IE-Collection1
信息抽取论文调研集合1。
IE Papers
MetaNER
Learning In-context Learning for Named Entity Recognition,[详细博客]
ACL 2023,中科院,代码。
Named entity recognition in real-world applications suffers from the diversity of entity types, the emergence of new entity types, and the lack of high-quality annotations. To address the above problems, this paper proposes an in-context learning-based NER approach, which can effectively inject in-context NER ability into PLMs and recognize entities of novel types on-the-fly using only a few demonstrative instances. Specifically, we model PLMs as a meta-function \(λ\) instruction, demonstrations, text .M 1 , and a new entity extractor can be implicitly constructed by applying new instruction and demonstrations to PLMs, i.e., \((λ.M)(instruction, demonstrations) \rightarrow F\) where \(F\) will be a new entity extractor, i.e., \(F: text \rightarrow entities\). To inject the above in-context NER ability into PLMs, we propose a meta-function pre-training algorithm, which pre-trains PLMs by comparing the (instruction, demonstration)-initialized extractor with a surrogate golden extractor. Experimental results on 4 few-shot NER datasets show that our method can effectively inject in-context NER ability into PLMs and significantly outperforms the PLMs+fine-tuning counterparts.
作者提出了一种让小参数量的预训练语言模型学会针对NER任务的in-context learning的方法。
少次NER任务的出现就是为了解决实体类型多样、新实体类型和高质量标注缺乏的问题。现有的少次NER方法包括fine-tuning-based和metric-based methods。
- The main drawbacks of fine-tuning-based methods are that re-training is often expensive (especially for large-scale models) and new entity types cannot be addressed on-the-fly.
- Metric-based methods are limited to the matching architectures and are sensitive to domain shift since they do not fully explore the information of target domain.
因此作者提出了让PLM模型学会ICL,根据新出现的样例学会抽取新的实体类型。(这一问题事实上LLM已经学会了,不需要额外的训练。这篇论文的重点在于如何让小的模型学会针对特定任务的上下文学习能力)。
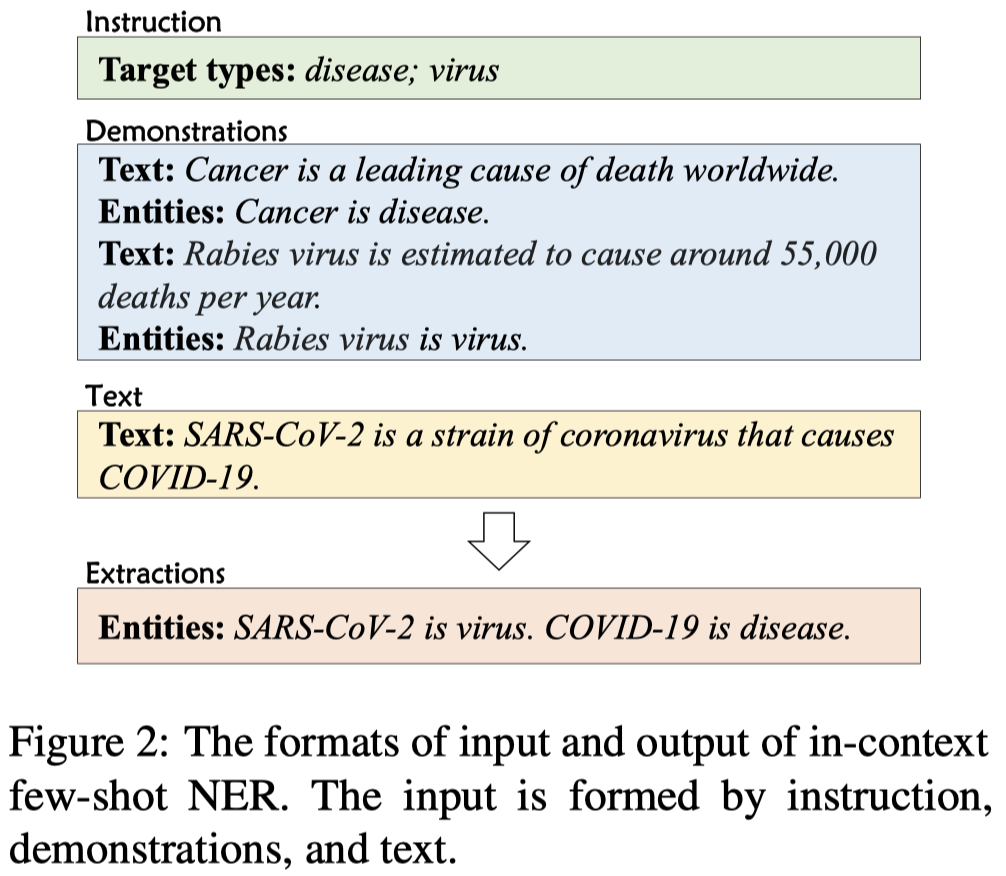
作者针对NER任务构造的ICL模板:
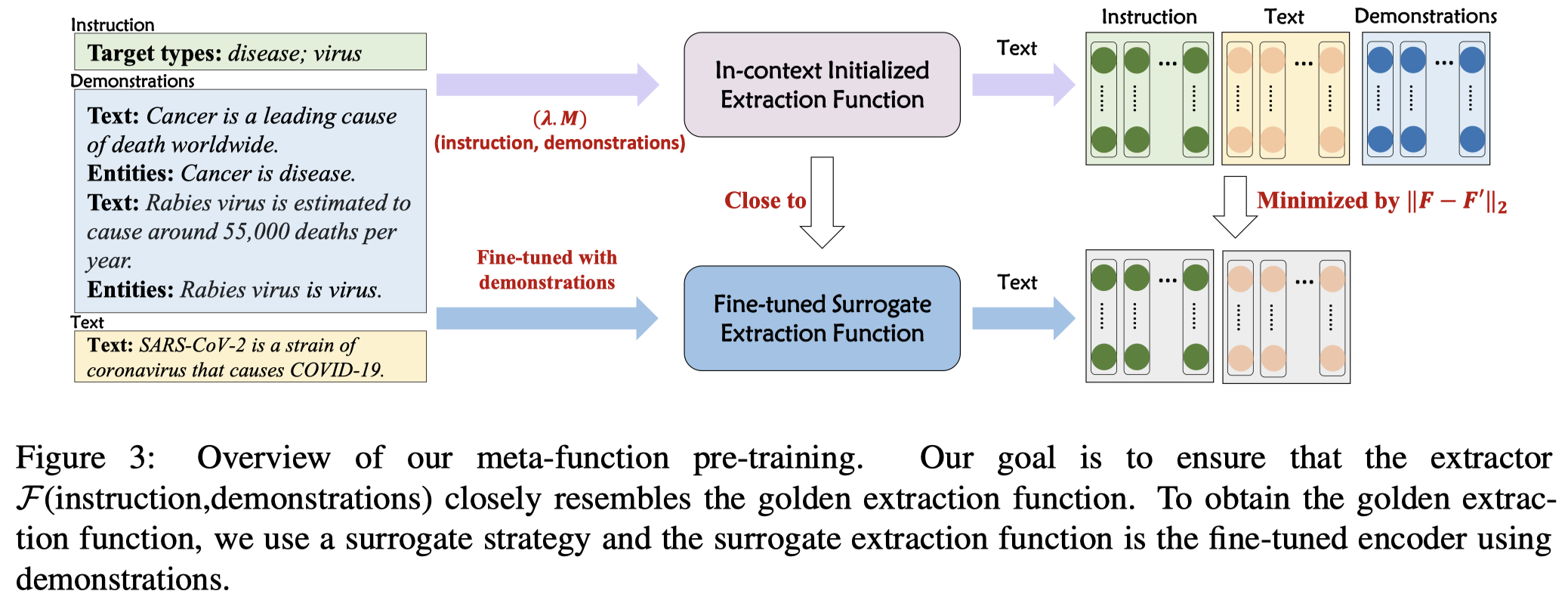
为了让PLM能够根据demonstrations学会抽取新的实体类型,作者提出了Meta-Function Pre-training for In-Context NER。
重点在于如何让PLM能够学会从demonstrations学习特征,然后能够抽取新的实体类型是重点。如果我们已知了理想的实体抽取函数,那我们只需要最小化PLM的上下文学习的输出和理想的实体抽取函数之间的差距即可。但是这样的理想函数并不存在。
因此,作者使用一个在demonstrations上进行参数更新的抽取模型作为替代(a surrogate extractor)。具体来说,在给定instruction \(I\), demonstration \(D\)和text \(T\)的情况下。先让PLM进行编码,获取到 \(I\), \(T\)的特征:
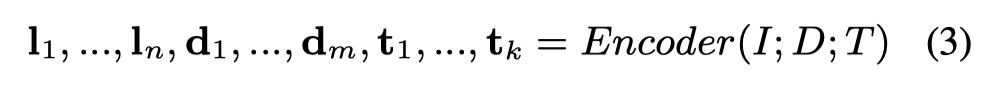
instruction \(I\)里包括了新的实体类型信息,text \(T\)包含了待抽取的文本信息。作者拿这两种feature去和一个经过了demonstrations训练后的模型,编码的特征靠拢:
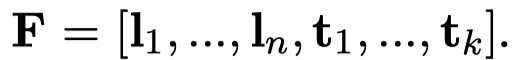
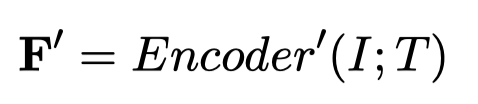

注意一下,这里的\(Encoder^\prime\)是拷贝了原来的encoder之后,进行梯度更新之后的编码器,不会影响原来的encoder。
仅仅是学习如何进行上下文学习是不够的,更重要的是我们要学会识别实体。因此作者还有一个loss是针对实体识别进行优化的。不过作者是用语言模型的loss来构造实体抽取的loss:
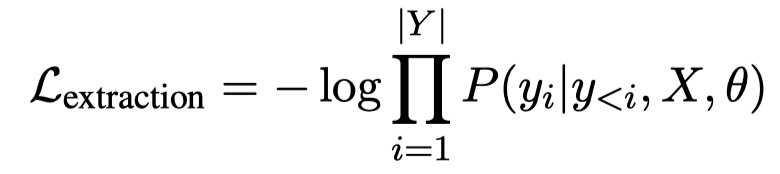
作者除了一般的信息抽取任务的形式,还提出了一种Pseudo Extraction Language Modeling Task。因为有实体标注的数据和没有实体标注数据之间的比例差距很大。因此作者想办法从一般的句子中也能够仿照NER任务构造出未标注来。比如:
instruction=Target types:<type2>;<type14>
demonstrations=Text: [MASK1] is cool and I really [MASK2] it [MASK3]. Entities: [MASK1] is <type2>. [MASK2] is <type14>(原来的句子I think this movie is cool and I really like it very much)
text=Text: I do not like it.
要预测的输出output是like is <type14>
将语言mask建模和span-based NER任务进行了统一。
实验部分:
预训练的数据是通过对齐Wikipedia和Wikidata进行构造的。
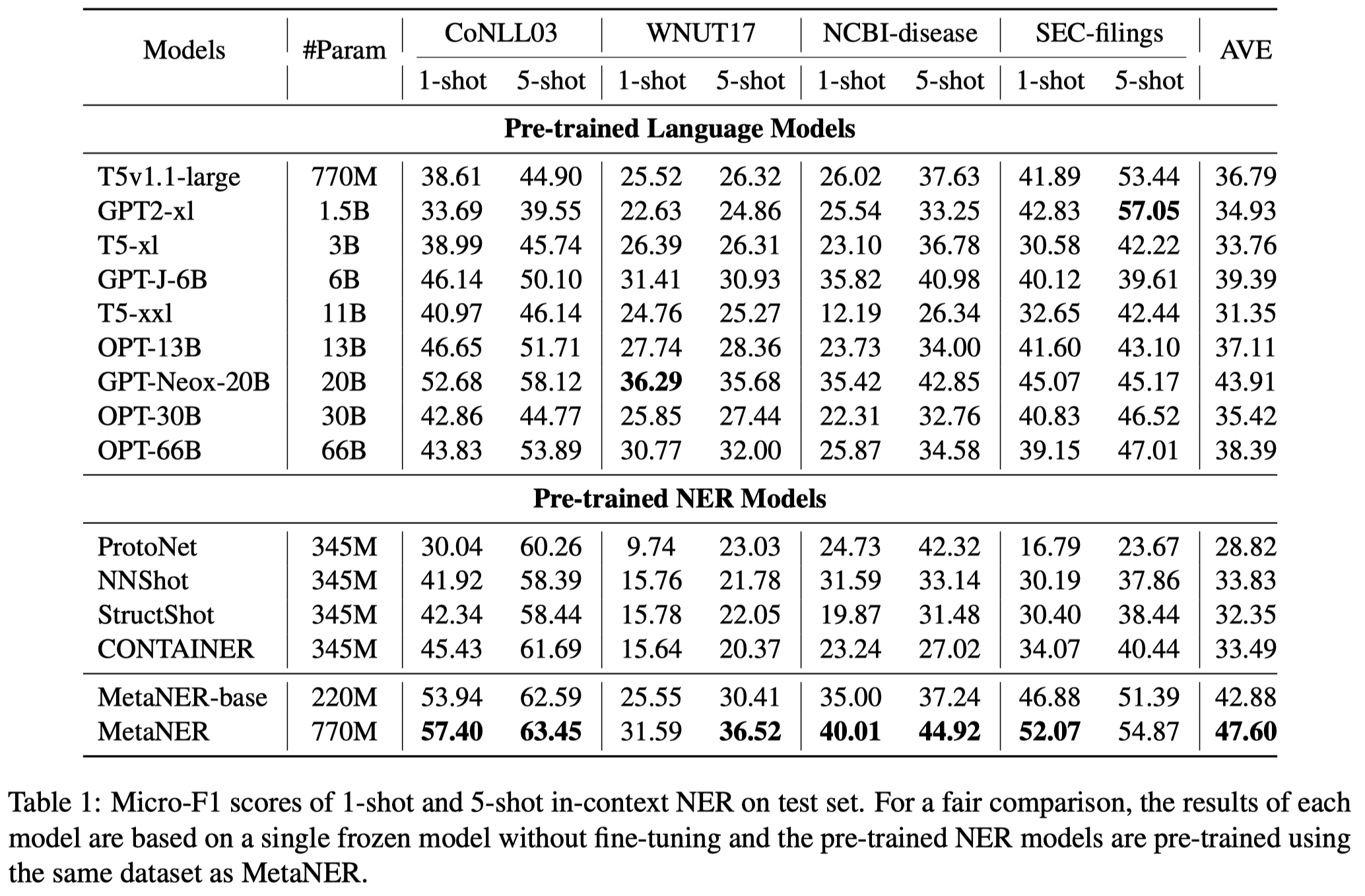
测试结果(没有在对应NER数据集上进行训练):
Demonstration-based NER
Good Examples Make A Faster Learner Simple Demonstration-based Learning for Low-resource NER [详细博客]
南加州大学,ACL 2022,代码。
Recent advances in prompt-based learning have shown strong results on few-shot text classification by using cloze-style templates. Similar attempts have been made on named entity recognition (NER) which manually design templates to predict entity types for every text span in a sentence. However, such methods may suffer from error propagation induced by entity span detection, high cost due to enumeration of all possible text spans, and omission of inter-dependencies among token labels in a sentence. Here we present a simple demonstration-based learning method for NER, which lets the input be prefaced by task demonstrations for in-context learning. We perform a systematic study on demonstration strategy regarding what to include (entity examples, with or without surrounding context), how to select the examples, and what templates to use. Results on in-domain learning and domain adaptation show that the model’s performance in low-resource settings can be largely improved with a suitable demonstration strategy (e.g., 4-17% improvement on 25 train instances). We also find that good demonstration can save many labeled examples and consistency in demonstration contributes to better performance.
作者试了几种为NER任务设计的demonstrations检索和对应的模板构造方法,只不过是在bert-base上进行的实验。
作者的方法图:
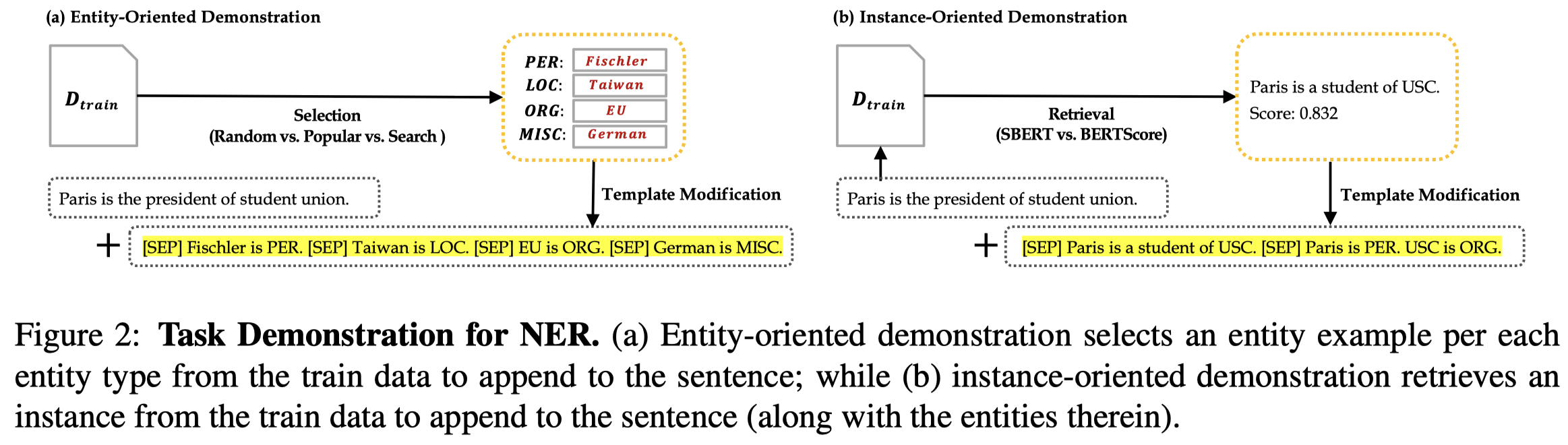
作者提了2种检索NER demonstrations的方法:
- Entity-oriented:就是以实体为核心进行检索,包括简单的3种方式:
- random:每一类entity type中,从训练集所有的对应实体进行检索(动态的)
- popular:每一类entity type中,选择出现次数最多top-k的对应实体(静态的)
- search:每一类entity type中,选择出现次数最多top-k的对应实体,grid search可能的实体组合,然后在验证集上找到效果最好的那种组合(静态的)
- Instance-oriented:以查询的当前句子为核心,进行检索,计算和其它训练集中句子的相似度,包括2种相似度计算方法:
- SBERT:计算两个句子编码后CLS token embedding的余弦相似度(动态的)
- BERTScore:两个句子不同token之间的相似度的和(动态的)
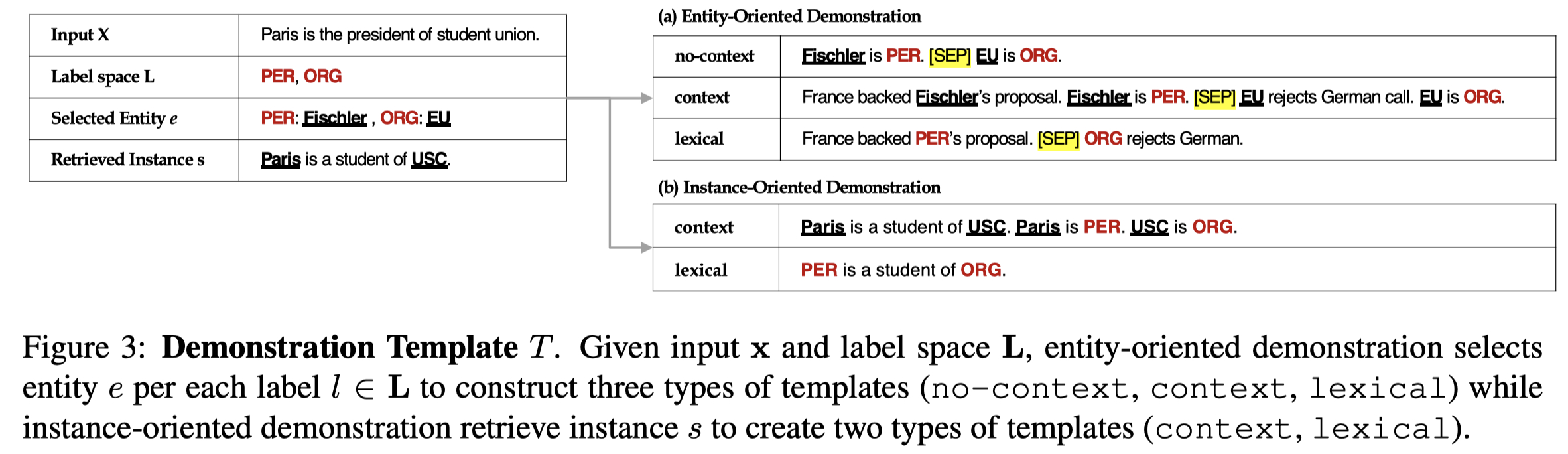
在找到了训练集中的demonstration之后,怎么样构造模板,作者提了3种方式:
- no-context:没有训练样例里面的句子,只保留实体,“entity is type."
- context:保留对应的句子,再加上“entity is type."的描述
- lexical:把原来句子中的entity替换为对应的entity type。这样获取能够直接捕获到不同label之间的对应关系
demonstration模板示例:
实验部分是基于bert-base-cased去做的。把找到的demonstrations拼接到要查询的query text前面,用bert编码以后的embedding过一个CRF,就得到了NER序列标注。
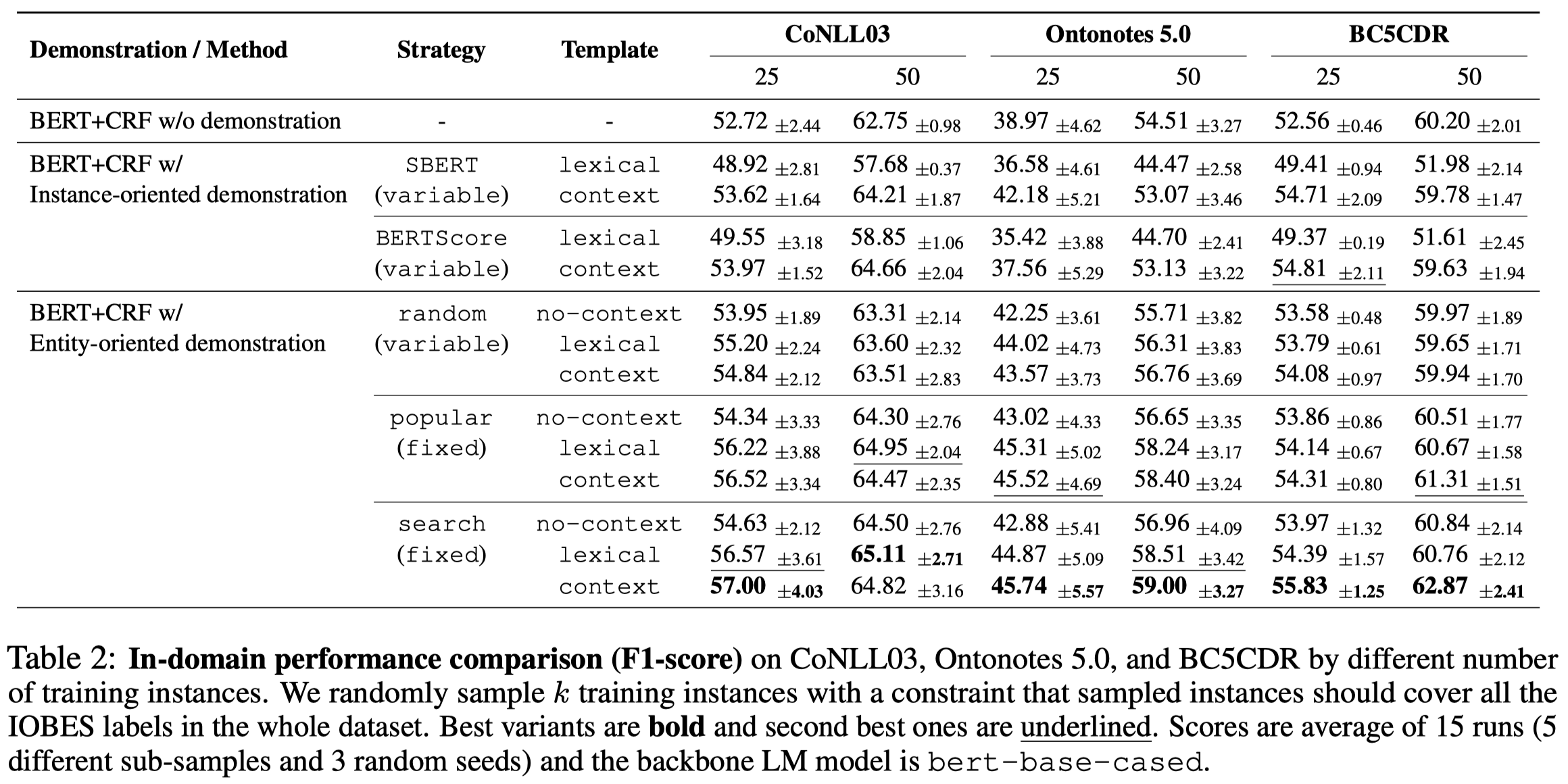
效果最好的,就是在验证集上进行评估,选择保留context。
PromptNER
PromptNER: Prompt Locating and Typing for Named Entity Recognition
ACL 2023,浙大,代码。
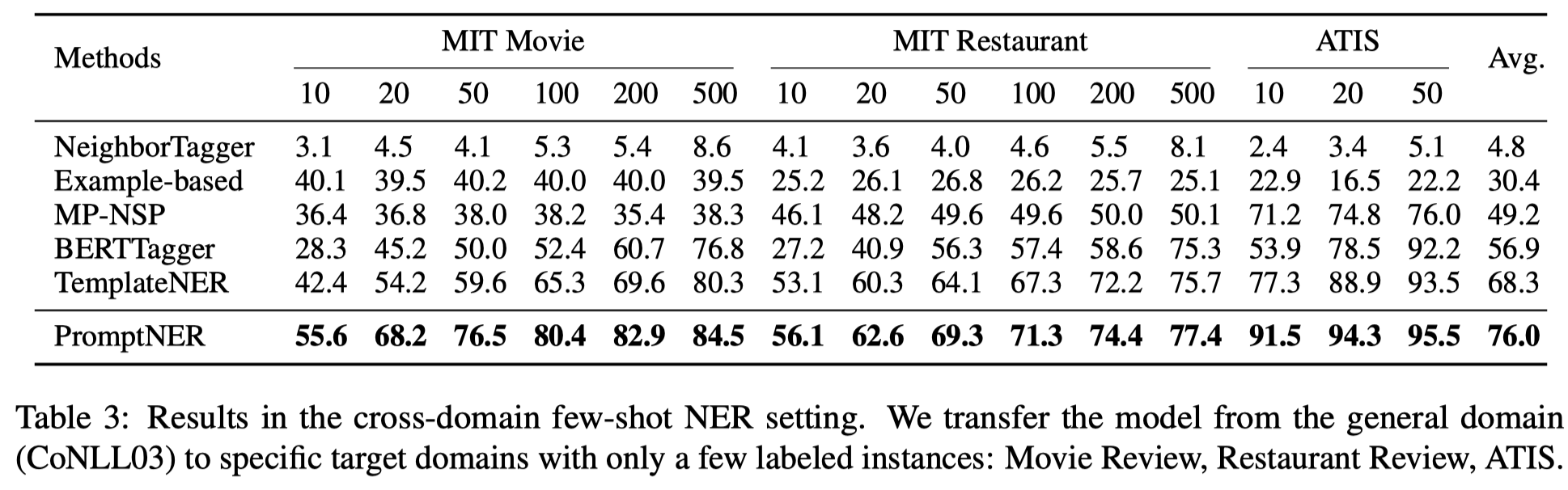
Prompt learning is a new paradigm for utilizing pre-trained language models and has achieved great success in many tasks. To adopt prompt learning in the NER task, two kinds of methods have been explored from a pair of symmetric perspectives, populating the template by enumerating spans to predict their entity types or constructing type-specific prompts to locate entities. However, these methods not only require a multi-round prompting manner with a high time overhead and computational cost, but also require elaborate prompt templates, that are difficult to apply in practical scenarios. In this paper, we unify entity locating and entity typing into prompt learning, and design a dual-slot multi-prompt template with the position slot and type slot to prompt locating and typing respectively. Multiple prompts can be input to the model simultaneously, and then the model extracts all entities by parallel predictions on the slots. To assign labels for the slots during training, we design a dynamic template filling mechanism that uses the extended bipartite graph matching between prompts and the ground-truth entities. We conduct experiments in various settings, including resource-rich flat and nested NER datasets and low-resource indomain and cross-domain datasets. Experimental results show that the proposed model achieves a significant performance improvement, especially in the cross-domain few-shot setting, which outperforms the state-of-the-art model by +7.7% on average.
这篇paper准确的讲不应该出现在cross-domain IE方向内。它只是在实验部分做了跨域IE的实验。
主要创新点在于作者期望能够一次性的用prompt的方法抽取出句子中包括的所有实体span和实体type。这样能够提高模型的速度。
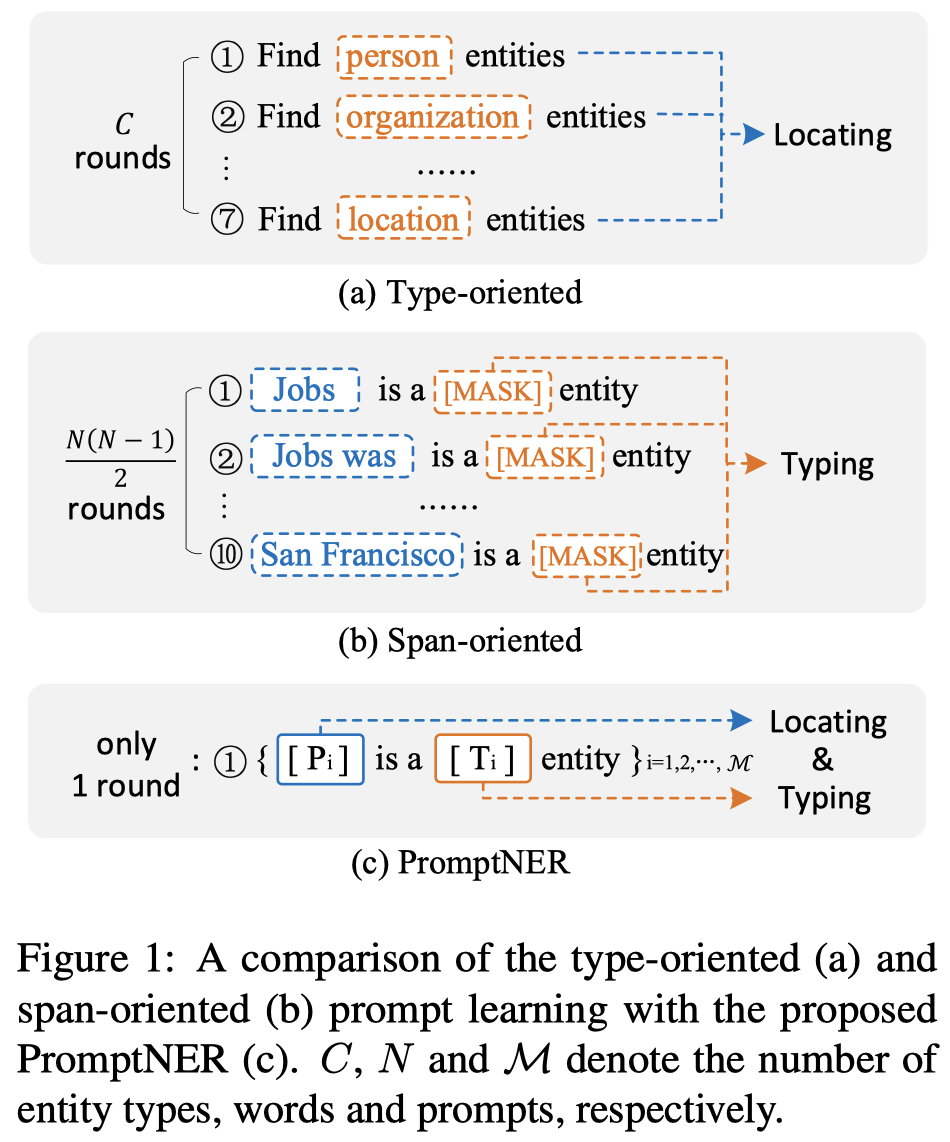
作者提出的方法:
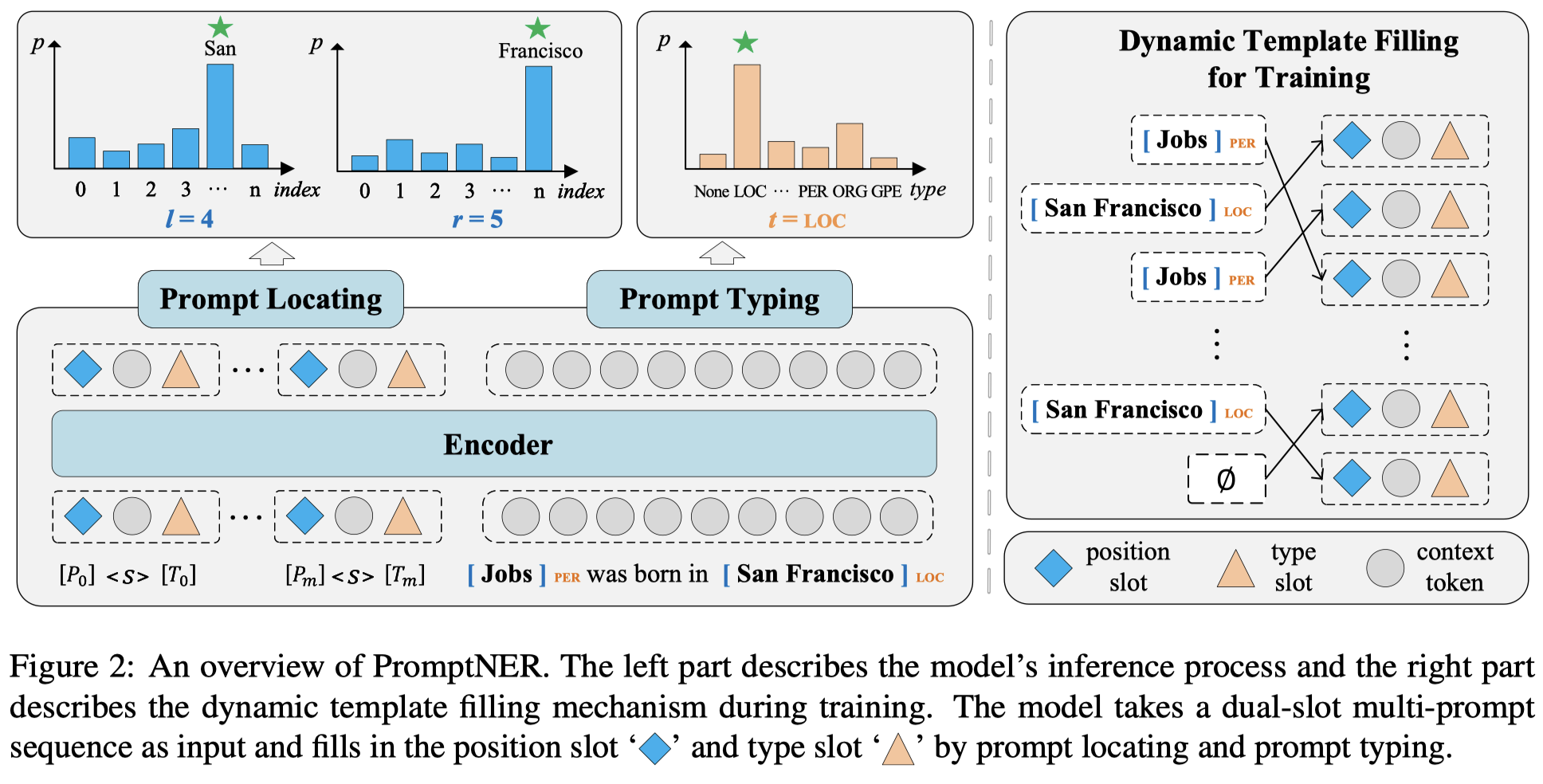
首先是提前构造\(M\)个prompt,实验中使用了\(M=50\)。所有的prompt里包括了一个position slot和type slot,最终和原始的句子一起输入到BERT中进行编码:
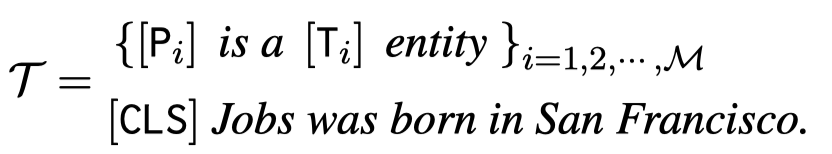
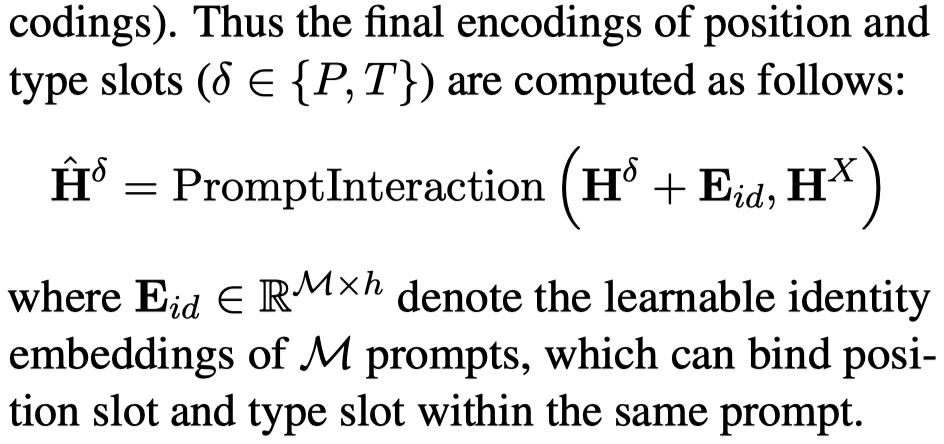
经过编码之后,作者还增加了一个不同prompt之间的interaction layer。即包括prompt之间的self-attention between slots with the same type,也包括从sentence to prompt slots的attention:
在进行解码阶段,不同prompt中的type slot的embedding直接拿出来进行softmax分类:

而position slot需要和不同位置的word embedding相加,然后判断是不是某个实体的左边界:
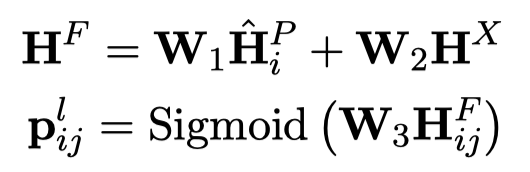
同样的可以获得右边界的预测值\(\mathbf{p}^r_{ij}\)。
现在我们要进行优化,那么就需要知道一个prompt输出的预测结果,真实期望是哪个entity,要不然无法优化。我们有很多个prompt,应该想一种办法对这些prompt的结果进行整合,最后和实际的entity对应上。
作者这里使用了一个bipartite graph matching的思路。就是期望那个最好的匹配结果,能够使prompts的预测结果和entities之间的cost最小:
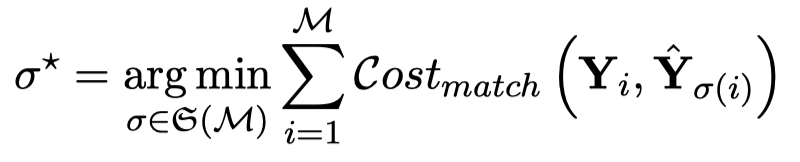
上面\(i\)是指\(i\)-th entity,\(\sigma(i)\)是指\(\sigma(i)\)-th prompt。\(Cost_{match}\)的定义如下,实际上就是让一个entity去和最倾向于预测它的prompt匹配,方便最后计算loss:
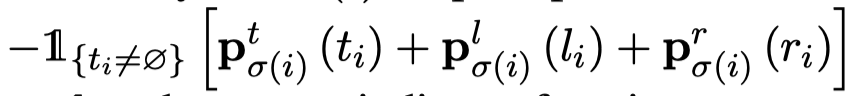
作者这里还提出了让一个entity能够和多个prompt匹配,具体做法就是重复多次相同的entity。作者使用Hungarian algorithm来求解最佳的匹配,然后计算loss:
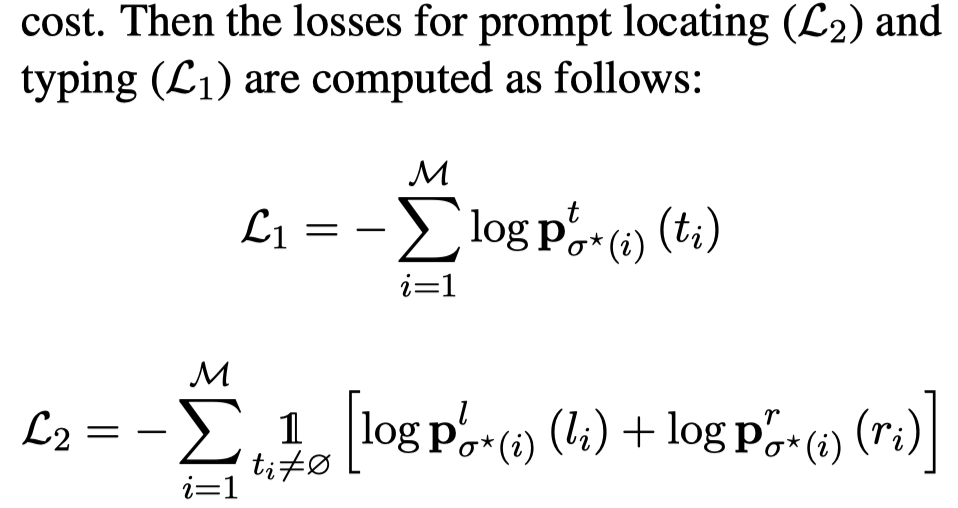
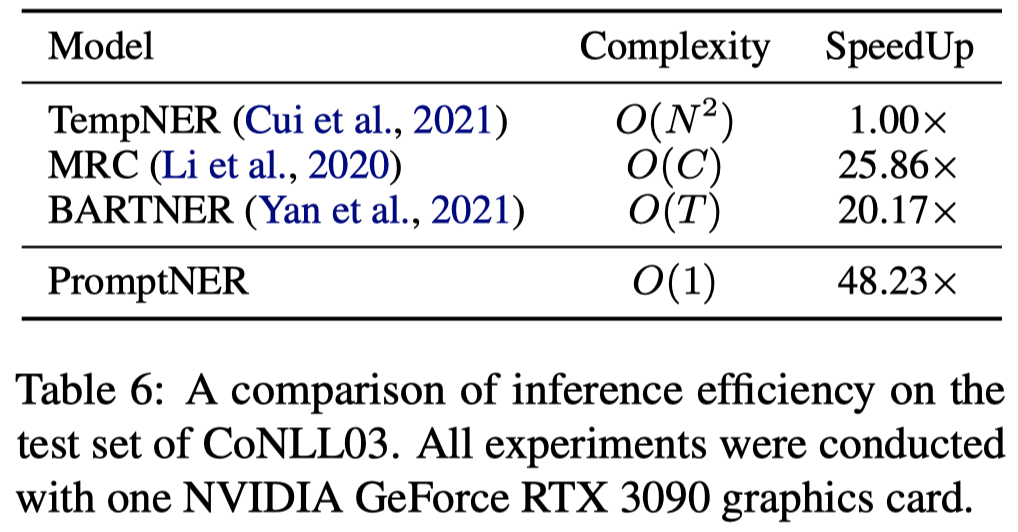
实验:
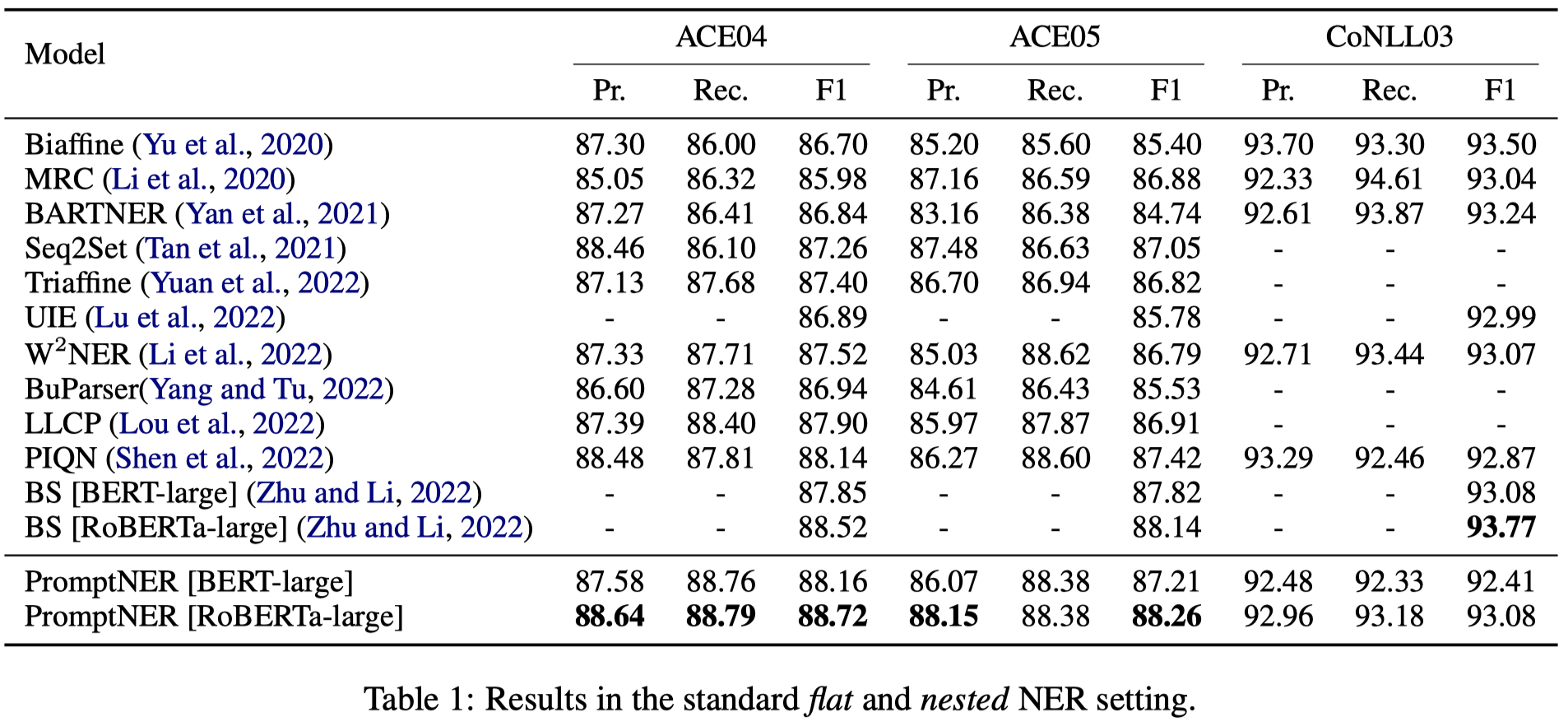
个人认为这篇工作更大的意义在于,可以一次性prompt可以快速抽取entity:
TemplateNER
Template-Based Named Entity Recognition Using BART
ACL 2021 Findings, 代码。
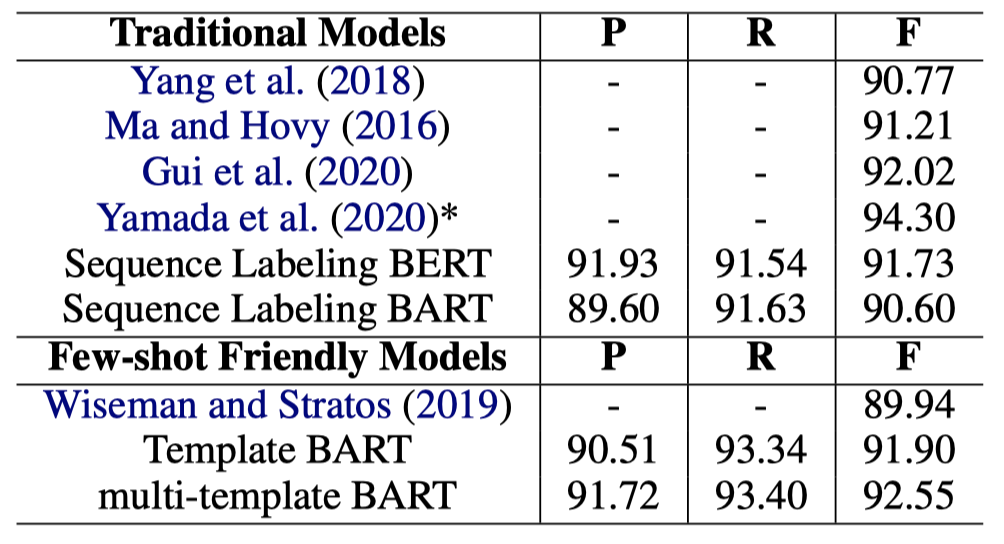
There is a recent interest in investigating fewshot NER, where the low-resource target domain has different label sets compared with a resource-rich source domain. Existing methods use a similarity-based metric. However, they cannot make full use of knowledge transfer in NER model parameters. To address the issue, we propose a template-based method for NER, treating NER as a language model ranking problem in a sequence-to-sequence framework, where original sentences and statement templates filled by candidate named entity span are regarded as the source sequence and the target sequence, respectively. For inference, the model is required to classify each candidate span based on the corresponding template scores. Our experiments demonstrate that the proposed method achieves 92.55% F1 score on the CoNLL03 (rich-resource task), and significantly better than fine-tuning BERT 10.88%, 15.34%, and 11.73% F1 score on the MIT Movie, the MIT Restaurant, and the ATIS (low-resource task), respectively.
首个把template-based的方法应用到NER的序列标注任务。作者提出这种方法一开始的出发点是期望从模型结构的角度能够更好的解决低资源NER任务。之前的利用CRF或者一个线性层的序列标注方法严格的限制了能够预测和匹配的标签范围,不同数据集下的标签不同,必须重新训练新的预测层。
作者提出的方法:
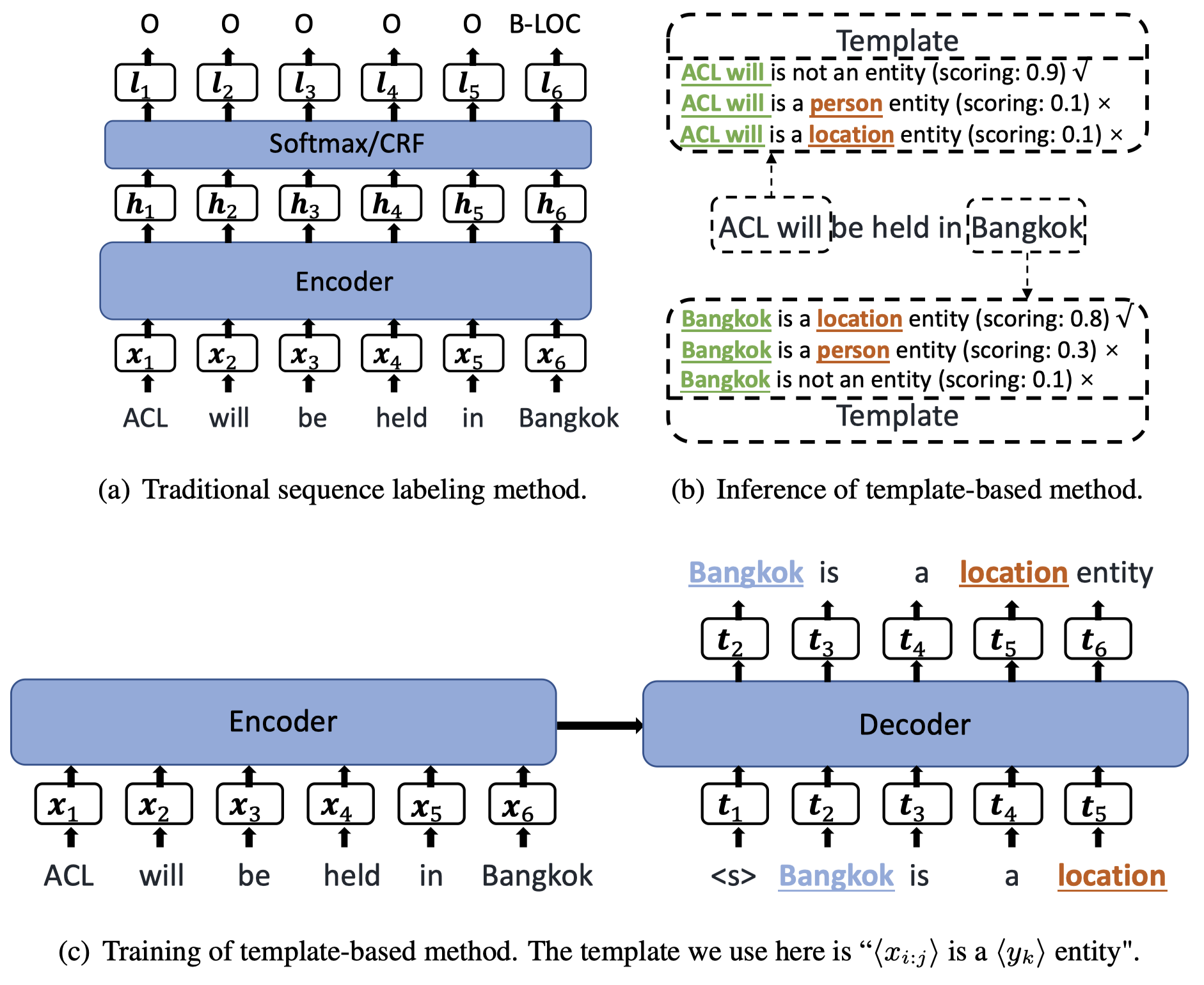
整体上是一个编码器+解码器的结构,编码器把整个句子进行编码,随后编码的embedding输入到解码器,和对应的查询prompt的编码进行对比计算。
核心是查询时候的prompt:
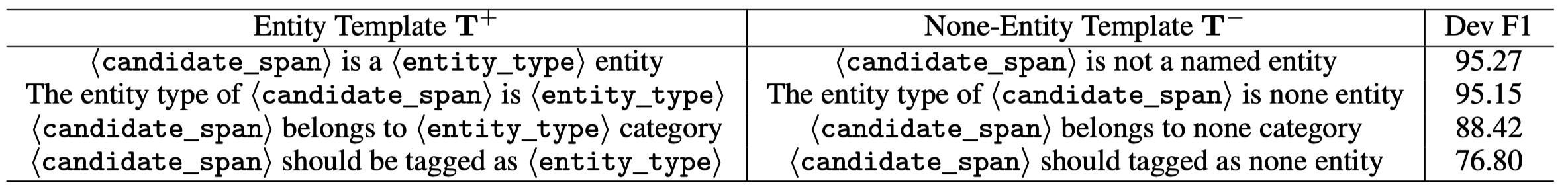
作者采用效果最好的第一种prompt。除此之前还有对应非实体的prompt template:
在推理的时候,对于长度为\(n\)的句子,可能的span数量是\(n(n-1)\),为了效率,作者设置一个span的最大长度为\(8\)。通过穷举span和对应的不同entity type,计算概率,然后排序。计算某个填充后的prompt是否成立的概率为:
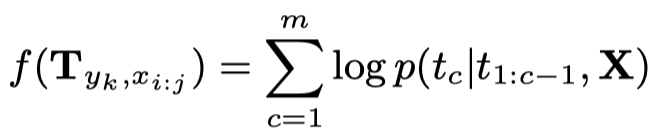
实现的时候基于BART:
实验结果:
UIE
Unified Structure Generation for Universal Information Extraction
中国信息处理实验室,百度,ACL 2022, 代码。
Information extraction suffers from its varying targets, heterogeneous structures, and demandspecific schemas. In this paper, we propose a unified text-to-structure generation framework, namely UIE, which can universally model different IE tasks, adaptively generate targeted structures, and collaboratively learn general IE abilities from different knowledge sources. Specifically, UIE uniformly encodes different extraction structures via a structured extraction language, adaptively generates target extractions via a schema-based prompt mechanism – structural schema instructor, and captures the common IE abilities via a large-scale pretrained text-to-structure model. Experiments show that UIE achieved the state-of-the-art performance on 4 IE tasks, 13 datasets, and on all supervised, low-resource, and few-shot settings for a wide range of entity, relation, event and sentiment extraction tasks and their unification. These results verified the effectiveness, universality, and transferability of UIE.
UIE的模型图:
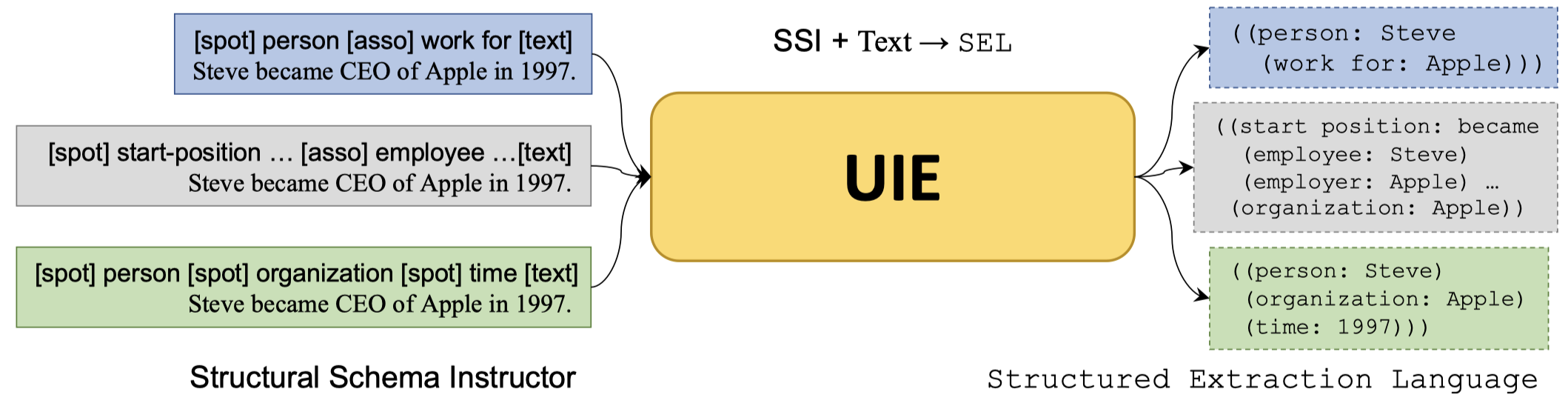
UIE从两个角度统一IE任务:
结构化信息的格式SEL:包括三个描述元素,Spot Name用来描述span的类型(Entity/Event Type);Asso Name用来描述和上级Spot关联的类型(Relation/Role Type);Info Span对应的在原始text中的文本(Entity mention/Argument mention/Trigger word);

统一的抽取prompt:指定要抽取的信息,通过加入特殊符号
[spot]+spot name,[asso]+Asso Name和[text]+source text指定要抽取的信息。可以参考上面的方法图示例。
UIE的训练包括两个阶段,一个是在大规模的抽取语料中进行预训练(这一部分参考原始论文);另一个是针对特定的任务进行快速的微调:
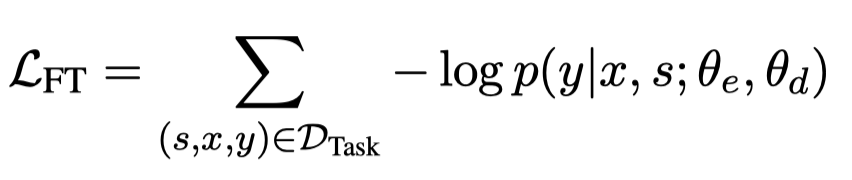
在微调阶段,有个需要特别注意的细节是,为了防止可能的exposure bias,作者引入了Rejection Mechanism。也就是说随机的插入负样例:(个人的理解就是让模型不要倾向于认为prompt中指定的要抽取的结构化信息是全部存在的,偏好给每一个要抽取的类型信息都要强制找到对应的span,而是能够学会判断各种结构化信息是否存在)
这一点在实验部分有非常大的影响,能够有12-13点左右的变化。
UIE基于T5,也是编码器+解码器的结构:
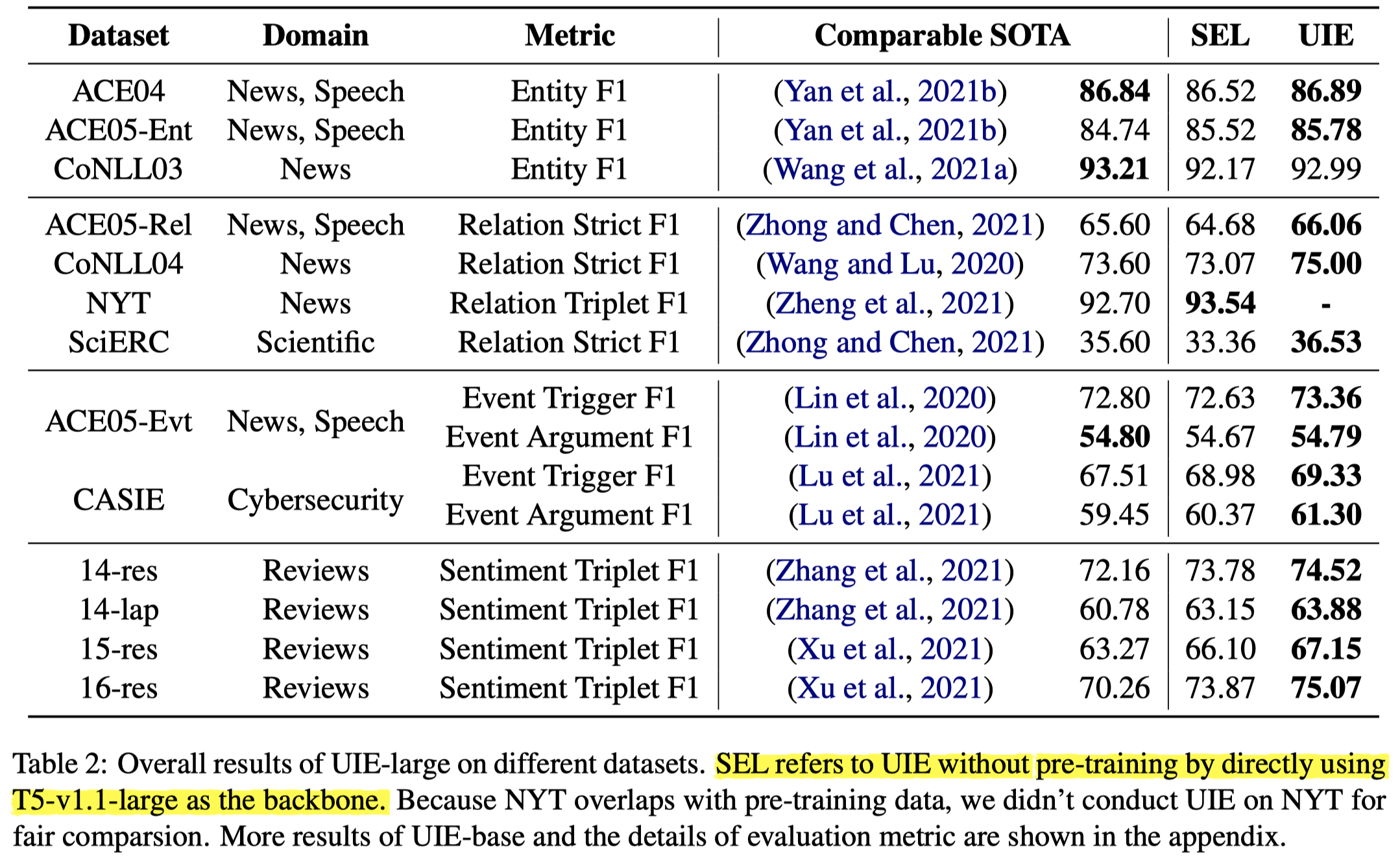
从实验结果来看,即使是不经过微调,直接在不同数据集上进行推理时的信息抽取(对应表格中的SEL列),也能够达到比较好的效果。
SuRE
Summarization as Indirect Supervision for Relation Extraction
EMNLP 2022,代码。
Relation extraction (RE) models have been challenged by their reliance on training data with expensive annotations. Considering that summarization tasks aim at acquiring concise expressions of synoptical information from the longer context, these tasks naturally align with the objective of RE, i.e., extracting a kind of synoptical information that describes the relation of entity mentions. We present SuRE, which converts RE into a summarization formulation. SuRE leads to more precise and resource-efficient RE based on indirect supervision from summarization tasks. To achieve this goal, we develop sentence and relation conversion techniques that essentially bridge the formulation of summarization and RE tasks. We also incorporate constraint decoding techniques with Trie scoring to further enhance summarization-based RE with robust inference. Experiments on three RE datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of SuRE in both full-dataset and low-resource settings, showing that summarization is a promising source of indirect supervision signals to improve RE models.
作者认为如果直接把RE任务看做是多分类任务的话有两个缺点:
- 缺少对实体之间关系语义的理解。因为关系被转化为了logits,仅仅是个分类的匹配标签,实际的关系语义信息没有被学习到。
- 非常依赖于足够的RE标注数据来提供direct supervision。而在少资源的情况下,效果下降非常严重。
因此作者将RE任务和Summarization task关联起来,引入了Summarization相关的和RE任务不是直接关联的监督信号。
方法图:
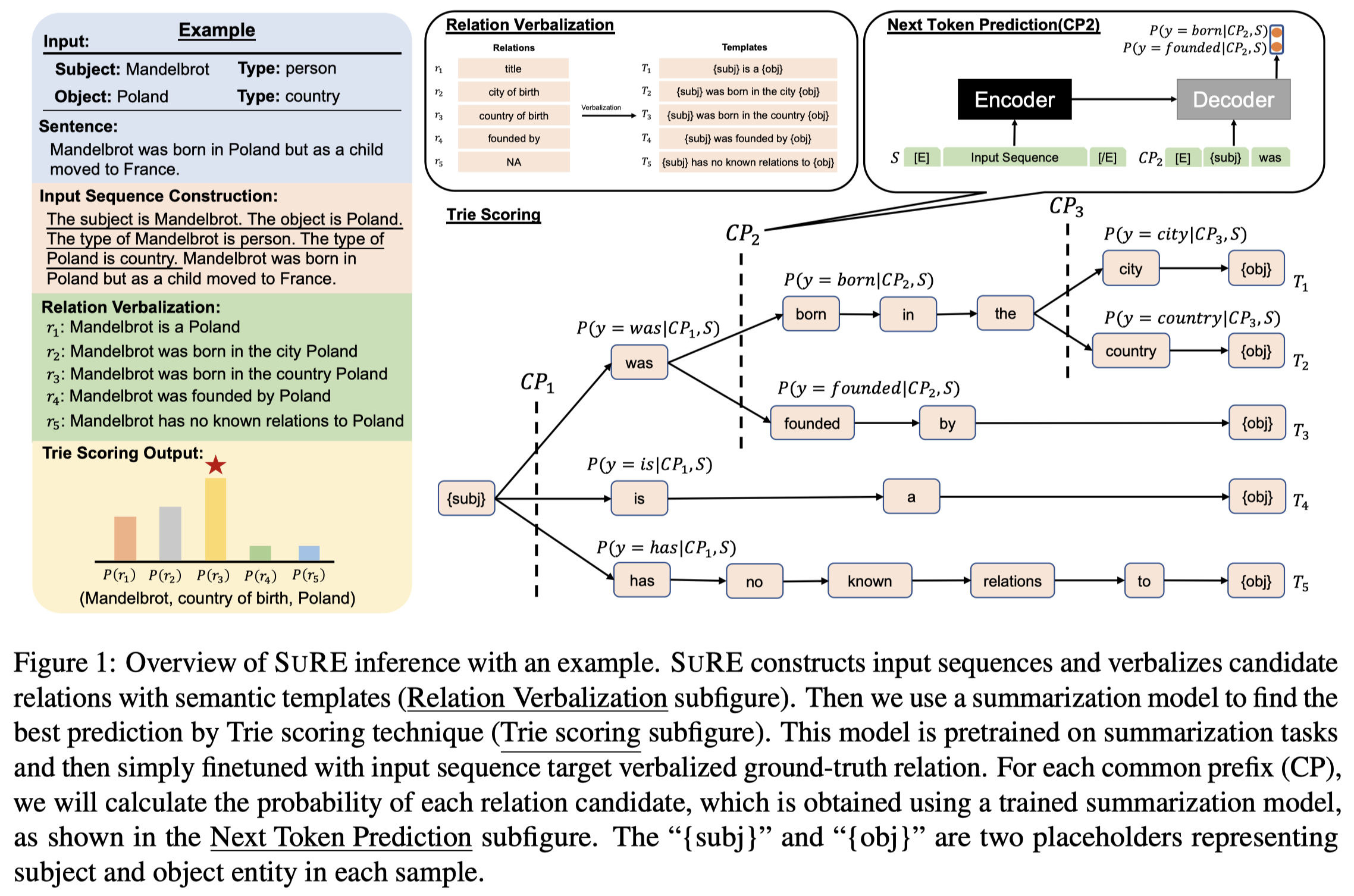
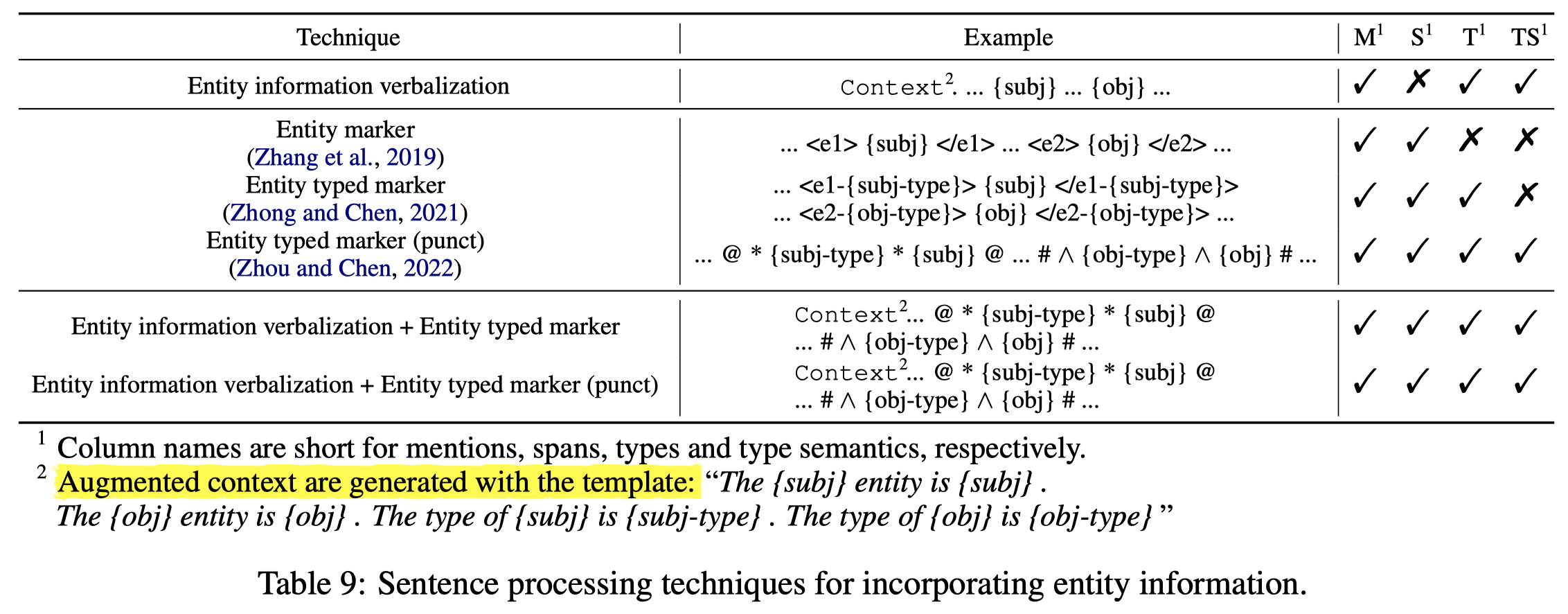
首先是如何处理输入的句子,能够进一步插入额外的实体信息,作者试验了两种方法:
Entity typed marker. 作者试了几种不同的标记方法,最终采用了下面的方法:

Entity information verbalization. 直接在句子前面加入实体信息的描述:

各种尝试的变化:
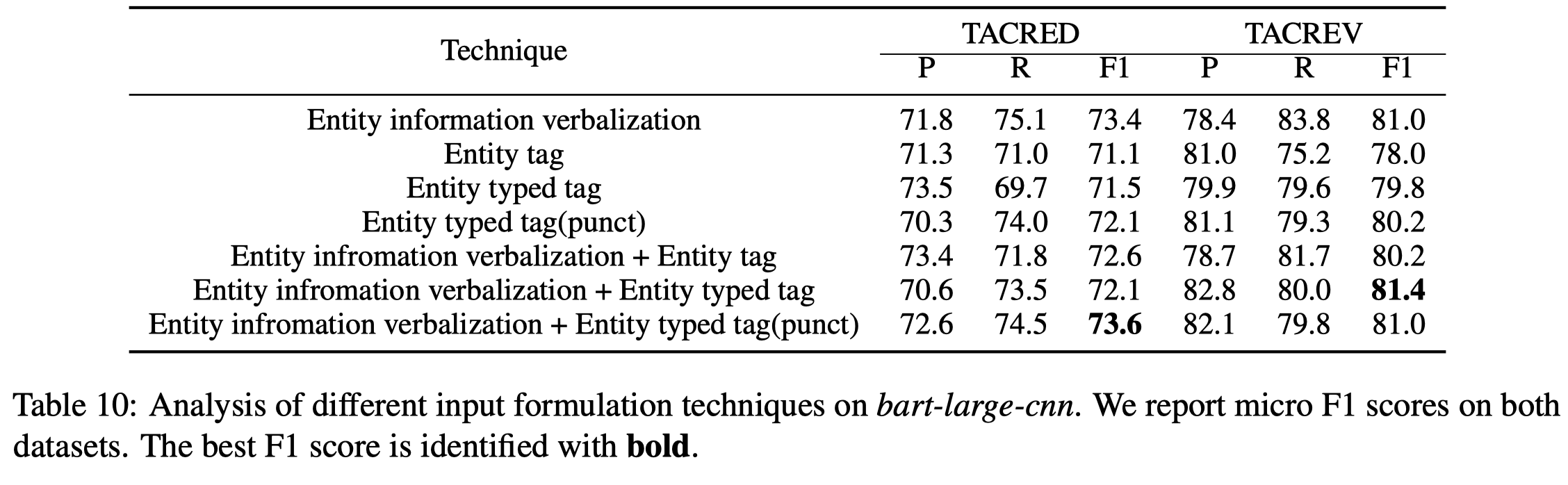
从实验效果来看,加入实体描述信息是有用的:
接下来的问题是怎么样描述relation,作者在前人的工作基础上,进行了微小的改动,获得了自己的模板:

作者在实现的时候,基于BART和Pegasus这两个已经在summarization相关数据上pre-train过的模型。然后在对应的RE数据集上按照sequence-to-sequence方法进行微调。
在推理阶段,作者将所有的relation template聚合在一起构造了一个Trie tree。通过在Trie树上计算每一个路径,得到最后的关系预测概率。编码器输入原始的句子,解码器不断输入对应的路径,具体可以参考方法图。
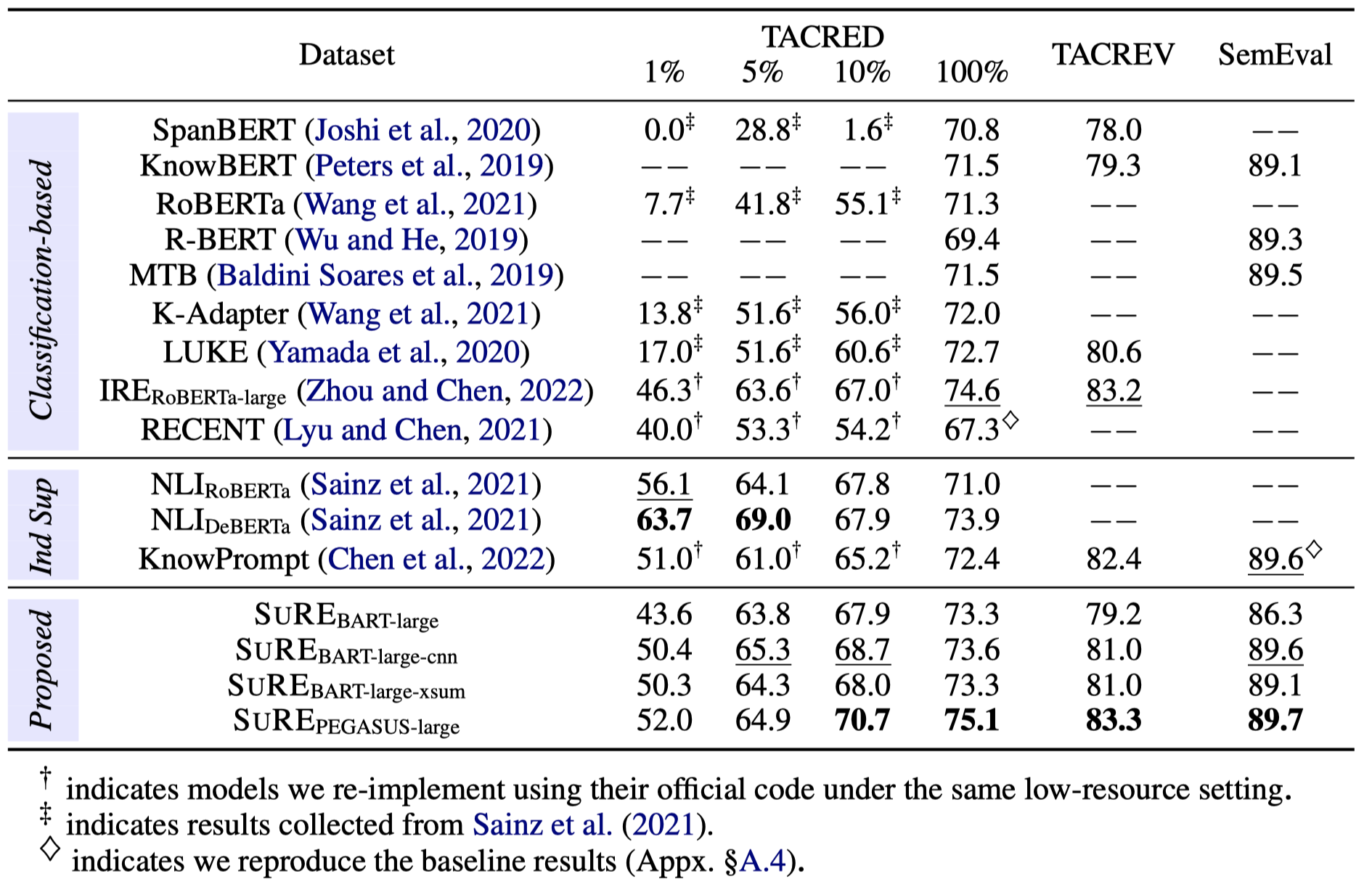
实验结果:
CLNER
Improving Named Entity Recognition by External Context Retrieving and Cooperative Learning
ACL 2021,Alibaba DAMO,代码。
Recent advances in Named Entity Recognition (NER) show that document-level contexts can significantly improve model performance. In many application scenarios, however, such contexts are not available. In this paper, we propose to find external contexts of a sentence by retrieving and selecting a set of semantically relevant texts through a search engine, with the original sentence as the query. We find empirically that the contextual representations computed on the retrieval-based input view, constructed through the concatenation of a sentence and its external contexts, can achieve significantly improved performance compared to the original input view based only on the sentence. Furthermore, we can improve the model performance of both input views by Cooperative Learning, a training method that encourages the two input views to produce similar contextual representations or output label distributions. Experiments show that our approach can achieve new state-of-the-art performance on 8 NER data sets across 5 domains.
这是一篇利用搜索引擎来为sentence-level NER任务寻找external context来提升性能的工作。
出发点是说在这篇工作前出现了用document-level contexts来作为外部知识提升NER性能的工作,但是很多情况下document-level contexts是没法获得的,比如social media domain。
方法:
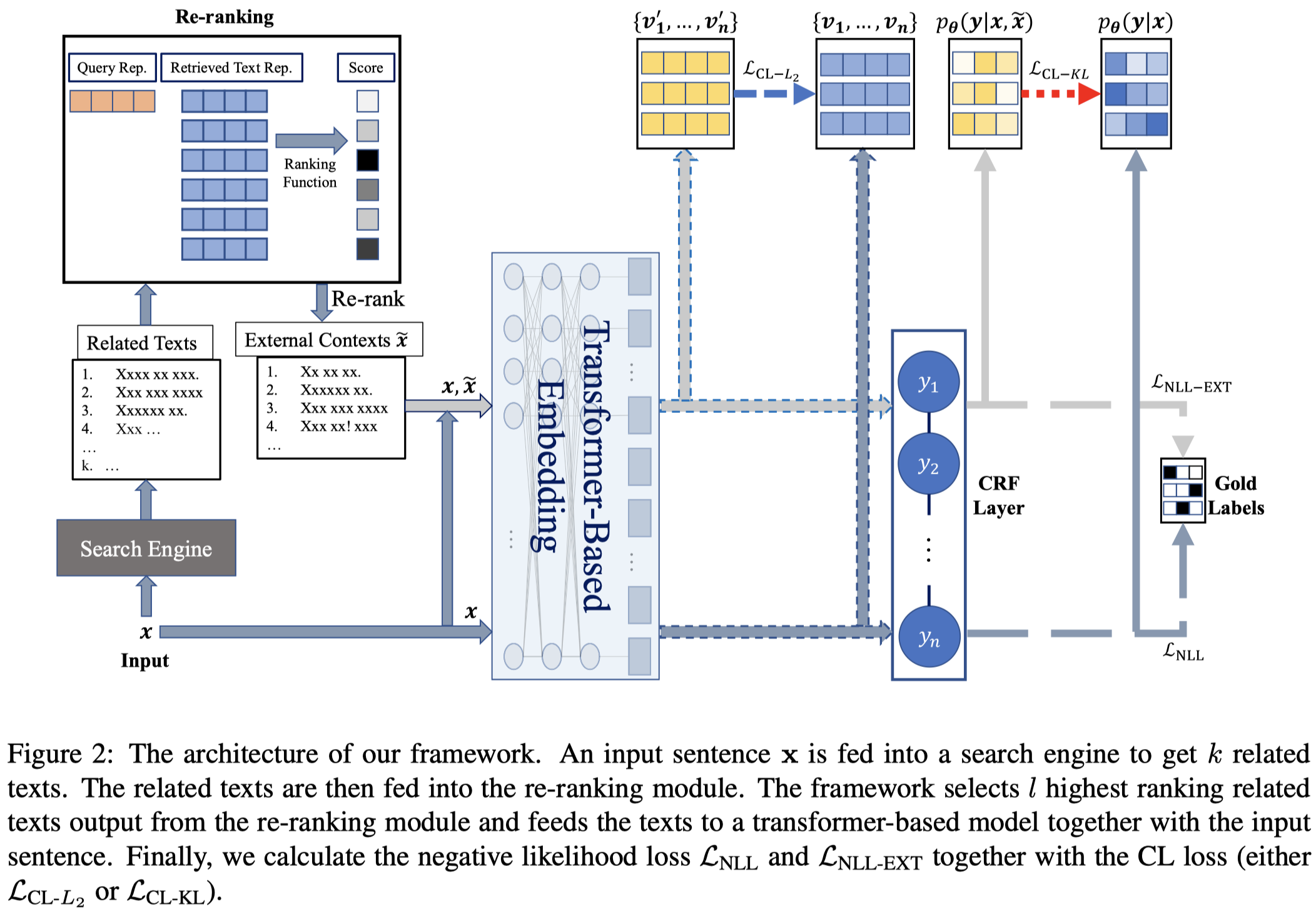
首先,作者利用Google search来寻找每个sentence的相关搜索结果。由于这个搜索结果可能是比较模糊的,还需要精排。因此作者用BERTScore(Roberta-Large based)来计算不同搜索结果和query之间的语义相似性。下面是计算Recall, Precision of BERTScore的公式:
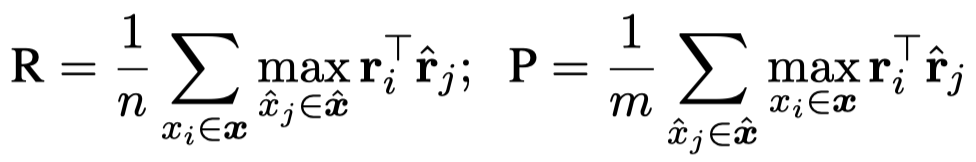
作者计算F1进行排序,取top-\(l\)的搜索结果以及对应的F1作为external context拼接到原始text上:
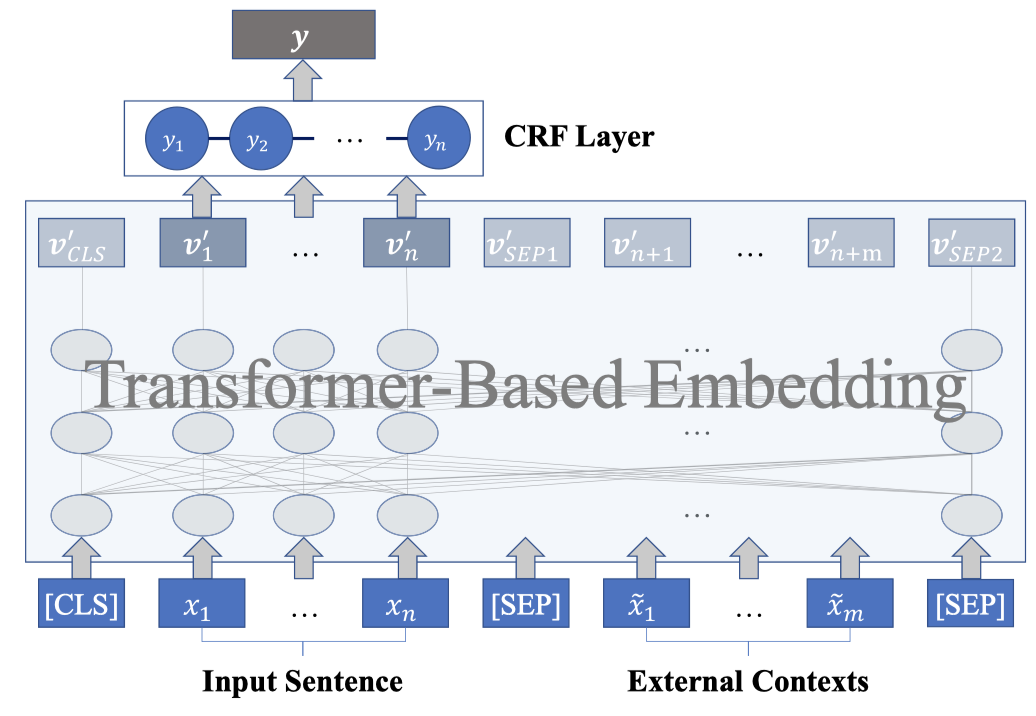
实现中如果要查询的句子太长,那么就按照标点符号拆分为不同的子句子,分别进行查询,然后汇聚结果。查询得到的结果首先要过滤掉可能包含了数据集内容的部分。最终保留最多\(l=6\)个查询结果作为外部上下文。
使用XLM-RoBERTa进行编码,除biomedical domain之外。
作者额外的考虑到有些情况下通过搜索引擎来寻找external context可能是不实际的,比如线上场景。在这种情况下,作者考虑使用Cooperative Learning来拉近retrieval-based input view和original input views without external contexts的差异:
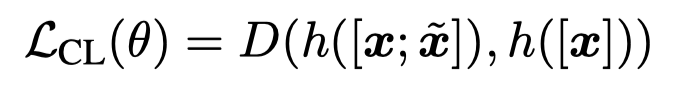
需要注意的是有external contexts的计算图,不会进行梯度传播。梯度只通过\(h([x])\)进行反向传播。
一个是用来\(L_2\) Norm拉近两种embedding的距离:
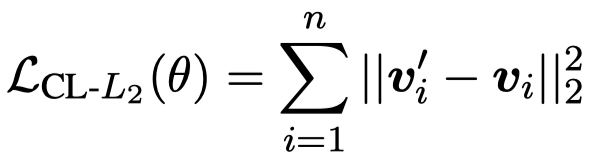
上面的\(v\)是指经过了Transformer,要输入到CRF层之前的embedding。
另一个是用KL散度拉近output distributions的差异:
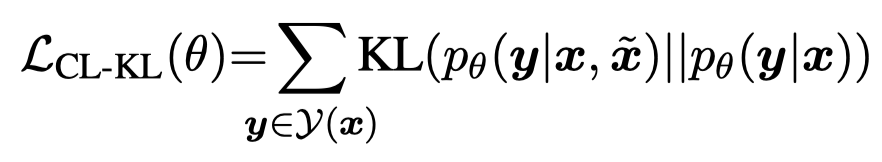
需要注意的一点是,由于使用了CRF作为decoder,上面的公式计算起来非常复杂(由于\(y\)的可能很多),作者通过独立计算每个位置上的\(y_i\)的概率\(q_i\)来估计上面的公式值:
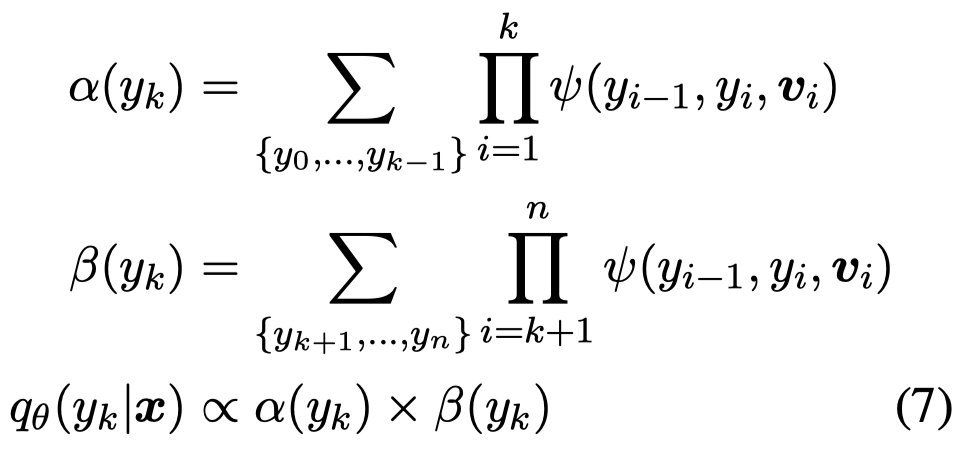
公式里的\(\psi(\cdot)\)函数是CRF中的potential function。最后计算公式:
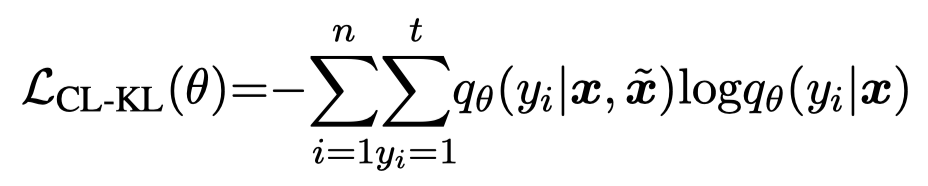
上面的公式思想不是作者第一个提出的,在之前的工作中有相关的论述 [Structural Knowledge Distillation: Tractably Distilling Information for Structured Predictor]。
实验结果:
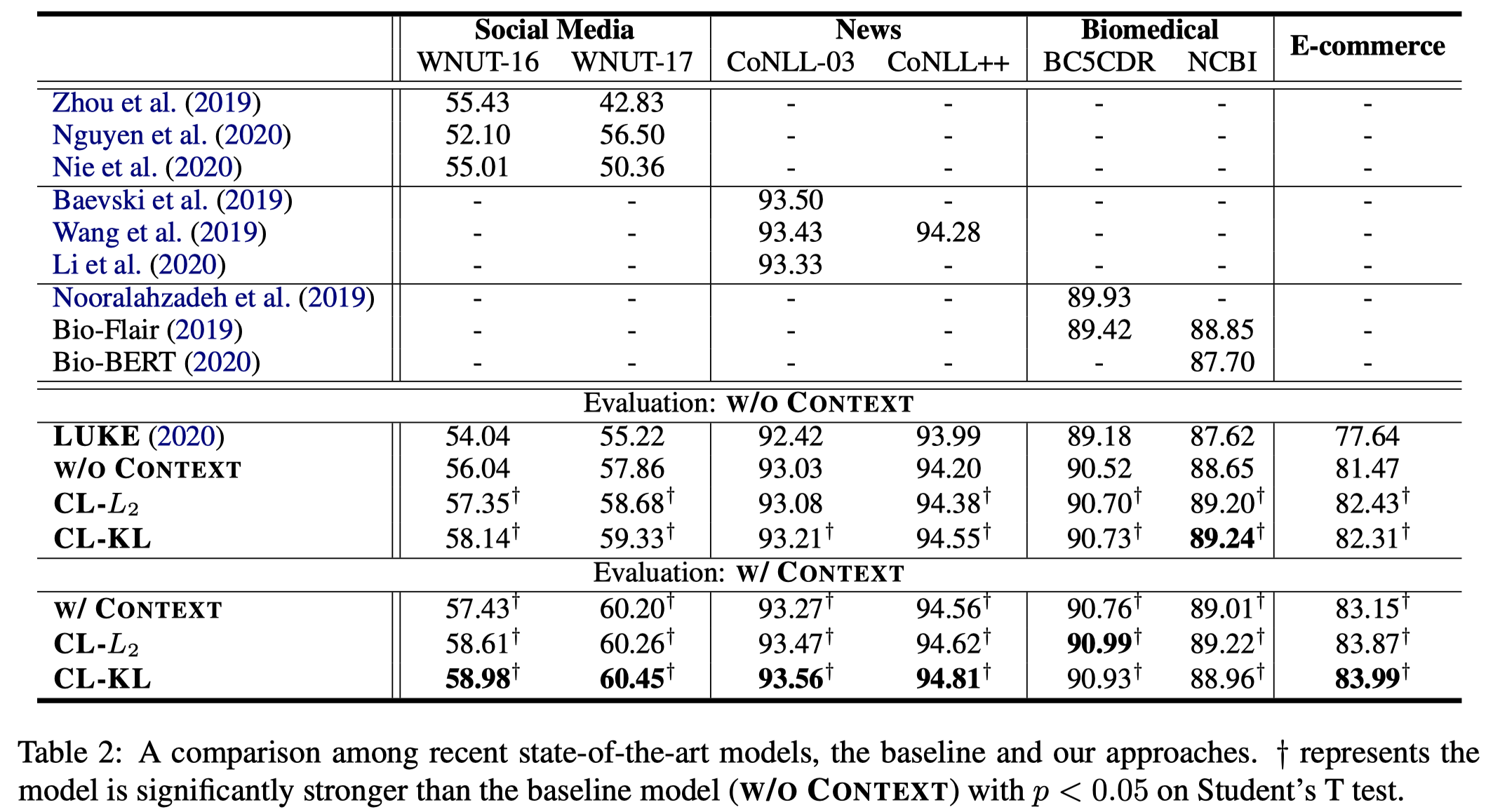
可以看到加入external context之后,不同数据集的提升幅度不一样。在social media domain上的提升幅度最大。在News和Biomedical domain上提升不是很显著。
LUKE
LUKE: Deep Contextualized Entity Representations with Entity-aware Self-attention
EMNLP 2020,日本Studio Ousia,代码。
Entity representations are useful in natural language tasks involving entities. In this paper, we propose new pretrained contextualized representations of words and entities based on the bidirectional transformer (Vaswani et al., 2017). The proposed model treats words and entities in a given text as independent tokens, and outputs contextualized representations of them. Our model is trained using a new pretraining task based on the masked language model of BERT (Devlin et al., 2019). The task involves predicting randomly masked words and entities in a large entity-annotated corpus retrieved from Wikipedia. We also propose an entity-aware self-attention mechanism that is an extension of the self-attention mechanism of the transformer, and considers the types of tokens (words or entities) when computing attention scores. The proposed model achieves impressive empirical performance on a wide range of entity-related tasks. In particular, it obtains state-of-the-art results on five well-known datasets: Open Entity (entity typing), TACRED (relation classification), CoNLL-2003 (named entity recognition), ReCoRD (cloze-style question answering), and SQuAD 1.1 (extractive question answering). Our source code and pretrained representations are available at https://github.com/studio-ousia/luke.
预训练+微调的例子,不仅仅是IE任务,作者还测试了QA等其它任务。
主要目的是为了在预训练的过程中,让模型能够学会对entity信息的建模。BERT的mask建模方式是针对单个token的,而一个entity有很多token组成。单纯的self-attention可能无法准确的推断不同entity之间的关系。
方法:
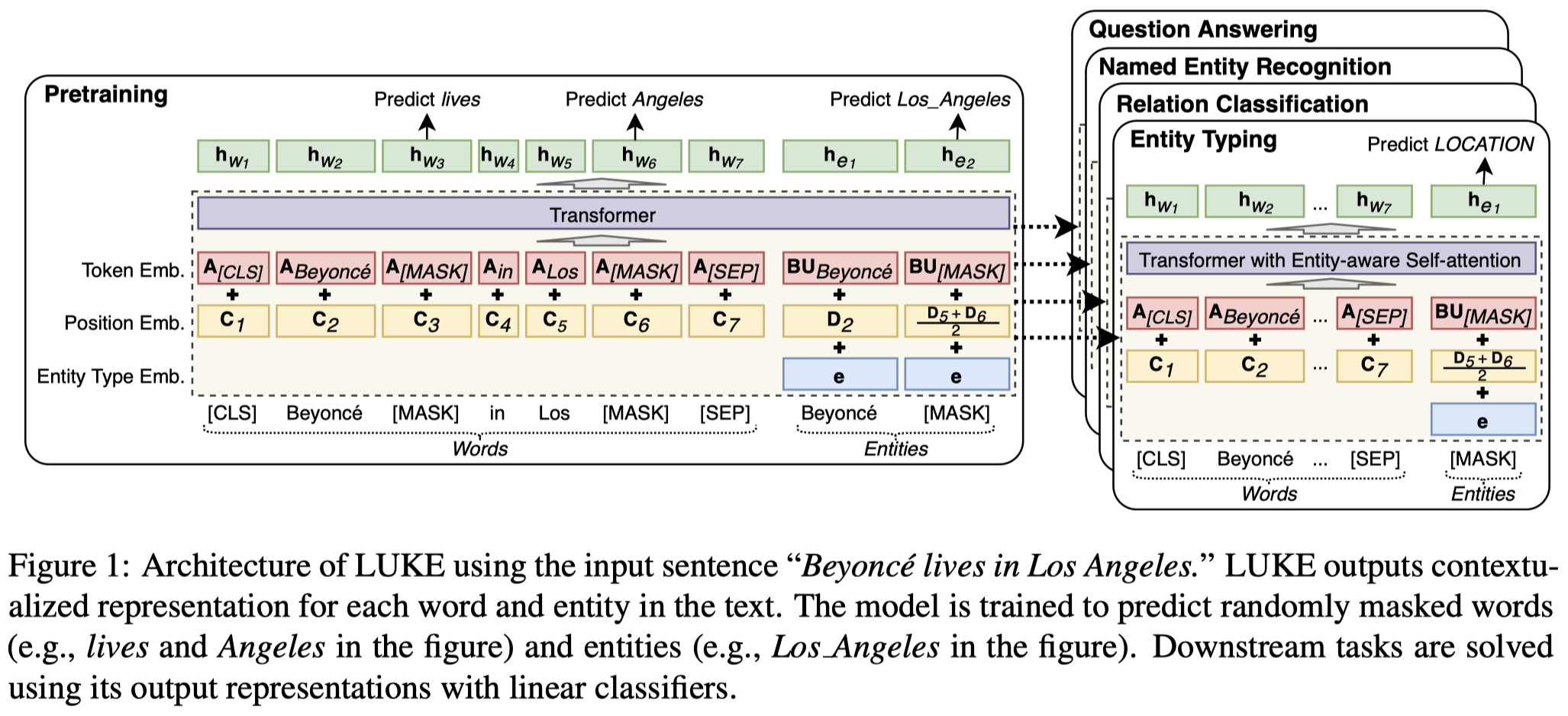
针对entity进行的预训练过程的优化:
除去token有自己的embedding matrix \(A\)之外,每个entity也有自己独立的embedding。为了减小entity embedding matrix 的参数量,使用了秩分解分为两个小的matrix \(B\times U\)。
token有自己的position embedding,entity也有自己的position embedding。
entity还额外加入了一个表示embedding是entity而不是token的type embedding \(\mathbf{e}\)。
在self-attention中,作者提出了一个Entity-aware Self-attention,就是根据embedding的类型,有不同的query matrix:
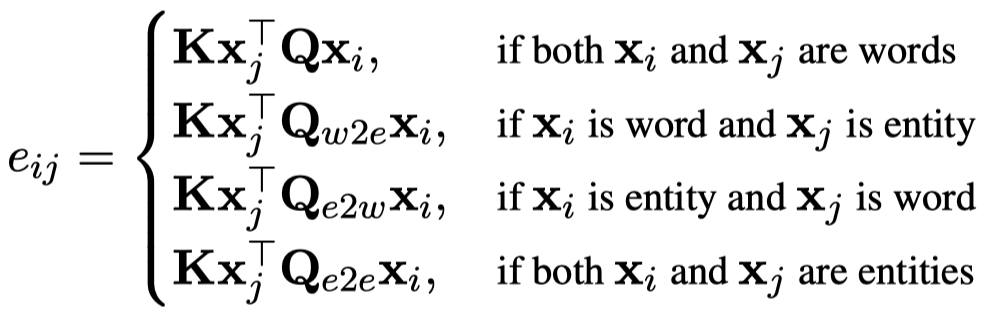
预训练的loss,除去BERT的mask token loss,还加入了一个mask entity的loss:
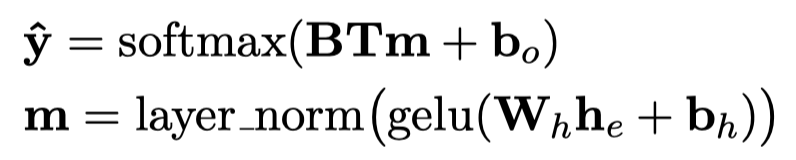
预训练的时候,在Wikipedia pages上进行预训练,所有被mask的entity就是有对应超链接的Wikipedia entity,一共包括了500K个实体。如果一个实体不在entity vocabulary内,就用\([UNK]\)来替换。
实验结果:
实体识别时穷举所有的span,然后经过线性分类器判断实体类别。
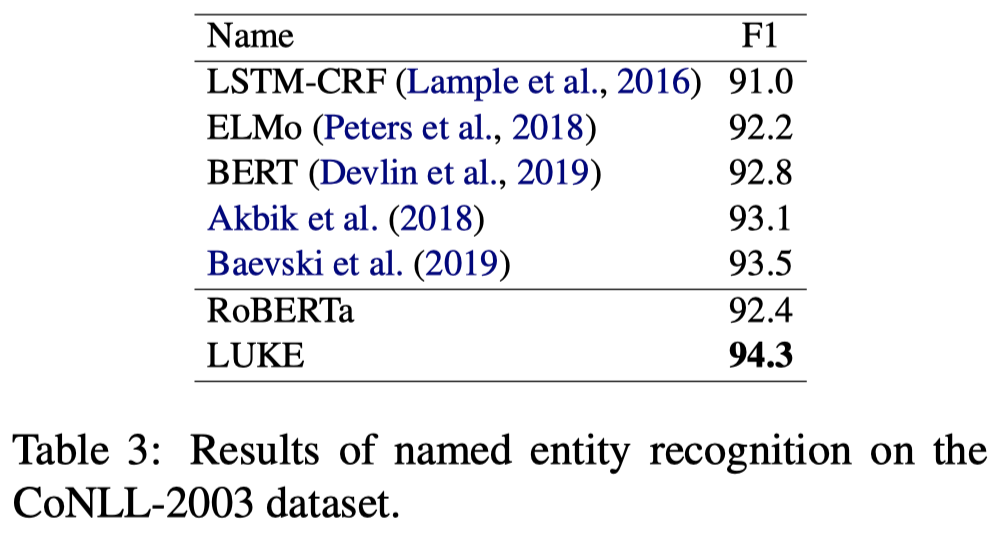
需要注意的一点是,这个方法follow了BERT在NER任务上的做法,加入了document-level context。在检查过源码后发现,CoNLL-2003的句子通过特殊的字符串-DOCSTART-是标记了是否来自于同一document的:

BERT和LUKE方法都通过将属于同一document的sentence拼接在一起进行预测,而不是一个一个句子的进行预测。这样原来一个sentence就能够获得来自其它sentence的语义,并且由于属于同一document,表达上是一致的。
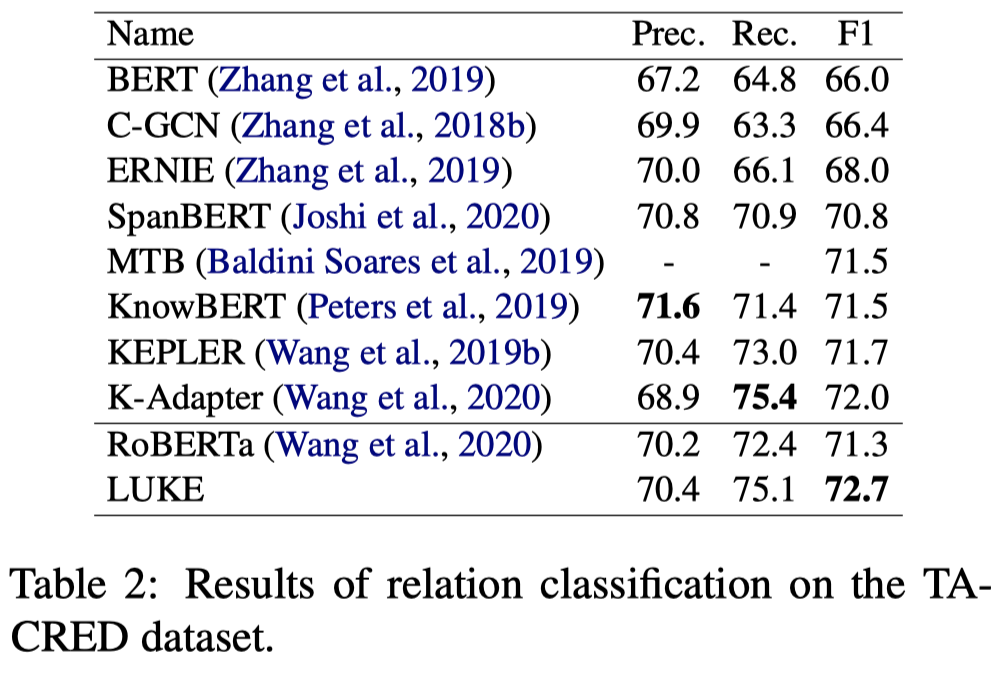
关系分类任务:
Retrieving Correlated Samples
Domain-Specific NER via Retrieving Correlated Samples
天津大学,COLING 2022,代码。
Successful Machine Learning based Named Entity Recognition models could fail on texts from some special domains, for instance, Chinese addresses and e-commerce titles, where requires adequate background knowledge. Such texts are also difficult for human annotators. In fact, we can obtain some potentially helpful information from correlated texts, which have some common entities, to help the text understanding. Then, one can easily reason out the correct answer by referencing correlated samples. In this paper, we suggest enhancing NER models with correlated samples. We draw correlated samples by the sparse BM25 retriever from large-scale in-domain unlabeled data. To explicitly simulate the human reasoning process, we perform a training-free entity type calibrating by majority voting. To capture correlation features in the training stage, we suggest to model correlated samples by the transformerbased multi-instance cross-encoder. Empirical results on datasets of the above two domains show the efficacy of our methods.
在某些情况下进行实体标注需要额外的knowledge,即使对于人类标注者来说也很难识别。人也通常需要去检索后再做决定。
因此作者提出可以通过检索和query text相关的text来辅助NER:
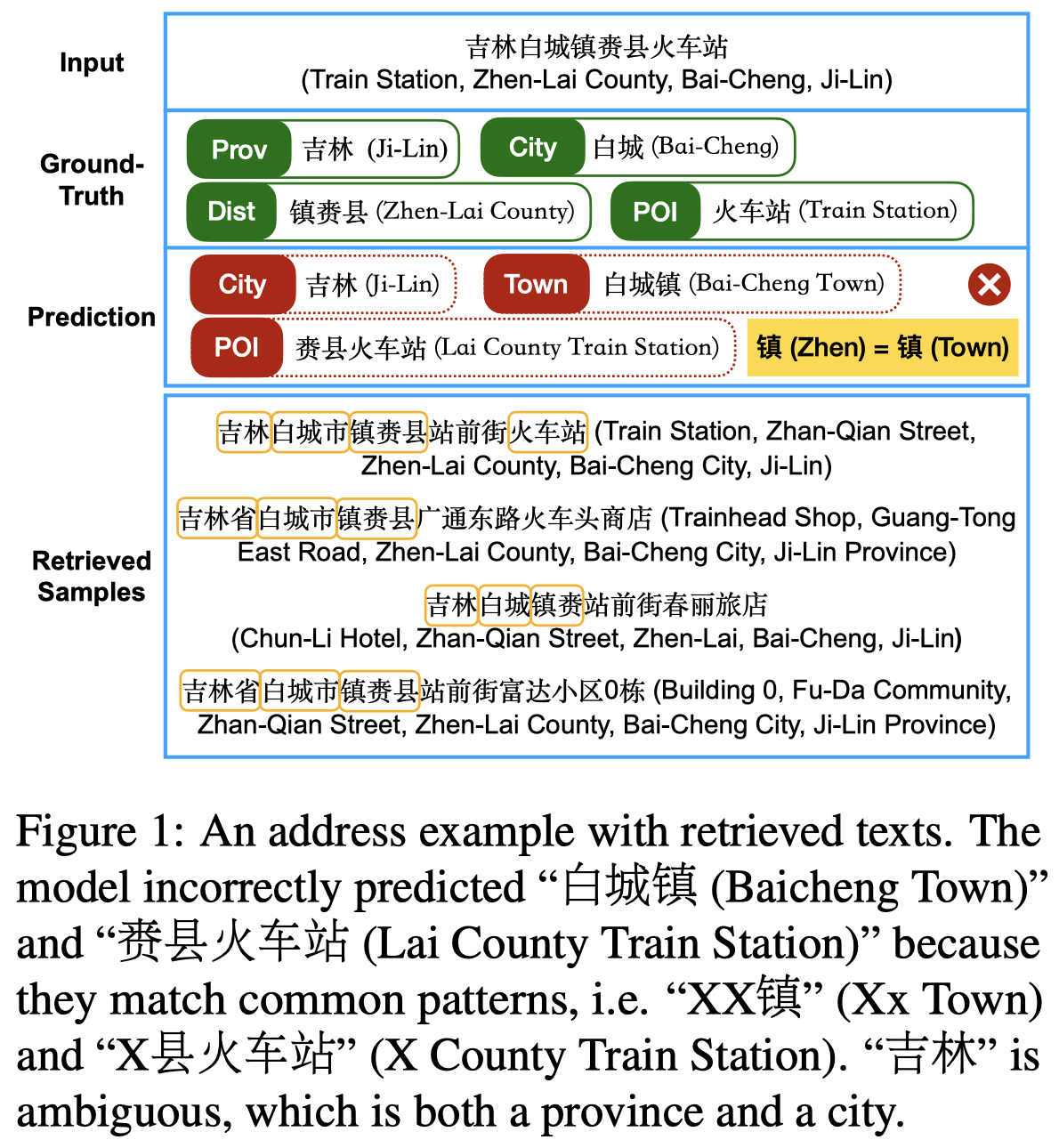
比如上图的白城和白城镇在没有对应背景知识的情况下是不可能分辨出来的。在检索到的额外样例中有白城市这样的关键描述能够帮助辅助判别。对于实例中的“吉林”也一样,到底是吉林省还是吉林市需要从额外样例中寻找。
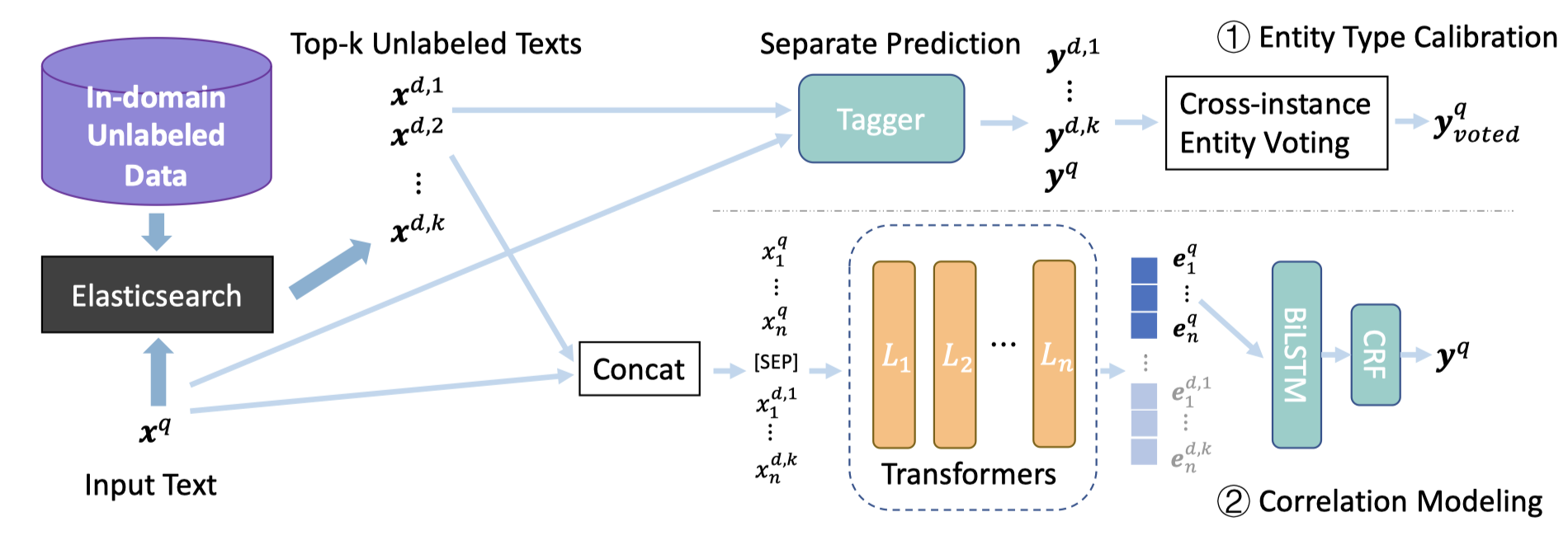
作者的检索源是一个large-scale in-domain unlabeled data,通过Elasticsearch搜索引擎,使用BM25获取top-K的correlated samples。检索的query text应该是整个待抽取的文本。而这个unlabeled data从哪里来,作者没有在论文中进行详细描述。
对于检索到的correlated samples怎么用,作者提出两种思路:
- 一种方法是使用一个已有的NER model对检索到的correlated samples和query text都进行初步NER标注。然后通过majority voting的思想对于shared entities的label进行修正Calibrating。这种方法不需要额外训练,是training-free的。(此时取\(K=100/50\))
- 另一种方法是把correlated samples和query拼接后作为一个input,经过SentenceBERT的cross-encoder编码后,利用BiLSTM-CRF预测。此时的correlated samples就是作为一个external context在输入层进行辅助。(此时取\(K=12\))
实验:
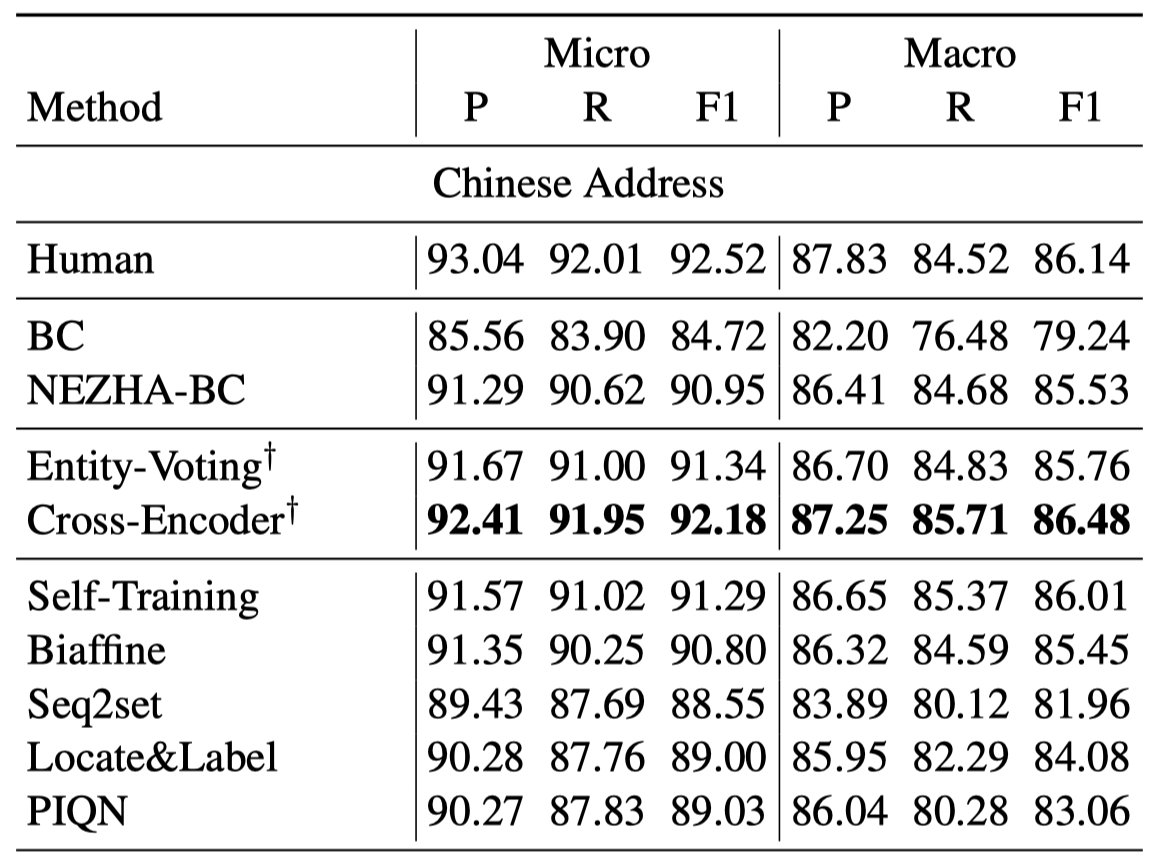
能够看到最终是第二种的方法好一点,但是第一种方法是没有单独训练过的。
KB-NER
DAMO-NLP at SemEval-2022 Task 11: A Knowledge-based System for Multilingual Named Entity Recognition
SemEval-2022 workshop,阿里达摩,代码。
The MultiCoNER shared task aims at detecting semantically ambiguous and complex named entities in short and low-context settings for multiple languages. The lack of contexts makes the recognition of ambiguous named entities challenging. To alleviate this issue, our team DAMO-NLP proposes a knowledge-based system, where we build a multilingual knowledge base based on Wikipedia to provide related context information to the named entity recognition (NER) model. Given an input sentence, our system effectively retrieves related contexts from the knowledge base. The original input sentences are then augmented with such context information, allowing significantly better contextualized token representations to be captured. Our system wins 10 out of 13 tracks in the MultiCoNER shared task.
在本地下载Wikipedia数据,通过ElasticSearch去检索相关的context,然后进行Multilingual NER任务。
方法:
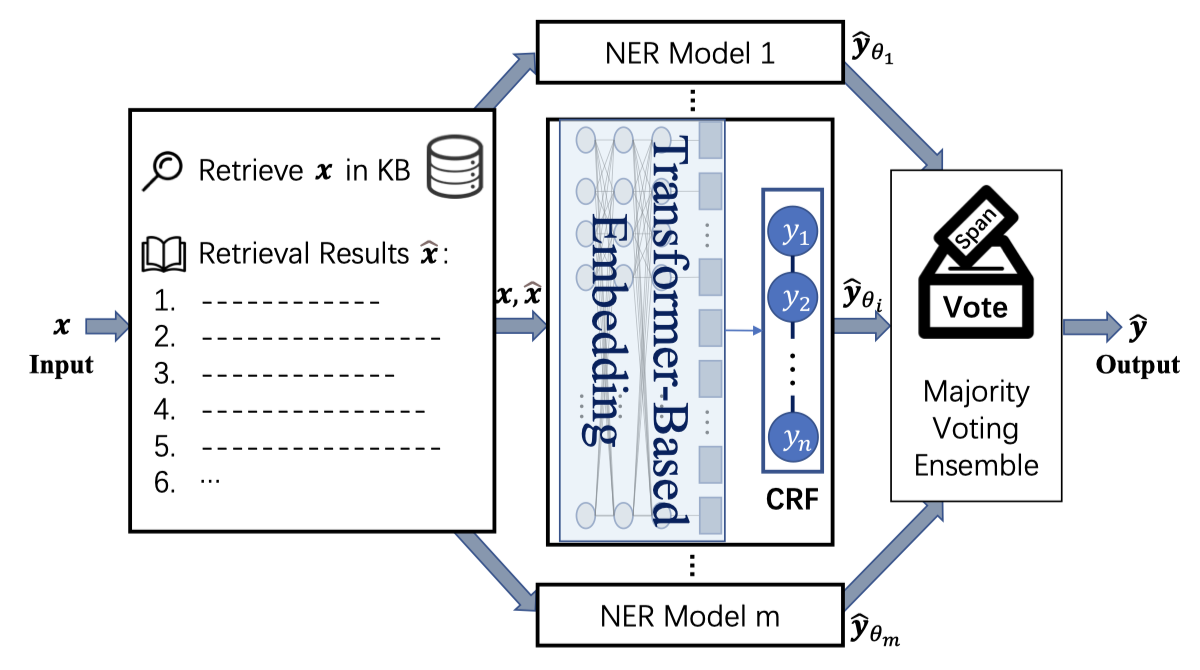
从Wikimedia上下载Wikipedia dump,然后定义了三个field:sentence, paragraph and title field。在sentence field和title field上创建了inverted indexes用于检索。
有两种检索策略:
- Sentence Retrieval:通过query sentence和sentence field进行匹配,然后返回top-k的结果
- Iterative Entity Retrieval:把query sentence中的entities拼接,用
|分割,和title field进行配。这种方法可以迭代T次
对于检索到的结果,有三类context可以作为external context和原有的query sentence一起输入:
- use the matched paragraph(paragraph包含了matched sentence的上下文)
- use the matched sentence(如
<e:Steve Jobs>Steve Jobs</e> founded <e:Apple_inc>Apple</e>) - use the matched sentence but remove the wiki anchors(如
Steve Jobs founded Apple)
使用的model是XLM-R large。
实验结果:

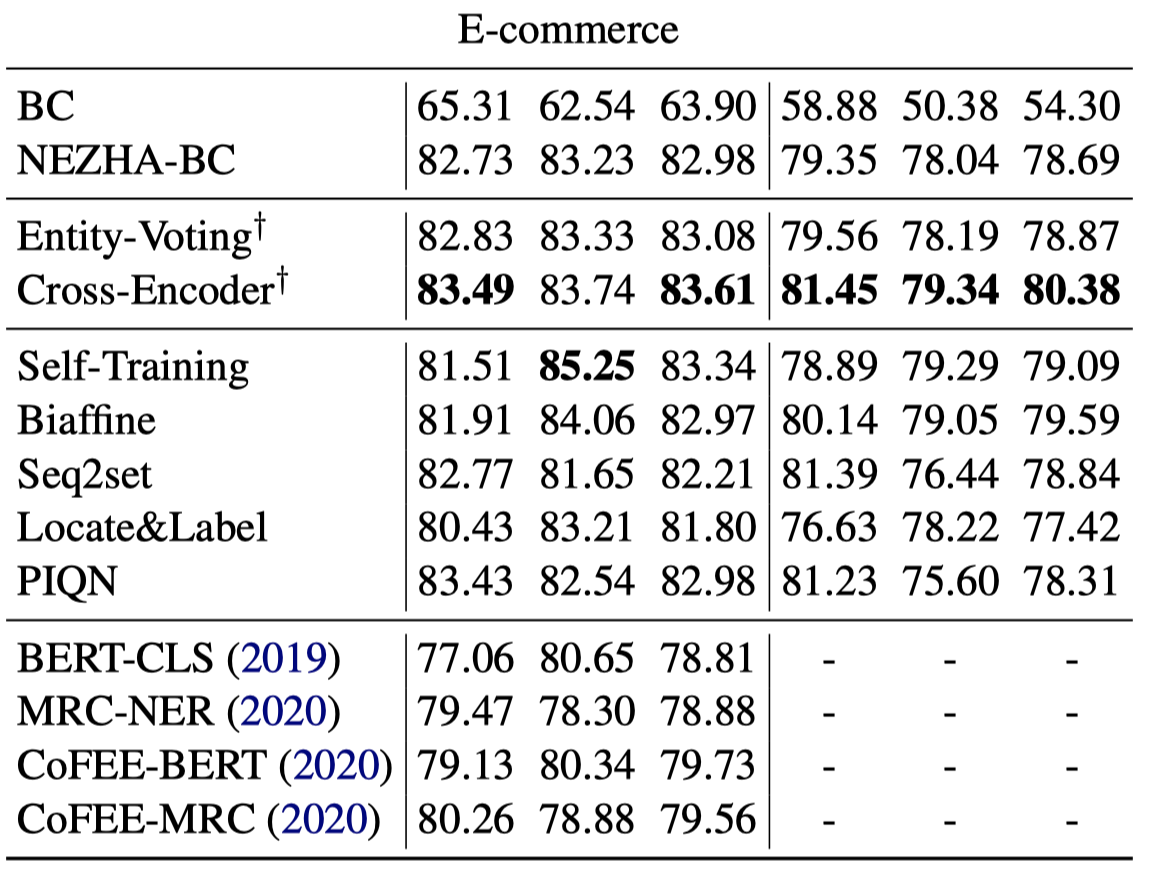
Table 1中的Baseline是指没有对应的Wikipedia搜索模块的变体,能够看到加入external knowledge之后,效果提升了有20%。
和用Google search的对比:
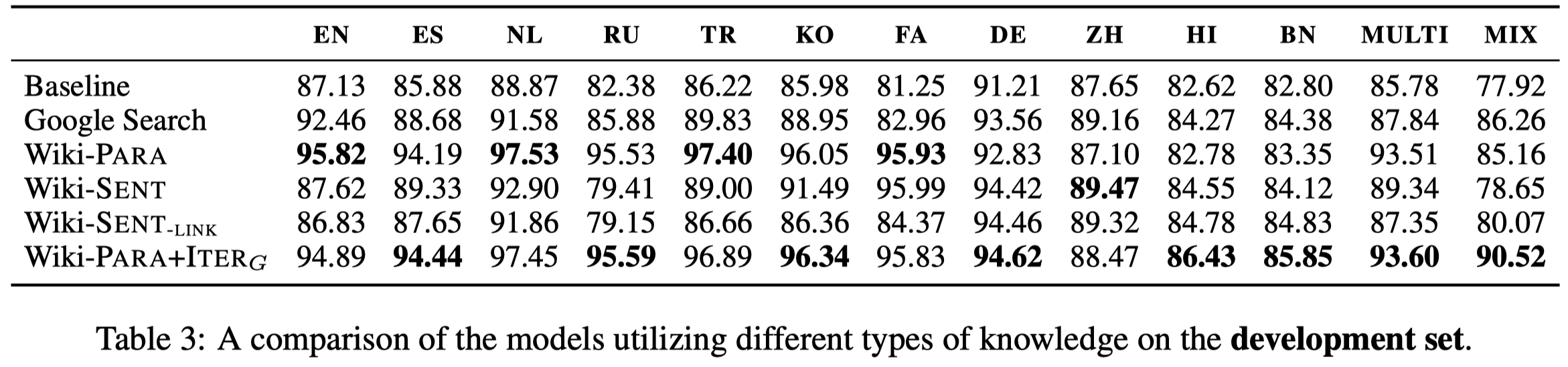
虽然Google search比Baseline要好,但是总体上效果比不上用Wikipedia进行检索。另外一个关键问题是Google search比在本地检索要慢很多,一个量级的差距(具体参考paper中的Table 6)。
Table 3中的Wiki-Para,Wiki-Sent,Wiki-Sent-Link分表代表上面说的三种处理检索结果的方法。Wiki-Para+IterG是指用dev set中的gold entity进行检索,并且之后使用match paragraph作为external context。
MetaRetriever
Universal Information Extraction with Meta-Pretrained Self-Retrieval
ACL Findings 2023,中科院与阿里达摩,代码。
Universal Information Extraction (Universal IE) aims to solve different extraction tasks in a uniform text-to-structure generation manner. Such a generation procedure tends to struggle when there exist complex information structures to be extracted. Retrieving knowledge from external knowledge bases may help models to overcome this problem but it is impossible to construct a knowledge base suitable for various IE tasks. Inspired by the fact that large amount of knowledge are stored in the pretrained language models (PLM) and can be retrieved explicitly, in this paper, we propose MetaRetriever to retrieve task-specific knowledge from PLMs to enhance universal IE. As different IE tasks need different knowledge, we further propose a Meta-Pretraining Algorithm which allows MetaRetriever to quicktly achieve maximum task-specific retrieval performance when fine-tuning on downstream IE tasks. Experimental results show that MetaRetriever achieves the new state-of-the-art on 4 IE tasks, 12 datasets under fully-supervised, low-resource and few-shot scenarios.
问题:
- 作者认为类似于UIE方法的通用IE model在面对复杂信息抽取结构的时候,由于缺乏对信息结构之间的上下文语义关联,而难以输出准确的抽取结果
- 利用检索增强的方法能够利用外部知识来获取与task相关的信息,但是很难搭建这样一种适用于各种IE任务的知识库/检索方式。事实上,搭建这样的通用知识库就是IE任务的终极目标。
最近,通过knowledge probing任务发现PLM中蕴含了很多knowledge,如果使用PLM就无需构造额外的外部知识库。因此作者提出利用PLM作为知识库,从PLM中检索相关knowledge并且提升通用信息抽取任务的效果:
In light of these findings, the question arises: can PLMs be used as knowledge bases to retrieve knowledge and improve universal IE models? If so, universal IE models would be able to generate more accurate results.
作者提出的MetaRetriever基于T5-base,方法图:
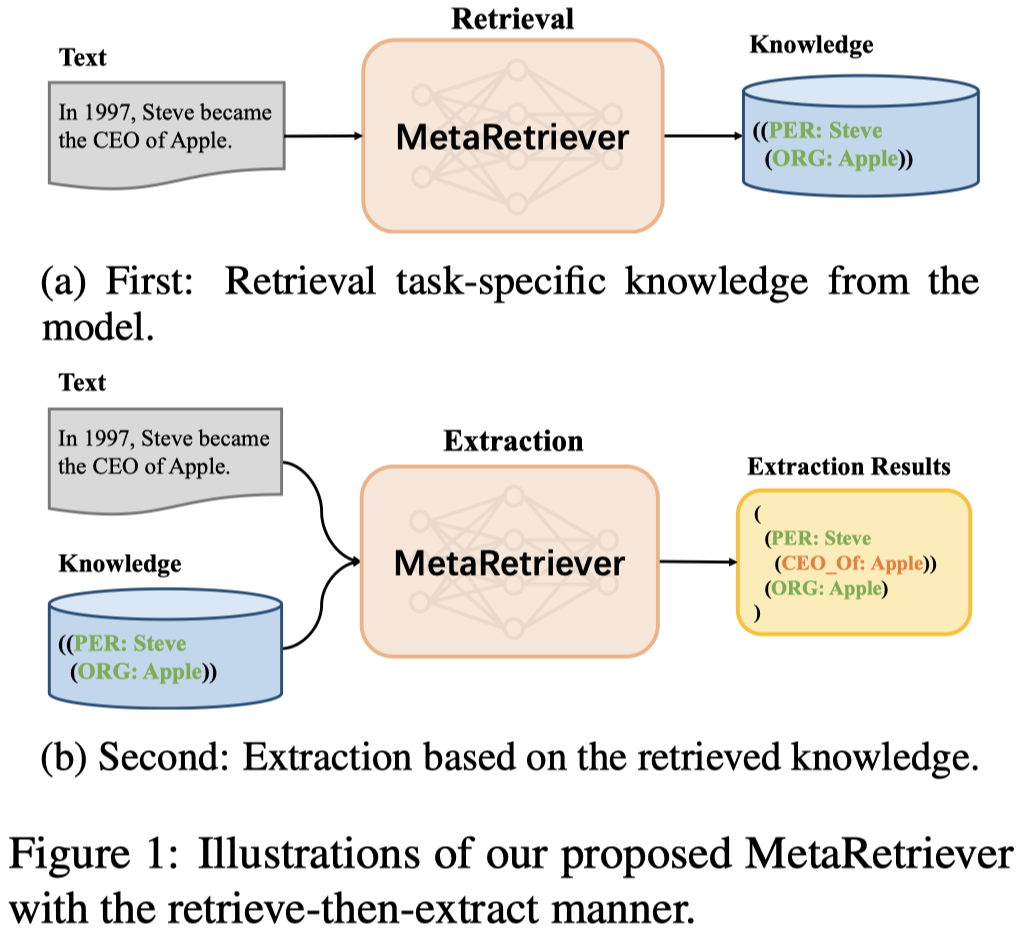
作者直接使用了UIE中提出的Structured extraction language来建模各类IE任务。
第一步是检索,作者对于PLM中能够辅助UIE的knowledge的定义很简单,就是直接使用预测的抽取结果作为knowledge。using the ground truth linearized SEL sequence of the corresponding input text as the knowledge we wish to retrieve. (个人认为这样不就是相当于进行了两次抽取吗?)
第二步是抽取,将上一步预测的抽取结果和原本的text拼接,输入model,进行最终的抽取。
为了让模型快速学会如何检索自身和IE任务相关的implicit knowledge,作者使用meta-learning的方法,分为inner loop和outer loop两步进行快速的梯度更新。经典的meta learning方法。
值得一提的是,为了训练MetaRetriever,作者构造了一个10-million-level的语料库,并且首次开源。
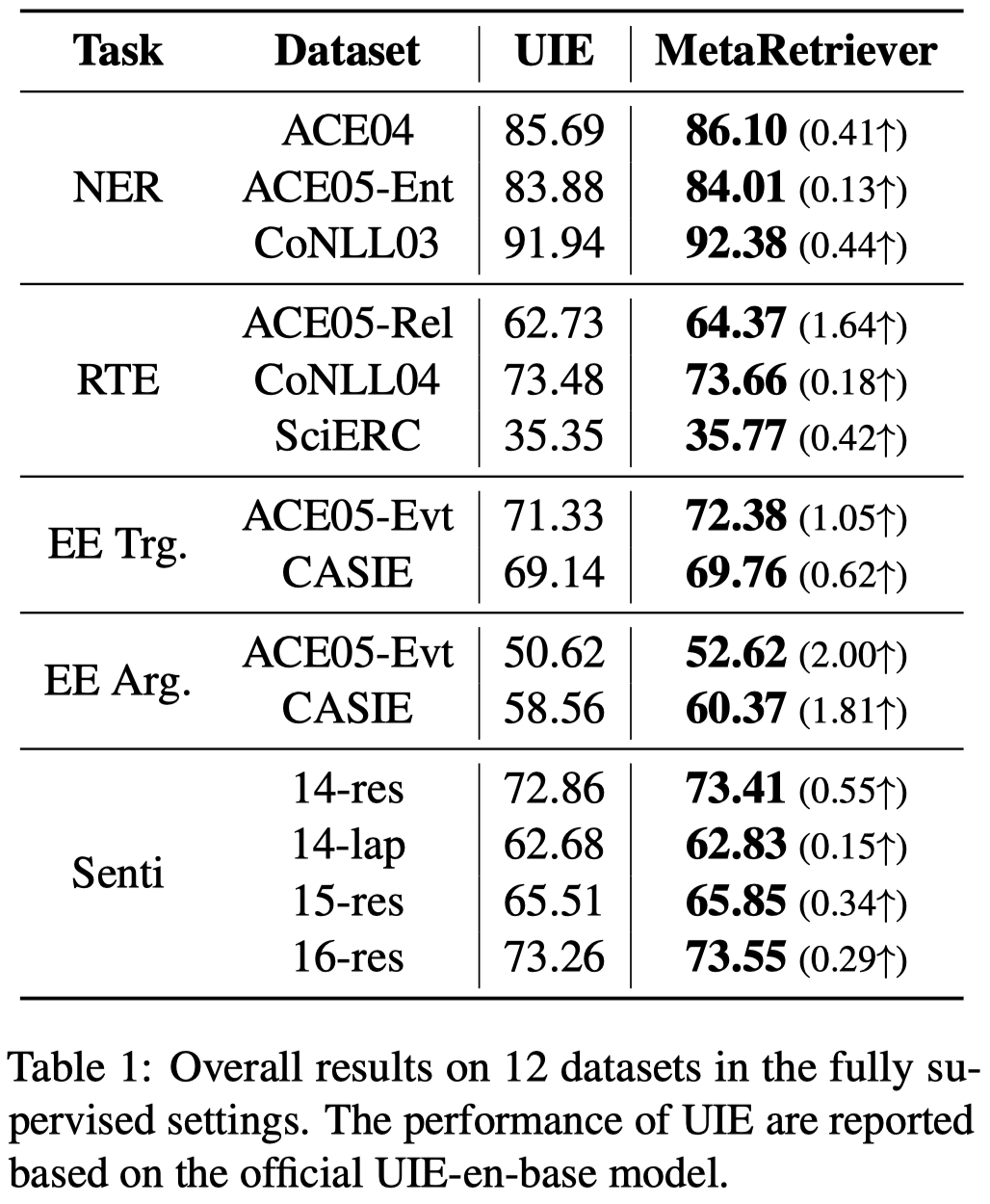
实验结果:
KnowPrompt
KnowPrompt: Knowledge-aware Prompt-tuning with Synergistic Optimization for Relation Extraction. 浙大. WWW 2022. 代码.
Recently, prompt-tuning has achieved promising results for specific few-shot classification tasks. The core idea of prompt-tuning is to insert text pieces (i.e., templates) into the input and transform a classification task into a masked language modeling problem. However, for relation extraction, determining an appropriate prompt template requires domain expertise, and it is cumbersome and time-consuming to obtain a suitable label word. Furthermore, there exists abundant semantic and prior knowledge among the relation labels that cannot be ignored. To this end, we focus on incorporating knowledge among relation labels into prompt-tuning for relation extraction and propose a Knowledge-aware Prompt-tuning approach with synergistic optimization (KnowPrompt). Specifically, we inject latent knowledge contained in relation labels into prompt construction with learnable virtual type words and answer words. Then, we synergistically optimize their representation with structured constraints. Extensive experimental results on five datasets with standard and low-resource settings demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach. Our code and datasets are available in GitHub 1 for reproducibility.
Issue: 基于prompt的方法比基于standard finetuning的方法能够更好的bridge the gap between pre-training and fine-tuning。而对prompt-tuning based RE存在的两个问题:
- 如何决定合适的prompt,人工的方法需要domain expertise;自动化方法需要额外的计算代价;
- 搜索合适的label需要很高的代价,而为RE任务构造合适的label并不是一个很easy的任务;直接使用数据集里原始的label不能够很好的适应RE任务。
Solution: 作者的解决思路是,利用knowledge注入到learnable prompts里。
具体来说,作者从数据集里的relation label出发,为entity type和relation分别构造了virtual words。
对于entity,作者没有假设数据集中会提前给定entity type。作者是利用人工的先验知识,判断某个relation对应的头尾实体类型。然后,基于frequency statistics,从整个数据集上计算不同实体类型的频率。根据频率和对应的type相应的embedding加权求和,得到了总体上的头尾实体的type embedding。这个entity type embedding,会作为特殊token \([sub]/[obj]\)插入到具体sample的头尾实体前后。
对于relation,作者分解原始的relation,然后使用分解后的不同word,相乘后作为初始化的relation embedding。

初始化后的entity type embedding会加入到prompt里,放在头尾实体左右,作为weakened type marker,然后初始化的relation embedding会作为候选的关系,和[MASK] token embedding相乘,选择最大概率的作为输出relation。下面是方法图:
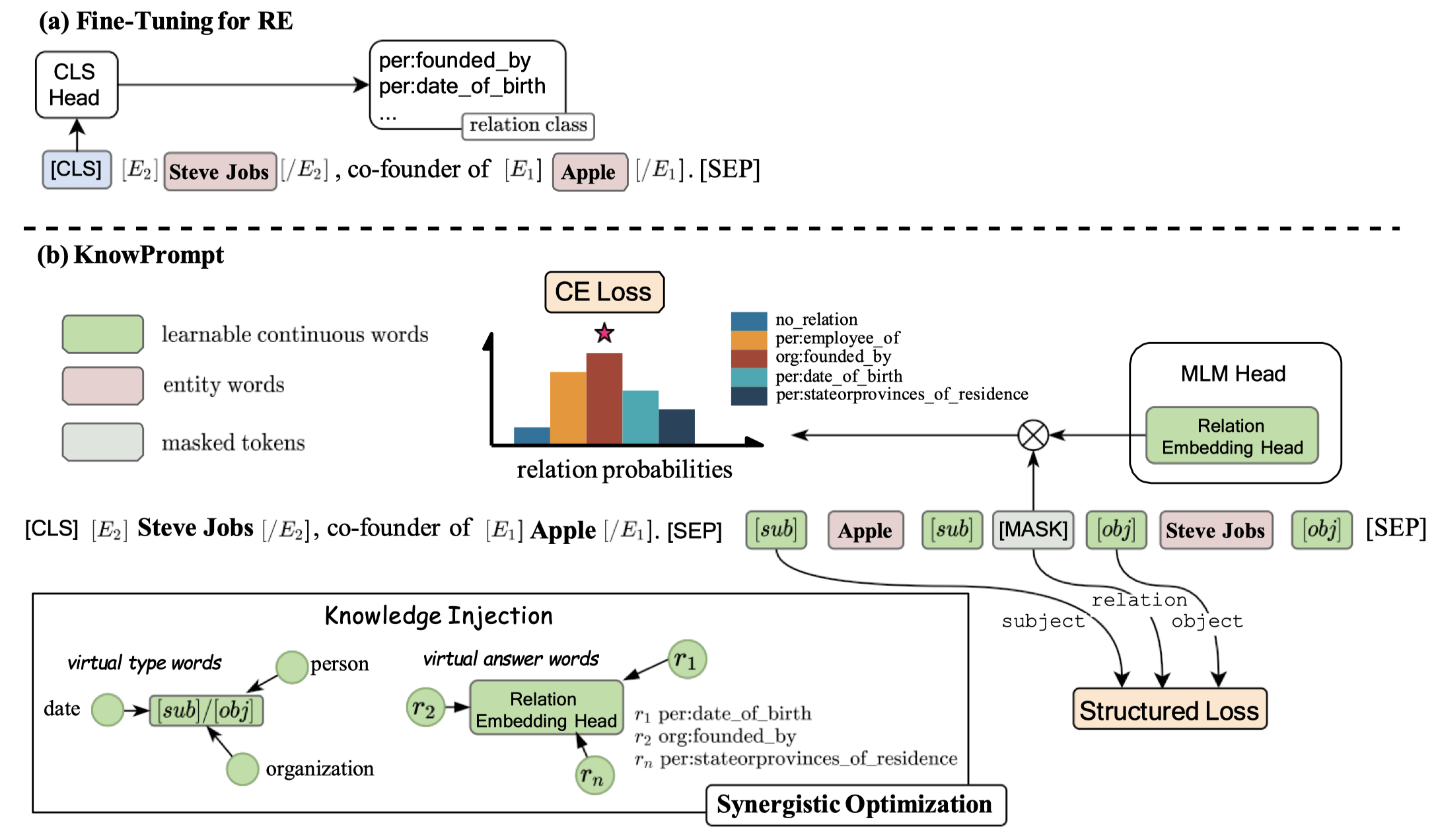
具体,作者在训练时使用了两步训练策略,有两种loss:
一个是给定了prompt之后,预测[MASK]是正确relation的交叉熵:
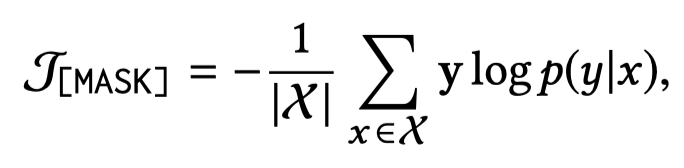
一个是期望学习structural knowledge的结构化loss,也就是利用TransE思想构造的判断\(<s,r,o>\)成立的loss。只不过,这里的\(<s><o>\)不是具体的entity embedding,而是他们句子中的\([sub]\)和\([obj]\) token的用来表示entity type的embedding:
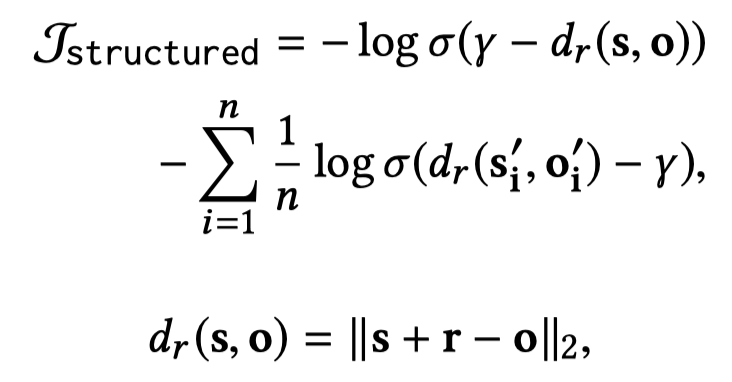
作者在full dataset和low-resource两种RE任务设置下进行了实验。基于RoBERT_large model,而在DialogRE数据集上基于RoBERTa_base model。

可以看到,这种提前注入knowledge来构造合适的soft prompt的方法在低资源的情况下,效果提升最明显。
Cross-domain IE
CP-NER
One Model for All Domains: Collaborative Domain-Prefix Tuning for Cross-Domain NER
IJCAI 2023,浙大ZJUNLP,代码。
Cross-domain NER is a challenging task to address the low-resource problem in practical scenarios. Previous typical solutions mainly obtain a NER model by pre-trained language models (PLMs) with data from a rich-resource domain and adapt it to the target domain. Owing to the mismatch issue among entity types in different domains, previous approaches normally tune all parameters of PLMs, ending up with an entirely new NER model for each domain. Moreover, current models only focus on leveraging knowledge in one general source domain while failing to successfully transfer knowledge from multiple sources to the target. To address these issues, we introduce Collaborative Domain-Prefix Tuning for cross-domain NER (Cp -NER) based on text-to-text generative PLMs. Specifically, we present textto-text generation grounding domain-related instructors to transfer knowledge to new domain NER tasks without structural modifications. We utilize frozen PLMs and conduct collaborative domain-prefix tuning to stimulate the potential of PLMs to handle NER tasks across various domains. Experimental results on the Cross-NER benchmark show that the proposed approach has flexible transfer ability and performs better on both one-source and multiple-source cross-domain NER tasks.
作者期望解决下面三个问题:
- 之前的跨域IE方法依赖于为不同的domain设计不同的architecture
- 大多数现有的方法需要tuning PLM的所有参数,计算代价较高
- 之前的方法只考虑单源的跨域IE
作者提出的方法
使用prefix-tuning,这样就不需要为不同的domain设计不同的architecture
使用frozen PLM parameters,这样就不需要更新模型的所有参数
考虑多源的跨域IE
下面是方法图:
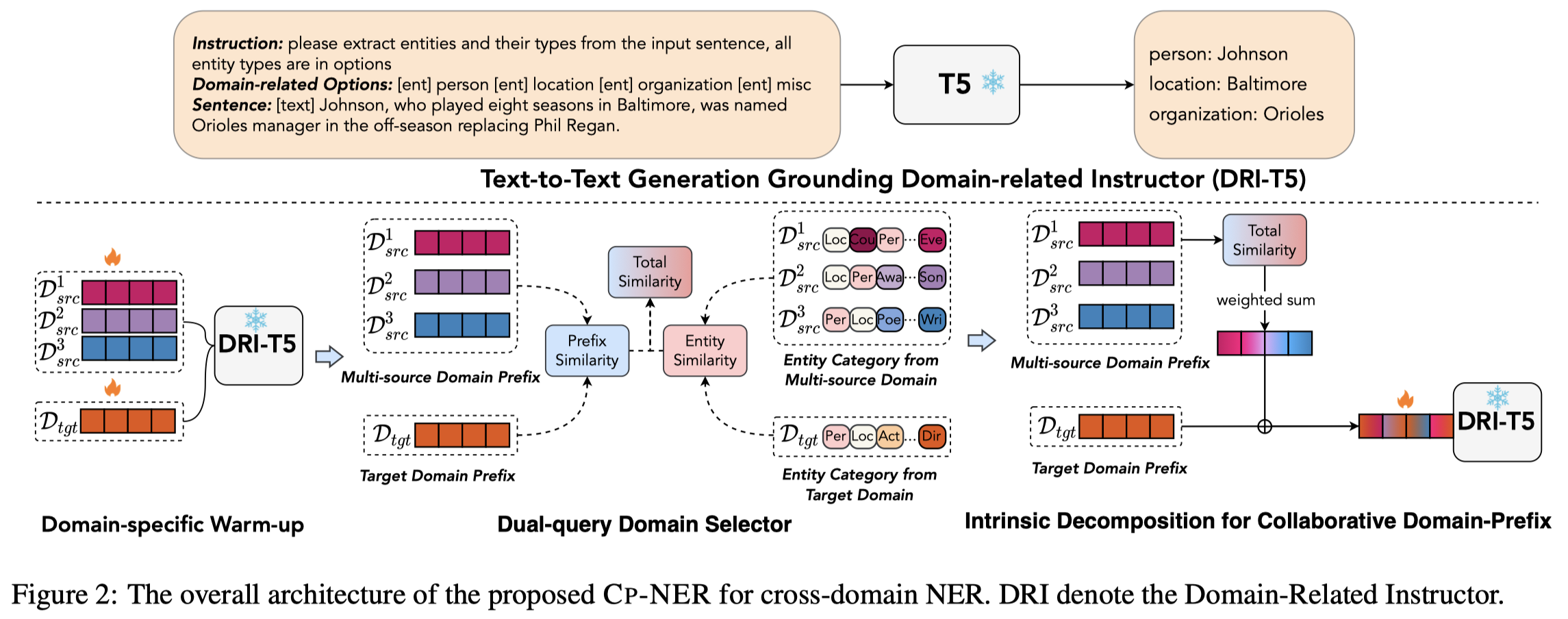
作者方法基于T5-base(220M参数),重点在于prefix embedding的学习,prefix embedding会加入到输入的sentence tokens的左边(简单看了下代码,应该是长度为10)。按照prefix-tuning的原论文,prefix-tuning可以看做是continuous instruction,是用来学习和task相关的context信息,进而激发LM去执行特定的任务,特别是对于那些没有表现出利用人类自然语言描述的instruction去执行特定任务的小模型(BERT、GPT-1,2等)。
prefix embedding是要从每个领域都进行训练学习,prefix embedding在T5的每一层都有独立的表示。学习的方法就是在加入prefix embedding之后,再按照T5的训练loss,在domain data下进行训练,过程中保持T5原来的所有参数不变。(对应图中的domain-specific warm-up过程)
之后,作者因为要考虑多源IE,因此通过source domain的实体label和target domain的实体label计算相似度;domain prefix embedding之间也计算相似度这样来评估不同来源对于target domain的影响大小。(对应图中的dual-query domain selector过程)
最后,在前一步计算得到的相似度经过softmax之后和多源prefix embedding进行加权求和,再加入到target domain的prefix embedding上。作者最后还进行了再一次的微调,训练最终学习到的target domain prefix embedding。
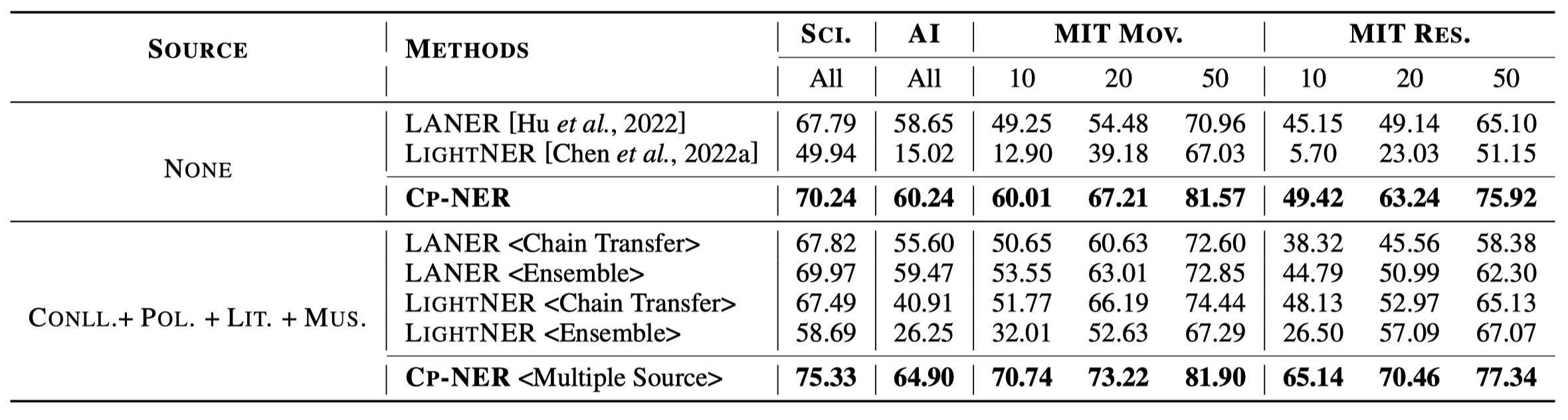
实验结果,下面是单源IE,以CONLL2003作为source domain,CrossNER数据集下的多个子集作为target domain:
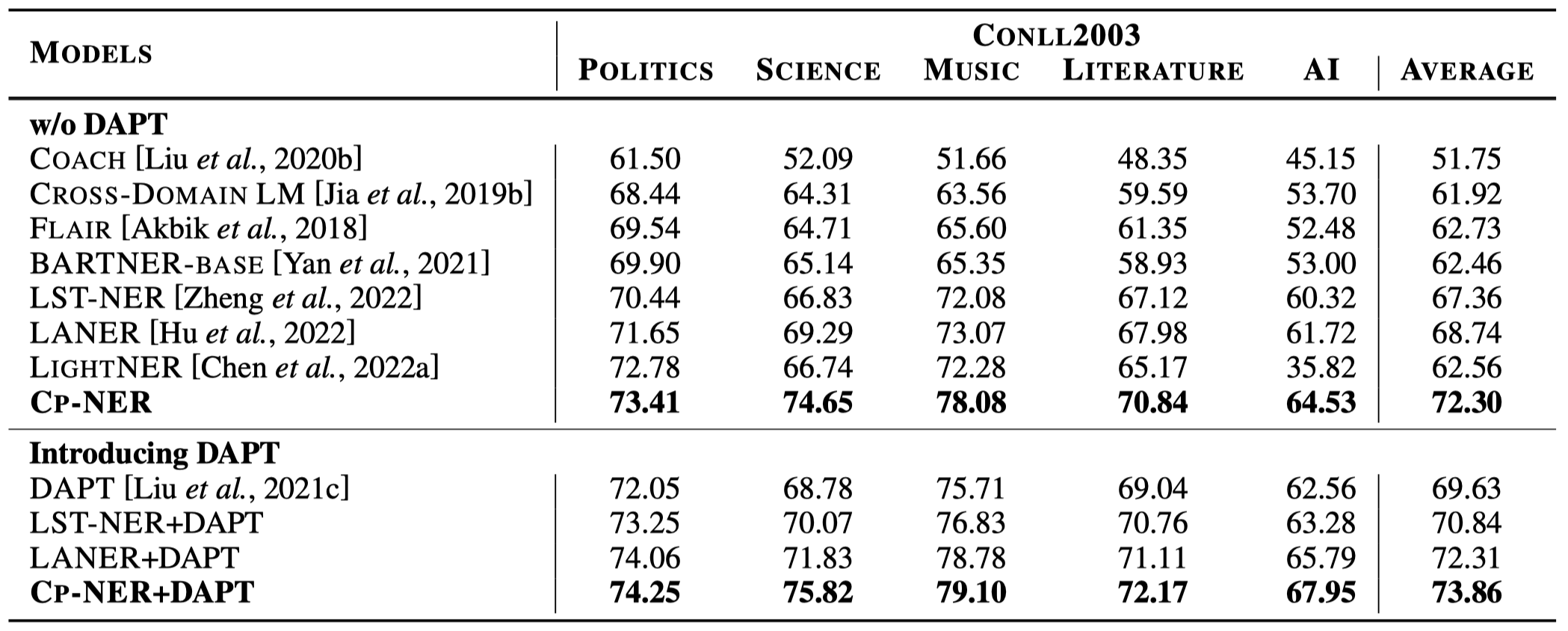
下面是多源的跨域抽取,以CoNLL 2003, Politics, Literature, and Music作为source domain,使用Mit-Movie, AI, Science, and Mit-Restaurant作为target domain: