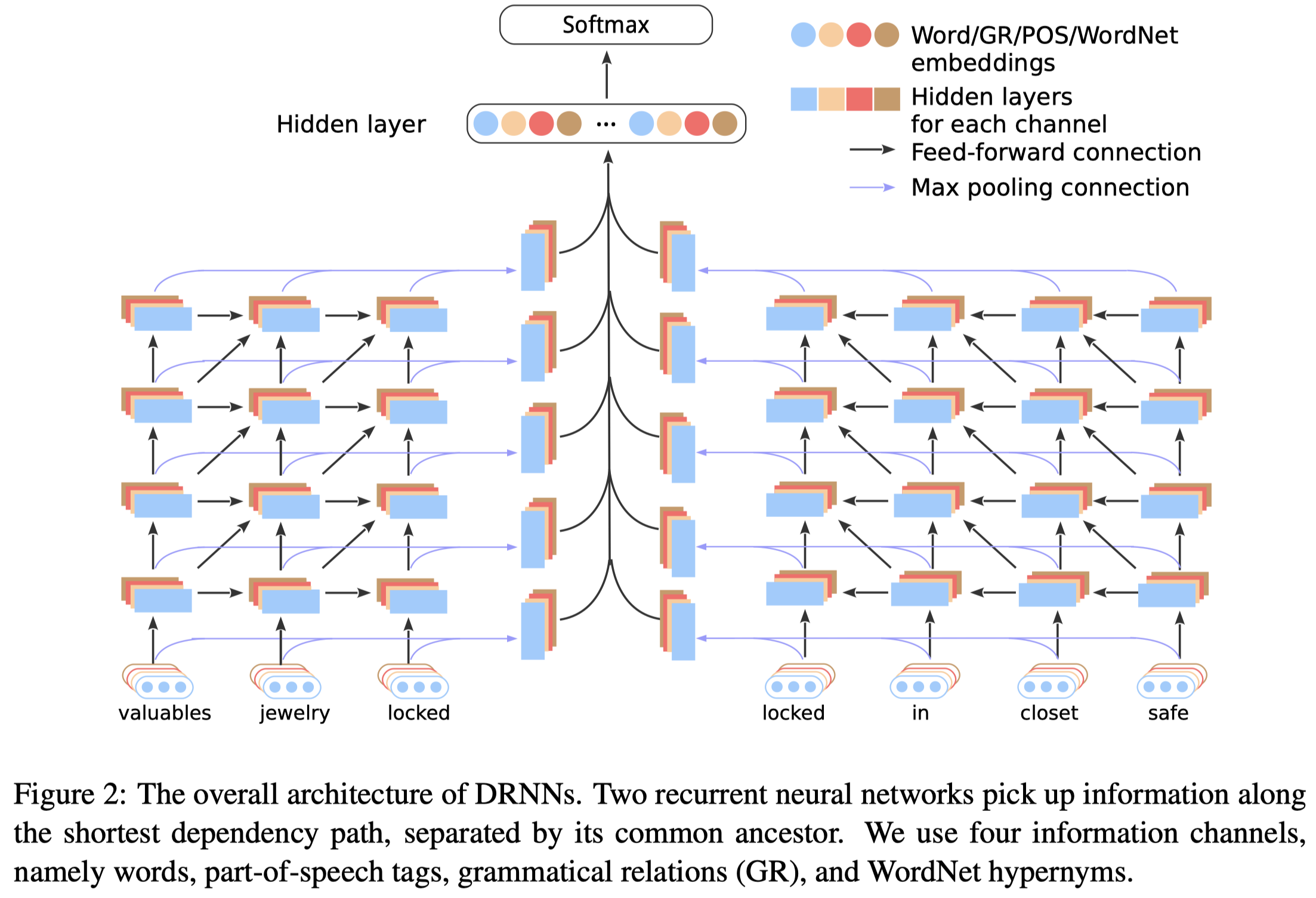
输入包括了4种信息通道,也就是4种不同的输入embedding。每种信息通道有自己独立的RNN网络。最终结果拼接起来进行分类。
模型的左右两侧的输入是句子里头尾实体在语法依赖树上到共同父结点的最短路径,作者认为这两条路径对应了subject-predicate和object-predicate两个relation components:

另外,作者提出了一种基于规则的,利用relation方向性的简单数据增强方法。通过互换头尾实体对应的路径,预测逆关系。比如原来预测的是relation \(Content-Container(e_1, e_2)\),互换路径后,输入model,应该预测逆关系\(Container-Content(e_1, e_2)\)。如上图右侧(b)所示。在实验里,作者发现对于有方向的relation进行增强效果最好,对于所有的relations都进行增强,模型效果反而降低。
总体实验结果,SemEval-2010 Task 8数据集:

GradLRE
Gradient Imitation Reinforcement Learning for Low Resource Relation Extraction. 清华. EMNLP 2021. 代码.
Low-resource Relation Extraction (LRE) aims to extract relation facts from limited labeled corpora when human annotation is scarce. Existing works either utilize self-training scheme to generate pseudo labels that will cause the gradual drift problem, or leverage meta-learning scheme which does not solicit feedback explicitly. To alleviate selection bias due to the lack of feedback loops in existing LRE learning paradigms, we developed a Gradient Imitation Reinforcement Learning method to encourage pseudo label data to imitate the gradient descent direction on labeled data and bootstrap its optimization capability through trial and error. We also propose a framework called GradLRE, which handles two major scenarios in low-resource relation extraction. Besides the scenario where unlabeled data is sufficient, GradLRE handles the situation where no unlabeled data is available, by exploiting a contextualized augmentation method to generate data. Experimental results on two public datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of GradLRE on low resource relation extraction when comparing with baselines. Source code is available.
Issue:低资源RE方法中,
- 远监督方法有个strong assumption假设外部KB中共同出现的实体具有某种特定关系,忽略了具体的context,这使得makes model generate relations based on contextless rules and limits the generalization ability.
- 自训练self-training的方法,容易受到noisy伪标注的影响,出现gradual drift problem问题(Curran et al., 2007; Zhang et al., 2016)
对于自训练的方法,直接将伪标注的数据加入进来不可避免的会出现selection bias,影响model的泛化能力。
Solution:作者提出,不要直接将伪标注数据加入进来,将现有的标注作为guideline,去选择伪标注;并且根据选择结果实现反馈feedback,更新模型参数,缓解selection bias,下一次实现更高质量的伪标注。
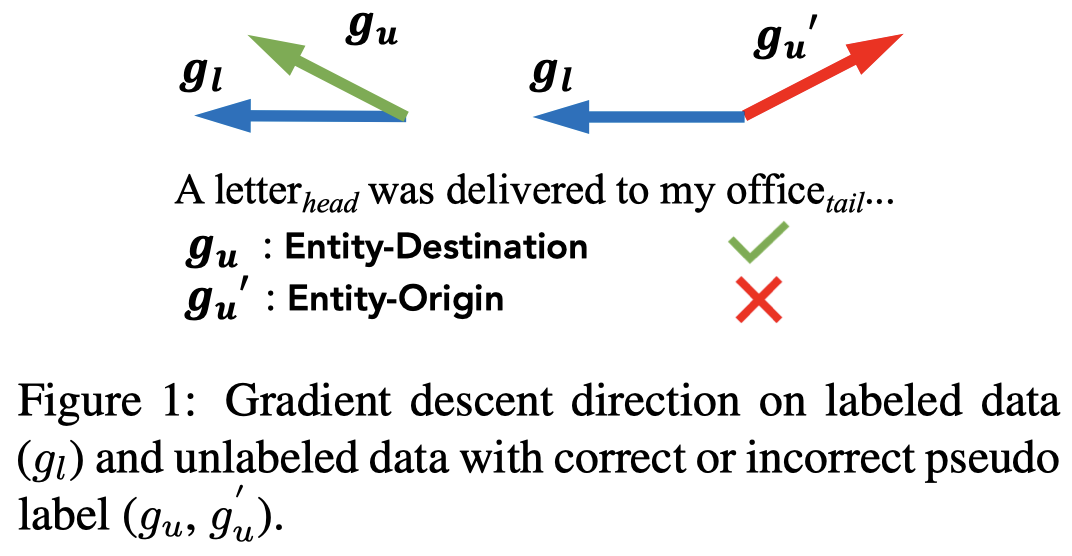
作者假设,正确的伪标注数据对应的梯度方向,应该和在实际数据上的平均梯度方向是接近的:
We assume that when pseudo-labeled data are correctly labeled in RLG, partial derivatives to the RLG parameters on the pseudo-labeled data would be highly similar to standard gradient descending.
作者提出的方法:
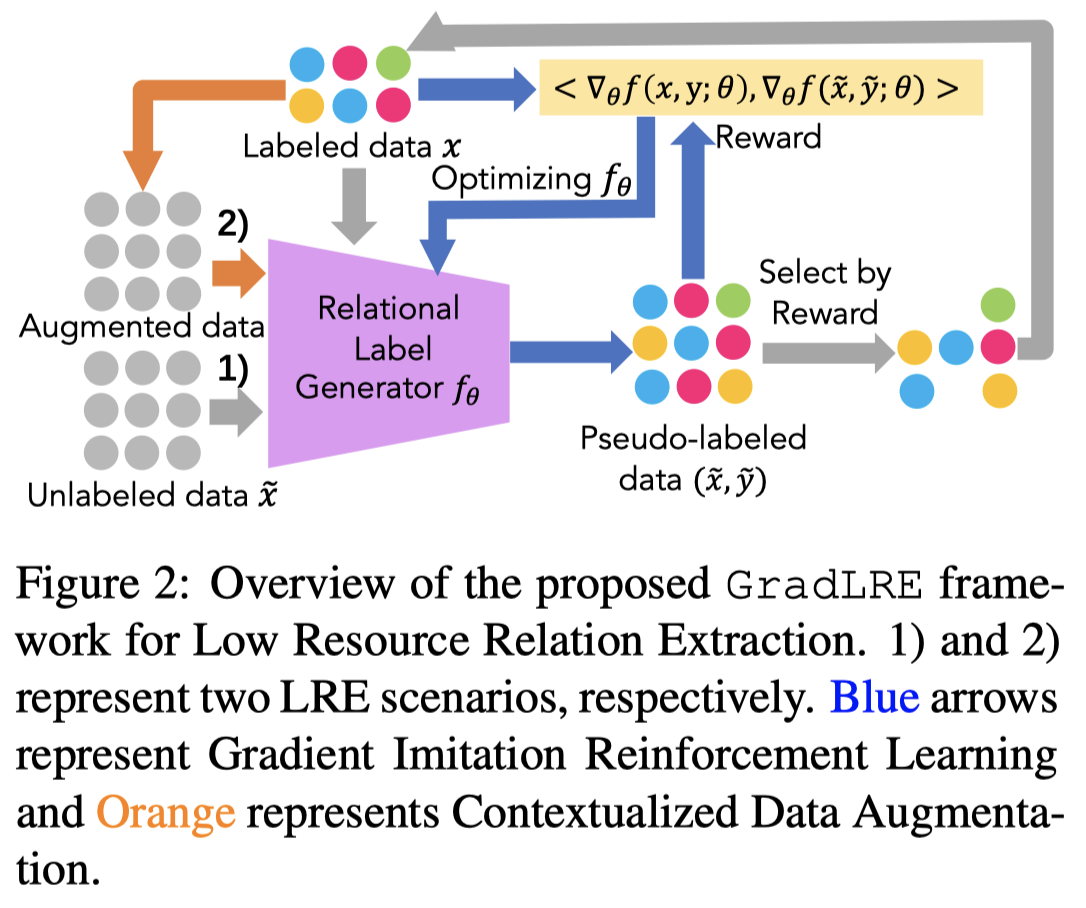
Relational Label Generator(RLG)用来作为weak annotator,基于BERT-Base_Cased,使用头尾实体对应的embedding,拼接后经过softmax分类层。RLG会提前在labeled data上进行训练。
Gradient Imitation Reinforcement Learning(GIRL)。使用上面的RLG对unlabeled data进行伪标注:
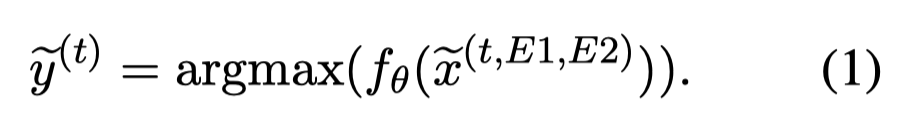
然后,分别计算在\(N\) labeled data上的standard gradient descent direction \(g_l\)和在某个pseudo-labeled data上的梯度\(g_p\):
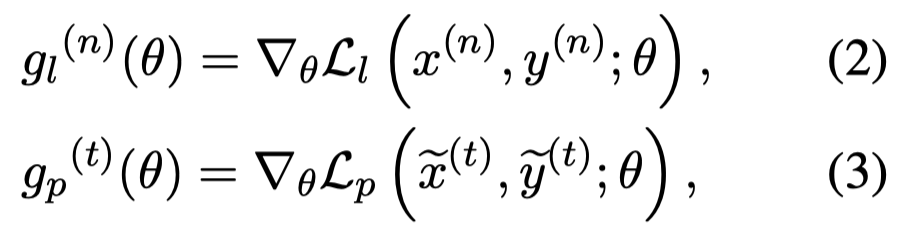
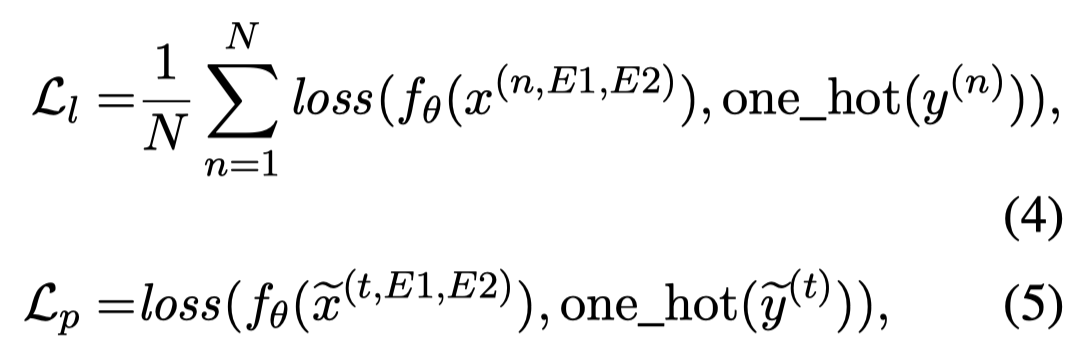
使用余弦相似度计算梯度下降方向的相似性,作为reward:
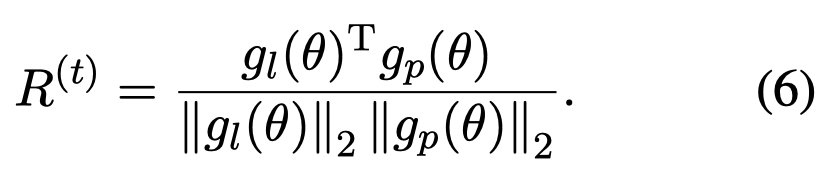
\(R^t\)超过阈值\(\lambda = 0.5\)的伪标注数据,会被看做是positive reinforcement能够用来进一步提升RLG的性能,将其加入到有标注数据集中。
最后,采用REINFORCE algorithm (Williams, 1992)进行优化:
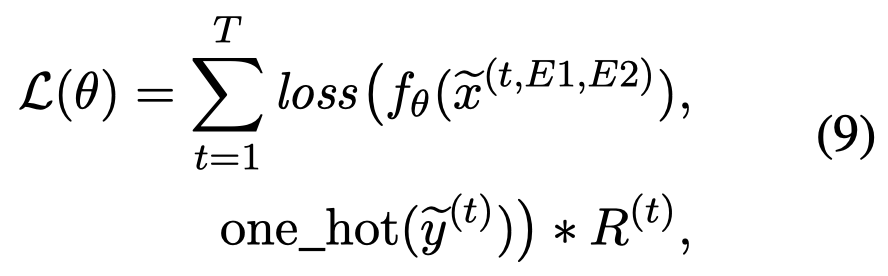
强迫选择出来的质量越高(即\(R^t\)越大)的伪标注,越要输出confidence的predictive distributions。
上面的过程是针对有无标注数据,需要生成伪标注的情况。作者还考虑了另外一种情况,也就是连无标注数据都没有,需要自己生成无标注数据的情况。
为此,作者提出了Contextualized Data Augmentation,简单的说,就是在句子中随机的采样mask头尾entities外的spans,破坏原有的context,然后利用BERT Masked Language Modeling填充mask,生成新的无标注数据。举例,如果将句子A letter was delivered to my office in this morning.中的delivered to移除,生成新句子A letter was sent from my office in this morning.,那么原来的relation就被改变了。具体的,作者follow了前人的工作,按照一定概率分布mask不同长度的context spans[Spanbert: Improving pre-training by representing and predicting spans. 2020]。
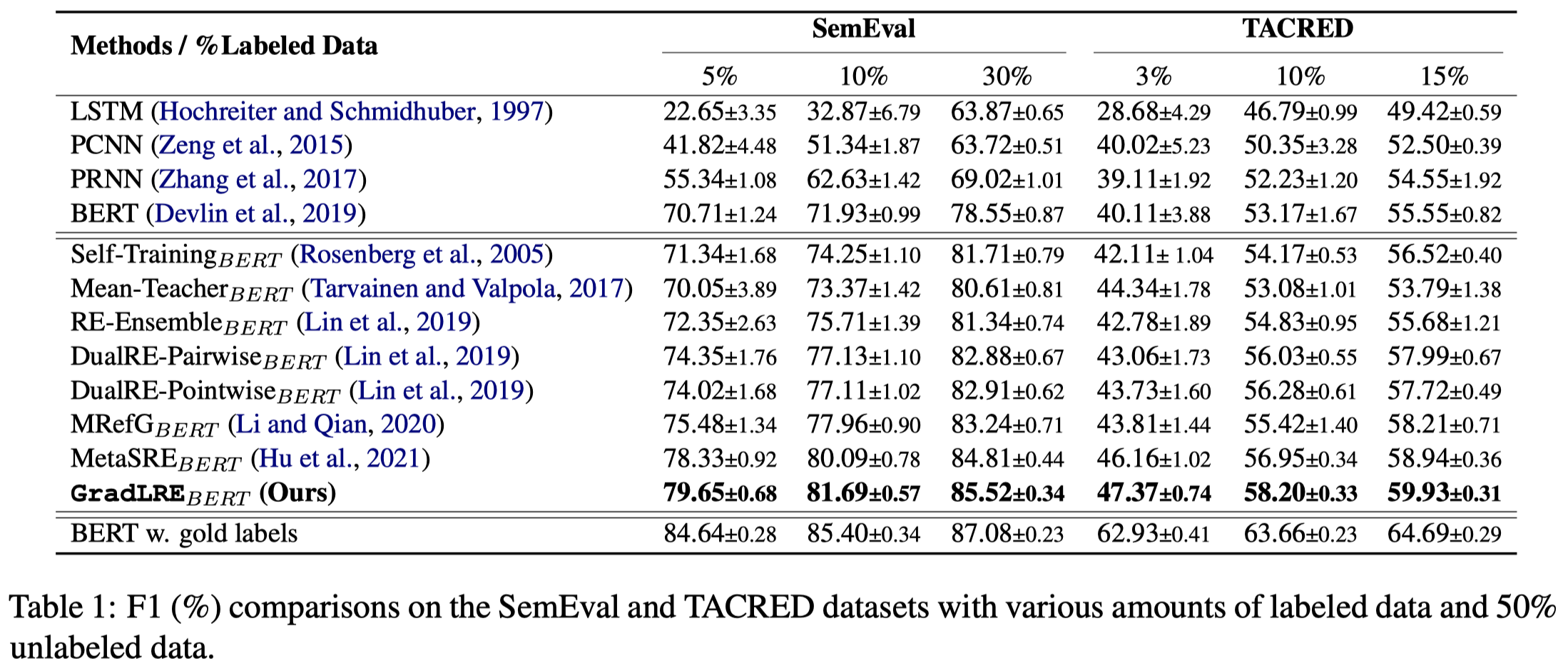
作者在SemEval 2010 Task 8 (SemEval)和TACRED数据集上的效果:
下面是作者提出的填充mask的数据增强方法的实例:

LREBench
Towards Realistic Low-resource Relation Extraction: A Benchmark with Empirical Baseline Study. EMNLP 2022 Findings. 浙大NLP. 代码.
This paper presents an empirical study to build relation extraction systems in low-resource settings. Based upon recent pre-trained language models, we comprehensively investigate three schemes to evaluate the performance in low-resource settings: (i) different types of promptbased methods with few-shot labeled data; (ii) diverse balancing methods to address the longtailed distribution issue; (iii) data augmentation technologies and self-training to generate more labeled in-domain data. We create a benchmark with 8 relation extraction (RE) datasets covering different languages, domains and contexts and perform extensive comparisons over the proposed schemes with combinations. Our experiments illustrate: (i) Though prompt-based tuning is beneficial in low-resource RE, there is still much potential for improvement, especially in extracting relations from cross-sentence contexts with multiple relational triples; (ii) Balancing methods are not always helpful for RE with longtailed distribution; (iii) Data augmentation complements existing baselines and can bring much performance gain, while self-training may not consistently achieve advancement to low-resource RE.
低资源关系抽取Low-resource RE (LRE)任务,较早传统的方法包括:
- Mintz et al. (2009) proposes distant supervision for RE, which leverages facts in KG as weak supervision to obtain annotated instances.
- Rosenberg et al. (2005); Liu et al. (2021a); Hu et al. (2021) try to assign pseudo labels to unlabeled data and leverage both pseudo-labeled data and gold-labeled data to improve the generalization capability of models iteratively.
- Some studies apply meta-learning strategies to endow a new model with the ability to optimize rapidly or leverage transfer learning to alleviate the data-hungry issue (Gao et al., 2019; Yu et al., 2020b; Li et al., 2020a; Deng et al., 2021).
- Other studies (Zhang et al., 2019) focus on the long-tailed class distribution, especially in tail classes that only allow learning with a few instances.
- More recently, a new methodology named prompt learning has made waves in the community by demonstrating astounding few-shot capabilities on LRE (Han et al., 2021; Chen et al., 2022d).
作者这篇empirical study主要针对下面三种思路的方法进行实验:
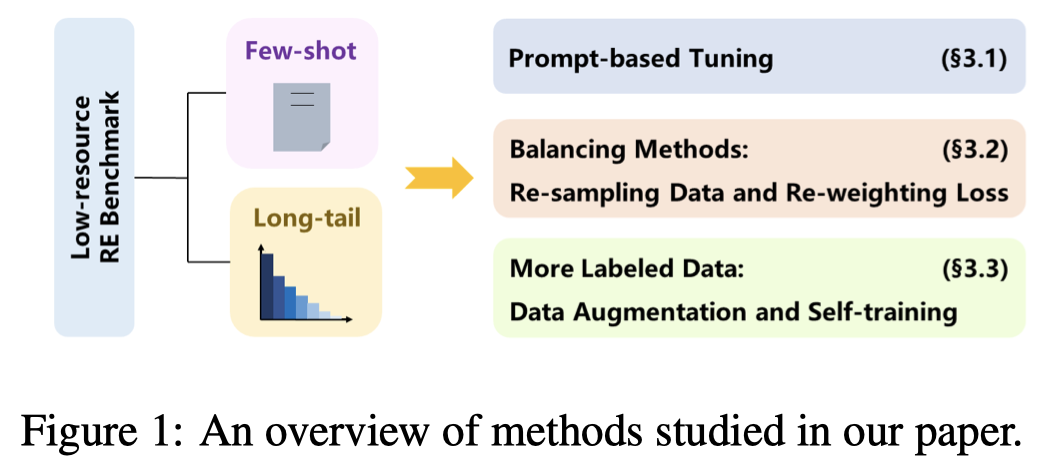
作者主要对比的方法示意图:
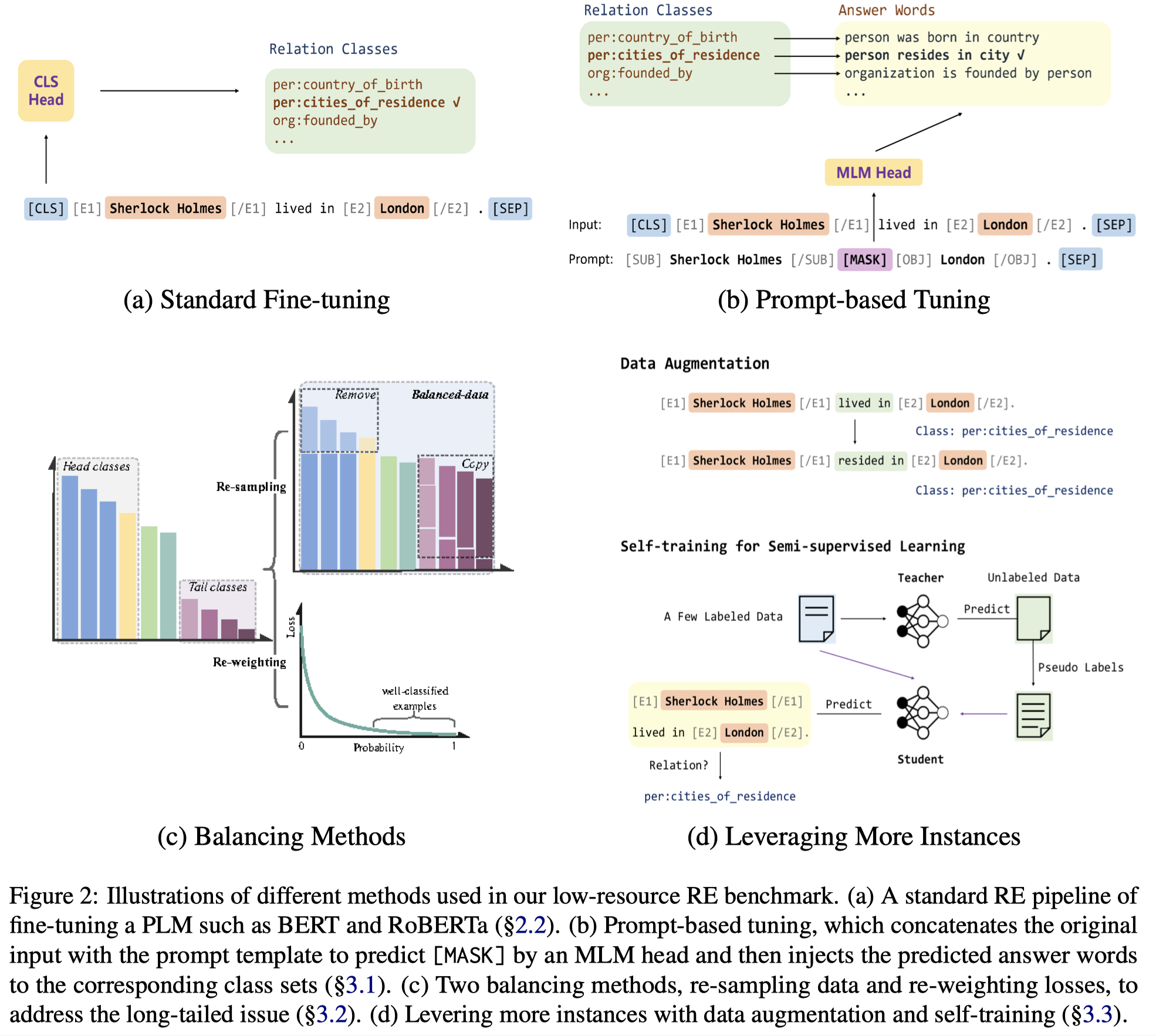
这里提一下基于prompt的方法,它通过提前创建和label相关的template,然后和原来的text拼接,让MLM去填充被mask的label tokens。这种方法之所以能够被用来解决LRE任务,主要是由于它通过提供task-specific information和relation label semantic,从而填充了pre-train到fine-tune阶段的gap。作者在实验里也发现,这种做法通常要比一般的方法效果好。
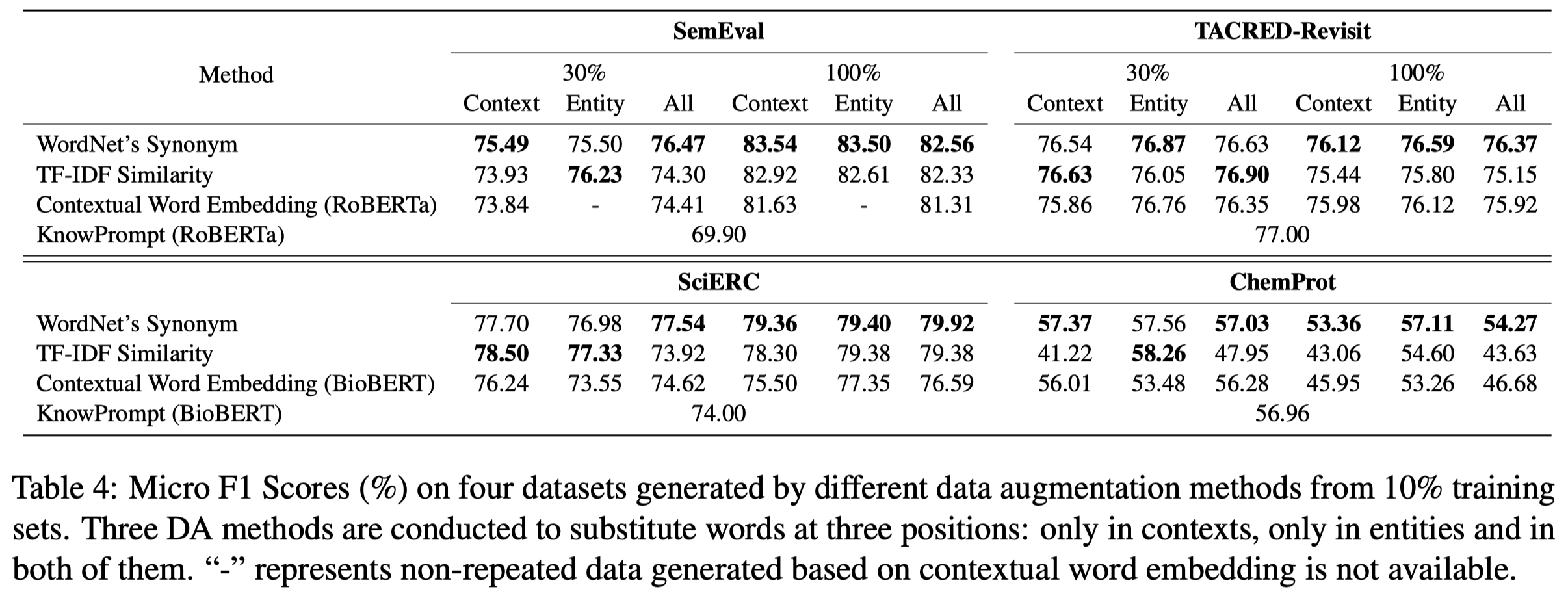
作者的数据增强方法是基于替换单词的方法,基于开源工具nlpaug从WordNet’s synonyms、TF-IDF similarity和contextual word embedding,替换原来句子中的contexts、entities、contexts与entities同时替换。在这一过程中,认为替换单词后,新句子和原来句子有相同的relation label。
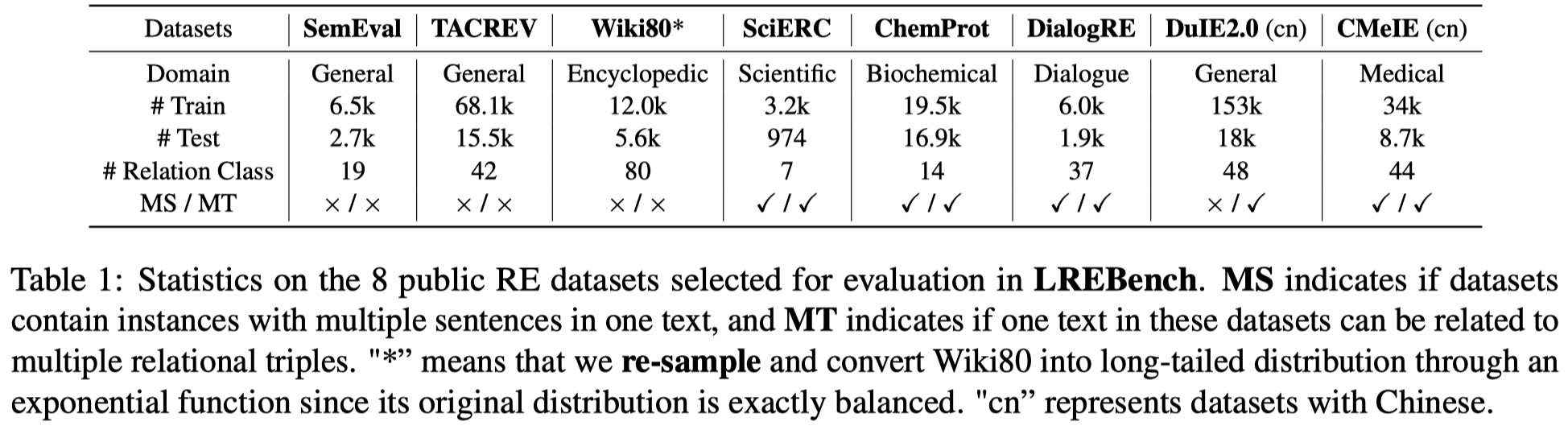
作者实验基于8个数据集:
基于RoBERTa-large作为RE model。
总体实验结果:
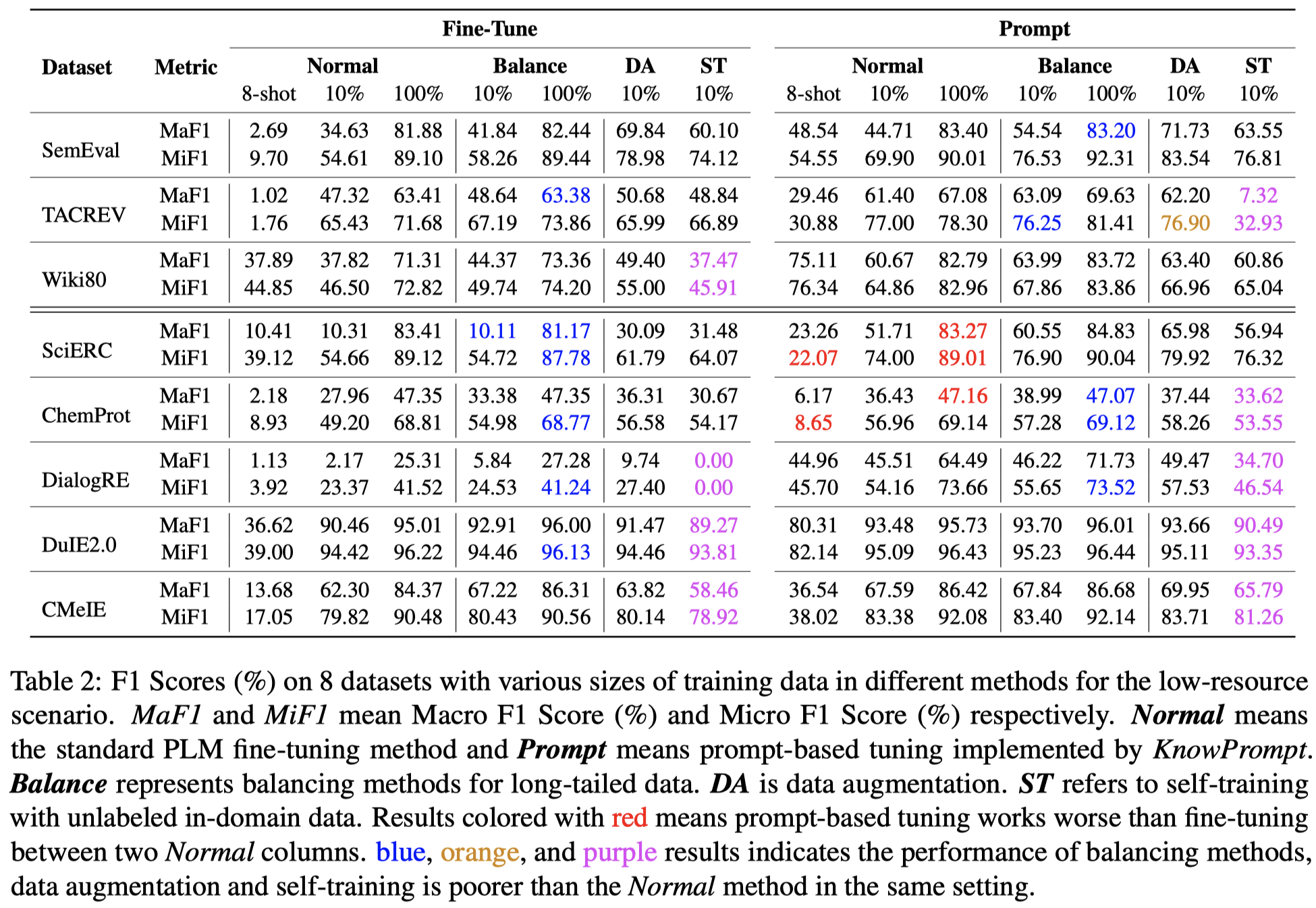
观察:
- prompt learning方法通常要好于一般的微调方法
- 数据增强策略通常是有效的
- self-training策略并不总能起到效果
不同prompt类型对比:
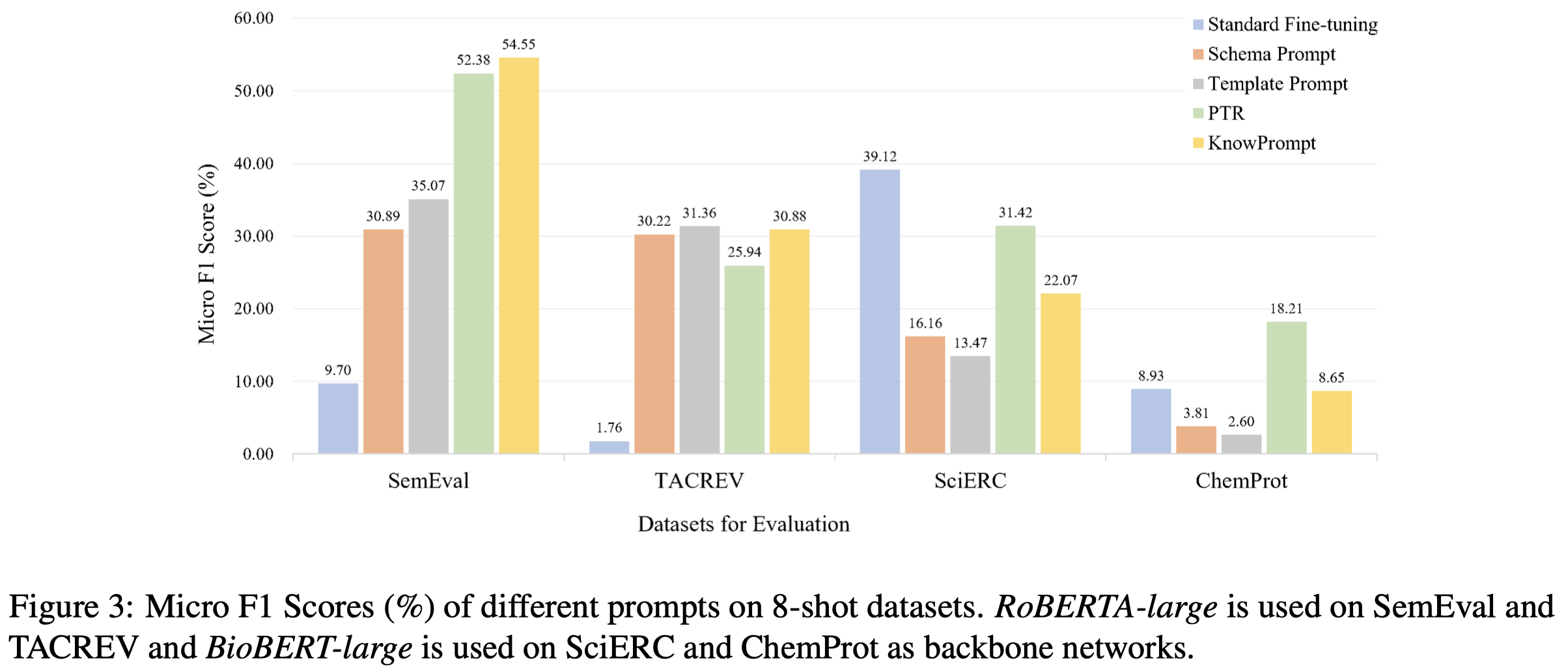
观察:
- Entity type information in prompts is helpful for low-resource RE. 类似于PTR和KnowPrompt这种加入了实体类型信息的prompt对于LRE任务来说是有帮助的
- PTR和KnowPrompt在TACREV数据集上效果比没有entity type类型信息的prompt效果差。作者认为这是由于TACREV数据集中存在标注错误的情况[An improved baseline for sentence-level relation extraction.],可能导致高估依赖于entity name、span和type信息的方法的效果
不同DA方法对比:
ParaphraseRE
Improving Relation Extraction with Relational Paraphrase Sentences. COLING 2020. 苏州大学. 代码.
Supervised models for Relation Extraction (RE) typically require human-annotated training data. Due to the limited size, the human-annotated data is usually incapable of covering diverse relation expressions, which could limit the performance of RE. To increase the coverage of relation expressions, we may enlarge the labeled data by hiring annotators or applying Distant Supervision (DS). However, the human-annotated data is costly and non-scalable while the distantly supervised data contains many noises. In this paper, we propose an alternative approach to improve RE systems via enriching diverse expressions by relational paraphrase sentences. Based on an existing labeled data, we first automatically build a task-specific paraphrase data. Then, we propose a novel model to learn the information of diverse relation expressions. In our model, we try to capture this information on the paraphrases via a joint learning framework. Finally, we conduct experiments on a widely used dataset and the experimental results show that our approach is effective to improve the performance on relation extraction, even compared with a strong baseline.
Issue: RE任务依赖于大量有标注数据,但是一个semantic relation fact有很多不同的expressions,比如Steve Jobs co-founded Apple Computer.; (2) Steve Jobs was the co-founder of Apple Computer.; and (3) Steve Jobs started Apple Computer with Wozniak.。前面两句话都有co-found,一个只见过前面两句话的model,可能无法从第3个句子中正确的识别出和前两句有一样的relation。引入更多的expressions是必要的。
为了引入更多的expressions,第一种解决方法是雇佣更多的人去标注,但受限于时间和money,不可能;第二种解决方法是远监督,但是远监督的强假设使得会带来很多错误的标注,存在大量噪音。
Issue: 因此,作者提出使用基于改写的方法来获得更多的expressions。
we use an alternative solution that uses a paraphrase data which collects sentences conveying the same meaning in different wording.
为了实现改写,作者考虑了直接使用目前已有的改写数据集,例如Simple Wikipedia (Kauchak, 2013), Twitter URL corpus (Lan et al., 2017), and Para-NMT (Wieting and Gimpel, 2018),但是在作者早期的实验中发现,仅仅是利用已有的general 的改写数据不能很好的适应RE任务。这就要求要构造适用于RE任务的paraphrase training data。
作者采用back-translation方法,为每个句子构造改写后的新句子,认为改写后的relation label保持不变(人工检查后发现,还是存在relation被改变的情况),构造Relational Paraphrase (ReP)数据集(首个适用于RE任务的paraphrase数据集):
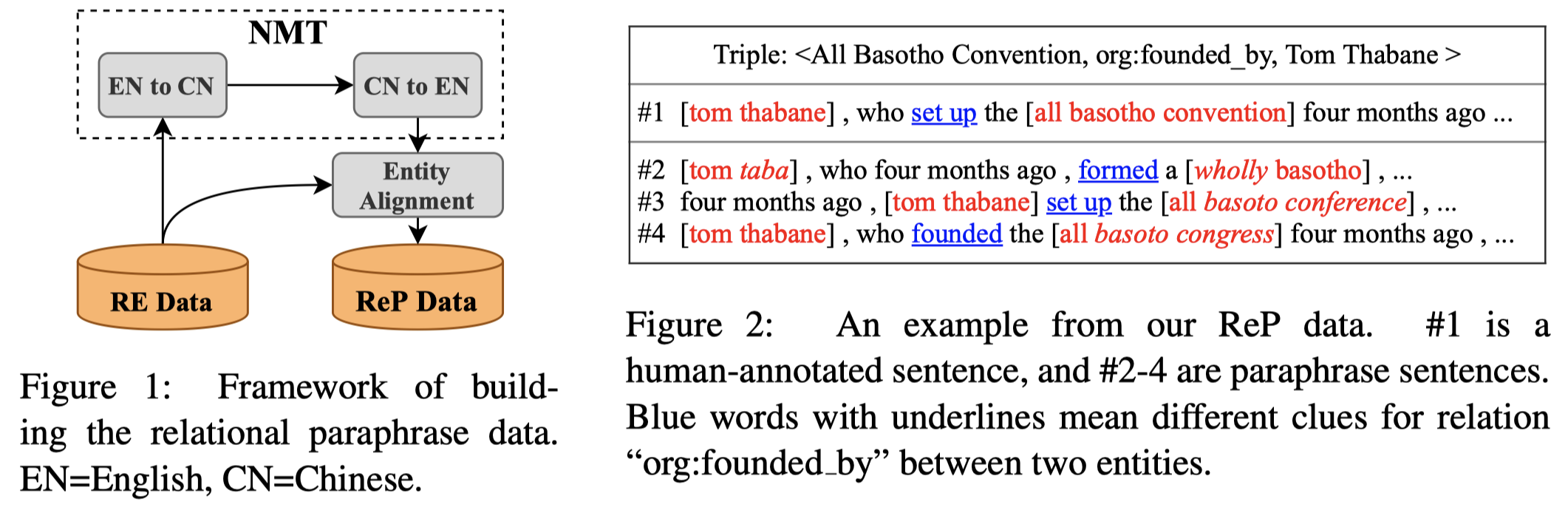
The back-translation is a procedure that first translates a sentence from a source language into a target language, then translates it back to the source language.
构造流程:
以特定的RE数据集TACRED为基础,对于其中的每个sentence,采用3个Neural Machine Translation (NMT) systems:Google Translation, Baidu Translation and Xiaoniu Translation。将原来English sentence翻译为Chinese,然后再翻译回来。这样每个sentence,会有对应3个翻译后被改写的新句子;
改写可能会导致原来sentence中的entities也被改写了,因此,作者利用BERT对应的不同sentence之间的embedding,计算余弦相似度,对齐改写后句子中的头尾entities和原来句子中的entities:
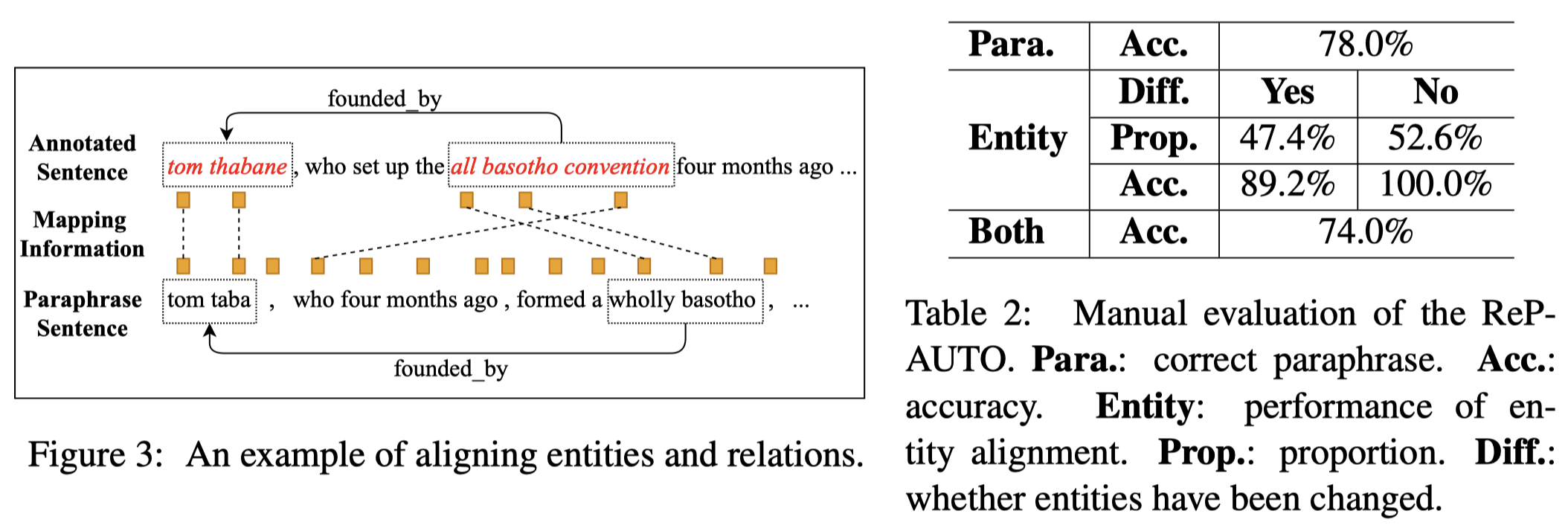
从上面,Table 2中能够看出,78%改写后的句子是对的。这说明了改写后的新句子是存在noise的。作者在实验中发现,如果直接把改写的句子和原有的gold data混合,反而降低了RE性能。因此,需要想办法解决这一问题:
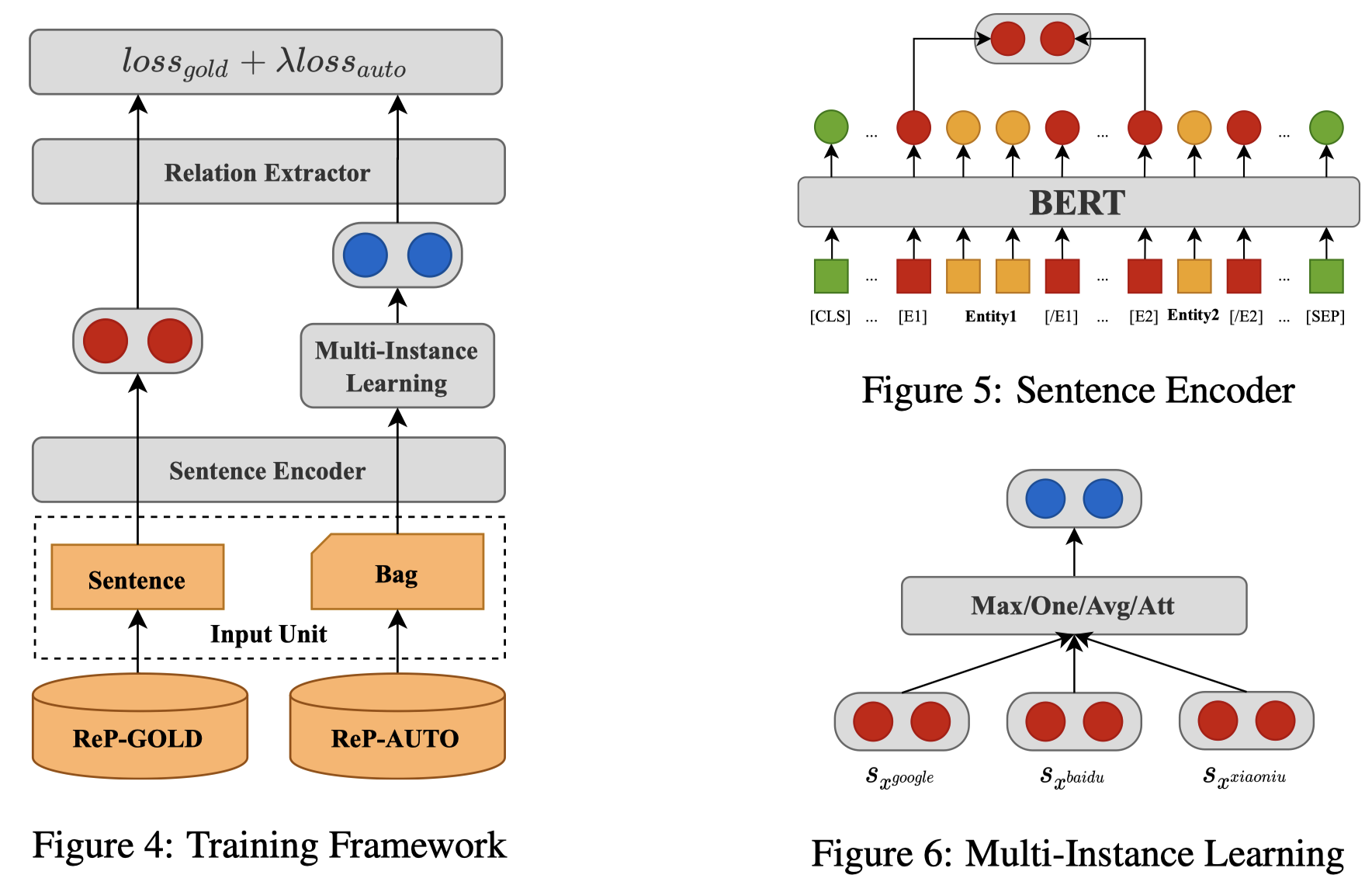
流程:
sentence encoder是
BERT-base或BERT-large;relation extractor是带softmax的线性分类层;对于原有的gold data还是一样的交叉熵loss
为了减小改写后新句子中的噪音问题,采用multi-instance learning strategies,也就是把3个对应的改写后的sentences作为一个bag,混合起来输出一个bag-level representation,用与进行最后的分类,这3句话有相同的relation label标注。背后的直觉是,每个句子可能有noise,但是3个句子总体上,应该是有类似的relation semantic的。具体混合方法可以是选择单独的某个句子、加权求和、attention、选择对应的预测probability最confidence的句子等。具体论文中有描述。
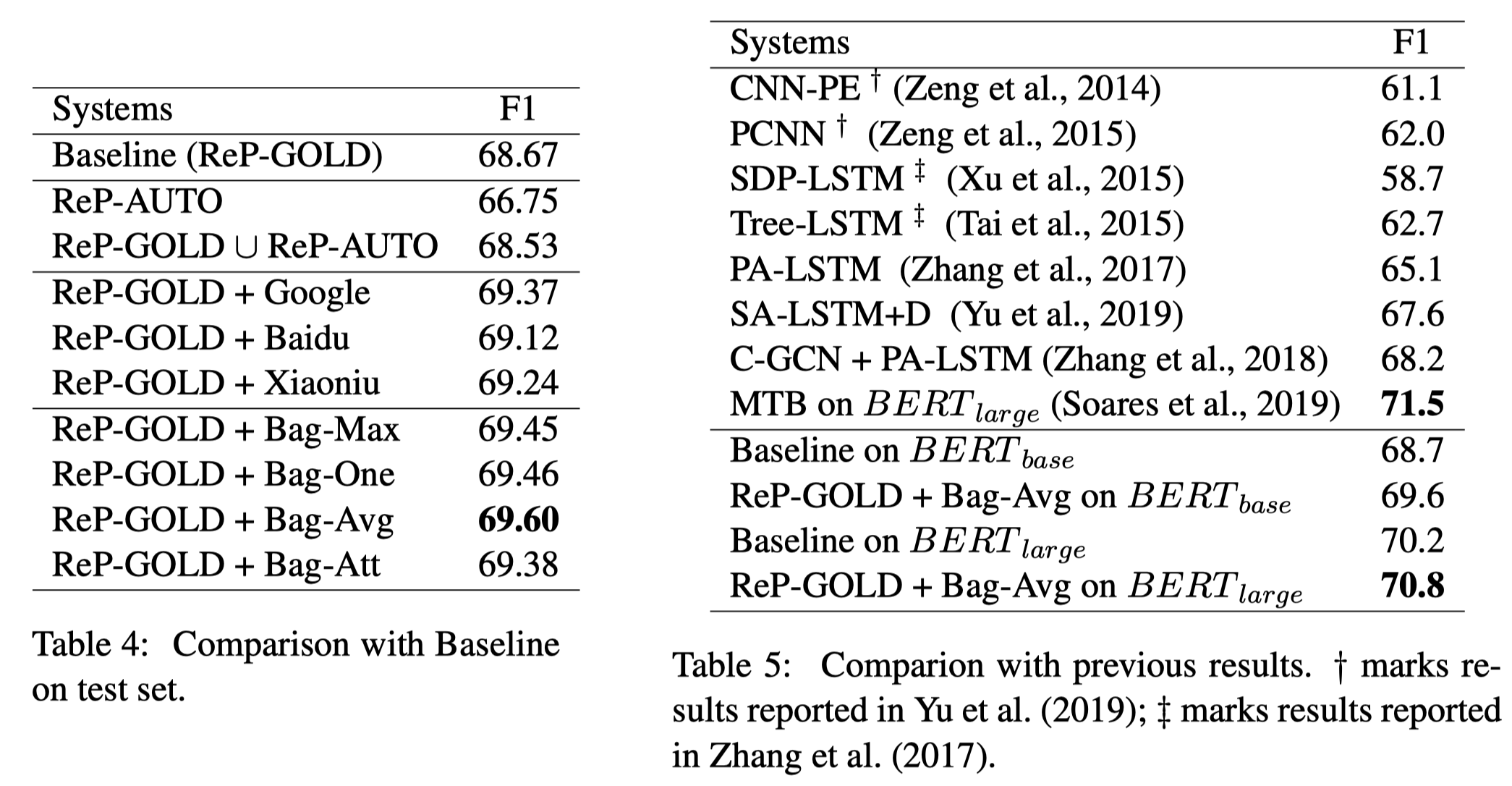
实验结果:
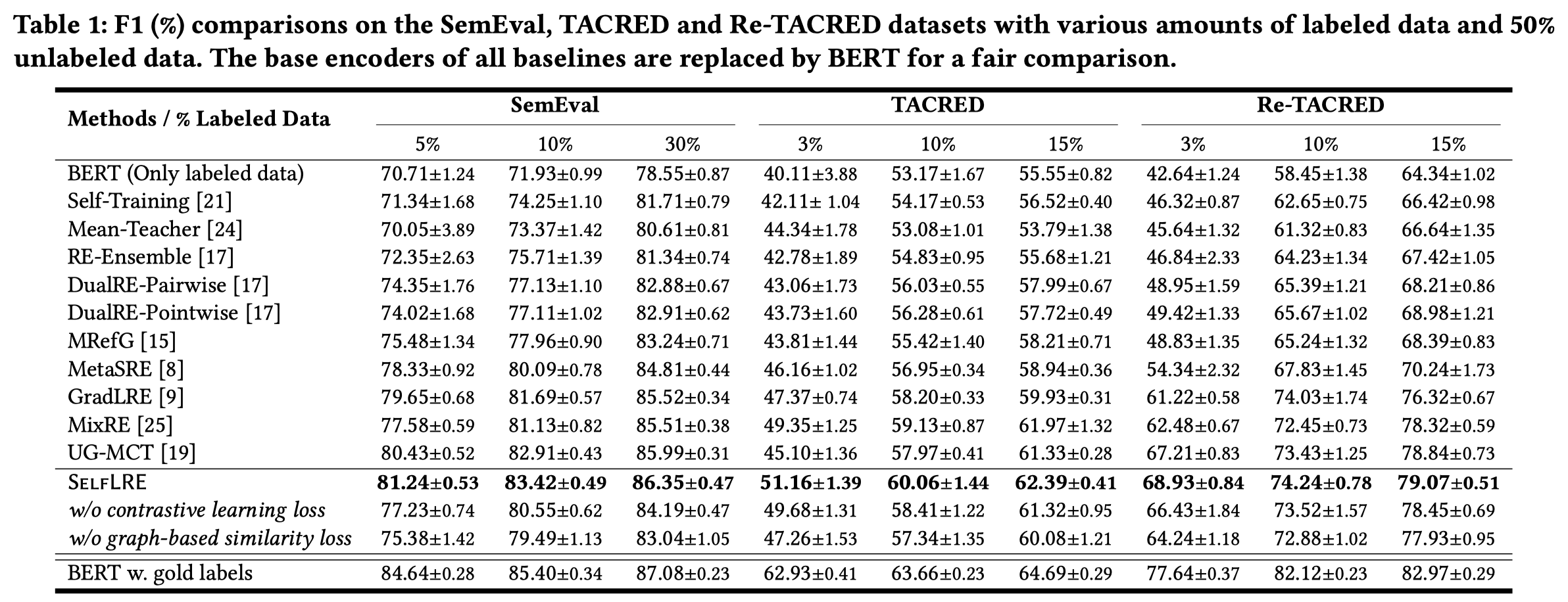
SelfLRE
SelfLRE: Self-refining Representation Learning for Low-resource Relation Extraction. SIGIR 2023. 清华. 代码.
Low-resource relation extraction (LRE) aims to extract potential relations from limited labeled corpus to handle the problem of scarcity of human annotations. Previous works mainly consist of two categories of methods: (1) Self-training methods, which improve themselves through the models’ predictions, thus suffering from confirmation bias when the predictions are wrong. (2) Self-ensembling methods, which learn task-agnostic representations, therefore, generally do not work well for specific tasks. In our work, we propose a novel LRE architecture named SelfLRE, which leverages two complementary modules, one module uses self-training to obtain pseudo-labels for unlabeled data, and the other module uses self-ensembling learning to obtain the taskagnostic representations, and leverages the existing pseudo-labels to refine the better task-specific representations on unlabeled data. The two models are jointly trained through multi-task learning to iteratively improve the effect of LRE task. Experiments on three public datasets show that SelfLRE achieves 1.81% performance gain over the SOTA baseline. Source code is available at: https://github.com/THU-BPM/SelfLRE.
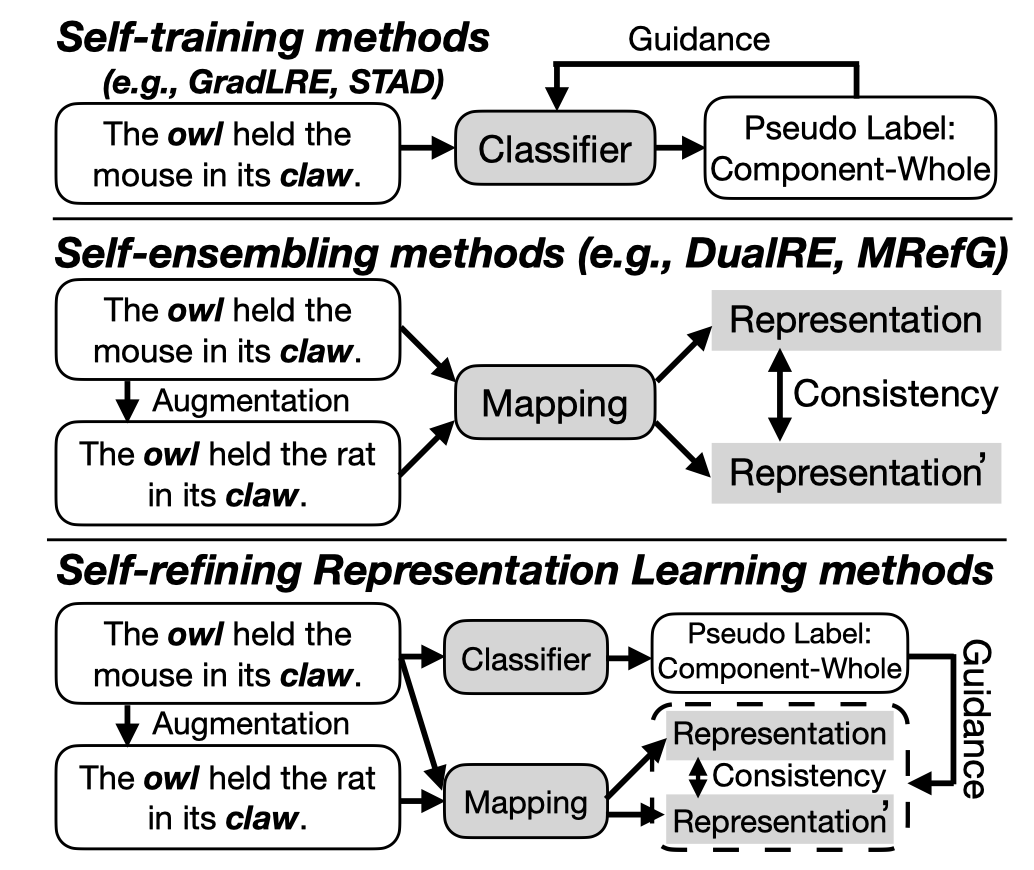
Issue:作者认为目前有两种利用unlabeled data解决LRE任务的方法:
- Self-training methods (e.g., Co-training [28], GradLRE [9], and STAD [27]) leverage the fine-tuned models to pseudo-label the unlabeled data, and adopt the pseudo-labeled data as the guidance to continue to optimize the model. However, these methods inevitably suffer from the confirmation bias when the pseudo labels are wrong. As incorrect pseudo-labeled data is continuously added to the labeled data for iterative training, the model will drift away from the local optimum.
- Self-ensembling methods (e.g., Mean Teacher [24], DualRE [17], and MRefG [16]) first adopt data augmentation methods to generate sentences with similar relational semantics, and leverages the fine-tuned mapping model to obtain representations of two sentences. However, these methods can only learn task-agnostic representations, while RE task-specific representations, such as relation labels, cannot be learned specifically.
这两种方法各有缺点。
Soluation:集成这两种方法,互补优缺点:
作者提出的SelfLRE方法,基于BERT,有两个head,classifier head分类relation,mapping head是个两层MLP用来映射从BERT中获得的relational representations。总体结构:
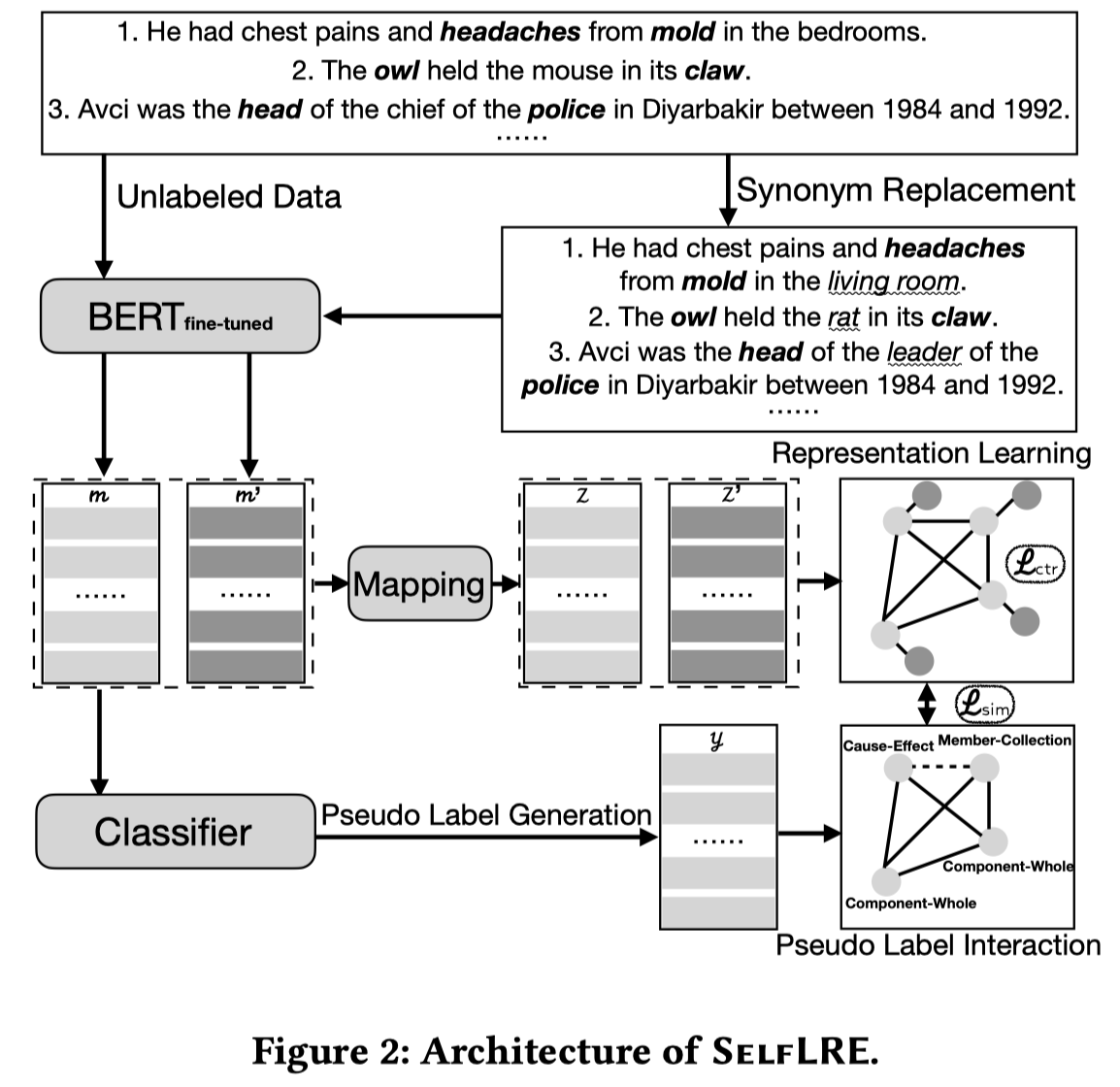
对于输入的句子,插入标记entities的特殊token,然后将头尾实体\([E1_{start}][E2_{start}]\)对应的embedding拼接,作为句子的relation representations \(\mathbf{m}\).
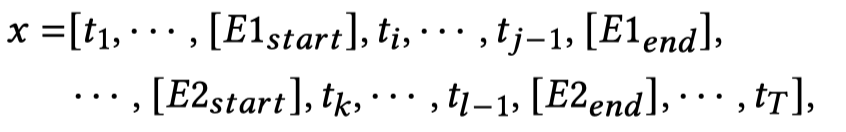
利用BERT可以给unlabeled data进行伪标注,然后作者表示pseudo-label graph,node是sample,edge是samples之间伪标注的相似度:
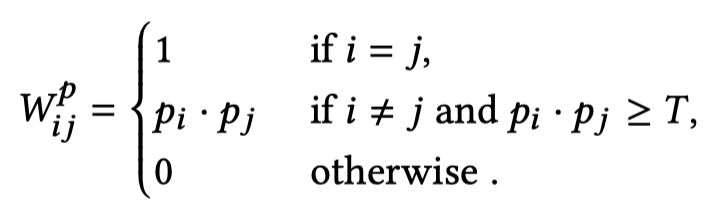
接下来,作者学习另一个embedding graph,通过随机除entities外的同义词替换获得新的句子。新的句子也可以通过BERT获得relation representation \(\mathbf{m}^\prime\)。然后\(\mathbf{m}\)和\(\mathbf{m}\)都经过mapping head获得新的表示\(\mathbf{e}\)。embedding graph的构造:
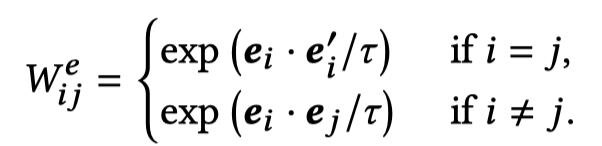
使用constrastive loss作为self-ensembling loss,优化embedding graph:
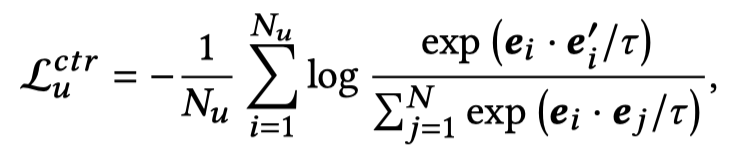
即让原始sentence relational embedding和同义词替换后的sentence relational embedding更加相近;和其它sentence relational embedding没有那么接近。
然后,作者利用pseudo-label graph去指导embedding graph:
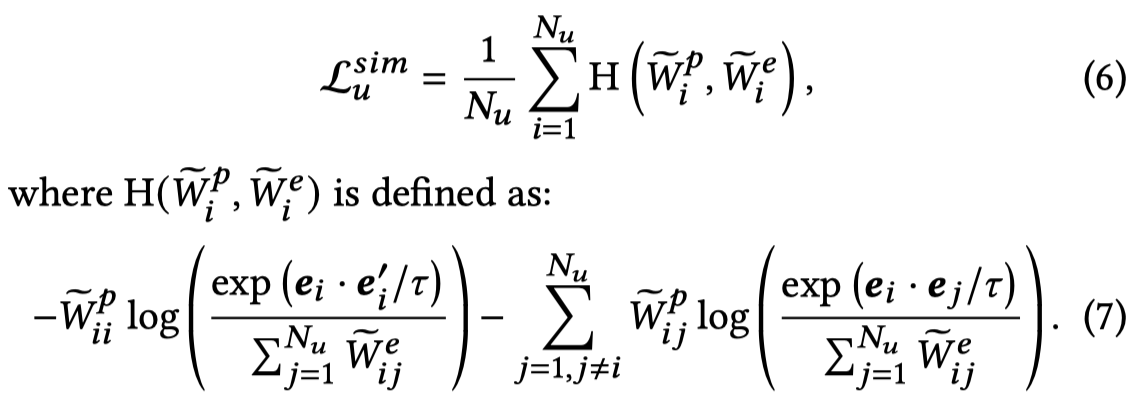
这个loss第一项,同样是让原始sentence relational embedding和同义词替换后的sentence relational embedding相近;第二项,是让有相似伪标注的sentences之间的relational embedding相近。
实验结果: